FreqSpatNet: Frequency and Spatial Dual-Domain Collaborative Learning for Low-Light Image Enhancement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Low-Light Image Enhancement
2.2. Fourier Frequency Information
3. Proposed Algorithm
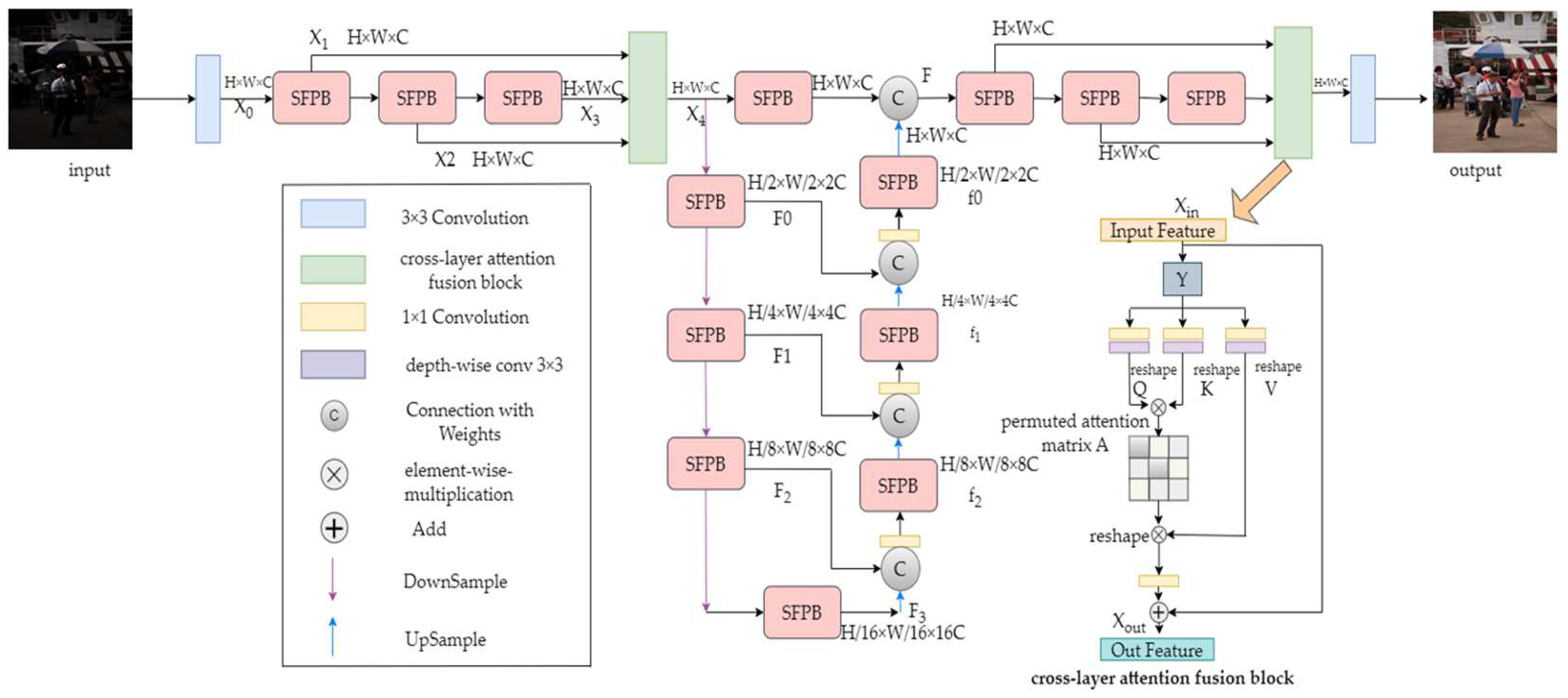
3.1. Network Architecture
3.2. Fourier Frequency Information
3.3. SFPB
3.4. Cross-Layer Attention Fusion Block
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Experimental Environment and Datasets
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Comparative Experiment
4.4. Ablation Study
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, B.; Wang, S.; Lu, Y.; Yi, Y.; Jiang, D.; Qiao, M. A New Pallet-Positioning Method Based on a Lightweight Component Segmentation Network for AGV Toward Intelligent Warehousing. Sensors 2025, 25, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, T.N.; Zhou, J.; Lakhiar, I.A.; Marinello, F.; Gemechu, T.T.; Rottok, L.T.; Jiang, Z. Enhancing Autonomous Orchard Navigation: A Real-Time Convolutional Neural Network-Based Obstacle Classification System for Distinguishing ‘Real’ and ‘Fake’ Obstacles in Agricultural Robotics. Agriculture 2025, 15, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.F.; Yang, Y.; Qu, X.D.; Cao, D.P.; Li, K.Q. A deep learning based image enhancement approach for autonomous driving at night. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 213, 106617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Chen, X.A.; Wang, F.F.; Xu, C.L.; Tang, Y.D. Image Recovery and Object Detection Integrated Algorithms for Robots in Harsh Battlefield Environments. In International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 575–585. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.D.; Chen, X.A.; Ren, W.H.; Han, Z.; Fan, H.J.; Tang, Y.D.; Liu, L.Q. Compensation Atmospheric Scattering Model and Two-Branch Network for Single Image Dehazing. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2024, 8, 2880–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounsfield, G.N. Computed medical imaging. Science 1980, 22, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.F.; Chen, X.A.; Wang, X.D.; Ren, W.H.; Tang, Y.D. Research on Object Detection Methods in Low-light Conditions. In International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 564–574. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.D.; Ren, W.H.; Chen, X.A.; Fan, H.J.; Tang, Y.D.; Han, Z. Uni-YOLO: Vision-Language Model-Guided YOLO for Robust and Fast Universal Detection in the Open World. In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia (MM’ 24), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 28 October–1 November 2024; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA; pp. 1991–2000. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.F.; Isa, N.A.M. Exposure based multi-histogram equalization contrast enhancement for non-uniform illumination images. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 70842–70861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.G.; Liang, Z.H.; Liu, C.L. A realtime image processor with combining dynamic contrast ratio enhancement and inverse gamma correction for pdp. Displays 2009, 30, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, E.H. The retinex theory of color vision. Sci. Am. 1977, 237, 108–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, J.W.; Guo, X.J. Kindling the darkness: A practical low-light image enhancer. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 1632–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Li, C.; Guo, J.; Loy, C.C.; Hou, J.; Kwong, S.; Cong, R. Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 21–23 June 2020; pp. 1780–1789. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Weng, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Jiang, J. Uretinex-net: Retinex based deep unfolding network for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5901–5910. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Hong, R.C.; Xu, M.L.; Yan, S.C.; Wang, M. Deep color consistent network for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1889–1898. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement. In Proceedings of the 29th British Machine Vision Conference, Newcastle, UK, 3–6 September 2018; BMVA Press: Durham, UK, 2018; Volume 14, pp. 155–167. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S. Restormer: Efficient transformer for high-resolution image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.H.; Bian, H.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.Q.; Radu Timofte Zhang, Y.L. Retinexformer: One-stage retinexbased transformer for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, K.H.; Shen, T.R.; Luo, W.H.; Bjorn Stenger Lu, T. Ultra-high-definition low-light image enhancement: A benchmark and transformer-based method. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 2654–2662. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhao, F.; Yan, K.Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Huang, Y.K.; Zhou, M.; Xiong, Z.W. Deep Fourier-Based Exposure Correction Network with Spatial-Frequency Interaction. In European Computer Vision Association; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 163–180. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Y.; Guo, C.L.; Zhou, M.; Liang, Z.X.; Zhou, S.C.; Feng, R.C.; Chen, C.L. Embedding Fourier for Ultra-High-Definition Low-Light Image Enhancement. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.11831. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Jin, Z. Fourllie: Boosting low-light image enhancement by fourier frequency information. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 7459–7469. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Ding, K.; Zhu, J. Exploiting Graph and Geodesic Distance Constraint for Deep Learning-Based Visual Odometry. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ma, T.; Liu, R.; Fan, X.; Luo, Z. Toward fast, flexible, and robust low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 11–15 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Brateanu, A.; Balmez, R.; Avram, A.; Orhei, C.; Ancuti, C. LYT-NET: Lightweight YUV Transformer-based Network for Low-light Image Enhancement. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2024, 32, 2065–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Hu, C.; Zhang, B.; Wu, F.; Cai, Z. Swin Transformer and ResNet Based Deep Networks for Low-light Image Enhancement. Multimed. Tools. Appl. 2024, 83, 26621–26642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jin, Z. CAPformer: Compression-Aware Pre-trained Transformer for Low-Light Image Enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 15–19 July 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Pei, S.; Qin, W.; Fu, B.; Li, X.; Huang, L. Wavelet-based mamba with fourier adjustment for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Hanoi, Vietnam, 8–12 December 2024; pp. 3449–3464. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Zheng, N.; Zhou, M.; Huang, J.; Xiao, Z.; Zhao, F. Frequency and spatial dual guidance for image dehazing. In Proceedings of the 2022 European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 181–198. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, M.L.; He, J.H.; He, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.P.; Wang, W.H.; Zhou, M.L. Low-light image enhancement via clip-fourier guided wavelet diffusion. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.03788. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Huang, J.; Zhao, F.; Gu, J.; Loy, C.C.; Meng, D.; Li, C. Deep fourier up-sampling. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systemsl; Curran Associates, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 35, pp. 22995–23008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Tao, H.; Zhou, H.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, P. A content-style control network with style contrastive learning for underwater image enhancement. Multimedia. Syst. 2025, 31, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tao, H.