A Deep Learning-Based Low-Overhead Beam Tracking Scheme for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Aided Multiple-Input and Single-Output Systems with Estimated Channels
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Related Work
1.3. Our Contributions
- (1)
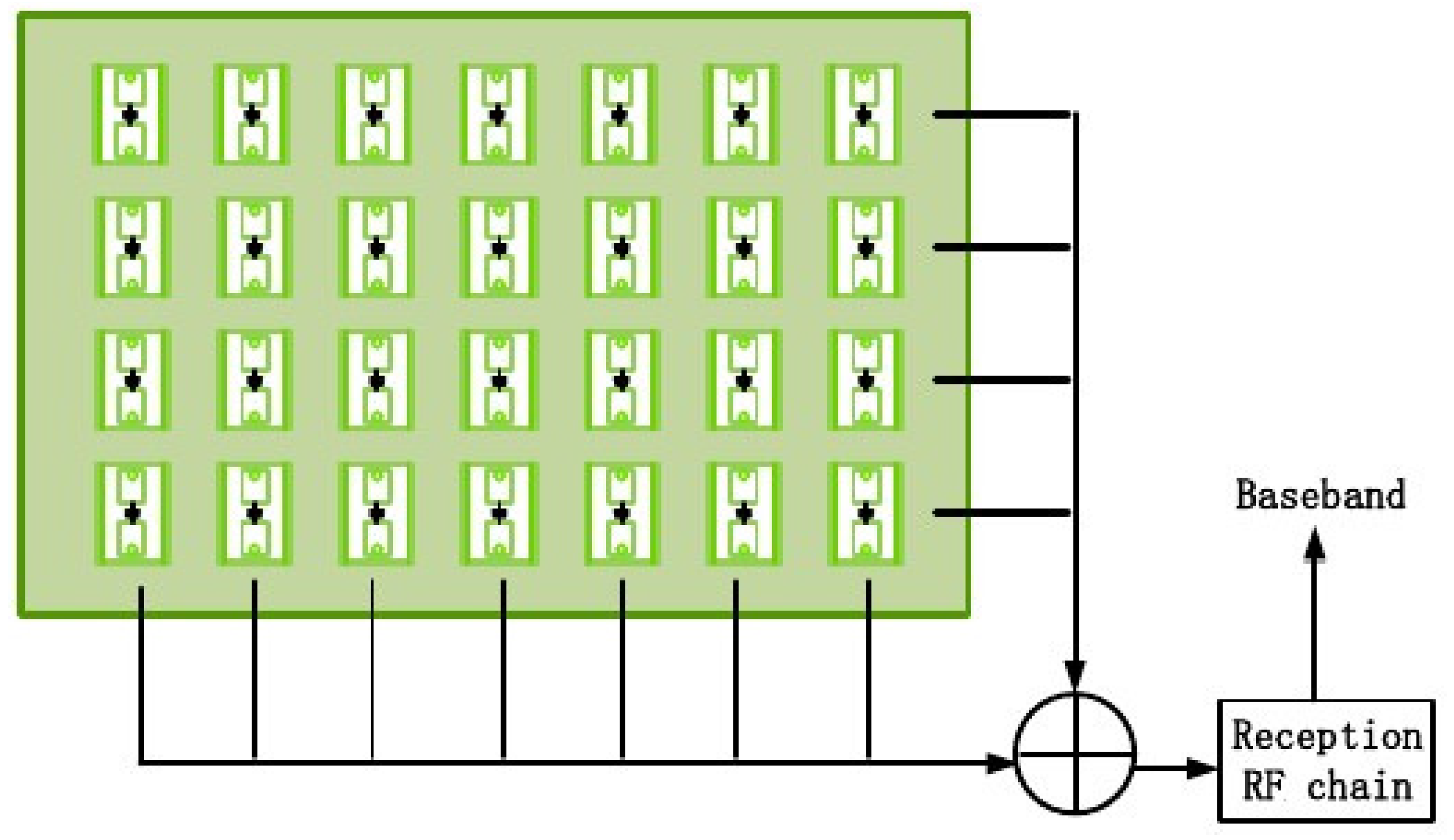
- Utilizing a semi-active RIS architecture that consists of passive unit elements and only one active RF chain, we propose a PCA-based CE scheme to estimate the CSI of the RIS-BS, the RIS-UT, and the UT-BS. The proposed CE scheme allows a trade-off between cost and performance;
- (2)
- Based on the estimated channel, we propose a DNN to realize low-complexity beam tracking of a semi-active RIS-aided system, which effectively improves the SNR on the UT side. Our simulation results verified the accuracy of the proposed schemes on beam tracking for semi-active RIS-aided MISO systems.
