Toward Building a Domain-Based Dataset for Arabic Handwritten Text Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Review of Existing Datasets
- Language: one language or multiple languages.
- Recognition Level: characters, digits, words, lines, or paragraphs.
- Task: text recognition, writer identification, and so on.
- Script Type: printed, handwritten, or both.
- Recognition Type: online or offline.
2.2. Review of Research for Legal Documents
3. REJD Dataset
3.1. Data Specifications
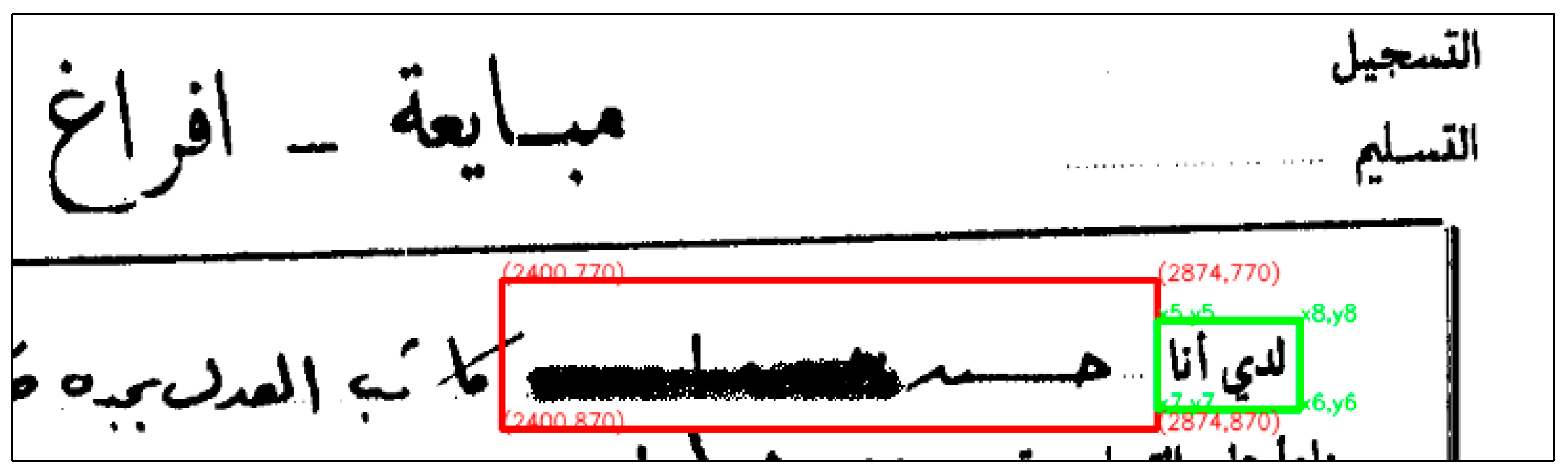
3.2. Data Preparation and Segmentation
3.2.1. Using OCR Software Tool
3.2.2. Pre-Processing of the Crops
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pechwitz, M.; Maddouri, S.S.; Märgner, V.; Ellouze, N.; Amiri, H. IFN/ENIT-database of handwritten Arabic words. In Proceedings of the Francophone International Conference on Writing and Document, CIFED’02, Hammamet, Tunisia, 20–23 October 2002; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, M.; Chan, A.; Mijar, A.; Habchi, G.; Younes, C.; Wong, C.W.; Khater, A. Muharaf: Manuscripts of handwritten Arabic dataset for cursive text recognition. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 58525–58538. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, S.A.; Ahmad, I.; Al-Khatib, W.G.; Alshayeb, M.; Parvez, M.T.; Märgner, V.; Fink, G.A. KHATT: An open Arabic offline handwritten text database. Pattern Recognit. 2014, 47, 1096–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoizou, A.; Zarghili, A.; Chaker, I. MOJ-DB: A new database of Arabic historical handwriting and a novel approach for subwords extraction. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2022, 159, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altwaijry, N.; Al-Turaiki, I. Arabic handwriting recognition system using convolutional neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 2249–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A. Arabic handwritten alphabets, words and paragraphs per user (AHAWP) dataset. Data Brief 2022, 41, 107947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaha, H.M.; Ali, H.A.; Saraya, M.; Badawy, M. A new Arabic handwritten character recognition deep learning system (AHCR-DLS). Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 6325–6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najam, R.; Faizullah, S. A scarce dataset for ancient Arabic handwritten text recognition. Data Brief 2024, 56, 110813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegel, A.; Shah, M.; Peaslee, G.; Roof, B.; Elwany, E. The law of large documents: Understanding the structure of legal contracts using visual cues. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08128. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrycks, D.; Burns, C.; Chen, A.; Ball, S. CUAD: An expert-annotated NLP dataset for legal contract review. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.06268. [Google Scholar]
- El-Farahaty, H.; Khallaf, N.; Alonayzan, A. Building the Leeds Monolingual and Parallel Legal Corpora of Arabic and English Countries’ Constitutions: Methods, Challenges and Solutions. Corpus Pragmat. 2023, 7, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Poplavska, E.; O’Toole, N.; Arora, S.; Norton, T.; Sadeh, N.; Wilson, S. Creation and analysis of an international corpus of privacy laws. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.14169. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; He, H. An artificial-intelligence-based semantic assist framework for judicial trials. Asian J. Law Soc. 2020, 7, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, T.; Wu, Q.; Jin, F. Convolutional-neural-network-based Multilabel Text Classification for Automatic Discrimination of Legal Documents. Sens. Mater. 2020, 32, 2659–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sando, K.; Suzuki, T.; Aiba, A. A constraint solving web service for a handwritten Japanese historical kana reprint support system. In Agents and Artificial Intelligence: 10th International Conference, ICAART 2018, Funchal, Madeira, Portugal, 16–18 January 2018; Revised Selected Papers 10; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Braz, F.A.; da Silva, N.C.; de Campos, T.E.; Chaves, F.B.S.; Ferreira, M.H.; Inazawa, P.H.; Coelho, V.H.; Sukiennik, B.P.; de Almeida, A.P.G.S.; Vidal, F.B.; et al. Document classification using a Bi-LSTM to unclog Brazil’s supreme court. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.11569. [Google Scholar]
