Effects of Porous Filling and Nanofluids on Heat Transfer in Intel i9 CPU Minichannel Heat Sinks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Formulations and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
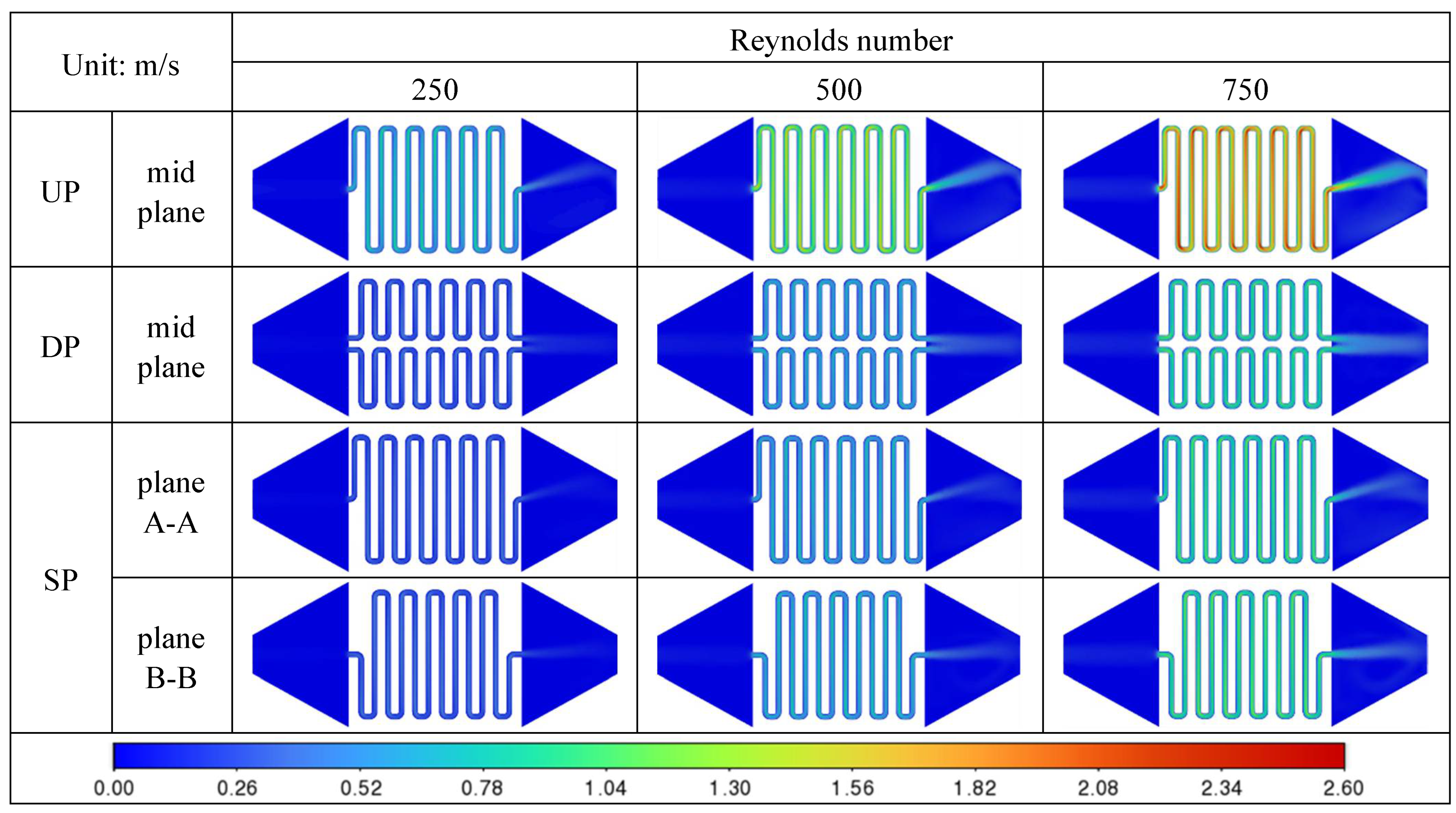
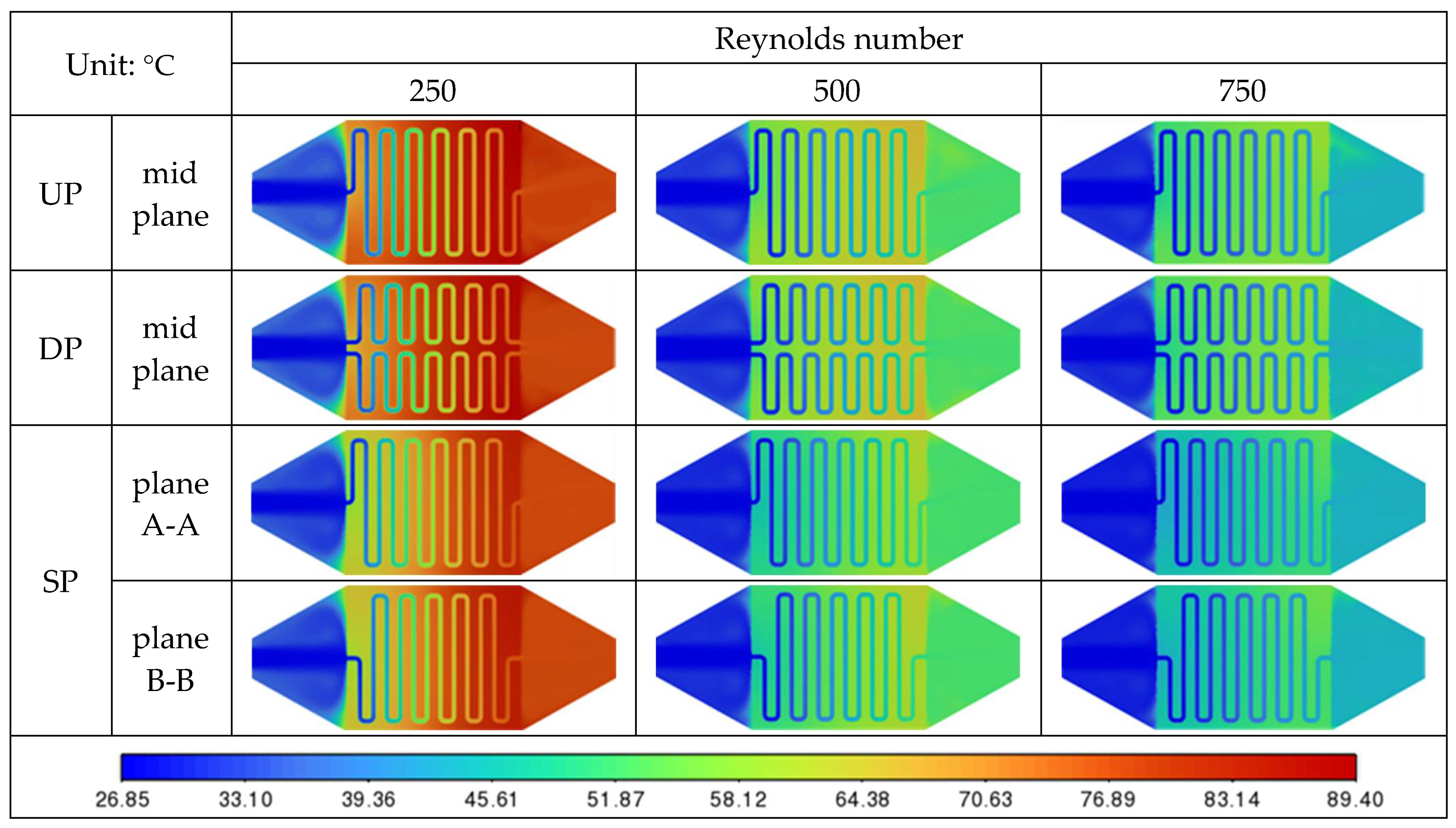
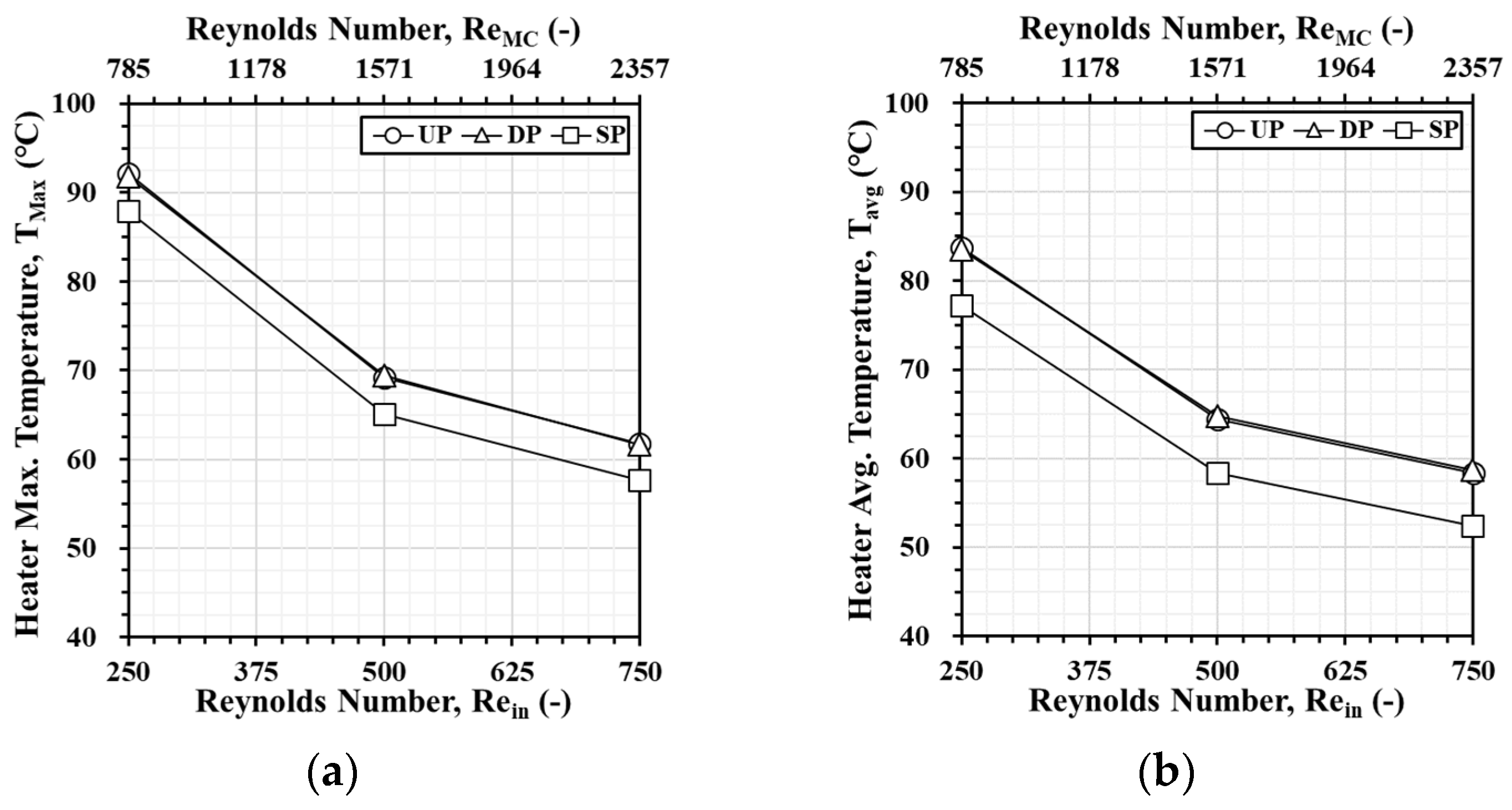
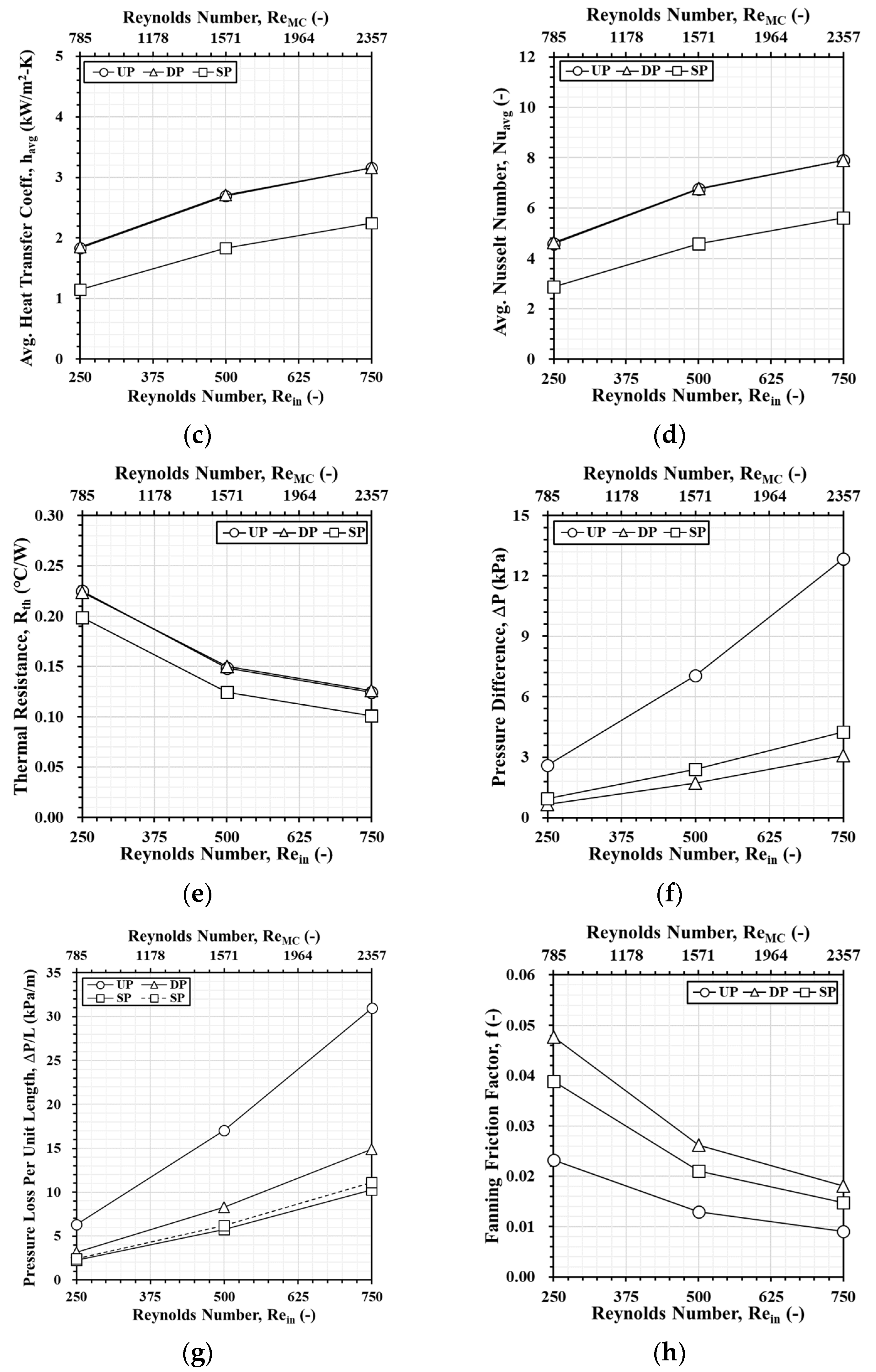
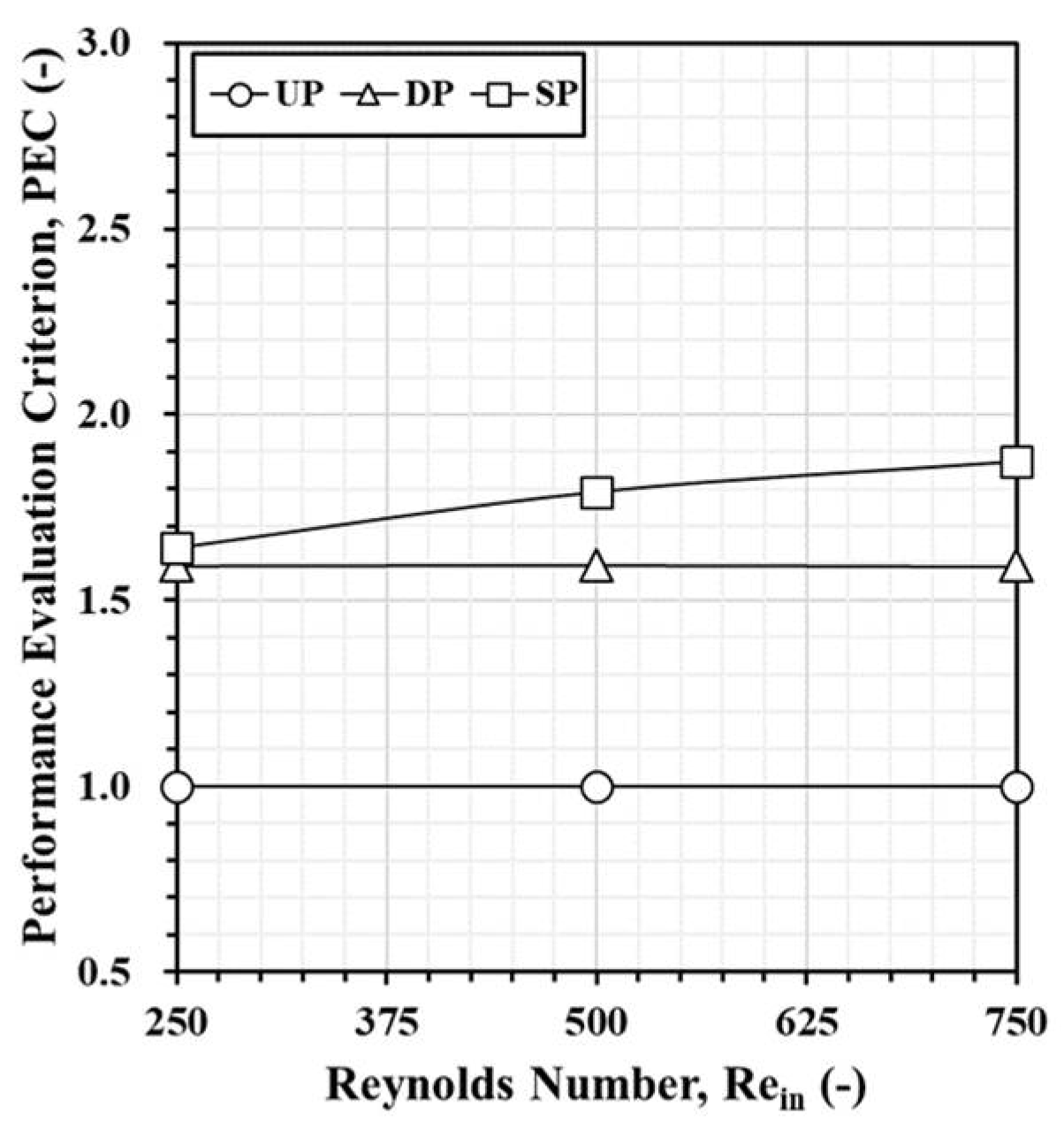
3.1. Pure Water
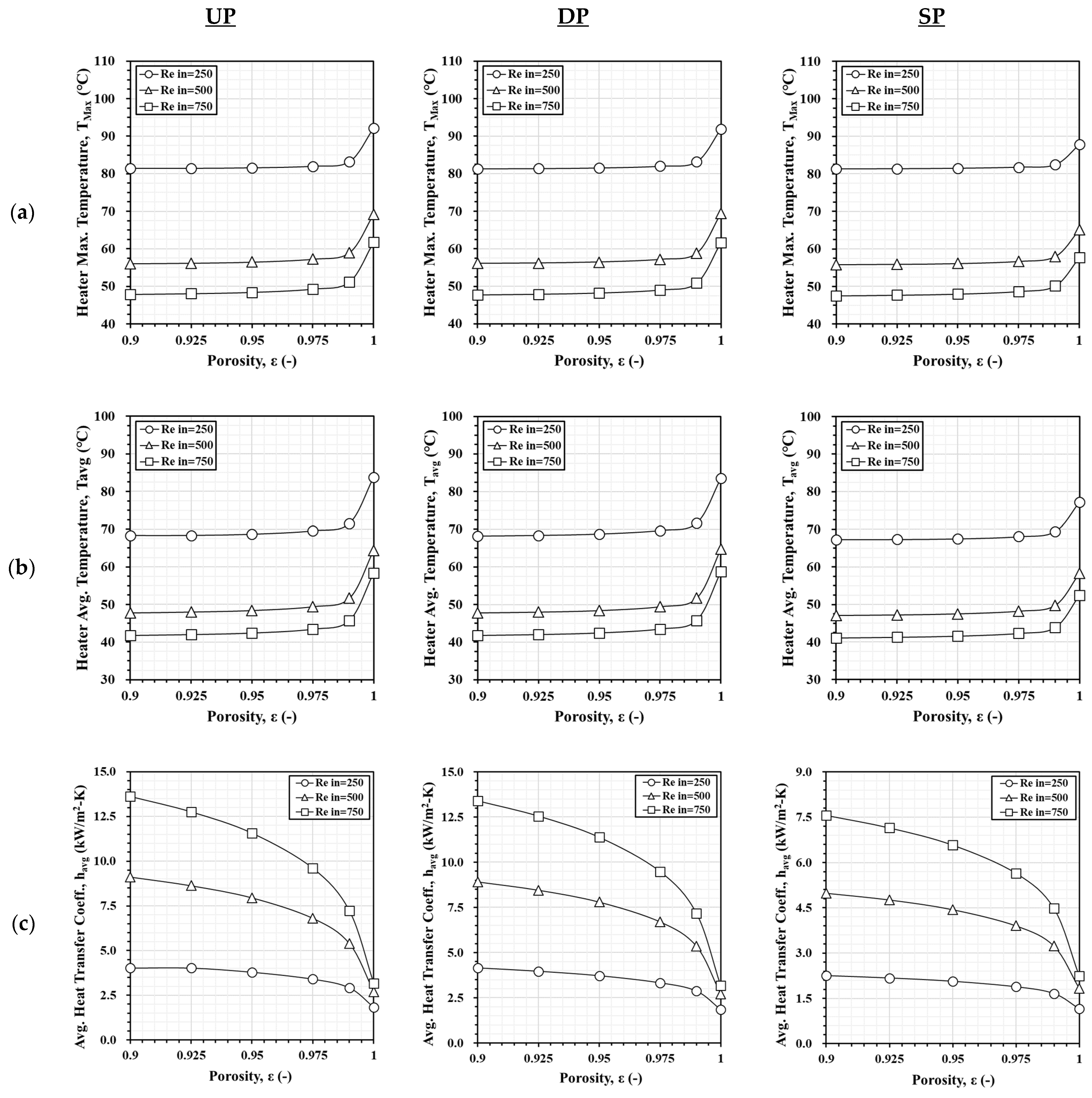
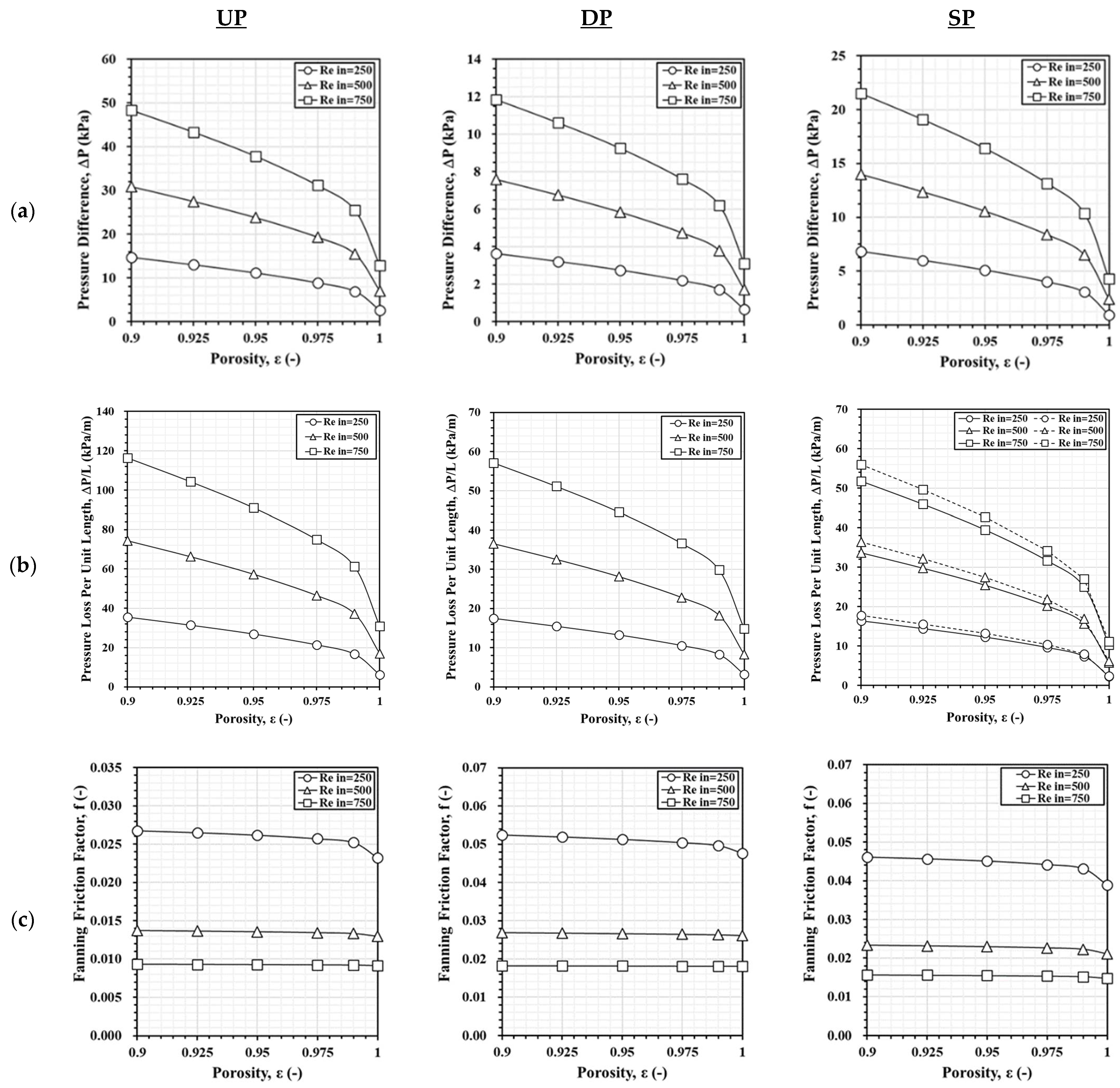
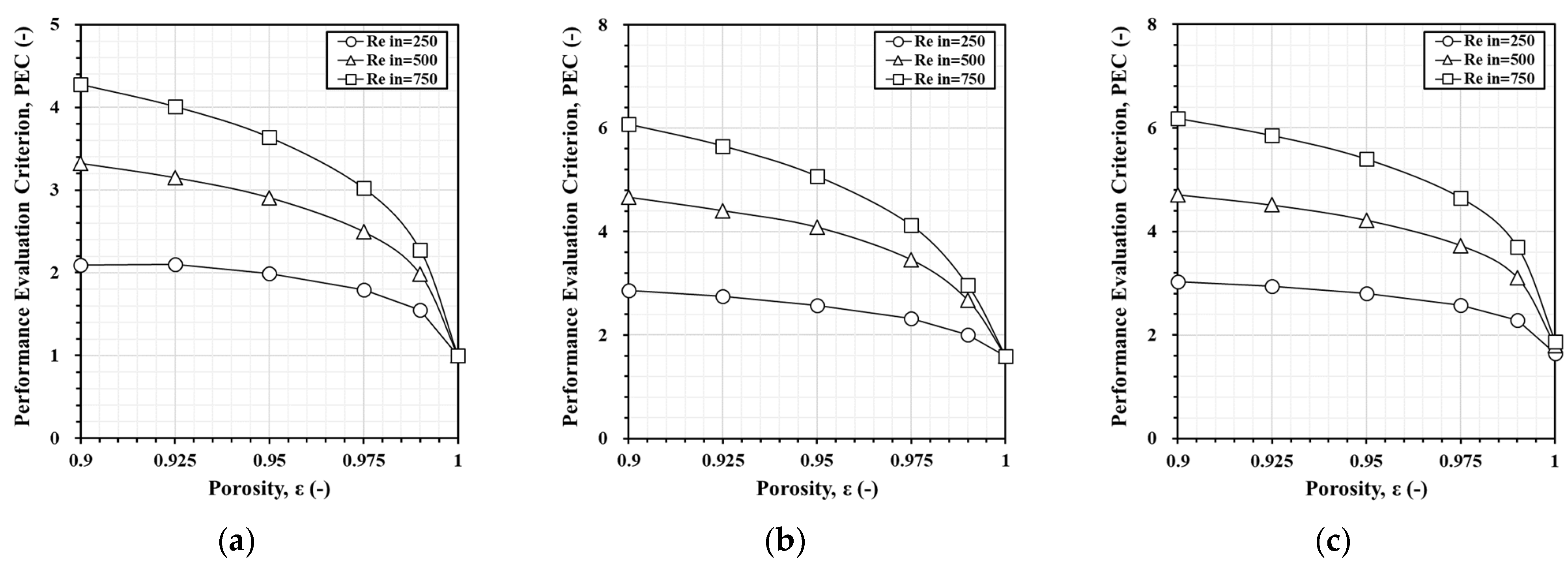
3.2. Pure Water with Aluminum Foam
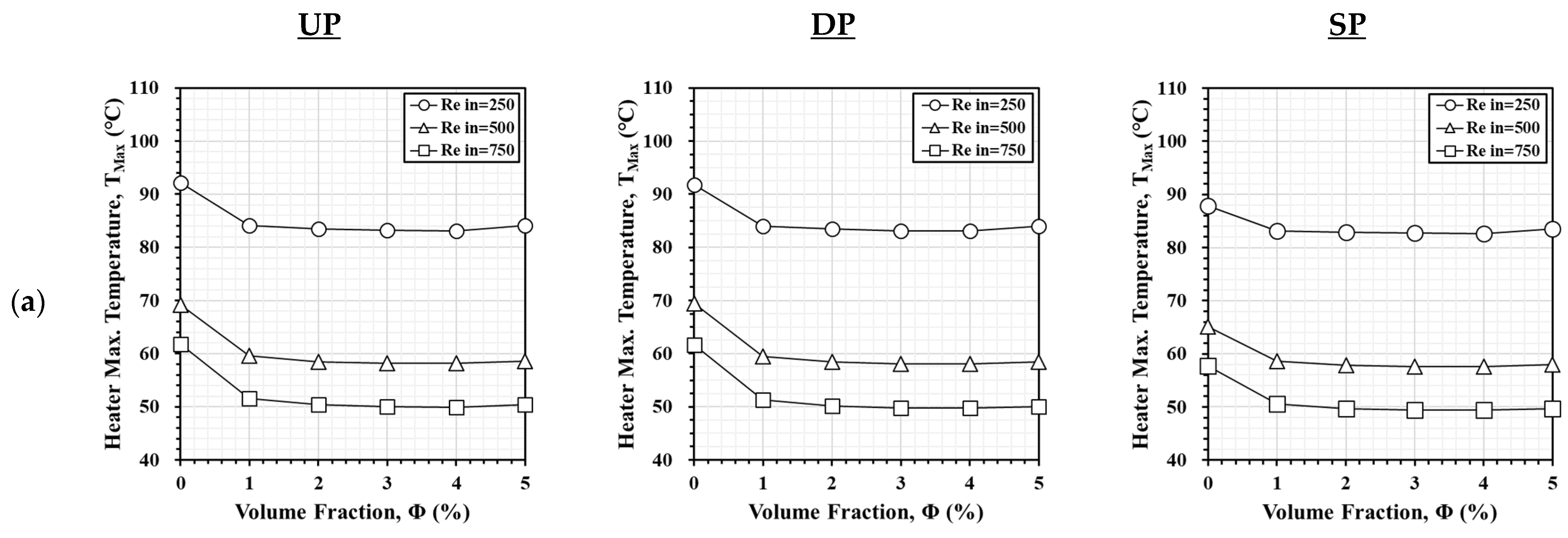
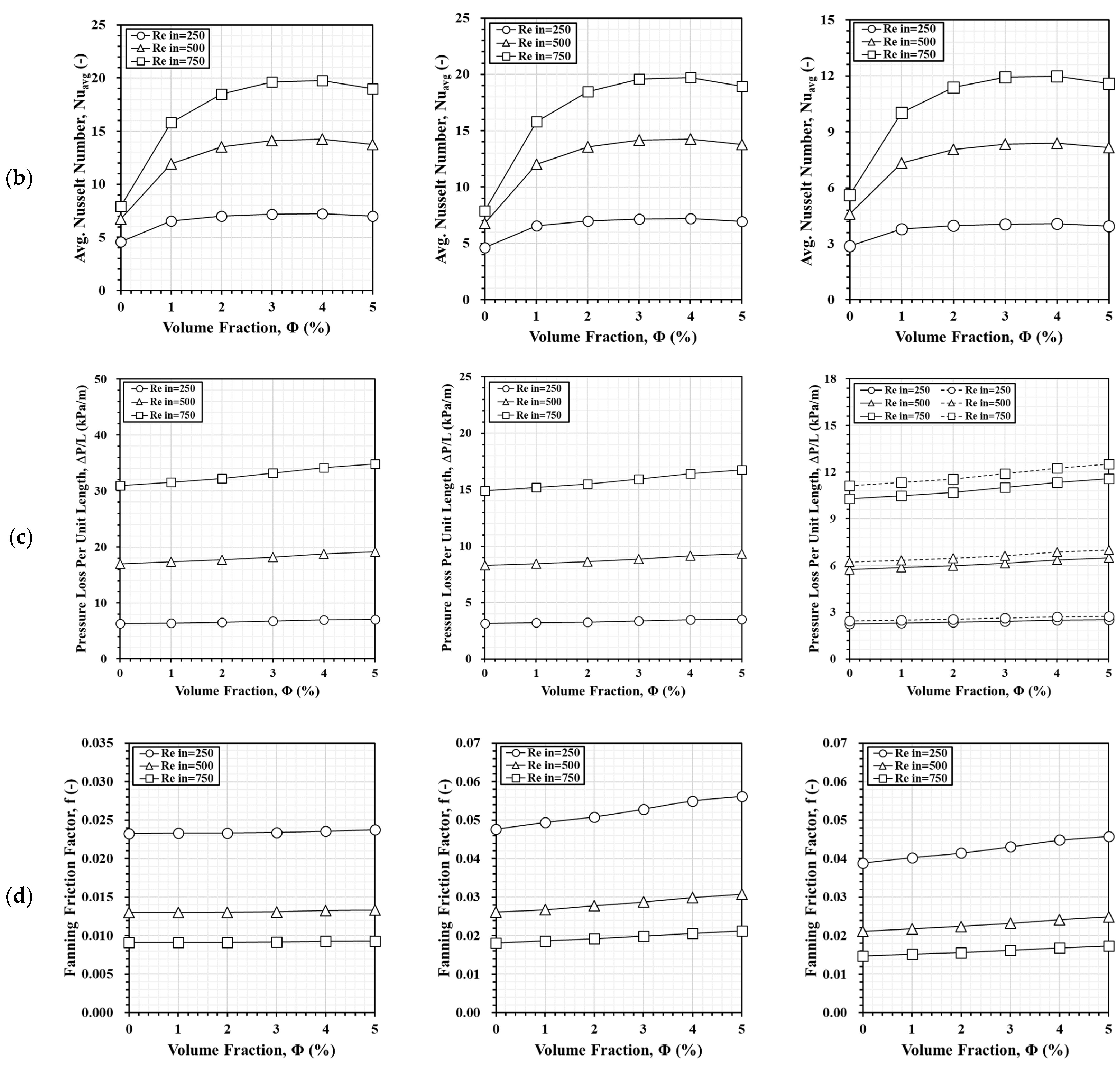
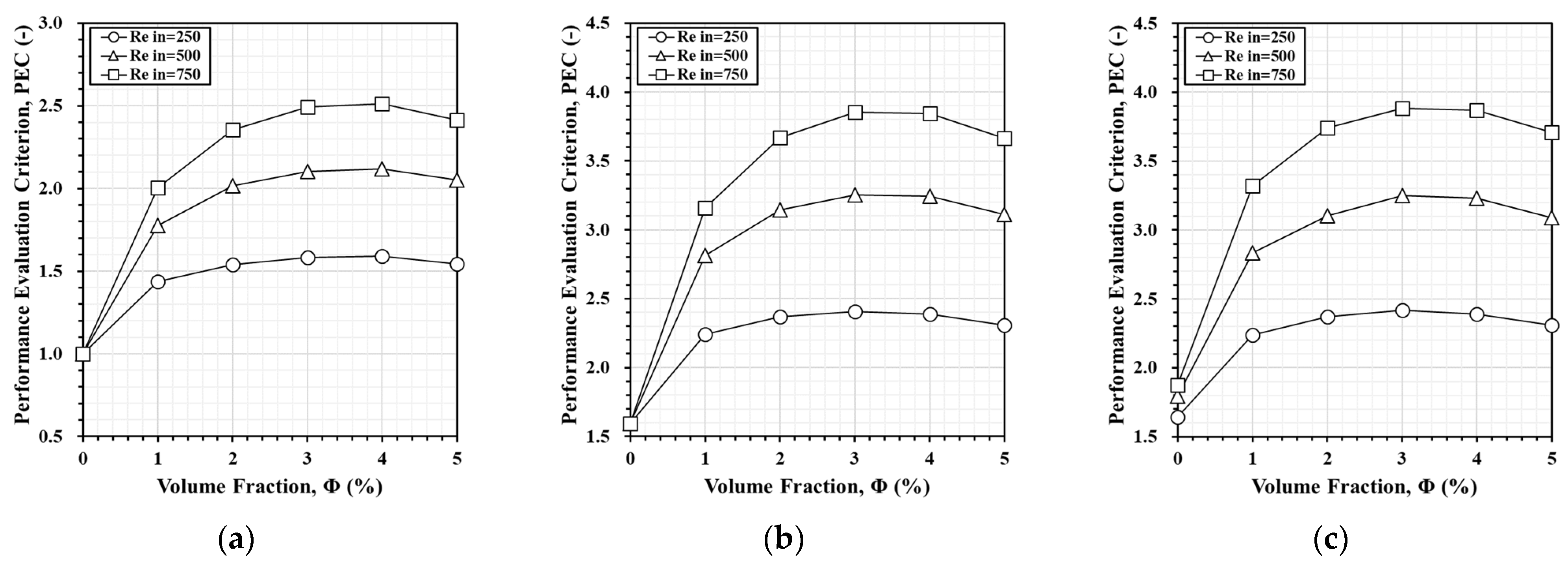
3.3. Improvement of Al2O3 Nanofluids
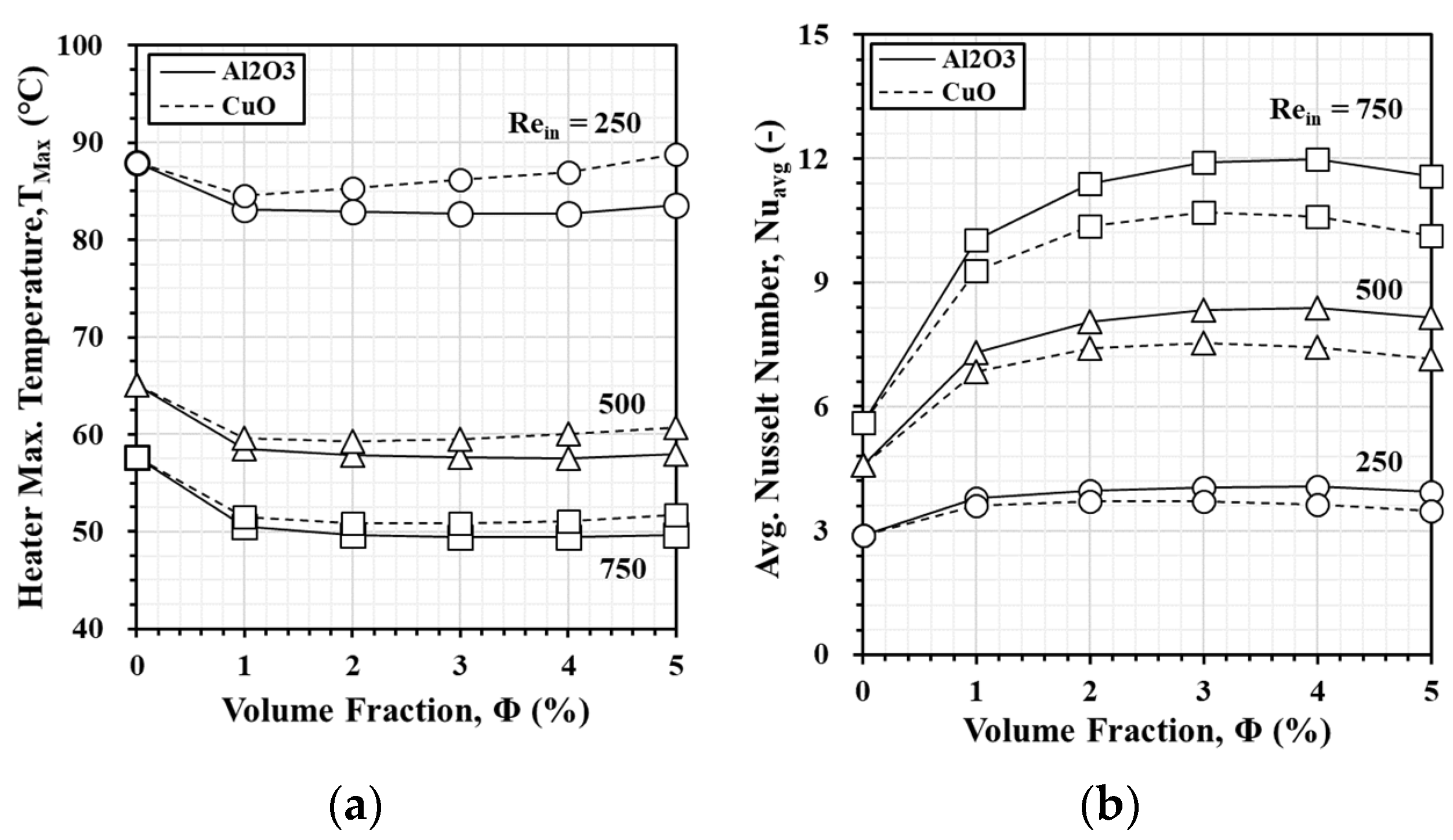
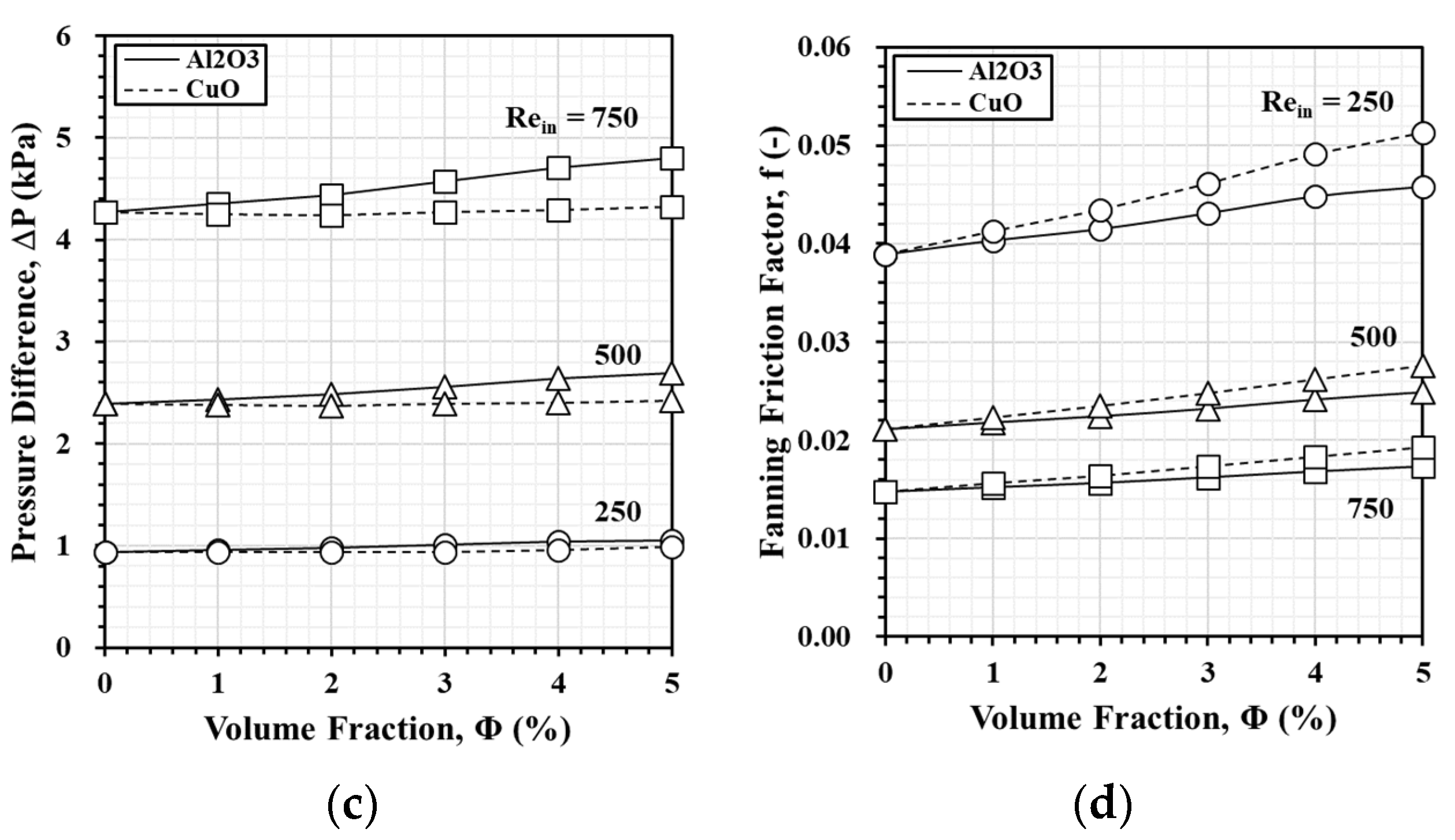
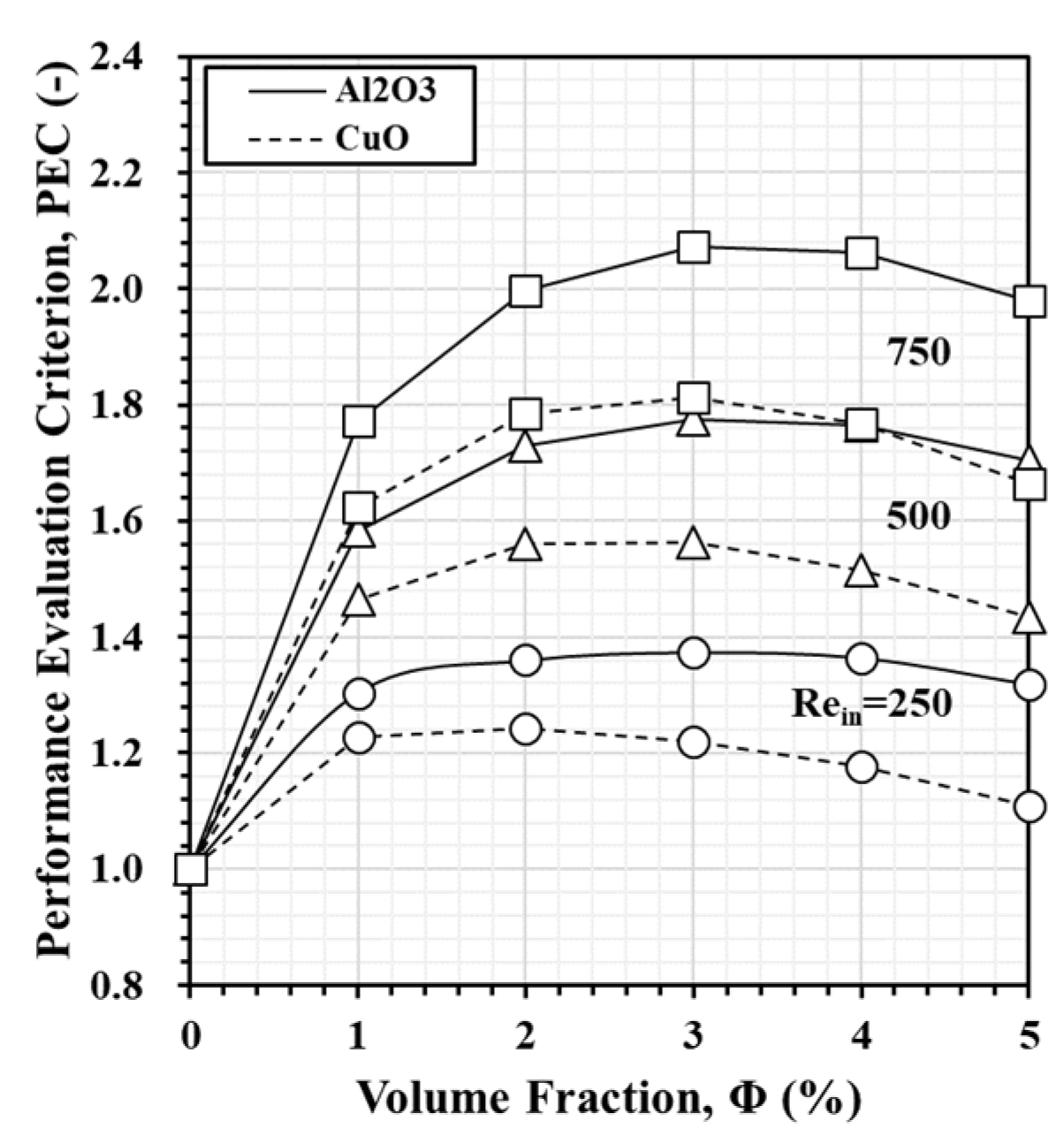
3.4. Comparison of Al2O3 and CuO Nanofluids
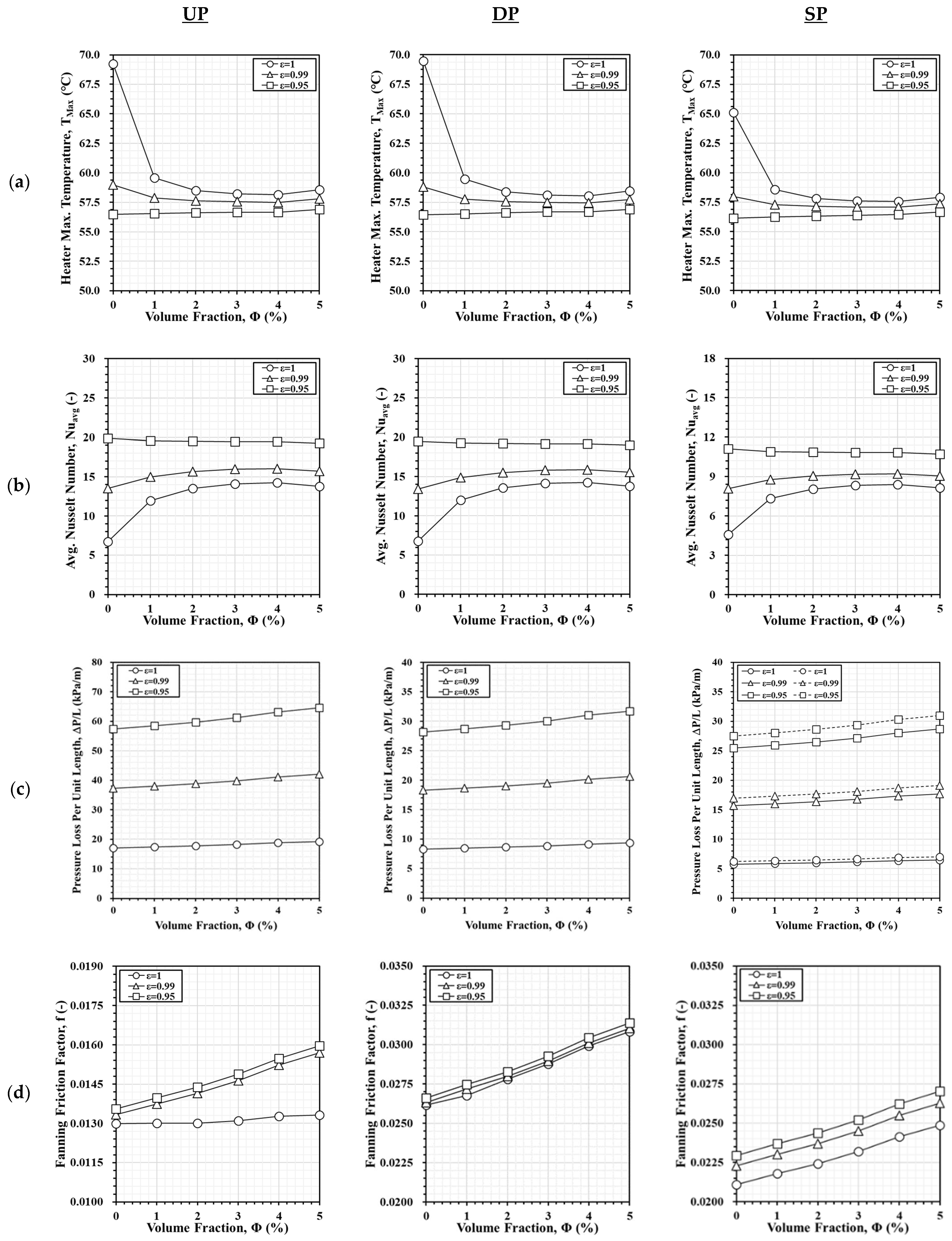
3.5. Combination of Al2O3 Nanofluid with Aluminum Foam
3.6. Performance Evaluation
4. Conclusions
- The SP model consistently outperforms the UP and DP models for all Reynolds numbers and conditions by offering the highest PEC values, the lowest temperature readings, as well as the lowest pressure loss and frictional resistance. The DP model performs better than the UP model, but it still lags behind the SP model in all performance metrics.
- Both Al2O3 and CuO nanofluids confirm their significant outperformance over pure water in terms of heat dissipation and PEC. Al2O3 consistently demonstrates better heat dissipation, especially at higher volume fractions. Meanwhile, CuO performs better at lower volume fractions due to its lower specific heat capacity.
- Lower foam porosity significantly enhances heat dissipation performance, particularly in the SP and DP models. However, lower porosity increases pressure loss and frictional resistance. Finding the optimal balance between porosity and volume fraction is crucial for efficient heat transfer.
- Using PEC instead of multiple thermal and flow performance indexes is a better approach, particularly for comparing heat dissipation efficiency across different heat sink models in this study. PEC integrates both thermal performance and flow resistance into a single metric, allowing a more comprehensive and effective evaluation of the overall effectiveness of all three models.
- Using PEC over a number of thermal and flow performance indexes can be considered a better approach, particularly when comparing the heat dissipation efficiency across different heat sink models in this study. PEC combines both thermal performance and flow resistance into a single metric. This allows a more comprehensive evaluation of the overall effectiveness of all three models.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu, R.C.; Simons, R.E.; Ellsworth, M.J.; Schmidt, R.R.; Cozzolino, V. Review of cooling technologies for computer products. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2004, 4, 568–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaj, A.H.; Halgamuge, S.K. A Review on efficient thermal management of air-and liquid-cooled data centers: From chip to the cooling system. Appl. Energy 2017, 205, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, M.A.; Sidik, N.A.C. A review on development of liquid cooling system for central processing unit (CPU). J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2020, 78, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R. Challenges in electronic cooling: Opportunities for enhanced thermal management techniques—Microprocessor liquid cooled minichannel heat sink. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Nanochannels, Microchannels, and Minichannels, New York, NY, USA, 24–25 April 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, D.; Cao, L.; Wang, Q.; Hou, F.; Wang, X. Experimental and numerical study of 3D stacked dies under forced air cooling and water immersion cooling. Microelectron. Reliab. 2017, 74, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuckerman, D.B.; Pease, R.F.W. High-Performance Heat Sinking for VLSI. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 1981, 2, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, R.J. Microchannel heat sinks. Linc. Lab. J. 1988, 1, 31–48. [Google Scholar]
- Goodling, J.S. Microchannel heat exchangers: A review. In Proceedings of the SPIE, High Heat Flux Engineering II 1993, San Diego, CA, USA, 11–16 July 1993; SPIE: Washington, DC, USA; pp. 66–82. [Google Scholar]
