Making Path Selection Bright: A Routing Algorithm for On-Chip Benes Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
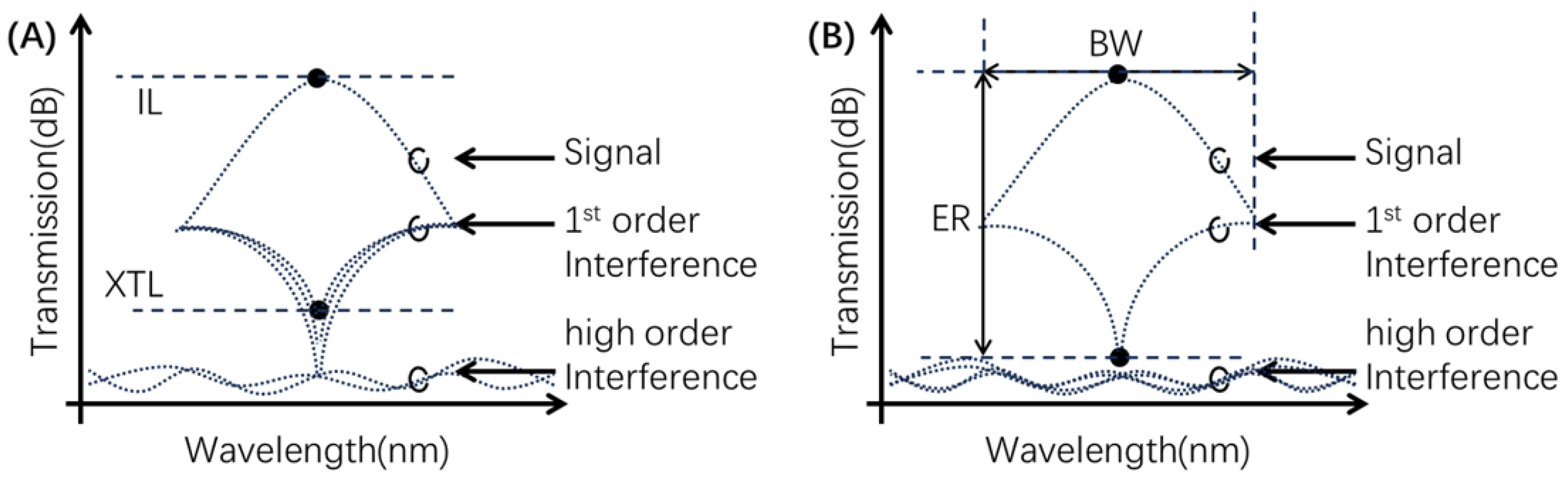
- The concept of IL fairness is applied to Benes networks. When fewer ports exist, the optimal routing algorithm (ORA) is proposed to reduce the imbalance at the receiver.
- As the number of ports increases, a greedy algorithm (GRA) is proposed to suppress the PDR, which allows the signal to propagate under one and only one first-order XTL.
- A cooperative ETS algorithm combining ORA and GRA improves ER performance by balancing maximum IL and XTL of the longest path.
2. Network Topology
2.1. Problem Statement
2.2. Mathematical Model
2.2.1. Model Parameters
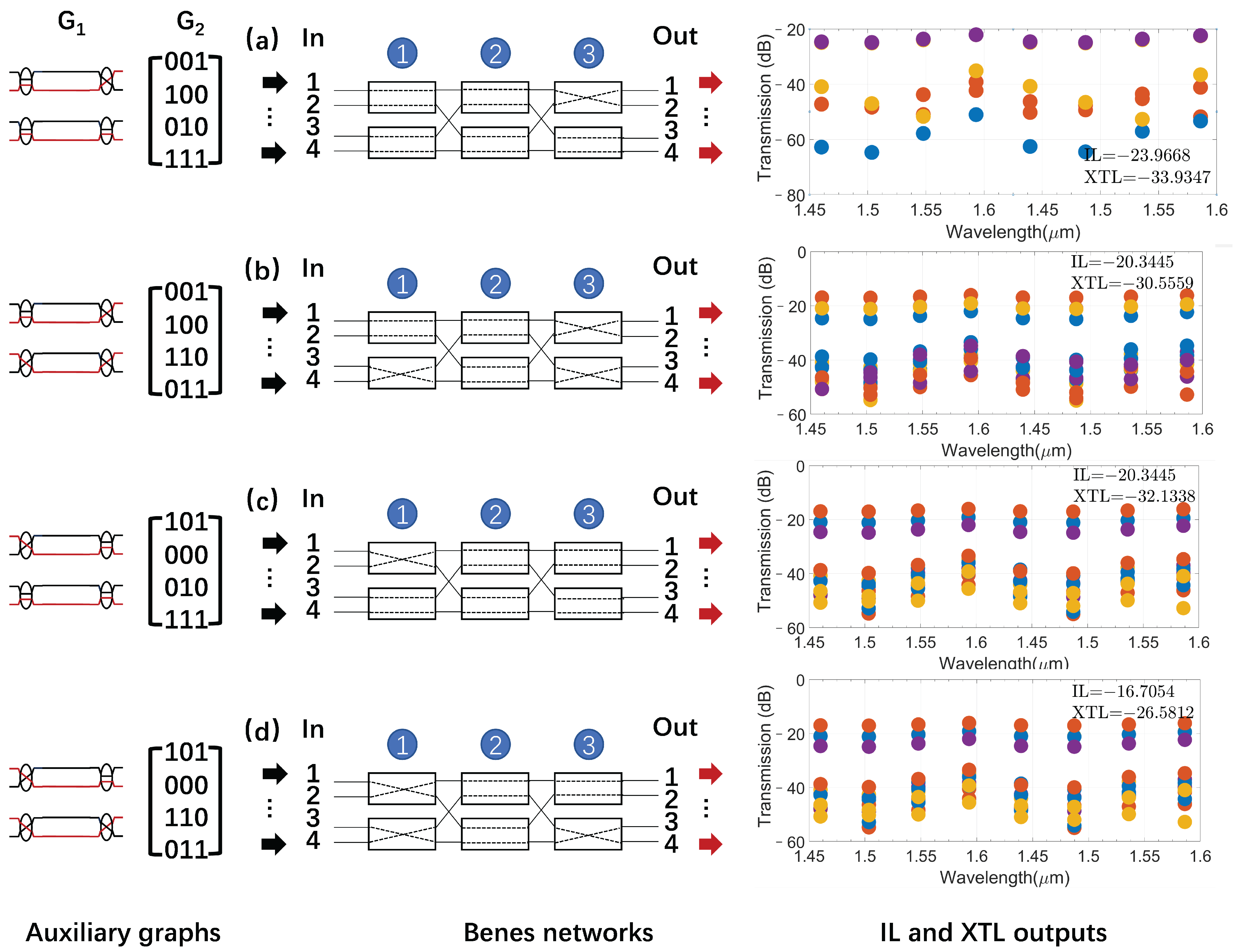
2.2.2. Auxiliary Graphs
2.2.3. MODEL and Constraints
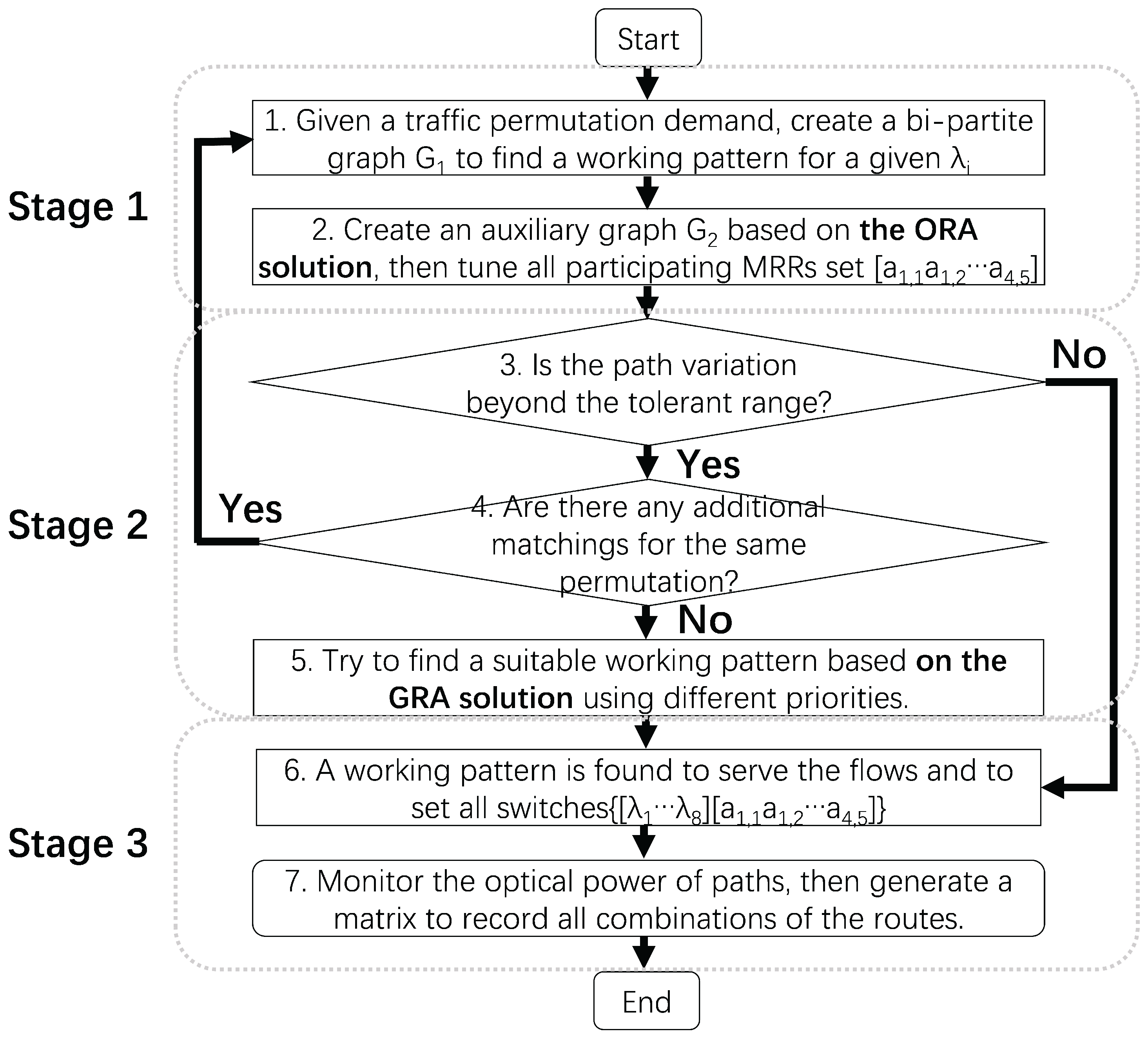
2.3. Algorithm and Constraints
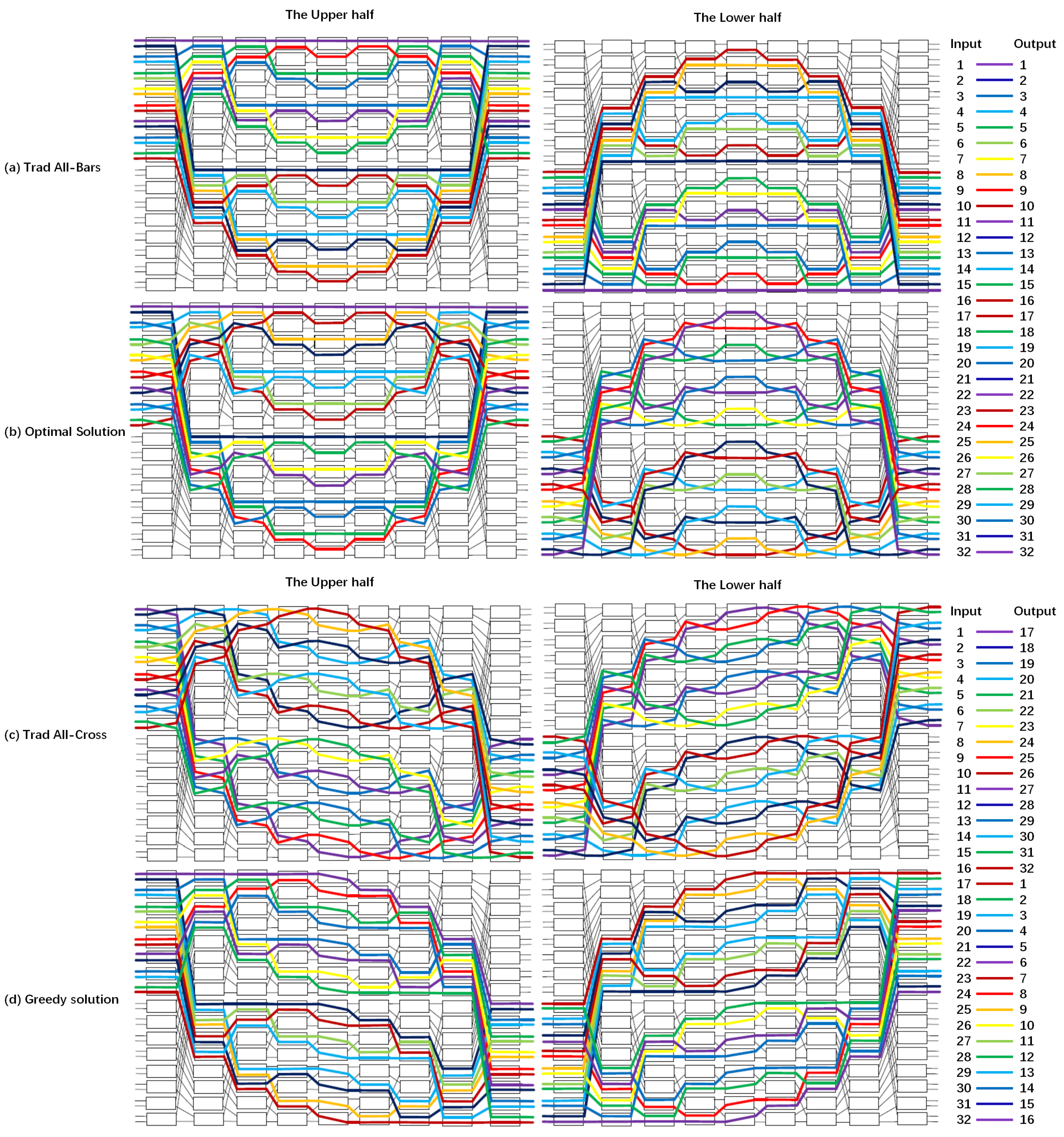
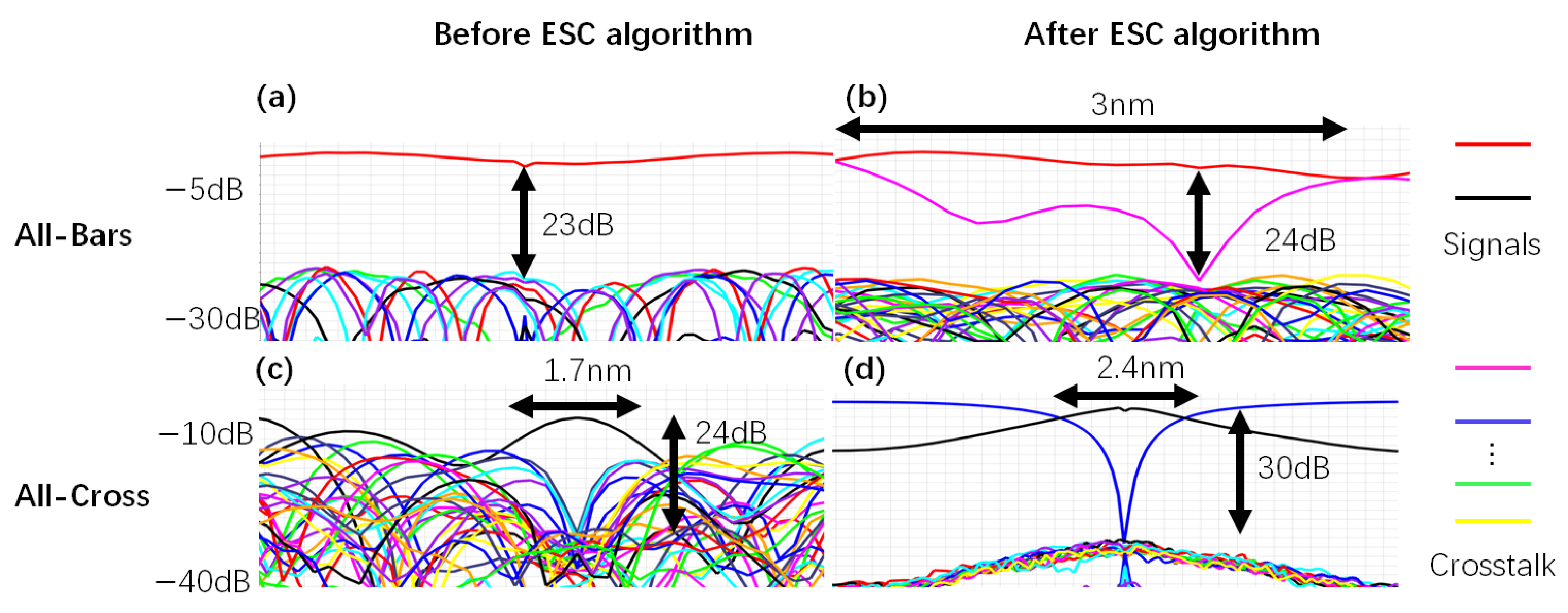
3. Numerical Results
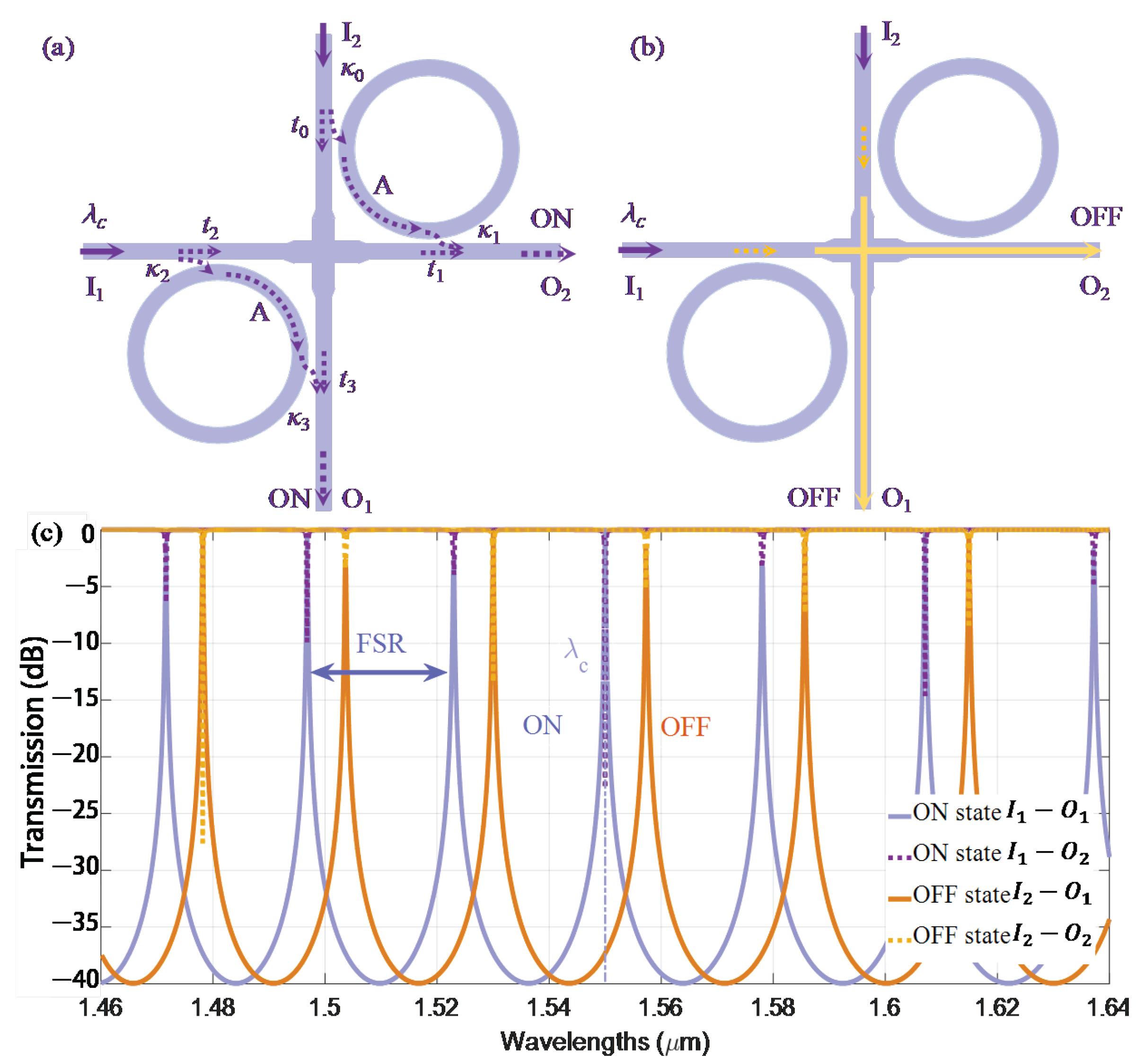
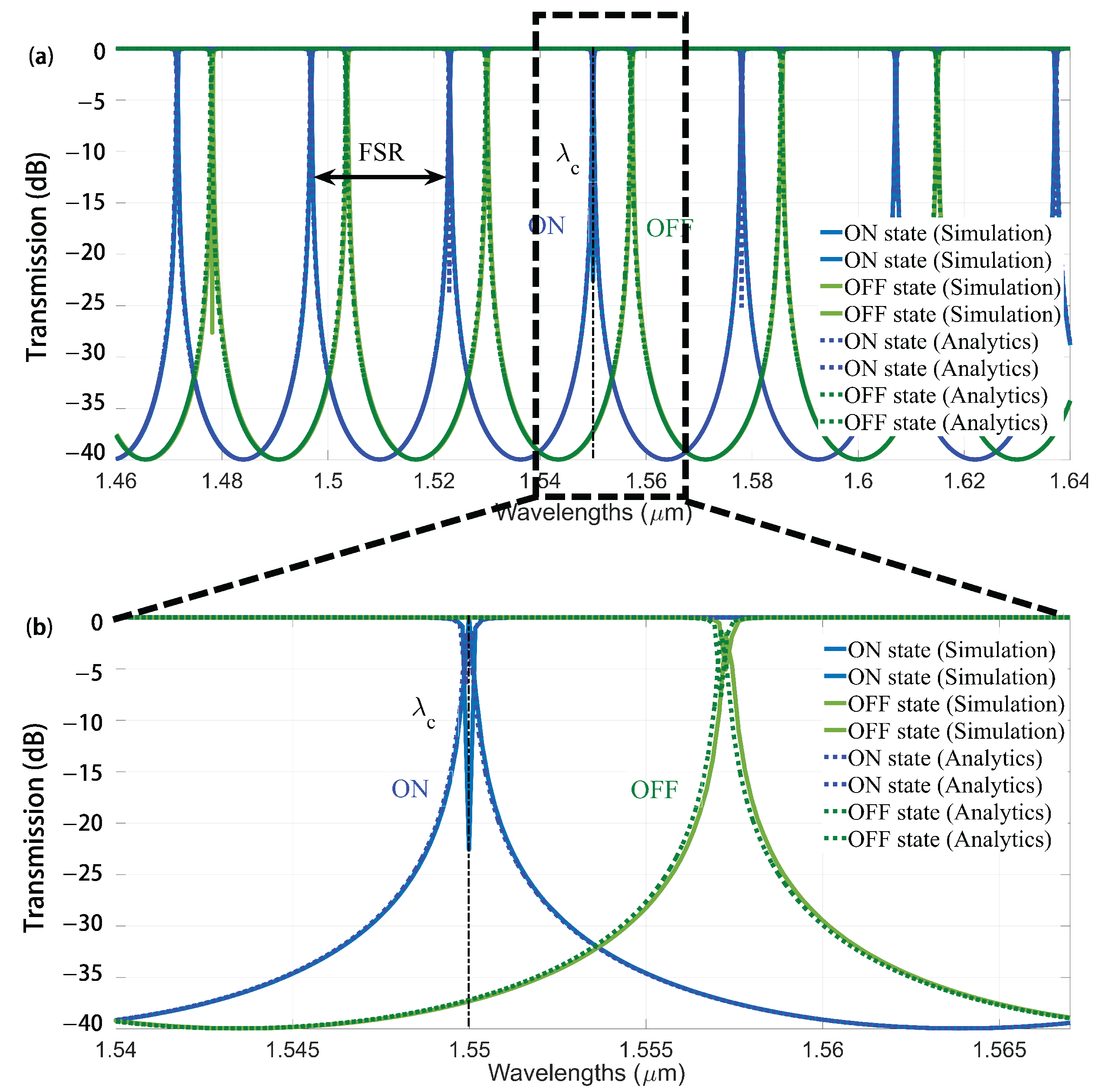
3.1. Two-Port Switching Element
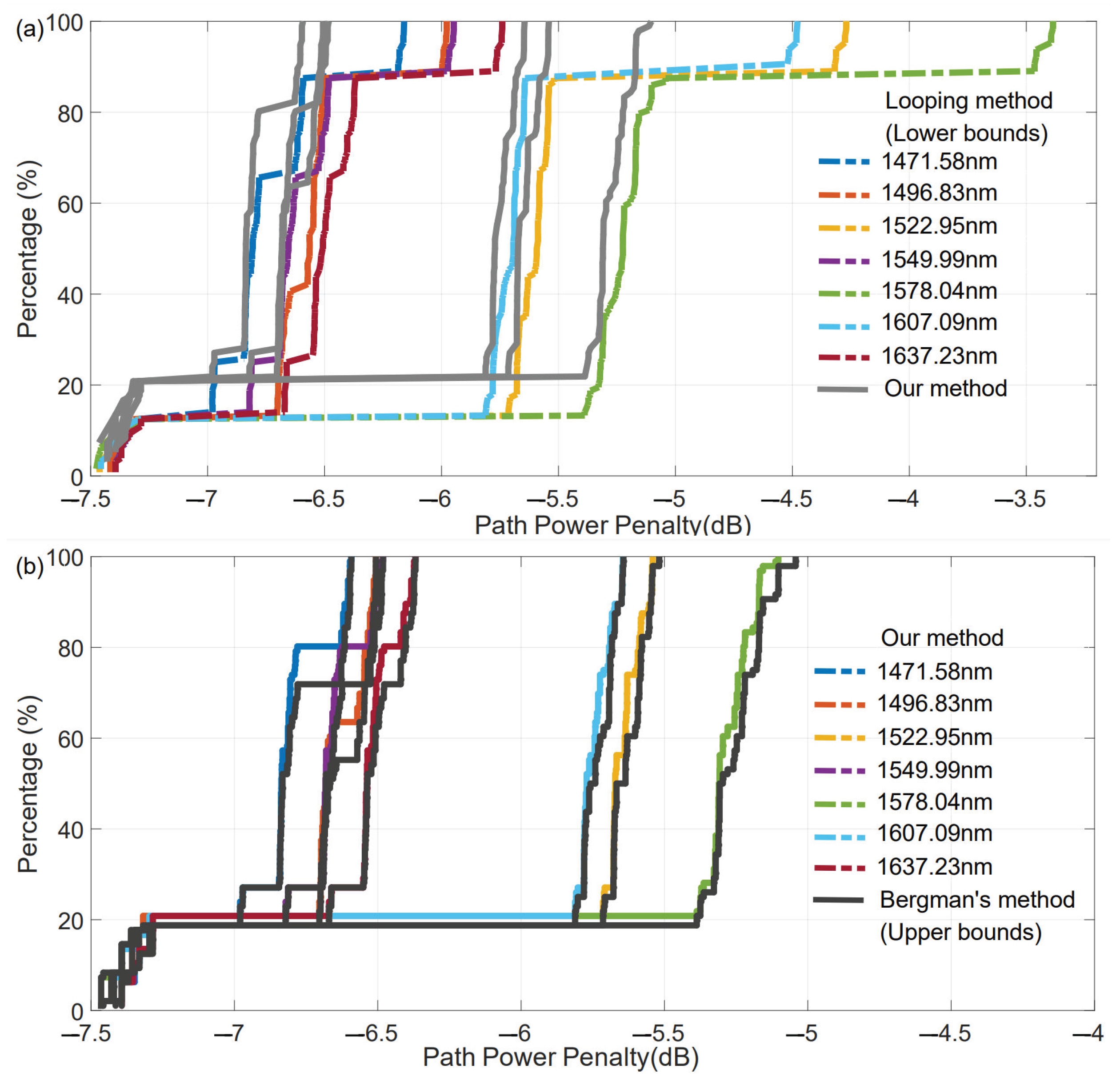
3.2. ORA Scheme
