Analytical Calculation of the No-Load Magnetic Field of a Hybrid Excitation Generator
Abstract
1. Introduction
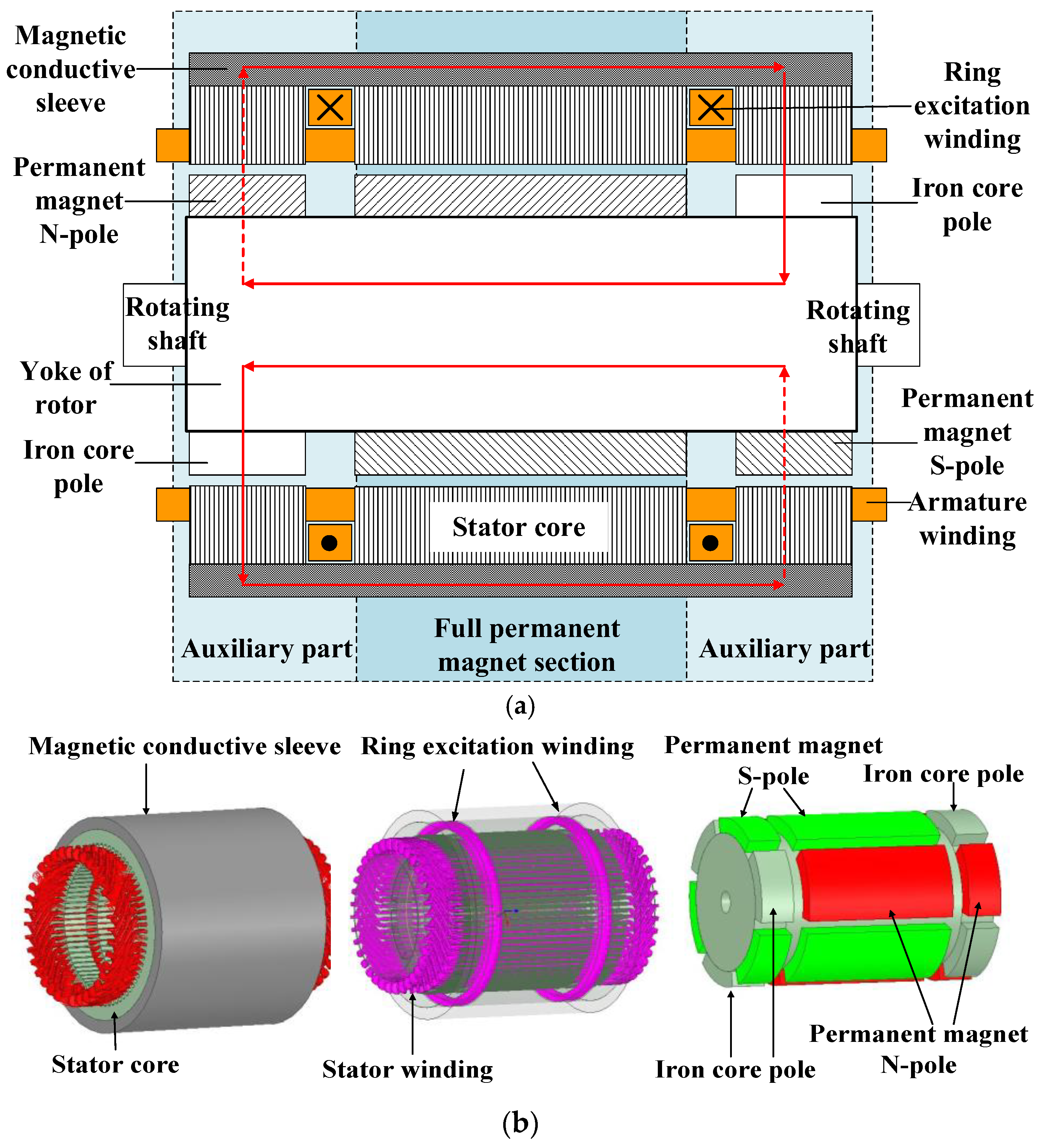
2. Basic Structure and Principles
2.1. Basic Structure
