Fundus Image Generation and Classification of Diabetic Retinopathy Based on Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Models and Methods
2.1. Images Dataset
2.2. Pre-Processing
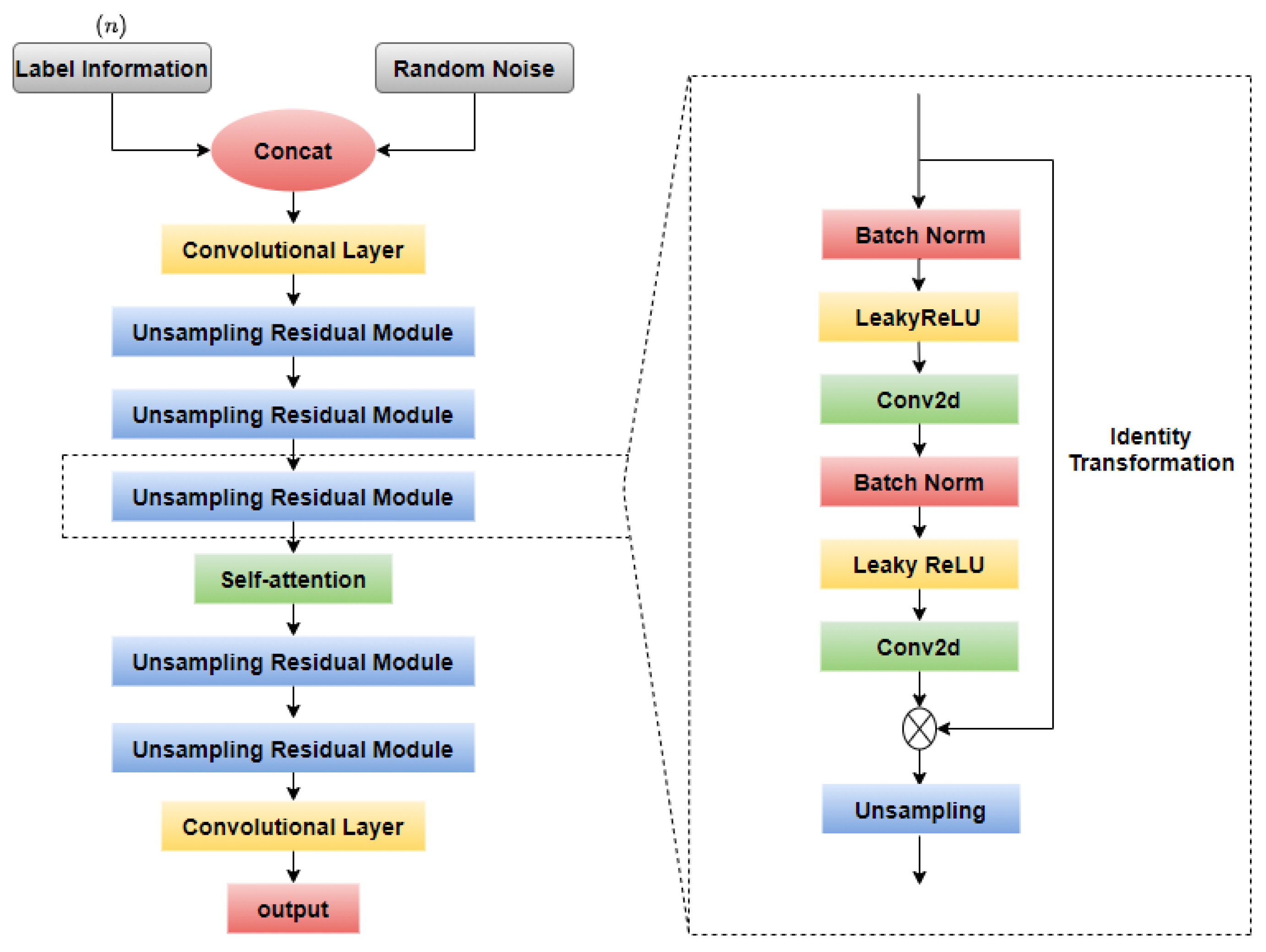
2.3. Fundus Image Generation
2.3.1. GAN-Based Model
2.3.2. Self-Attention Module
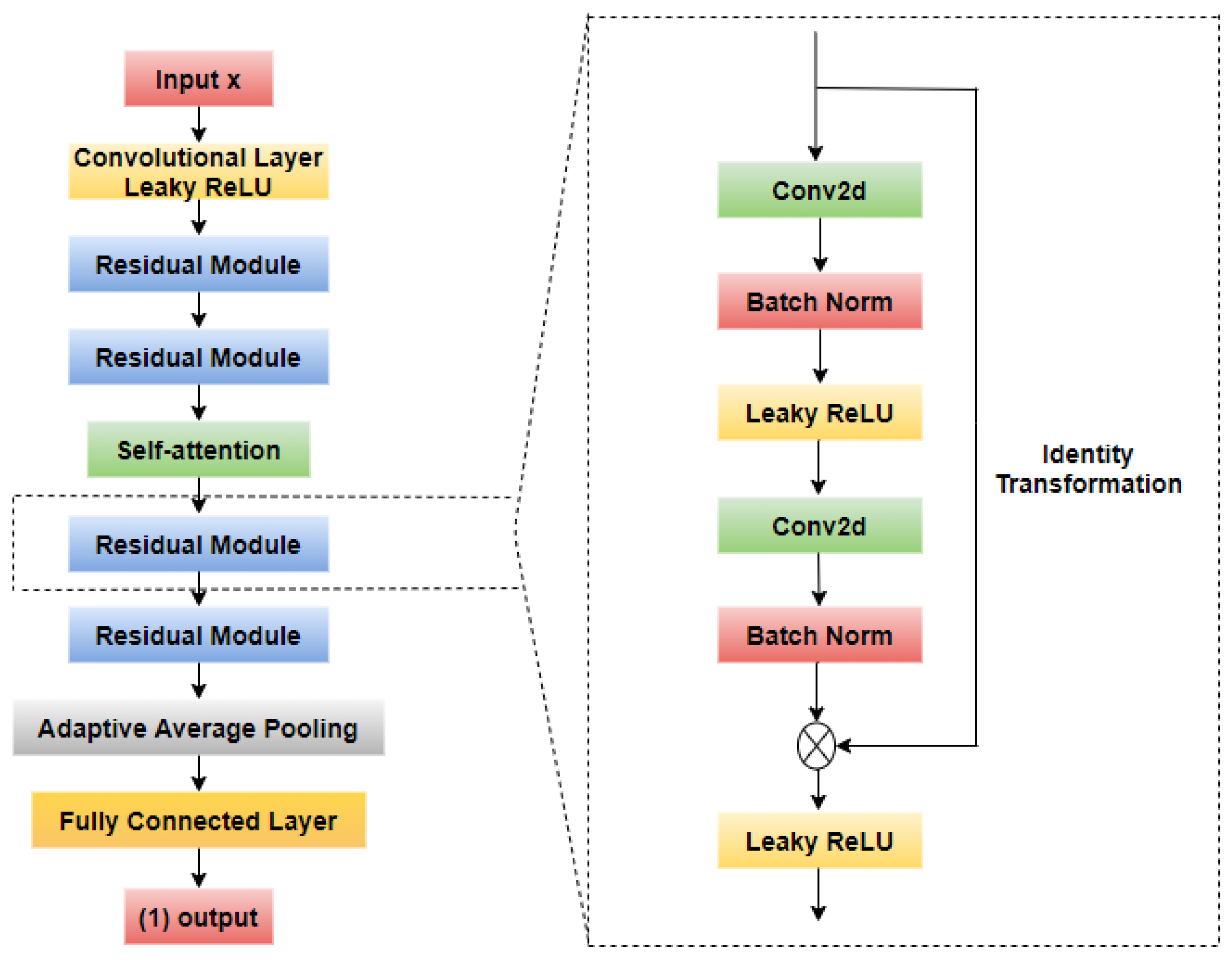
2.4. Fundus Image Classification
2.4.1. CNN-Based Model
2.4.2. Channel Attention Mechanism
2.4.3. Class Activation Map
3. Results
3.1. Hardware and Resources
3.2. Evaluation Indicators
3.3. Fundus Image Generation Result
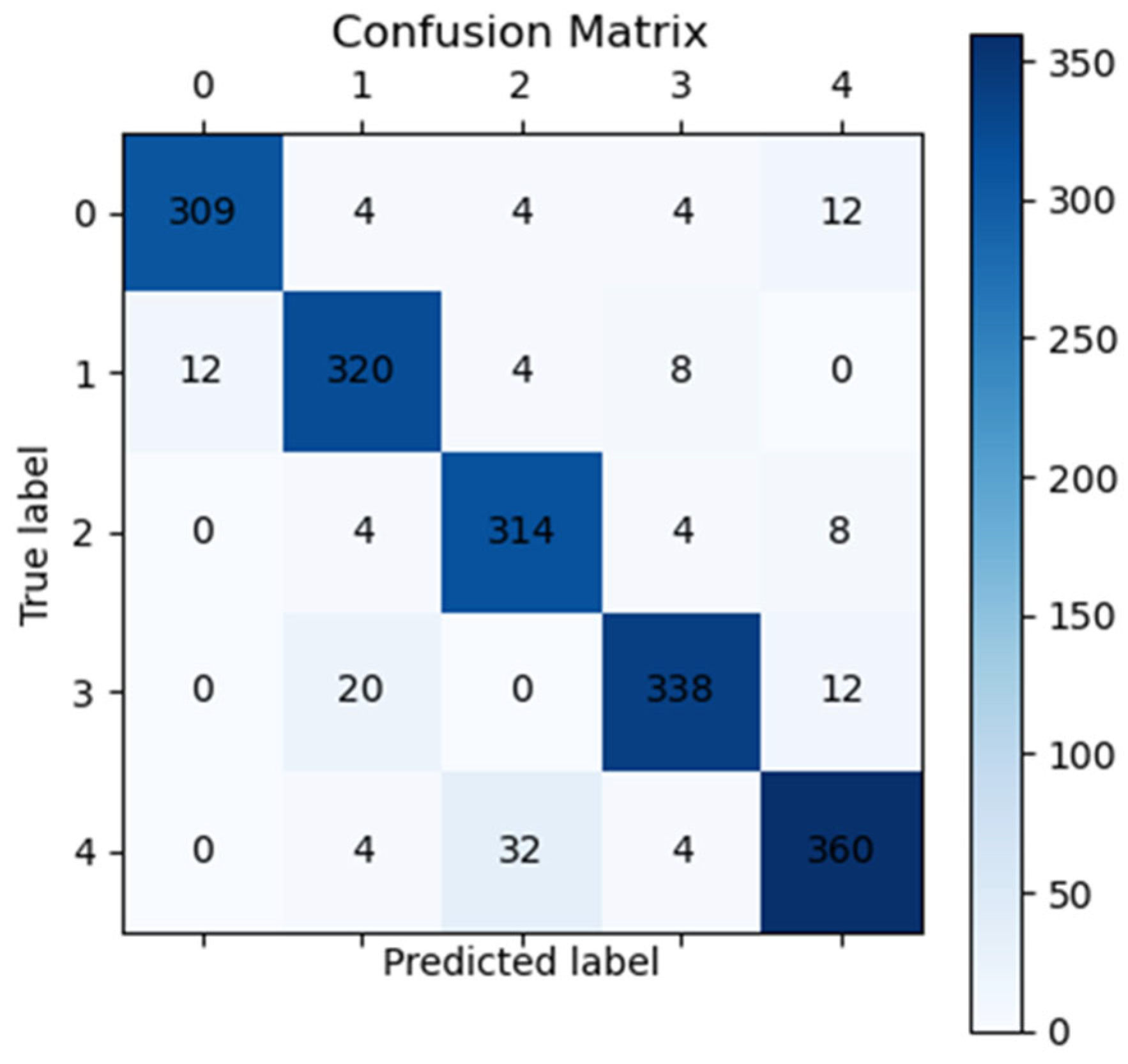
3.4. Fundus Image Classification Result
3.5. Additional Generalization Experiment with the Clinical Data
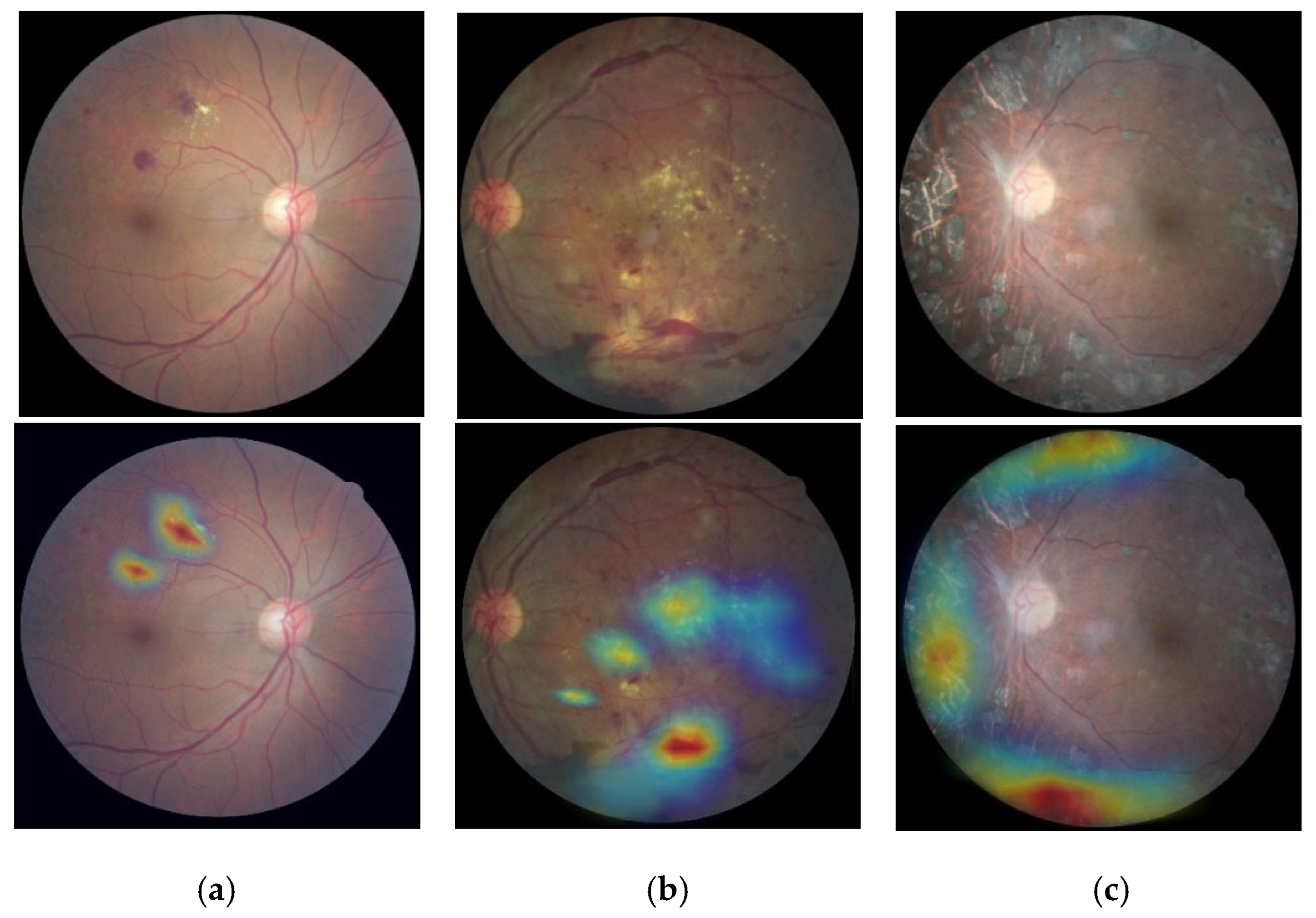
3.6. Classification Based on Visualization
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roglic, G. Who global report on diabetes: A summary. Int. J. Noncommun. Dis. 2016, 1, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, Z.L.; Tham, Y.C.; Yu, M.; Chee, M.L.; Rim, T.H.; Cheung, N.; Bikbov, M.M.; Wang, Y.X.; Tang, Y.; Lu, Y.; et al. Global prevalence of diabetic retinopathy and projection of burden through 2045: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 1580–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.M.S.; Hasan, M.M.; Abdullah, S. Deep learning based early detectionand grading of diabetic retinopathy using retinal fundus images. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.10595. [Google Scholar]