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, P.; Deng, Y. Hierarchical and progressive learning with key point sensitive loss for sonar image classification. Multimed. Syst. 2024, 30, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, W.; Huang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, J. Sparse gradient regularized deep retinex network for robust low-light image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2072–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychkovsky, V.; Paris, S.; Chan, E.; Durand, F. Learning photographic global tonal adjustment with a database of input/output image pairs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Li, K.; Gu, L.; Su, S.; Gao, P.; Jiang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Harada, T. You Only Need 90K Parameters to Adapt Light: A Light Weight Transformer for Image Enhancement and Exposure Correction. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, London, UK, 21–24 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Ling, H. Lime: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 26, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.F.; Gong, X.Y.; Liu, D.; Cheng, Y.; Fang, C.; Shen, X.H.; Yang, J.C.; Zhou, P.; Wang, Z.Y. Enlightengan: Deep light enhancement without paired supervision. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2340–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.X.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, C.H.; Shen, X.Y.; Zheng, W.S.; Jia, J.Y. Underexposed photo enhancement using deep illumination estimation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 6842–6850. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Yang, X.; Yin, B.C. Learning to restore low-light images via decomposition-and-enhancement. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2278–2287. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.H.; Wang, S.Q.; Fang, Y.M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.Y. Band representation-based semi-supervised low-light image enhancement: Bridging the gap between signal fidelity and perceptual quality. TIP 2021, 30, 3461–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.S.; Ma, L.; Zhang, J.A.; Fan, X.; Luo, Z.X. Retinex-inspired unrolling with cooperative prior architecture search for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 10556–10565. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Tu, X.; Huang, Y.; Ding, X.; Ma, K.K. Learning a simple low-light image enhancer from paired low-light instances. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 22252–22261. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.Q.; Liu, D.; Zhang, L.G.; Tian, Y.; Xia, X.Z.; Fu, X.J. ZERO-IG: Zero-shot illumination-guided joint denoising and adaptive enhancement for low-light images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 3015–3024. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.; Xu, S.; Xiao, N.; Cheng, X.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, X. Boosting the Performance of LLIE Methods via Unsupervised Weight Map Generation Network. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lu, P.; Sun, S.; Wang, F. Multimodal Sentiment Analysis in Realistic Environments Based on Cross-Modal Hierarchical Fusion Network. Electronics 2023, 12, 3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Jiang, G.; Yu, M.; Chen, Y.; Cui, Y.; Jiang, Z. Quality assessment for multi-exposure fusion light field images with dynamic region segmentation. Digit. Signal Process. 2024, 154, 104666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chulwoo, L.; Chul, L.; Chang, S.K. Contrast enhancement based on layered difference representation of 2D histograms. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 5372–5384. [Google Scholar]