2.2. Working Principle
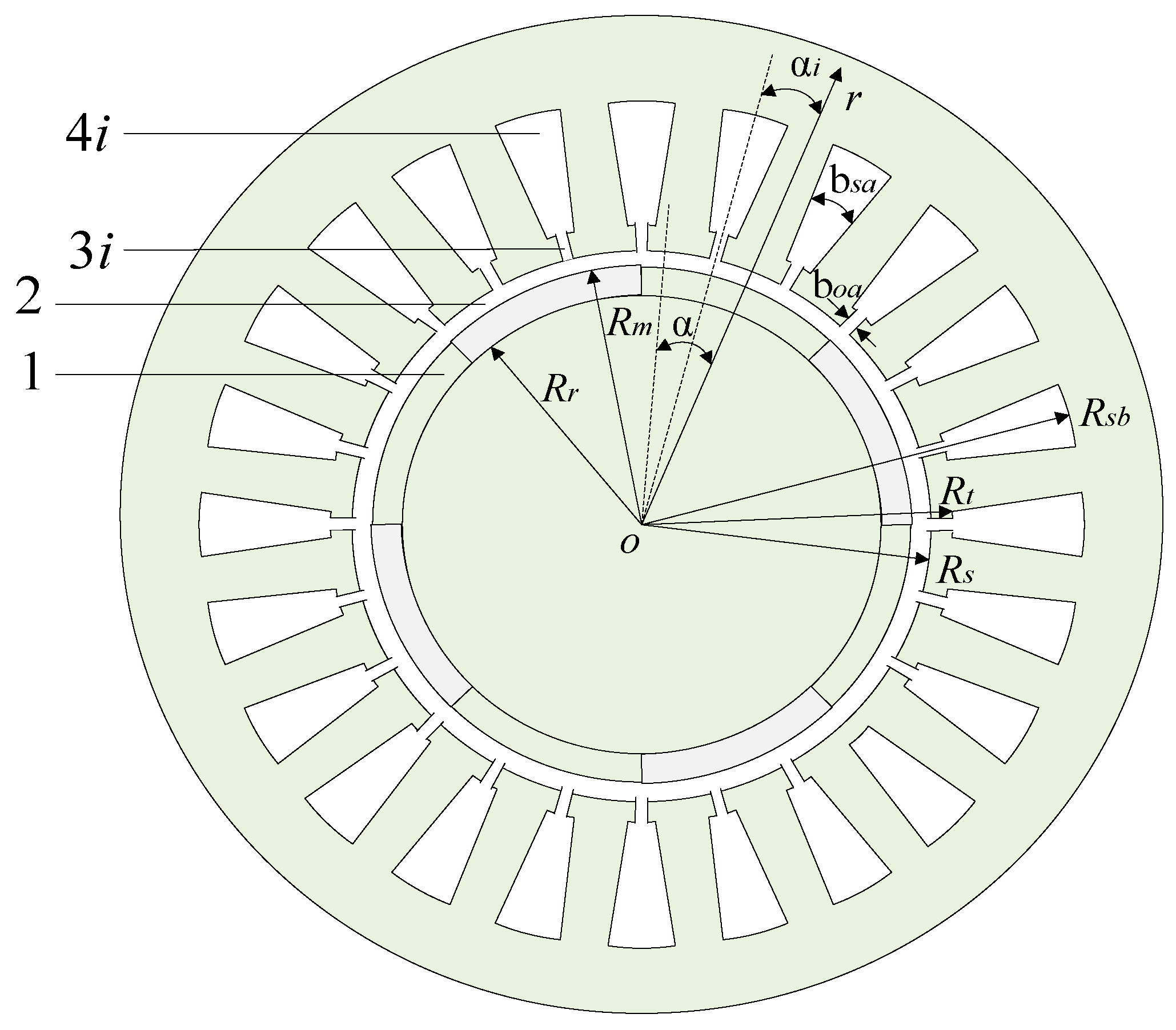
3. Accurate Subdomain Model Analysis
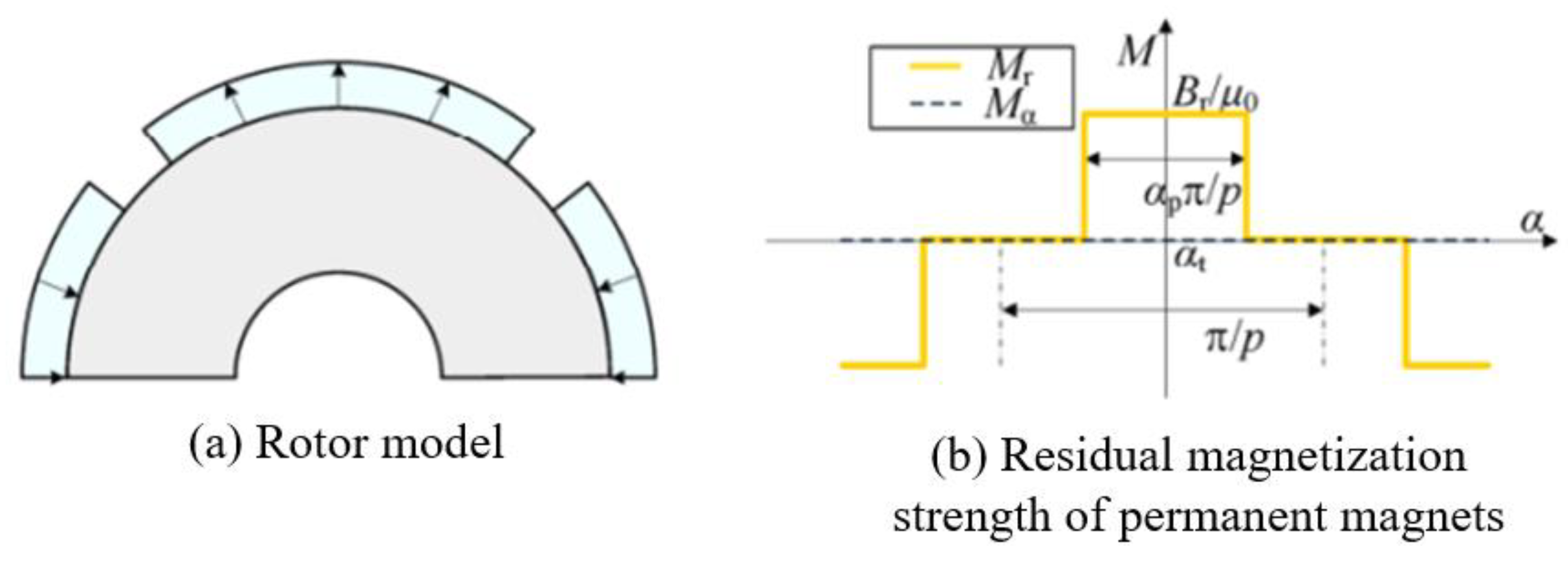
3.1. Basic Assumptions
- (1)
- The magnetic permeability of the stator and rotor core is infinite;
- (2)
- The demagnetization curve of the permanent magnet material is linear;
- (3)
- Ignoring the conductance effect and eddy current effect of ferromagnetic materials.