2. System Model and Problem Formulation
2.1. System Model
2.2. Problem Formulation
3. The Proposed PCA-Based Channel Estimation Algorithm
3.1. Channel Estimation
3.2. SVD Operation
3.3. The PCA-Based Channel Estimation Algorithm
3.4. Staged Channel Estimation Scheme
4. The Proposed RIS Beam Tracking Scheme
4.1. The SDR-Based Algorithm
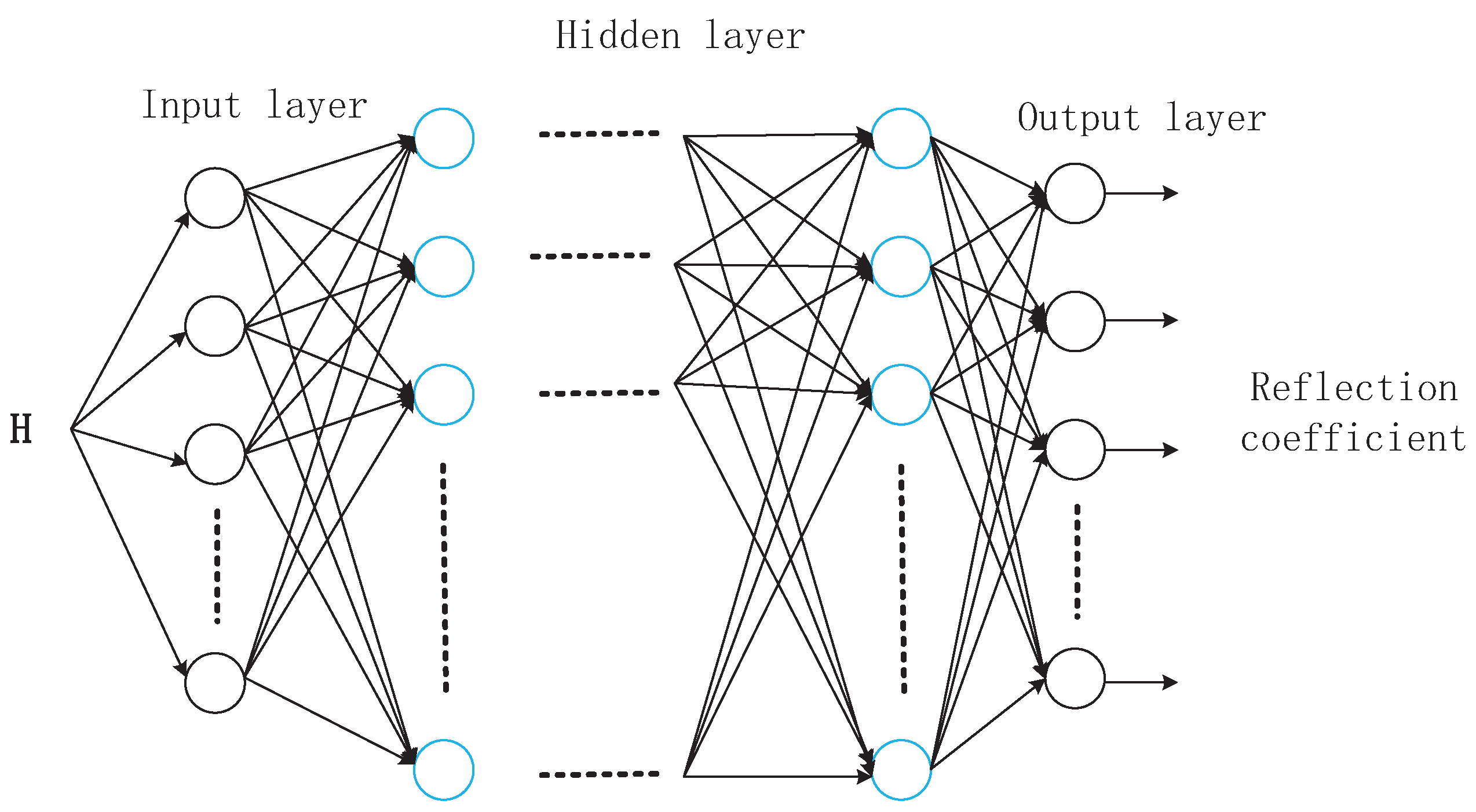
4.2. The Proposed Beam Tracking Scheme Based on DL
| Algorithm 1 The proposed beam tracking scheme for RIS-aided MISO system |
|
5. Simulation Results
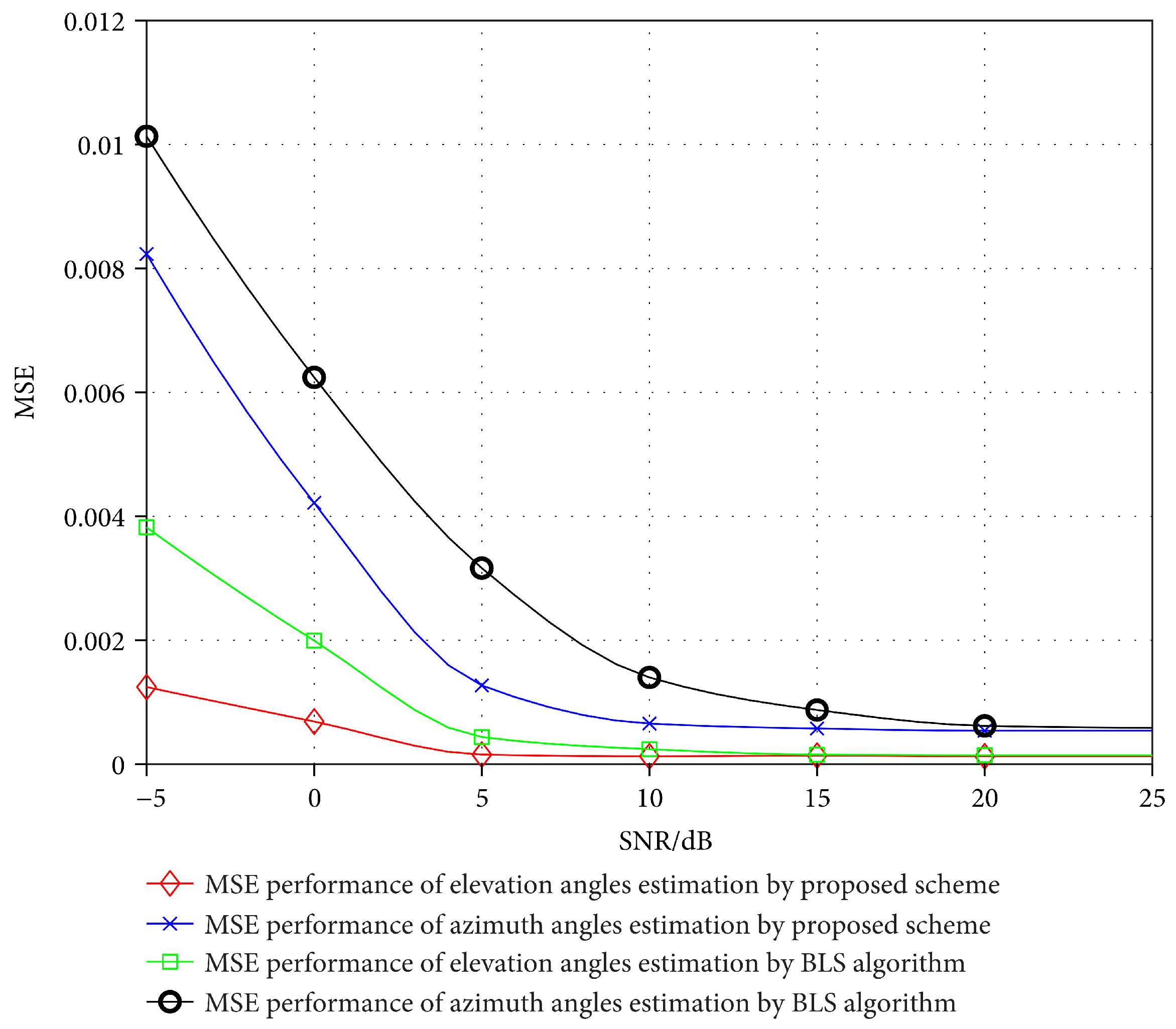
5.1. The Estimation Accuracy
5.2. Convergence Analysis under Different Network Structures
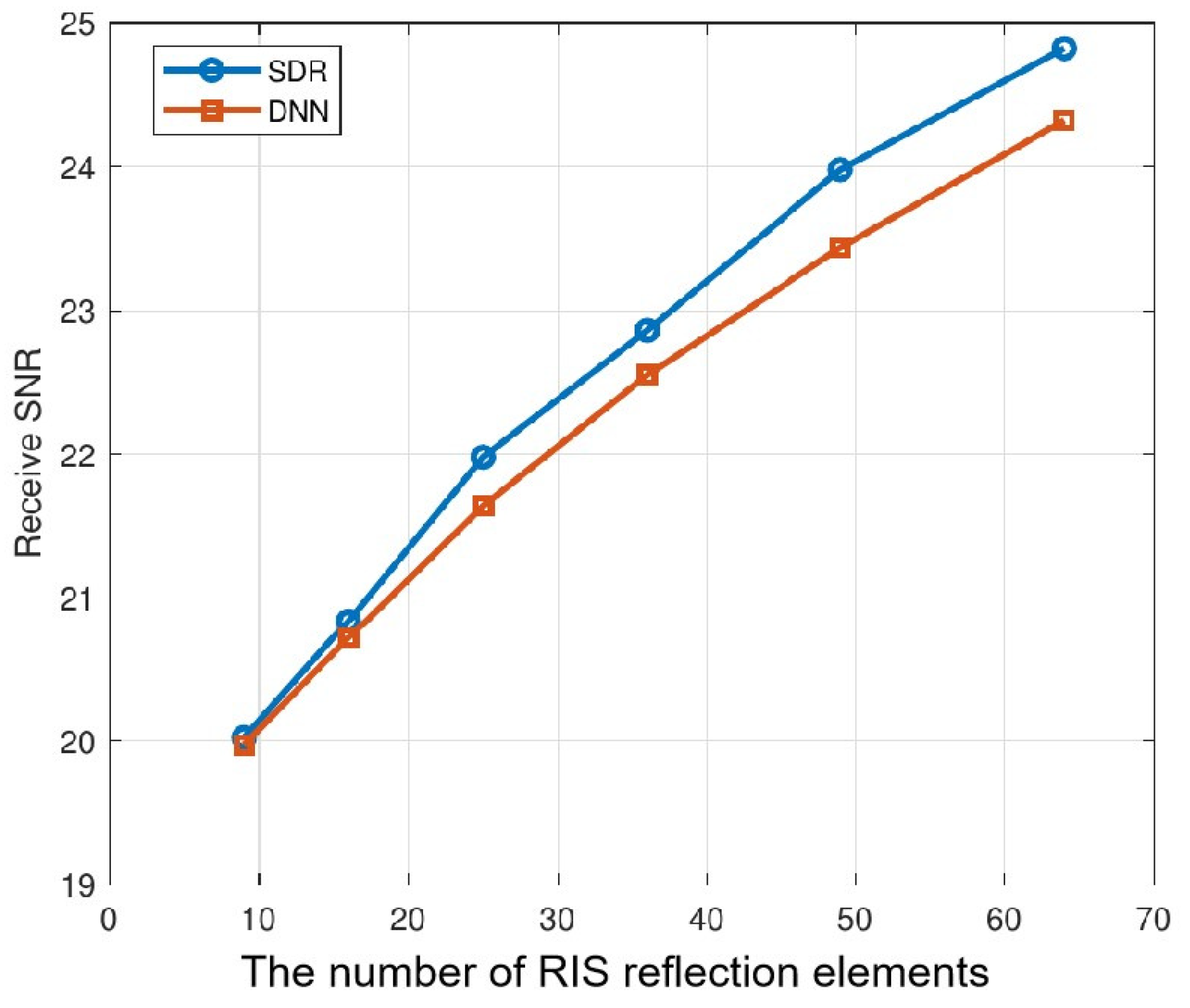
5.3. Performance Analysis under Different Configurations
5.4. Complexity Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liaskos, C.; Nie, S.; Tsioliaridou, A.; Pitsillides, A.; Ioannidis, S.; Akyildiz, I. A new wireless communication paradigm through software-controlled metasurfaces. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.C.; Long, R.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Cheng, H.V.; Guo, H. Large intelligent surface/antennas (LISA): Making reflective radios smart. J. Commun. Inf. Netw. 2019, 4, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Rusek, F.; Edfors, O. Beyond massive MIMO: The potential of data transmission with large intelligent surfaces. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 2746–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.J.; Qi, M.Q.; Wan, X.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, Q. Coding metamaterials, digital metamaterials and programmable metamaterials. Light. Sci. Appl. 2014, 3, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Chen, M.Z.; Dai, J.Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jin, S.; Cheng, Q.; Cui, T.J. Wireless Communications with Programmable Metasurface: New Paradigms, Opportunities, and Challenges on Transceiver Design. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2020, 27, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-de Rioja, E.; F. Vaquero, A.; Arrebola, M.; Carrasco, E.; Encinar, J.; Achour, M. Passive intelligent reflecting surfaces based on reflectarray panels to enhance 5G millimeter-wave coverage. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2022, 15, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freni, A.; Beccaria, M.; Mazzinghi, A.; Massaccesi, A.; Pirinoli, P. Low-Profile and Low-Visual Impact Smart Electromagnetic Curved Passive Skins for Enhancing Connectivity in Urban Scenarios. Electronics 2023, 12, 4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liang, Y.C.; Cheng, H.V.; Yu, W. Channel Estimation for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Aided Multi-User mmWave MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 22, 6853–6869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tang, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; So, D.K.C.; Jin, S.; Wong, K.K. Hybrid evolutionary-based sparse channel estimation for IRS-assisted mmWave MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 21, 1586–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.Q.; Yuan, X. Cascaded channel estimation for large intelligent metasurface assisted massive MIMO. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2019, 9, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, J.; Ali, B. Channel estimation method and phase shift design for reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted MIMO networks. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2021, 7, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Y.J.A. Matrix-calibration-based cascaded channel estimation for reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted multiuser MIMO. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 38, 2621–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, W.; Du, Y. Channel estimation and transmission for intelligent reflecting surface assisted THz communications. In Proceedings of the ICC 2020–2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Dublin, Ireland, 7–11 June 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, S.; Xing, C.; An, J. Training Optimization for Subarray-Based IRS-Assisted MIMO Communications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 2890–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ge, N.; Wang, Z.; Hanzo, L. Joint transmit precoding and reconfigurable intelligent surface phase adjustment: A decomposition-aided channel estimation approach. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2020, 69, 1228–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, N.K.; McKay, M.R. Channel Estimation for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Aided MISO Communications: From LMMSE to Deep Learning Solutions. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2021, 2, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.; Alrabeiah, M.; Alkhateeb, A. Enabling large intelligent surfaces with compressive sensing and deep learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 44304–44321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Di Renzo, M.; Alouini, M.S. Deep denoising neural network assisted compressive channel estimation for mmWave intelligent reflecting surfaces. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 9223–9228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandropoulos, G.C.; Vlachos, E. A hardware architecture for reconfigurable intelligent surfaces with minimal active elements for explicit channel estimation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020–2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 9175–9179. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhong, C. Semi-passive elements assisted channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface-aided communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 21, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, R. Capacity characterization for intelligent reflecting surface aided MIMO communication. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 38, 1823–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmer, D.; Foglia Manzillo, F.; Gharbieh, S.; Śmierzchalski, M.; D’Errico, R.; Doré, J.B.; Clemente, A. Hybrid Precoding Applied to Multi-Beam Transmitting Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (T-RIS). Electronics 2023, 12, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, R. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced wireless network via joint active and passive beamforming. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2019, 18, 5394–5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, R. Beamforming optimization for wireless network aided by intelligent reflecting surface with discrete phase shifts. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2019, 68, 1838–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Fan, J.; Shen, W.; Qin, Z.; Li, G.Y. Deep learning and compressive sensing-based CSI feedback in FDD massive MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 9217–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Ye, H.; Li, G.Y.; Juang, B.H.F. Deep learning in physical layer communications. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2019, 26, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Zhu, Y. Beamforming design for large-scale antenna arrays using deep learning. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2019, 9, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbir, A.M.; Papazafeiropoulos, A.K. Hybrid precoding for multiuser millimeter wave massive MIMO systems: A deep learning approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 69, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Mo, R.; Yuen, C. Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Assisted Multiuser MISO Systems Exploiting Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 38, 1839–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Fan, J. Beamforming Optimization for Intelligent Reflecting Surface Assisted MISO: A Deep Transfer Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 3902–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waraiet, A.; Cumanan, K.; Ding, Z.; Dobre, O.A. Robust Design for IRS-Assisted MISO-NOMA Systems: A DRL-Based Approach. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2024, 13, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waraiet, A.; Cumanan, K.; Ding, Z.; Dobre, O.A. Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Robust Design for an IRS-Assisted MISO-NOMA System. IEEE Trans. Mach. Learn. Commun. Netw. 2024, 2, 424–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.; Alrabeiah, M.; Alkhateeb, A. Deep learning for large intelligent surfaces in millimeter wave and massive MIMO systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 9–13 December 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, A.; Zhang, Y.; Mismar, F.B.; Alkhateeb, A. Deep reinforcement learning for intelligent reflecting surfaces: Towards standalone operation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 21st international workshop on signal processing advances in wireless communications (SPAWC), Atlanta, GA, USA, 26–29 May 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, K.