Abstract
Building facade completion is an important part of digitizing the structures of buildings using computer technology. Due to the intricate textures and structures in building facade images, existing image-completion algorithms cannot accurately restore the rich texture and detailed information. In response, this paper proposes a novel network to simultaneously recover the texture and semantic structural features of building facades. By incorporating dynamic convolutions into each layer of the feature encoder, the shallow layers of the completion network can create a global receptive field, thus enhancing the model’s feature-extraction capability. Additionally, a spatial attention branch is integrated into the dynamic convolution module to boost the correlation between the completion area and its surrounding edge area, resulting in improved edge clarity and accuracy of the completed facade image. Experimental results on multiple public image datasets demonstrate that the proposed model in this paper achieves state-of-the-art results when applied to real-world datasets.
1. Introduction
Urban environments are characterized by their complexity and often contain obstructions such as vegetation, pedestrians and vehicles, which unavoidably occlude building facades [1]. These obstructions can impede subsequent applications such as semantic segmentation, facade analysis, building structure recovery and facade reconstruction. Recovering the occluded portions of facade images is a recurrent problem that is currently facing three main challenges: (1) The lack of large-scale datasets for building facade completion has made it difficult for many advanced image-completion networks to train high-precision completion models [2]. (2) Unlike images of faces or natural landscapes, building facade images are artificial scenes that contain various features, including texture, structure, dimension and regularity. However, existing image-completion algorithms struggle to maintain consistency in both local and global building facade features, resulting in completion results that do not adhere to building priors (as shown in the yellow box in Figure 1 NS algorithm). (3) The deep learning-based image-completion framework represented by Yu et al. [3] has introduced contextual attention mechanisms to capture long-range dependencies between the completion area and global features. However, it does not adequately handle the correlation between the completion area and its edge region, often resulting in distortions in the edge structures and blurred textures (as shown in the red box in Figure 1, Deepfill).

Figure 1.
Building facade-completion results of different algorithms: NS [4], Deepfill [3] and ours. The yellow box indicates the completion region, which lacks architectural prior knowledge and appears unreasonable. The red box indicates the blurred edge structures.
To address the aforementioned challenges, we developed a dynamic convolution module to extract features. Dynamic convolution continuously updates the weights of the convolution kernel according to the input data, which effectively increases the model’s capacity. As a result, the model can learn the features of building facades with fewer parameters, reducing the risk of overfitting and dependence on large-scale datasets. Additionally, we enhanced the global receptive field based on dynamic convolution, effectively capturing the long-range dependencies of the completion area and ensuring the consistency of the overall structure of the building facade. Furthermore, we incorporated a spatial attention branch to identify the edge features. It enhanced the correlation between the completion area and the surrounding area, making the edges of the completion area clearer. Finally, we conducted comprehensive comparative experiments based on multiple benchmarks. the results showed that the proposed model achieved state-of-the-art performance on real-world building facades.
In summary, the technical contributions of this paper are as follows:
- 1.
- We propose a novel facade-completion network based on dynamic convolution that allows training with fewer model parameters, reducing the risk of overfitting. The network uses a global receptive field to process image features, ensuring the relevance between texture and semantic structural features in both the completion area and the global area of the building facade.
- 2.
- We introduce a spatial attention branch to enhance the feature representation of the missing parts by strengthening the features of the edge region of the mask and weakening the background features, effectively improving the local structural correlation between the completion area and the surrounding area in building facades.
2. Related Work
2.1. Image Completion for Facade
Existing building facade-completion algorithms can be roughly divided into two categories: example-based methods and neural network-based methods.
Example-based methods generally aim to infer the layout of the facade occlusion based on the known structure arrangement. For example, Dai et al. [5] adopted irregular rectangular lattice (IRL) to partition the layout of semantic components on the building facade, such as doors and windows, and represent them as a semantic label map. Then, a genetic algorithm is used to guide the completion of missing areas based on the uncovered parts, ensuring overall structural consistency. Huang et al. [6] proposed an automatic guided patch-based building facade-restoration method utilizing mid-level structural clues. First, the feature points of the known area are detected, and then the arrangement rules are extracted. Finally, the completion area’s texture pixels are guided based on the regularity between the feature points, and the texture completion is performed using pixel offsets. Kottler et al. [7] adopted an improved patch-based completion method, where a rough structure completion is first performed based on context information and average pixel values. Then, an intuitively selected parameter is weighted with image pixels to further optimize the completion results. However, these methods lack the generalization capabilities of deep learning algorithms and are only suitable for a small number of building facade images with regular arrangements.
Guided by [5], Hensel et al. [8] also employed IRL to parse the semantic components of facades and represent them as a semantic label map. In contrast to [5], they used LSTM to learn the arrangement of doors and windows on building facades and utilized neural network learning to infer the semantic layout of missing areas of doors and windows. Then they combined the texture information to realize facade completion. However, this method had limitations in dealing with irregular facade structures since it relied on the regular arrangement structure of unobstructed parts to infer the consistent arrangement of obstructed parts. Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) [9] has been used for a number of computer vision tasks such as face completion [10], image dehazing [11], image deraining [12,13], facade synthesis [14] and facade completion. Reference [15] proposed the use of semantic segmentation and GANs for building facade completion, which was implemented using the general image-completion algorithm, DeepFillV2 [16]. This method can achieve facade completion for a wider range of building types. However, it relies on large-scale training data. Obtaining a large number of building facade images is a challenging task, and existing open-source building facade datasets are typically small, which limits the application of this method. DeepFillV2 has a relatively complex network structure, which includes two stages: coarse network and fine network. The coarse network is mainly used for structural completion, while the fine network is used for texture repair. However, training a complex network structure on a small dataset is prone to overfitting, which often leads to blurred edges between the completion area and the surrounding areas. Kottler et al. [17] proposed a three-stage GAN for completing the facade contours, facade semantic structures and facade textures, respectively. However, obtaining a building facade semantic label dataset is a massive task, and the joint training of the three GAN networks increases the model’s complexity, reducing its stability.
2.2. Image-Completion Algorithm
Existing image-completion methods can be broadly classified into two categories: traditional image-completion methods and deep learning-based image-completion methods.
