Methods for Determining Losses and Parameters of Cylindrical-Rotor Medium-Power Synchronous Generators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Objects of Investigation
3. Time-Stepping Two-Dimensional Field-Circuit Simulation
4. Calculation of Losses in the Core of a Synchronous Machine with a Cylindrical Rotor Using the Analytical Method
5. Determination of Parameters of the Equivalent Scheme of a Synchronous Machine with a Cylindrical Rotor
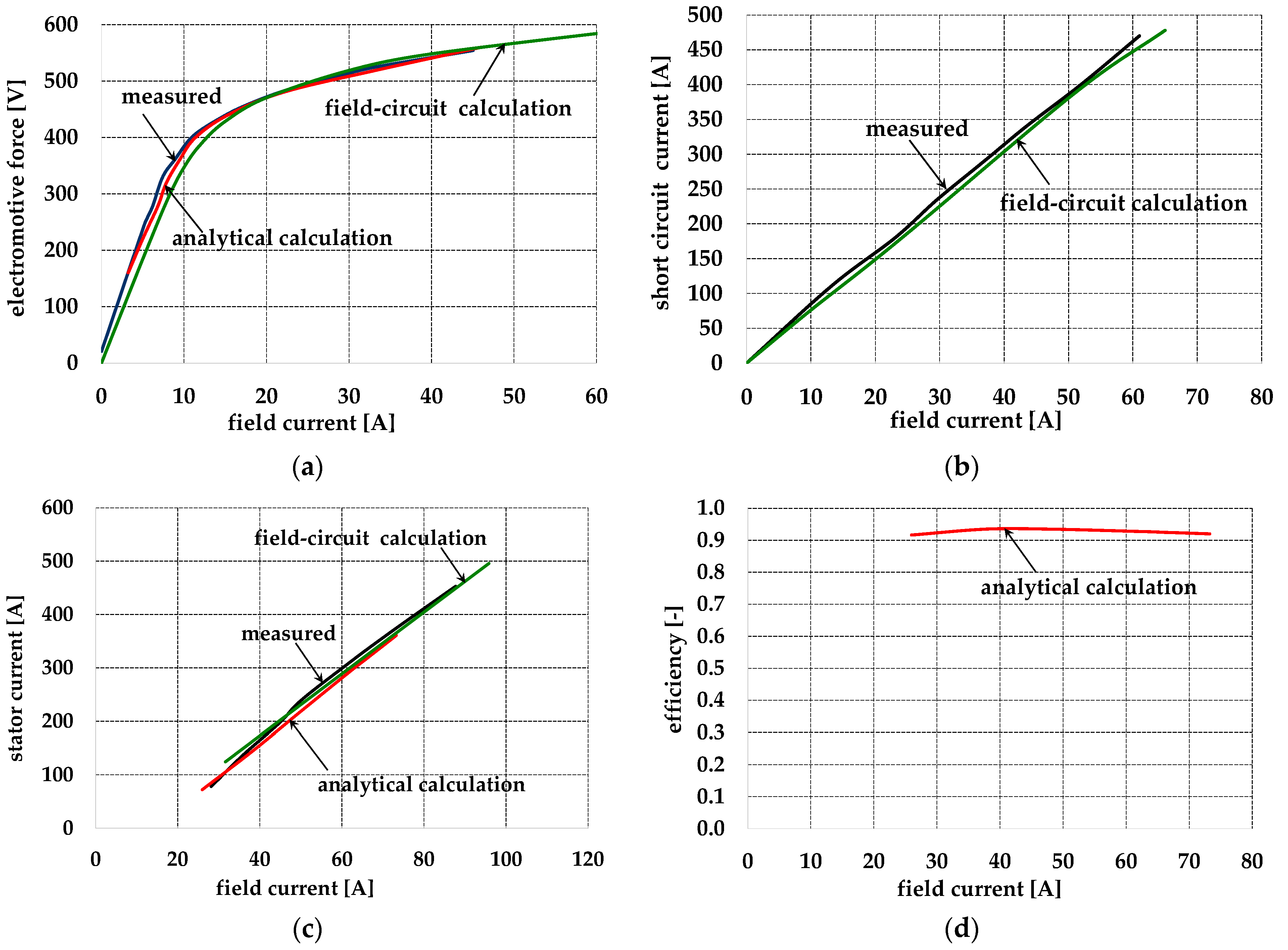
6. Determination of Steady-State Operating Characteristics of a Synchronous Machine with a Cylindrical Rotor
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nøland, J.K.; Nuzzo, S.; Tessarolo, A.; Alves, E.F. Excitation System Technologies for Wound-Field Synchronous Machines: Survey of Solutions and Evolving Trends. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 109699–109718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Dutta, R.; Chu, G.; Xiao, D.; Thippiripati, V.K.; Rahman, M.F. Open-Winding Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator for Renewable Energy—A Review. Energies 2023, 16, 5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raouf, A.; Tawfiq, K.B.; Eldin, E.T.; Youssef, H.; El-Kholy, E.E. Wind Energy Conversion Systems Based on a Synchronous Generator: Comparative Review of Control Methods and Performance. Energies 2023, 16, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensalah, A.; Barakat, G.; Amara, Y. Electrical Generators for Large Wind Turbine: Trends and Challenges. Energies 2022, 15, 6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, J.; Bendtsen, J.D.; Andersen, P.; Madsen, K.K.; Sterregaard, C.H. Supervisory Control Implementation on Diesel-Driven Generator Sets. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 9698–9705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivetta, R.E.; Luiz Dal Forno, I.; Scherer, L.G.; de Camargo, R.F.; Grigoletto, F.B. Self-Excited Induction Generator Based Generation System Regulation Using Synchronous Generator as Reactive Power Compensator. In Proceedings of the 2022 14th Seminar on Power Electronics and Control (SEPOC), Santa Maria, Brazil, 12–15 November 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozegnał, B.; Albrechtowicz, P.; Mamcarz, D.; Radwan-Pragłowska, N.; Cebula, A. The Short-Circuit Protections in Hybrid Systems with Low-Power Synchronous Generators. Energies 2021, 14, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutt, F.; Michna, M.; Kostro, G.; Ronkowski, M. Modelling of steady state and transient performance of the synchronous generator considering harmonic distortions caused by non-uniform saturation of the pole shoe. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 143, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mon-Nzongo, D.L.; Ekemb, G.; Song-Manguelle, J.; Ipoum-Ngome, P.G.; Jin, T.; Doumbia, M.L. LCIs and PWM-VSIs for the Petroleum Industry: A Torque Oriented Evaluation for Torsional Analysis Purposes. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 8956–8970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graffeo, F.; Vaschetto, S.; Tenconi, A.; Cavagnino, A. No-Load Characteristic Computation for Wound Field Synchronous Propulsion Motors. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Electrical Systems for Aircraft, Railway, Ship Propulsion and Road Vehicles & International Transportation Electrification Conference (ESARS-ITEC), Venice, Italy, 29–31 March 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, K.; Hu, W.; Qu, Y.; Geng, Y. A double -magnetic -bridge based brushless hybrid excitation synchronous machine for ship propulsion. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 5th International Electrical and Energy Conference (CIEEC), Nangjing, China, 27–29 May 2022; pp. 3072–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipo, T.A.; Du, Z.S. Synchronous motor drives-a forgotten option. In Proceedings of the 2015 Intl Aegean Conference on Electrical Machines & Power Electronics (ACEMP), 2015 Intl Conference on Optimization of Electrical & Electronic Equipment (OPTIM) & 2015 Intl Symposium on Advanced Electromechanical Motion Systems (ELECTROMOTION), Side, Turkey, 2–4 September 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Baig, Z.; Toor, W.T.; Ali, U.; Idrees, M.; Shloul, T.A.; Ghadi, Y.Y.; Alkahtani, H.K. Wound Rotor Synchronous Motor as Promising Solution for Traction Applications. Electronics 2022, 11, 4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graffeo, F.; Vaschetto, S.; Cossale, M.; Kerschbaumer, M.; Bortoni, E.C.; Cavagnino, A. Cylindrical Wound-Rotor Synchronous Machines for Traction Applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Gothenburg, Sweden, 23–26 August 2020; pp. 1736–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Santiago, J.; Bernhoff, H.; Ekergård, B.; Eriksson, S.; Ferhatovic, S.; Waters, R.; Leijon, M. Electrical Motor Drivelines in Commercial All-Electric Vehicles: A Review. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2012, 61, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehaoulia, H.; Henao, H.; Capolino, G.A. Modeling of synchronous machines with magnetic saturation. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2007, 77, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanic, Z.; Vrazic, M.; Maljkovic, Z. Steady-state synchronous machine model which incorporates saturation and cross-magnetization effects. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Power Engineering, Energy and Electrical Drives, Istanbul, Turkey, 13–17 May 2013; pp. 1553–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabhula, M.; Kamper, M.J. Model Parameter and Performance Calculation of Cylindrical Wound-Rotor Synchronous Motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouni, E.; Tnani, S.; Champenois, G. Comparative study of three modelling methods of synchronous generator. In Proceedings of the IECON 2006—32nd Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics, Paris, France, 7–10 November 2006; pp. 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutt, F.; Michna, M.; Kostro, G. Multiple Reference Frame Theory in the Synchronous Generator Model Considering Harmonic Distortions Caused by Nonuniform Pole Shoe Saturation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallows, D.; Nuzzo, S.; Galea, M. Exciterless Wound-Field Medium-Power Synchronous Machines: Their History and Future. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2022, 16, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, K. Magnetic Field Analysis and Operating Characteristics of a Brushless Electrical Excitation Synchronous Generator With DC Excitation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 8106007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, S.; Galea, M.; Gerada, C.; Brown, N. Analysis, Modeling, and Design Considerations for the Excitation Systems of Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 2996–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slemon, G.R. An equivalent circuit approach to analysis of synchronous machines with saliency and saturation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1990, 5, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laldin, O.; Sudhoff, S.D.; Pekarek, S. An Analytical Design Model for Wound Rotor Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cramer, A.M. Unified Model Formulations for Synchronous Machine Model With Saturation and Arbitrary Rotor Network Representation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 31, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Cheng, M. Unified Analysis of Induction Machine and Synchronous Machine Based on the General Airgap Field Modulation Theory. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 9205–9216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Matsushita, M.; Makino, H.; Tsuboi, Y.; Amemiya, N. A Novel Modeling Method for No-Load Saturation Characteristics of Synchronous Machines Using Finite Element Analysis. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 7400605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, J. Electrical Machine Iron Loss Predictions—A Unique Engineering Approach Utilizing Transient Finite-Element Methods—Part II: Application and Validation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 2871–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, S.; Bolognesi, P.; Gerada, C.; Galea, M. Simplified Damper Cage Circuital Model and Fast Analytical–Numerical Approach for the Analysis of Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 8361–8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiji, K.S.; Jayadas, N.H.; Babu, C.A. FEM-Based Virtual Prototyping and Design of Third Harmonic Excitation System for Low-Voltage Salient-Pole Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, L.; Shangguan, M.; Fu, W.N. Finite Element Analysis of 1 MW High Speed Wound-Rotor Synchronous Machine. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 4650–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; El-Serafi, A.M.; Faried, S.O. Application of the Finite-Element Method for the Determination of the Parameters Representing the Cross-Magnetizing in Saturated Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomičić, B.; Car, S.; Štih, Ž. An improved model of synchronous generator based on Finite Element Method analysis. In Proceedings of the 2012 XXth International Conference on Electrical Machines, Marseille, France, 2–5 September 2012; pp. 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedjar, B.; Merkhouf, A.; Al-Haddad, K. Co-simulation for Finite Element Model Calibration of Synchronous Generators Connected to an Infinite Bus. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Valencia, Spain, 5–8 September 2022; pp. 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovski, P.; Veljanovski, G.; Arapinovski, B.; Atanasovski, M. Electromagnetic Analysis of Synchronous Generator. In Proceedings of the 2021 56th International Scientific Conference on Information, Communication and Energy Systems and Technologies (ICEST), Sozopol, Bulgaria, 16–18 June 2021; pp. 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbégbé, Z.; Rouached, B.; Cros, J.; Bergeron, M.; Viarouge, P. Damper Currents Simulation of Large Hydro-Generator Using the Combination of FEM and Coupled Circuits Models. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, S.; Viarouge, P.; Cros, J. Real-Time Digital Twin of a Wound Rotor Induction Machine Based on Finite Element Method. Energies 2020, 13, 5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, J.; Bian, X.; Sun, Y.; Ge, B. Design and Analysis of Complex End Region of Pumped Storage Generator Motor Based on Novel Electromagnetic Vector Method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 12082–12092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gong, C.; Gallandat, N.A.; Mayor, J.R.; Harley, R.G. Analyzing the impact of press plate structure on the flux and loss distributions in the end region of large generators by transient 3-dimensional finite-element method with an improved core loss model. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference (IEMDC), Miami, FL, USA, 21–24 May 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Luong, H.T.; Messine, F.; Hénaux, C.; Mariani, G.B.; Voyer, N.; Mollov, S.; Harribey, D. Optimization, 3D-Numerical Validations and Preliminary Experimental Tests of a Wound Rotor Synchronous Machine. Energies 2021, 14, 8118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Jin, L.; Zhang, W.; Fan, Y.; Hua, W.; Cheng, M. Influence of PWM Excitation on DC Winding Induced Voltage Pulsation in Wound Field Switched Flux Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 460–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, S.; Galea, M.; Gerada, C.; Brown, N. A Fast Method for Modeling Skew and Its Effects in Salient-Pole Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 7679–7688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadri, Q.H.; Nuzzo, S.; Rashed, M.; Gerada, C.; Galea, M. Modeling of Classical Synchronous Generators Using Size-Efficient Lookup Tables with Skewing Effect. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 174551–174561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, S.; Galea, M.; Bolognesi, P.; Vakil, G.; Fallows, D.; Gerada, C.; Brown, N. A Methodology to Remove Stator Skew in Small–Medium Size Synchronous Generators via Innovative Damper Cage Designs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 4296–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drubel, O. Challenges in calculation and design of large synchronous generators. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Workshop on Electrical Machines Design, Control and Diagnosis (WEMDCD), Paris, France, 11–12 March 2013; pp. 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Yang, N.; Zhang, W.; Cao, W.; Xing, N.; Tan, Z.; Li, G. Improved Synchronous Machine Rotor Design for the Easy Assembly of Excitation Coils Based on Surrogate Optimization. Energies 2018, 11, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siphepho, N.N.; Garner, K.S. Effects of Structure Shape Optimizing Techniques on the Performance of a Large Scale Wound Rotor Synchronous Machine. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Electrical, Computer, Communications and Mechatronics Engineering (ICECCME), Maldives, Maldives, 16–18 November 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virlan, B.; Livadaru, L.; Munteanu, A.; Nacu, I.; Nastas, I.; Simion, A. Comparative Analysis Between Distributed and Fractional Slot Concentrated Winding of a Wound Rotor Synchronous Machine. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Electromechanical and Energy Systems (SIELMEN), Craiova, Romania, 11–13 October 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeager, K.E.; Willis, J.R. Modeling of emergency diesel generators in an 800 megawatt nuclear power plant. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1993, 8, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaha, M.; Krost, G. Performance study of self-sufficient and renewables based electricity supply of a hospital in the Near East Region. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–26 July 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamedica, R.; Gatta, F.M.; Ruvio, A.; Olevano, F.; Buffarini, G.G.; Castellani, M. Modeling of electrical systems powered by generator sets for long railway tunnels. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Annual Conference (AEIT), Catania, Italy, 23–25 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidgoli, M.A.; Bagheri, A.; Barzegari, M.; Ouni, S. Optimal Energy Management of Isolated Micro-Grid Including Solar and Diesel Power with Pumped Storage. In Proceedings of the 2019 Smart Grid Conference (SGC), Tehran, Iran, 18–19 December 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kumar, A. Active power control method for wind diesel system based on energy storage. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Power and Embedded Drive Control (ICPEDC), Chennai, India, 16–18 March 2017; pp. 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, P.A.; Mecrow, B.C.; Hall, R. Calculation of iron loss in electrical generators using finite element analysis. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 15–18 May 2011; pp. 1368–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratila, M.; Benabou, A.; Tounzi, A.; Dessoude, M. Iron Loss Calculation in a Synchronous Generator Using Finite Element Analysis. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ployard, M.; Ammar, A.; de la Barrière, O.; Vido, L.; Gillon, F. Comparison of Iron Loss Models Under Synchronous Generator Waveforms. In Proceedings of the 2018 XIII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Alexandroupoli, Greece, 3–6 September 2018; pp. 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Nysveen, A.; Fagermyr, B.J.; Nilssen, R.; Ehya, H. Virtual-stator Loss Model for Synchronous Generators. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Detroit, MI, USA, 9–13 October 2022; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertotti, G. General properties of power losses in soft ferromagnetic materials. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1988, 24, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dems, M.; Komeza, K. Performance Characteristics of a High-Speed Energy-Saving Induction Motor with an Amorphous Stator Core. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 3046–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, H. Die ferromagnetischen konstanten fur schwache wechselfelder. Elektr. Nach. Technol. 1924, 1, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Dems, M.; Komeza, K.; Szulakowski, J. Practical Approximation of Sheet Losses Taking into Account the Guillotine and Laser Cutting Effect. Energies 2023, 16, 2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dems, M.; Komeza, K.; Majer, K. Core losses of the induction motor operating in a wide frequency range supplied from the inverter. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2020, 64, S65–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dems, M.; Komeza, K. Finite element and analytical calculations of no-load core losses in energy-saving induction motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 2934–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dems, M.; Komeza, K. The Influence of Electrical Sheet on the Core Losses at No-Load and Full-Load of Small Power Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 2433–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dems, M.; Komeza, K.; Rodríguez, H.G. Methods for increasing the efficiency of an asynchronous motor with increased speed fed from the PWM inverter. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2018, 57, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dems, M.; Komeza, K. Designing an energy-saving induction motor operating in a wide frequency range. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 4387–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochmann, T. Relationship between rotational and alternating losses in electrical steel sheets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1996, 160, 145–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youguang, G.; Jian Guo, Z.; Jinjiang, Z.; Haiyan, L.; Jian Xun, J. Measurement and Modeling of Rotational Core Losses of Soft Magnetic Materials Used in Electrical Machines: A Review. IEEE Trans. Mag. 2008, 44, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, T.; Sridharbabu, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Matsui, N. Design Studies on Hybrid Excitation Motor for Main Spindle Drive in Machine Tools. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 3807–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmaker, H.C. Open Circuit Tooth Ripple Losses in Slotted Laminated Poles of Electrical Machines with Amortisseur Windings. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1982, PAS-101, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drubel, O.; Stoll, R.L. Comparison between analytical and numerical methods of calculating tooth ripple losses in salient pole synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2001, 16, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkhouf, A.; Guillot, E.; Hudon, C.; Desnoyers, M.; Aguiar, A.B.M.; Al-Haddad, K. Electromagnetic loss computation in large hydro electrical generator using different existing models. In Proceedings of the 2012 XXth International Conference on Electrical Machines, Marseille, France, 2–5 September 2012; pp. 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasilo, P.; Belahcen, A.; Arkkio, A. Experimental determination and numerical evaluation of core losses in a 150-kVA wound-field synchronous machine. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2012, 7, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.-I.; Ahn, J.; Nam, Y.-J.; Lee, J.; Jang, H. Open-Circuit Core Loss of Large Turbine Generators Considering the Influence of Key Bar Design. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 70662–70670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Nysveen, A.; Fagermyr, B.J.; Chen, A.; Ehya, H.; Nilssen, R. Material Characterization and Stator Core Loss Computation of Synchronous Generators With Stacking Force Accounted. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitsi, K.; Kowal, D.; Moghaddam, R.-R. 3-D FEM Investigation of Eddy Current Losses in Rotor Lamination Steel Sheets. In Proceedings of the 2018 XIII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Alexandroupoli, Greece, 3–6 September 2018; pp. 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyaert, B.; Swint, E.; Pennington, W.W.; Preindl, M. Real Time Core Loss Estimation for the Wound Rotor Synchronous Machine. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 14th International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives (SDEMPED), Chania, Greece, 28–31 August 2023; pp. 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Std 115-2019 (Revision of IEEE Std 115-2009); IEEE Guide for Test Procedures for Synchronous Machines Including Acceptance and Performance Testing and Parameter Determination for Dynamic Analysis. IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–246. [CrossRef]
- IEC 60034-4-1:2018; Rotating Electrical Machines—Part 4-1: Methods for Determining Electrically Excited Synchronous Machine Quantities from Tests. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Lidenholm, J.; Lundin, U. Estimation of Hydropower Generator Parameters Through Field Simulations of Standard Tests. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidenholm, J.; Ranlöf, M.; Lundin, U. Comparison of field and circuit generator models in single machine infinite bus system simulations. In Proceedings of the XIX International Conference on Electrical Machines—ICEM 2010, Rome, Italy, 6–8 September 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guorui, X.; Yiping, H.; Yang, Z.; Haisen, Z.; Jinping, K. Parameter identification of synchronous generator based on the results of time stepping finite element model. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1–5 October 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiver, O.; Neamt, L.; Horgos, M.; Erdei, Z. Study of salient poles synchronous generator by finite elements analysis. In Proceedings of the 2013 12th International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering, Wroclaw, Poland, 5–8 May 2013; pp. 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escarela-Perez, R.; Niewierowicz, T.; Campero-Littlewood, E. Synchronous machine parameters from frequency-response finite-element simulations and genetic algorithms. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2001, 16, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutt, F.; Racewicz, S.; Michna, M. SSFR test of synchronous machine for different saturation levels using finite-element method. In Proceedings of the IECON 2014—40th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Dallas, TX, USA, 29 October–1 November 2014; pp. 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros-González, M.; Hernandez, C.; Morales-Caporal, R.; Bonilla-Huerta, E.; Arjona, M.A. Parameter Estimation of a Synchronous-Generator Two-Axis Model Based on the Standstill Chirp Test. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2013, 28, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, R. Finite Element Computation of Transient Parameters of a Salient-Pole Synchronous Machine. Energies 2017, 10, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escarela-Perez, R.; Niewierowicz, T.; Campero-Littlewood, E. A study of the variation of synchronous machine parameters due to saturation: A numerical approach. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2014, 72, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micev, M.; Ćalasan, M.; Aleem, S.H.E.A.; Hasanien, H.M.; Petrović, D.S. Two Novel Approaches for Identification of Synchronous Machine Parameters From Short-Circuit Current Waveform. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 5536–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micev, M.; Ćalasan, M.; Radulović, M.; Aleem, S.H.E.A.; Hasanien, H.M.; Zobaa, A.F. Artificial Neural Network-Based Nonlinear Black-Box Modeling of Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 2826–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakides, E.; Heydt, G.T.; Vittal, V. Online parameter estimation of round rotor synchronous generators including magnetic saturation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2005, 20, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Zhao, J.; Netto, M. A General Decentralized Dynamic State Estimation With Synchronous Generator Magnetic Saturation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2023, 38, 960–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overlin, M.R.; Macomber, J.; Smith, C.L.; Daniel, L.; Corbett, E.G.; Kirtley, J.L. A Hybrid Algorithm for Parameter Estimation (HAPE) for Diesel Generator Sets. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 1704–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rallabandi, V.; Taran, N.; Ionel, D.M.; Zhou, P. Inductance testing according to the new IEEE Std 1812-application and possible extensions for IPM machines. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1–5 October 2017; pp. 4302–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Std 1812-2023 (Revision of IEEE Std 1812-2014); IEEE Guide for Testing Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1–88. [CrossRef]
- Nanda, B.; Kumar, P. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Different Inductance Measurement Techniques for IPM Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 3305–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Li, M.; Ge, L.; Liao, W.; Powell, K. Two-line-same-phase AC standstill measurement method for obtaining accurate PMSM d–q-axis inductance values. J. Power Electron. 2023, 23, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, R.; Rahman, M.F. A Comparative Analysis of Two Test Methods of Measuring d- and q-Axes Inductances of Interior Permanent-Magnet Machine. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2006, 42, 3712–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertan, H.B.; Sahin, I. Inductance Measurement Methods for Surface-Mount Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 2000116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafaq, M.S.; Jung, J.-W. A Comprehensive Review of State-of-the-Art Parameter Estimation Techniques for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors in Wide Speed Range. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 4747–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Demerdash, N.A. Comprehensive salient-pole synchronous machine parametric design analysis using time-step finite element-state space modeling techniques. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1998, 13, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

