Time-Division Subbands Beta Distribution Random Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation Method for the High-Frequency Harmonic Dispersion
Abstract
1. Introduction
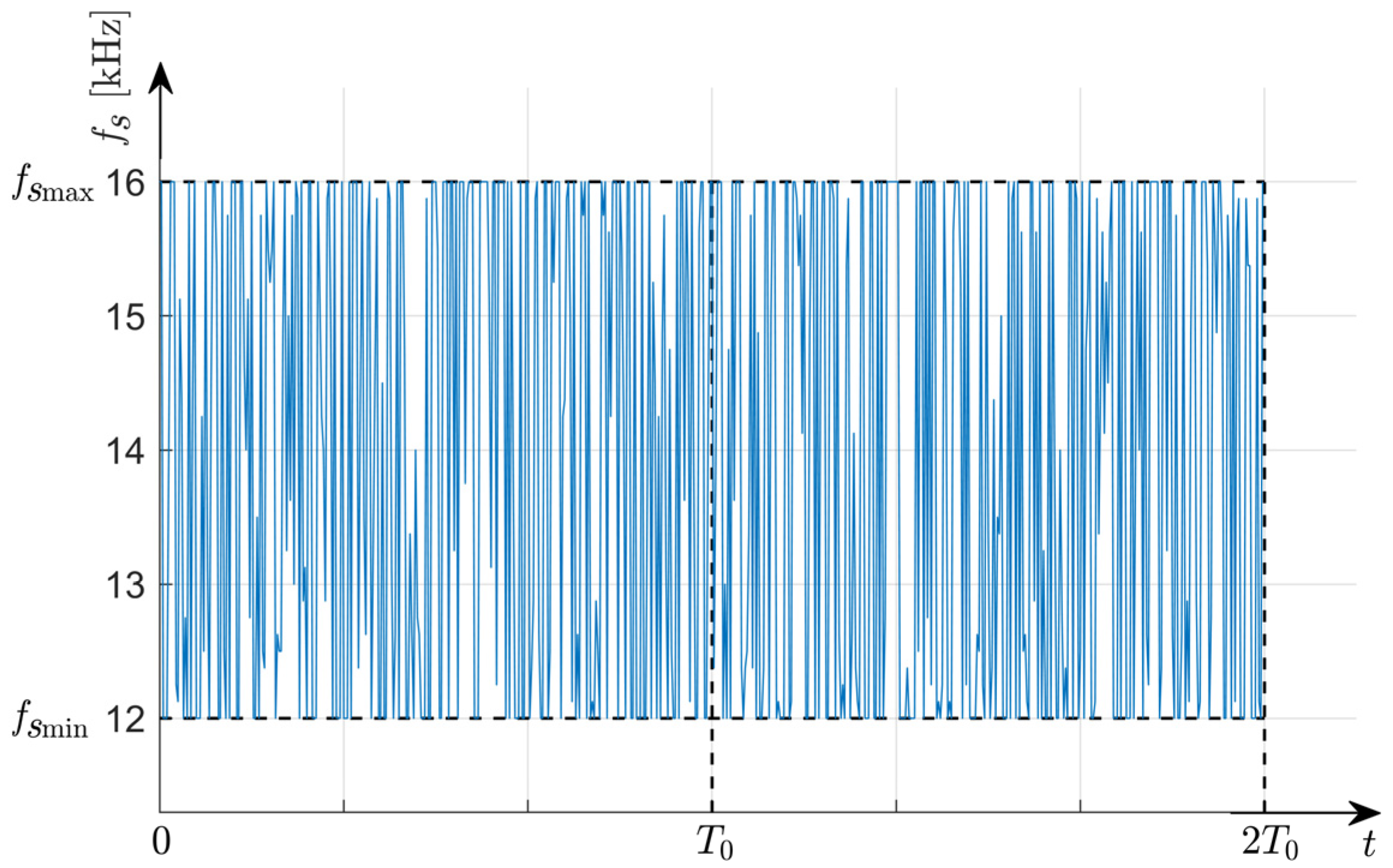
2. Proposed TSBDR-SVPWM Method to Improve the Harmonic Spreading Effect
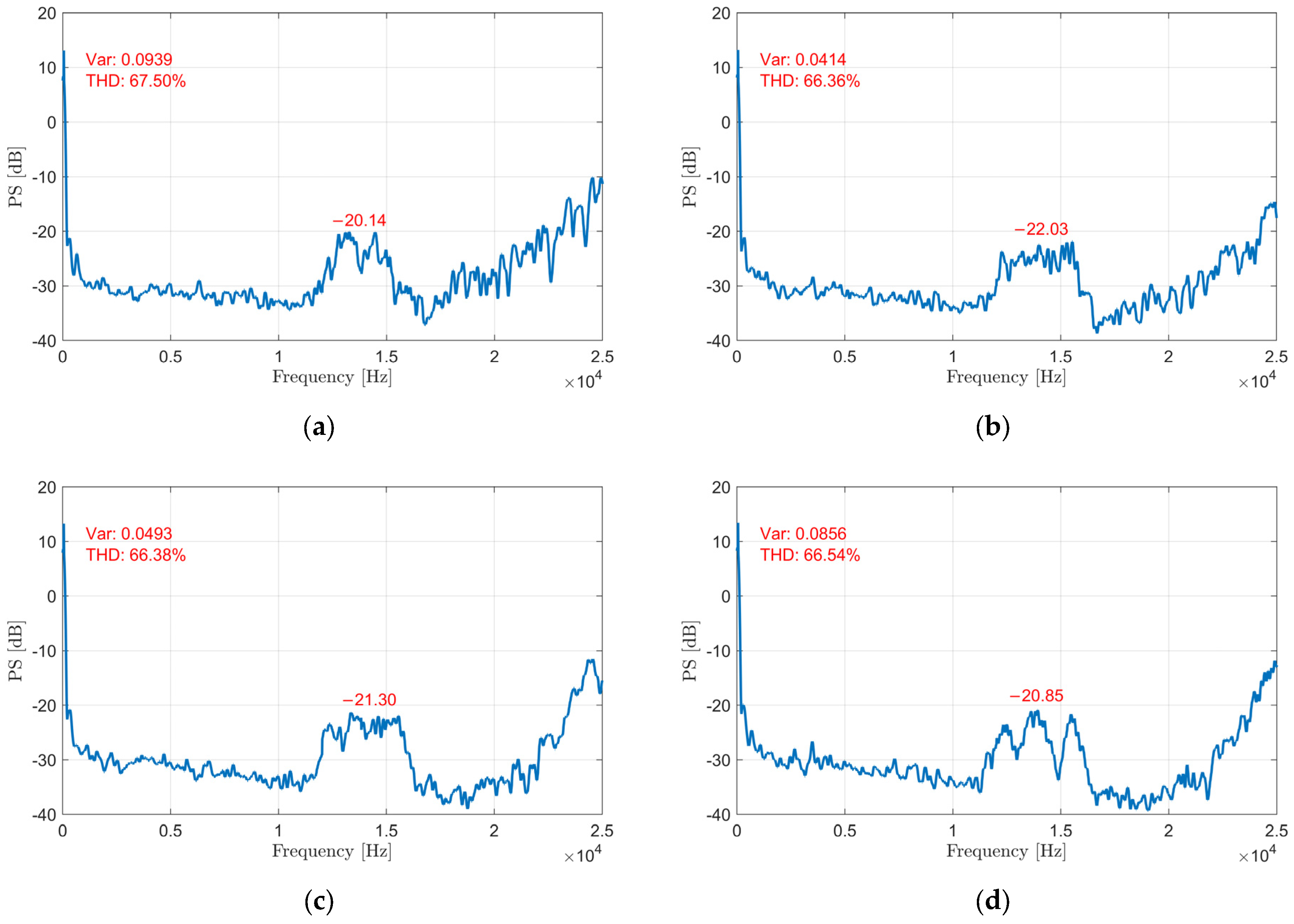
3. Simulation and Experimental Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, C.; Wang, S.; Moallem, M.; Fahimi, B.; Tschida, C. Analysis of vibration in permanent magnet synchronous machines due to variable speed drives. IEEE Trans. Energy Conv. 2017, 32, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.T.; Chan, C.C.; Liu, C. Overview of permanent-magnet brushless drives for electric and hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 2246–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Zuo, S. Electromagnetic vibration and noise of the permanent-magnet synchronous motors for electric vehicles: An overview. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2019, 5, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Zuo, S. Comparative study of sideband electromagnetic force in internal and external rotor PMSMs with SVPWM technique. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Huang, J.; Qian, Z.; Qian, C.; Zhong, D. A random pulse position-based selective noise cancellation modulation method for SVPWM driven PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 2190–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, K. A hybrid calculation method of electromagnetic vibration for electrical machines considering high-frequency current harmonics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 10385–10395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Y.; Zou, J. Reduction method of high-frequency audible PWM noise for three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motors. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colak, I.; Kabalci, E. Developing a novel sinusoidal pulse width modulation (SPWM) technique to eliminate side band harmonics. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 44, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Ding, L.; Yao, K. SVPWM sideband harmonic analysis in permanent magnet synchronous motor driven by voltage source inverter. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Zhuhai, China, 5–8 November 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Zou, J. PWM frequency voltage noise cancelation in three-phase VSI using the novel SVPWM strategy. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8596–8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, W.; Tao, T.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X. High frequency harmonics dispersion for dual three-phase PMSM drives with random switching sequence. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2024; early access. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Yao, X.; Liu, H. PWM harmonic cancellation of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on periodic spread spectrum modulation. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2023, 19, 2413–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, K. Suppressing the maximum EMI spectral peak through asynchronous carriers in the three-phase inverter with the periodic CFM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 3702–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Zou, J.; Xu, Y.; Yu, G.; Wang, L.; Zanchetta, P. High-frequency current harmonic analysis and suppression in dual three-phase PMSMs with advanced carrier phase-shift PWM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 39, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Cheng, S.; Li, X.; Lv, Y.; Wang, D. An optimal periodic carrier frequency PWM scheme for suppressing high-frequency vibrations of permanent magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 13008–13018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ouyang, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhu, W.; Nie, Z. Performance and characterization of optimal harmonic dispersion effect in double FrequencyBand random PWM strategy. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 14680–14690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Feng, J.; Tao, T.; Wang, C.; Liu, S. High frequency harmonics and vibration reduction for dual three phase PMSM using multiple randomized SVPWM strategy. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 11455–11467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyghambari, A.; Dastfan, A.; Ahmadyfard, A. Strategy for switching period selection in random pulse width modulation to shape the noise spectrum. IET Power Electron. 