Horizontal Attack Against EC kP Accelerator Under Laser Illumination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Combining SCA with Laser Illumination
2.1. SCA and Laser Illumination Attacks
- to inject a fault in a logic cell via switching one of the illuminated transistors, or
- to increase the power consumption of the illuminated logic cells without switching transistor(s) of the attacked circuit.
2.2. State-of-the-Art
3. Cryptographic Accelerator and Attack Setup
3.1. IHP’s Elliptic Curve Scalar Multiplication Accelerator
- The field multiplier block (further denoted also as Multiplier) calculates a field product of two different operands (A · B) mod f(t).
- The block denoted as ALU performs a field addition of two operands (A + B) mod f(t) or a field squaring operation A2 mod f(t).
3.2. Attack Setup
3.3. Setup Configuration and Initial Parameters

4. Performed Attacks and Their Results
4.1. SCA Without Laser Illumination
4.1.1. Power Trace Analysis
- Each slot has its own shape due to the processing of different values during slot execution, i.e., shapes of all the slots are (at least) slightly different.
- The shapes of the slots from the same subset differ less than the shapes of the slots from different subsets, i.e., two ‘0’ slots are more similar to each other than a ‘0’ slot and a ‘1’ slot.
4.1.2. Measurements with the Current Probe from Riscure
4.1.3. Measurements with the Differential Probe from Teledyne LeCroy
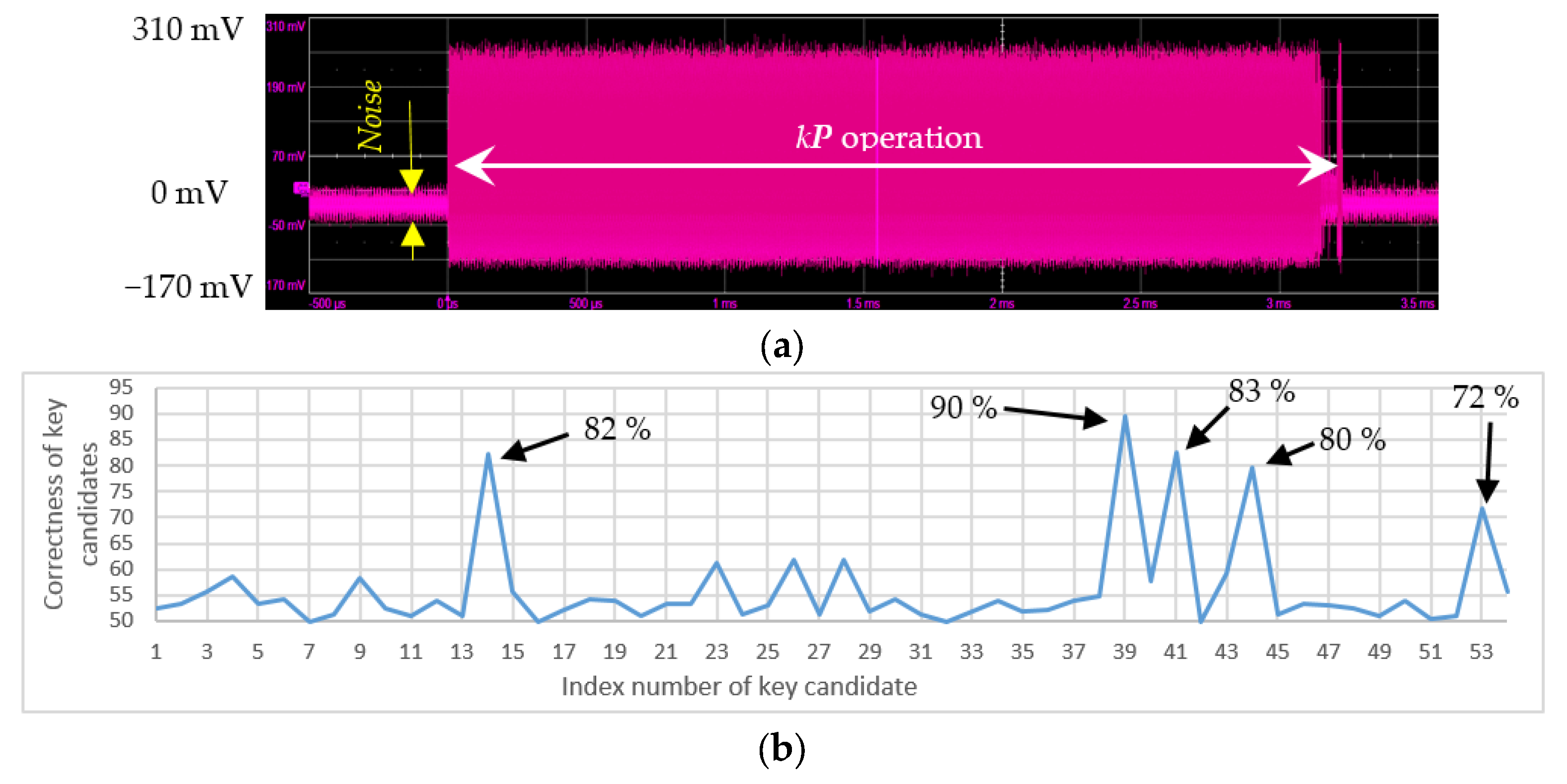
4.2. SCA Under Laser Illumination
| Performed kP | Nr. of Experiment | Laser Beam Power, % | Control Current, mA | Laser Beam Spot Area (in Comparison to the Chip’s Area *) | Offset **, mV | Correctness of the Best Key Candidate δ, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1P1 | 1 | Reference trace (i.e., without laser illumination) | - | 91 *** | ||
| 2 | 3 | 13.5 | 143 µm2 (0.005% of the chip area) | −0.13 ± 3.92 | 89 | |
| 3 | 5 | 22.5 | −0.29 ± 4.29 | 92 | ||
| 4 | 20 | 90.0 | −0.36 ± 4.08 | 89 | ||
| 5 | 50 | 225.0 | 5.93 ± 4.27 | 91 | ||
| 6 | 100 | 450.0 | 17.06 ± 4.60 | 92 | ||
| 7 | 13 | 60.0 | 509 µm2 (0.017% of the chip area) | −0.19 ± 4.21 | 92 | |
| 8 | 59 | 265.5 | 2050 µm2 (0.068% of the chip area) | 7.49 ± 4.05 | 90 | |
| 9 | 100 | 450.0 | 3004 µm2 (0.1% of the chip area) | 16.10 ± 4.32 | 90 | |
| k1P2 | 10 | Reference trace (i.e., without laser illumination) | - | 89 | ||
| 11 | 5 | 22.5 | 143 µm2 (0.005% of the chip area) | 0.23 ± 4.51 | 89 | |
| 12 | 100 | 450.0 | 3004 µm2 (0.1% of the chip area) | 15.29 ± 4.43 | 90 | |
| k2P1 | 13 | Reference trace (i.e., without laser illumination) | - | 90 | ||
| 14 | 5 | 22.5 | 143 µm2 (0.005% of the chip area) | −0.20 ± 4.62 | 89 | |
| 15 | 100 | 450.0 | 3004 µm2 (0.1% of the chip area) | 14.98 ± 4.27 | 89 | |

5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
| Logic Cell | buffer | inverter | NOR2 | NAND | XNOR | OR2-AND2 | OR2-AND3 | AND2-OR2 | AND3-OR2 | D-flip-flops |
| number | 167 | 1979 | 514 | 5241 | 3893 | 1048 | 473 | 1145 | 406 | 830 |

References
- Clavier, C.; Feix, B.; Gagnerot, G.; Roussellet, M.; Verneuil, V. Horizontal correlation analysis on exponentiation. In Proceedings of the Information and Communications Security: 12th International Conference, ICICS 2010, Barcelona, Spain, 15–17 December 2010; Volume 6476, pp. 46–61. [Google Scholar]
