A Misalignment-Insensitive Hybrid IPT System with Constant Current Output Based on Parameter Optimization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- The hybrid topology model with parasitic impedance is established, and the influence of parasitic impedance on system output is summarized and analyzed. In addition, the proposed hybrid topology can safely operate without secondary side, which utilizes the characteristics of the circuit without additional control schemes.
- (2)
- The DDQ coils are adopted in this system, which can eliminate the influence of the cross coupling on system output. The PSO parameter optimization design method is proposed to maintain constant output against coupling variation, which can effectively simplify the complexity of the system design.
2. Theoretical Analysis
3. Magnetic Coupler Design Additionally, Parametric Design
3.1. Magnetic Coupler Design
3.2. Parametric Design Method
- (1)
- Generate a certain number of particles randomly in the feasible domain, and each particle has a random position and random initial velocity. Additionally, define a population optimal position and initialize it to 0.
- (2)
- Select the particle with the best position from all the particles and save its position information into the best position of the group.
- (3)
- Perform iteration, and the particle updates the new position after iteration according to its current position and speed.
- (4)
- Each particle updates the speed of the next iteration according to the current optimal position of the group and its own position.
- (5)
- Determine whether each particle meets the iteration stop condition in turn. If so, it is confirmed as the optimal solution. If not, then go to (2).

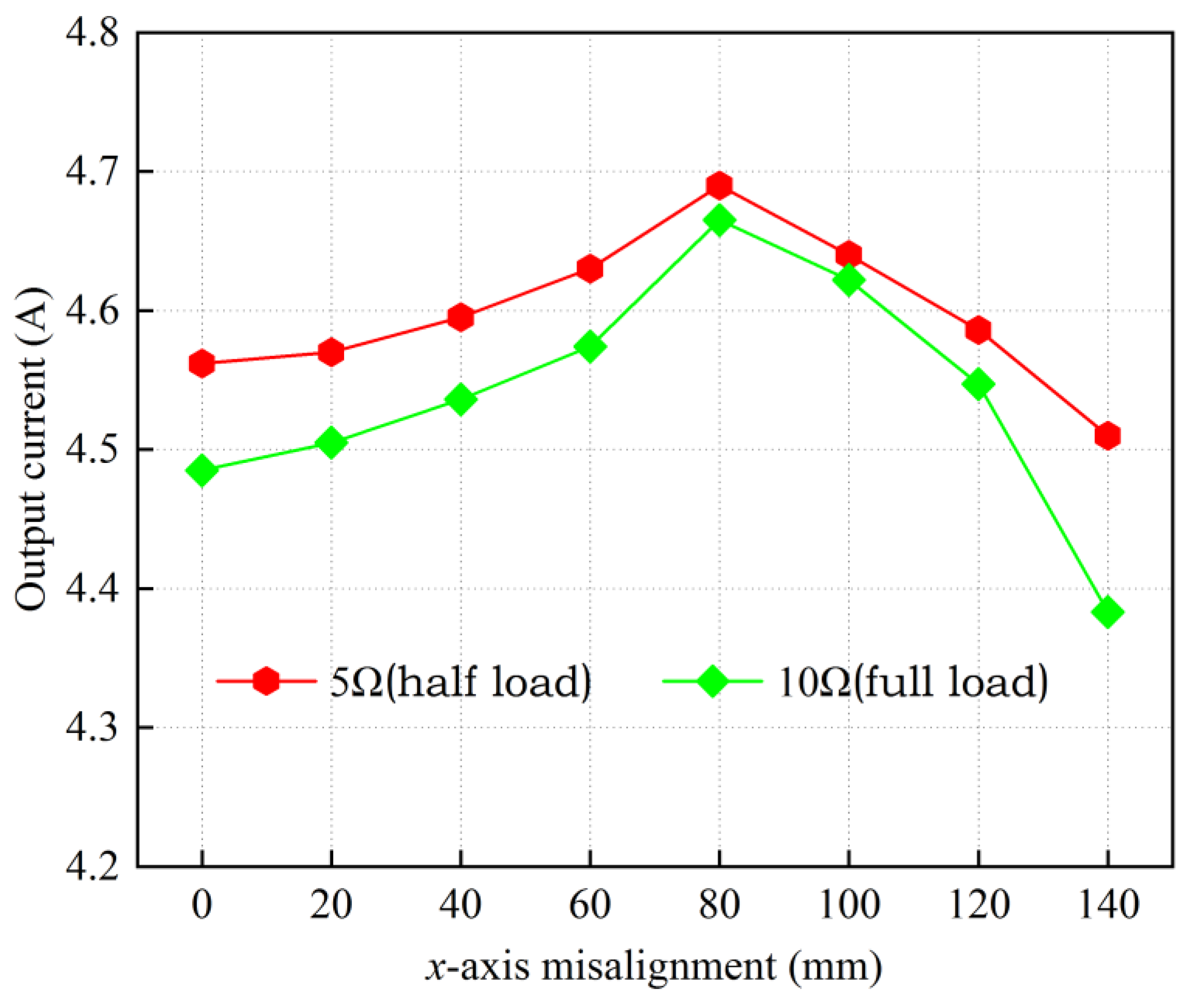
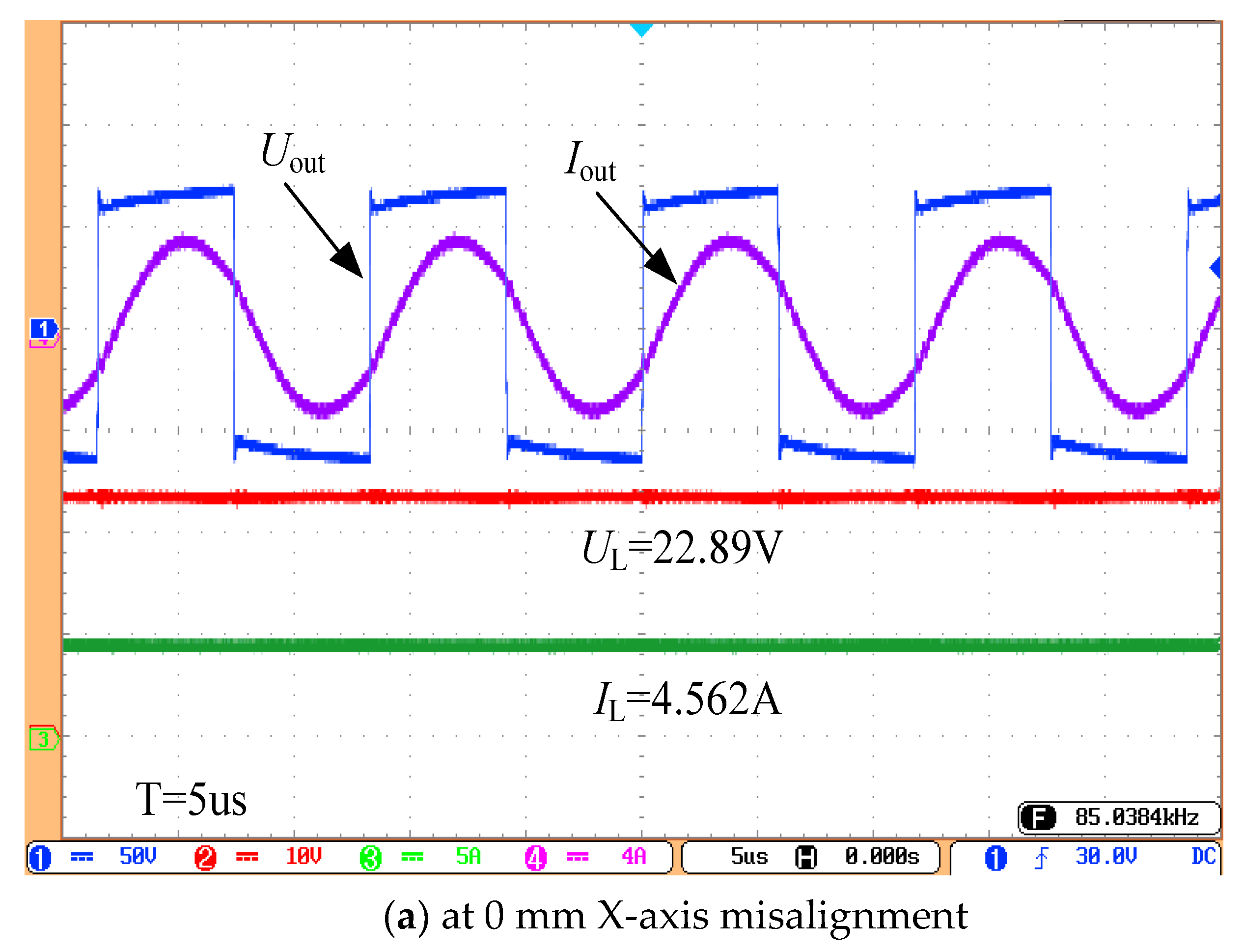
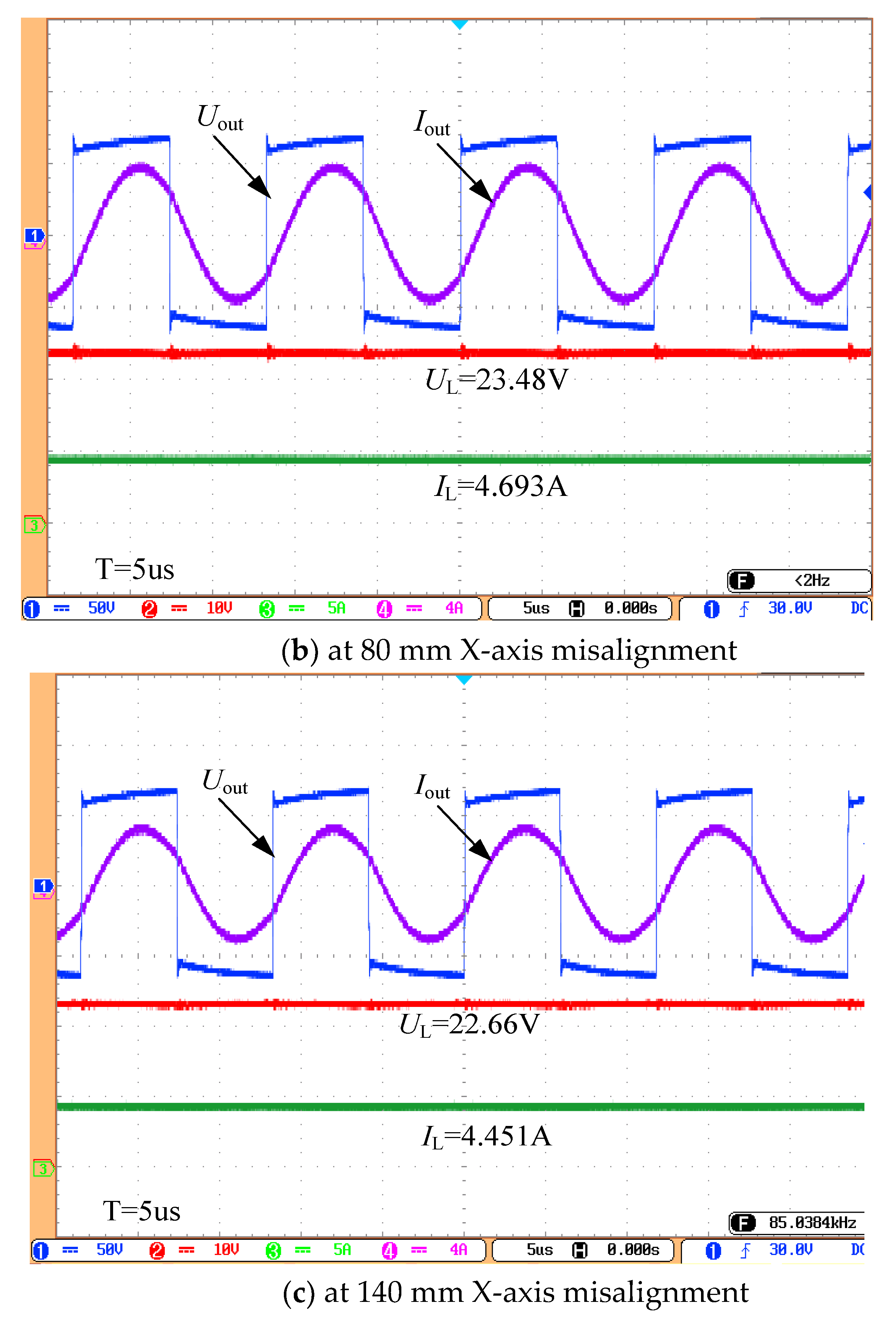
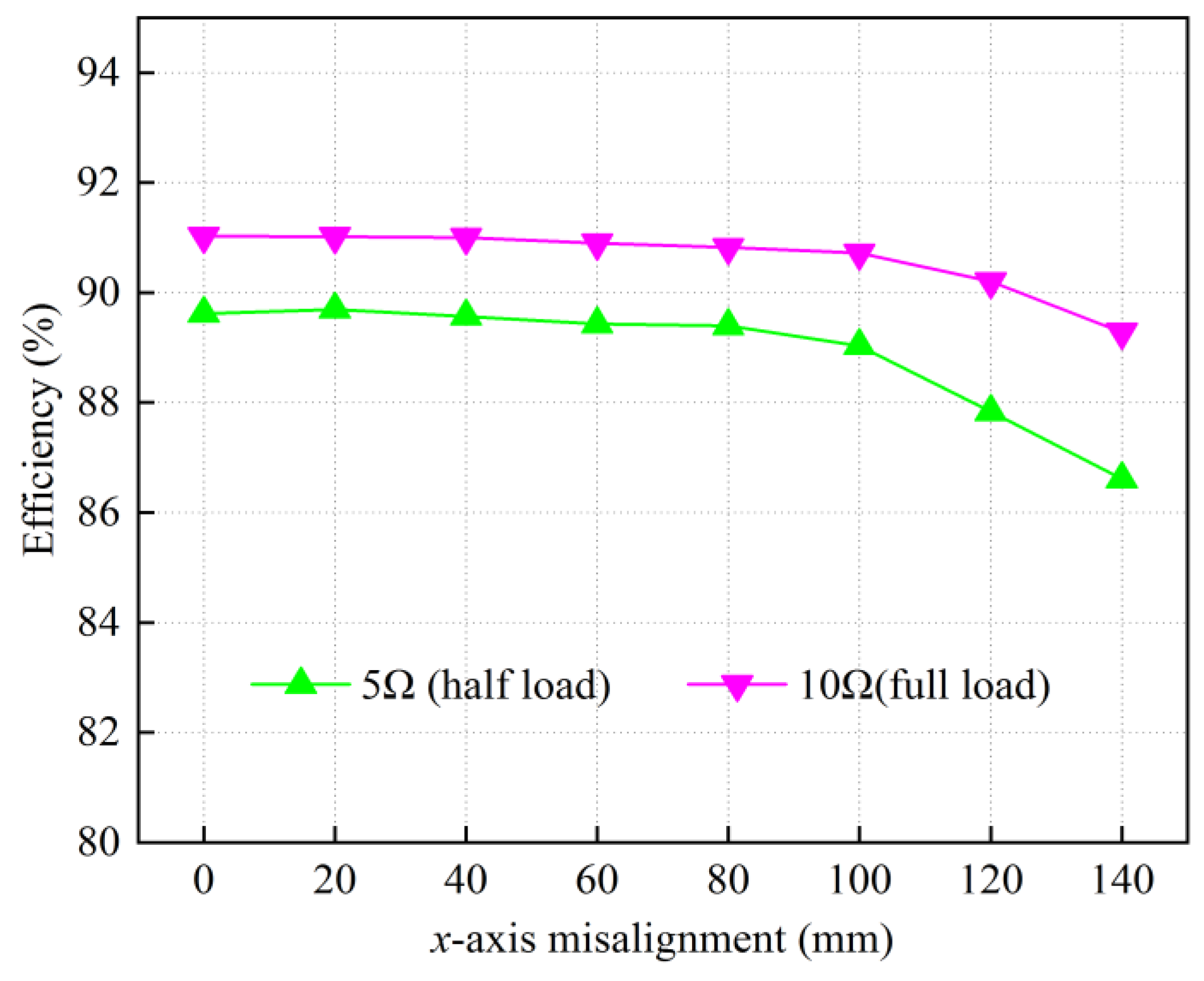
4. Experiment Verification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lu, F. 3.5-kW 94.2% DC–DC Efficiency Capacitive Power Transfer with Zero Reactive Power Circulating. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 1479–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Li, J.; Tong, X. Misalignment-Tolerant Series Hybrid with Active Adjustable Constant Current and Constant Voltage Output Wireless Charging System. Energies 2021, 14, 7594–7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Dai, X.; Gao, R.; Jiang, J. A Coupling Mechanism with Multi-degree Freedom for Bidirectional