3.3. Routing Table for Four-Port Benes
3.4. Ratio of the Optimal to Near-Optimal Algorithm
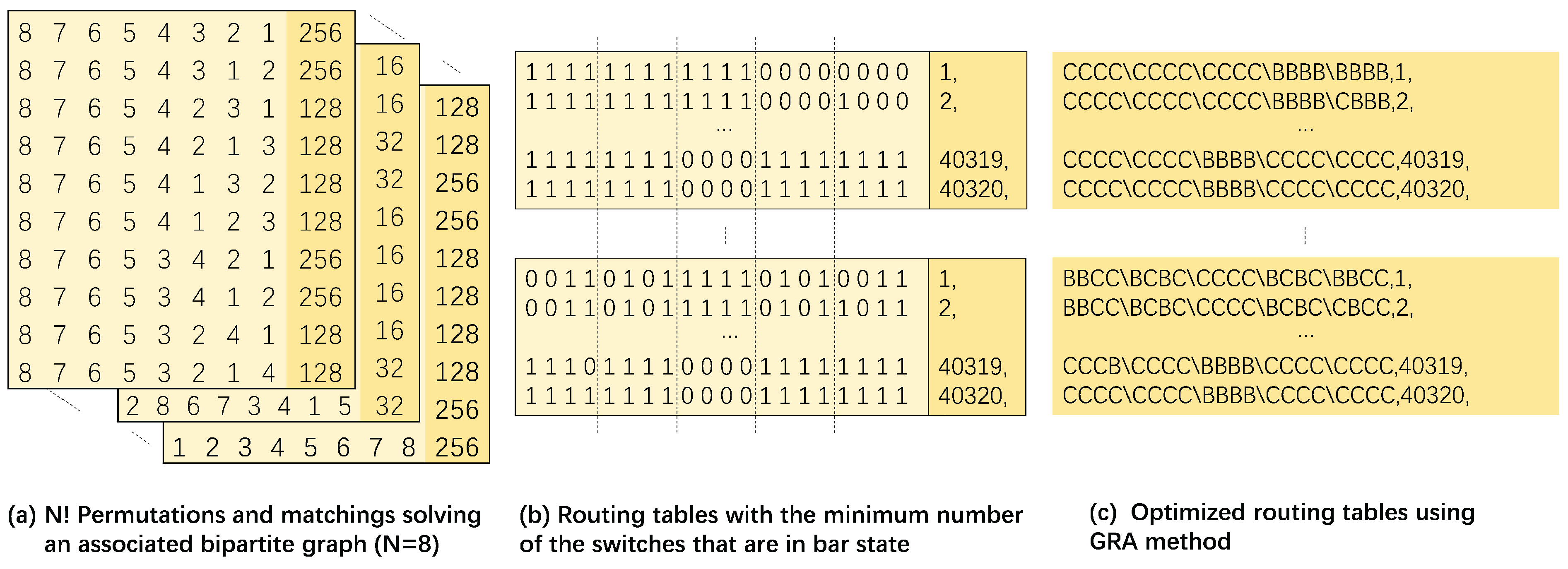
3.5. Routing Table for Eight-Port Benes
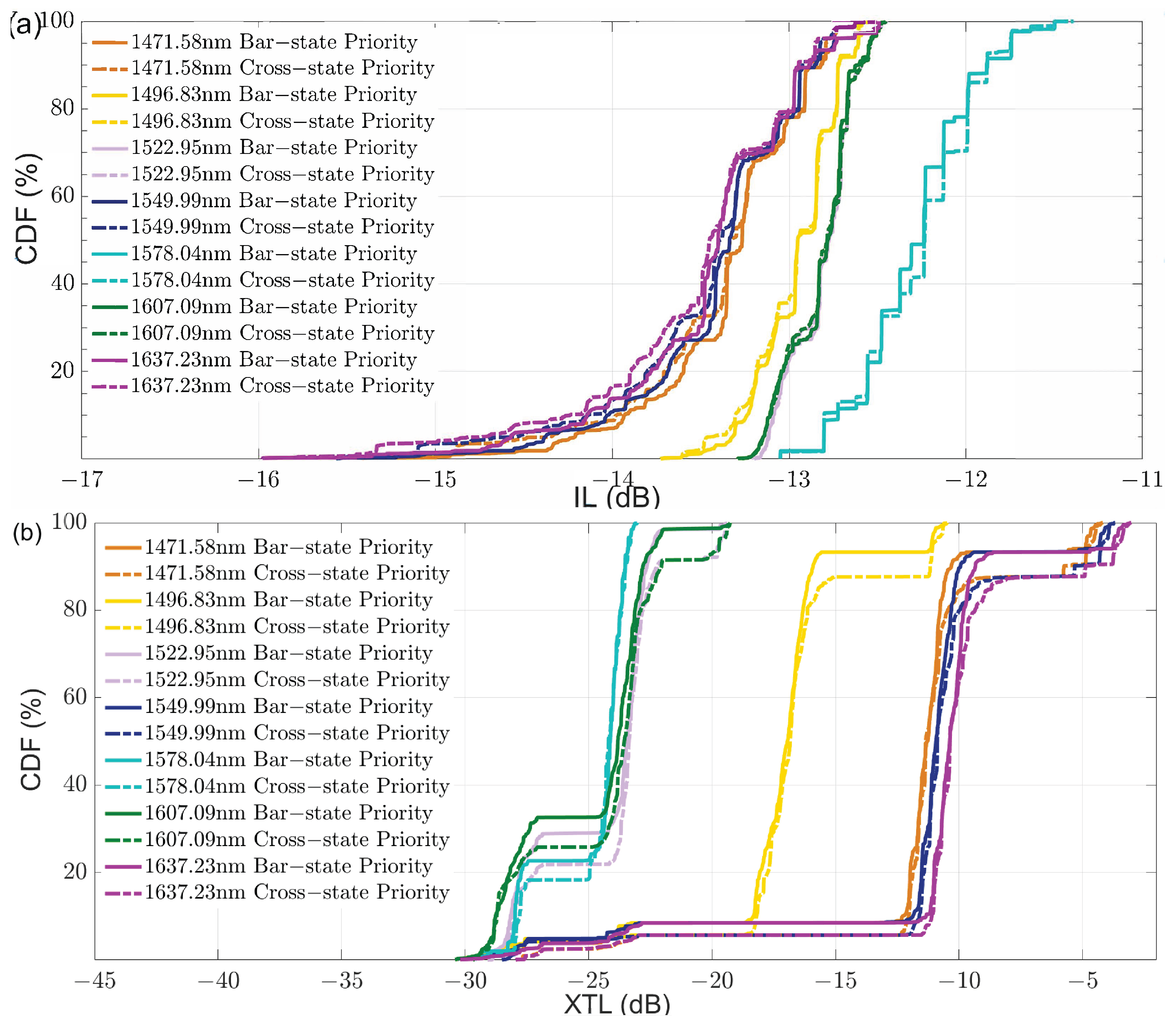
3.6. Routing Table for 32-Port Benes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BW | Bandwidth |
| CDF | Cumulative Distribution Function |
| ER | Extinction Ratio |
| ETS | Efficient Two-Step Algorithm |
| GRA | Greedy Algorithm |
| IL | Insertion loss |
| ORA | Optimal Routing Algorithm |
| PDR | Power Dynamic Range |
| XTL | Crosstalk |
References
- Pamidighantam, V.R.; Yeluripati, R.K. Intra-board Free-space Optical Interconnects for Data Centers. In Frontiers in Optics; Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; p. JW5A-97. [Google Scholar]
- Shabka, Z.; Zervas, G. Network-aware Compute and Memory Allocation in Optically Composable Data Centers with Deep Reinforcement Learning and Graph Neural Networks. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2023, 15, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Shi, P.; Zhang, H. Bi-directional Benes with Large Port-Counts and Low Waveguide Crossings for Optical Network-On-Chip. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 115788–115800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Shi, P. A Universal Method for Constructing N-Port Reconfigurable Non-Blocking Optical Switches on a Silicon Chip. IEEE Access 2021, 10, 1850–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L. Power-Aware Path Selection Routing Algorithm for Benes Integrated Photonic Switches. In Eighth Symposium on Novel Photoelectronic Detection Technology and Applications; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2022; Volume 12169, pp. 1102–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Weninger, D.; Serna, S.; Jain, A.; Kimerling, L.; Agarwal, A. High Density Vertical Optical Interconnects for Passive Assembly. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 2816–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Unnithan, R.R.; Su, Y.; Hu, W.; Shieh, W. Photonic Integrated Self-Coherent Homodyne Receiver without Optical Polarization Control for Polarization-Multiplexing Short-Reach Optical Interconnects. J. Light. Technol. 2022, 41, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Yang, F.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F. Ultrahigh-Speed Optical Interconnects with Thin Film Lithium Niobate Modulator. J. Light. Technol. 2022, 41, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraj, A.; Anand, M.V.; Mageshkumar, N.; Deepan, S.; Karuppiah, S. Allocating Resources in Load Balancing using Elastic Routing Table. Ann. Rom. Soc. Cell Biol. 2021, 25, 13051–13063. [Google Scholar]
- Tamaz, L.; Nino, Z. Compile a Routing Table using a Static Routing Algorithm. Peerian J. 2021, 1, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, H.; Nguyen, S.; Yen, I.; Bastani, F. IoT Data Discovery: Routing Table and Summarization Techniques. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.10791. [Google Scholar]
- Hemalatha, M.; Rukmanidevi, S.; Shanker, N. Searching Time Operation Reduced IPV6 Matching Through Dynamic DNA Routing Table for Less Memory and Fast IP Processing. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 3455–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tian, B.; Hu, N.; Zhao, Q.; Niu, Y.; Lin, L.; Yang, Y. SQRT: A Secure Querying Scheme of Routing Table Based on Oblivious Transfer. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.G.; Dupuis, N.; Pepeljugoski, P.; Schares, L.; Budd, R.; Bickford, J.R.; Schow, C.L. Silicon Photonic Switch Fabrics in Computer Communications Systems. J. Light. Technol. 2015, 33, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Bahadori, M.; Huang, Y.; Rumley, S.; Bergman, K. Smart Routing Tables for Integrated Photonic Switch Fabrics. In Proceedings of the 2017 European Conference on Optical Communication (ECOC), Gothenburg, Sweden, 17–21 September 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.; Wonfor, A.; Cheng, Q.; Penty, R.V.; White, I.H. Hybrid MZI-SOA InGaAs/InP Photonic Integrated Switches. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2017, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Huang, Y.; Yang, H.; Bahadori, M.; Abrams, N.; Meng, X.; Glick, M.; Liu, Y.; Hochberg, M.; Bergman, K. Silicon Photonic Switch Topologies and Routing Strategies For Disaggregated Data Centers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2019, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Hung, Y.H.; Guan, H.; Meng, X.; Novack, A.; Streshinsky, M.; Hochberg, M.; Bergman, K. Multi-Stage 8 × 8 Silicon Photonic Switch Based on Dual-Microring Switching Elements. J. Light. Technol. 2020, 38, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.C. Fault-Tolerant General Beneš Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2023, 71, 6928–6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seznec. A New Interconnection Network for SIMD Computers: The Sigma Network. IEEE Trans. Comput. 1987, 100, 794–801. [Google Scholar]
- Opferman, D.C.; Tsao-Wu, N.T. On a Class of Rearrangeable Switching Networks Part I: Control Algorithm. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1971, 50, 1579–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Tang, W.; Chu, T. 32× 32 Silicon Electro-Optic Switch with Built-In Monitors and Balanced-Status Units. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çam, H.; Fortes, J.A.B. Work-efficient routing algorithms for rearrangeable symmetrical networks. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 1999, 10, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, A.W.; Luo, X.; Xu, F.; Chen, H. Cascaded Microresonator-based Matrix Switch for Silicon On-Chip Optical Interconnection. Proc. IEEE 2009, 97, 1216–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastwirth, J.L. A