3.1. Constructive Heuristics
Our approach is based on the general principle of constructive heuristics, which iteratively builds a solution. Let
represent a specific heuristic from the set of all possible constructive heuristics
, where each heuristic satisfies the assumptions outlined in this section. For instance, the set
includes all variants of MAXRECTS heuristics [
21], Skyline heuristics [
23], but also heuristics based on Corner Points and Extreme Points [
19,
20]. However, this set is defined in a generic sense and can also encompass other potential constructive heuristics, including those not yet known. A constructive heuristic
h starts with an initial solution
, i.e., an empty bin and all items
to be packed, and iteratively chooses an item and its placement in a bin, possibly adding a new bin. The notation related to the general and neural-based constructive heuristic algorithm, along with explanations of the terms used, is compiled in
Table 3.
At the beginning of the k-th iteration, , the current partial solution is denoted as , where represents the packing configuration after placing items, and the remaining items to be packed are denoted by . The set contains all possible partial solutions, i.e., all possible packings of any subset of items.
In iteration k, a new item must be chosen, possibly rotated, and placed into a bin. Let denote a potential decision in iteration k, where is the set of all feasible decisions given the current partial solution , and is the set of all possible decisions across any partial solution. Decision d is a triplet , where denotes the item chosen in decision d, is its location (e.g., coordinates of its bottom left corner), and is a boolean indicator of item i rotation (item non-rotated or rotated by 90 degrees).
Each decision made by a constructive heuristic transforms the current partial solution into an updated solution. This transformation is represented by a function:
where
adds one item according to the decision
to the current packing
, producing a new partial or final solution,
.
The selection of an item and its placement is specific to each constructive heuristic and is guided by heuristic rules or criteria, which are typically chosen based on prior knowledge or computational experiments. These criteria often take into account the item’s properties (e.g., width, height) and/or characteristics of the current packing state (e.g., wasted space).
Let
denote a property function that assigns an
m-dimensional vector to a partial solution
and a candidate decision
d under heuristic
. Typical properties considered in the bin packing problem include item size, aspect ratio, and space utilization.
Each heuristic
h evaluates a decision
d based on properties
and greedily selects the decision that maximizes the evaluation function:
where
assigns a scalar score to the decision
d at state
. For instance, if
computes the item’s area and the wasted space after the placement, the heuristic might choose the largest item and place it at the position that minimizes wasted space.
The generic constructive heuristic algorithm follows these steps:
Initialize: Set and initialize set of items , and the partial solution (empty bin).
Start an iteration: Set
Select a Decision: Find the decision
that maximizes the evaluation function
E:
Update Solution: Apply the decision
to extend the current partial solution:
Update set of items: Remove newly inserted item
from the set of items to pack:
Iterate: If there are still items to pack, start a new iteration from step 2. Otherwise, stop.
Constructive heuristics typically rely on a limited set of item properties and features of the current partial solution. In most cases, these heuristics consider only one property of the item and one characteristic of the partial solution at a time. For example, the Maximal Rectangles Bottom-Left (MAXRECTS-BL) heuristic determines placement based on the
x and
y coordinates of all possible positions [
44]. The evaluation function, denoted as
E, selects the placement with the smallest
y-coordinate, and if multiple positions share the same
y-value, the smallest
x-coordinate is used as a tiebreaker. However, different properties perform better for different problem instances, making it impossible to identify a single best heuristic
.
Furthermore, the function E, which evaluates and prioritizes different placement options, is usually defined by simple, static rules that dictate item selection, placement, and orientation. For example, the MaxRects heuristic orders items based on predefined criteria such as descending area, descending perimeter, aspect ratio, or the difference between rectangle sides. Similarly, placement decisions follow rigid selection rules, including:
Bottom-Left: selecting the position that minimizes the y-coordinate of the top side.
Best Area Fit: choosing the smallest available space.
Best Long Side Fit: placing the item where the longest remaining side is minimized.
Once these sorting and placement strategies are defined, they remain fixed throughout the entire algorithm execution, without adapting to the current partial solution. This rigid approach means that the effectiveness of a given heuristic can vary significantly across different problem instances, depending on the characteristics of the input data.
3.2. Concept of New Neural-Driven Heuristics
Observations we stated in the previous section led us to formulate the following expectations for the new heuristic:
It should incorporate a broader set of properties from the current partial solution and dynamically adjust the relevance of these properties based on the specific problem instance.