- Maken, P.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, M.K. A study on various techniques involved in gender prediction system: A comprehensive review. Cybern. Inf. Technol. 2019, 19, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Mo, J.; Chow, E.; Chen, H.; Guo, J.; Gong, Z. Multi-Task CNN for classification of Chinese legal questions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 14th International Conference on e-Business Engineering (ICEBE), Shanghai, China, 4–6 November 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Alrasheed, N.; Prasanna, S.; Rowland, R.; Rao, P.; Grieco, V.; Wasserman, M. Evaluation of deep learning techniques for content extraction in Spanish colonial notary records. In Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Structuring and Understanding of Multimedia heritAge Contents, Chengdu, China, 20 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kirmizialtin, S.; Wrisley, D. Automated transcription of non-Latin script periodicals: A case study in the Ottoman Turkish print archive. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.01139. [Google Scholar]
- Noëmie, L.; Salah, C.; Vidal-Gorène, C. New Results for the Text Recognition of Arabic Maghrib {ī} Manuscripts—Managing an Under-resourced Script. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.16147. [Google Scholar]
- Bhusal, A.; Chhetri, G.B.; Bhattarai, K.; Pandey, M. “Nepali OCR”; Institute of Engineering, Pulchowk Campus: Lalitpur, Nepal, 2023; Available online: https://elibrary.tucl.edu.np/items/1c6b2978-08e9-4208-a521-371442a4d452 (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- Shihab, I.H.; Hasan, R.; Emon, M.R.; Hossen, S.M.; Ansary, N.; Ahmed, I.; Rakib, F.R.; Dhruvo, S.E.; Dip, S.S.; Pavel, A.H.; et al. Badlad: A large multi-domain Bengali document layout analysis dataset. In International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alghamdi, M.A.; Alkhazi, I.S.; Teahan, W.J. Arabic OCR evaluation