Abstract
The performance of multiple-input single-output (MISO) transmission is highly dependent on the accuracy of the channel state information (CSI) at the base station (BS), which necessitates precise CSI estimation and reliable feedback from the user equipment. However, the overhead of the CSI feedback occupies substantial uplink bandwidth resources. To alleviate the overhead, this paper proposes a novel task-based quantizer for uplink MISO visible light communication (VLC) systems. In particular, a hybrid radio frequency (RF)/VLC system is considered, where VLC links are mainly used for large-volume downlink transmissions and RF links are used for uplink CSI feedback. Since the RF bandwidth resources are limited, the CSI is quantified to reduce the uplink resource requirements, which, however, inevitably causes CSI estimation errors at the BS. To guarantee the CSI estimation accuracy while minimizing the RF resource cost, a task-based quantization scheme for channel estimation (TQ-CE) is proposed. In the TQ-CE, both the quantized codebook and the post-processing matrix are optimized to minimize the mean square error (MSE) of the channel estimation. Taking the minimum MSE as the target task, the TQ-CE leverages vector quantization (VQ) to generate a codebook, which is designed to reduce the feedback overhead without compromising the precision of the channel estimation. Then, an optimal closed-form solution of the post-processing matrix is derived based on the minimum mean square error (MMSE) criterion. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed TQ-CE achieved and higher data rates compared with the conventional scalar quantization-based channel estimation (SQ-CE) schemes and vector quantization-based channel estimation (VQ-CE) schemes, respectively. Moreover, in terms of the feedback overhead, compared with the 18-bit SQ-CE, the 4-bit TQ-CE achieved a 22.2% reduction in uplink bits.
1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Motivation
Visible light communication (VLC) is a novel communication technique that relies on high-speed on-and-off characteristics of light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Since VLC has the dual function of high-speed data transmission and illumination [1], multiple LEDs are typically required to achieve sufficient illumination, as standardized in [2], which provides the hardware basis for implementing multiple-input single-output (MISO) technologies in VLC. The MISO technology can improve the system channel capacity without extra bandwidth requirements, thus significantly enhancing the VLC performance [3].
The superior performance of MISO relies on techniques such as precoding [4], spatial modulation [5], spatial diversity [6], and multiplexing [7]. All these techniques require accurate channel state information (CSI) at the transmitter, i.e., base station (BS) [8]. Due to the safety concern for the human eye from uplink optical radiation, uplink transmission has always been a challenge of VLC. With the emergence of IoT applications, such as smart manufacturing, healthcare monitoring, and large-scale indoor automation, VLC has gained increasing attention due to its high spatial reuse and immunity to electromagnetic interference [9]. In these scenarios, hybrid RF/VLC systems are particularly attractive. Specifically, VLC provides high-speed downlink transmission using lighting infrastructure, while RF links support uplink control and feedback. However, the massive number of bandwidth-constrained IoT devices imposes strict limitations on the uplink bandwidth, making efficient CSI feedback schemes essential for practical MISO VLC deployment. To address this issue, radio frequency (RF)/VLC systems have been extensively studied [10,11,12,13], where the RF link is used for uplink transmission. Moreover, when considering a MISO VLC system with a large number of LEDs, the feedback of the downlink CSI in uplink transmission can be costly [14]. However, accurate CSI is essential for beamforming or precoding. This challenge becomes even more critical when considering the severe scarcity of RF spectrum resources. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the cost of uplink VLC transmissions through quantization, encoding, and spectrum reuse. Among these methods, quantization stands out for its simplicity and efficiency, which has attracted considerable attention [15]. Since the RF bandwidth resources are limited, CSI is often quantized to reduce the uplink overhead, particularly in uplink-constrained systems, such as IoT [16,17], though this inevitably introduces estimation errors at the base station.
1.2. Related Works
There is a plethora of prior art on quantization algorithms for channel estimation, including scalar quantization (SQ) [18,19,20] and vector quantization (VQ) [21,22,23,24,25]. SQ is a fundamental quantization method, which translates an array of continuous signal values into a finite set of discrete quanta [18]. Scalar quantization can be divided into uniform quantization [26,27] and non-uniform quantization [19,20]. Uniform quantization is simple but prone to large errors in low-amplitude signals. In contrast, non-uniform quantization is flexible and can optimize the quality of low-amplitude signals. However, its implementation is complex and the quantization process is variable, requiring high hardware and software requirements [28].
Different from SQ algorithms, VQ algorithms can simultaneously quantify multiple parameters of the channel, such as the amplitude, phase, and delay, to provide a more comprehensive characterization of CSI [21,22,23,29]. The VQ-based codebook must be carefully designed to cover the main regions of the CSI. In [30], a two-stage vector channel quantifier is proposed, which reduces quantization errors through adaptive quantization and optimizes multi-user diversity gain. The first stage is channel gain information (CGI) quantization, which is directly related to VQ. The second stage is the adaptive quantization of channel direction information, which is aimed at compensating for the impact of the residual errors after CGI quantization in VQ on performance. The authors in [31] proposed a structured non-uniform codebook, which can adapt to any Rician factor by optimizing the codebook design parameters to minimize the upper bound of the quantization error. Recently, an environmental-knowledge-based codebook-based CSI feedback framework is proposed in [32]. By utilizing neural networks to refine codebook-based CSI feedback, the feedback accuracy of downlink CSI in large-scale MISO systems is improved while reducing the feedback overhead. Although interesting, all these works ignore the impact of quantization errors in codebook recovery and only focus on the design of quantized codebooks. A recent study [16] proposed a quantization approach for CSI feedback in VLC systems by reducing feedback overhead via position information feedback, leveraging offline pre-defined sub-region quantization tables. This work provides valuable insights into reducing the feedback overhead via positioning information and lookup-based CSI recovery.