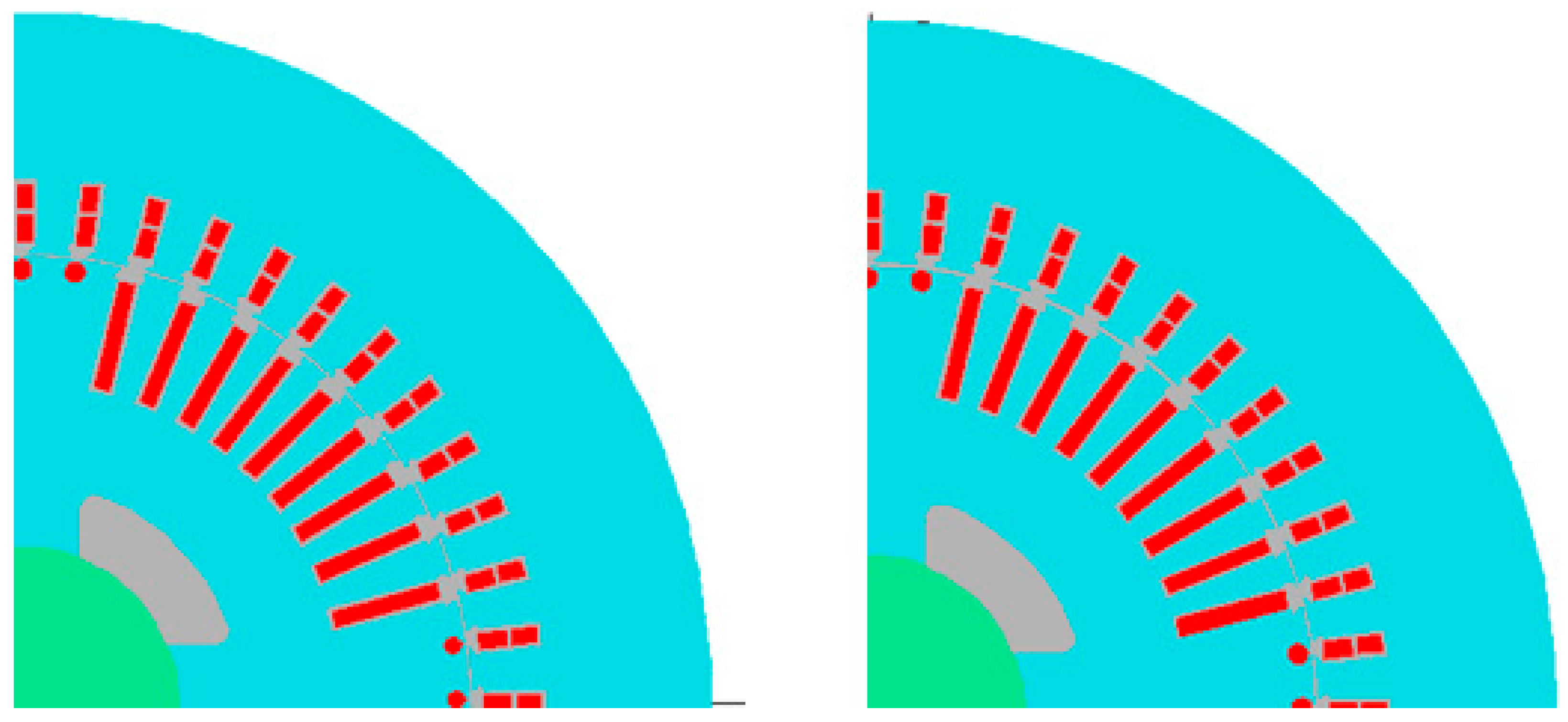
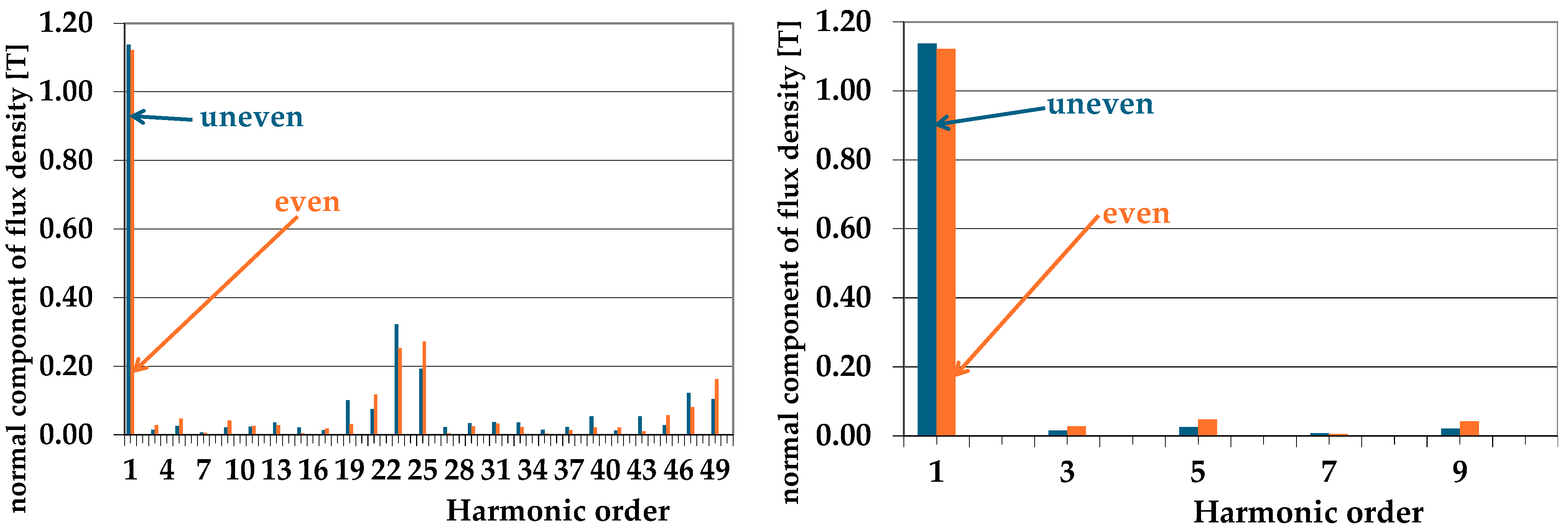

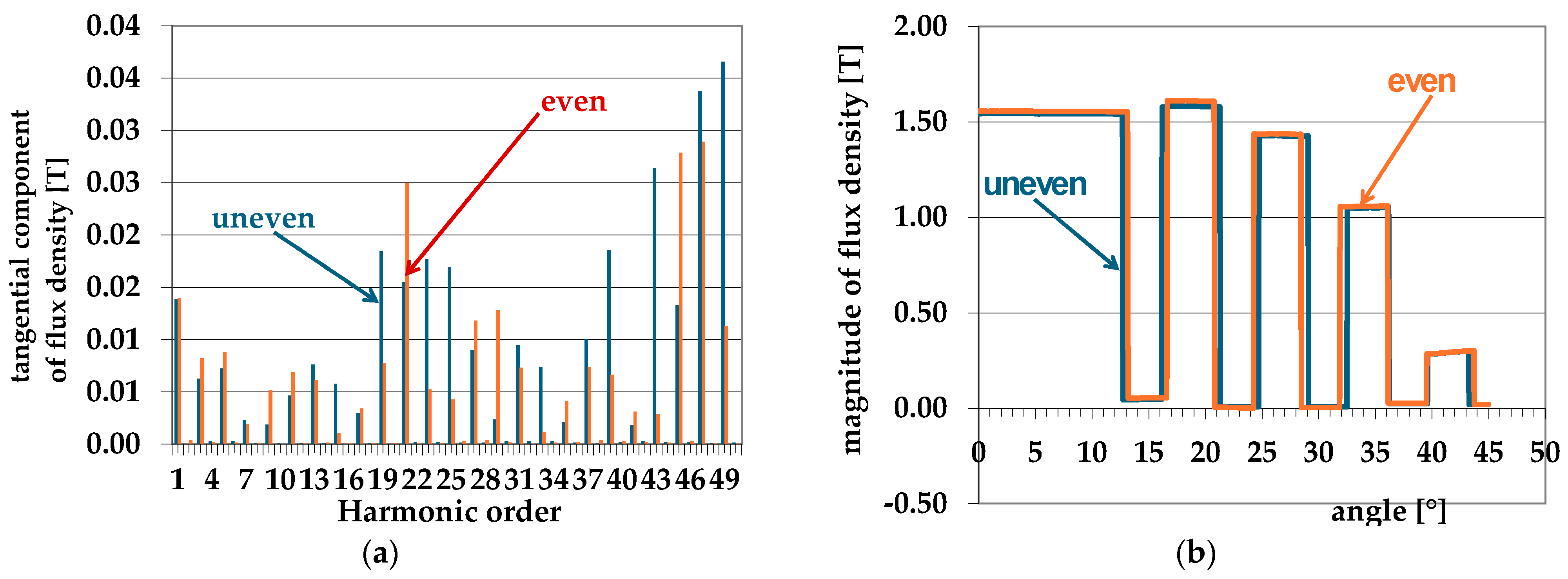
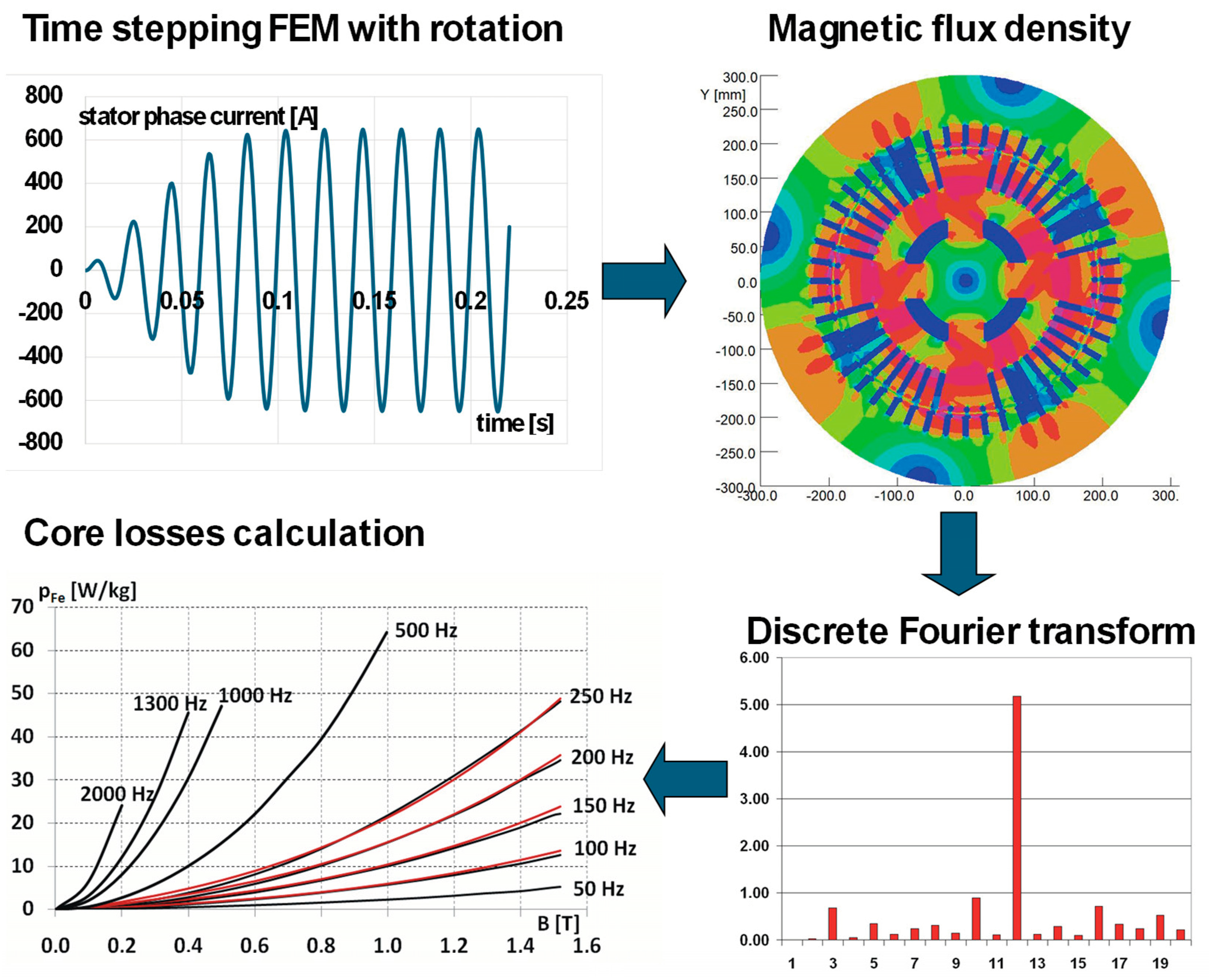

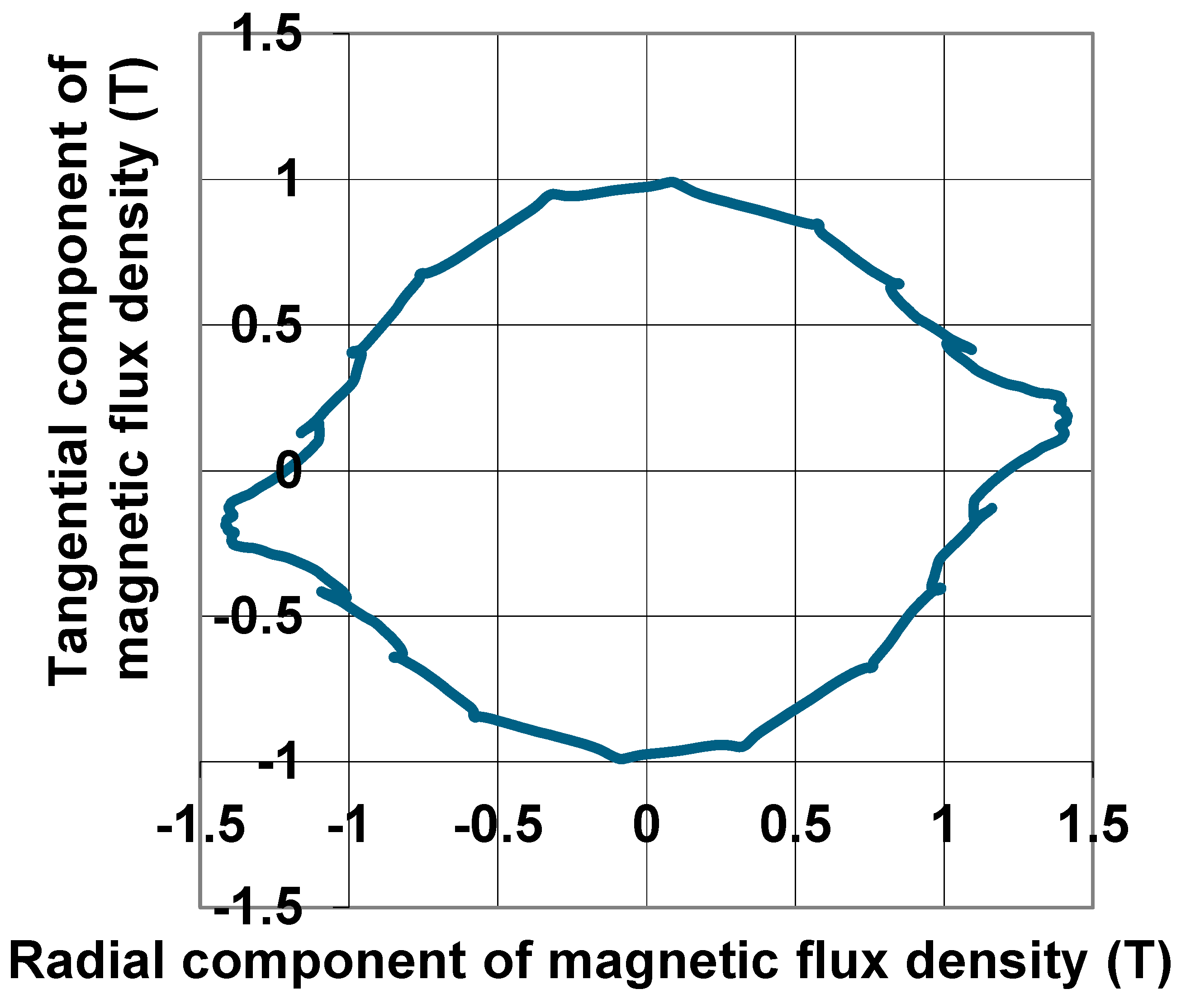
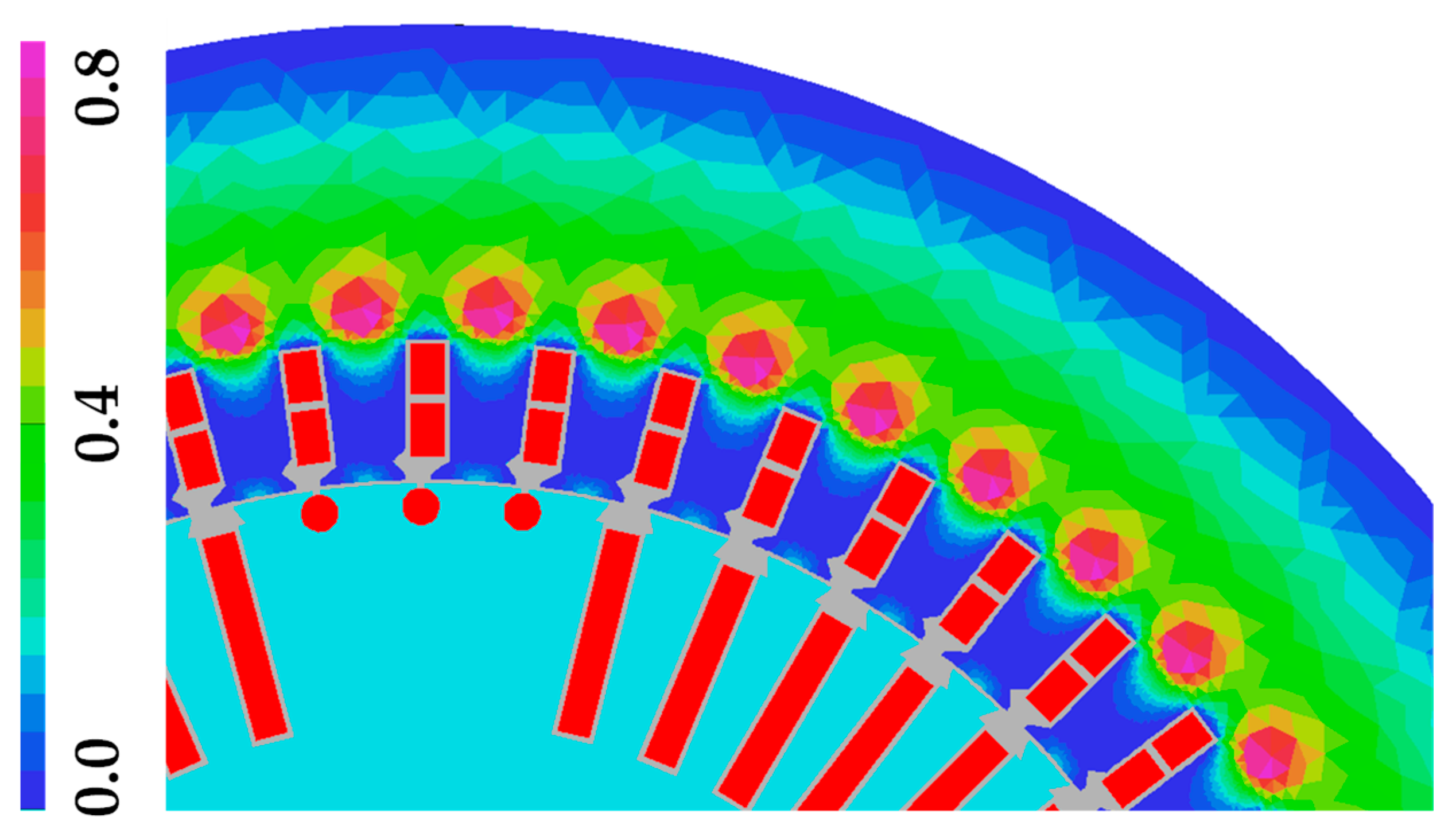
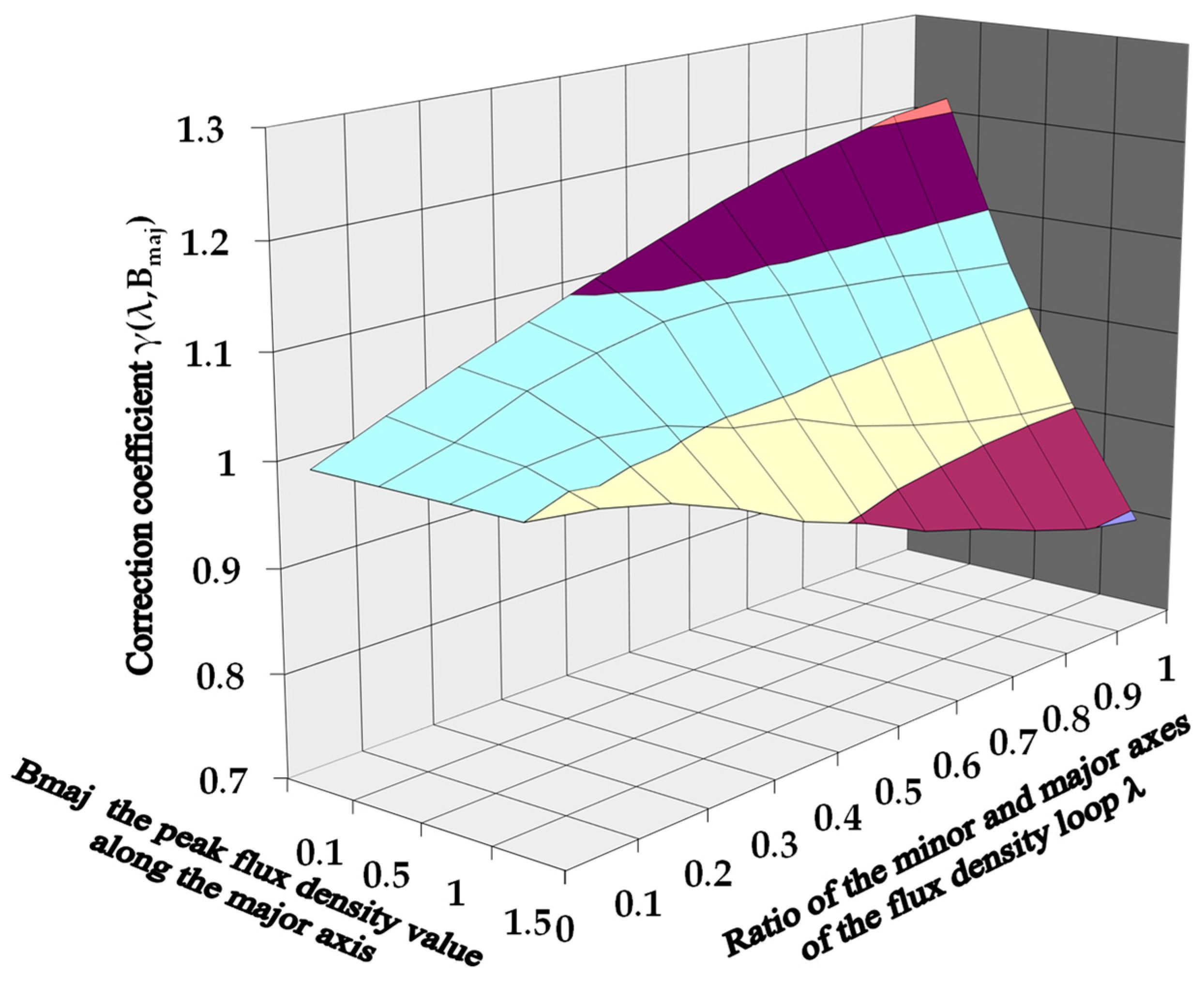
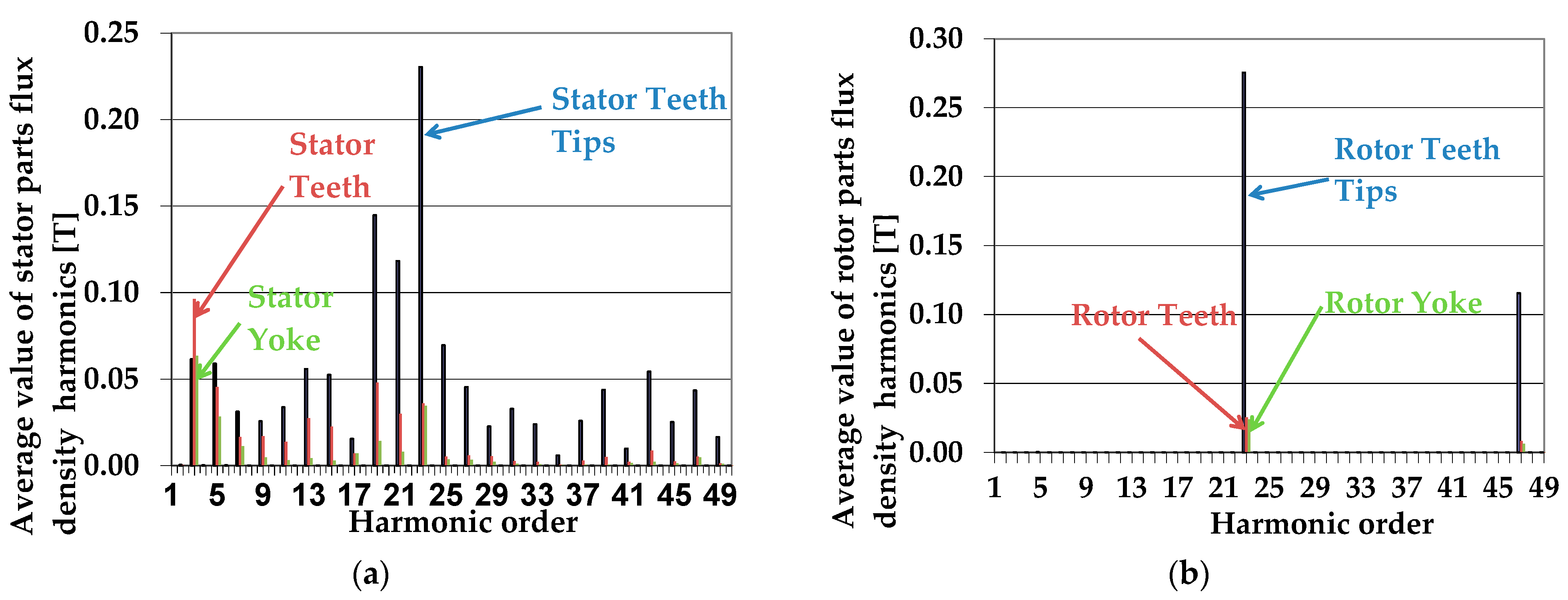

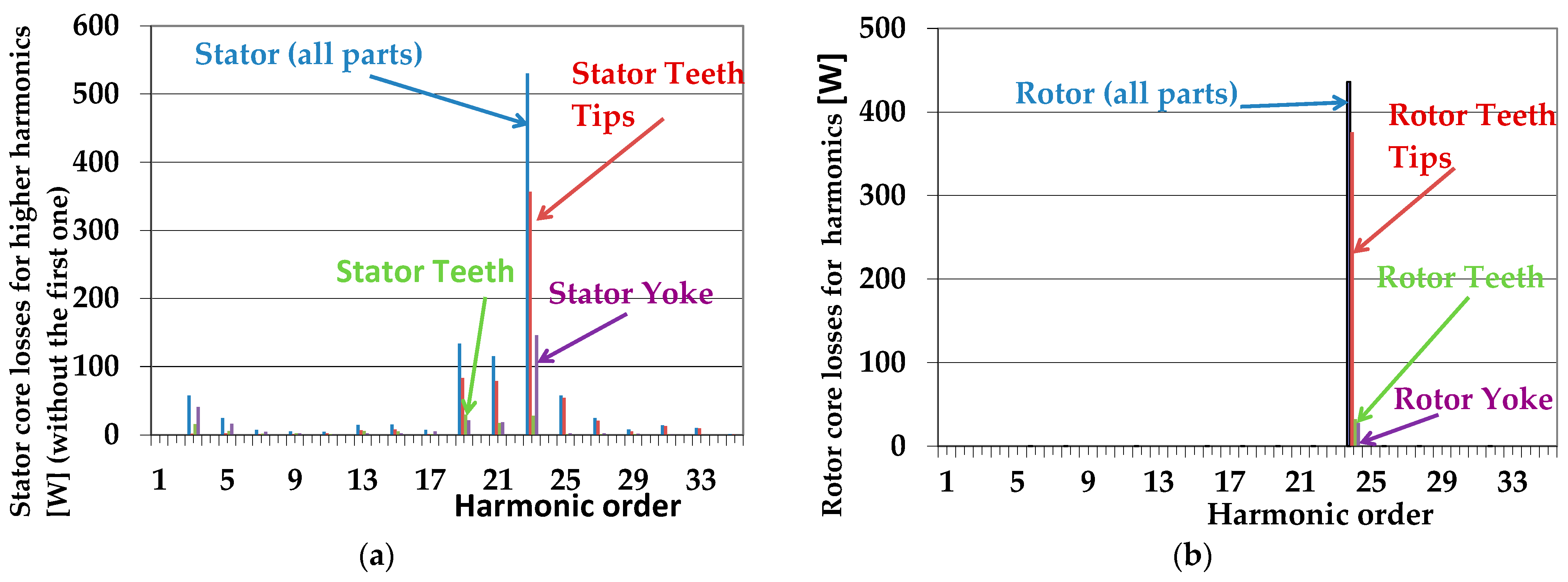
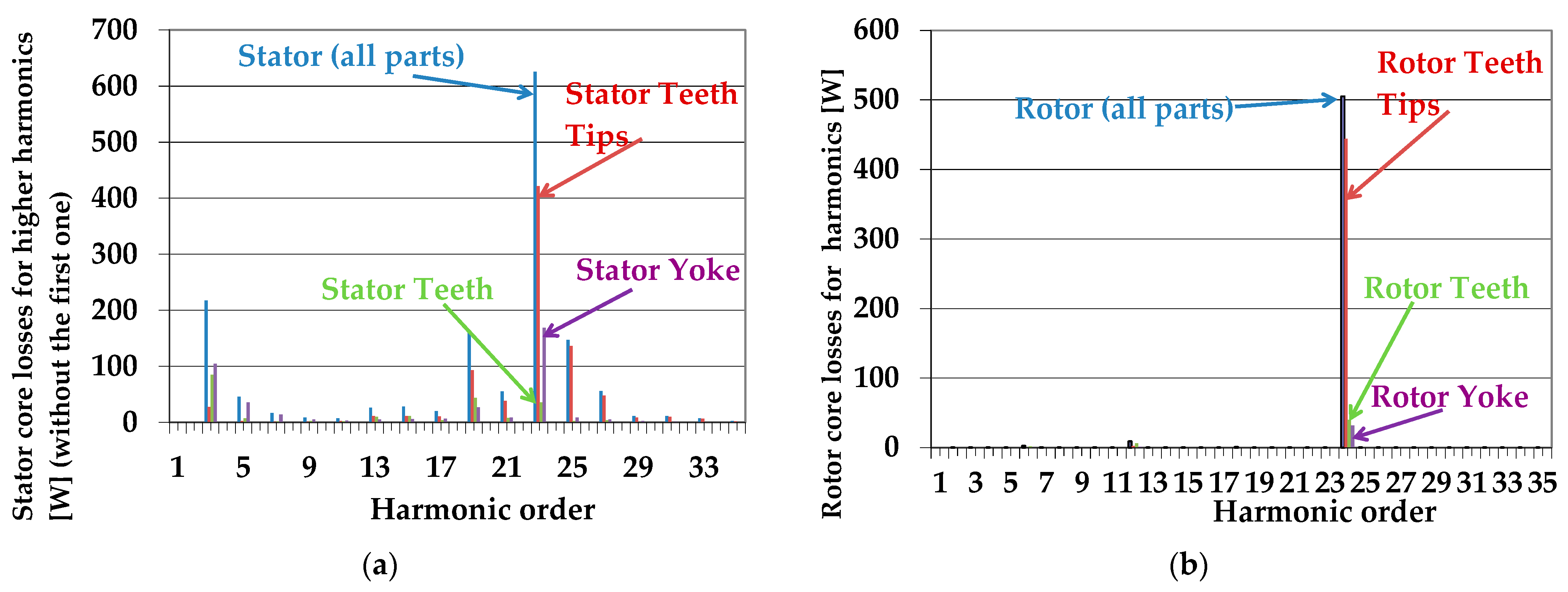
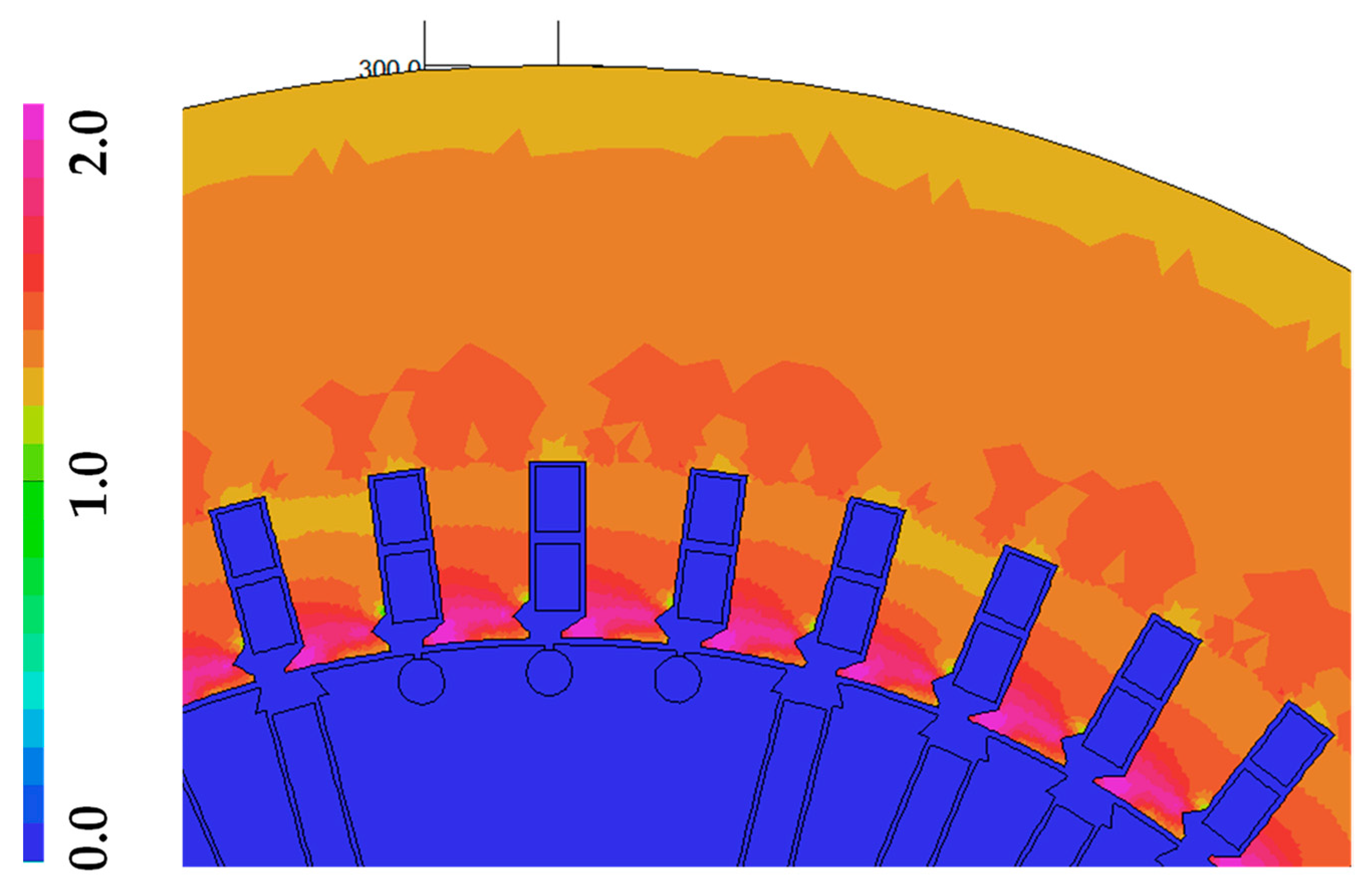
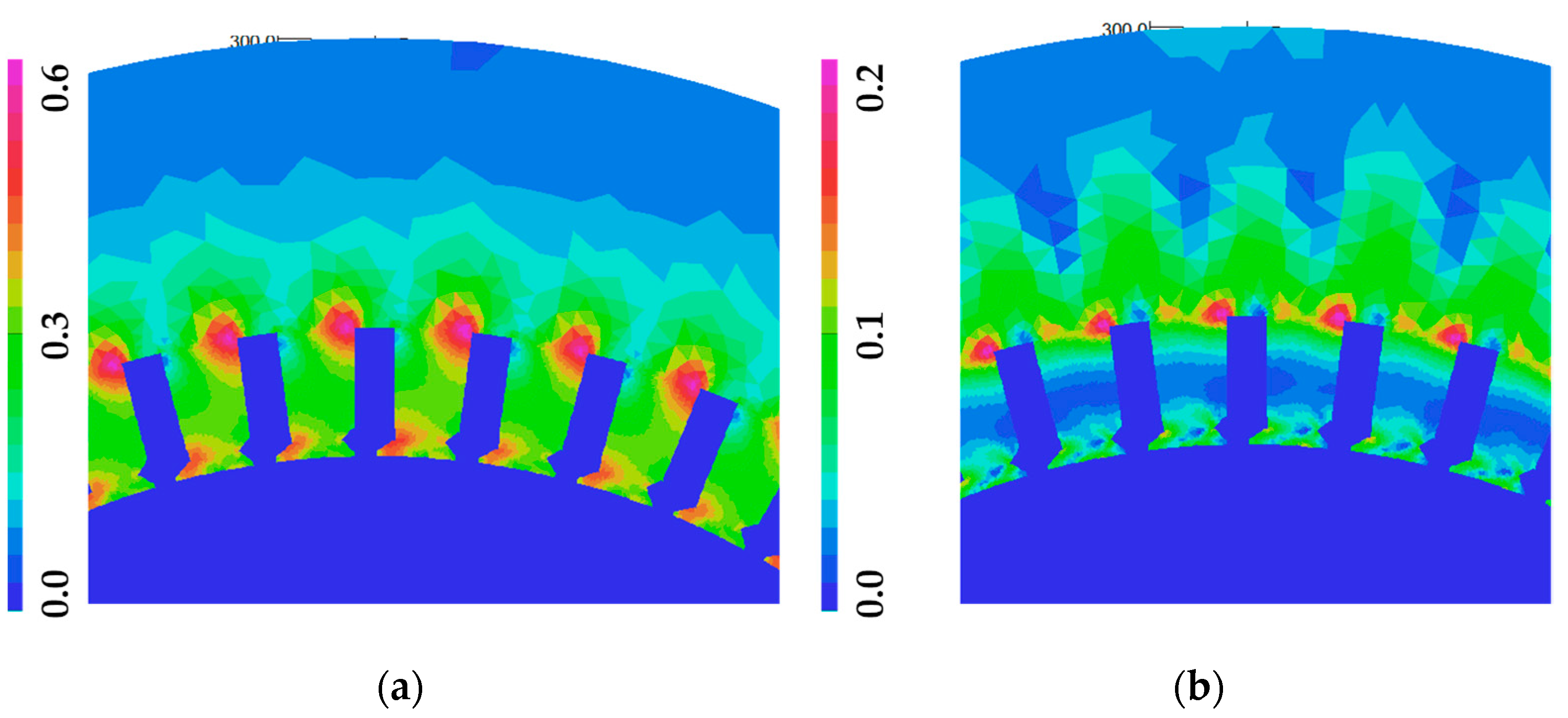
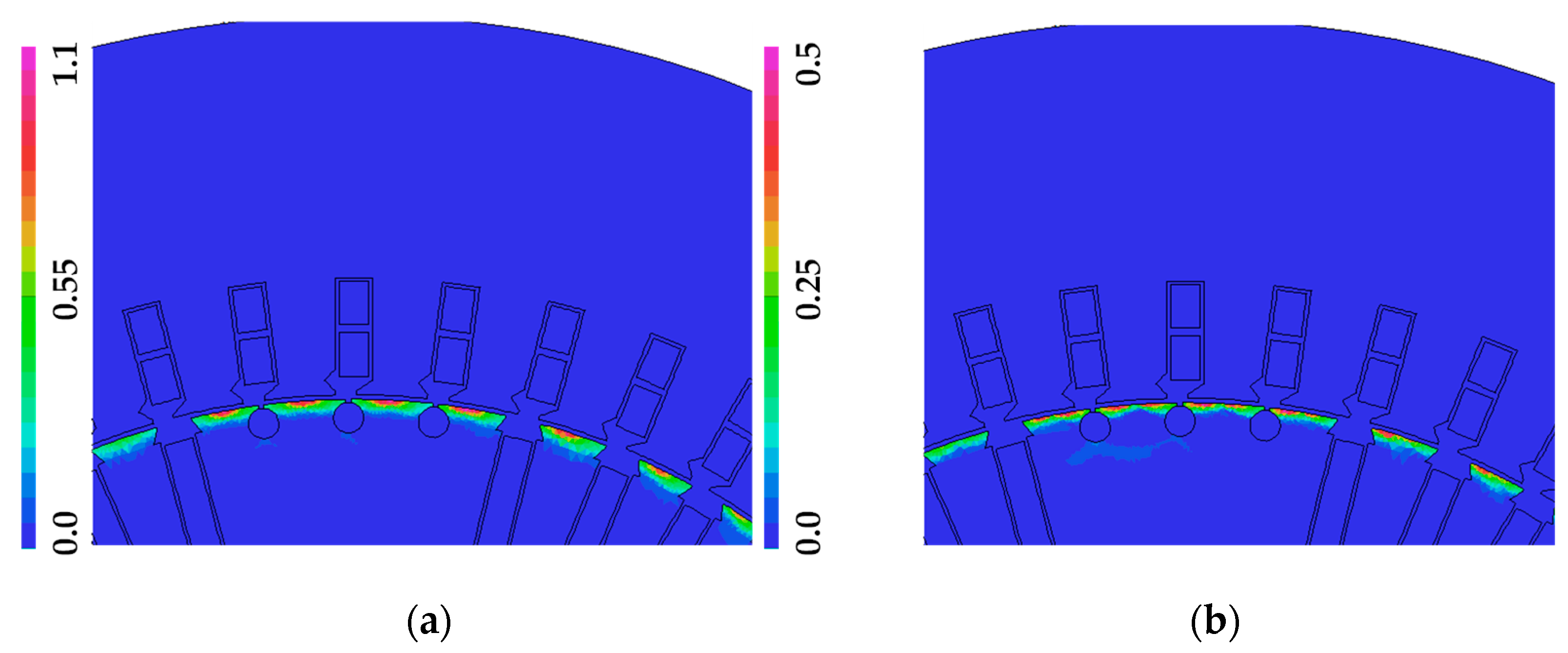
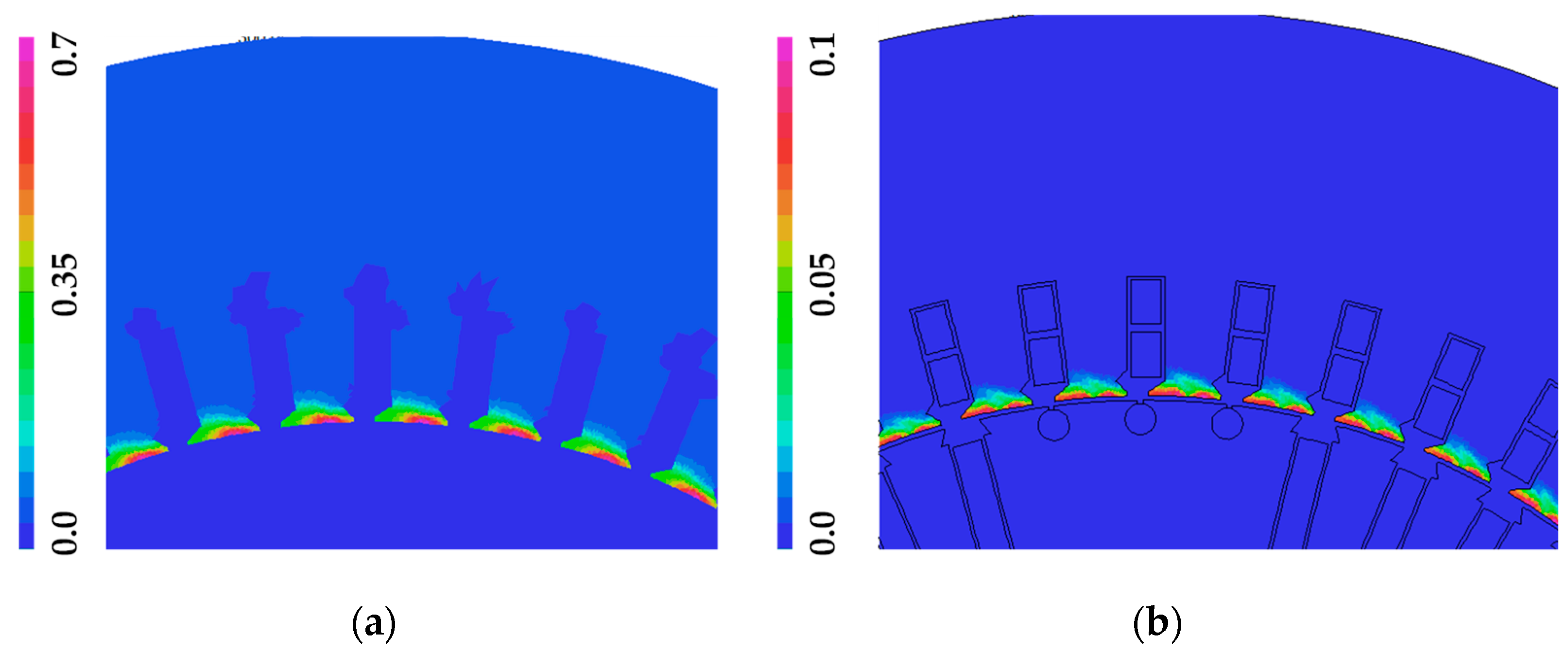



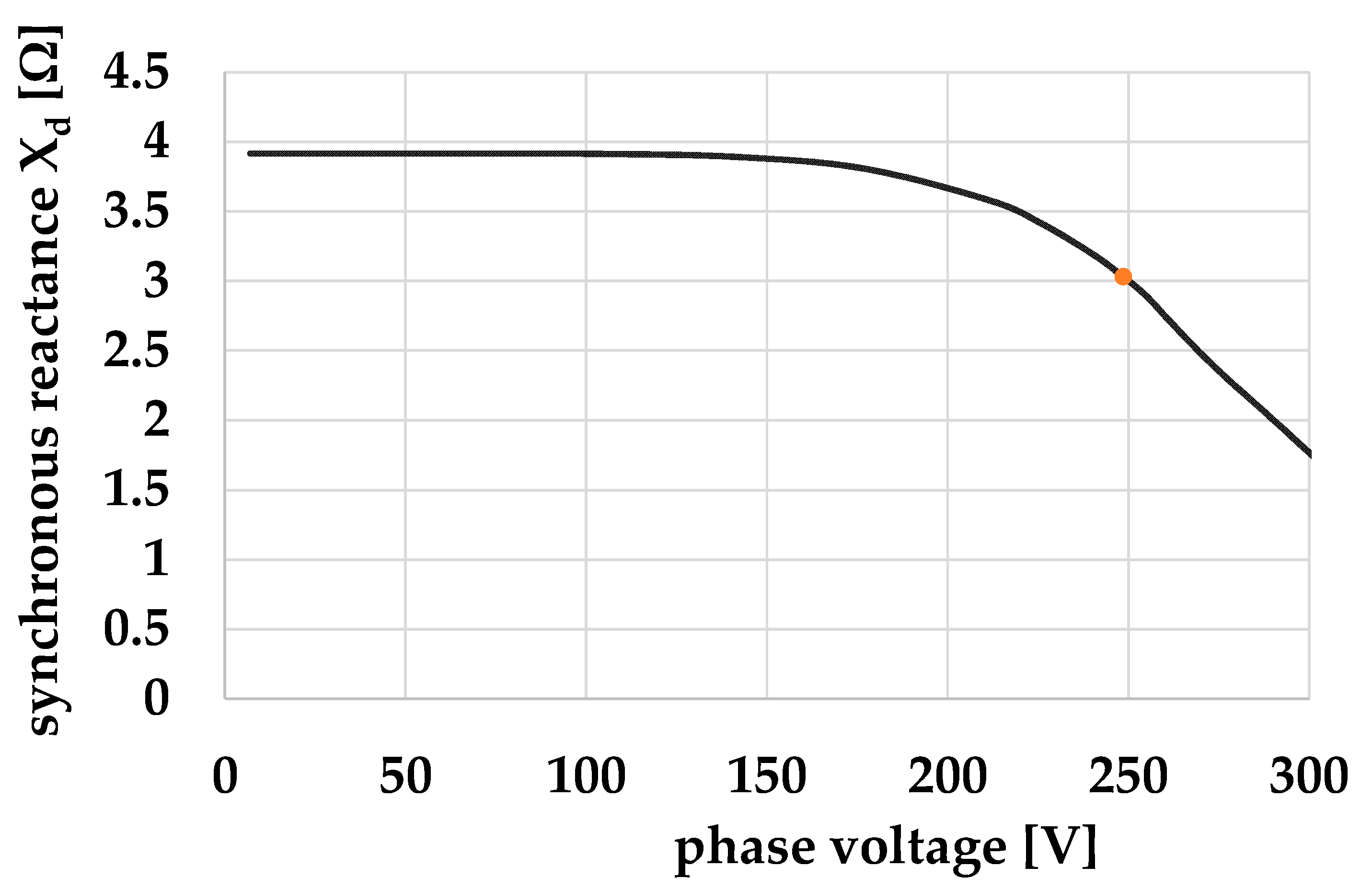
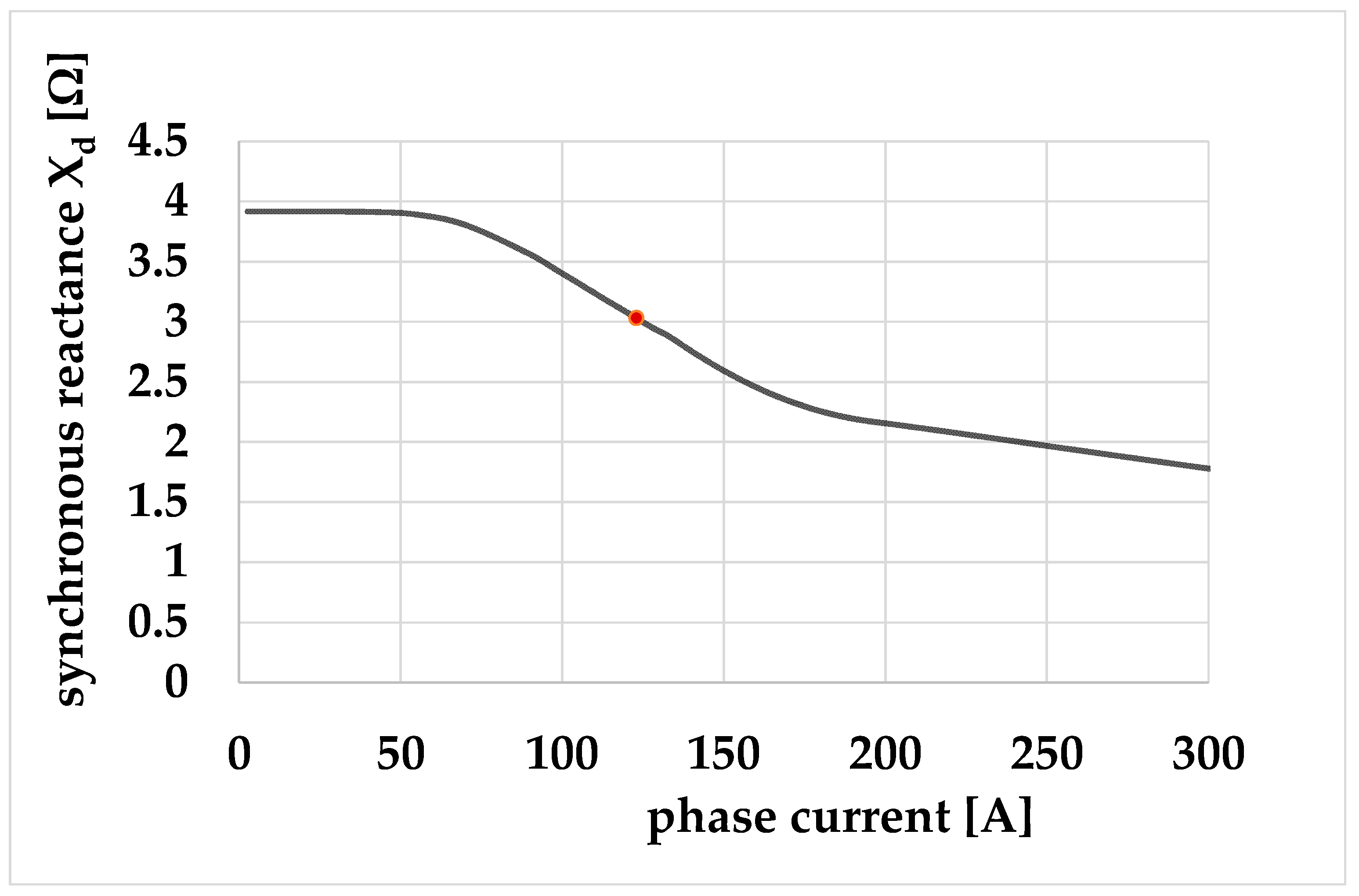

| Quantity | Unit | Generator A | Generator B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated power SN | kVA | 400 | 200 |
| Rated line voltage UN | V | 400 (Y) | 400 (Y) |
| Rated stator current IsN | A | 577 | 289 |
| Rated field current IfN | A | 110 | 65 |
| Number of poles 2p | - | 4 | 4 |
| Power factor cos φ | - | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Rated efficiency η | % | 93.1 | 91.7 |
| The outer diameter of the stator core Dse | mm | 600 | 495 |
| The inner diameter of the stator core Dsi | mm | 390 | 358 |
| Stator core length Ls | mm | 490 | 390 |
| Number of stator slots Qs | - | 48 | 48 |
| Number of rotor slots Qr | - | 36 | 32 |
| Number of serial turns of the stator-phase winding | - | 12 | 24 |
| Number of turns of field winding | - | 288 | 352 |
| Air gap thickness | mm | 1.25 | 1.25 |
| Number of rotor damping winding slots per pole | - | 3 | 3 |
| Model | Basic Core Losses Pc | Additional Core Losses in Stator Pcdds | Total Core Losses in Stator | Additional Core Losses in Rotor Pcdds | Total Core Losses sPc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | W | W | W | W | |
| analytical | 2476.6 | 1730.9 | 4207.5 | 924.0 | 5131.5 |
| field-circuit | 2325.2 | 1813.2 | 4138.4 | 923.6 | 5062.0 |
| Model | Basic Core Losses Pc | Additional Core Losses in Stator Pcdds | Total Core Losses in Stator | Additional Core Losses in Rotor Pcdds | Total Core Losses sPc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | W | W | W | W | |
| analytical | 1179.2 | 108.9 | 1288.1 | 680.6 | 1968.7 |
| field-circuit | 1291.5 | 121.1 | 1412.6 | 666.2 | 2078.8 |
| Generator | Reactance Xs | Reactance Xd0 | Reactance Xd | Reactance Xq0 | Reactance Xq |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ω | Ω | Ω | Ω | Ω | |
| A | 0.03427 | 1.5572 | 1.1096 | 1.6144 | 1.1500 |
| B | 0.0952 | 3.9432 | 2.5120 | 4.0816 | 2.5992 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Komeza, K.; Dems, M. Methods for Determining Losses and Parameters of Cylindrical-Rotor Medium-Power Synchronous Generators. Electronics 2024, 13, 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13142766
Komeza K, Dems M. Methods for Determining Losses and Parameters of Cylindrical-Rotor Medium-Power Synchronous Generators. Electronics. 2024; 13(14):2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13142766
Chicago/Turabian StyleKomeza, Krzysztof, and Maria Dems. 2024. "Methods for Determining Losses and Parameters of Cylindrical-Rotor Medium-Power Synchronous Generators" Electronics 13, no. 14: 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13142766
APA StyleKomeza, K., & Dems, M. (2024). Methods for Determining Losses and Parameters of Cylindrical-Rotor Medium-Power Synchronous Generators. Electronics, 13(14), 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13142766