tool. In Proceedings of the 2016 7th International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology (CSIT), Amman, Jordan, 13–14 July 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Salehudin, M.; Basah, S.; Yazid, H.; Basaruddin, K.; Som, M.M.; Sidek, K. Analysis of optical character recognition using easyocr under image degradation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2641, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukundo, O. Effects of Image Size on Deep Learning. Electronics 2023, 12, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menassel, Y.; Marie, R.R.; Abbas, F.; Gattal, A.; Al-Sarem, M. Dynamic Feature Weighting for Efficient Multi-Script Identification Using YafNet: A Deep CNN Approach. J. Intell. Syst. Internet Things 2025, 14, 260–273. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nugraha, G.S.; Darmawan, M.I.; Dwiyansaputra, R. Comparison of CNN’s Architecture GoogleNet, AlexNet, VGG-16, Lenet-5, Resnet-50 in Arabic Handwriting Pattern Recognition. Kinet. Game Technol. Inf. Syst. Comput. Netw. Comput. Electron. Control 2023, 8, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudeyer, R.S.; Almoosawi, N.M. Combination of machine learning algorithms and Resnet50 for Arabic Handwritten Classification. Informatica 2023, 46, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyahya, H.M.; Ben Ismail, M.M.; Al-Salman, A. Intelligent ResNet-18 based Approach for Recognizing and Assessing Arabic Children’s Handwriting. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Smart Computing and Application (ICSCA), Hail, Saudi Arabia, 5–6 February 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Finjan, R.H.; Rasheed, A.S.; Hashim, A.A.; Murtdha, M. Arabic handwritten digits recognition based on convolutional neural networks with resnet-34 model. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2021, 21, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Durayhim, A.; Al-Ajlan, A.; Al-Turaiki, I.; Altwaijry, N. Towards accurate children’s Arabic handwriting recognition via deep learning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zendel, O.; Culpepper, J.S.; Scholer, F.; Thomas, P. Enhancing