- Gulshan, V.; Peng, L.; Coram, M.; Stumpe, M.C.; Wu, D.; Narayanaswamy, A.; Venugopalan, S.; Widner, K.; Madams, T.; Cuadros, J.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Algorithm for Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy in Retinal Fundus Photographs. JAMA 2016, 316, 2402–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.; Zhao, E.J.; Lam, C.K.; Rubin, D.L. Segmentation-assisted fully convolutional neural network enhances deep learning performance to identify proliferative diabetic retinopathy. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theckedath, D.; Sedamkar, R.R. Detecting affect states using VGG16, ResNet50 and SE-ResNet50 networks. SN Comput. Sci. 2020, 1, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lin, L.; Cheng, P.; Lyu, J.; Tam, R.; Tang, X. Identifying the key components in resnet-50 for diabetic retinopathy grading from fundus images: A systematic investigation. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.; Araujo, T.; Aresta, G.; Galdran, A.; Mendonça, A.M.; Smailagic, A.; Campilho, A. EyeWeS: Weakly Supervised Pre-Trained Convolutional Neural Networks for Diabetic Retinopathy Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA), Tokyo, Japan, 27–31 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.; Li, L.; He, M.; Wang, N.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z. Joint learning of multi-level tasks for diabetic retinopathy grading on low-resolution fundus images. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 26, 2216–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, D.A.D.; Ferreira, F.M.F.; Peixoto, Z. Diabetic retinopathy classification using VGG16 neural network. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 38, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 13713–13722. [Google Scholar]
- He, A.; Li, T.; Li, N.; Wang, K.; Fu, H. CABNet: Category Attention Block for Imbalanced Diabetic Retinopathy Grading. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 40, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhati, A.; Gour, N.; Khanna, P.; Ojha, A. Discriminative kernel convolution network for multi-label ophthalmic disease detection on imbalanced fundus image dataset. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 153, 106519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, Z.; Zou, B.; Xiao, X.; Peng, Q.; Yan, J.; Zhang, W.; Yue, K. A novel approach for intelligent diagnosis and grading of diabetic retinopathy. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 172, 108246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, F.; Ma, H. CRA-Net: Transformer guided category-relation attention network for diabetic retinopathy grading. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 170, 107993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kazeminia, S.; Baur, C.; Kuijper, A.; van Ginneken, B.; Navab, N.; Albarqouni, S.; Mukhopadhyay, A. GANs for medical image analysis. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 109, 101938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesaranghader, A.; Wang, Y.; Havaei, M. CT-SGAN: Computed tomography synthesis GAN. In Deep Generative Models, and Data Augmentation, Labelling, and Imperfections, Proceedings of the First Workshop, DGM4MICCAI 2021, and First Workshop, DALI 2021, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2021, Strasbourg, France, 1 October 2021; Proceedings 1; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 67–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, B.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Wu, X.; Pu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Shen, D. D2FE-GAN: Decoupled dual feature extraction based GAN for MRI image synthesis. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 252, 109362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Bi, L.; Peng, Y.; Fulham, M.; Feng, D.D.; Kim, J. PET Synthesis via Self-supervised Adaptive Residual Estimation Generative Adversarial Network. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2023, 8, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadros, J.; Sim, I. EyePACS: An open source clinical communication system for eye care. In MEDINFO 2004; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 207–211. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.; Zhan, K.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Shen, F. Lesion-aware network for diabetic retinopathy diagnosis. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2023, 33, 1914–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


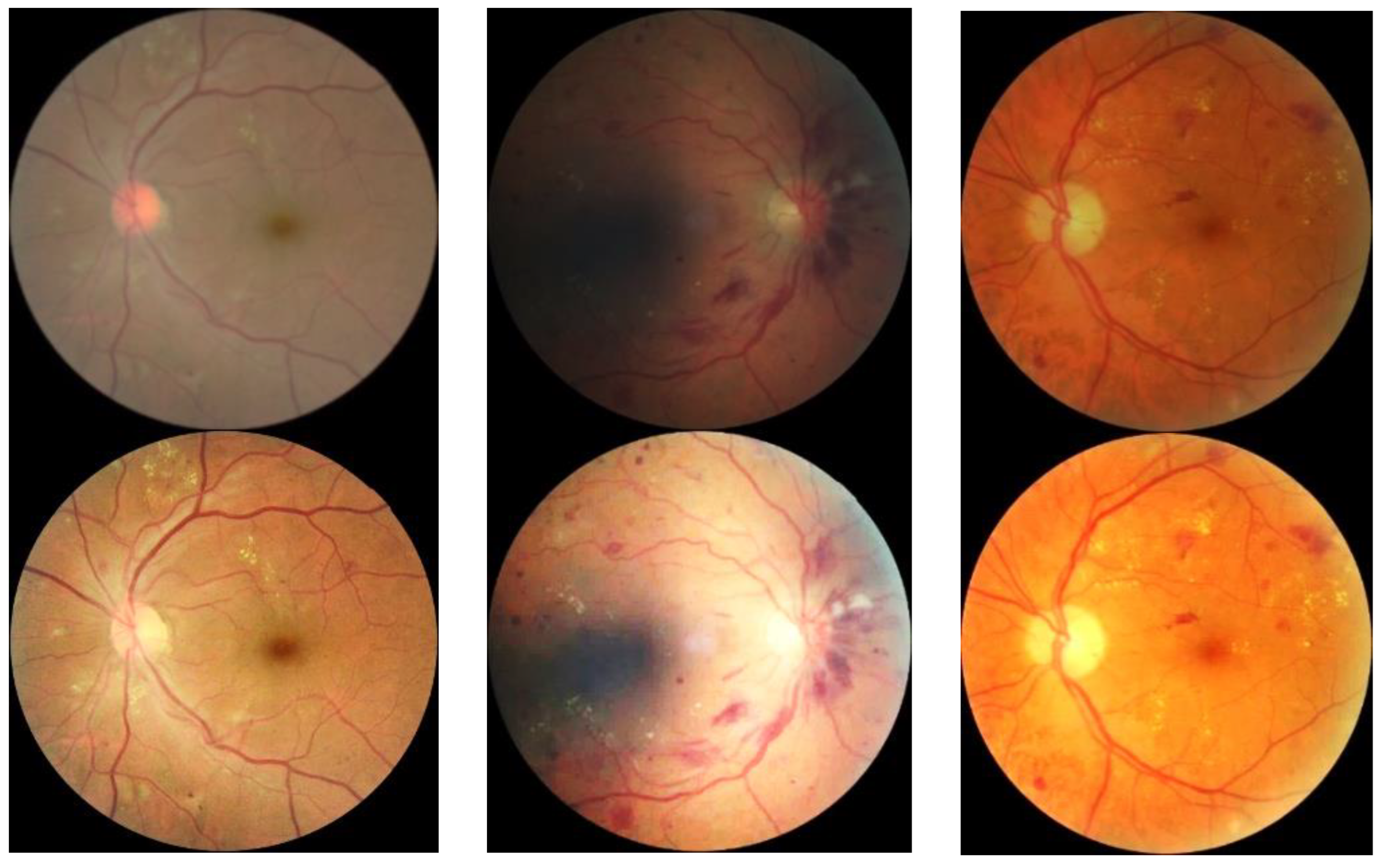






| Disease Category | Findings Observable upon Dilated Ophthalmoscopy | Numbers |
|---|---|---|
| No apparent retinopathy | No abnormalities | 25,810 |
| Mild NPDR | Microaneurysms only | 2443 |
| Moderate NPDR | Severer than just microaneurysms but milder than severe NPDR | 5292 |
| Severe NPDR | Any of the following and no signs of proliferative retinopathy:
| 873 |
| PDR | One of the following two:
| 708 |
| Dataset | Health | Mild NPDR | Moderate NPDR | Severe NPDR | PDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eye-PACS | 25,810 | 2443 | 5292 | 873 | 708 |
| Data pre-processing | 3821 | 2034 | 3733 | 658 | 643 |
| Image generation | 3821 | 3813 | 3733 | 3678 | 3528 |
| Method | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DenseNet-121 | 83.4 | 82.3 | 82.3 |
| Inception-V3 | 87.3 | 89.4 | 87.2 |
| ResNet-50 | 89.5 | 90.7 | 85.6 |
| RepVGG | 90.1 | 91.2 | 91.2 |
| Proposed method | 92.3 | 92.5 | 92.5 |
| Method | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ResNeXt-50 | 89.9 | 90.8. | 88.9 |