It should enable an adaptive decision-making for item selection, orientation, and placement, allowing the heuristic to evolve as the solution is constructed.
The core concept of our approach is to replace the traditional evaluation function E with a neural network, which learns to assess the properties of available alternatives regarding items and their placements at each step of the constructive heuristic. This neural network identifies which features are most important in a given context and determines which item, placement, and orientation decisions contribute to an optimal solution.
Unlike conventional heuristics that follow predefined rules, our model evaluates each alternative separately based on the current partial solution. This makes it possible to handle a variable number of candidate placements while maintaining a fixed-size input representation for the neural network.
The input to the neural network is a vector of properties, denoted as , where:
represents the current state of the partial solution,
denotes a candidate decision,
m is the number of considered properties, which is expected to be larger than those used in conventional heuristics.
In the most general case, the decision space
of the construction heuristic for the bin-packing problem is huge. That means an item can be placed all over the empty space of bins. To make it computationally feasible, we decided to limit the set of possible placing positions to certain, sensible alternatives. In the algorithm proposed by Martello et al. [
19], the authors utilize a set of placing positions called Corner points. These are non-dominated locations, where the envelope of items already in the bin changes from horizontal to vertical, see
Figure 2.
Although there is no guarantee that the optimal solution to every problem can be constructed by placing properly ordered items in the right Corner points (see [
20,
45]), we show in the next section that this approach gives very good results when combined with the proposed neural-driven construction heuristic. Moreover, the use of Corner points ensures robotic packing. Due to the definition of Corner points as a breaking point of the envelope, it is always possible to insert an item from two sides.
In general, there are four decision types to be made: which item, rotated or not, at which bin, and which position within that bin. However, for the bin selection, we assume that only one bin is opened at a time. A bin is closing and a new bin is opened only if none of the remaining small items fit in an already opened bin.
At step
k, a neural network
with weights
is used to score all item types still available for placement in their original and rotated versions and all feasible Corner points in an opened bin. So, the decision
is to choose a triplet consisting of an item type, its rotation, and a placement position that maximizes the evaluation
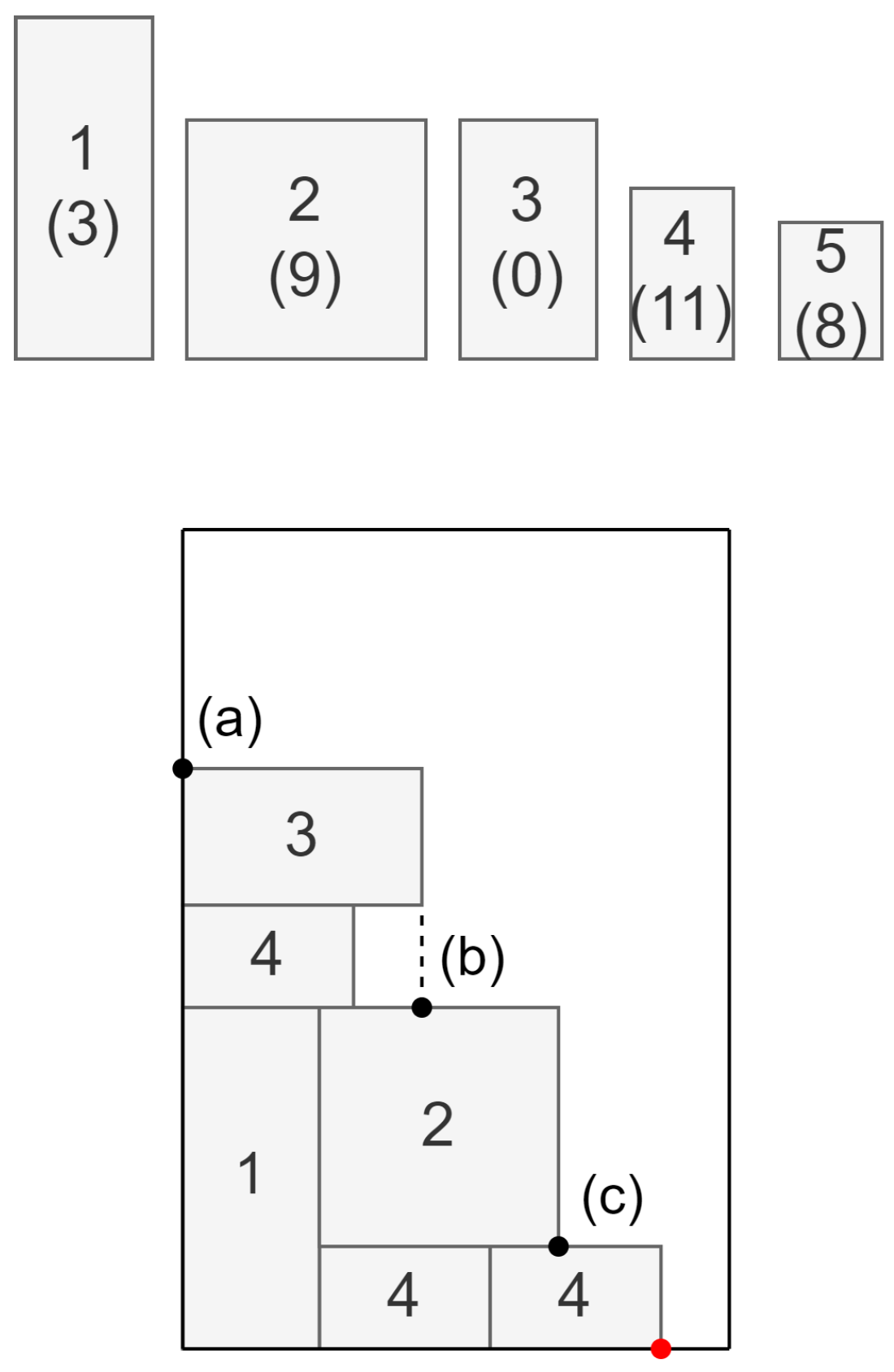
. For example, in the situation depicted in
