Machine Learning-Based Anomaly Detection for Securing In-Vehicle Networks
Abstract
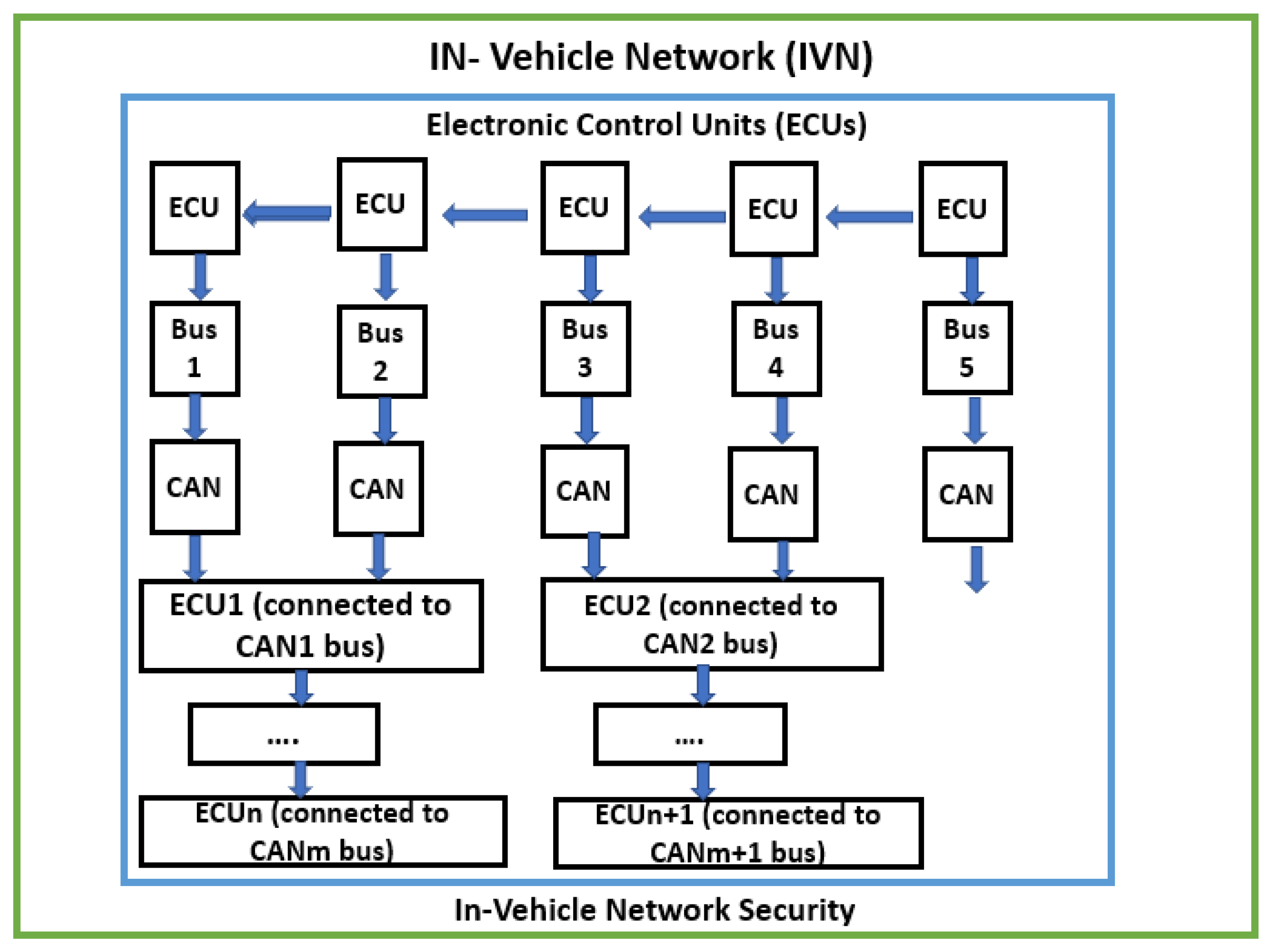
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
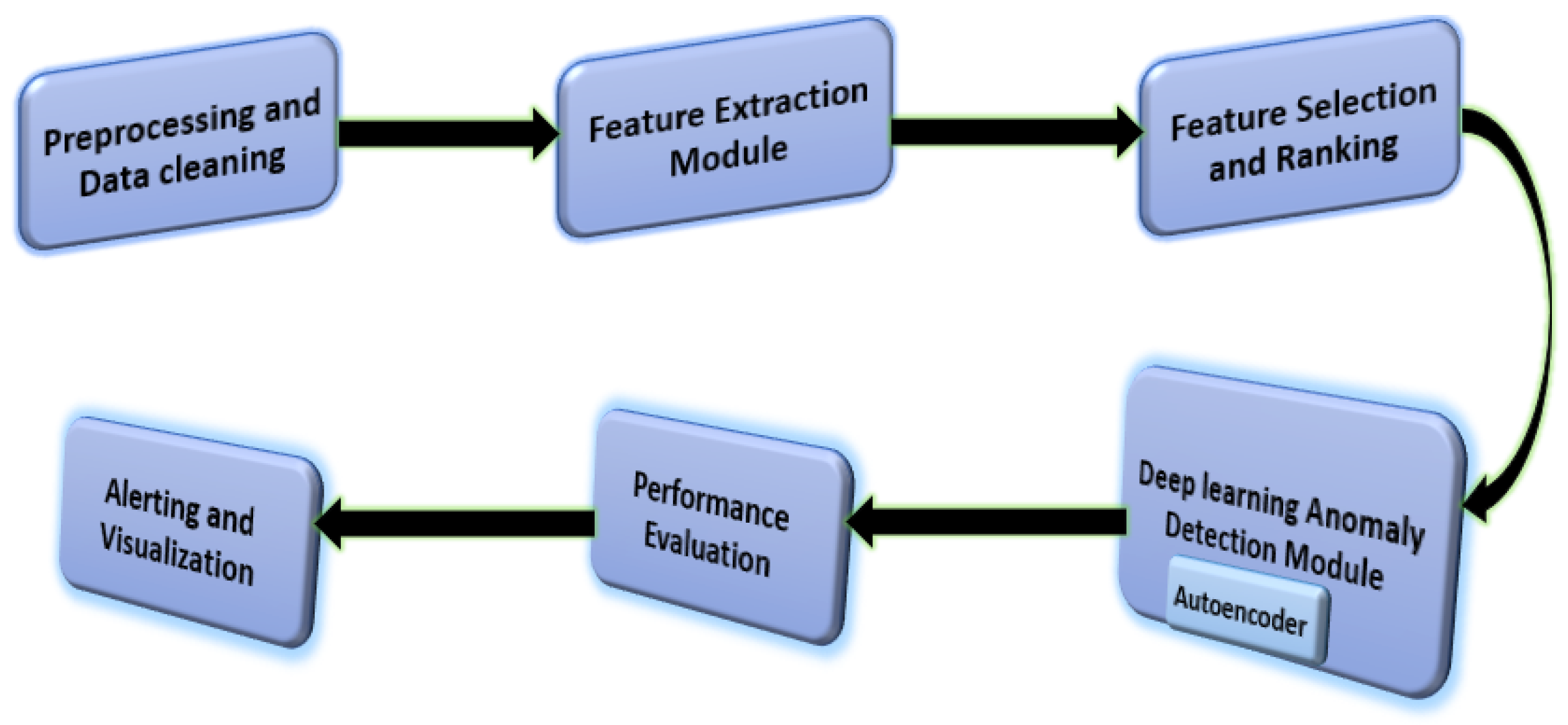
3. Proposed Approach
3.1. Data Preprocessing
3.2. Feature Extraction
- Statistical features including mean, variance, skewness, and kurtosis of the data.
- Frequency-domain features including power spectral density (PSD) and spectral entropy.
- Time-domain features including auto-correlation and cross-correlation between different network traffic signals.
- Learned features: we use a convolutional neural network (CNN) to learn high-level features from the raw network traffic data.
3.3. Anomaly Detection
4. Experiments and Results Analysis
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Data Preprocessing and Feature Extraction
4.3. Deep Learning Model
4.4. Evaluation Metrics
4.5. Fine-Tuning Hyper-Parameters
4.5.1. Hyper-Parameter Sensitivity
4.5.2. Grid Search and Cross-Validation
4.6. Experimental Results
4.7. Discussion of Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NHTSA. Cybersecurity Best Practices for Modern Vehicles. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. 2022. Available online: https://www.nhtsa.gov/sites/nhtsa.gov/files/2022-09/cybersecurity-best-practices-safety-modern-vehicles-2022-pre-final-tag_0_0.pdf (accessed on 3 September 2022).