human annotation: Leveraging large language models and efficient batch processing. In Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Human Information Interaction and Retrieval, Sheffield, UK, 10–14 March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, D.L.; Akdogan, M.U.; Altindag, C.; Alkim, E. ePAD: An image annotation and analysis platform for quantitative imaging. Tomography 2019, 5, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




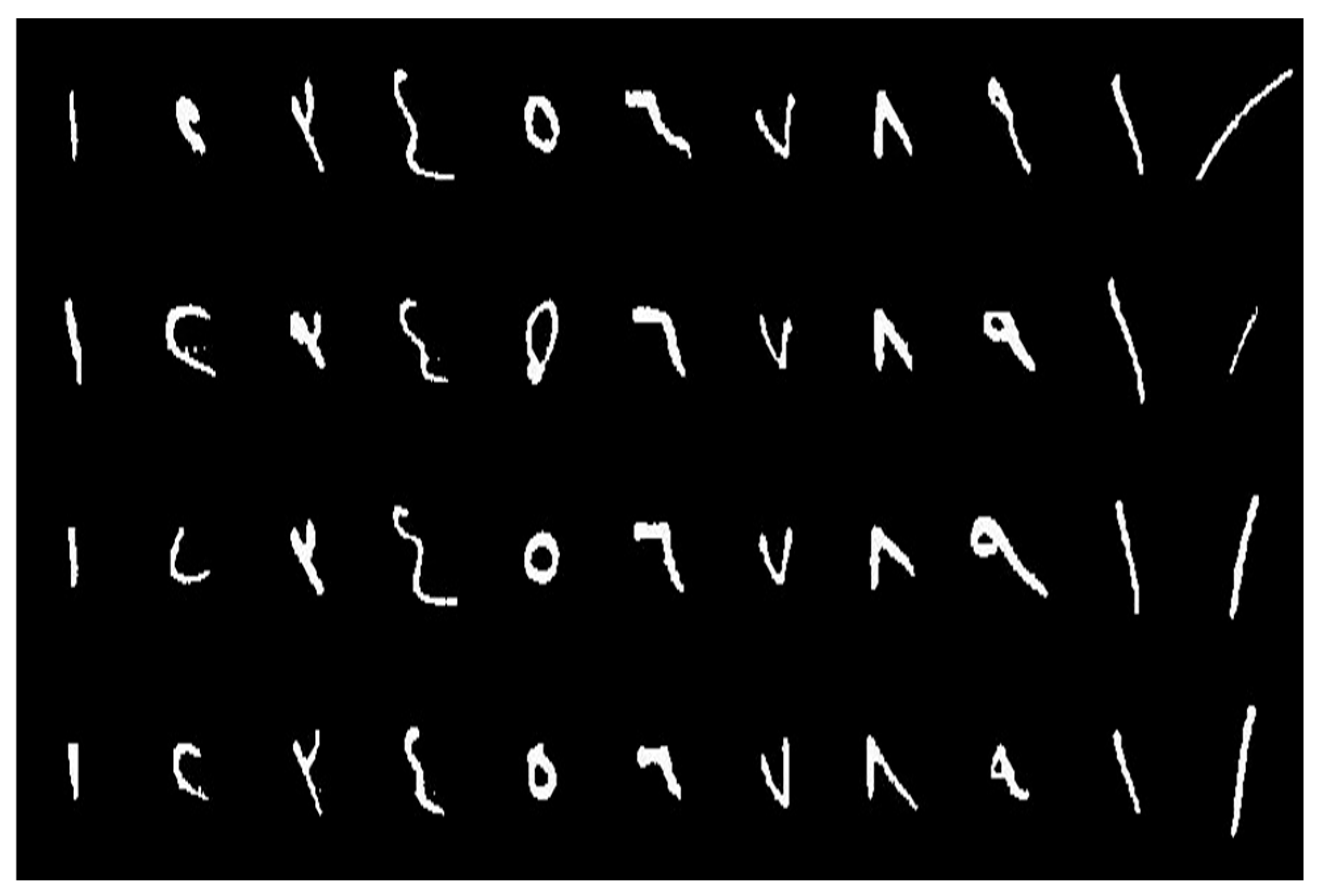



| Dataset | Reference | Data Level | Data Size (# Images) | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFN/ENIT (2002) | M. Pechwitz et al. [1] | Words | 26,549 | Public/free |
| KHATT (2012) | S. A. Mahmoud et al. [3] | Paragraphs | 4000 | Public/free |
| Hijja (2021) | N. Altwaijry et al. [5] | Characters (alphabets) | 47,434 | Public/free |
| HMBD (2021) | H. M. Balaha et al. [7] | Numbers, Characters | 54,115 | Public |
| MOJ-DB (2022) | A. Zoizou et al. [4] | Sub-words | 560,000 | Public/free/upon request |
| AHAWP (2022) | M. A. Khan [6] | Words, alphabets, paragraphs | 61,584 | Public/free |
| Muharaf (2025) | Saeed et al. [2] | Text lines | 1644 | Partially public |
| Reference | Year | Script Language | Document Type | Main Task | Methodology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [15] | 2018 | Japanese | Historical manuscripts | Reprint support system for reading manuscripts | Constraint solving web service |
| [16] | 2018 | English script (Brazil) | Lawsuit cases in courts | Document classification | BDLSTM |
| [17] | 2019 | Multiple languages | Many datasets | Gender prediction | Feature extraction and classification methods (GLBP and HOG) |
| [18] | 2020 | Chinese | Legal documents | Document multilabel classification | MLTCNN |
| [19] | 2021 | English script (Spanish) | Colonial notary records | Content extraction | Deep learning pre-trained model evaluation |
| [20] | 2022 | Arabic script (Ottoman/Turkish) | 19′th–20′th-century periodicals | Automated transcription | Deep learning method of HTR models |
| [21] | 2022 | Arabic script (Maghrebi) | Old manuscripts | Text recognition | Word-based neural approach |