Figure 3, item types are illustrated at the top of the figure. The number of items of a given type to be packed is shown in parentheses, which means there are no more items of type 3. Therefore, four item types (1, 2, 4, and 5), each in two possible rotations, together with three Corner points (a–c) (the leftmost corner point highlighted with red color is ruled out, as the accompanying free space is smaller than any of the dimensions of the small items), are under consideration. Thus, the total number of alternative decisions equals
. Each decision is checked against its feasibility. For example, placing element type 1 rotated by 90 degrees at the Corner point (c) is not possible since the element would protrude beyond the bin. For each feasible combination, the properties
of the partial solution
and each decision
d are evaluated by the neural network
.
As discussed later in this section, our algorithm applies a population of neural networks for training purposes. That implies the evaluation procedure should be very efficient. Therefore, we use a small-scale and simple feed-forward neural network for
with an architecture depicted in
Figure 4. The network has a four-layer architecture with 24 inputs and 1 output. While the output is a numerical evaluation, the inputs are discussed in depth in the following subsection. The hidden layer sizes are 32 and 16, respectively. The hidden layers and the output are equipped with bias values. Only hidden layers utilize the tanh activation function. The total number of network parameters (weights) is 1345. Initially, all the weights are set to 0.
The output of the neural network is a scalar evaluation score, which quantifies the quality of each possible decision given the current state . A higher score indicates a better placement decision. However, this value does not have an explicit probabilistic interpretation—it is solely used to rank and select the best available placement at each step.
The overall solution construction process is illustrated in
Figure 5, where the role of the traditional heuristic evaluation function
is replaced by a trained neural network
, parameterized by weights
.
A key distinction of our approach is that once the neural network is trained, no additional search over the solution space is required, unlike traditional metaheuristics that rely on iterative search strategies. Instead, the model performs a single-pass construction, incrementally building the solution in a sequential and adaptive manner. The procedure is highly efficient, as the utilized neural network is of a simple feed-forward type with a relatively small size.
3.3. Inputs to the Neural Network
The properties evaluated by the neural network try to reflect the state of the bin affecting the future decision, the state of the remaining small items that are to be placed, and the actual decision. Selecting the properties is crucial since too little knowledge may block the selection of good decisions, and the algorithm may lack generalization. On the other hand, too many properties reduce the efficiency and make the neural network overcomplicated.