In addition to quantization-based CSI feedback schemes, alternative approaches, such as channel prediction and interpolation, have also been explored to reduce the CSI acquisition overhead and improve the estimation accuracy. For instance, neural network-based CSI prediction has shown potential in capturing the temporal correlation of the VLC channel, thereby reducing the need for frequent feedback [33]. Similarly, spline interpolation methods can effectively recover CSI from sparse pilot samples, especially in ACO-OFDM systems where regular pilot structures may not be optimal [34]. Moreover, some studies have addressed the unique challenges of input signal-dependent noise in VLC environments, which complicates traditional channel estimation and necessitates more adaptive solutions [35]. These works provide valuable complementary strategies to quantization-based methods, and our proposed task-based quantization scheme can be integrated with such approaches for further performance gains. Furthermore, in VLC systems, ref. [36] assessed the channel quality through the feedback of a limited number of bits conveying a distance and average vertical angle. Although this approach can significantly reduce the feedback overhead, it can only roughly obtain the relative CSI quality between non-orthogonal multiple access links, which, however, is inapplicable to methods that rely on accurate CSI estimation, such as MISO. Therefore, an efficient and accurate quantization scheme for channel estimation for VLC systems deserves further investigation. In summary, while prior quantization methods provide useful tools, they lack awareness of the task-specific demands in VLC systems. None of the existing approaches explicitly considers how quantization should serve the ultimate task performance in VLC, such as maximizing the transmission quality in multi-user MISO setups. This disconnect between the quantization design and task objectives highlights the urgent need for a task-based CSI quantization framework tailored for VLC, which formed the central motivation of our work.
1.3. Main Contribution
The main contribution of this work is a task-based quantization scheme for a channel estimation (TQ-CE) scheme, which achieves a favorable trade-off between feedback overhead and channel estimation performance by leveraging a VQ-based codebook and an optimal post-processing matrix based on the minimum mean square error (MMSE) criterion. As shown in Table 1, we summarized the differences between our method and representative works. The main contributions of this paper can be summarized as follows:

Table 1.
Comparison between existing algorithms and TQ-CE.
- We propose the TQ-CE scheme, which focuses on optimizing the end-task performance rather than minimizing the raw quantization error. Unlike traditional quantizers, TQ-CE is designed to preserve the features critical for accurate CSI reconstruction rather than the original channel matrix itself.
- To reduce the uplink feedback overhead, we designed a compact vector quantization (VQ)-based codebook. In addition, a closed-form MMSE-based post-processing matrix was derived to refine the quantized representation, thereby enhancing the channel estimation accuracy.
- The simulation results show that the proposed TQ-CE achieved data rate gains of and over the conventional SQ-CE [27] and VQ-CE [25], respectively. Moreover, in terms of the feedback overhead, compared with the 18-bit SQ-CE, the 4-bit TQ-CE achieved a 22.2% reduction in uplink bits. Thus, our proposed TQ-CE can achieve a high data rate with few bits, which makes them ideal for deployment in hybrid RF/VLC-based IoT environments where the uplink bandwidth is scarce and bandwidth-efficient processing is essential.
Notations: Capital boldface letters, such as , represent matrices, while small boldface letters, such as , represent vectors. denotes the diagonal matrix created from . denotes the transpose of matrix . denotes the 1 norm. denotes the all-zeros matrix, and denotes the identity matrix.
2. System Model and Problem Formulation
In this section, we first present the uplink (UL) and downlink (DL) system model of a typical hybrid RF/VLC system. Here, DL relies on VLC links to transmit large-volume useful information, while UP is used to feed back CSI information for MISO systems. Then, we formulate an optimization problem to minimize the MSE of the CSI to jointly optimize the pre-quantization mapping and post-quantization mapping.
2.1. DL System Model
As illustrated in Figure 1, a typical hybrid RF/VLC system is considered. In the DL, a BS with LEDs is used to serve users, where each user is equipped with one PD. Since in practical VLC models, the UL typically operates in infrared or RF bands [10], a MISO RF system was deployed to support UL communication.