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Wen, C.K. Deep reinforcement learning based intelligent reflecting surface optimization for MISO communication systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2020, 9, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. Least mean square error reconstruction principle for self-organizing neural-nets. Neural Netw. 1993, 6, 627–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adali, T.; Haykin, S. Adaptive Signal Processing: Next Generation Solutions; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 55. [Google Scholar]
- Jorge Nocedal, S.J.W. Numerical Optimization; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]



| Configuration | Run Time | |
|---|---|---|
| SDR | DNN | |
| 49.8893s | 0.1816s | |
| 107.0052s | 0.2233s | |
| 121.5610s | 0.2613s | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, R.; Yuan, J.; Wang, G.; Xu, C.; Yin, R. A Deep Learning-Based Low-Overhead Beam Tracking Scheme for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Aided Multiple-Input and Single-Output Systems with Estimated Channels. Electronics 2024, 13, 3732. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13183732
Guo R, Yuan J, Wang G, Xu C, Yin R. A Deep Learning-Based Low-Overhead Beam Tracking Scheme for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Aided Multiple-Input and Single-Output Systems with Estimated Channels. Electronics. 2024; 13(18):3732. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13183732
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Rongbin, Jiantao Yuan, Guan Wang, Congyuan Xu, and Rui Yin. 2024. "A Deep Learning-Based Low-Overhead Beam Tracking Scheme for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Aided Multiple-Input and Single-Output Systems with Estimated Channels" Electronics 13, no. 18: 3732. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13183732
APA StyleGuo, R., Yuan, J., Wang, G., Xu, C., & Yin, R. (2024). A Deep Learning-Based Low-Overhead Beam Tracking Scheme for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Aided Multiple-Input and Single-Output Systems with Estimated Channels. Electronics, 13(18), 3732. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13183732






