A Self-Powered Smart Glove Based on Triboelectric Sensing for Real-Time Gesture Recognition and Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of Ecoflex Film
2.2. Assembly of Arc-Shaped Glove-Based HMI Sensors
2.3. Characterization and Measurement
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of TENG Sensor
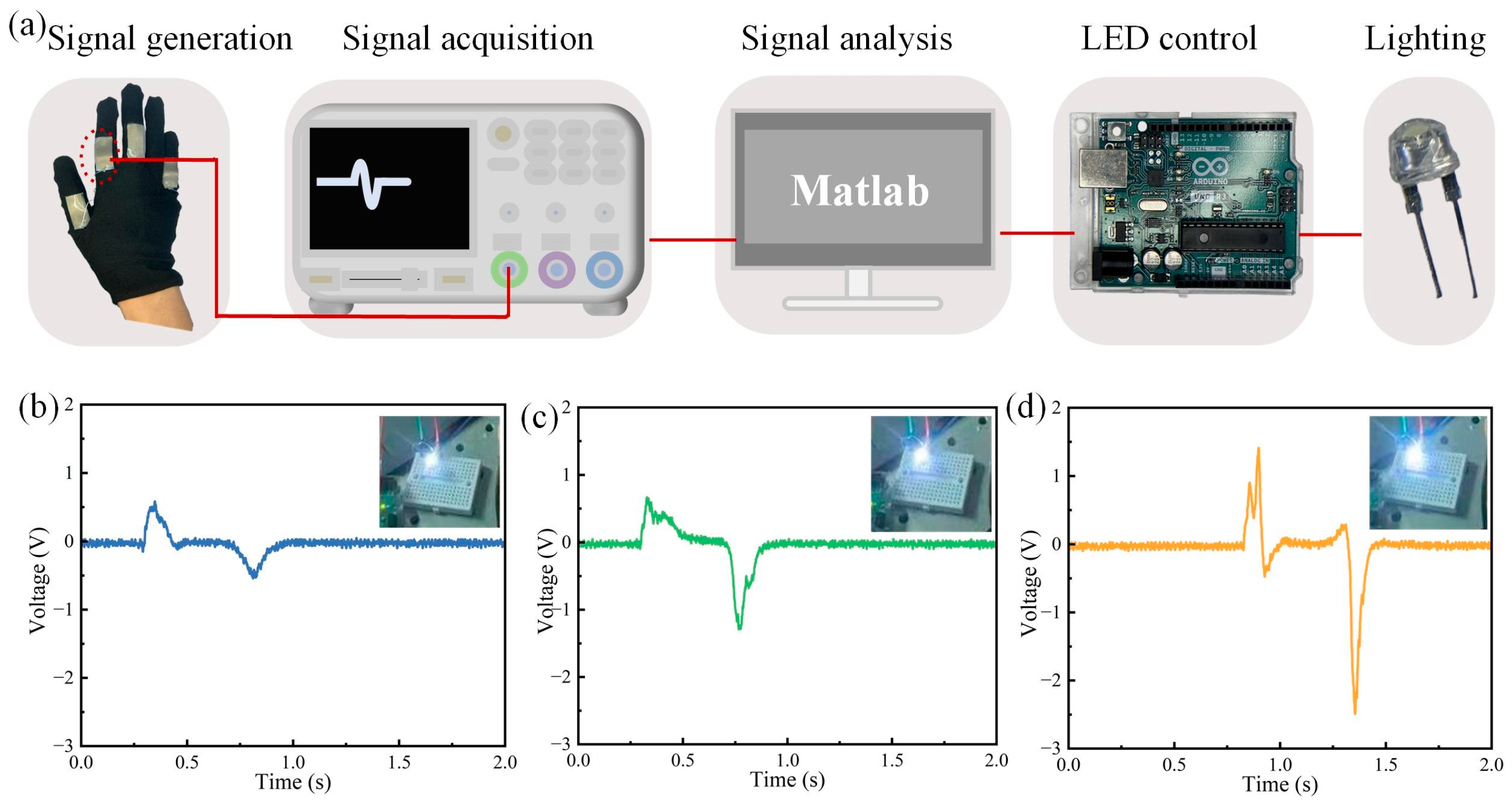
3.2. Glove-Based HMI for LED Control
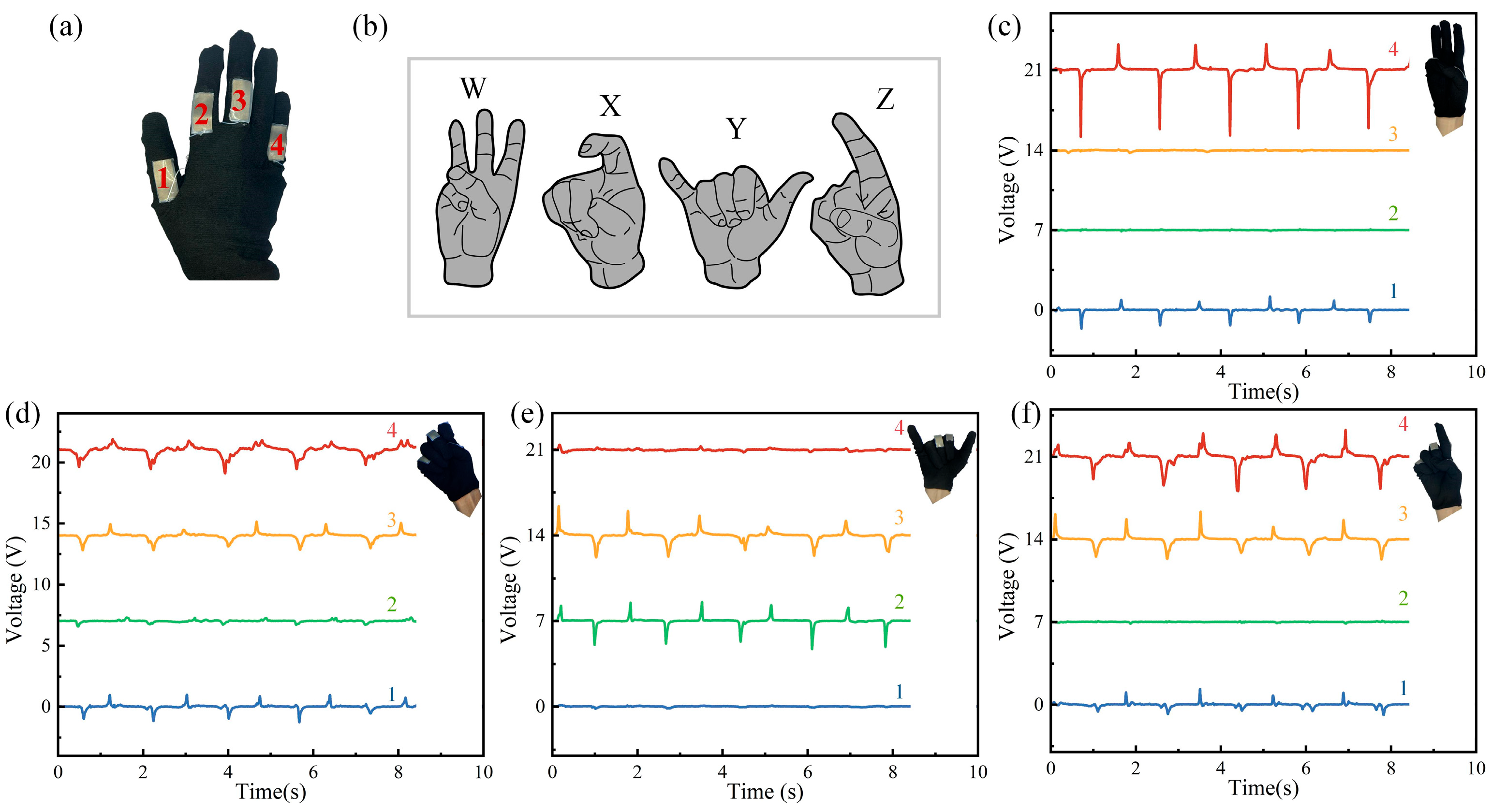
3.3. Multi-Sensor Integration for Hand Motion Capture and American Sign Language (ASL) Recognition
3.4. Deep Learning-Assisted Glove-Based HMI for Human and Object Recognition
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.; Niu, H.; Shen, G.; Li, Y. Self-Healing Hydrogel-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator in Smart Glove System for Integrated Drone Safety Protection and Motion Control. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 35, 2419809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Xiao, X.; Li, Q.; Ding, W.; Fu, H.Y. Triboelectric Bending Sensor Based Smart Glove towards Intuitive Multi-Dimensional Human-Machine Interfaces. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Q.; He, T.; Liu, H.; Chen, T.; Lee, C. Haptic-Feedback Smart Glove as a Creative Human-Machine Interface (HMI) for Virtual/Augmented Reality Applications. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz8693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Xu, Z.; Occhipinti, E.; Yi, W.; Xu, M.; Kumar, S.; Virk, G.; Gao, S.; Occhipinti, L. From brain to movement: Wearables-based motion intention prediction across the human nervous system. Nano Energy 2023, 115, 108712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, S.E.; Granat, M.H. Intention Detection Using a Neuro-Fuzzy EMG Classifier. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2002, 21, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Maýe, A.; Görner, M.; Ruppel, P.; Engel, A.K.; Zhang, J. Coordinating Human-Robot Collaboration by EEG-Based Human Intention Prediction and Vigilance Control. Front. Neurorobotics 2022, 16, 1068274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Bi, L.; Feleke, A.G. Detection of Emergency Braking Intention From Soft Braking and Normal Driving Intentions Using EMG Signals. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 131637–131647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Sun, Z.; Lee, C. Soft Modular Glove with Multimodal Sensing and Augmented Haptic Feedback Enabled by Materials’ Multifunctionalities. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 14097–14110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Zhu, M.; Lee, C. Progress in the Triboelectric Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs)-Moving from Smart Gloves to AI/Haptic Enabled HMI in the 5G/IoT Era. Nanoenergy Adv. 2021, 1, 81–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Yang, L.; Fortino, G. Stretchable Human Machine Interface Based on Smart Glove Embedded With PDMS-CB Strain Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 8073–8081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchantchane, R.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Dunn, A.; Sariyildiz, E.; Alici, G. Advancing Human-Machine Interface (HMI) Through Development of a Conductive-Textile Based Capacitive Sensor. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2025, 10, 2401458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozioko, O.; Dahiya, R. Smart Tactile Gloves for Haptic Interaction, Communication, and Rehabilitation. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2022, 4, 2100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glauser, O.; Wu, S.; Panozzo, D.; Hilliges, O.; Sorkine-Hornung, O. Interactive Hand Pose Estimation Using a Stretch-Sensing Soft Glove. ACM Trans. Graph. 2019, 38, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qiu, Z.; Kan, H.; Guan, T.; Zhou, C.; Qian, K.; Wang, C.; Li, Y. Incorporating Machine Learning Strategies to Smart Gloves Enabled by Dual-Network Hydrogels for Multitask Control and User Identification. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 1886–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yiu, C.; Song, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yao, K.; Wong, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, L.; Huang, X.; Nejad, S.K.; et al. Electronic Skin as Wireless Human-Machine Interfaces for Robotic VR. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabl6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakori, A.; Jiang, Z.; Servati, A.; Soltanian, S.; Narayana, H.; Le, K.; Nakayama, C.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z.J.; Eng, J.J.; et al. Capturing Complex Hand Movements and Object Interactions Using Machine Learning-Powered Stretchable Smart Textile Gloves. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2024, 6, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, W.; Wang, F.; Sun, L. Smart Glove Human-Machine Interface Based on Strain Sensors Array for Control UAV. IJEETC 2023, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L. Packaged Elastomeric Optical Fiber Sensors for Healthcare Monitoring and Human-Machine Interaction. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2301415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, B.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J.; He, X.-D.; Yuan, J.; Wu, Q. Plastic-Optical-Fiber-Enabled Smart Glove for Machine-Learning-Based Gesture Recognition. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 4252–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Cheng, J.; Qu, X.; Song, Y.; Yang, L.; Shen, J.; Bai, Z.; Ji, L. Triboelectric-Inertial Sensing Glove Enhanced by Charge-Retained Strategy for Human-Machine Interaction. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2408689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.T.; Zhang, X.; Pan, J.; Thean, A.V.-Y. Hybrid Integration of Wearable Devices for Physiological Monitoring. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 10386–10434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical Systems of Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 161–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Z.L. The Current Development and Future Outlook of Triboelectric Nanogenerators: A Survey of Literature. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Dong, K.; Ye, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zhai, S.; Cheng, R.; Liu, D.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. A Breathable, Biodegradable, Antibacterial, and Self-Powered Electronic Skin Based on All-Nanofiber Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhu, M.; Shan, X.; Lee, C. Augmented Tactile-Perception and Haptic-Feedback Rings as Human-Machine Interfaces Aiming for Immersive Interactions. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.; Fang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Wang, L.; He, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, P. Performance-Enhanced Flexible Self-Powered Tactile Sensor Arrays Based on Lotus Root-Derived Porous Carbon for Real-Time Human–Machine Interaction of the Robotic Snake. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 9333–9342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Xi, G.; Mao, R.; Ma, Y.; Wang, D.; Tang, M.; Xu, Z.; Luan, H. Ultrastretchable, Self-Healing Conductive Hydrogel-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Human–Computer Interaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 5128–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nayak, S.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Salila Vijayalal Mohan, H.K.; Pan, J.; Liu, Z.; Heng, C.H.; Thean, A.V.