Traditional image-completion methods mainly include diffusion-based completion and exemplar-based completion. Diffusion-based methods [18,19,20] grow the edge pixels at the completion location inward along the same feature as the effective area of the image, diffusing to fill the entire area to be repaired. Example-based methods [21,22,23] search for similar image blocks in the original image and copy them to the completion area. However, due to the high computation cost of the search and optimization process, these methods are not suitable for handling building facade images with complex textures. Traditional image-completion algorithms only rely on shallow texture information, which is inadequate for completing building facades that contain objects such as windows and doors with rich geometric structure features.
Compared to traditional image-completion methods, deep learning-based completion methods can obtain high-level image features, strong independence and robustness, and achieve high accuracy and good results in image completion. Pathak et al. [24] combined the encoding–decoding structure with convolutional neural networks and utilized GANs as auxiliary structures to develop a context encoder. The context encoder uses multiple convolutional layers in the encoding–decoding structure to parameterize the semantic-sensitive content, with the ability to synthesize high-order features in a more extensive spatial range. However, this method can only handle very low-resolution inputs due to the difficulty in training. Global-Local Consistent Image Completion (GL) [25] employed a fully convolutional network for image completion. Two global and local discriminator networks are adopted to significantly improve the image-completion quality. The partial convolution algorithm [26] greatly enhanced computational efficiency by incorporating a mask into the convolution operation and distinguishing between completion and incompletion pixels, thus improving its sensitivity. Deepfill [3] proposes a coarse-to-fine network based on the GL method. This method also has two discriminators, a global discriminator and a local discriminator, and the generator part consists of two-stage feed-forward generation networks, including rough and refined completion. Additionally, a content-aware layer is introduced into the generator to extract relevant information for completion from effective features that are far away from the completion part, increasing the spatial consistency of image module perception. Cr-fill [27] used joint training with an auxiliary context-reconstruction branch (CR-loss) to achieve good completion performance without using any attention layers.
However, existing deep learning-based image-completion methods often have complex network structures and suffer from overfitting when trained on small-scale building facade datasets. Additionally, these methods struggle to maintain global and local consistency in building facade images which possess rich geometric structures and texture features.
Compared to the previous methods, the proposed facade-completion network has the advantage of a simple network structure, strong feature representation ability and less dependence on large datasets and facade semantic labels.
3. Method
As shown in Figure 2, our facade-completion network consists of a generator and a multi-scale discriminator. The generator employs dynamic convolution to adaptively extract complex structural features of the facade and produce more realistic completion results. The multi-scale discriminator, on the other hand, evaluates the fidelity of the completed image across various resolutions, thereby boosting the overall quality of the completed building facade. Our network aims to tackle the challenge of missing texture in building facade images and accurately distinguish between real and fake generated images to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of image restoration.
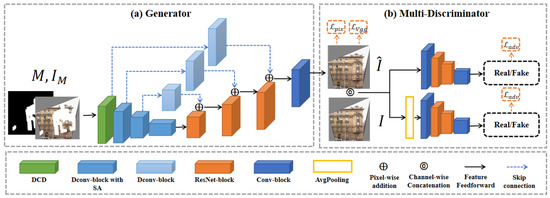
Figure 2.
Overview of the model architecture. (a) Generator, where M represents the binary mask of completion area, represents the input data, which is processed by DCD (dynamic convolution with dynamic channel fusion) to extract features. The Dconv-block consists of multiple DCD blocks, while the Dconv-block with SA includes a spatial attention branch. The ResNet-block is used for upsampling and restoring the image size, and the image channel number is finally recovered through a standard convolution block. (b) Multi-scale discriminator, where represents the generated image, and I represent the real image. One branch evaluates the texture of the image at its original size, while the other branch evaluates the texture of the image at half of its original size.
3.1. Dynamic Convolution with Dynamic Channel Fusion
In the task of image completion, a sufficiently large receptive field is required to predict the contextual information of the missing region. The larger the receptive field, the more contextual information the model can perceive, thereby improving the accuracy of image completion.
In recent image-completion works [3,16,25], dilated convolutions have been used to achieve this functionality. However, the convolution kernels of dilated convolutions are sparse and may skip some local details, affecting the completion results. Multi-scale fusion has been adopted in some work [28,29] to expand the receptive field and ensure dense convolution kernels. However, because of the complex texture and structure features of building facades, with multi-scale fusion it is difficult to adaptively extract complex structural details. The fixed convolution kernel cannot adapt to missing objects of different sizes and irregular shapes. The weights of the fixed convolution kernel also cannot be adjusted for the different characteristics of the input data. On the other hand, conventional dynamic convolutions, such as Condconv [30] and DRconv [31], also have drawbacks. They need to calculate the weighted sum of multiple static convolution kernels, which undoubtedly increases the computational cost of the model. Moreover, conventional dynamic convolutions calculate the weighting coefficients between static convolution kernels through attention mechanisms, which can cause smaller weighting coefficients to have a disproportionate impact on feature representation in network layers.
Inspired by [32], we propose a dynamic convolution module based on dynamic channel fusion. As shown in Figure 3, our dynamic convolution module utilizes dynamic channel fusion to generate convolution kernels. Firstly, image features are fed into a dynamic attention mechanism similar to the Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) module [33]. The dynamic attention mechanism performs global average pooling on the feature maps of each channel to reduce the input image to one dimension, obtaining a global description vector . This effectively overcomes the problem that the receptive field of the convolution operation can only obtain local contextual information.
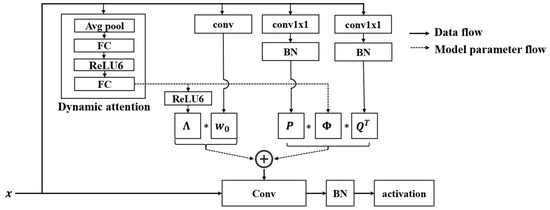
Figure 3.
Dynamic channel fusion convolutional structure diagram.