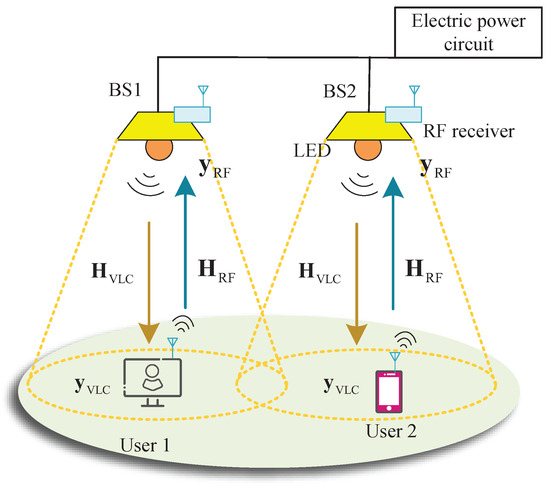
Figure 1.
The hybrid RF/VLC scenario.
The diagram of our considered hybrid RF/VLC system is shown in Figure 2. For the DL, we assumed all the LEDs simultaneously transmit pilot signals to users, where represents the number of pilot signal vectors. Since the LOS channel of the optical wireless channel contains most parts of the transmitted energy [37], only the LOS channel was considered. In particular, the LOS channel gain between the i-th PD and the j-th LED is given by
with the Lambert order , where is the transmitter semiangle (at half power). In addition, is the irradiance angle, the incidence angle, is the receiver field of vision (FOV) semiangle, A is the detector area, is the distance between the i-th PD and the j-th LED, is the gain of optical filter, and is the gain of the optical concentrator. By gathering the channel gains for and , we can obtain a channel matrix with in the i-th row and the j-th column.
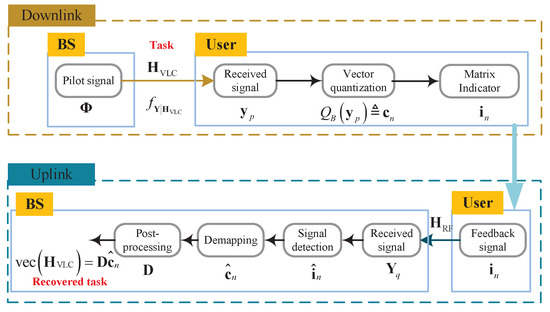
Figure 2.
The diagram of the hybrid RF/VLC system.
The received VLC signal matrix can be expressed as
where is the noise matrix whose elements are real-valued Gaussian variables with zero mean and variance . Furthermore, the vector form of (2) can be expressed as
where denotes the vectorization of the matrix, ⊗ represents the Kronecker product, and denotes the identity matrix.
Since the VQ algorithm is adopted, vectors will be mapped onto a finite codebook, where each codeword corresponds to a possible channel state of the MISO VLC system. This mapping enables users to simply transmit the index of the respective codeword back to the BS, thus significantly reducing the feedback overhead and enhancing the overall communication efficiency. The quantized signal obtained after the B-bit VQ can be expressed as
where denotes the n-th code in codebook set , and the number of elements in set is , i.e., . The notation specifically denotes a vector quantization operation, which maps an input vector from a continuous or high-dimensional space into a finite set of discrete codewords. The subscript B indicates the number of quantization bits used, which determines the size of the codebook as .
2.2. UL System Model
Let be the index vector of in codebook set . To feed back , an RF system is used for the uplink transmission. Figure 3 shows the considered UL system model, where the RF transmitter transmits the quantized CSI index vector over wireless channels to accomplish the recovery of the quantized CSI index vector at the RF receiver.
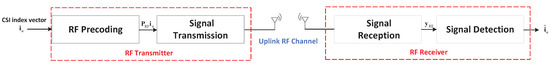
Figure 3.
The UL RF transmission model.
In particular, the RF transmitter mainly consists of an RF precoding module represented by the precoding matrix and a signal transmission module to transmit the signal. was assumed to be ideally designed to match using singular value decomposition (SVD)-based methods. In this work, we assumed that the RF channel matrix was perfectly known at the BS [38], which can be estimated by RF channel estimation techniques, such as pilot-based estimation [39]. Specifically, to match the channel matrix , we can perform SVD as follows
where and are unitary matrices, is a diagonal matrix containing the singular values of , and represents the optimal precoding directions.
The precoding matrix is then designed as
where consists of the first k columns of corresponding to the k largest singular values. This selection ensures that the transmitted signal aligns with the dominant eigen-directions of , maximizing the effective channel gain. Then, the output of this RF precoding module, , is transmitted over the RF channel.
As shown in Figure 3, the RF receiver mainly contains a signal reception module to receive the noised signal from the wireless channel and a signal detection module. The signal detection module processes the received signal . The received signal can be modeled as
where denotes the RF channel matrix; denotes the precoding matrix of the uplink signal; and is the noise matrix, whose elements are real-valued Gaussian variables with a zero mean and variance .
After receiving , the signal detection module applies the zero-forcing (ZF) algorithm to reconstruct the transmitted index vector from the noisy received signal. The objective of the ZF algorithm is to minimize the mean-squared error between the received signal and the modeled signal, allowing for an optimal estimate of . Mathematically, the ZF solution is derived by solving the following optimization problem:
where denotes the -norm. By employing the LS algorithm, the LS solution is given by
where represents the Moore–Penrose pseudoinverse of the matrix .