- Mahbod, A.; Dehghantanha, A.; Choo, K.K.R.; Conti, M. Applications of machine learning in cybersecurity. Comput. Secur. 2019, 83, 48–65. [Google Scholar]
- Auto-ISAC. Best Practices Auto-ISAC. 2021. Available online: https://automotiveisac.com/best-practices (accessed on 15 July 2016).
- Yoshizawa, T.; Singelée, D.; Muehlberg, J.T.; Delbruel, S.; Taherkordi, A.; Hughes, D.; Preneel, B. A Survey of Security and Privacy Issues in V2X Communication Systems. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; He, J. In-vehicle network anomaly detection using wavelet transform and unsupervised clustering. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 869–881. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Zeng, X.; Huang, L. A PCA-based anomaly detection method for in-vehicle networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 23616–23624. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, J.R.S.; Vieira, M.A.M.; Almeida, J.M. Anomaly detection in in-vehicle networks using a rule-based approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 3284–3296. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Chen, J.; Yu, H. Anomaly detection in in-vehicle network traffic using Gaussian mixture model. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 776–786. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, H.; Li, B.; Li, D. Anomaly detection for in-vehicle networks based on principal component analysis and support vector machine. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 2995–3006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Li, H. Anomaly Detection in In-Vehicle Networks Based on Wavelet Transform and LSTM. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 2903–2916. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Q. Anomaly detection in in-vehicle networks using clustering algorithms. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 106539–106549. [Google Scholar]
- Zong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. Deep Auto-Encoder-Based Anomaly Detection in In-Vehicle Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 3389–3400. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Gong, L.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, X. A distributed anomaly detection system for in-vehicle network using HTM. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 9091–9098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, R.J.; Rubin, D.B. Statistical Analysis with Missing Data; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chandola, V.; Banerjee, A.; Kumar, V. Anomaly detection: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. CSUR 2009, 41, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkan, S.C.; Sahingoz, O.K. In-vehicle intrusion detection system on controller area network with machine learning models. Proceedings of 2020 11th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kharagpur, India, 1–3 July 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Yan, J.; Cao, J. A deep autoencoder-based approach for traffic anomaly detection in intelligent transportation system. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 107298–107308. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, K.; Chen, S.; Lu, K. Traffic anomaly detection based on a deep autoencoder network in vehicular ad hoc networks. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 15041–15051. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, T.; Wu, L.; Yang, Y. A deep learning approach for anomaly detection in maritime traffic. J. Navig. 2019, 72, 373–388. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, Q.; Wang, X.; Yang, X. A deep learning framework for network anomaly detection in intelligent transportation systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 126–137. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Yu, S.; Du, Y. An improved deep auto-encoder network for anomaly detection in the internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 10523–10531. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Anomaly detection in network traffic based on one-class SVM. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 902, 012034. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zheng, S.; Gao, S.; Tang, X. Network anomaly detection based on random forests. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Chongqing, China, 27–29 June 2018; pp. 874–878. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, M.; He, Y. KNN-based deep learning for network anomaly detection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 65597–65607. [Google Scholar]

| Hyper-Parameter | LR | Batch Size | Num Layers | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Configuration | 0.001 | 64 | 3 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.94 | 0.91 |
| Tuned Configuration | 0.0005 | 128 | 4 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.95 |
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | 95% |
| Precision | 93% |
| Recall | 97% |
| F1 Score | 0.95 |
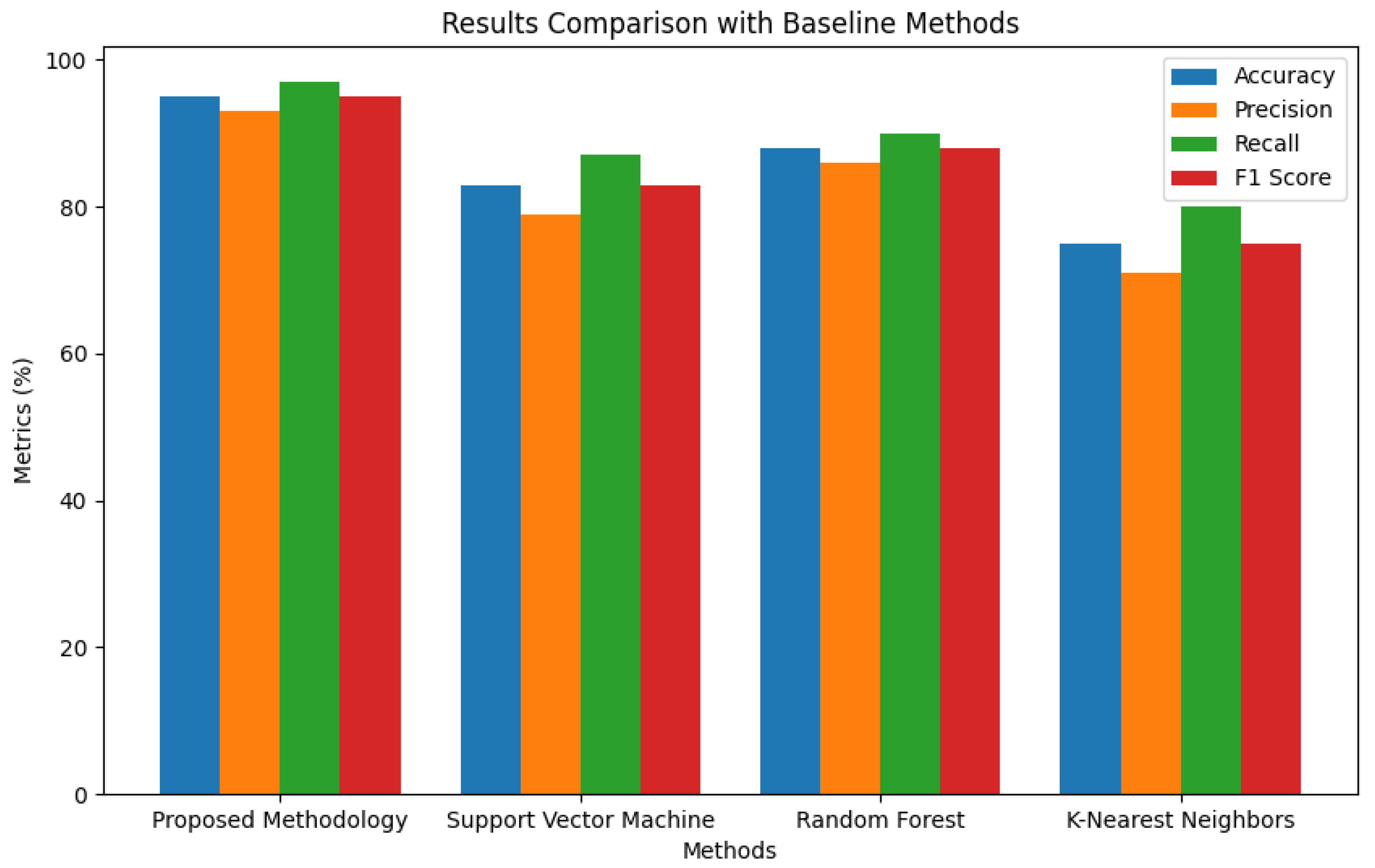
| Method | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed Approach/Method | 95 | 93 | 97 | 0.95 |
| Support Vector Machine | 83 | 79 | 87 | 0.83 |
| Random Forest | 88 | 86 | 90 | 0.88 |
| K-Nearest Neighbors | 75 | 71 | 80 | 0.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfardus, A.; Rawat, D.B. Machine Learning-Based Anomaly Detection for Securing In-Vehicle Networks. Electronics 2024, 13, 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13101962
Alfardus A, Rawat DB. Machine Learning-Based Anomaly Detection for Securing In-Vehicle Networks. Electronics. 2024; 13(10):1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13101962
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfardus, Asma, and Danda B. Rawat. 2024. "Machine Learning-Based Anomaly Detection for Securing In-Vehicle Networks" Electronics 13, no. 10: 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13101962
APA StyleAlfardus, A., & Rawat, D. B. (2024). Machine Learning-Based Anomaly Detection for Securing In-Vehicle Networks. Electronics, 13(10), 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13101962






