KPV-UNet: KAN PP-VSSA UNet for Remote Image Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
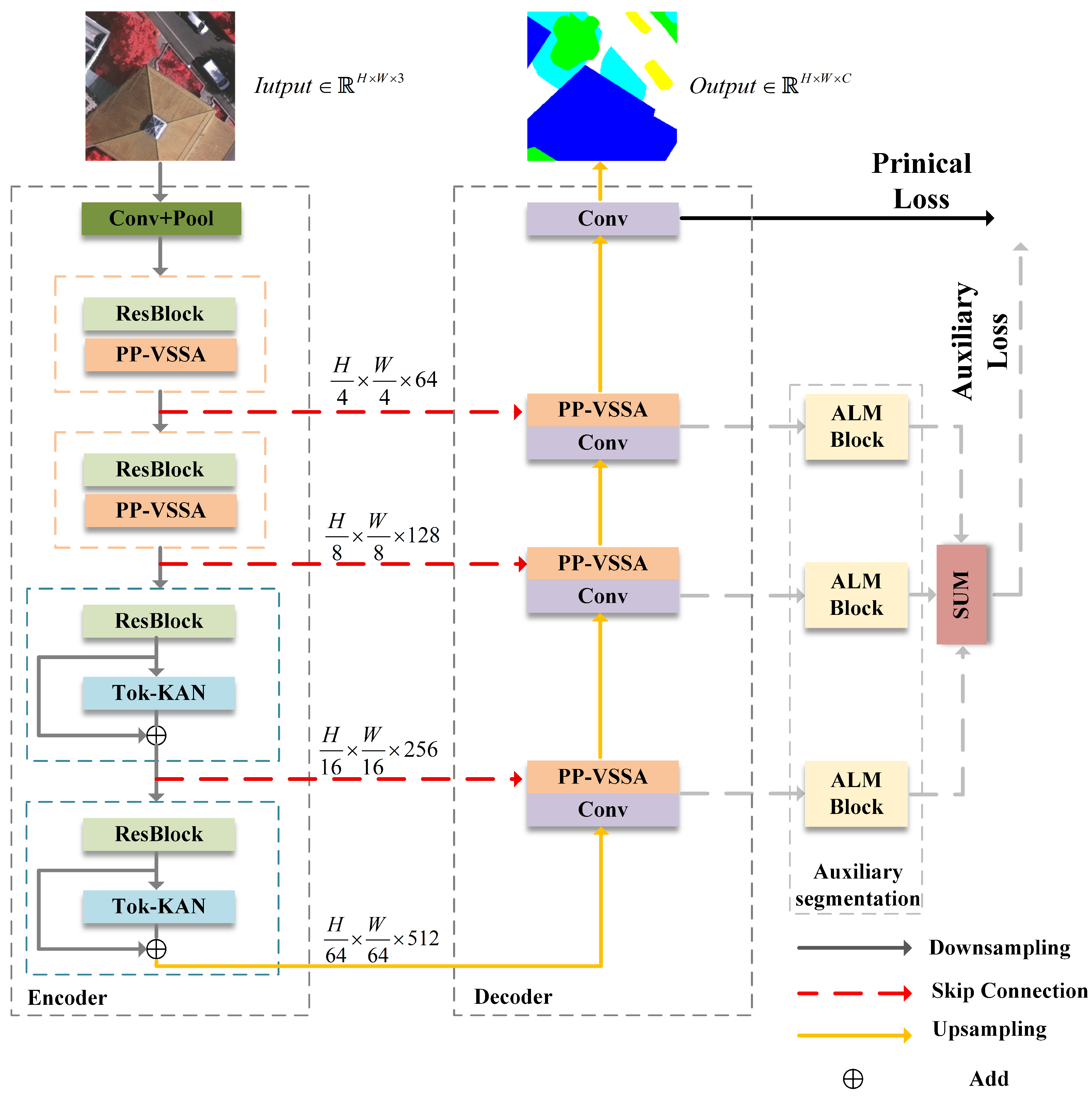
- A dual-branch encoding structure is proposed, integrating CNN, Mamba, and KAN. This design fully leverages the local modeling capability of CNNs, Mamba’s long range dependency modeling, and KAN’s nonlinear representation power to accurately recognize small objects and blurred boundaries in remote sensing images. As a result, it effectively enhances the synergy between local detail perception and global context understanding.