- Vonikakis, V.; Kouskouridas, R.; Gasteratos, A. On the evaluation of illumination compensation algorithms. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 9211–9231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, J.; Hu, H.M.; Li, B. Naturalness preserved enhancement algorithm for non-uniform illumination images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 3538–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Method | LOL-v2-Synthetic | MIT-Adobe-FiveK | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | |
| LIME [39] | 16.88 | 0.776 | 17.79 | 0.826 |
| RetinexNet [16] | 17.13 | 0.798 | 12.69 | 0.644 |
| EnGAN [40] | 16.57 | 0.734 | 15.01 | 0.768 |
| KinD [12] | 13.29 | 0.578 | 17.17 | 0.696 |
| DeepUPE [41] | 15.08 | 0.623 | 18.78 | 0.822 |
| FIDE [42] | 15.20 | 0.613 | 17.17 | 0.696 |
| DRBN [43] | 23.22 | 0.927 | 15.95 | 0.704 |
| RUAS [44] | 16.55 | 0.652 | 9.53 | 0.610 |
| DCC [15] | 18.35 | 0.790 | 13.75 | 0.618 |
| SCI [25] | 22.20 | 0.887 | 16.29 | 0.795 |
| URetinex-Net [14] | 22.89 | 0.895 | 14.10 | 0.734 |
| Restormer [18] | 21.41 | 0.830 | 21.20 | 0.812 |
| PairLIE [45] | 19.07 | 0.794 | 10.55 | 0.642 |
| FourLLIE [23] | 24.65 | 0.919 | 25.18 | 0.908 |
| LLFormer [20] | 24.60 | 0.920 | 25.46 | 0.906 |
| Zero-IG [46] | 14.83 | 0.721 | 18.33 | 0.588 |
| Ours | 24.98 | 0.922 | 25.57 | 0.910 |
| Methods | MEF | LIME | NPE | VV | DICM | AVG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LIME [39] | 4.447 | 4.155 | 3.796 | 2.750 | 3.001 | 3.630 |
| RetinexNet [16] | 4.408 | 4.361 | 3.943 | 3.816 | 4.209 | 4.147 |
| KinD [12] | 4.819 | 4.772 | 4.175 | 3.835 | 3.614 | 4.194 |
| DRBN [43] | 4.869 | 4.562 | 3.921 | 3.671 | 4.369 | 4.278 |
| RUAS [44] | 5.435 | 5.322 | 7.198 | 4.987 | 7.306 | 6.050 |
| DCC [15] | 4.593 | 4.424 | 3.703 | 3.283 | 3.704 | 3.941 |
| SCI [25] | 3.608 | 4.463 | 4.124 | 5.312 | 4.519 | 4.405 |
| URetinex-Net [14] | 4.231 | 4.694 | 4.028 | 3.851 | 4.774 | 4.316 |
| Restormer [18] | 3.815 | 4.365 | 3.729 | 3.795 | 3.964 | 3.934 |
| PairLIE [45] | 4.063 | 4.582 | 4.184 | 3.572 | 4.033 | 4.087 |
| FourLLIE [23] | 4.362 | 4.402 | 3.909 | 3.168 | 3.374 | 3.907 |
| Zero-IG [46] | 3.528 | 4.233 | 2.463 | 3.576 | 4.225 | 3.605 |
| Ours | 3.496 | 4.150 | 3.472 | 3.662 | 3.070 | 3.570 |
| Methods | RetinexNet | KinD | DRBN | RUAS | URetinex-Net | EnGAN | Restormer | LLFormer | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Params (M) | 0.838 | 8.540 | 0.577 | 0.001 | 0.360 | 8.367 | 26.133 | 24.523 | 4.291 |
| FLOPs (G) | 148.54 | 36.57 | 42.41 | 0.28 | 233.09 | 72.61 | 144.25 | 22.52 | 12.11 |
| Ablation Module | LOL-v2-Synthetic | MIT-Adobe-5k | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | |
| w/o F | 24.15 | 0.915 | 24.22 | 0.908 |
| w/o S | 18.50 | 0.755 | 19.21 | 0.826 |
| w/o CAFB | 23.88 | 0.919 | 24.37 | 0.907 |
| w/o OF | 23.25 | 0.910 | 24.10 | 0.825 |
| Ours | 24.98 | 0.922 | 25.57 | 0.910 |
| Dim | FLOPs | Params | PSNR | SSIM | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 12.11 G | 4.291 M | 24.98 | 0.922 | 0.045 s |
| 32 | 20.56 G | 4.571 M | 24.99 | 0.920 | 0.082 s |
| 48 | 30.24 G | 5.661 M | 24.91 | 0.924 | 0.114 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Luan, X. FreqSpatNet: Frequency and Spatial Dual-Domain Collaborative Learning for Low-Light Image Enhancement. Electronics 2025, 14, 2220. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112220
Guan Y, Liu M, Chen X, Wang X, Luan X. FreqSpatNet: Frequency and Spatial Dual-Domain Collaborative Learning for Low-Light Image Enhancement. Electronics. 2025; 14(11):2220. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112220
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Yu, Mingsi Liu, Xi’ai Chen, Xudong Wang, and Xin Luan. 2025. "FreqSpatNet: Frequency and Spatial Dual-Domain Collaborative Learning for Low-Light Image Enhancement" Electronics 14, no. 11: 2220. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112220
APA StyleGuan, Y., Liu, M., Chen, X., Wang, X., & Luan, X. (2025). FreqSpatNet: Frequency and Spatial Dual-Domain Collaborative Learning for Low-Light Image Enhancement. Electronics, 14(11), 2220. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112220