The dynamism of our network is mainly reflected in the fact that the weights of our convolution kernels are obtained from the conv and conv1×1 layers shown in Figure 3. In other words, the weights for feature processing are dynamically determined by the input image information. We capture the dependencies between channels through two fully connected layers to improve the overall consistency of the feature map. The fully connected layers output two matrices, set the dimension of the fully connected layer to to obtain the channel attention matrix and set the dimension of the fully connected layer to to obtain the channel fusion matrix . is a diagonal matrix of size , where the values on the diagonal represent the attention weights of each channel. Compared with the traditional weights of size , it offers more feature details, further improving the feature learning ability of the image-completion network. In contrast to the SE module, we adopt three convolutional branches parallel to the dynamic channel attention module to obtain the static feature weight matrix, , where k is the dimension of the convolution kernel, as well as the matrices and , used for channel compression and expansion. The final dynamic convolution kernel weight can be expressed by the following equation:
where x represents the input data, ∗ represents matrix multiplication. By performing matrix multiplication between the channel attention matrix and the static feature weight , the convolution kernel’s ability to learn complex structural features in the image is enhanced. performs dynamic channel fusion on the input feature weights, which not only improves the compactness of the model and avoids the suppression of key features by small dynamic coefficients, but also overcomes the problem of joint optimization between static kernel weights and dynamic attention mechanisms.
3.2. Spatial Attention Branch
In convolutional neural networks, the receptive field refers to the size of the input data region where each neuron in the input layer can extract features. Larger receptive fields can help the network learn more global features and improve the model’s generalization ability. Increasing the receptive field of a network is usually achieved by increasing the network depth or introducing a global receptive field module in the deeper layers. In image-completion tasks, a global receptive field should be introduced in the shallower layers of the network to enable the model to obtain a larger receptive field as early as possible [34]. Therefore, we use dynamic convolutions with larger receptive fields in the first layer of the generator to extract global features from the input image. The kernel size of the first dynamic convolution is . We propose the Dconv-block module that incorporates dynamic convolution into residual blocks to improve the ability of the image-completion network to learn features of building facade images, thus further enhancing the accuracy of the network. Specifically, dynamic convolution can dynamically adjust the weights of the convolution kernels based on the different features of the input data, thereby better adapting to the complexity of the data. Meanwhile, residual modules can avoid problems such as gradient disappearance when using deep dynamic convolution. As shown in Figure 4, the generator in our network uses a residual network module composed of dynamic convolutions to construct a deep feature-extraction network. Each residual block contains three dynamic convolution layers of kernel size .
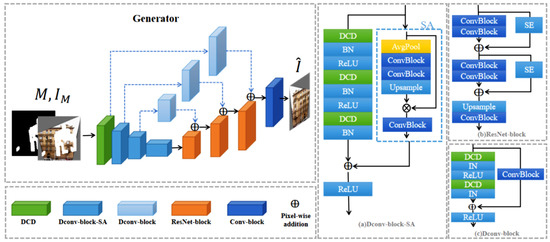
Figure 4.
Generator and its network modules. (a) Dconv-block-SA is a dynamic convolution module with a spatial attention branch. (b) ResNet-block is a residual module used for feature-decoding operation. (c) Dconv-block is a dynamic convolution module used for feature processing across channels.
Although the dynamic convolution layer based on dynamic channel fusion can effectively transmit valid global feature information to the deep layers of the network, ensuring the structural consistency of the complete features and global features. However, during the training process, the channel feature weight corresponding to local feature information with a less influential role in learning key features is small, which may cause the network model to ignore this detailed information. The local detail information is also crucial to obtain more realistic building facade-completion images. As shown in Figure 4a, we introduce the spatial attention mechanism (SA) into the branch to enable the dynamic residual module to learn this local feature information. The spatial attention mechanism first performs average pooling to reduce the feature map and expand the receptive field while reducing the computation cost. Then, two standard convolution modules with convolution kernel sizes of are used for local feature sampling to improve the model’s attention to the edge parts of the completion area. Next, an upsampling module is used to restore the features to their original size, obtaining locally enhanced features. Finally, pixel-wise multiplication is performed between the input feature map and locally enhanced features to increase the weight of local features in the completion area of the feature map. Therefore, the SA module can be expressed by the formula:
where represents the input feature map, represents the locally enhanced feature information and ⨂ represents the pixel-wise feature multiplication operation.
Next, we use the feature addition method to achieve feature fusion between the globally features obtained after processing through a three-layer dynamic convolutional network, and the locally enhanced features . Finally, the fused features are input into the ReLU activation function to obtain the output result y of the Dconv-block-SA module.
where represents the ReLU activation function, and represents the element-wise addition of feature values.
3.3. Network Structure
The overall generator adopts the structural framework of U-Net [35], with the key difference being the introduction of the dynamic convolution module, Dconv-block, in the skip connection part. Utilizing the dynamic convolution module for dynamic convolution operation on features within the skip connection part enables better extraction of image features and makes the generated results more accurate.
The feature-decoding part of the model, as shown in Figure 4b, is represented by ResNet-blocks, where the residual modules in the decoding part consist of two residual networks and an upsampling layer. These components effectively extracting information from low-resolution feature maps and gradually restore them to high-resolution images. Each residual network consists of two standard convolution operations and an SE module branch, which can further enhance the expression power of feature maps and the ability to extract key features, thus generating more realistic images.
We use a multi-scale discriminator for adversarial training to ensure that the completed images exhibit realistic texture details, effectively differentiating between the real high-resolution image and the synthesized image . Consequently, the loss function of the discriminator is given by , where N denotes the number of discriminator sub-modules in the multi-scale discriminator, which is set to in this study, and , where represents the nth discriminator, G represents the generator, M represents the mask of the completion area. The features at different scales are averaged using average pooling.
3.4. Loss Functions
The loss function of the image-completion network aims to measure the difference between the generated image and the real image, thereby guiding the optimization of the generator network. By optimizing the loss function, the generated images can be made closer to the real images. We use adversarial loss, pixel-wise loss and VGG loss to train the facade-completion network.
GAN loss: The role of the adversarial loss function is to train a discriminator network to make the generated images from the generator network as close as possible to real images, thereby improving the quality and realism of image completion. We first train the discriminator to increase the probability of accurately identifying real samples, inproving its ability to distinguish real samples. Subsequently, we train the generator to maximize the function , that is, to reduce by generating better quality images . Therefore, our adversarial generative loss function can be represented by Equation (4):
where represents the predicted image, represents the real image, represents the probability of the discriminator identifying the fake image and similarly, represents the probability of the discriminator identifying the real image.