3.2. Analytic Model of the Magnetic Field in the Rotor Domain
3.3. Analytic Model of the Magnetic Field in the Stator Domain
3.3.1. The Stator Slot Sub-Domain
3.3.2. Stator Slot Hole Field
3.4. Analytic Model of the Magnetic Field in the Air-Gap Domain
3.5. Boundary Conditions
3.6. Equation Solution and Correlation Coefficient
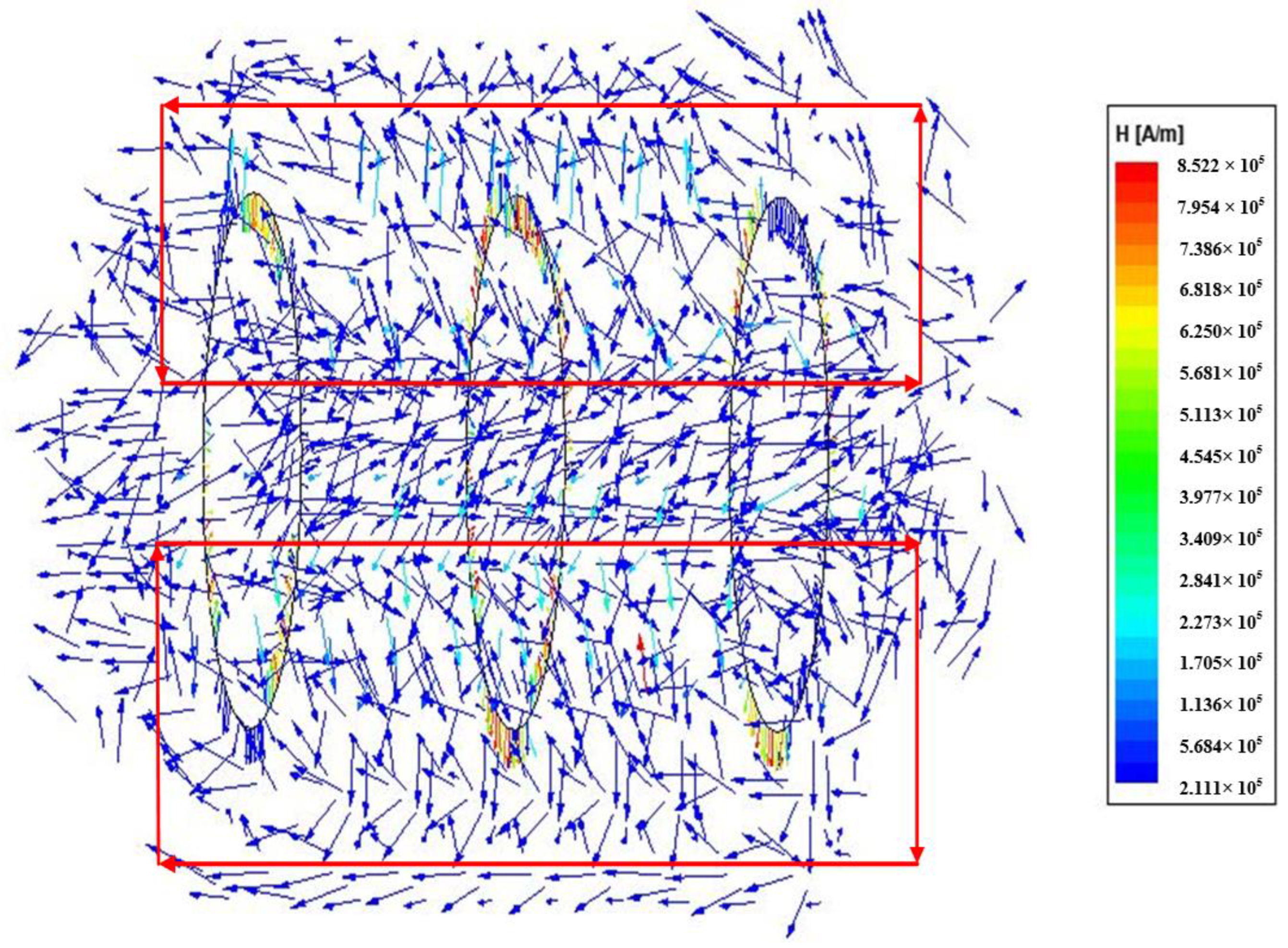
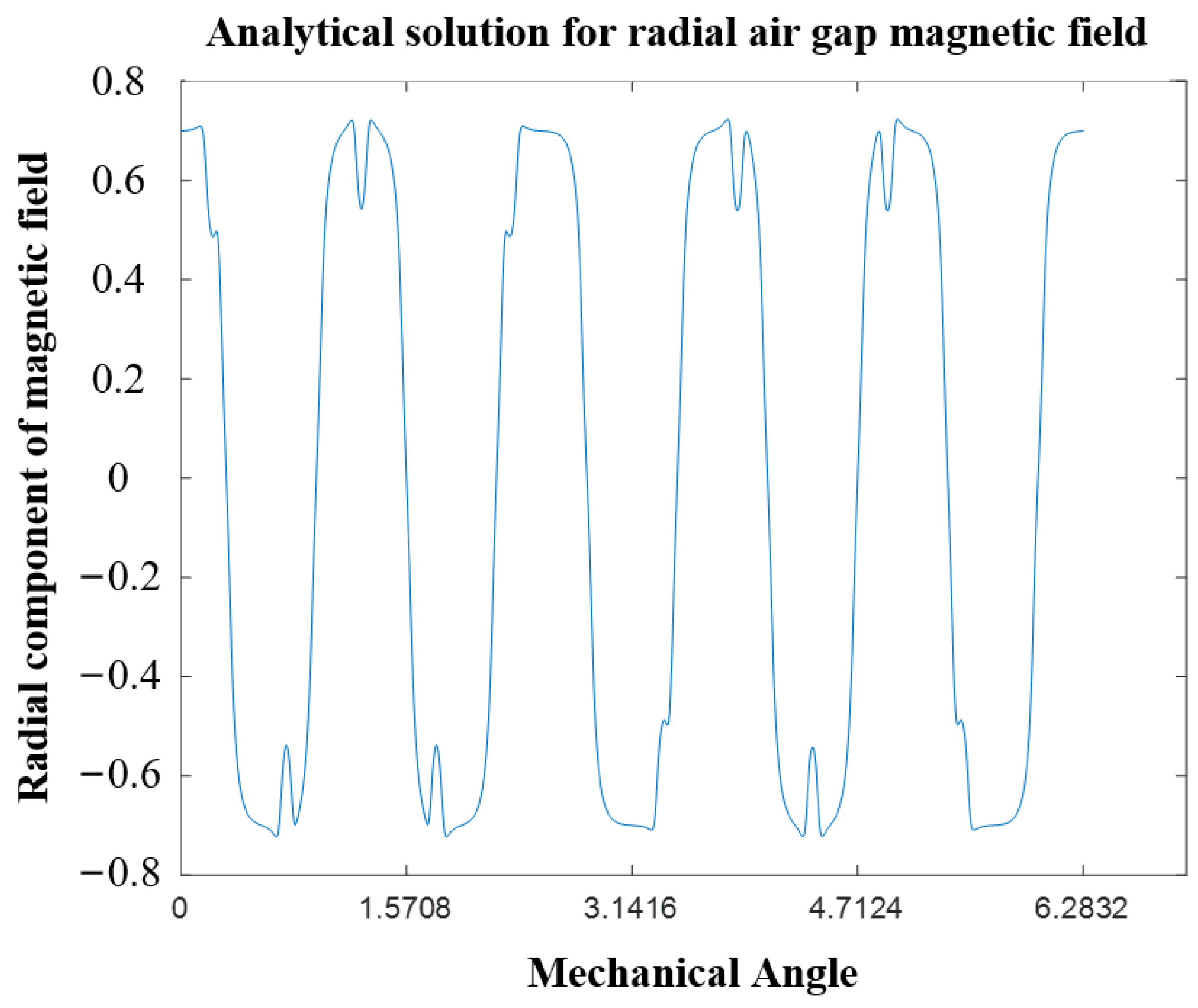
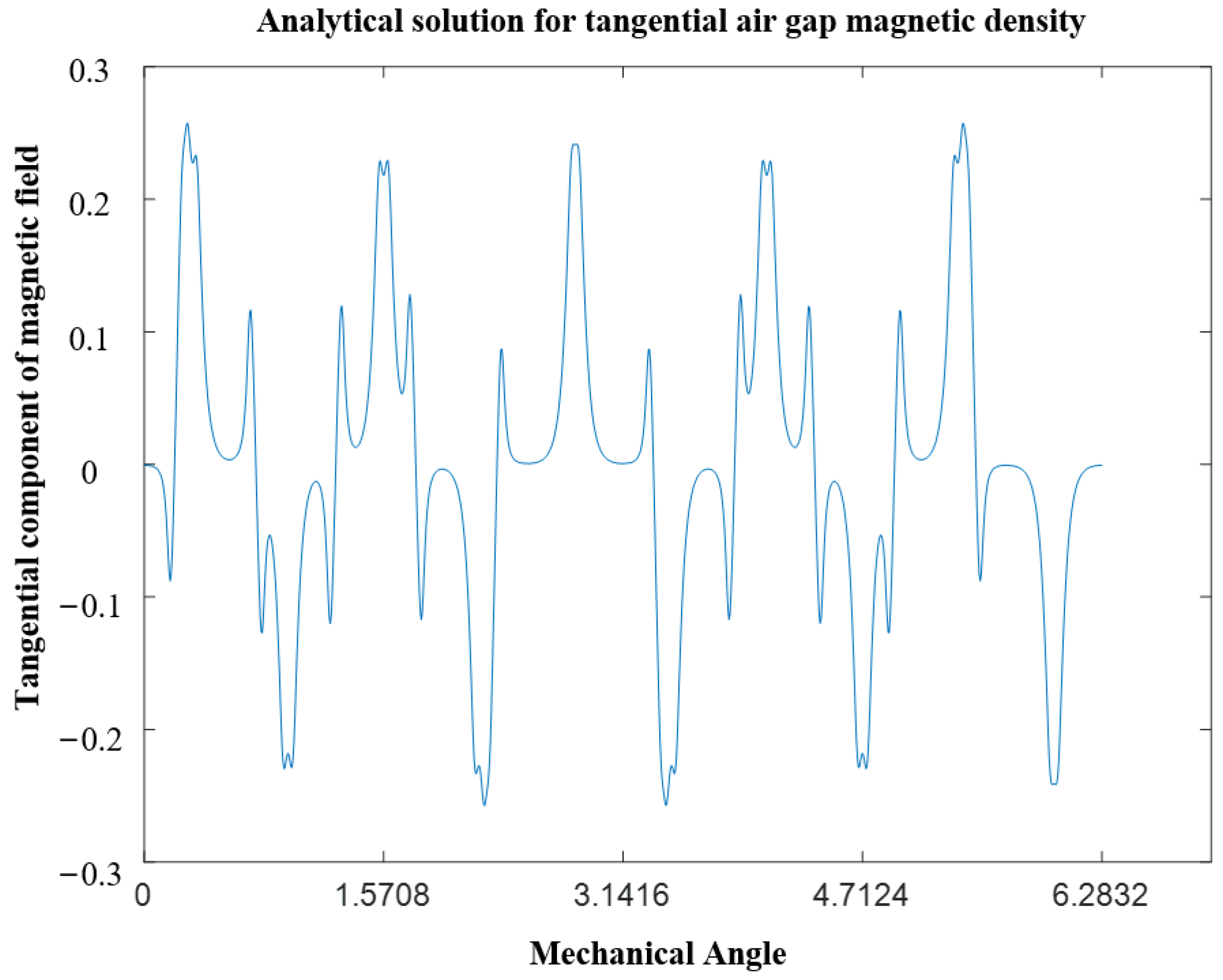
4. Simulation, Analysis and Verification
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The solution results of the subdomain method are highly consistent with the finite element analysis results, indicating that the subdomain method can be used to carry out the magnetic field calculation and analysis of the motor.