Let us analyze the situation presented in
Figure 6. The decision that needs to be evaluated is to insert the item of type 1 into one of the Corner points. Based on our experience and intuition, we defined 24 features that result in the best algorithm performance. The vector quantifying decision
d incorporates the following properties:
Information on the item being placed under the decision d
Width and height.
Area.
Information on the remaining items
Total remaining area.
Remaining area of items of given type.
# of items
# of items of given type
Information on the state after the placement
1D view of the strip state.
This is the eight-long element vector holding the distance of the non-dominated envelope of the packed items (including the item
that is about to be inserted) from the top edge of the bin. The distances are marked with red line segments on
Figure 6. The distance is sampled in positions evenly spread over the width of the bin.
Wasted space.
Horizontal distance.
The horizontal distance of the item
from the right side of the bin, denoted with
(blue line segment) in
Figure 6.
Vertical distance.
Similarly, the vertical distance from the top edge of the current bin, denoted with
(vertical blue line segment) in
Figure 6.
Horizontal and vertical positions.
Horizontal size fit.
Let w be the width of item (after possible rotation). Then, the horizontal size fit is computed as , which tries to quantify how well other items of the same type t, such as , would fit into the remaining space if there were enough of them and they were inserted into this space.
Vertical size fit.
Horizontal mismatch.
This property quantifies how well the envelope of the white item is aligned with adjacent items, horizontally. In
Figure 6, this value is represented by the length of the green line segment connecting the corners of the white item and the item of type 3. Its value may be positive or negative, depending on the alignment.
Vertical mismatch.
Similarly, this property quantifies how well the envelope of the new item is aligned, vertically. In
Figure 6, this value is represented by the green dot in the corner of items of type 1 and 2, which means they are perfectly aligned.
Values of each property are scaled, and whenever the network should focus on smaller values, but larger ones (outliers) can also occur, we apply a hyperbolic tangent function to fit values to range (these include the following properties: remaining area, number of the remaining items, 1D view of the strip state, horizontal and vertical mismatch, wasted space, vertical distance and position).
3.4. Network Training with Black-Box Optimization
Given that the neural network is integrated into a combinatorial construction heuristic and lacks a direct method for determining correct outputs, conventional backpropagation techniques are inapplicable. Instead, black-box optimization approaches have emerged as a promising alternative for neural network training, attracting considerable interest within the machine learning field [
46,
47,
48]. For this reason, we selected black-box optimization as the most adaptable method to determine the neural network’s parameters, specifically the weights