2015, 8, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyghambari, A.; Dastfan, A.; Ahmadyfard, A. Selective voltage noise cancellation in three-phase inverter using random SVPWM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 4604–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fu, Z.; Wang, Y. Electromagnetic vibration and noise suppression of induction motor based on RPWM selective spectrum shaping. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 54509–54517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Cheng, X.; Gao, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhao, F. Towards harmonic cancellation in motors using selective noise suppression random SVPWM method. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives (PEMD), Nottingham, UK, 10–13 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Jiao, T.; Wang, M.; Mo, G. Characterization and selection of probability density function in a discrete random switching period SVPWM strategy. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 7475–7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Cheng, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; Ji, P.; Yang, J. An optimization method in the random switching frequency SVPWM for the sideband harmonic dispersion. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2024, 12, 4801–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Roy, J.; Ayyanar, R. Optimal variable switching frequency scheme to reduce loss of single-phase grid-connected inverter with unipolar and bipolar PWM. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | 24 V |
| Rated Current | 4 A |
| Rated Speed | 3000 rpm |
| Rated Torque | 0.2 N·m |
| Rated Power | 62 W |
| Resistance | 1.02 Ω |
| Inductance | 0.59 mH |
| B-Emf Constant | 4.3 V/krpm |
| Pole Number | 4 |
| Equipment | Type |
|---|---|
| MCU | STM32F407 |
| MOSFET of VSI | Infineon IRFS3607 |
| Motor | SPMSM |
| Magnetic damper | MTB-05 |
| Power analyzer | Everfine PF330A |
| Oscilloscope | Tektronix DPO2024 |
| No-Load | 0.1 N·m | 0.2 N·m | 0.3 N·m | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSVPWM (M = 1) | −14.52 dB | −13.04 dB | −12.08 dB | −10.06 dB |
| UD-DRSF-SVPWM (N = 1, (a = b) ∧ (b = 1), M = 9) | −18.82 dB | −20.86 dB | −14.35 dB | −16.21 dB |
| BD-DRSF-SVPWM (N = 1, (a = b) ∧ (b = 0.15), M = 9) | −21.02 dB | −21.32 dB | −20.12 dB | −17.92 dB |
| TSBDR-SVPWM (N = 4, (a = b) ∧ (b = 0.15), M = 9) | −23.11 dB | −22.75 dB | −21.88 dB | −19.06 dB |
| 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSVPWM (M = 1) | 95.80% | 97.68% | 98.23% | 98.65% | 98.78% |