According to the codebook , we can easily obtain from . Furthermore, the vector of the estimated channel matrix can be expressed as
where is the estimated task vector (i.e., estimated VLC CSI matrix), denotes the post-processing matrix. The target of the designed system is to recover from the quantized measurement signal . Therefore, in the next subsection, we formulated an optimization problem to minimize the MSE of the true CSI matrix and the estimated CSI matrix .
2.3. Problem Formulation
For simplicity, we defined the task vector and its estimation to be and , respectively. In this work, we formulate the problem of minimizing channel estimation error as a joint optimization of a quantized codebook and post-processing matrix. Mathematically, the optimization problem is formulated as
where is the MMSE estimator of for a given . In particular, the MSE outlined in (11) is divided into the sum of two terms. The first term represents the estimation error between the CSI of the VLC link and its approximation . The second term represents the quantization error induced by the quantization of and the feedback through the uplink. Since the main target of the proposed scheme is to minimize the uplink CSI quantization error, which is only related to the second term, Section 3 focuses on optimizing the second term and the first term is an irrelevant constant.
3. Task-Based Quantizer for CSI Estimation (TQ-CE)
This section proposes a novel task-based quantizer for CSI feedback in MISO VLC systems. First, we employed the VQ algorithm to obtain a codebook with a limited B quantization bit length. Then, we derived the optimal post-processing matrix with a given codebook to minimize the MSE of the task vector .
3.1. VQ-Based Codebook Design
The main concept of the codebook design is to classify the training set according to specified measurements. In particular, vectors from the training set are categorized into multiple vector classes, and the center vector of each vector class is defined as the codeword of this vector class [40]. To acquire the initial training dataset for vector quantization, we generated ample random displacement coordinates for users within the room following the random walk model [41]. Then, various CSI vectors can be calculated for users at various locations, utilizing their respective coordinates. These vectors reflect the characteristics of the wireless communication channel and are the basis for subsequent quantization processing. The CSI vector is stored in the training set .
After that, the VQ algorithm is employed to calculate the codebook . Algorithm 1 provides the specific implementation steps of the VQ algorithm. Specifically, the training set is provided, the distortion threshold is set to a very small integer, and the quantization bit number B and the maximum number of iterations are initialized. Subsequently, the number of code vectors n is set to 1, the mean value of the entire training dataset is calculated in step three, and the overall distortion is calculated in step four. After that, the code vectors are split. Each code vector is individually multiplied by the perturbation factors and and split into two new code vectors. This process is repeated iteratively until B code vectors are obtained. Subsequently, the optimized vector codebook is calculated through iterative computation. Furthermore, each training vector is divided into the corresponding vector class according to the nearest neighbor condition and the mean of all training samples within the encoding region associated with is calculated to serve as the new code vector for that particular encoding region. In line 15, the total distortion of the vector quantization algorithm is calculated when the iteration count is . In lines 16 to 19, whether a further iteration is necessary is determined. Finally, the optimal vector quantization codebook is outputted.
In line with [42], the Bussgang decomposition is employed to represent the quantization process as a noisy linear function of the input. Then, the quantization process can be decomposed into a linear transformation and a random noise term that is independent of the input signal, and the progress can be expressed as
where is a zero-mean random variable, and is the Bussgang gain. The Bussgang gain is obtained by calculating the covariance matrix between the quantized output , the original input , and the transpose of the autocorrelation matrix of , and is specifically represented as
where denotes the cross-correlation matrix of and , and denotes the auto-correlation matrix of . Furthermore, through the Bussgang decomposition, a linear representation can be established between the codebook and the original pilot signals, providing a theoretical foundation for the design and optimization of the TQ-CE scheme.
| Algorithm 1 Vector quantization algorithm |
|
3.2. Post-Processing Matrix Optimization
Based on the codebook calculated in Section 3.1, this subsection further optimizes the post-processing matrix . A post-processing operation refers to an algorithm at the BS that converts the received codebook information into a channel matrix after receiving the feedback pilot information and mitigates errors introduced during the quantization process. Based on the calculated codebook in Section 3.1, the optimization problem Equation (11) can be further expressed as
where denotes the estimated value of when the pilot-received signal is known. In particular, can be calculated using
Note that the first term of Equation (14) represents the estimation error of using the pilot-received signal , and the second part represents the quantization distortion error. Therefore, we focused only on the second part of Equation (14), which can be expanded as
The first-order derivative of can be expressed as
To compute the closed-form solution of the optimal post-processing matrix, let , and assume that the error between the estimated quantization vector and the true quantization vector is negligible, i.e., . Then, the optimal post-processing matrix is a closed-form solution of
where represents the index of the quantized CSI vector in the quantized codebook. After receiving the index values, the BS first recovers the corresponding quantized vectors from the index values using the codebook, and then performs post-processes on the quantized vectors to obtain the final estimated CSI matrix.
From a mathematical perspective, the proposed TQ-CE scheme leverages the characteristics of the downlink VLC channel matrix to optimize the compression and quantization of the CSI, demonstrating its close association with MISO VLC systems. Specifically, the TQ-CE first quantizes by vector quantization, thereby reducing the feedback overhead. Then, TQ-CE optimizes a post-processing matrix to improve the accuracy of the MISO VLC channel estimation. Therefore, the proposed TQ-CE scheme effectively addresses the uplink CSI feedback challenges, which achieves a low UL feedback overhead and accurate CSI estimation simultaneously.