- Steinke, M.E.; Kandlikar, S.G. Single-phase heat transfer enhancement techniques in microchannel and mini-channel flows. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Microchannels and Minichannels, New York, NY, USA, 17–19 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.G.; Fartaj, A. A review on microchannel heat exchangers and potential applications. Int. J. Energy Res. 2011, 35, 553–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, T.; Ghosh, I. Review of micro-and mini-channel heat sinks and heat exchangers for single phase fluids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 1298–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, K.N.; Sharma, T.K.; Rao, G.A.P. Latest advancements in heat transfer enhancement in the micro-channel heat sinks: A review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 3135–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandlikar, S.G.; Grande, W.J. Evolution of microchannel flow passages-thermohydraulic performance and fabrication technology. Heat Transf. Eng. 2003, 24, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavnani, S.; Narayanan, V.; Qu, W.; Jensen, M.; Kandlikar, S.; Kim, J.; Thome, J. Boiling augmentation with micro/nanostructured surfaces: Current status and research outlook. Nanoscale Microscale Thermophys. Eng. 2014, 18, 197–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidik, N.A.C.; Muhamad, M.N.A.W.; Japar, W.M.A.A.; Rasid, Z.A. An overview of passive techniques for heat transfer augmentation in microchannel heat sink. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 88, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Mudawar, I. Analysis of three-dimensional heat transfer in micro-channel heat sinks. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2002, 45, 3973–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Neama, A.F.; Kapur, N.; Summers, J.; Thompson, H.M. An experimental and numerical investigation of the use of liquid flow in serpentine microchannels for microelectronics cooling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 116, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Jia, L.; Yang, W.W.; Taler, J.; Oclon, P. Numerical analysis and parametric optimization on flow and heat transfer of a microchannel with longitudinal vortex generators. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 141, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Chen, T.; Tian, M.; Ding, G. Fluid and heat transfer characteristics of microchannel heat sink with truncated rib on sidewall. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 148, 119142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ji, Z.; Wang, J.; Lv, X. Research progress on structural optimization design of microchannel heat sinks applied to electronic devices. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 235, 121294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.U.S.; Eastman, J.A. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–17 November 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Hwang, K.S.; Jang, S.P.; Lee, B.H.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, S.U.S.; Choi, C.J. Effective viscosities and thermal conductivities of aqueous nanofluids containing low volume concentrations of Al2O3 nanoparticles. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2008, 51, 2651–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.J.; Chen, W.C. An experimental study on thermal performance of Al2O3/water nanofluid in a minichannel heat sink. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 50, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaghan, A.; Edalatpour, M.; Moghadam, M.C.; Roohi, E.; Niazmand, H. Nanofluid flow and heat transfer in a microchannel with longitudinal vortex generators: Two-phase numerical simulation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 100, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, W.; Ali, H.M. Experimental investigation of heat transfer and pressure drop in a straight minichannel heat sink using TiO2 nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 110, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadasi, H.; Aminian, E.; Saffari, H.; Mahjoorghani, M.; Emamifar, A. Numerical analysis on laminar forced convection improvement of hybrid nanofluid within a U-bend pipe in porous media. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 179, 105659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siricharoenpanich, A.; Wiriyasart, S.; Naphon, P. Study on the thermal dissipation performance of GPU cooling system with nanofluid as coolant. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 25, 100904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.M.; Farooq, U.; Mishra, N.K.; Ahmad, Z.; Zulfiqar, F.; Yasmin, S.; Khan, S.A. CFD analysis of hybrid nanofluid-based microchannel heat sink for electronic chips cooling: Applications in nano-energy thermal devices. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 44, 102818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.J.; Hwang, G.J.; Yeh, R.H.; Chao, C.H. Measurement of interstitial convective heat transfer and frictional drag for flow across metal foams. J. Heat Transf. 2002, 124, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Zhao, C.Y.; Tassou, S.A. Thermal analysis on metal-foam filled heat exchangers. Part I: Metal-foam filled pipes. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2006, 49, 2751–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gong, L.; Xu, M.; Joshi, Y. Enhancing the performance of aluminum foam heat sinks through integrated pin fins. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 151, 119376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gong, L.; Ding, B.; Xu, M.; Joshi, Y. Thermal management of power electronics with liquid cooled metal foam heat sink. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 163, 106796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyf, H.R.; Layeghi, M. Numerical analysis of convective heat transfer from an elliptic pin fin heat sink with and without metal foam insert. J. Heat Transf. 2010, 132, 07140-1–071401-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayomy, A.M.; Saghir, M.Z.; Yousef, T. Electronic cooling using water flow in aluminum metal foam heat sink: Experimental and numerical approach. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2016, 109, 182–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhajaj, Z.; Bayomy, A.M.; Saghir, M.Z.; Rahman, M.M. Flow of nanofluid and hybrid fluid in porous channels: Experimental and numerical approach. Int. J. Thermofluids 2020, 1–2, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafai, K.; Zhu, L. Analysis of two-layered micro-channel heat sink concept in electronic cooling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1999, 42, 2287–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.M.; Zhao, J.Y.; Tseng, K.J. Parametric study on the performance of double-layered microchannels heat sink. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 80, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahiraei, M.; Jamshidmofid, M.; Goodarzi, M. Efficacy of a hybrid nanofluid in a new microchannel heat sink equipped with both secondary channels and ribs. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 273, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.-C.; Muezzin, F.N.A. Heat transfer of a parallel flow two-layered microchannel heat sink. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 49, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wang, F.; Hong, J.; Sigmund, O. Topology optimization of microchannel heat sinks using a two-layer model. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 143, 118462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Meng, W.J.; Mei, F. Experimental investigation of Cu-based, double-layered, microchannel heat exchangers. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 23, 035017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.E.; Ahmed, M.I.; Seder, I.M.; Salman, B.H. Experimental investigation for sequential triangular double-layered microchannel heat sink with nanofluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 77, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Mehta, H.B. Experimental investigations on a variable channel width double layered minichannel heat sink. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 165, 120633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendran, G.; Mallikarjuna, B.; Nagesha, B.K.; Gnanasekaran, N. Experimental investigation on additive manufactured single and curved double layered microchannel heat sink with nanofluids. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 59, 1311–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.C.; Yan, W.M.; Li, W.P. Analysis of heat transfer characteristics of double-layered microchannel heat sink. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 3090–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.C.; Yan, W.M. Enhancement of thermal performance in double-layered microchannel heat sink with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 3225–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.C.; Yan, W.M.; Wang, X.D.; Huang, Y.X. Optimal design of geometric parameters of double-layered microchannel heat sinks. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 3262–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Pi, G.; Zhang, W.; Wang, P.; Fu, T. Numerical study of double-layered microchannel heat sinks with different cross-sectional shapes. Entropy 2018, 21, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Chen, W. Numerical investigation of heat transfer in the double-layered minichannel with microencapsulated phase change suspension. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 119, 104918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Chen, L.Y.; Zhang, B.X.; Yang, Y.R.; Wang, X.D. A new design of double-layered microchannel heat sinks with wavy microchannels and porous-ribs. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 141, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvar-Ardeh, S.; Rafee, R.; Rashidi, S. Hybrid nanofluids with temperature-dependent properties for use in double-layered microchannel heat sink; hydrothermal investigation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 124, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshanpour, K.; Kamali, R.; Eslami, M. Improving performance of single and double-layered microchannel heat sinks by cylindrical ribs: A numerical investigation of geometric parameters. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 126, 105440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.M.; Cheng, P.; Ma, H.B. An experimental investigation of a three-dimensional flat-plate oscillating heat pipe with staggered microchannels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 54, 3951–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Xia, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, H. A novel flow arrangement of staggered flow in double-layered microchannel heat sinks for microelectronic cooling. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 79, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, C.; Wang, X.D.; Wang, T.H. An improved design of double-layered microchannel heat sink with truncated top channels. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 79, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Jin, X.; Zhang, F.; Xie, G.; Sunden, B.; Yan, H. Computational optimization of counter-flow double-layered microchannel heat sinks subjected to thermal resistance and pumping power. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 121, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.C.; Xie, G. Comparative study for convective heat transfer of counter-flow wavy double-layer microchannel heat sinks in staggered arrangement. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 137, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Xie, G.; Wang, C.C. Heat transfer and thermodynamic analysis by introducing multiple alternation structures into double-layer microchannel heat sinks. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 145, 105975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ge, X.; Liu, H.; Xie, G.; Wang, C.C. Thermal analysis and experimental verification on double-layer microchannel heat sinks with impact jet nested arrays. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2023, 209, 124169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.; Patel, R.I.; Dewan, A. A study on thermal characteristics of double-layered microchannel heat sink: Effects of bifurcation and flow configuration. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 162, 106791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cao, Z.; Xu, C.; Zhang, L.; Sun, T. Investigation of fluid flow and heat transfer characteristics in a microchannel heat sink with double-layered staggered cavities. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 187, 122535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J.J.; Wu, C.M.; Li, Y.R. A novel microchannel heat sink with staggered inlet and outlet to improve base surface temperature uniformity. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 241, 122365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Gu, J.; Li, L.; Lyu, J. A narrow shape double-layer microchannel heat sink (DL-MCHS) designed for high-power laser crystal. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 211, 118456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakrouh, R.; Varedi-Koulaei, S.M.; Rahimi, M. Swarm-based multi-objective optimization of double-layered microchannel heat sink with hybrid solid-porous ribs. Numer. Heat Transf. Part B Fundam. 2024, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; An, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, H.; Lei, L.; Xin, G. Multi objective optimization of manifold microchannel heat sink with staggered microchannels. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 159, 108106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, S.; Cao, Y. Thermohydraulic performance of the microchannel heat sinks with three types of double-layered staggered grooves. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2024, 201, 109032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, M.H.; Khiabani, R.H. Forced Convective Heat Transfer in Parallel Flow Multilayer Microchannels. J. Heat Transf. 2007, 129, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.W.; Wong, K.C.; Ng, H.K. Thermal performance of three-layered microchannel heat sink with tapered channel profile. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2019, 56, 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Skandakumaran, P.; Ortega, A.; Jamal-Eddine, J.; Vaidyanathan, R. Multi-Layered Sic Microchannel Heat Sinks—Modeling and Experiment. In Proceedings of the Ninth Intersociety Conference on Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronic Systems (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37543), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 1–4 June 2004; Volume 1, pp. 352–360. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, B.; Wang, L.; Cheng, H.; Li, J. Optimization and numerical simulation of multi-layer microchannel heat sink. Procedia Eng. 2012, 31, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Siyabi, I.; Khanna, S.; Sundaram, S.; Mallick, T. Experimental and numerical thermal analysis of multi-layered microchannel heat sink for concentrating photovoltaic application. Energies 2018, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Li, L.; Cui, W.; Xiao, F. Optimization analysis of multi-layered microchannel heat sink. Numer. Heat Transf. Part B Fundam. 2024, 85, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Tao, W.Q. Heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics of microchannel cold plate in commercial CPU-package cooling system. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2025, 246, 127060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naphon, P.; Wiriyasart, S. Liquid cooling in the mini-rectangular fin heat sink with and without thermoelectric for CPU. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 36, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naphon, P.; Klangchart, S.; Wongwises, S. Numerical investigation on the heat transfer and flow in the mini-fin heat sink for CPU. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 36, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndao, S.; Peles, Y.; Jensen, M.K. Multi-Objective Thermal Design Optimization and Comparative Analysis of Electronics Cooling Technologies. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 52, 4317–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.W.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Souayeh, B.; Dey, K.; Hammami, F.; Rahimi-Gorji, M.; Biswas, R. CPU heat sink cooling by triangular shape micro-pin-fin: Numerical study. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 112, 104455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangalee, M.Z.I.; Rahman, M.M.; Zaimi, K.; Ferdows, M. Numerical optimization of a CPU heat sink geometry. CFD Lett. 2021, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, F.; Güder, T.B. Numerical investigation of CPU cooling with micro-pin–fin heat sink in different shapes. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2022, 137, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siahchehrehghadikolaei, S.; Gholinia, M.; Ghadikolaei, S.S.; Lin, C.X. A CFD modeling of CPU cooling by eco-friendly nanofluid and fin heat sink passive cooling techniques. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, S.K.; Ramakrishnan, B.; Alissa, H.; Kim, W.; Belady, C.; Bakir, M.S. Integrated silicon microfluidic cooling of a high-power overclocked CPU for efficient thermal management. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 59259–59269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samudre, P.; Kailas, S.V. Thermal performance enhancement in open-pore metal foam and foam-fin heat sinks for electronics cooling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 205, 117885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attar, M.R.; Kazemi, M.; Salami, B.; Noori, H.; Passandideh-Fard, M.; Hosseinpour, S.; Davoodi, A.; Mohammadi, M. Improving thermal management of CPU by surface roughening of heat sinks. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 49, 2153–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Duan, W.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Song, M.; Liao, S.; Shi, E.; Sun, X. Thermal performance of pin fin heat sinks with phase change material for electronic devices thermal management. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 250, 123456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Mochizuki, M. Sintered porous heat sink for cooling of high-powered microprocessors for server applications. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 52, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Long, E.; Zhang, M. Experimental study on heat sink with porous copper as conductive material for CPU cooling. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 15004–15009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyestani, M.; Nazari, M.; Shahmardan, M.M.; Sharifpur, M.; Ashouri, M.; Meyer, J.P. Thermal characteristics of CPU cooling by using a novel porous heat sink and nanofluids: Comparative experimental study. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, A.A.; Rasam, H. Thermal management of the central processing unit cooling system using a cylindrical metal foam heat sink under the influence of magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid flow. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2024, 34, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, A.; Saeed, M.; Ikhlaq, M.; Imran, M.; Yan, Y. Heat and fluid flow analysis of micro-porous heat sink for electronics cooling: Effect of porosities and pore densities. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2025, 57, 103129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahiraei, M.; Heshmatian, S. Application of a novel biological nanofluid in a liquid block heat sink for cooling of an electronic processor: Thermal performance and irreversibility considerations. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 149, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, H.A.; Alquziweeni, Z.; Sopian, K. Heat transfer enhancement using nanofluids for cooling a Central Processing Unit (CPU) system. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2018, 51, 145–157. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, M.; Taheri, A.; Passandideh-Fard, M.; Sardarabadi, M. Electronic chipset thermal management using a nanofluid-based mini-channel heat sink: An experimental study. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 118, 104836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moita, A.; Moreira, A.; Pereira, J. Nanofluids for the next generation thermal management of electronics: A review. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khouly, M.M.; El Bouz, M.A.; Sultan, G.I. Experimental and computational study of using nanofluid for thermal management of electronic chips. J. Energy Storage 2021, 39, 102630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, S.E.; Ranjbar, A.A.; Hoseini, M.J.; Mohsenian, S. Design optimization and experimental investigation of CPU heat sink cooled by alumina-water nanofluid. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 2276–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadikolaei, S.S.; Siahchehrehghadikolaei, S.; Gholinia, M.; Rahimi, M. A CFD modeling of heat transfer between CGNPs/H2O Eco-friendly nanofluid and the novel nature-based designs heat sink: Hybrid passive techniques for CPU cooling. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2023, 37, 101604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcu, G.; Ercetin, U.; Timuralp, C. CFD analysis of liquid-cooled heatsink using nanofluids in computer processors. Sci. Iran. 2024, 31, 1916–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siahchehrehghadikolaei, S.; Ghadikolaei, S.; Gholinia, M.; Ahmadi, G. Application of CNTs/H2O nanofluid and the wavy fin with dimples in thermal management of CPU: A numerical modeling of hybrid passive cooling. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 2024, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Won, M.H.; Kim, J.W.; Back, B.J. Heat pipe cooling technology for desktop PC CPU. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2003, 23, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siricharoenpanich, A.; Wiriyasart, S.; Srichat, A.; Naphon, P. Thermal management system of CPU cooling with a novel short heat pipe cooling system. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2019, 15, 100545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Duan, J. Experimental investigation of the thermal performance of a heat sink with U-shaped heat pipes. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 186, 116387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motevalizadeh, M.; Rooberahan, A.; Namaghi, M.S.; Mohammadi, M.; Passandideh-Fard, M.; Sardarabadi, M. Cooling enhancement of portable computers processor by a heat pipe assisted with phase change materials. J. Energy Storage 2022, 56, 106074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Mochizuki, M.; Mashiko, K.; Saito, Y.; Sauciuc, I. Use of heat pipe/heat sink for thermal management of high performance CPUs. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth Annual IEEE Semiconductor Thermal Measurement and Management Symposium, San Jose, CA, USA, 23 March 2000; pp. 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Gan, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, F.; Li, Y. Experimental study on the thermal performance of a liquid-cooled heat sink integrating heat pipes for dual CPU servers. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 236, 121851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Pinjala, D.; Wong, T.N.; Toh, K.C.; Joshi, Y.K. Single-phase liquid cooled microchannel heat sink for electronic packages. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2005, 25, 1472–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.J.; Cheng, P.; Wu, H.Y. Characterization on the performance of a fractal-shaped microchannel network for microelectronic cooling. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 065018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhour, Y.; Olivier, J.; Costa-Patry, E.; Paredes, S.; Michel, B.; Thome, J.R. Flow boiling of R134a in a multi-microchannel heat sink with hotspot heaters for energy-efficient microelectronic CPU cooling applications. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 1, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncuoğlu, A.; Jafari, R.; Okutucu-Özyurt, T.; Külah, H. Heat transfer and pressure drop experiments on CMOS compatible microchannel heat sinks for monolithic chip cooling applications. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2012, 56, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpyś, M.; Al-Rashed, M.; Dzido, G.; Wójcik, J. CPU heat sink cooled by nanofluids and water: Experimental and numerical study. In Computer Aided Chemical Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 32, pp. 409–414. [Google Scholar]