- Rivest, R.L.; Shamir, A.; Adleman, L. A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems. Commun. ACM 1978, 21, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, V.S. Use of Elliptic Curves in Cryptography. In Advances in Cryptology—CRYPTO ’85 Proceedings; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; pp. 417–426. [Google Scholar]
- Koblitz, N. Elliptic curve cryptosystems. Math. Comp. 1987, 48, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mulder, E.; Buysschaert, P.; Ors, S.B.; Delmotte, P.; Preneel, B.; Vandenbosch, G.; Verbauwhede, I. Electromagnetic Analysis Attack on an FPGA Implementation of an Elliptic Curve Cryptosystem. In Proceedings of the EUROCON 2005—The International Conference on “Computer as a Tool”, Belgrade, Serbia, 21–24 November 2005; Volume 2, pp. 1879–1882. [Google Scholar]
- Kadir, S.A.; Sasongko, A.; Zulkifli, M. Simple power analysis attack against elliptic curve cryptography processor on FPGA implementation. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics, Bandung, Indonesia, 17–19 July 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, C.D. Sliding Windows Succumbs to Big Mac Attack. In Proceedings of the Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems—CHES 2001, Paris, France, 14–16 May 2001; pp. 286–299. [Google Scholar]
- Heyszl, J.; Mangard, S.; Heinz, B.; Stumpf, F.; Sigl, G. Localized Electromagnetic Analysis of Cryptographic Implementations. In Topics in Cryptology—CT-RSA 2012; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Dunkelman, O., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 7178. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, A.; Jaulmes, E.; Prouff, E.; Wild, J. Horizontal and Vertical Side-Channel Attacks against Secure RSA Implementations. In Proceedings of the Topics in Cryptology—CT-RSA 2013, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25 February–1 March 2013; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, A.; Jaulmes, E.; Prouff, E.; Wild, J. Horizontal Collision Correlation Attack on Elliptic Curves. In Proceedings of the Selected Areas in Cryptography—SAC 2013, Burnaby, BC, Canada, 14–16 August 2013; pp. 553–570. [Google Scholar]
- Skorobogatov, S.; Anderson, R. Optical Fault Induction Attacks. In Proceedings of the Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Redwood Shores, CA, USA, 13–15 August 2002; pp. 2–12. [Google Scholar]
- Petryk, D.; Dyka, Z.; Langendörfer, P. Sensitivity of Standard Library Cells to Optical Fault Injection Attacks in IHP 250 nm Technology. In Proceedings of the 2020 9th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing (MECO), Budva, Montenegro, 8–11 June 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Courrege, J.D.-B.J.-C.; Rouzeyre, B.; Torres, L.; Perdu, P. When Failure Analysis Meets Side-Channel Attacks. In Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, CHES 2010; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Mangard, S., Standaert, F.X., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 6225, pp. 188–202. [Google Scholar]