4. Simulation Results
As shown in this section, the effectiveness of the TQ-CE algorithm was first verified, and the conventional SQ-CE [27] and VQ-CE [25] were selected as baseline schemes. A hybrid RF/VLC MISO system was constructed, in which the downlink communication was based on VLC, and the uplink communication was based on RF. Table 2 lists the simulation parameters. Unless otherwise specified, a VLC system with an adjacent LED distance of 2 m on the ceiling was considered.

Table 2.
Simulation parameters.
First, we compared the MSE performance curves of the TQ-CE and its baselines under different quantization bits when training a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of 5 dB. Note that a smaller number of quantization bits B leads to a lower uplink transmission overhead. As shown in Figure 4a, with a fixed SNR, all the schemes could obtain decreasing MSE as the number of quantized bits increased. Furthermore, when the SNR of the pilot transmission was greater than 30 dB, all the schemes tended to have a stable MSE. Specifically, when the actual pilot transmission SNR was 45 dB, the channel estimation MSE based on a 4-bit TQ-CE was about and smaller than those based on the 18-bit quantization SQ-CE and 4-bit quantization VQ-CE, respectively. As shown in Figure 4a, when the SNR exceeded 30 dB, the performance tended to saturate as the quantization distortion dominated. This significant gain was attributed to the task-aware codebook and MMSE-based refinement in the TQ-CE, which preserved the task-relevant information more effectively under low-bit budgets.
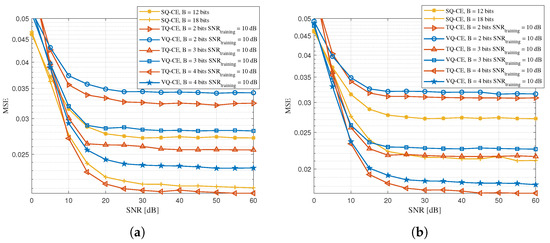
Figure 4.
Comparisons of channel estimation MSEs between TQ-CE and its comparison schemes at different training SNRs. (a) Training SNR = 5 dB. (b) Training SNR = 10 dB.
As shown in Figure 4b, the vector quantization code books of the TQ-CE and VQ-CE were obtained based on the training set generated when the training SNR was 10 dB. The TQ-CE could obtain smaller channel estimation errors even with fewer quantization bits when compared with the baselines. For instance, the TQ-CE scheme based on 4-bit quantization and VQ-CE based on 4-bit quantization both obtained a lower channel estimation mean square error than the SQ-CE scheme based on 18-bit quantization. Specifically, when the actual pilot transmission SNR was 45 dB, the mean square error of the channel estimation based on the 4-bit TQ-CE was smaller than that based on the SQ-CE with 18 bits and that based on the VQ-CE with 4 bits by and . This highlights that the task-based optimization in the TQ-CE enabled more efficient use of limited feedback bits by prioritizing estimation-relevant features in the learned codebook.
Figure 5 evaluates the influence of different LED layouts on the system performance. In particular, Figure 5a compares the channel estimation mean square error (MSE) of the TQ-CE with the baselines when the distance between adjacent LEDs was 1.5 m and the training SNR was 10 dB. It can be observed that the TQ-CE could still maintain its performance advantage under this configuration. Specifically, when the actual pilot transmission SNR was 15 dB, the MSE of the channel estimation based on the 4-bit TQ-CE was approximately and lower than that based on the 18-bit quantization SQ-CE and 4-bit quantization VQ-CE, respectively. This demonstrates that the proposed scheme maintained robustness to layout variations by adapting quantization to the task-specific channel distribution.
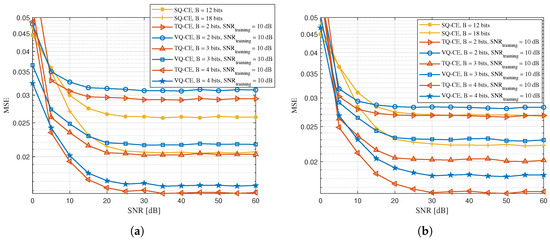
Figure 5.
Comparison curve of the channel estimation mean square error between the TQ-CE and its comparison schemes at a training SNR of 10 dB, with different distances between the two adjacent LEDs. (a) Distance between two adjacent LEDs = 1.5 m. (b) Distance between two adjacent LEDs = 1 m.