| Proposed method | 92.3 | 92.5 | 92.5 |
| Method | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DenseNet-121 | 81.7 | 80.6 | 82.4 |
| Inception-V3 | 87.0 | 90.2 | 84.3 |
| ResNet-50 | 87.6 | 87.4 | 84.6 |
| RepVGG | 89.9 | 86.1 | 90.8 |
| Proposed method | 90.6 | 91.5 | 93.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, W. Fundus Image Generation and Classification of Diabetic Retinopathy Based on Convolutional Neural Network. Electronics 2024, 13, 3603. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13183603
Zhang P, Zhao J, Liu Q, Liu X, Li X, Gao Y, Li W. Fundus Image Generation and Classification of Diabetic Retinopathy Based on Convolutional Neural Network. Electronics. 2024; 13(18):3603. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13183603
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Peiming, Jie Zhao, Qiaohong Liu, Xiao Liu, Xinyu Li, Yimeng Gao, and Weiqi Li. 2024. "Fundus Image Generation and Classification of Diabetic Retinopathy Based on Convolutional Neural Network" Electronics 13, no. 18: 3603. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13183603
APA StyleZhang, P., Zhao, J., Liu, Q., Liu, X., Li, X., Gao, Y., & Li, W. (2024). Fundus Image Generation and Classification of Diabetic Retinopathy Based on Convolutional Neural Network. Electronics, 13(18), 3603. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13183603