- We propose the Pyramid Pooling Visual State Space Attention (PP-VSSA) module, which fuses the efficient global dependency modeling capability of the EMA attention mechanism with the multi-scale context fusion capability of pyramid pooling, aiming to make up for the deficiencies of Mamba in terms of local detail portrayal and cross-scale semantic associations.
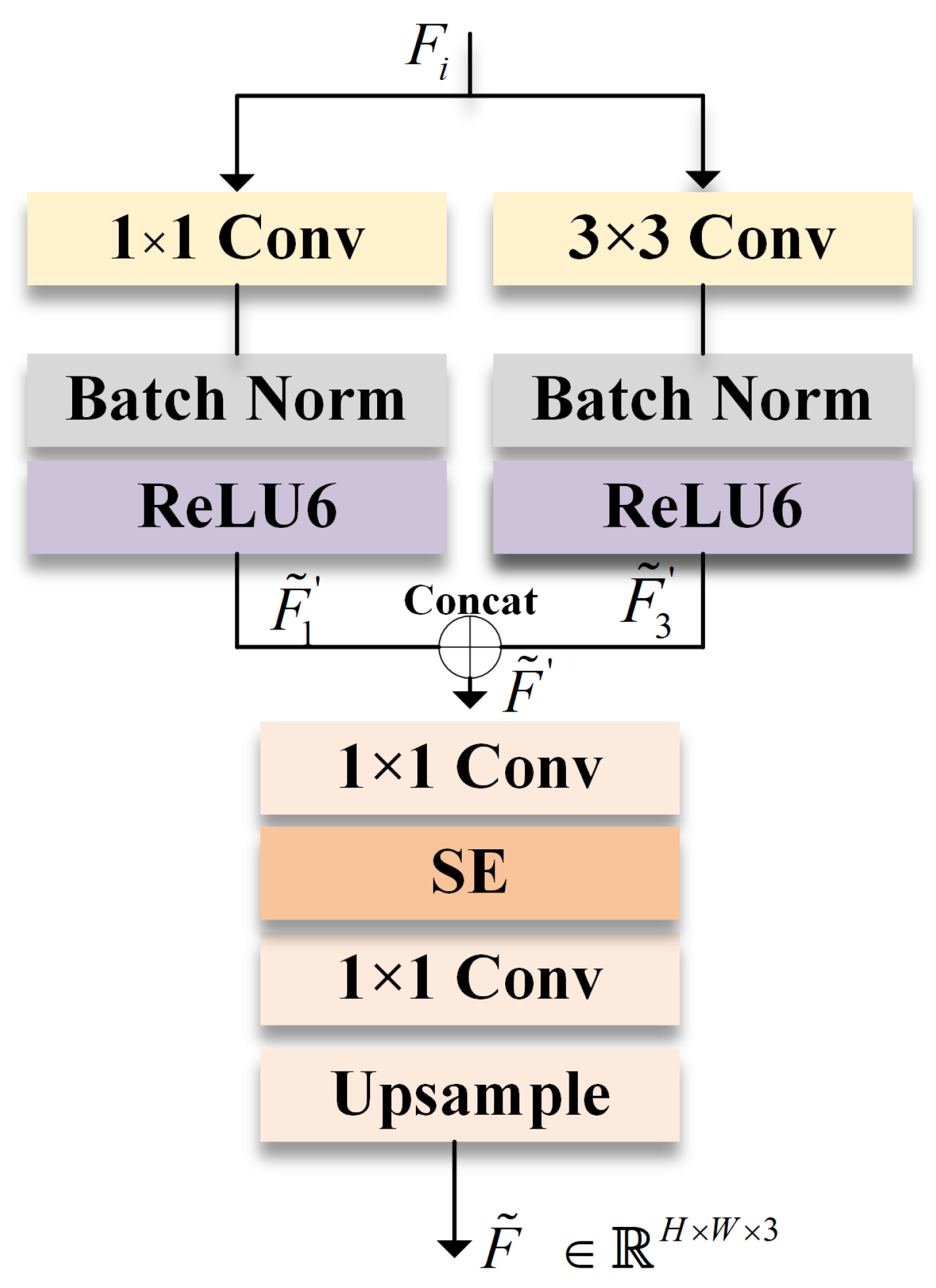
- We propose an Auxiliary Local Monitoring (ALM) block to address the decoder’s insufficient perception of local information. By using two convolution operations of different scales and introducing an auxiliary loss function, the model’s perception of local semantic information is enhanced with the help of supervised training. The restrictive configuration is only performed during the training phase, which saves inference costs and ensures overall application efficiency.