Pixel-wise loss: Pixel-wise loss function, as knowns as L1 loss or mean absolute error (MAE) loss is used to measure the difference between the generator output image and the real image. The pixel-wise loss function calculates the difference between each pixel of the generated image and the real image and sums these differences to obtain a scalar value representing the degree of difference between the generated and real images. By minimizing the pixel-wise loss function, the generator can learn how to reconstruct missing areas in the image, making the generated image as similar as possible to the real image at the pixel level. Therefore, our pixel-wise loss function, which can be expressed as:
where represents the predicted image, represents the real image and represents L1 norm.
VGG loss: The VGG loss function aims to leverage a pre-trained VGG network to extract features. It calculates the difference between the generated image and the real image in the feature space, and guide the generator to learn how to generate completion results that are closer to the real image. We use a pre-trained VGG19 model to extract features, which consists of two parts: perceptual loss function and style loss function.
The formula for the perceptual loss function is as follows:
where represents VGG feature-extraction function, and represent the number of channels and size of the image in the layer j, respectively.
The style loss function takes as input the corresponding regions in the predicted completed image and the real image . And then feeds them into the pre-trained VGG19 network. The feature values are then extracted from each layer and a Gram matrix is used to measure the correlation between features in different parts of the image. Finally, the L1 loss is used to calculate the distance between them. As shown in Equation (7):
where M represents the binary mask, and ⊙ denotes multiplying the pixel values at corresponding positions.
Therefore, the VGG loss function can be represented by the Formula (8).
where and are, respectively, the weights for the perceptual loss function and the style loss function.
As a result, the loss function of the proposed completion network can be formulated as shown in Equation (9):
where , and are, respectively, the weights for the adversarial loss function , pixel-wise loss function and VGG loss function . We set , , .
4. Experiment
4.1. Experimental Settings
Data and metrics: We used a total of 606 images from CMP facade dataset [36], 15,000 images from Paris Street View dataset [24], 180,000 images from CelebA dataset [37] and 4631 images from Places2 dataset [38]. Due to limited memory space of the device, we only extracted a portion of Places2 dataset to train the network model. In real life, the occluded parts of building facades are irregular. Therefore, we used the irregular mask dataset provided by [26] to generate irregular missing regions. To quantitatively evaluate the completion performance of the model on different datasets, we used the following different metrics:
- MAE: Mean Absolute Error (MAE) between predicted values and ground truth can roughly reflect the ability of the model to reconstruct the content of the original image. The smaller the MAE value, the better the generated result.
- PSNR: Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) is a widely used objective image quality evaluation metric that calculates the error between corresponding pixels in two images. The higher the PSNR value, the less distortion and better performance.
- SSIM: Structural Similarity (SSIM) [39,40] is another reference image quality evaluation metric that measures image similarity from three aspects: luminance, contrast and structure. SSIM has a value range of [0,1], with a larger value indicating smaller image distortion.
- FID: Fréchet Inception Distance [41] uses the Inception v3 [42] image classification model to extract visual features from original images to separately measure the similarity between two sets of images. It is a metric that calculates the distance between feature vectors of real and generated images.
- LPIPS: LPIPS [43] uses a pre-trained VGG or Alex network to measure the perceptual image similarity between images, where a smaller value indicates a higher level of similarity.
We set the training images dimension to , and perform random cropping and flipping operations on the data. Subsequently, we concatenate the data with the mask image at the channel level to form four-channel image data as input to the model. For our image-completion network, we use Adam optimization function, which dynamically adjusts the learning rate of each parameter using the first and second-order moment estimates of the gradient. We define the initial learning rate as . All the model training and evaluation were conducted on the same platform: an Ubuntu server with an Intel i7-9700F CPU running at 3 GHz, 32 GB of memory, 512 GB of swap space and two 2080Ti graphics cards with a total of 24 G of GPU memory.
4.2. Comparison with Existing Work
Quantitative Comparisons: In this study, we quantitatively compare our proposed model with several other image-completion algorithms, including three non-deep learning algorithms: FRS [44], NS [4], Telea [45] and four deep learning-based algorithms: PEN-Net [28], Cr-fill [27], DeepFillV2 [16] and Lama [34].
Firstly, we conducted experiments on CMP facade dataset and evaluated the algorithm performance using three quantitative metrics, namely PSNR, SSIM and LPIPS.
As shown in Table 1, in terms of SSIM, when the missing area of an image is extremely small, i.e., when the coverage rate of the mask is between 10% and 20%, the structure of the building facade image is relatively intact. Therefore, traditional image-completion algorithms such as Telea utilize the available information in the image for completion and achieve good results in terms of SSIM. However, in this scenario, our proposed completion algorithm achieves SSIM results second only to the Telea algorithm. Moreover, as the missing area increases, our proposed algorithm demonstrates much better completion performance in terms of SSIM than other image-completion algorithms. The Lama algorithm utilizes the global receptive field of Fourier convolution to effectively handle images with large areas missing. When the missing area of an image is extremely large, i.e., when the coverage rate of the mask is between 40% and 60%, our proposed image-completion algorithm performs only second to the Lama algorithm in terms of PSNR. However, considering the three metrics of SSIM, PSNR and LPIPS, as well as the completion results of building facades with different coverage rates, our algorithm demonstrates better overall completion quality, far exceeding existing image-completion algorithms.

Table 1.
The quantitative evaluation results on CMP facade dataset [36] for various mask coverage rates in the ranges 10–20%, 20–40% and 40–60%. The symbol “↓” indicates that a lower value is better, while “↑” indicates the opposite. The best scores are in bold for emphasis. The following text follows the same notation and will not be annotated individually.
Next, we will conduct a quantitative evaluation of the inpainting results of our proposed algorithm on the Paris Street View dataset and the CMP facade building semantic structure label dataset. This time, we will use three quantitative metrics, MAE, PSNR and SSIM, to evaluate the quality of the inpainting algorithm and compare it with several state-of-the-art image inpainting algorithms. As shown in Table 2, our algorithm demonstrated a high peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) on the Paris Street View dataset. It also achieved the highest structural similarity index (SSIM) compared to other inpainting algorithms, indicating that the structure of our output was most similar to the ground truth. Concerning mean absolute error (MAE), our algorithm had smaller content differences with the ground truth compared to other algorithms. On the CMP facade semantic label dataset, our proposed inpainting algorithm still outperformed other inpainting algorithms in terms of MAE, PSNR and SSIM, demonstrating better inpainting results.

Table 2.