- (2)
- In the present study, the sub-domain method was adopted considering the opening of the stator slot, and the influence of the stator slot effect could be considered. Therefore, the influence of the slot effect on motor performance can be studied to provide a basis for motor design.
- (3)
- Using the theory and method to solve the hybrid excitation motor equivalent to a full permanent magnet motor, the no-load magnetic field is correct and effective. This method can be used to accurately analyze and calculate the magnetic field of the hybrid excitation motor, which lays a solid foundation for further study of the motor.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Ma, W. Some thoughts on the development of frontier technology in electrical discipline. J. Electr. Technol. 2021, 36, 4627–4636. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Lu, J. Research status and challenges of electromagnetic emission technology. J. Electr. Technol. 2023, 38, 3943–3959. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W. The direction of ship power development-Integrated power system. J. Nav. Univ. Eng. 2002, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, G.; Ma, F.; Ye, Z.; Ji, F.; Liu, L. Research progress of MV DC integrated power system in China. China Ship Res. 2016, 11, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Di Barba, P.; Bonislawski, M.; Palka, R.; Paplicki, P.; Wardach, M. Design of Hybrid Excited Synchronous Machine for Electrical Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 2424392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörée, G.; Leijon, M. Overview of Hybrid Excitation in Electrical Machines. Energies 2022, 15, 7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, M.; Fu, X.; Huang, Y.; Xu, D. An Overview and New Progress of Hybrid Excited Synchronous Machines and Control Technologies. Proc. Chin. Soc. Electr. Eng. 2014, 34, 5876–5887. [Google Scholar]
- Di Barba, P.; Mognaschi, M.E.; Bonislawski, M.; Palka, R.; Paplicki, P.; Piotuch, R.; Wardach, M. Hybrid excited synchronous machine with flux control possibility. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2016, 52, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, L.; Michieletto, D.; Bianchi, N.; Bertoluzzo, M. Hybrid Excited Permanent Magnet Motor: Analytical Sizing, Finite Element Analysis and Tests. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 6645–6654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Wang, D.; Wei, K.; Cheng, S.; Yi, X. Structure and voltage regulating performance of high-speed mixed excitation generator. J. Electrotech. Technol. 2016, 31, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Xing, Z.; Yu, A.; Li, C. Reduction of cogging torque and electromagnetic vibration based on different combination of pole arc coefficient for interior permanent magnet synchronous machine. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2021, 5, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Howe, D. Instantaneous magnetic field distribution in brushless permanent magnet DC motors. Part I: Open-circuit field. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1993, 29, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faradonbeh, V.Z.; Rahideh, A.; Boroujeni, S.T.; Markadeh, G.A. 2-D. Analytical No-Load Electromagnetic Model for Slotted Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 3118–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faradonbeh, V.Z.; Rahideh, A. 2-D analytical on-load electromagnetic model for double-layer slotted interior permanent magnet synchronous machines. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2022, 16, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymoori, S.; Rahideh, A.; Moayed-Jahromi, H.; Mardaneh, M. 2-D Analytical Magnetic Field Prediction for Consequent-Pole Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruda, A.; Louf, F.; Boucard, P.-A.; Mininger, X.; Verbeke, T. A parallel implementation of a mixed multiscale domain decomposition method applied to the magnetostatic simulation of 2D electrical machines. Finite Elements Anal. Des. 2024, 235, 104136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, A.; Leonardi, F.; Lipo, T.A. Consequent-pole permanent-magnet machine with extended field-weakening capability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 1704–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D. Mathematical model and equivalent analysis of new hybrid excitation synchronous motor. J. Electr. Technol. 