2. Related Work
2.1. Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation
2.2. Mamba
2.3. KAN
3. Materials and Methods
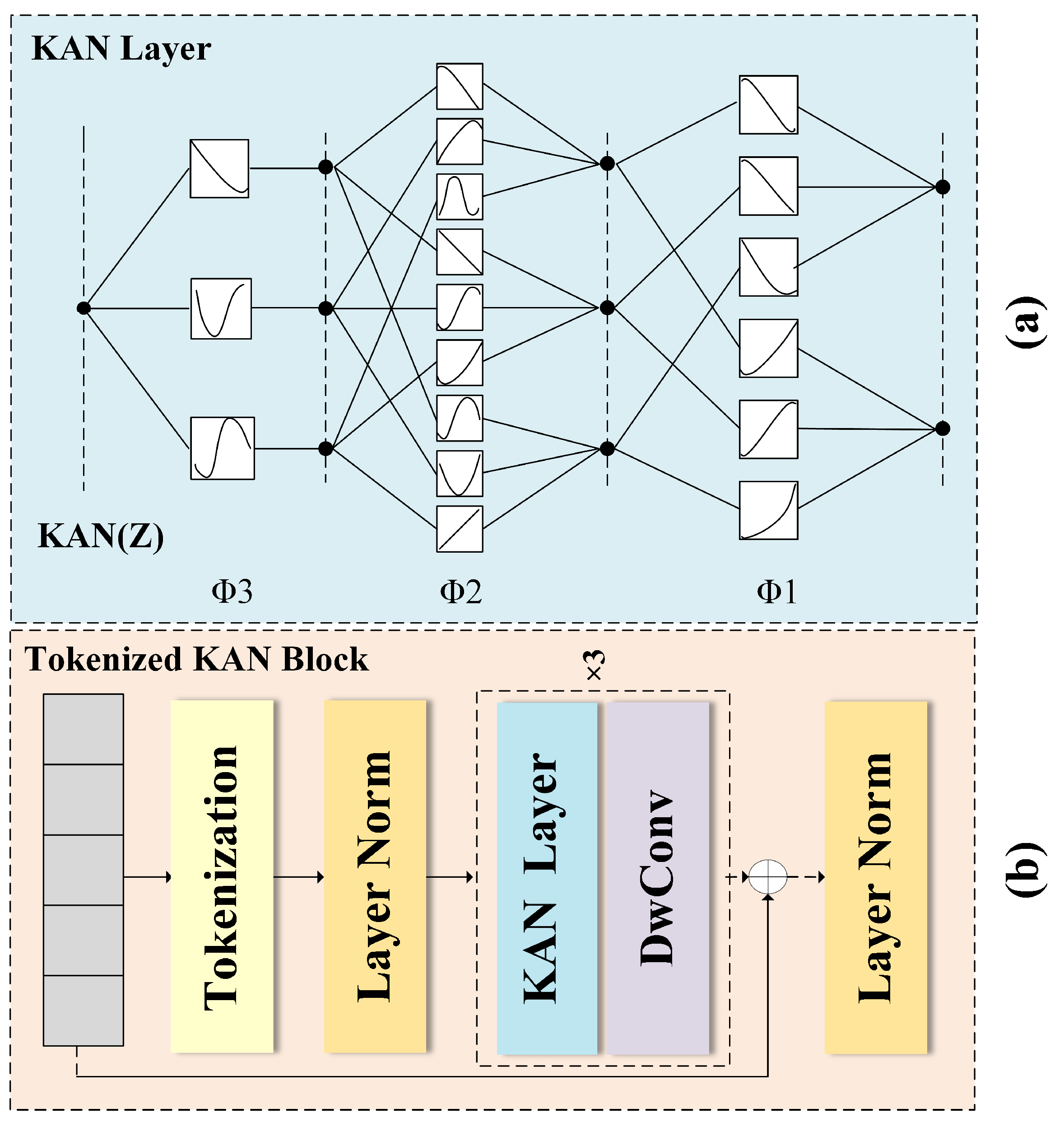
3.1. Tok-KAN Architecture Design for Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation
3.2. PP-VSSA: Pyramid Pooling Visual State Space Attention Module
3.3. Loss Function
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Dataset
4.1.1. ISPRS Vaihingen
4.1.2. LoveDA Urban
4.1.3. WHDLD
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.3. Performance Comparison
- ABCNet [15]: A bilateral network with a spatial path for detail preservation and a Res-Net-18-based context path enhanced by linear attention (AEM). Features are fused via channel-weighted aggregation (FAM) to combine local and global information.