- Belohoubek, J.; Fiser, P.; Schmidt, J. Optically induced static power in combinational logic: Vulnerabilities and countermeasures. Microelectron. Reliab. 2021, 124, 114281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alioto, M.; Bongiovanni, S.; Scotti, G.; Trifiletti, A. Leakage Power Analysis attacks against a bit slice implementation of the Serpent block cipher. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems (MIXDES), Lublin, Poland, 19–21 June 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, A. Side-Channel Leakage through Static Power. In Proceedings of the Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems—CHES 2014, Busan, Republic of Korea, 23–26 September 2014; pp. 562–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo, S.M.; Standaert, F.-X.; Kamel, D.; Moradi, A. Side-channel attacks from static power: When should we care? In Proceedings of the 2015 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Grenoble, France, 9–13 March 2015; pp. 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Cassiers, G.; Masure, L.; Momin, C.; Moos, T.; Standaert, F.-X. Prime-Field Masking in Hardware and its Soundness against Low-Noise SCA Attacks. TCHES 2023, 2023, 482–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, J.; Mankali, L.; Nabeel, M.; Sinanoglu, O.; Karri, R.; Knechtel, J. Beware Your Standard Cells! On Their Role in Static Power Side-Channel Attacks. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2024, 43, 4439–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabin, I.; Dyka, Z.; Sigourou, A.-A.; Langendoerfer, P. Static Power Consumption as a New Side-Channel Analysis Threat to Elliptic Curve Cryptography Implementations. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and Resilience (CSR), London, UK, 2–4 September 2024; pp. 884–889. [Google Scholar]
- Skorobogatov, S. Optically Enhanced Position-Locked Power Analysis. In Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems—CHES 2006; Goubin, L., Matsui, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 4249, pp. 61–75. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto, J.S.D.; Matsumoto, T. Laser irradiation on EEPROM sense amplifiers enhances side-channel leakage of read bits. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Asian Hardware-Oriented Security and Trust (AsianHOST), Yilan, Taiwan, 19–20 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Petryk, D.; Dyka, Z.; Krstic, M.; Bělohoubek, J.; Fišer, P.; Steiner, F.; Blecha, T.; Langendörfer, P.; Kabin, I. On the Influence of the Laser Illumination on the Logic Cells Current Consumption. In Proceedings of the 2023 30th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), Istanbul, Turkiye, 4–7 December 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bělohoubek, J.; Fišer, P.; Schmidt, J. Using Voters May Lead to Secret Leakage. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 22nd International Symposium on Design and Diagnostics of Electronic Circuits & Systems (DDECS), Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 24–26 April 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Bělohoubek, J.; Fišer, P.; Schmidt, J. CMOS Illumination Discloses Processed Data. In Proceedings of the 2019 22nd Euromicro Conference on Digital System Design (DSD), Kallithea, Greece, 28–30 August 2019; pp. 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- IHP—Leibniz Institute for High Performance Microelectronics. Available online: https://www.ihp-microelectronics.com (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- FIPS 186-4; Request for Comments on the NIST-Recommended Elliptic Curves. Digital Signature Standard: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2015.