Additionally, Figure 5b compares the channel estimation MSE of the TQ-CE with its comparison scheme when the distance between adjacent LEDs was 1 m and the training SNR was 10 dB. When the distance between adjacent LEDs was narrowed to 1 m, the proposed TQ-CE achieved even higher performance gains than the SQ-CE scheme in scenarios where the distance between adjacent LEDs was 1.5 or 2 m. This was because the more compact LED arrangement enhanced the correlation of the VLC channel matrix. Thus, the VQ algorithm could capture the statistical characteristics of the data more effectively, which led to a significant reduction in quantization distortion. In particular, when the actual pilot transmission SNR was 15 dB, the MSE of the channel estimation based on the 4-bit TQ-CE was approximately and lower than those based on the 18-bit quantization SQ-CE and 4-bit quantization VQ-CE, respectively. As shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5, it is also worth noting that in the low-SNR region (e.g., below 5 dB), the TQ-CE exhibited a higher MSE compared with the SQ-CE, which appeared counter to the trend observed at moderate and high SNRs. This was primarily due to the fact that TQ-CE was optimized to minimize the quantization-induced estimation errors under the assumption of relatively clean channel conditions. At low SNRs, the additive noise became the dominant factor affecting channel estimation, and the advantage of task-based quantization diminished. In such cases, the MMSE-based post-processing module in the TQ-CE could also become less reliable due to inaccurate prior statistics, whereas the SQ-CE, being simple and model-free, remained relatively robust against heavy noise. This observation highlights a practical trade-off between task-oriented optimization and noise resilience under extreme conditions.
Figure 6 evaluates the capacity of the considered system. Figure 6a compares the channel capacity of the TQ-CE with its comparison schemes at different quantization bits with a training SNR of 5 dB. Compared with Figure 4a, it can be observed that when the channel estimation MSE was smaller, a higher channel capacity could be obtained. Specifically, when the SNR was 45 dB, the channel capacity of the 4-bit TQ-CE was about 0.25 Mbit/s and 0.62 Mbit/s higher than those of the 18-bit SQ-CE and 4-bit-based VQ-CE, respectively. This improvement stemmed from the reduced CSI distortion enabled by task-aware quantization and MMSE post-processing, which directly enhanced the precoding quality and effective channel utilization.
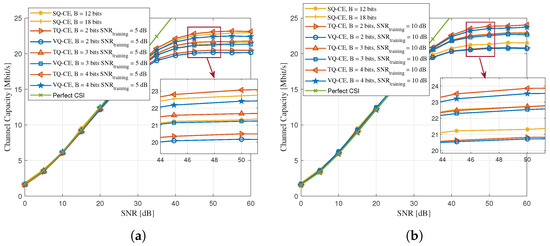
Figure 6.
Comparison curve of channel capacity between TQ-CE and its comparison scheme with different training SNRs. (a) Training SNR = 5 dB. (b) Training SNR = 10 dB.
Figure 6b compares the channel capacity of the TQ-CE and the baseline schemes under different quantized bits when the training SNR was 10 dB. Here, the simulation results were in line with the results in Figure 4b. Specifically, when the pilot transmission SNR was 45 dB, the channel capacity of the 4-bit-based TQ-CE was about 1.04 Mbit/s and 0.31 Mbit/s higher than that of the 18-bit-based SQ-CE and the 4-bit-based VQ-CE, respectively. In summary, compared with the traditional SQ-CE, both the VQ-CE and TQ-CE could obtain a more accurate estimate of the CSI with fewer quantization bits. Moreover, when compared with the VQ-CE, the proposed TQ-CE scheme with the VQ algorithm and post-processing optimization could obtain an even more accurate CSI under the same quantization bits, and thus, provide a higher channel capacity. This again confirmed that accurate task-specific CSI feedback enabled a better beamforming and transmission rate, even with limited bit resources.
Table 3 presents the transmission overhead of the conventional scheme and our proposed TO-CE. Since multiple users were considered, the number of transmitted bits of each scheme could be computed as . It can be noted that our proposed TQ-CE () simply required transmitted bits of the conventional SQ-CE (). Our proposed TQ-CE had the same transmission bits but a more accurate CSI compared with the VQ-CE, as shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5. Overall, our proposed TQ-CE improved the performances of both the accurate CSI and transmission overhead. This indicates that the proposed scheme achieved a better estimation-to-bit efficiency by jointly optimizing the quantizer and refinement process for the downstream estimation task.

Table 3.
Comparison of the number of transmission bits in different schemes.
Computational Complexity Analysis
The computational complexity of the proposed TQ-CE algorithm consisted of two components: the complexity of the VQ stage and the post-processing matrix operation stage. Following the analysis in [43], the computational complexity of the VQ was given by
where N is the number of multiply–add operations required for each distortion calculation, L is the number of quantization levels, and represents the number of transmission bits per codeword.
As described in (19), the post-processing matrix involves a matrix inversion operation, which was implemented using the Gauss–Jordan elimination algorithm. The corresponding computational complexity was
where denotes the number of transmit antennas.
For comparison, the complexity of the VQ-CE scheme included only the VQ component:
For the SQ-CE scheme, which used scalar quantization, the complexity was significantly lower and could be approximated as
In summary, while the TQ-CE incurred additional complexity due to the post-processing step, it achieved a significantly improved estimation accuracy and robustness under limited feedback conditions, as demonstrated in the above simulation results.