- MAResUNet [29]: MAResUNet proposes a linear attention mechanism (LAM), which reduces the computational complexity of dot product attention from O(N2) to O(N) through first-order Taylor expansion approximation and feature normalization, and based on this, reconstructs U-Net jump connections to construct a multistage attention ResU-Net (MAResU-Net).
- UNetFormer [16]: UNetFormer proposes a UNet-like Transformer architecture, which works together with a lightweight ResNet18 encoder and a global–local attention decoder to form global–local collaborative optimization.
- ST-UNet [19]: ST-UNet adopts a dual encoder architecture in which the CNN-based main encoder and the Swin Transformer auxiliary encoder are processed in parallel. The auxiliary encoder embeds the spatial interaction module (SIM) to enhance the spatial information encoding through pixel-level correlation, and the feature compression module (FCM) retains small-scale feature details in patch token downsampling and hierarchically integrates global dependencies into the main encoder features through the relationship aggregation module (RAM).
- GBDNet [21]: GDBNet proposes a three-branch semantic segmentation network that optimizes boundary segmentation by working together with the global branch (Swin Transformer), detail branch (ResNet), and boundary branch (ResNet), combined with the feature preservation module (FPM), spatial interaction module (SIM), and balanced feature module (BFM).
- RS3Mamba [17]: RS3Mamba is a dual-branch semantic segmentation framework that extracts local features through the main branch based on ResNet. It models global dependencies through the auxiliary branch based on the VSS module (Mamba architecture) and realizes feature adaptive fusion in combination with the Collaborative Completion Module (CCM).
- PPMamba [33]: PPmamba utilizes a lightweight CNN–Mamba hybrid architecture to achieve global context modeling with linear complexity through the SS2D module.
4.3.1. Performance Comparison on ISPRS Vaihingen
4.3.2. Performance Comparison on LoveDA Urban
4.3.3. Performance Comparison on WHDLD
4.3.4. Ablation Experiments
4.3.5. Model Complexity Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, Q.; Shen, H.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, H.; Tan, W.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. Deep learning in environmental remote sensing: Achievements and challenges. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Huang, X. A coarse-to-fine weakly supervised learning method for green plastic cover segmentation using high-resolution remote sensing images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 188, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, J.; Lv, J.; Guan, Q. A cross-domain object-semantic matching framework for imbalanced high spatial resolution imagery water-body extraction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Tan, X.; Yuan, X. Extraction of Urban Built-Up Area Based on Deep Learning and Multi-Sources Data Fusion—The Application of an Emerging Technology in Urban Planning. Land 2022, 11, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, M. Smart city urban planning using an evolutionary deep learning model. Soft Comput. 2024, 28, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Gong, C.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, F. Clouds detection in Polar Icy Terrains: A Deformable Attention-based Deep Neural Network for Multispectral Polar Scene Parsing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 9954–9967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikle, S.; Anand, V.; Das, S. Geospatial practices for airpollution and meteorological monitoring, prediction, and forecasting. In Geospatial Practices in Natural Resources Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Wu, D.; Gao, J. The high spatial resolution Drought Response Index (HiDRI): An integrated framework for monitoring vegetation drought with remote sensing, deep learning, and spatiotemporal fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 312, 114324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, H. A guideline of u-net-based framework for precipitation estimates. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Sci. (IJAI4S) 2025, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.04597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, C.; Duan, C.; Wang, L.; Atkinson, P.M. ABCNet: Attentive bilateral contextual network for efficient semantic segmentation of Fine-Resolution remotely sensed imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 181, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, C.; Fang, S.; Duan, C.; Meng, X.; Atkinson, P.M. UNetFormer: A UNet-like transformer for efficient semantic segmentation of remote sensing urban scene imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 190, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Pun, M.O. Rs3 mamba: Visual state space model for remote sensing image semantic segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, D.; Yao, R.; Xue, Y. Swin transformer embedding UNet for remote sensing image semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, X.; Li, M.; Ma, Z. GDBNet: Boundary improving three-branch semantic segmentation network for remote sensing images. J. Electron. Imaging 2024, 33, 063019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Dao, T. Mamba: Linear-time sequence modeling with selective state spaces. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.00752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liao, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. Vision Mamba: Efficient Visual Representation Learning with Bidirectional State Space Model. In Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 21–27 July 2024; Salakhutdinov, R., Kolter, Z., Heller, K., Weller, A., Oliver, N., Scarlett, J., Berkenkamp, F., Eds.; PMLR: New York, NY, USA, 2024; Volume 235, pp. 62429–62442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Vaidya, S.; Ruehle, F.; Halverson, J.; Soljačić, M.; Hou, T.Y.; Tegmark, M. Kan: Kolmogorov-arnold networks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.19756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearst, M.A.; Dumais, S.T.; Osuna, E.; Platt, J.; Scholkopf, B. Support vector machines. IEEE Intell. Syst. Their Appl. 1998, 13, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018; Proceedings 4. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zheng, S.; Duan, C.; Su, J.; Zhang, C. Multistage attention ResU-Net for semantic segmentation of fine-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12077–12090. Available online: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/3540261.3541185 (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, H.; Xie, L.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Jiao, J.; Liu, Y. Vmamba: Visual state space model. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 103031–103063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Zhou, S.; Sun, X. PPMamba: Enhancing Semantic Segmentation in Remote Sensing Imagery by SS2D. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2025, 22, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, Y. U-kan makes strong backbone for medical image segmentation and generation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 25 February–4 March 2025; Volume 39, pp. 4652–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. KM-UNet KAN Mamba UNet for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.02559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, M. Kolmogorov-arnold network for satellite image classification in remote sensing. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.00600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xu, J.; Lei, T.; Wang, Y.; Du, X.; Zhang, W.; Lv, Z.; Gong, M. AEKAN: Exploring Superpixel-based AutoEncoder Kolmogorov-Arnold Network for Unsupervised Multimodal Change Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydi, S.T.; Bozorgasl, Z.; Chen, H. Unveiling the power of wavelets: A wavelet-based kolmogorov-arnold network for hyperspectral image classification. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.07869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Guo, H.; Zhan, J.; Huang, Z. Efficient multi-scale attention module with cross-spatial learning. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, A.; Lu, X.; Zhong, Y. LoveDA: A remote sensing land-cover dataset for domain adaptive semantic segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.08733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Zhou, W.; Deng, X.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, Q. Multilabel remote sensing image retrieval based on fully convolutional network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Method | Impsurf | Building | Low veg | Tree | Car | mIoU | mFl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAResUNet [29] | 85.45 | 91.74 | 67.22 | 82.56 | 74.11 | 80.22 | 88.76 |