-Y. A Soft Polydimethylsiloxane Liquid Metal Interdigitated Capacitor Sensor and Its Integration in a Flexible Hybrid System for On-Body Respiratory Sensing. Materials 2019, 12, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Li, Z.; Ji, L. Development and Application of Nanogenerators in Humanoid Robotics. Nano Trends 2023, 3, 100013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wang, H.; Zhao, G.; Fu, J.; Yao, K.; Jia, S.; Shi, R.; Huang, X.; Wu, P.; Li, J.; et al. Self-Powered Electrotactile Textile Haptic Glove for Enhanced Human-Machine Interface. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eadt0318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Zhang, Z.; He, T.; Lee, C. AI Enabled Sign Language Recognition and VR Space Bidirectional Communication Using Triboelectric Smart Glove. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, F.; Sun, Z.; He, T.; Shi, Q.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Lee, C. Machine Learning Glove Using Self-Powered Conductive Superhydrophobic Triboelectric Textile for Gesture Recognition in VR/AR Applications. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H. Highly stretchable PTFE particle enhanced triboelectric nanogenerator for droplet energy harvestings. Nano Energy 2023, 118, 109000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Sun, Z.; Shi, Q.; Zhu, M.; Anaya, D.V.; Xu, M.; Chen, T.; Yuce, M.R.; Thean, A.V.-Y.; Lee, C. Self-powered glove-based intuitive interface for diversified control applications in real/cyber space. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Duan, X.; Wen, J.; Tian, Q.; Shi, L.; Dong, S.; Peng, L. A Self-Powered Smart Glove Based on Triboelectric Sensing for Real-Time Gesture Recognition and Control. Electronics 2025, 14, 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122469
Liu S, Duan X, Wen J, Tian Q, Shi L, Dong S, Peng L. A Self-Powered Smart Glove Based on Triboelectric Sensing for Real-Time Gesture Recognition and Control. Electronics. 2025; 14(12):2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122469
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shuting, Xuanxuan Duan, Jing Wen, Qiangxing Tian, Lin Shi, Shurong Dong, and Liang Peng. 2025. "A Self-Powered Smart Glove Based on Triboelectric Sensing for Real-Time Gesture Recognition and Control" Electronics 14, no. 12: 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122469
APA StyleLiu, S., Duan, X., Wen, J., Tian, Q., Shi, L., Dong, S., & Peng, L. (2025). A Self-Powered Smart Glove Based on Triboelectric Sensing for Real-Time Gesture Recognition and Control. Electronics, 14(12), 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122469