2017, 32, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, G.; Ye, C.; Deng, C.; Wan, S.; Liu, K.; Yao, K.; Qi, X.; Lu, J.; Wang, Z. Theoretical Analysis for Rapid Design of Hybrid Excitation Synchronous Machine with Consequent Pole Rotor. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 1-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yin, H.; Wang, D.; Fang, Y. A Nonlinear Subdomain and Magnetic Circuit Hybrid Model for Open-Circuit Field Prediction in Surface-Mounted PM Machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 1485–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. Practical Design of Magnetostatic Structure Using Numerical Simulation; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, L.; Zhao, C.; Shen, H. Research on Tangential Magnetization Parallel Magnetic Path HybridExcitation Synchronous Machine. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2022, 17, 2761–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guan, P.; Liu, S.; Wu, S.; Shi, T.; Guo, L. Modeling and Analyzing for Magnetic Field of Segmented Surface-Mounted PM Motors with Skewed Poles. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2022, 17, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Gu, F.; Wang, L.; Ma, S.; Golmohammadi, A.-M.; Zhang, S. The Design and Optimization of a Novel Hybrid Excitation Generator for Vehicles. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 15, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Zhao, C.; Shen, H. Properties of Adjust Magnetic Field of Hybrid Excitation Synchronous Machine with Tangential Accumulation of Magnetic Field Shunt-wound Magnetic Path. In Proceedings of the 2021 24th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Gyeongju, Republic of Korea, 31 October–3 November 2021; pp. 1538–1543. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.; Ma, C.; Zhang, N.; Guo, Y.; Degano, M.; Gerada, C.; Bu, F.; Yin, X.; Li, Q.; Zhou, S. Calculation Model of Armature Reaction Magnetic Field of Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Segmented Skewed Poles. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Pang, L.; Hu, H.; Qin, H.; Zhao, C. The effect of excitation current on radial electromagnetic force wave of tangential magnetizing parallel structure hybrid excitation synchronous motor. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2024, 74, 209–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Guo, L.; Wang, H. Modeling and Analyzing of Magnetic Field of Segmented Halbach Array Permanent Magnet Machine Considering Gap between Segments. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 2336835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Guo, Y.; Wang, D.; Wei, K. Semi-Analytical Calculation of No-Load Radial and Tangential Electromagnetic Force Waves of a Non-Salient Pole Synchronous Generator. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 2956–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Numeric Value | Parameter | Numeric Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stator core outer diameter Dso/mm | 234 | Rotor core outer diameter Dro/mm | 154 |
| Stator core inner diameter Dsi/mm | 160 | Rotor core inner diameter Dri/mm | 20 |
| Number of stator slots Q | 72 | Permanent magnet thickness hpm/mm | 14 |
| Axial length of the alternating polar part ljc/mm | 30 | Gas length hg/mm | 2 |
| Axial length of the permanent magnet part lpm/mm | 135 | Pole embrace | 0.85 |
| Number of pole-pairs | 3 | Remanent flux density | 1.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yan, S.; Wei, K. Analytical Calculation of the No-Load Magnetic Field of a Hybrid Excitation Generator. Electronics 2024, 13, 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132574
Xiong Y, Zhao J, Yan S, Wei K. Analytical Calculation of the No-Load Magnetic Field of a Hybrid Excitation Generator. Electronics. 2024; 13(13):2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132574
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Yiyong, Jinghong Zhao, Sinian Yan, and Kun Wei. 2024. "Analytical Calculation of the No-Load Magnetic Field of a Hybrid Excitation Generator" Electronics 13, no. 13: 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132574
APA StyleXiong, Y., Zhao, J., Yan, S., & Wei, K. (2024). Analytical Calculation of the No-Load Magnetic Field of a Hybrid Excitation Generator. Electronics, 13(13), 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132574