| ST-UNet [19] | 76.19 | 83.42 | 57.02 | 72.54 | 62.21 | 70.28 | 79.77 |
| ABCNet [15] | 85.80 | 92.73 | 67.31 | 83.50 | 80.73 | 82.01 | 89.88 |
| UNetFormer [16] | 84.46 | 91.73 | 67.59 | 84.00 | 83.88 | 82.33 | 90.09 |
| GBDNet [21] | 84.52 | 91.58 | 66.78 | 82.56 | 81.35 | 81.37 | 89.03 |
| RS3Mamba [17] | 86.30 | 93.75 | 67.11 | 83.70 | 83.01 | 82.77 | 90.32 |
| PPMamba [33] | 86.60 | 93.49 | 67.06 | 83.59 | 84.38 | 83.03 | 90.47 |
| KPV-UNet | 87.03 | 94.16 | 68.68 | 84.12 | 86.16 | 84.03 | 91.09 |
| Method | Background | Building | Road | Water | Barren | Forest | Agriculture | mIoU | mF1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAResUNet [29] | 34.70 | 49.75 | 42.45 | 49.84 | 32.31 | 37.10 | 6.38 | 36.08 | 51.30 |
| ST-UNet [19] | 34.57 | 52.12 | 46.45 | 50.12 | 35.23 | 40.23 | 30.12 | 41.26 | 52.24 |
| ABCNet [15] | 36.96 | 55.62 | 50.87 | 54.71 | 38.75 | 33.55 | 32.80 | 43.32 | 53.36 |
| UNetFormer [16] | 37.53 | 59.15 | 52.63 | 69.10 | 30.13 | 44.94 | 39.90 | 47.63 | 63.57 |
| GBDNet [21] | 38.45 | 56.76 | 56.33 | 66.34 | 31.45 | 44.15 | 46.45 | 48.56 | 64.15 |
| RS3Mamba [17] | 40.53 | 59.08 | 57.36 | 67.01 | 26.45 | 44.76 | 47.96 | 49.02 | 64.80 |
| PPMamba [33] | 39.45 | 63.17 | 61.56 | 66.83 | 38.07 | 41.00 | 38.46 | 49.79 | 65.60 |
| KPV-UNet | 37.84 | 61.79 | 59.99 | 69.56 | 32.44 | 46.55 | 50.75 | 51.27 | 66.82 |
| Method | Bare Soil | Water | Pavement | Road | Vegetation | Building | mIoU | mF1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAResUNet [29] | 38.63 | 93.23 | 42.17 | 59.12 | 79.48 | 54.82 | 61.24 | 74.21 |
| ST-UNet [19] | 38.72 | 93.21 | 41.69 | 58.16 | 78.91 | 54.98 | 60.94 | 73.93 |
| ABCNet [15] | 38.38 | 93.71 | 41.85 | 58.88 | 79.66 | 54.56 | 61.17 | 74.11 |
| UNetFormer [16] | 39.06 | 93.81 | 43.00 | 59.62 | 79.76 | 55.15 | 61.73 | 74.61 |
| GBDNet [21] | 41.77 | 94.25 | 42.03 | 58.76 | 80.32 | 56.77 | 62.32 | 74.88 |
| RS3Mamba [17] | 39.49 | 94.02 | 42.29 | 58.39 | 80.31 | 56.08 | 61.76 | 74.61 |
| PPMamba [33] | 39.65 | 94.15 | 44.11 | 61.08 | 80.41 | 56.05 | 62.58 | 75.30 |
| KPV-UNet | 38.96 | 94.55 | 44.59 | 61.37 | 80.55 | 57.11 | 62.87 | 75.52 |
| Dataset | Model | PP-VSSA | Tok-KAN | ALM | mFl | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaihingen | PPMamba [33] | 90.47 | 83.03 | |||
| Vaihingen | KPV-UNet | × | × | × | 89.51 | 81.39 |
| Vaihingen | KPV-UNet | ✓ | × | × | 90.00 | 82.57 |
| Vaihingen | KPV-UNet | ✓ | ✓ | × | 90.53 | 83.09 |
| Vaihingen | KPV-UNet | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 91.09 | 84.03 |
| WHDLD | PPMamba [33] | 75.30 | 62.58 | |||
| WHDLD | KPV-UNet | × | × | × | 73.93 | 61.51 |
| WHDLD | KPV-UNet | ✓ | × | × | 73.93 | 61.51 |
| WHDLD | KPV-UNet | ✓ | ✓ | × | 74.57 | 62.01 |
| WHDLD | KPV-UNet | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 75.52 | 62.87 |
| Method | FLOPs (G) | Parameter (M) | Memory (MB) | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAResUnet [29] | 35.18 | 26.28 | 279 | 80.22 |
| ABCNet [15] | 15.69 | 13.41 | 207 | 82.01 |
| ST-UNet [19] | 79.73 | 187 | 4167 | 70.28 |
| UNetFormer [16] | 11.74 | 11.68 | 219 | 82.33 |
| GBDNet [21] | 113.90 | 199 | 4434 | 81.37 |
| RS3Mamba [17] | 63.97 | 49.65 | 499 | 82.77 |
| PPMamba [33] | 56.32 | 30.23 | 1006 | 83.03 |
| KPV-UNet | 63.18 | 28.01 | 1043 | 84.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Rao, Q.; Wang, L.; Tang, T.; Chen, C. KPV-UNet: KAN PP-VSSA UNet for Remote Image Segmentation. Electronics 2025, 14, 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14132534
Zhang S, Rao Q, Wang L, Tang T, Chen C. KPV-UNet: KAN PP-VSSA UNet for Remote Image Segmentation. Electronics. 2025; 14(13):2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14132534
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shuiping, Qiang Rao, Lei Wang, Tang Tang, and Chen Chen. 2025. "KPV-UNet: KAN PP-VSSA UNet for Remote Image Segmentation" Electronics 14, no. 13: 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14132534
APA StyleZhang, S., Rao, Q., Wang, L., Tang, T., & Chen, C. (2025). KPV-UNet: KAN PP-VSSA UNet for Remote Image Segmentation. Electronics, 14(13), 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14132534