| [22] | 2023 | Devanagari script (Nepali) | Students’ handwritten scripts | Text recognition | CRNN |
| [23] | 2023 | Bengali | Six domains, including public domain government documents and property deeds | Document layout analysis (DLA) | Building a large multi-domain DLA dataset |
| [8] | 2024 | Arabic | Historical book and page-level transcriptions | Text recognition | Deep learning OCR modeling and testing |
| Digits in English Script | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | Total |
| Digits in Arabic Script | ۰ | ۱ | ۲ | ۳ | ٤ | ٥ | ٦ | ۷ | ۸ | ۹ | |
| # HMBD Digits | 480 | 241 | 379 | 459 | 200 | 464 | 489 | 474 | 488 | 474 | 3668 |
| # REJD Digits | 0 | 33 | 105 | 119 | 277 | 51 | 73 | 36 | 45 | 64 | 803 |
| Total | 480 | 274 | 484 | 578 | 477 | 515 | 562 | 510 | 533 | 538 | 4471 |
| Word/Special Character | محمد | علي | عبد | لله | / | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | 182 | 182 | 182 | 182 | 44 | 772 |
| Related Work | Model | Dataset | Type | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [30] 2022 | ResNet-50 | AIA9K | Alphabets | 92.37% |
| AHCD | Alphabets | 98.39% | ||
| Hijja | Alphabets | 91.64% | ||
| [31] 2023 | ResNet-18 | AHCD | Alphabets | 97.26% |
| [32] 2021 | ResNet-34 | MADBase | Digits | 99.6% |
| This work | ResNet-50 | HMBD | Digits | 92% |
| REJD + HMBD | Digits | 98% | ||
| REJD | Words | 96.3% |
| Training Metrics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
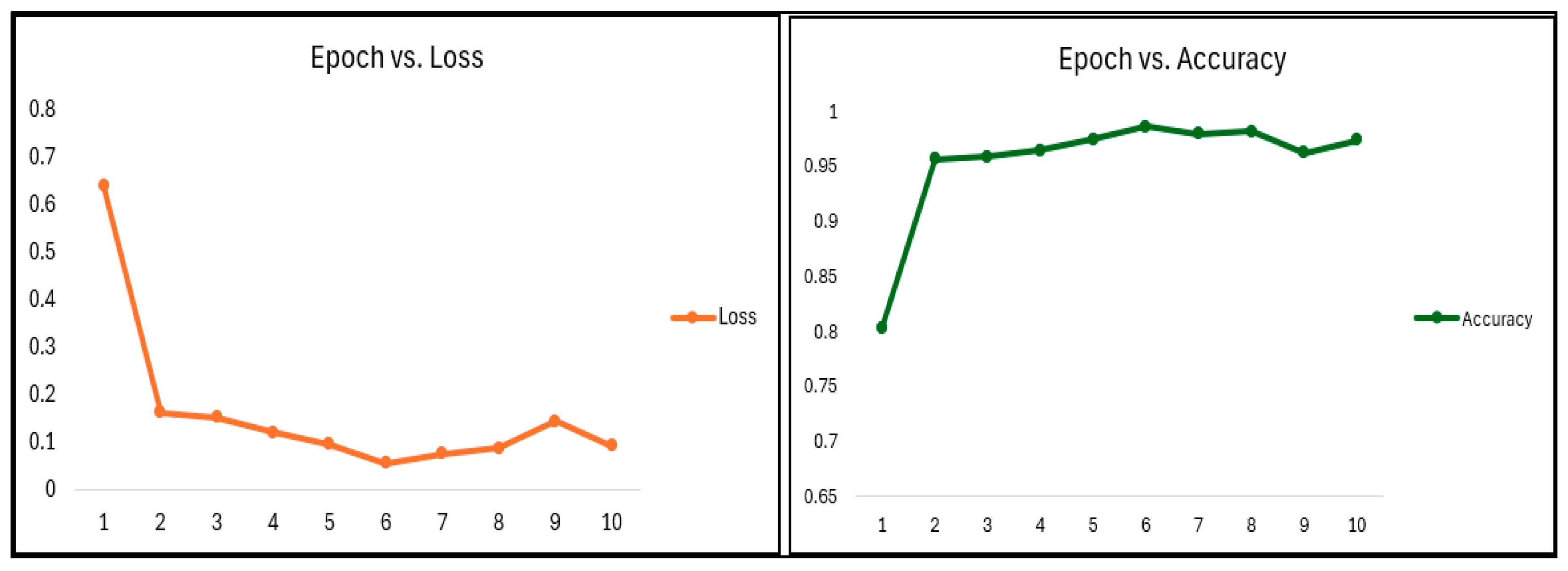
| Epoch | Loss | Accuracy | |||||
| 1 | 64.01% | 80.20% | |||||
| 2 | 16.24% | 95.58% | |||||
| 3 | 15.24% | 95.84% | |||||
| 4 | 12.12% | 96.39% | |||||
| 5 | 9.66% | 97.37% | |||||
| 6 | 5.57% | 98.55% | |||||
| 7 | 7.56% | 97.92% | |||||
| 8 | 8.81% | 98.09% | |||||
| 9 | 14.38% | 96.16% | |||||
| 10 | 9.27% | 97.34% | |||||
| Validation Metrics | Test Metrics | ||||||
| Accuracy | Error Rate | F1 Score | Precision | Accuracy | Error Rate | F1 Score | Precision |
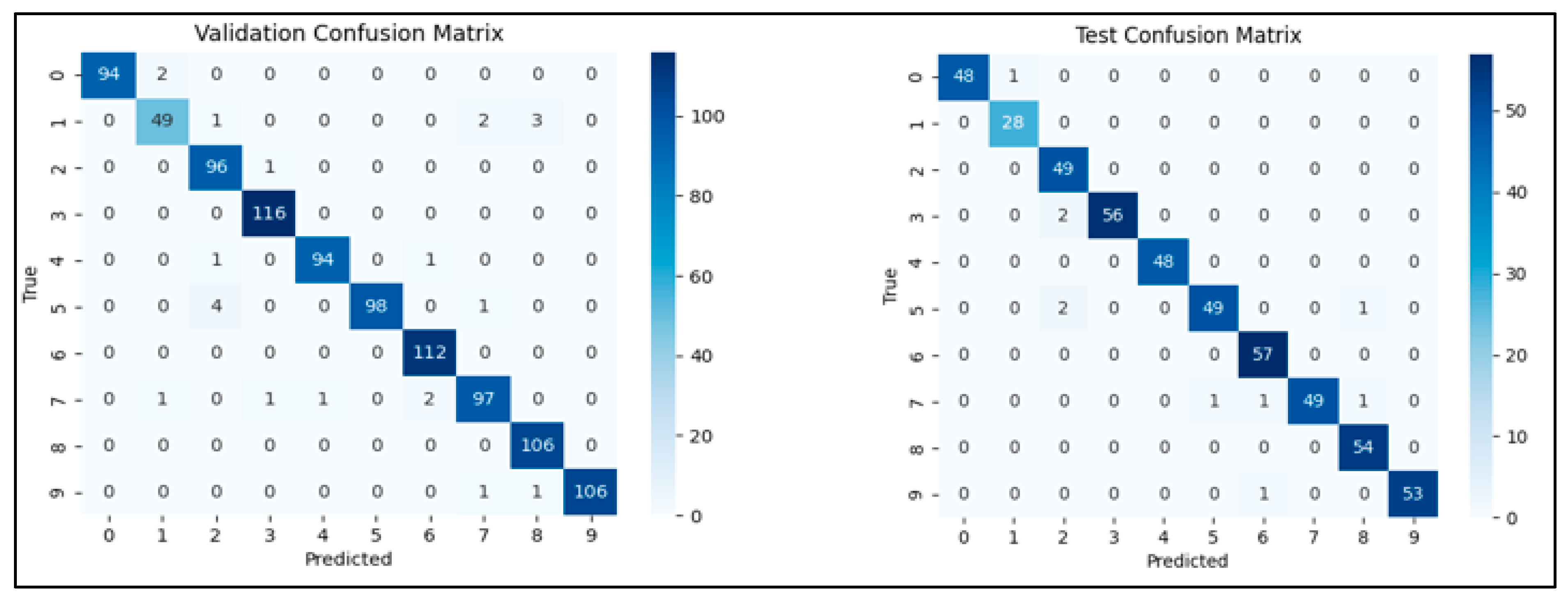
| 97.48% | 2.52% | 97.48% | 97.52% | 96.81% | 3.19% | 96.84% | 96.99% |
| Class | Accuracy | Class | Accuracy | ||||