General Definition of the Lorenz Curve. Econ. J. Econ. Soc. 1971, 39, 1037–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeck, R.; Jaeger, N.A.F.; Rouger, N.; Chrostowski, L. Series-coupled Silicon Racetrack Resonators and The Vernier Effect: Theory and Measurement. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 25151–25157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Coupling efficient | |
| Group refractive/Effective refractive index | 2.6/2.6 |
| Free spectrum range (FSR) | 26 nm |
| Maximum attenuation | 3 dB/cm |
| The perimeter of the ring (On state) | 4/12 µm |
| The perimeter of the ring (Off state) | 3.48/10.45 µm |
| References | Solutions | Power Imbalances | Physical Indicators | Time Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Looping Algorithm [21] | Always | High | Not given | O() |
| Work Efficient Algorithm [23] | Sometimes | Low | Not given | O() |
| Lee’s Algorithm [17] | Always | Low | MLSE | O() |
| This Work | Always | Low | Without MLSE | min(O(, O()) |
| Key Indicators | [14] | Our Previous Work [3,4] | This Work |
|---|---|---|---|
| Port number | 64 | 32 | 32 |
| Data rate | 25 | 25 | 25/50 |
| Link power budget | −15 dBm | −10.9 dBm | −10.9 dBm |
| Power imbalance | 1.5 dB to 95 dB | 1.5 dB to 45 dB | 5 dB to 36 dB |
| Eye width | Almost closed | 1.7 nm−110 nm | 2.4 nm−60 nm |
| Number of the first-order XTLs | n | n | 1 or p |
| BER | |||
| WDM | 16 | 8 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Ma, T. Making Path Selection Bright: A Routing Algorithm for On-Chip Benes Networks. Electronics 2024, 13, 981. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13050981
Zhao L, Li Z, Ma T. Making Path Selection Bright: A Routing Algorithm for On-Chip Benes Networks. Electronics. 2024; 13(5):981. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13050981
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Li, Zhiwei Li, and Tianming Ma. 2024. "Making Path Selection Bright: A Routing Algorithm for On-Chip Benes Networks" Electronics 13, no. 5: 981. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13050981
APA StyleZhao, L., Li, Z., & Ma, T. (2024). Making Path Selection Bright: A Routing Algorithm for On-Chip Benes Networks. Electronics, 13(5), 981. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13050981