- Gaikwad, V.P.; More, S.P. CPU processor cooling by using microchannel heat sink with PCM as coolant. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2017, 6, 214–219. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.; Wu, L.; Wang, M.; Yang, Z.; Du, P. Heat transfer improvement in microchannel heat sink by topology design and optimization for high heat flux chip cooling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 129, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.; Yang, Y.; Ding, G.; Du, X.; Hu, Z. Optimization of microchannel heat sink with rhombus fractal-like units for electronic chip cooling. Int. J. Refrig. 2020, 116, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, T.; Rehman, Z.; Tariq, H.A.; Manzoor, S.; Ali, M.; Wadood, A.; Rajski, K.; Park, H. Thermal performance investigation of slotted fin minichannel heat sink for microprocessor cooling. Energies 2021, 14, 6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, J. Experimental study of ultralow flow resistance fractal microchannel heat sinks for electronics cooling. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 179, 107723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavar, A.; Jafari, M.; Talebizadehsardari, P.; Toghraie, D. Hydrothermal and entropy generation specifications of a hybrid ferronanofluid in microchannel heat sink embedded in CPUs. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 32, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nada, S.A.; El-Zoheiry, R.M.; Elsharnoby, M.; Osman, O.S. Enhancing the thermal performance of different flow configuration minichannel heat sink using Al2O3 and CuO-water nanofluids for electronic cooling: An experimental assessment. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 181, 107767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorzin, M.; Ranjbar, A.A.; Hosseini, M.J. Experimental and numerical investigation on thermal and hydraulic performance of novel serpentine minichannel heat sink for liquid CPU cooling. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 3375–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Du, J.; Li, M.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Wen, B.; Zhang, C.; Jin, Y.; Wang, W. Embedded microfluidic cooling with compact double H type manifold microchannels for large-area high-power chips. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 197, 123340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, Y.P.; Qahiti, R.; Jafaryar, M.; Alazwari, M.A.; Abu-Hamdeh, N.H.; Issakhov, A.; Selim, M.M. Simulation of hybrid nanofluid flow within a microchannel heat sink considering porous media analyzing CPU stability. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.H.; Wang, D.H.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, Y. Cooling chip on PCB by embedded active microchannel heat sink. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 196, 123251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzutuğ, M.E. Design of a CPU heat sink with minichannel-fins & its thermal analysis. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2023, 25, 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, M.; Heyhat, M.M.; Targhi, M.Z.; Bigham, S. Porous-fin microchannel heat sinks for future micro-electronics cooling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 202, 123662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, L.; Xi, L.; Ran, H.; Gao, J.; Li, Y. Numerical analysis of enhanced heat transfer and nanofluid flow mechanisms in fan groove and pyramid truss microchannels. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2024, 109, 109559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Yaji, K. Topology optimization for microchannel heat sinks with nanofluids using an Eulerian-Eulerian approach. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.16749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussien, A.A.; Abdullah, M.Z.; Al-Nimr, M.A. Single-phase heat transfer enhancement in micro/minichannels using nanofluids: Theory and applications. Appl. Energy 2016, 164, 733–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.; Wu, H.; Zhang, W.; Angelopoulou, A. Overview of recent trends in microchannels for heat transfer and thermal management applications. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2022, 181, 109155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, P.; Singh, J.; Kumar, K.; Ranakoti, L. A review on active techniques in microchannel heat sink for miniaturization problem in electronic industry. Acta Innov. 2022, 45, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Fan, X.; Qi, F.; He, H. Topological structures for microchannel heat sink applications—A review. Manuf. Rev. 2023, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, A.; Shiblemon, K.V.; Baby, B. Review on fabrication and experimental study of microchannel heat sinks for cooling of electronic components. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 72, 2985–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Roux, S.; Castelain, C.; Fan, Y.; Luo, L. Design and optimization of heat sinks for the liquid cooling of electronics with multiple heat sources: A literature review. Energies 2023, 16, 7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Q.; Li, M.T.; Cao, B.Y. A comprehensive review on microchannel heat sinks for electronics cooling. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2024, 6, 022005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intel Core i9 Processor 14900K. Available online: https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/236773/intel-core-i9-processor-14900k-36m-cache-up-to-6-00-ghz.html (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Sauciuc, I.; Prasher, R.; Chang, J.Y.; Erturk, H.; Chrysler, G.; Chiu, C.P.; Mahajan, R. Thermal performance and key challenges for future CPU cooling technologies. In Proceedings of the ASME International Technical Conference and Exhibition on Packaging and Integration of Electronic and Photonic Microsystems (IPACK2005-73242), San Francisco, CA, USA, 17–22 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nield, D.A.; Bejan, A. Convection in Porous Media, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Du Plessis, P.; Montillet, A.; Comiti, J.; Legrand, J. Pressure drop prediction for flow through high porosity metallic foams. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1994, 49, 3545–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, M.T.; Perrot, C. Identifying local characteristic lengths governing sound wave properties in solid foams. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 084905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Bai, J.; Lu, T. A simplistic analytical model of permeability for open-cell metallic foams. Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 2014, 46, 982–986. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.H.; Lu, T.J.; Kim, T. A simplistic model for the tortuosity in two-phase close-celled porous media. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 125305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heris, S.Z.; Esfahany, M.N.; Etemad, S.G. Experimental investigation of convective heat transfer of Al2O3/water nanofluid in circular tube. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2007, 28, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.; Kleinstreuer, C. A new thermal conductivity model for nanofluids. J. Nanopart. Res. 2004, 6, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Lee, P.S. Topology optimization of liquid-cooled microchannel heat sinks: An experimental and numerical study. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 142, 118401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, R.L.; Eckert, E.R.G. Application of rough surfaces to heat exchanger design. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1972, 15, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
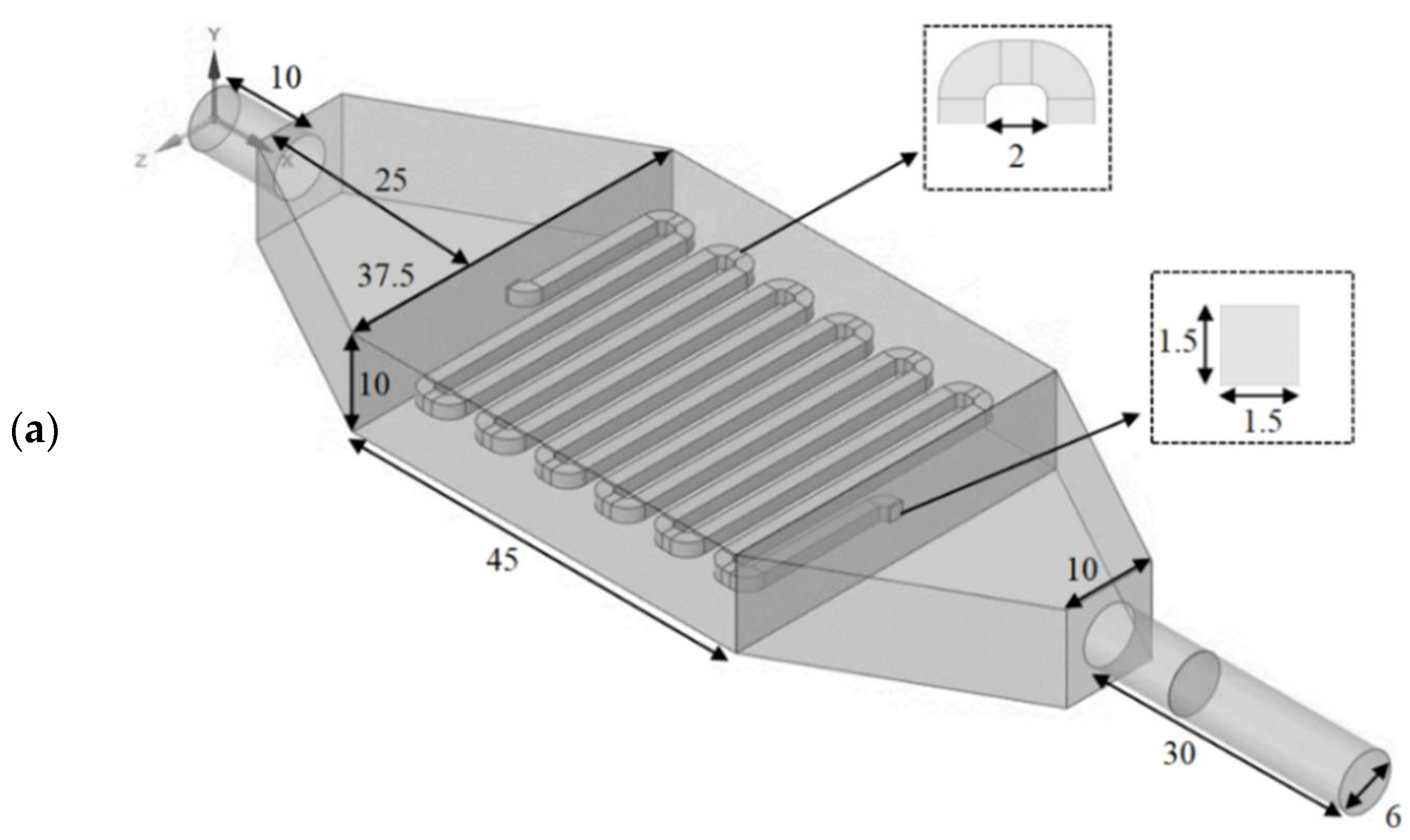

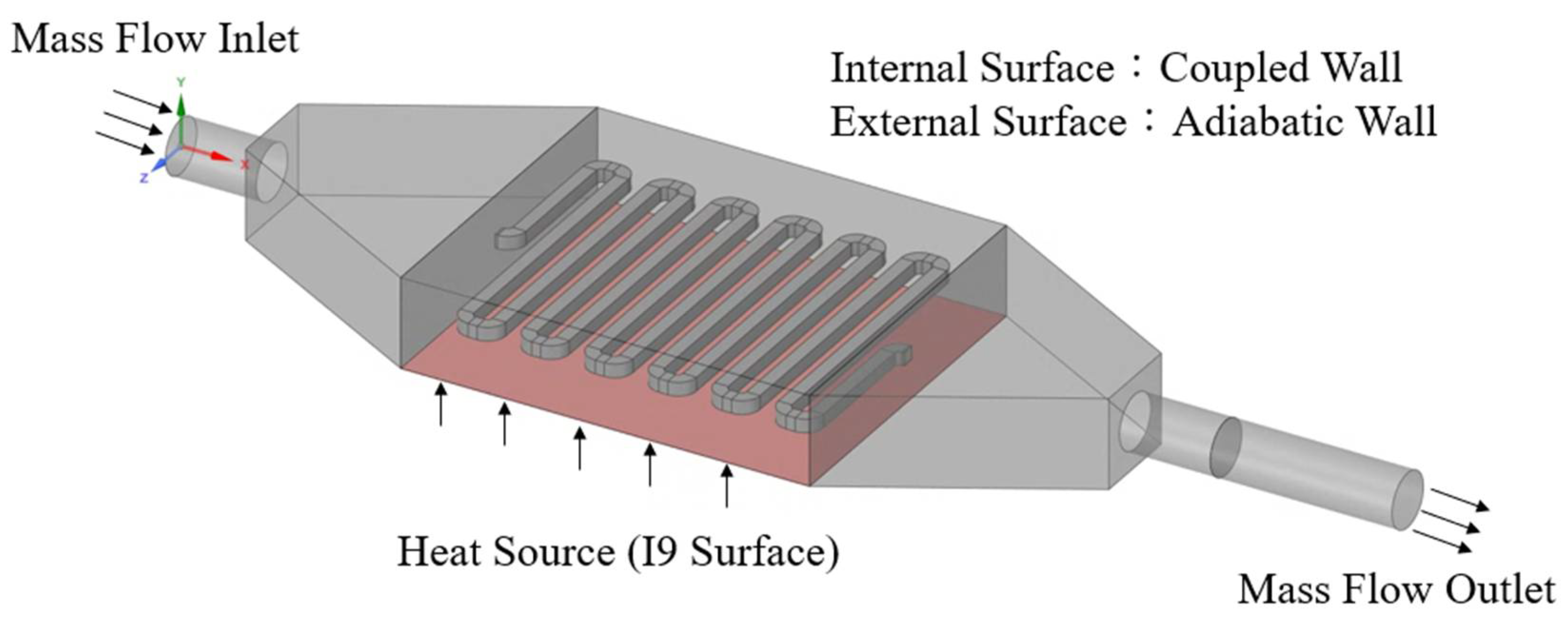
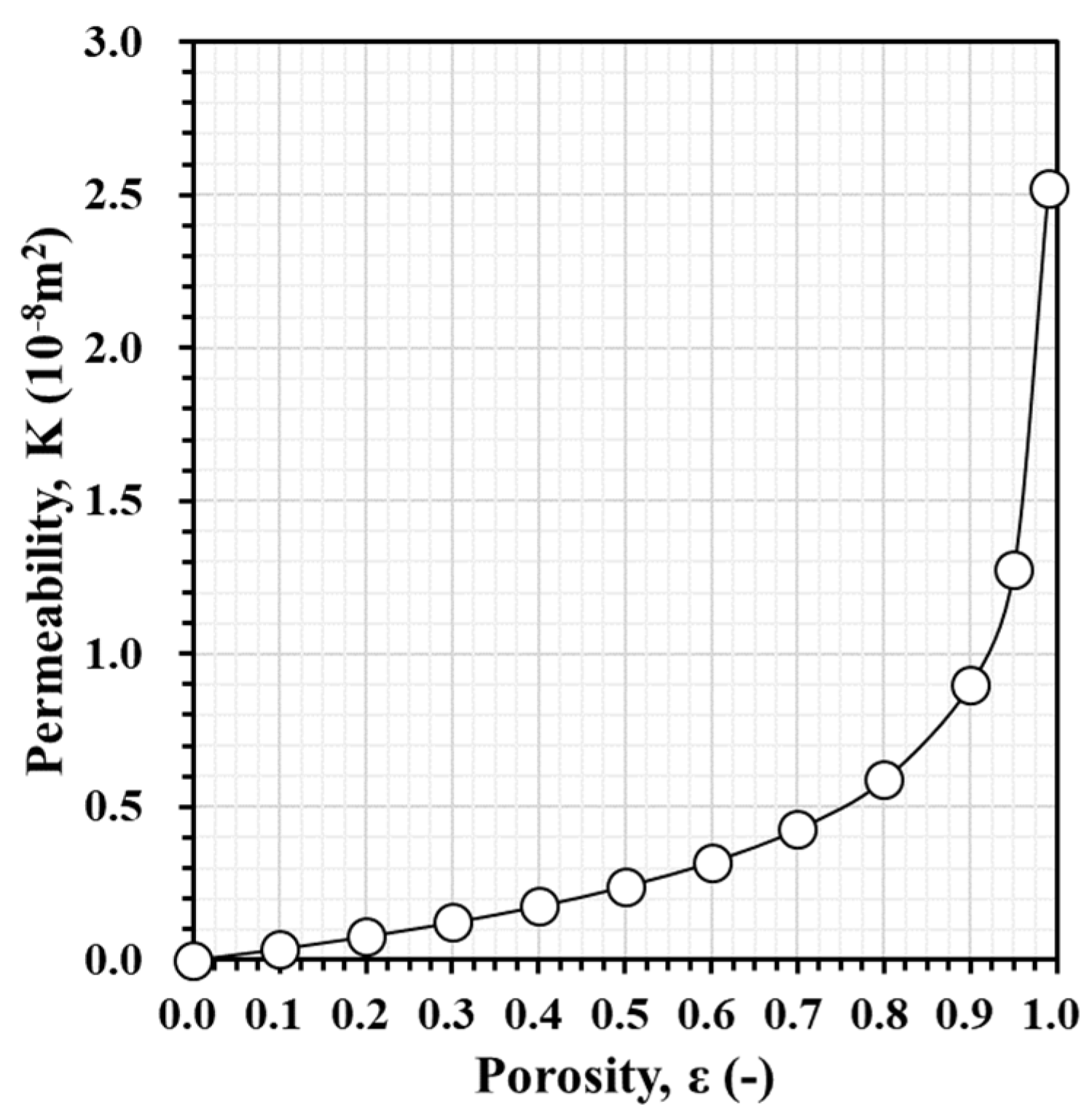

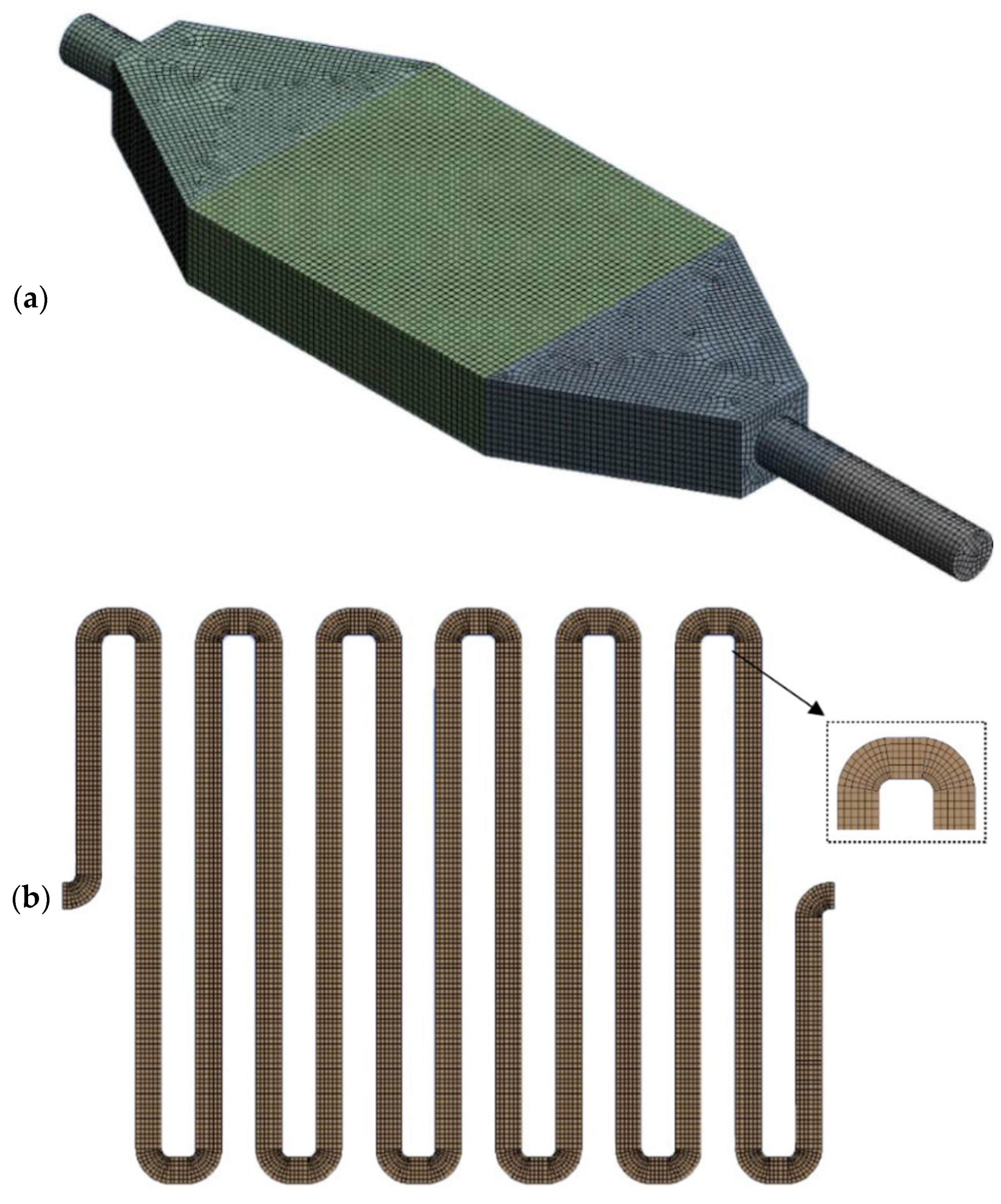
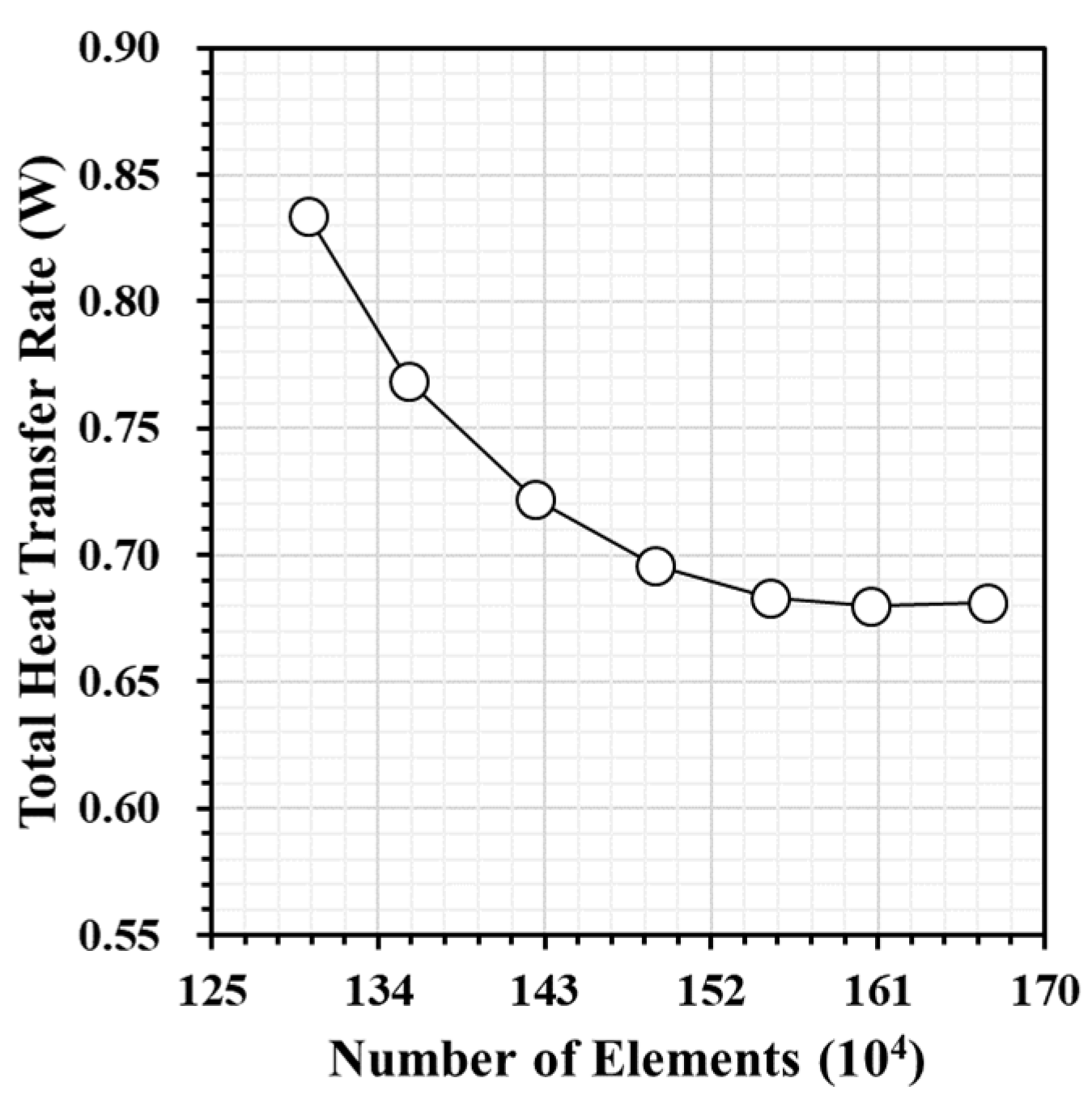


| Properties | Pure Aluminum | Water | Al2O3 [26] | CuO [26] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density ρ (kg/m3) | 2719 | 998.2 | 3970 | 6500 |
| Specific heat capacity Cp (J/kg·K) | 817 | 4182 | 765 | 540 |
| Thermal conductivity k (W/m·K) | 202.4 | 0.6 | 40 | 18 |
| Dynamic viscosity μ (Pa·s) | – | 0.001003 | – | – |
| Metric | Minimum | Maximum | Average | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skewness | 1.3037 × 10−2 | 0.79989 | 0.20963 | 0.12234 |
| Orthogonality | 0.20011 | 1.0 | 0.78771 | 0.11906 |
| Aspect Ratio | 1.0025 | 10.724 | 1.8015 | 0.4689 |
| Element Quality | 0.21283 | 1.0 | 0.8497 | 9.7565 × 10−2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Leong, J.C. Effects of Porous Filling and Nanofluids on Heat Transfer in Intel i9 CPU Minichannel Heat Sinks. Electronics 2025, 14, 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14101922
Li L, Leong JC. Effects of Porous Filling and Nanofluids on Heat Transfer in Intel i9 CPU Minichannel Heat Sinks. Electronics. 2025; 14(10):1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14101922
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Lie, and Jik Chang Leong. 2025. "Effects of Porous Filling and Nanofluids on Heat Transfer in Intel i9 CPU Minichannel Heat Sinks" Electronics 14, no. 10: 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14101922
APA StyleLi, L., & Leong, J. C. (2025). Effects of Porous Filling and Nanofluids on Heat Transfer in Intel i9 CPU Minichannel Heat Sinks. Electronics, 14(10), 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14101922