The quantitative evaluation results of several deep learning-based completion algorithms and our proposed building facade-completion algorithm on Paris Street View dataset [24] and CMP facade semantic label dataset [36] in terms of MAE, PSNR and SSIM.
Overall, our algorithm outperformed other image-completion methods on the building facade image datasets, exhibiting higher completion quality and more accurate detail preservation for both texture and structural information. This was demonstrated through better performance in terms of PSNR, SSIM and MAE on both the Paris Street View and CMP facade semantic label datasets.
Qualitative Comparisons: Similarly, we compared the quality of the proposed building facade-completion algorithm’s generated results with several commonly used non-deep learning image-completion algorithms: FRS, NS, Telea and state-of-the-art deep learning-based image-completion algorithms: PEN-Net, DeepFillV2, Cr-fill and Lama.
As shown in Figure 5, we trained our proposed dynamic convolution-based completion network and several commonly used image-completion models on the CMP facade dataset. We can see that compared to non-deep learning image-completion algorithms, our proposed image-completion algorithm can better restore the structural and texture information, resulting in more realistic completion results. Compared to deep learning-based image-completion algorithms, our proposed building facade-completion algorithm has a larger receptive field, which allows for obtaining more information from surrounding pixels and a better understanding of the contextual relationships in the image. Therefore, Our algorithm’s results exhibit improved texture feature integrity and diversity.
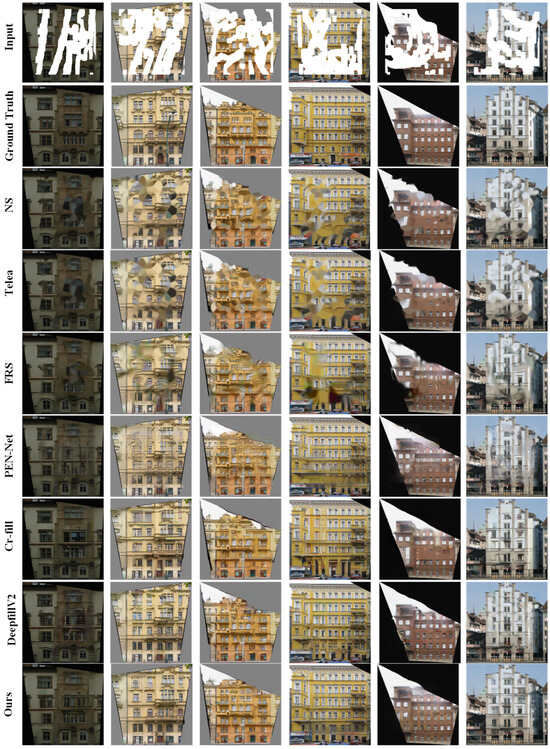

Figure 5.
The first row shows the input data, and from top to bottom, each row shows the output results of the NS algorithm, Telea algorithm, FRS algorithm, PEN-Net algorithm, Cr-fill algorithm, DeepFillV2 algorithm, the ground truth data and the output results of our proposed model.
Lama algorithm uses Fourier convolution to construct the image-completion network, to give the model a global receptive field during feature learning. However, Fourier convolution can only process signals in the frequency domain, and the convolution kernel in the spatial domain is still a fixed small matrix, which cannot adapt to complex features to a certain extent. Moreover, the frequency domain convolution operation performed in the Fourier domain may lose spatial information. We use dynamic convolution to extract features by dynamically adjusting the weights of the convolution kernel, enabling it to adaptively extract complex feature information from the input data. This approach can better handle the complex texture and structural features of building facades. Additionally, we introduce a spatial attention branch to preserve the spatial information of pixel features. As shown in Figure 6, compared with the Lama algorithm, our completion algorithm has more realistic completion effects on texture details.

Figure 6.
The three rows show the comparison between our proposed algorithm and the Lama algorithm in terms of the completion effect on the CMP facade dataset.
As shown in Figure 7, we conducted experiments on the Paris Street View dataset, and compared with the existing image-completion algorithms, our completion algorithm still has more realistic visual effects.

Figure 7.
That shows the experimental results of several deep learning-based image-completion algorithms on the Paris Street View dataset. The top row is the input image, and the bottom row is the experimental result of our proposed completion algorithm. The results of the four most advanced image-completion algorithms are shown in the middle.
Semantic Fill Study: To demonstrate the effectiveness of our algorithm in recovering the semantic structure of building facades, we conducted experiments on the building facade semantic label image dataset provided by the CMP facade dataset and compared it with several existing image-inpainting algorithms. As shown in Figure 8, we can see that our proposed inpainting network has a larger receptive field, which can better capture the contextual structural information of the images. Additionally, we introduced a spatial attention mechanism to preserve the positional information between pixels. Therefore, our algorithm produces visually superior inpainting results on the building facade semantic structure dataset compared to other image-inpainting algorithms.
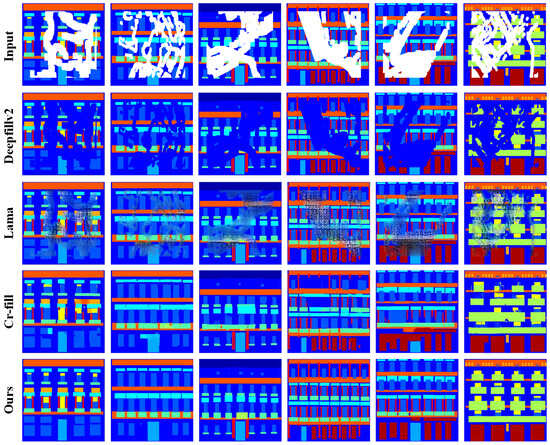
Figure 8.
That shows the experimental results of our proposed algorithm and several popular image-inpainting algorithms on the semantically labeled images from the CMP facade dataset. From top to bottom, the first row shows the input image, the last row shows the results of our proposed algorithm and the middle part shows the output results of three state-of-the-art image-inpainting algorithms, namely DeepFillV2, Lama and Cr-fill.
User Study: We conducted a user study on the results of building facade completion using the test set of the CMP facade dataset. We set up A/B/C/D options on a WeChat questionnaire, with one algorithm’s result image in each option, and the order of the result images for each algorithm was randomized. One of the images was the result of our completion algorithm, and the other three were the results of the existing algorithms for completion. We invited 12 participants to choose which image was closer to the real building facade image out of the four result images. We collected 36 sets of data for evaluation and counted the frequency of each algorithm selected. As shown in Figure 9, our algorithm outperformed the other compared algorithms in the user evaluation.