| 0 | 100.00% | 0 | 97.96% | ||||
| 1 | 90.91% | 1 | 96.43% | ||||
| 2 | 95.88% | 2 | 93.88% | ||||
| 3 | 98.28% | 3 | 94.83% | ||||
| 4 | 97.92% | 4 | 95.83% | ||||
| 5 | 97.09% | 5 | 98.08% | ||||
| 6 | 96.43% | 6 | 96.49% | ||||
| 7 | 97.06% | 7 | 98.08% | ||||
| 8 | 99.06% | 8 | 98.15% | ||||
| 9 | 99.07% | 9 | 98.15% | ||||
| Training Metrics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoch | Loss | Accuracy | |||||
| 1 | 86.28% | 67.68% | |||||
| 2 | 49.11% | 84.92% | |||||
| 3 | 27.10% | 90.66% | |||||
| 4 | 20.11% | 95.15% | |||||
| 5 | 22.87% | 94.43% | |||||
| 6 | 10.55% | 96.59% | |||||
| 7 | 13.19% | 96.05% | |||||
| 8 | 9.75% | 96.41% | |||||
| 9 | 6.08% | 97.85% | |||||
| 10 | 6.65% | 97.85% | |||||
| Validation Metrics | Test Metrics | ||||||
| Accuracy | Error Rate | F1 Score | Precision | Accuracy | Error Rate | F1 Score | Precision |
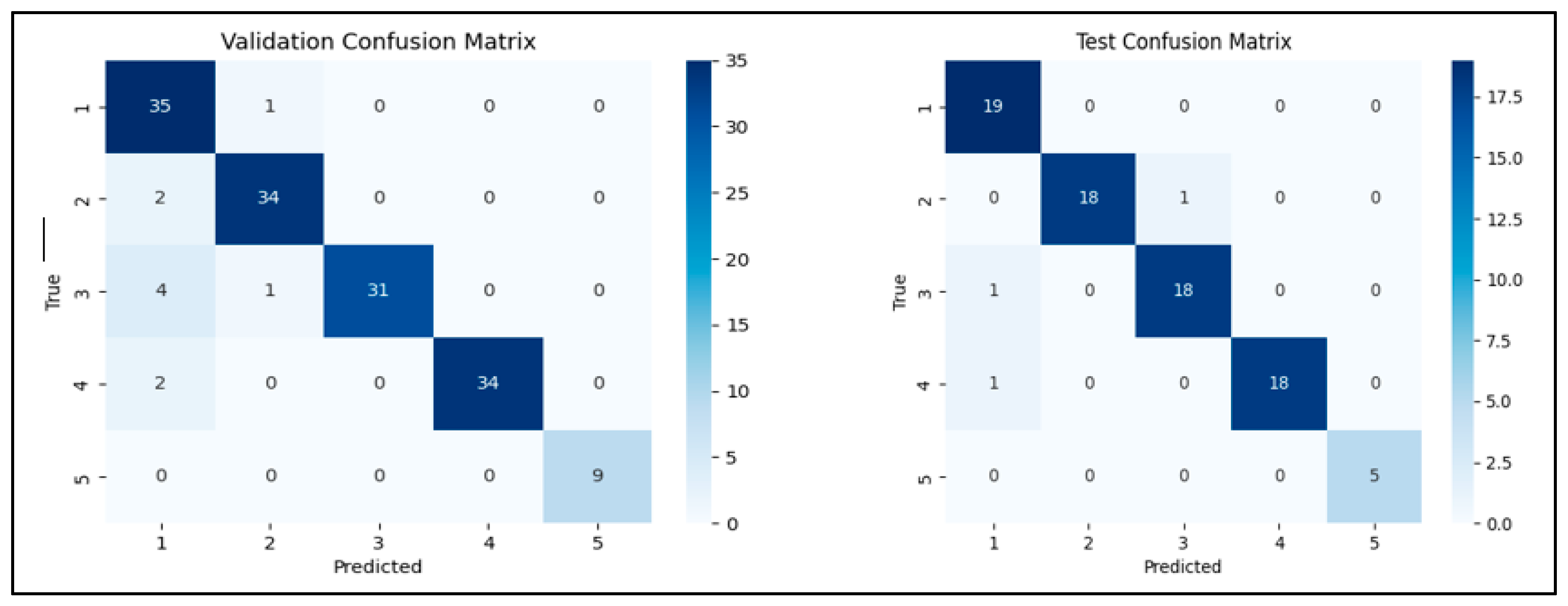
| 93.46% | 6.54% | 93.58% | 94.32% | 96.30% | 3.70% | 96.32% | 96.53% |
| Class | Accuracy | Class | Accuracy | ||||
| 1 | 97.22% | 1 | 100.00% | ||||
| 2 | 94.44% | 2 | 94.74% | ||||
| 3 | 86.11% | 3 | 94.74% | ||||
| 4 | 94.44% | 4 | 94.74% | ||||
| 5 | 100.00% | 5 | 100.00% | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhefdhi, K.; Alsalman, A.; Faizullah, S. Toward Building a Domain-Based Dataset for Arabic Handwritten Text Recognition. Electronics 2025, 14, 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122461
Alhefdhi K, Alsalman A, Faizullah S. Toward Building a Domain-Based Dataset for Arabic Handwritten Text Recognition. Electronics. 2025; 14(12):2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122461
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhefdhi, Khawlah, Abdulmalik Alsalman, and Safi Faizullah. 2025. "Toward Building a Domain-Based Dataset for Arabic Handwritten Text Recognition" Electronics 14, no. 12: 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122461
APA StyleAlhefdhi, K., Alsalman, A., & Faizullah, S. (2025). Toward Building a Domain-Based Dataset for Arabic Handwritten Text Recognition. Electronics, 14(12), 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14122461