- Montgomery, P.L. Speeding the Pollard and elliptic curve methods of factorization. Math. Comp. 1987, 48, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.; Dahab, R. Fast Multiplication on Elliptic Curves Over GF(2m) without precomputation. In Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems; Koç, Ç.K., Paar, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; Volume 1717, pp. 316–327. [Google Scholar]
- Hankerson, D.; Lopez, J.; Menezes, A. Software Implementation of Elliptic Curve Cryptography over Binary Fields. In Proceedings of the Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems—CHES 2000, Worcester, MA, USA, 17–18 August 2000; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kabin, I. Horizontal Address-Bit SCA Attacks Against ECC and Appropriate Countermeasures. Ph.D. Thesis, BTU Cottbus, Senftenberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coron, J.-S. Resistance Against Differential Power Analysis For Elliptic Curve Cryptosystems. In Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems; Koç, Ç.K., Paar, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; Volume 1717, pp. 292–302. [Google Scholar]
- Batina, L.; Hogenboom, J.; Mentens, N.; Moelans, J.; Vliegen, J. Side-channel evaluation of FPGA implementations of binary Edwards curves. In Proceedings of the 2010 17th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems, 12–15 December 2010; pp. 1248–1251. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, K.; Izu, T.; Takenaka, M. A Practical Countermeasure against Address-Bit Differential Power Analysis. In Proceedings of the Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems—CHES 2003, Cologne, Germany, 8–10 September 2003; pp. 382–396. [Google Scholar]
- Izumi, M.; Ikegami, J.; Sakiyama, K.; Ohta, K. Improved countermeasure against Addressbit DPA for ECC scalar multiplication. In Proceedings of the 2010 Design, Automation Test in Europe Conference Exhibition (DATE 2010), Dresden, Germany, 8–12 March 2010; pp. 981–984. [Google Scholar]
- Joye, M.; Yen, S.-M. The Montgomery Powering Ladder. In Proceedings of the Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems—CHES 2002, Redwood Shores, CA, USA, 13–15 August 2002; pp. 291–302. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, K.; Izu, T.; Takenaka, M. Address-Bit Differential Power Analysis of Cryptographic Schemes OK-ECDH and OK-ECDSA. In Proceedings of the Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems—CHES 2002, Redwood Shores, CA, USA, 13–15 August 2002; pp. 129–143. [Google Scholar]
- Kabin, I.; Dyka, Z.; Klann, D.; Aftowicz, M.; Langendoerfer, P. Resistance of the Montgomery Ladder Against Simple SCA: Theory and Practice. J. Electron. Test. 2021, 37, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riscure. Current Probe. Available online: https://getquote.riscure.com/en/quote/2101059/current-probe.htm (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- Teledyne Lecroy. Differential Probe ZD1500. Available online: https://www.teledynelecroy.com/probes/differential-probes-1500-mhz/zd1500 (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- Teledyne Lecroy WavePro 604HD Oscilloscope. Available online: https://teledynelecroy.com/oscilloscope/wavepro-hd-oscilloscope/wavepro-604hd (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- R&S HMP4040 Power Supply. Available online: https://www.rohde-schwarz.com/products/test-and-measurement/dc-power-supplies/rs-hmp4000-power-supply-series_63493-47360.html (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- Riscure. Diode Laser Station Datasheet. 2011. Available online: https://getquote.riscure.com/en/inspector-fault-injection.html (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- ALPhANOV Optical and Laser Technology Center. Available online: https://www.alphanov.com/en (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- TANGO Desktop. Available online: https://www.marzhauser.com/produkte/steuerungen/tango-desktop.html (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- Petryk, D. Investigation of Sensitivity of Different Logic and Memory Cells to Laser Fault Injections. Ph.D. Thesis, BTU Cottbus, Senftenberg, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petryk, D.; Kabin, I.; Langendörfer, P.; Dyka, Z. On the Importance of Reproducibility of Experimental