On the Asymmetry of Resistive Switching Transitions
Abstract
1. Introduction
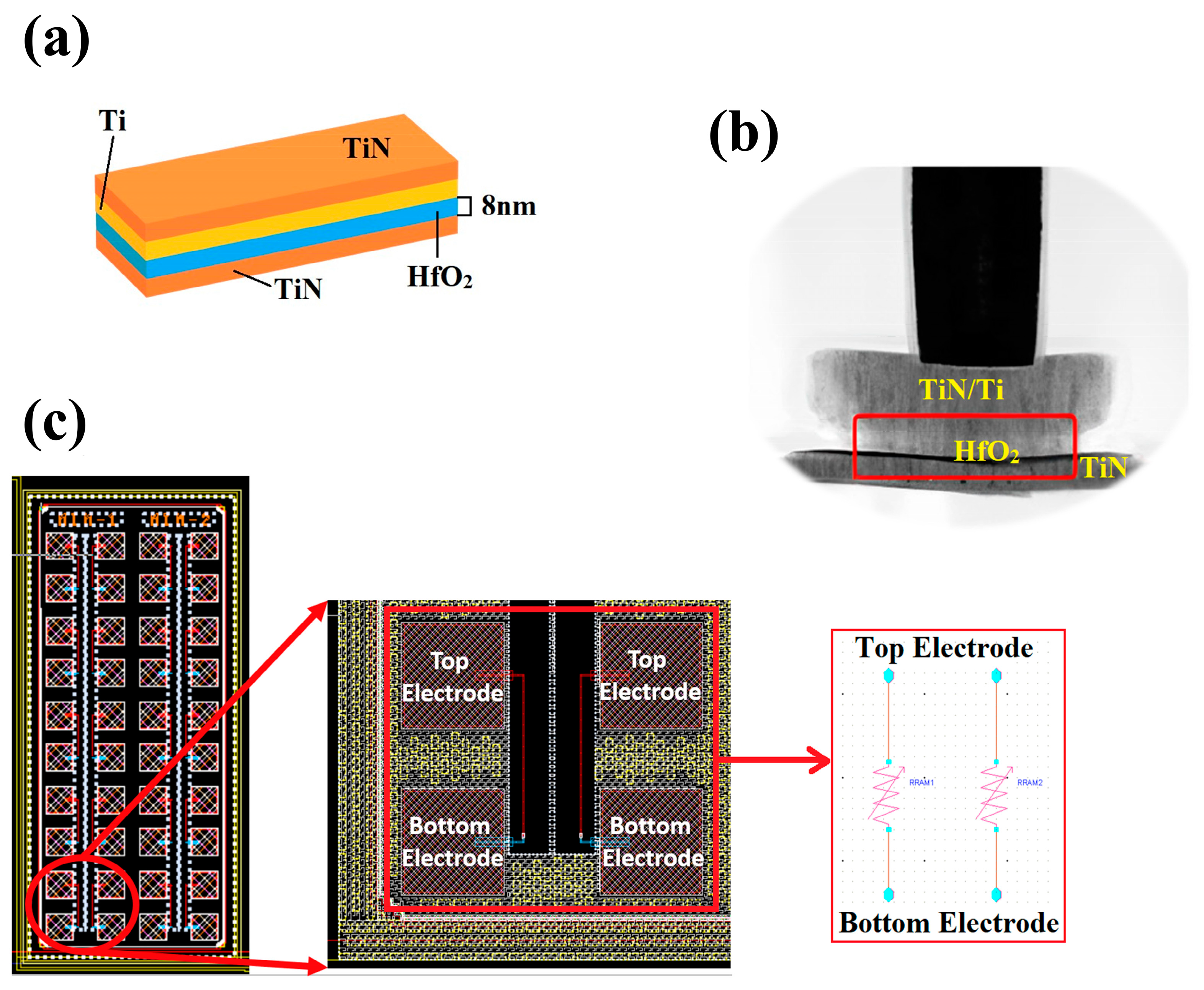
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chou, C.C.; Lin, Z.J.; Lai, C.A.; Su, C.I.; Tseng, P.L.; Chen, W.C.; Tsai, W.C.; Chu, W.T.; Ong, T.C.; Chuang, H.; et al. A 22 nm 96KX144 RRAM macro with a self-tracking reference and a low ripple charge pump to achieve a configurable read window and a wide operating voltage range. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Honolulu, HI, USA, 16–19 June 2020; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Lanza, M.; Sebastian, A.; Lu, W.D.; Le Gallo, M.; Chang, M.F.; Akinwande, D.; Puglisi, F.M.; Alshareef, H.; Liu, M.; Roldan, J.B. Memristive technologies for data storage, computation, encryption, and radio-frequency communication. Science 2022, 376, eabj9979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Kapur, S.; Saurabh, S.; Grover, A. Resistive random access memory: A review of device challenges. IETE Tech. Rev. 2020, 37, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Mirzakuchaki, S.; Arumí, D.; Manich, S.; Gómez-Pau, A.; Campabadal, F.; González, M.B.; Rodríguez-Montañés, R. True random number generator based on the variability of the high resistance state of RRAMs. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 66682–66693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yao, P.; Gao, B.; Liu, Q.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Qin, Q.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Edge learning using a fully integrated neuro-inspired memristor chip. Science 2023, 381, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiga, S.; Sebastian, A.; Querlioz, D.; Rajendran, B. (Eds.) Memristive Devices for Brain-Inspired Computing: From Materials, Devices, and Circuits to Applications-Computational Memory, Deep Learning, and Spiking Neural Networks; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2020; pp. xix–xx. [Google Scholar]
- Jasmin, A.C. Filamentary model in resistive switching materials. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1901, 060004. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.; Noh, T.W. Resistive switching phenomena: A review of statistical physics approaches. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2015, 2, 031303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waser, R.; Menzel, S.; Rana, V. Recent progress in redox-based resistive switching. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 20–23 May 2012; pp. 1596–1599. [Google Scholar]
- Waser, R. Redox-based resistive switching memories. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 7628–7640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmann, R.; Menzel, S.; Waser, R. Nanoionic memristive phenomena in metal oxides: The valence change mechanism. Adv. Phys. 2021, 70, 155–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, G.; Demetriadou, A.; Li, W.; Kos, D.; Zhu, B.; Wang, X.; de Nijs, B.; Wang, H.; MacManus-Driscoll, J.; Baumberg, J.J. Real-time in situ optical tracking of oxygen vacancy migration in memristors. Nat. Electron. 2020, 3, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Redondo, F.; López-Vallejo, M. Self-controlled multilevel writing architecture for fast training in neuromorphic RRAM applications. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 405203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wen, D. Switching-enhanced RRAM for reliable synaptic simulation and multilevel data storage. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 892, 162180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Mahata, C.; Kwon, O.; Kim, S. Neuromorphic synapses with high switching uniformity and multilevel memory storage enabled through a Hf-Al-O alloy for artificial intelligence. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 1288–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Fernandez, A.; Cagli, C.; Perniola, L.; Suñé, J.; Miranda, E. Effect of the voltage ramp rate on the set and reset voltages of ReRAM devices. Microelectron. Eng. 2017, 178, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, H.; Vinuesa, G.; García-Ochoa, E.; Aguirre, F.L.; González, M.B.; Jiménez-Molinos, F.; Campabadal, F.; Roldán, J.B.; Miranda, E.; Dueñas, S.; et al. Effects of the voltage ramp rate on the conduction characteristics of HfO2-based resistive switching devices. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2023, 56, 365108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestro, M.; Martin-Martinez, J.; Diaz, J.; Crespo-Yepes, A.; Gonzalez, M.B.; Rodriguez, R.; Campabadal, F.; Nafría, M.; Aymerich, X. Analysis of Set and Reset mechanisms in Ni/HfO2-based RRAM with fast ramped voltages. Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 147, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleck, K.; Böttger, U.; Waser, R.; Menzel, S. Interrelation of sweep and pulse analysis of the SET process in SrTiO3 resistive switching memories. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2014, 35, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, G.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jia, C. Asymmetric Resistive Switching Effect in Au/Nb:SrTiO3 Schottky Junctions. Phys. Status Solidi A 2018, 215, 1700912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Q.; Wu, M.H.; Li, X.Y.; Bai, Y.; Deng, N.; Yu, Z.P.; Qian, H. Asymmetric resistive switching processes in W: AlOx/WOy bilayer devices. Chin. Phys. B 2015, 24, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.H.; Äkäslompolo, L.; Tuomisto, N.; Yao, L.; Majumdar, S.; Vijayakumar, J.; Casiraghi, A.; Inkinen, S.; Chen, B.; Zugarramurdi, A.; et al. Resistive Switching in All-Oxide Ferroelectric Tunnel Junctions with Ionic Interfaces. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6852–6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Li, J.; Yang, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W. Ferroelectric Field Effect Induced Asymmetric Resistive Switching Effect in BTiO3Nb:SrTiO3 Epitaxial Heterojunctions. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, D.; Cantudo, A.; Perez, E.; Romero-Zaliz, R.; Perez-Bosch Quesada, E.; Mahadevaiah, M.K.; Jimenez-Molinos, F.; Wenger, C.; Roldan, J.B. TiN/Ti/HfO2/TiN memristive devices for neuromorphic computing: From synaptic plasticity to stochastic resonance. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1271956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, E.; Zambelli, C.; Mahadevaiah, M.K.; Olivo, P.; Wenger, C. Toward Reliable Multi-Level Operation in RRAM Arrays: Improving Post-Algorithm Stability and Assessing Endurance/Data Retention. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 2019, 7, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, E.; González Ossorio, Ó.; Dueñas, S.; Castán, H.; García, H.; Wenger, C. Programming Pulse Width Assessment for Reliable and Low-Energy Endurance Performance in Al:HfO2-Based RRAM Arrays. Electronics 2020, 9, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.; Chen, W.; Gao, L.; Yu, W.; Yu, S. Low-temperature characteristics of HfOx-based resistive random access memory. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2015, 36, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, F.C. A review on conduction mechanisms in dielectric films. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 578168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.W.; Ismail, R. Conduction mechanism of valence change resistive switching memory: A survey. Electronics 2015, 4, 586–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Chen, P.S.; Wu, T.Y.; Chen, Y.S.; Chen, F.; Wang, C.C.; Tzeng, P.J.; Lin, C.H.; Tsai, M.J.; Lien, C. HfOx Bipolar Resistive Memory with Robust Endurance Using AlCu as Buffer Electrode. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2009, 30, 703–705. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.Y.; Chen, P.S.; Wu, T.Y.; Chen, Y.S.; Chen, F.; Wang, C.C.; Tzeng, P.J.; Tsai, M.J.; Lien, C. Low-power and nanosecond switching in robust hafnium oxide resistive memory with a thin Ti cap. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2010, 31, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Huang, C.W.; Lee, D.Y.; Tseng, T.Y.; Chang, T.C. Multilevel resistive switching in Ti/CuxO/Pt memory devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 114110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jeong, H.Y.; Choi, S.Y.; Choi, Y.K. Comprehensive modeling of resistive switching in the Al/TiOx/TiO2/Al heterostructure based on space-charge-limited conduction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 033508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Xu, D.; Tang, M.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, R.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y. Improvement of resistive switching performances via an amorphous ZrO2 layer formation in TiO2-based forming-free resistive random access memory. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 124514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Huang, C.Y.; Panda, D.; Hung, C.J.; Tsai, T.L.; Jieng, J.H.; Lin, C.A.; Chand, U.; Anwar, M.R.; Ahmed, E.; et al. Forming-free bipolar resistive switching in nonstoichiometric ceria films. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Wang, X.P.; Sohn, J.; Bin Weng, B.; Zhang, Z.P.; Chen, Z.X.; Tang, Y.Z.; Lo, G.-Q.; Provine, J.; Wong, S.S.; et al. The Role of Ti Capping Layer in HfOx-Based RRAM Devices. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2014, 35, 912–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Yu, S.; Xu, N.; Liu, L.; Sun, B.; Liu, X.; Han, R.; Kang, J.; Yu, B.; Wang, Y. Oxide-Based RRAM Switching Mechanism: A New Ion-Transport-Recombination Model. In Proceedings of the IEDM, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–17 December 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Dirkmann, S.; Kaiser, J.; Wenger, C.; Mussenbrock, T. Filament Growth and Resistive Switching in Hafnium Oxide MemristiveDevices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 14857–14868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cordero, G.; Pedro, M.; Martín-Martínez, J.; González, M.B.; Jiménez-Molinos, F.; Campabadal, F.; Nafría, N.; Roldán, J.B. Analysis of resistive switching processes in TiN/Ti/HfO2/W devices to mimic electronic synapses in neuromorphic circuits. Solid-State Electron. 2019, 157, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldana, S.; García-Fernández, P.; Romero-Zaliz, R.; González, M.B.; Jiménez-Molinos, F.; Gómez-Campos, F.; Campabadal, F.; Roldán, J.B. Resistive switching in HfO2 based valence change memories, a comprehensive 3D kinetic Monte Carlo approach. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 225106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinuesa, G.; García, H.; Ossorio, Ó.G.; García-Ochoa, E.; González, M.B.; Kalam, K.; Kukli, K.; Tamm, A.; Campabadal, F.; Castán, H.; et al. Effect of Temperature on the Multilevel Properties and Set and Reset Transitions in HfO2-Based Resistive Switching Devices. In Proceedings of the 2023 14th Spanish Conference on Electron Devices, Valencia, Spain, 6–8 June 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- García, H.; Dueñas, S.; Ossorio, Ó.G.; Castán, H. Current pulses to control the conductance in RRAM devices. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 2020, 8, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vinuesa, G.; García, H.; Pérez, E.; Wenger, C.; Íñiguez-de-la-Torre, I.; González, T.; Dueñas, S.; Castán, H. On the Asymmetry of Resistive Switching Transitions. Electronics 2024, 13, 2639. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132639
Vinuesa G, García H, Pérez E, Wenger C, Íñiguez-de-la-Torre I, González T, Dueñas S, Castán H. On the Asymmetry of Resistive Switching Transitions. Electronics. 2024; 13(13):2639. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132639
Chicago/Turabian StyleVinuesa, Guillermo, Héctor García, Eduardo Pérez, Christian Wenger, Ignacio Íñiguez-de-la-Torre, Tomás González, Salvador Dueñas, and Helena Castán. 2024. "On the Asymmetry of Resistive Switching Transitions" Electronics 13, no. 13: 2639. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132639
APA StyleVinuesa, G., García, H., Pérez, E., Wenger, C., Íñiguez-de-la-Torre, I., González, T., Dueñas, S., & Castán, H. (2024). On the Asymmetry of Resistive Switching Transitions. Electronics, 13(13), 2639. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132639