.
Among the array of evolutionary strategies available, the Covariance Matrix Adaptation Evolution Strategy (CMA-ES) stands out as a leading derivative-free optimization technique. Its suitability for black-box optimization stems from its reliance on function evaluations alone, eliminating the need for derivative calculations [
49].
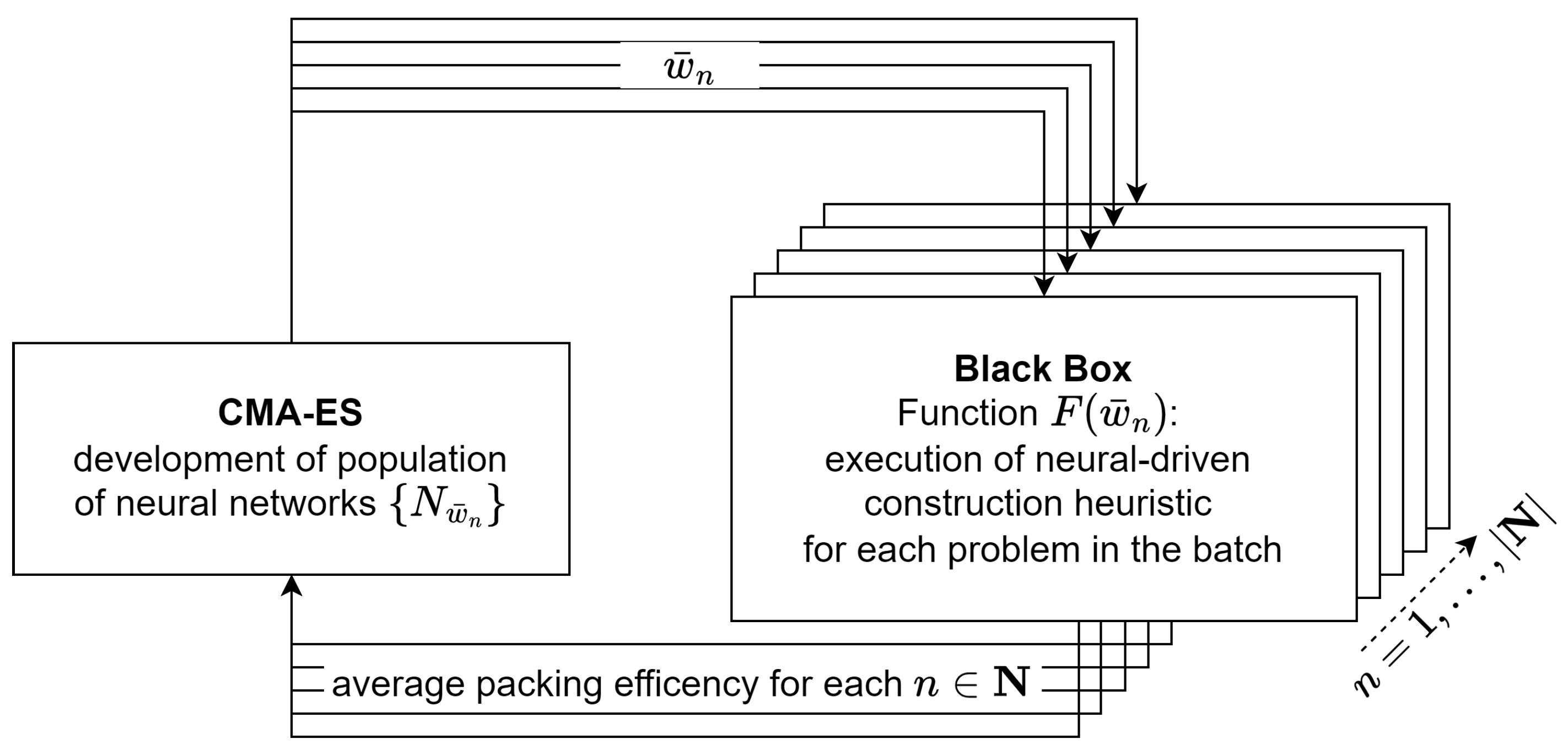
The training procedure is illustrated in
Figure 7. CMA-ES, as an evolutionary strategy algorithm, searches the space of neural network weights and optimizes a given function
F. The algorithm operates iteratively on a population
, where each individual
represents a distinct set of neural network weights
, and thus a unique neural network
. To control the evolution of the population, CMA-ES evaluates every individual
in the population. To mitigate the computational burden associated with evaluating all training instances, we adopt a batch-based approach, using only a subset of instances per iteration. Specifically, for each CMA-ES iteration, 100 problem instances are randomly drawn from a pool of 500,000. Thus, the population is evaluated against a newly sampled subset of instances at each cycle.
Evaluation of an individual
involves executing the algorithm depicted in
Figure 5 with the individual’s weights
on each problem in the batch. As illustrated in
Figure 7, weights
are passed to the black-box evaluation in parallel for each
. This process results in a set of packings for each
n, corresponding to the batch of problems.
For each packing, the packing efficiency factor is computed based on the number of closed bins and the fill factor of the last (potentially partially filled) bin. The average packing efficiency over all problems in the batch serves as the quality metric for the corresponding individual, effectively acting as a fitness function.
From the perspective of CMA-ES, the evaluation of an individual n is perceived as a black-box function, as no explicit information about the function structure is available. The average packing efficiencies are collected for all individuals, and CMA-ES uses this information to guide the evolution of the population, generating the next generation of individuals.
This random selection of a modest subset per iteration effectively alters the objective function throughout the optimization process. Nevertheless, the algorithm sustains convergence while keeping computational demands manageable. Additionally, this unconventional strategy reduces the risk of the algorithm becoming trapped in local optima.
Notably, unlike many other optimization methods [
50], CMA-ES relies on the relative ranking of evaluation outcomes rather than their precise numerical values. This means that the optimization is driven by the performance order of individuals rather than their specific scores, enhancing the algorithm’s robustness and supporting convergence even when the objective function fluctuates during training.
Every 10th iteration, the best solution found in that iteration is evaluated against a predefined validation set of 10,000 problems. The best-performing solution on the validation set so far is stored as the final solution of the algorithm.