Results Especially in the Domain of Security. In Proceedings of the 2024 13th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing (MECO), Budva, Montenegro, 11–14 June 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Petryk, D.; Dyka, Z.; Langendörfer, P. Optical Fault Injections: A Setup Comparison. In Proceedings of the PhD Forum of the 8th BELAS Summer School, Tallinn, Estonia, 20–22 June 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- ALPhANOV. PDM LASERS Pulse-on-Demand Modules. Available online: https://www.alphanov.com/sites/default/files/2019-09/Catalogue%20PDM_092019W.pdf (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Mitutoyo. Microsope Units and Objectives. Available online: https://www.mitutoyo.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/E4191-378_010611.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- Heyszl, J. Impact of Localized Electromagnetic Field Measurements on Implementations of Asymmetric Cryptography. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität München, München, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mangard, S.; Oswald, E.; Popp, T. Power Analysis Attacks: Revealing the Secrets of Smart Cards; Springer Science+Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-387-30857-9. [Google Scholar]
- KEYSIGHT. Device Vulnerability Analysis. Riscure. Riscure is Now Part of Keysight. Available online: https://www.keysight.com/us/en/products/network-test/device-vulnerability-analysis.html (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Kokyo LaseView-CA50-NCG-BE Laser Beam Profiler. Available online: https://en.symphotony.com/beam-profiler/cameraset/ (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- Riscure. PDM2+ HP. Single-Mode Diode Laser An ALPhANOV & Riscure Product. Datasheet v1. Available online: https://getquote.riscure.com/picdb/filedb/3792/Alphanov%20laser%20datasheet.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Sarafianos, A.; Gagliano, O.; Serradeil, V.; Lisart, M.; Dutertre, J.-M.; Tria, A. Building the electrical model of the pulsed photoelectric laser stimulation of an NMOS transistor in 90nm technology. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS), Monterey, CA, USA, 14–18 April 2013; pp. 5B.5.1–5B.5.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafianos, A.; Gagliano, O.; Lisart, M.; Serradeil, V.; Dutertre, J.-M.; Tria, A. Building the electrical model of the pulsed photoelectric laser stimulation of a PMOS transistor in 90nm technology. In Proceedings of the 20th IEEE International Symposium on the Physical and Failure Analysis of Integrated Circuits (IPFA), Suzhou, China, 20–23 July 2013; pp. 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyence. 3D Laserscanning-Microscope. Available online: https://www.keyence.de/products/microscope/laser-microscope/vk-x3000/ (accessed on 5 May 2025).







| Correctness of Selected Key Candidates δ, % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index nr. of Key Cand. | 14 | 39 | 41 | 44 |
| Exp. Nr. | ||||
| 1 | 85.65 | 90.87 | 88.70 | 86.52 |
| 5 | 84.35 | 90.87 | 87.39 | 90.43 |
| 6 | 78.26 | 91.74 | 87.83 | 83.91 |
| 8 | 81.74 | 90.43 | 85.65 | 85.65 |
| 9 | 81.30 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 83.48 |
| 10 | 81.30 | 89.13 | 83.91 | 75.65 |
| 12 | 76.09 | 90.43 | 85.65 | 74.78 |
| 13 | 80.87 | 88.70 | 90.43 | 77.83 |
| 15 | 85.22 | 86.96 | 89.13 | 83.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petryk, D.; Kabin, I.; Langendoerfer, P.; Dyka, Z. Horizontal Attack Against EC kP Accelerator Under Laser Illumination. Electronics 2025, 14, 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102072
Petryk D, Kabin I, Langendoerfer P, Dyka Z. Horizontal Attack Against EC kP Accelerator Under Laser Illumination. Electronics. 2025; 14(10):2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102072
Chicago/Turabian StylePetryk, Dmytro, Ievgen Kabin, Peter Langendoerfer, and Zoya Dyka. 2025. "Horizontal Attack Against EC kP Accelerator Under Laser Illumination" Electronics 14, no. 10: 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102072
APA StylePetryk, D., Kabin, I., Langendoerfer, P., & Dyka, Z. (2025). Horizontal Attack Against EC kP Accelerator Under Laser Illumination. Electronics, 14(10), 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102072