| UD-DRSF-SVPWM (N = 1, (a = b) ∧ (b = 1), M = 9) | 95.73% | 97.68% | 98.25% | 98.66% | 98.77% |
| BD-DRSF-SVPWM (N = 1, (a = b) ∧ (b = 0.15), M = 9) | 95.82% | 97.65% | 98.20% | 98.65% | 98.72% |
| TSBDR-SVPWM (N = 4, (a = b) ∧ (b = 0.15), M = 9) | 95.78% | 97.70% | 98.22% | 98.63% | 98.75% |
| Harmonic Spreading Effect | THD | Inverter Efficiency | Implementation of Complexity in the MCU | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSVPWM (M = 1) | Worst | Baseline value | Baseline value | Easy |
| UD-DRSF-SVPWM (N = 1, (a = b) ∧ (b = 1), M = 9) | Moderate | Significant increase | Equal to baseline | Moderate |
| BD-DRSF-SVPWM (N = 1, (a = b) ∧ (b < 1), M = 9) | Good | Significant increase | Equal to baseline | Moderate |
| TSBDR-SVPWM (N = 4, (a = b) ∧ (b < 1), M = 9) | Best | Slight increase | Equal to baseline | Complex |
| Sideband Harmonic Amplitude | Torque Ripple | SRAM Usage in the MCU | CPU Load in the MCU | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSVPWM (M = 1) | −12.08 dB | 2.1% | 17.8% | 23.5% |
| UD-DRSF-SVPWM (N = 1, (a = b) ∧ (b = 1), M = 9) | −14.35 dB | 3.8% | 21.2% | 27.6% |
| BD-DRSF-SVPWM (N = 1, (a = b) ∧ (b < 1), M = 9) | −20.12 dB | 3.7% | 21.2% | 27.6% |
| TSBDR-SVPWM (N = 4, (a = b) ∧ (b < 1), M = 9) | −21.88 dB | 2.8% | 22.0% | 28.2% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, J.; Cheng, X. Time-Division Subbands Beta Distribution Random Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation Method for the High-Frequency Harmonic Dispersion. Electronics 2025, 14, 2852. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142852
Wen J, Cheng X. Time-Division Subbands Beta Distribution Random Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation Method for the High-Frequency Harmonic Dispersion. Electronics. 2025; 14(14):2852. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142852
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Jian, and Xiaobin Cheng. 2025. "Time-Division Subbands Beta Distribution Random Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation Method for the High-Frequency Harmonic Dispersion" Electronics 14, no. 14: 2852. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142852
APA StyleWen, J., & Cheng, X. (2025). Time-Division Subbands Beta Distribution Random Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation Method for the High-Frequency Harmonic Dispersion. Electronics, 14(14), 2852. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14142852