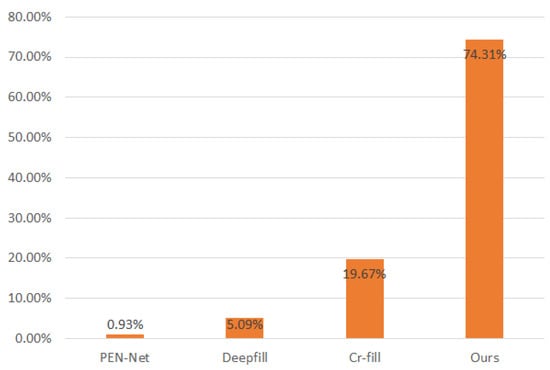
Figure 9.
Bar chart of the user study results on the CMP facade dataset.
Few-sample Completion Study: We proposed an image-inpainting algorithm based on the dynamic convolution module, which can synthesize corresponding convolution kernels according to the complex structural features of building facades, thus achieving effective feature extraction of the input data. Therefore, dynamic convolution can be more generalizable than traditional convolution in some scenarios. To further explore the generalization ability of our proposed inpainting algorithm, we conducted experiments on the Paris Street View dataset in four stages. In the first stage, we used all the data in the dataset for experiments. In the second stage, we randomly sampled half of the data in the original dataset for experiments. In the third stage, we randomly sampled one-quarter of the data in the original dataset for experiments. In the fourth stage, we randomly sampled one-eighth of the data in the original dataset for experiments. We compared our proposed algorithm with two other image-inpainting algorithms, Cr-fill and DeepFillV2, and recorded the changes in PSNR values. As shown in Figure 10, with a decrease in the number of samples in the dataset, the gap between the PSNR values of the completion results of our proposed algorithm and the other two completion algorithms becomes larger. Moreover, as the number of samples in the dataset decreases, our algorithm only experiences a slight decrease in the PSNR value of the completion results, while the PSNR values of the completion results of the other two algorithms have a significant downward trend. Therefore, it can be concluded that our proposed building facade-completion algorithm has a strong generalization ability. This also indicates that our proposed building facade-completion algorithm can still exhibit good performance when dealing with datasets with a small number of samples, demonstrating its practicality.
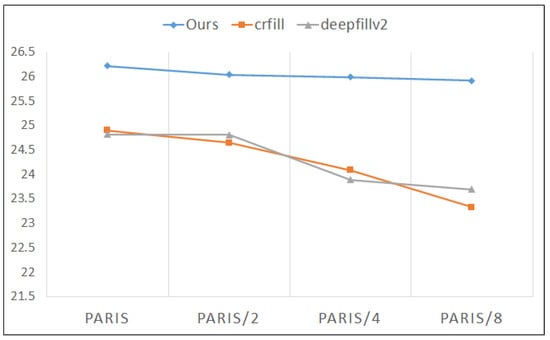
Figure 10.
That shows the PSNR value change curves of the completion results for our algorithm, Cr-fill and DeepFillV2 as the number of samples in the Paris Street View dataset decreases. The vertical axis represents the PSNR value, the blue curve represents the variation curve of our proposed algorithm, the orange curve represents the variation curve of the Cr-fill algorithm and the gray curve represents the variation curve of the DeepFillV2 algorithm.
4.3. Ablation Study
In this section, we will conduct ablation experiments to analyze the roles of our proposed algorithm components, the dynamic convolution module based on dynamic channel fusion and the spatial attention module, in image completion.
Effectiveness of Dconv-block: We set the structure-completion network of structureFlow [46] as the baseline and then added different dynamic convolution modules to help the model learn features better, namely baseline+condconv and baseline+DRconv. Condconv and DRconv are popular dynamic convolution modules proposed in recent years. Similarly, we added our proposed dynamic convolution module to the baseline and conducted experiments using the CMP facade dataset. We used four metrics, namely MAE, PSNR, LPIPS and FID, to quantitatively evaluate the performance. As shown in Table 3, after adding the other two dynamic convolution modules, the completion performance of the baseline has been improved in terms of LPIPS and FID indicators, indicating that dynamic convolutions can provide better feature representation for image-completion networks. When the baseline is combined with the Dconv-block, it achieves the best performance in terms of the MAE, PSNR, LPIPS and FID metrics. Therefore, the effectiveness of the dynamic convolution module in the image-inpainting task was demonstrated through the ablation experiment, which indicates a positive impact of dynamic convolution on complex structure image inpainting. Moreover, compared with other dynamic convolution modules, Dconv-lock is more effective in improving the quality of image inpainting.

Table 3.
The quantitative evaluation results on the facade validation set for different dynamic convolution modules on the CMP facade dataset [36].
Effectiveness of SA Module: To validate the positive impact of the spatial attention mechanism on the performance of the entire completion network, we compared the completion network model without the SA module and the complete structure-completion network model on the CMP facade dataset, with the baseline as a reference for both. As shown in Table 4, we found that the removal of the SA Module resulted in a decrease in the generation performance of the completion network model in terms of MAE, PSNR, LPIPS and FID. Comparing to the baseline, adding the SA Module resulted in improvements in the MAE and PSNR metrics, while the LPIPS and FID metrics were consistently better than those of the baseline.

Table 4.
The quantitative evaluation of image-inpainting results with and without the spatial attention (SA) branch on the CMP facade dataset [36].
4.4. Experiments with Other Typed Data
The experiments were not only conducted on the building facade dataset but also on other style image datasets to evaluate the generality of our proposed inpainting algorithm. We conducted experiments on other style image datasets to evaluate the universality of our proposed inpainting algorithm. Specifically, we evaluated our method on the Places2 dataset and the CelebA face dataset. The Places2 dataset is a large-scale scene classification dataset, consisting of over 1.8 million 256 × 256 resolution images. To validate the inpainting performance of the model on a small-sample dataset, we selected only 4631 images from the dataset, dividing them into 3631 images for model training and 1000 images for model testing. The CelebA dataset is a large-scale facial dataset containing 180,000 facial images. We divided it into 162,079 images for training and 40,520 images for testing. In addition, we conducted visual evaluations of our proposed image-inpainting algorithm and compared it with commonly used image-inpainting algorithms, DeepFillV2 and Cr-fill, on these two datasets. The evaluation models of these two algorithms on the Places2 dataset were trained using their official pre-trained models. As shown in Figure 11, on the Places2 dataset, the training performance of our proposed completion algorithm on a small dataset is comparable to that of the other two completion algorithms on a large dataset. Comparing the test results on the CelebA dataset, we found that our proposed completion algorithm still has a more realistic completion effect for larger-scale facial missing regions.