5. Conclusions
This paper proposes a TQ-CE scheme to address the trade-off between the feedback overhead and estimation performance in MISO VLC systems. By incorporating vector-quantization-based codebook design and deriving a closed-form post-processing matrix, the TQ-CE effectively aligned the quantization process with the downstream task requirements. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed TQ-CE achieved and higher data rates compared with the conventional SQ-CE schemes and VQ-CE schemes, respectively. Moreover, in terms of the feedback overhead, compared with the 18-bit SQ-CE, the 4-bit TQ-CE achieved a 22.2% reduction in uplink bits. Despite the effectiveness of the proposed TQ-CE scheme, the current evaluation was based on a simulation under idealized channel models without practical experiments. In future work, we plan to deploy the TQ-CE framework on a hardware testbed to validate its robustness under practical RF/VLC scenarios.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.H. and C.W.; methodology, F.H.; software, Y.N.; validation, Y.N., X.F., and C.Z.; formal analysis, Y.Y.; investigation, C.Z.; resources, F.H.; data curation, Y.N.; writing—original draft preparation, F.H., C.W., and Y.N.; writing—review and editing, F.H., X.F., C.Z., and Y.Y.; visualization, C.W., Y.N., and X.F.; supervision, Y.Y.; project administration, Y.Y.; funding acquisition, F.H. and C.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of this manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61702375, the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing under Grant QY24191, the Natural Science Research Project of Colleges and Universities in Anhui Province under Grant No. 2022AH051782 and WXZR202220, the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province under Grant 2108085QA10, the open fund of Information Materials and Intelligent Sensing Laboratory of Anhui Province under Grant No. IMIS202010, the Excellent Young Talents Support Program in universities of Anhui Province under Grant No. 2022AH020091, the Outstanding Youth Talent Support Program in Universities of Anhui Province under Grant No. gxyqZD2021128, the major project of the Anhui Education Department under Grant KJ2021ZD0116, the Research Foundation of High-Level Talent of West Anhui University under Grant No. WGKQ2025011 and WGKQ202001006, the University Key Research Project of Department of Education Anhui Province (No. 2022AH051683), and the University Innovation Team Project of Department of Education Anhui Province (No. 2023AH010078).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available on request by the corresponding authors without undue reservation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CSI | Channel state information |
| MISO | Multiple-input single-output |
| VLC | Visible light communication |
| CGI | Channel gain information |
| BS | Base station |
| RF | Radio frequency |
| TQ-CE | Task-based quantization for channel estimation |
| SQ-CE | Scalar quantization-based channel estimation |
| VQ-CE | Vector quantization-based channel estimation |
References
- Abidin, Z.; Mahendra, A.G.R.; Mahendra, D.F.; Imami, M.R.N.; Mehanny, W.M.H. Performance Analysis of LED Driver for Transmitter of Visible Light Communication Using Pulse Width Modulation. In Proceedings of the 2020 10th Electrical Power, Electronics, Communications, Controls and Informatics Seminar (EECCIS), Malang, Indonesia, 26–28 August 2020; pp. 178–182. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. An Optimal Power Allocation for Multi-LED Phase-Shifted-Based MISO VLC Systems. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2015, 27, 2391–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massive MIMO Systems for 5G and beyond Networks—Overview, Recent Trends, Challenges, and Future Research Direction. Sensors 2020, 20, 2753. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Gao, J.; Zhong, C. A Deep Learning-Based Framework for Low Complexity Multiuser MIMO Precoding Design. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 11193–11206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wen, M.; Renzo, M.D. Single-RF MIMO: From Spatial Modulation to Metasurface-Based Modulation. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2021, 28, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh, P.; Hempel, M.; Banerjee, S.; Sharif, H. A Spatial-Diversity MIMO Dataset for RF Signal Processing Research. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, O.; Hofbauer, C.; Feger, R.; Huemer, M. Range-Division Multiplexing for MIMO OFDM Joint Radar and Communications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Fan, J.; Shen, W.; Qin, Z.; Li, G.Y. Deep Learning and Compressive Sensing-Based CSI Feedback in FDD Massive MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 9217–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, F.; Pan, C.; Song, J.; Han, Z. Joint illumination and communication optimization in indoor VLC for IoT applications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 20788–20800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narmanlioglu, O.; Uysal, M. Limited feedback channel estimation for multi-user massive mimo visible light communications. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Dublin, Ireland, 7–11 June 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zargari, S.; Kolivand, M.; Nezamalhosseini, S.A.; Abolhassani, B.; Chen, L.R.; Kahaei, M.H. Resource Allocation of Hybrid VLC/RF Systems with Light Energy Harvesting. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2022, 6, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, F.; Pan, C.; Song, J.; Han, Z. Hybrid VLC-RF Systems with Multi-Users for Achievable Rate and Energy Efficiency Maximization. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 22, 6157–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimaiti, S.; Huang, S.; Zhang, K.; Liu, X.; Xu, Z.; Mi, J. Collaborative Online Learning-Based Distributed Handover Scheme in Hybrid VLC/RF 5G Systems. Electronics 2025, 14, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolba, B.; Elsabrouty, M.; Abdu-Aguye, M.G.; Gacanin, H.; Kasem, H.M. Massive MIMO CSI Feedback Based on Generative Adversarial Network. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 2805–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Chang, H.; Li, H.; Gu, X.; Zhang, L. Changeable Rate and Novel Quantization for CSI Feedback Based on Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 10100–10144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Fan, J.; Lin, B.; Chen, C. A Quantized CSI Acquisition Strategy Based on Position Information Feedback for Indoor VLC-Based IoT Systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025; Early Access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Kang, Y.; Jeon, Y.S. Vector Quantization for Deep-Learning-Based CSI Feedback in Massive MIMO Systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2024, 13, 2382–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskin, C.; Liss, N.; Schwartz, E.; Zheltonozhskii, E.; Giryes, R.; Bronstein, A.; Mendelson, A. Uniq: Uniform noise injection for non-uniform quantization of neural networks. ACM Trans. Comput. Syst. 2021, 37, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderipour, M.; Taherpour, A.; Taherpour, A.; Gazor, S. Design of Optimal Non-Uniform Quantizer in Imperfect Noisy Reporting Channels for Collaborative Spectrum Sensing. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 12870–12882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Li, L.; Bi, M.; Li, J.; Hu, M.; Hu, W. A study on performance improvement of IMDD-UFMC with modified k-means non-uniform quantization. Opt. Commun. 2020, 476, 126324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielczarek, B.; Krzymien, W.A. Vector Quantization of Channel Information in Linear Multi-User MIMO Systems. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Ninth International Symposium on Spread Spectrum Techniques and Applications, Manaus, Brazil, 28–31 August 2006; pp. 302–306. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, J.; Rao, B. Vector quantization techniques for multiple-antenna channel information feedback. In Proceedings of the 2004 International Conference on Signal Processing and Communications (SPCOM), Bangalore, India, 11–14 December 2004; pp. 402–406. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.M.; Harris, R. A comparison of several vector quantization codebook generation approaches. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1993, 2, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Xie, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, Y. Adaptive Modem Based on LSTM-AutoEncoder with Vector Quantization. Electronics 2024, 13, 3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, O.; Pascual-Iserte, A.; San Arranz, G. Robust precoding for multi-user visible light communications with quantized channel information. Sensors 2022, 22, 9238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widrow, B.; Kollar, I.; Liu, M.C. Statistical theory of quantization. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1996, 45, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, B.; Zou, L. Recursive Fault Estimation with Energy Harvesting Sensors and Uniform Quantization Effects. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2022, 9, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, N.I.; Zhu, J.; Eldar, Y.C.; Evans, J. Design and Analysis of Hardware-limited Non-uniform Task-based Quantizers. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2023, 71, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Wu, L.; Gao, H. Channel Prediction Technology Based on Adaptive Reinforced Reservoir Learning Network for Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing Wireless Communication Systems. Electronics 2025, 14, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, W. Unified Codebook Design for Vector Channel Quantization in MIMO Broadcast Channels. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 2509–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Choi, W. Novel Codebook Design for Channel State Information Quantization in MIMO Rician Fading Channels with Limited Feedback. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 2858–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wen, C.; Chen, M.; Jin, S. Environment Knowledge-Aided Massive MIMO Feedback Codebook Enhancement Using Artificial Intelligence. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 4527–4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palitharathna, K.W.S.; Suraweera, H.A.; Godaliyadda, R.I.; Herath, V.R.; Thompson, J.S. Neural network-based channel estimation and detection in spatial modulation VLC systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 16–20 May 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Şaylı, O.; Doğan, H.; Panayırcı, E. Spline interpolation based channel estimation for ACO-OFDM over visible light channels. In Proceedings of the the 24th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Zonguldak, Turkey, 16–19 May 2016; pp. 333–336. [Google Scholar]
- Yaseen, M.; Canbilen, A.E.; Ikki, S. Channel estimation in visible light communication systems: The effect of input signal-dependent noise. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 14330–14340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapıcı, Y.; Güvenç, I. NOMA for VLC Downlink Transmission with Random Receiver Orientation. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2019, 67, 5558–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossaad, M.S.A.; Hranilovic, S.; Lampe, L. Visible Light Communications Using OFDM and Multiple LEDs. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2015, 63, 4304–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hammadi, A.; Sofotasios, P.C.; Muhaidat, S.; Al-Qutayri, M.; Elgala, H. Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access for Hybrid VLC-RF Networks with Imperfect Channel State Information. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, Y.S.; Alias, M.Y.; Abdulkafi, A.A. On performance analysis of LS and MMSE for channel estimation in VLC systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 12th International Colloquium on Signal Processing & Its Applications (CSPA), Melaka, Malaysia, 4–6 March 2016; pp. 204–209. [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.; Zhuang, H.; Qiu, X. Moving targets detection and tracking based on improved codebook algorithm and Kalman filtering. In Proceedings of the 2017 36th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Dalian, China, 26–28 July 2017; pp. 11494–11498. [Google Scholar]
- Codling, E.A.; Plank, M.J.; Benhamou, S. Random walk models in biology. J. R. Soc. Interface 2008, 5, 813–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shlezinger, N.; Eldar, Y.C. Task-based quantization with application to MIMO receivers. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.04290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radfar, M.; Dansereau, R.; Sayadiyan, A. A novel low complexity VQ-based single channel speech separation technique. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 27–30 August 2006; pp. 572–577. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).