Figure 11.
That shows the experimental results on the Places2 and CelebA datasets. The first row displays the input data, the second row shows the results of Cr-fill, the third row displays the results of DeepFillV2 and the fourth row shows the results of our proposed algorithm. The first three columns are the experimental results on the Places2 dataset, while the last three columns are the experimental results on the CelebA dataset.
We compared our proposed image-inpainting algorithm with DeepFillV2 and Cr-fill on CelebA and Places2 datasets and evaluated the quality of the completion results using three metrics: MAE, PSNR, SSIM, LPIPS and FID. As shown in Table 5, for the completion results on the CelebA face dataset, our proposed image-completion algorithm outperforms the other two image-completion algorithms in terms of MAE, PSNR, SSIM, LPIPS and FID. This indicates that our proposed algorithm has good performance and superior results in completing missing parts of face images, improving the visual quality and realism of the images. It also demonstrates the feasibility and effectiveness of the algorithm in practical applications. When comparing the completion results on the Places2 dataset, it can be observed that the DeepFillV2 algorithm performs better in terms of PSNR and SSIM. However, it should be noted that our proposed image completion model was trained on a small sample dataset. Compared with image-completion algorithms trained on large-scale datasets, our proposed algorithm performs similarly in terms of PSNR and SSIM, although it still has advantages, such as good performance on the MAE, LPIPS and FID metric.

Table 5.
Quantitative evaluation comparison on datasets CelebA [37] and Places2 [38].
The experimental results show that our proposed building facade-completion network not only successfully handles the task of building facade completion, but also has universality in other data sets. This means that the network can be extended to deal with other types of image-completion problems, and satisfactory results are obtained.
5. Discussion
In this study, we introduced an image-completion algorithm that leverages dynamic convolution and spatial attention modules to effectively restore building facade images. Our experimental results substantiate the efficacy of our proposed approach, specifically when compared to existing algorithms such as Cr-fill and DeepFillV2 under few sample sizes in the Paris Street View dataset.
This study has two key findings. (1) Effectiveness of Dynamic Convolution Blocks (Dconv-blocks): The dynamic convolution modules enable adaptive adjustment of convolutional kernel weights, facilitating the extraction of complex feature information. By integrating these dynamic convolution modules, we observed a significant improvement in the image-completion outcomes. (2) Introduction of the Spatial Attention Module: Incorporating a spatial attention branch demonstrated a notable ability to preserve the spatial information of pixel features. Comparative experiments highlighted that our algorithm delivers superior visual results.
Although our algorithm shows considerable advantages, there are limitations that warrant discussion. For example, our method may result in noticeable artifacts in the completed areas when synthesize high-definition pixel structures for high-resolution images. Additionally, when performing large-area completion on images with few repetitive features, the restoration effect of our method may be suboptimal. For future work, we plan to explore other state-of-the-art technologies, such as diffusion models [47,48], to further enhance image-completion performance.
6. Conclusions
This paper proposes an image-completion algorithm based on dynamic convolution modules and conducts experiments using a building facade dataset. We have demonstrated through experiments that the dynamic channel aggregation mechanism of dynamic convolutions can enlarge the receptive fields in the encoder of the image-completion network, improve the long-range dependencies of the completion network and effectively alleviate the joint optimization problem between static convolutional kernels and dynamic attention mechanisms. This ensures the structural integrity of the completion region and global features and significantly improves the generation results of the image-completion algorithm for building facade completion. In the dynamic convolution module, we introduced a spatial attention branch to optimize the problem of insensitivity of dynamic convolution to edge information in the completion area. This improvement effectively improves the performance of dynamic convolution and provides the ability to perceive edge information in the completion area. Compared with the state-of-the-art completion algorithms, our proposed completion algorithm can achieve better completion results on building facade images.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.C. and Y.L.; methodology, Z.C. and Y.L.; software, Z.C.; validation, Z.C. and Y.L.; formal analysis, Y.L.; investigation, Z.C.; resources, X.H. and Z.W.; data curation, Z.C.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.C.; writing—review and editing, Y.L. and Z.Z.; visualization, Z.C.; supervision, Y.L.; project administration, Y.L.; funding acquisition, Y.L., X.H. and Z.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (Grant No. 2023J01804), the Natural Science Foundation of Xiamen Municipality of China (Grant No. 3502Z202373035), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (Grant No. 2020J05146) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62006096).
Data Availability Statement
The source code of our method is available at https://github.com/all1new/Dynamic-Convolutional-GAN. More research data of this paper are available by contacting the corresponding authors upon reasonable requests.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Zhenhuang Cai was employed by the company FuJian Zixun Technology Co., Limited. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Yu, B.; Hu, J.; Dong, X.; Dai, K.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, B.; Wu, T.; Hu, Y.; Wang, B. A Robust Automatic Method to Extract Building Facade Maps from 3D Point Cloud Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Nakashima, Y. Improving facade parsing with vision transformers and line integration. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2024, 60, 102463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Lin, Z.; Yang, J.; Shen, X.; Lu, X.; Huang, T.S. Generative Image Inpainting With Contextual Attention. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; Computer Vision Foundation/IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 5505–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertalmío, M.; Bertozzi, A.L.; Sapiro, G. Navier-Stokes, Fluid Dynamics, and Image and Video Inpainting. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2001), with CD-ROM, Kauai, HI, USA, 8–14 December 2001; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; pp. 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.; Riemenschneider, H.; Schmitt, G.; Gool, L.V. Example-Based Facade Texture Synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2013, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Kang, S.B.; Ahuja, N.; Kopf, J. Image completion using planar structure guidance. ACM Trans. Graph. 2014, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottler, B.; Bulatov, D.; Zhang, X. Context-aware Patch-based Method for Façade Inpainting. In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications, VISIGRAPP 2020, Volume 1: GRAPP, Valletta, Malta, 27–29 February 2020; Bouatouch, K., de Sousa, A.A., Braz, J., Eds.; SCITEPRESS: Setúbal, Portugal, 2020; pp. 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensel, S.; Goebbels, S.; Kada, M. LSTM Architectures for Facade Structure Completion. In Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications, VISIGRAPP 2021, Volume 1: GRAPP, Online Streaming, 8–10 February 2021; de Sousa, A.A., Havran, V., Braz, J., Bouatouch,, K., Eds.; SCITEPRESS: Setúbal, Portugal, 2021; pp. 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27 (NIPS 2014), Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, X.; Qiang, Z.; Dai, F.; He, L.; Lin, H. Face Image Completion Based on GAN Prior. Electronics 2022, 11, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Chen, Z.; Lin, J.; Zhou, W.; Chen, J.; Shan, C. AI-GAN: Signal de-interference via asynchronous interactive generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), Shanghai, China, 8–12 July 2019; pp. 228–233. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Chen, Z.; Lin, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, W. Unsupervised single image deraining with self-supervised constraints. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 2761–2765. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, W. AI-GAN: Asynchronous interactive generative adversarial network for single image rain removal. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 100, 107143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, Y.; Loizou, M.; Kelly, T.; Averkiou, M. FacadeNet: Conditional Facade Synthesis via Selective Editing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 5384–5393. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Fukuda, T.; Yabuki, N. Automatic Object Removal with Obstructed Façades Completion Using Semantic Segmentation and Generative Adversarial Inpainting. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 117486–117495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Lin, Z.; Yang, J.; Shen, X.; Lu, X.; Huang, T.S. Free-Form Image Inpainting With Gated Convolution. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2019, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 4470–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottler, B.; List, L.; Bulatov, D.; Weinmann, M. 3GAN: A Three-GAN-based Approach for Image Inpainting Applied to the Reconstruction of Occluded Parts of Building Walls. In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications, VISIGRAPP 2022, Volume 4: VISAPP, Online Streaming, 6–8 February 2022; Farinella, G.M., Radeva, P., Bouatouch, K., Eds.; SCITEPRESS: Setúbal, Portugal, 2022; pp. 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertalmio, M.; Vese, L.; Sapiro, G.; Osher, S. Simultaneous structure and texture image inpainting. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2003, 12, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Zomet, A.; Weiss, Y. Learning How to Inpaint from Global Image Statistics. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2003), Nice, France, 14–17 October 2003; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weickert, J. Coherence-Enhancing Diffusion Filtering. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1999, 31, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.; Shechtman, E.; Finkelstein, A.; Goldman, D.B. PatchMatch: A randomized correspondence algorithm for structural image editing. ACM Trans. Graph. 2009, 28, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yuan, L.; Jia, J.; Shum, H. Image completion with structure propagation. ACM Trans. Graph. 2005, 24, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criminisi, A.; Pérez, P.; Toyama, K. Region filling and object removal by exemplar-based image inpainting. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 1200–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, D.; Krähenbühl, P.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Efros, A.A. Context Encoders: Feature Learning by Inpainting. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 2536–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, S.; Simo-Serra, E.; Ishikawa, H. Globally and locally consistent image completion. ACM Trans. Graph. 2017, 36, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Reda, F.A.; Shih, K.J.; Wang, T.; Tao, A.; Catanzaro, B. Image Inpainting for Irregular Holes Using Partial Convolutions. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2018—15th European Conference, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Proceedings, Part XI. Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 11215, pp. 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Lin, Z.; Lu, H.; Patel, V.M. CR-Fill: Generative Image Inpainting with Auxiliary Contextual Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2021, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 14144–14153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Fu, J.; Chao, H.; Guo, B. Learning Pyramid-Context Encoder Network for High-Quality Image Inpainting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Gao, X. Image Fine-grained Inpainting. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.02609. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Bender, G.; Le, Q.V.; Ngiam, J. CondConv: Conditionally Parameterized Convolutions for Efficient Inference. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2019, NeurIPS 2019, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Wallach, H.M., Larochelle, H., Beygelzimer, A., d’Alché-Buc, F., Fox, E.B., Garnett, R., Eds.; pp. 1305–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J. Dynamic Region-Aware Convolution. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.12243. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Dai, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, D.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, M.; Vasconcelos, N. Revisiting Dynamic Convolution via Matrix Decomposition. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2021, Virtual Event, Austria, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Wu, E. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suvorov, R.; Logacheva, E.; Mashikhin, A.; Remizova, A.; Ashukha, A.; Silvestrov, A.; Kong, N.; Goka, H.; Park, K.; Lempitsky, V. Resolution-robust Large Mask Inpainting with Fourier Convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, WACV 2022, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 3172–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015—18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III. Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W., Frangi, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 9351, pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylecek, R.; Sára, R. Spatial Pattern Templates for Recognition of Objects with Regular Structure. In Proceedings of the Pattern Recognition—35th German Conference, GCPR 2013, Saarbrücken, Germany, 3–6 September 2013; Proceedings. Weickert, J., Hein, M., Schiele, B., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 8142, pp. 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, T.; Aila, T.; Laine, S.; Lehtinen, J. Progressive growing of gans for improved quality, stability, and variation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.10196. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Lapedriza, A.; Khosla, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Places: A 10 Million Image Database for Scene Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Gong, X.; Cong, W.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y. A Method for Extracting Contours of Building Facade Hollowing Defects Using Polarization Thermal Images Based on Improved Canny Algorithm. Buildings 2023, 13, 2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusel, M.; Ramsauer, H.; Unterthiner, T.; Nessler, B.; Hochreiter, S. Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Deep Features as a Perceptual Metric. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; Computer Vision Foundation/IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaup, A.; Meisinger, K.; Aach, T. Frequency selective signal extrapolation with applications to error concealment in image communication. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2005, 59, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telea, A.C. An Image Inpainting Technique Based on the Fast Marching Method. J. Graph. GPU Game Tools 2004, 9, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, R.; Li, T.H.; Liu, S.; Li, G. StructureFlow: Image Inpainting via Structure-Aware Appearance Flow. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2019, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 10684–10695. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Knowledge-Driven and Diffusion Model-Based Methods for Generating Historical Building Facades: A Case Study of Traditional Minnan Residences in China. Information 2024, 15, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).