Multistage WPT System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 1376–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, P.; Wang, Y.G.; Mai, J.; Yao, Y.; Gao, S.; Huang, S.; Xu, D.G. A Three-Stage-Five-Coil IPT System Based on Cylindrical Solenoid Coupler Applied to State Detection Equipment of HV Device. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 2382–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, C.C.; Buja, G.; Choi, S.Y.; Rim, C.T. Modern Advances in Wireless Power Transfer Systems for Roadway Powered Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6533–6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y. Impedance-Matching Range Extension Method for Maximum Power Transfer Tracking in IPT System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 4419–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Lu, Y.; Peng, Y.; He, S.; Chen, Y.; He, Z.; Mai, R.; Wang, Z. Analysis and Design of A T/S Compensated IPT System for AGV Maintaining Stable Output Current Versus Air Gap and Load Variations. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 6217–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, S.; Yang, B.; Chen, S.; He, Z.; Mai, R. Reconfigurable Rectifier-Based Detuned Series-Series Compensated IPT System for Anti-Misalignment and Efficiency Improvement. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 2720–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Mai, R.; Liu, S.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Fu, L. Minimizing Input Current of the Rectifier Of LCC-LCC Compensated IPT Systems by Switch-Controlled Capacitor for Improving Efficiency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Tong, X. Research and Design of Misalignment-Tolerant LCC–LCC Compensated IPT System With Constant-Current and Constant-Voltage Output. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Ruan, W.; Liu, H.; Ren, Y.; Mai, R. Current Stress Optimization for Double-Sided CLLLC Topology-Based IPT System with Constant Output Current Tolerating Pad Misalignments. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 1032–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, A.; Neath, M.; Beh, H.Z.Z.; Covic, G.A. A Dynamic EV Charging System for Slow Moving Traffic Applications. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrification 2017, 3, 354–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, A.P. Maximum Efficiency Tracking for Wireless Power Transfer Systems with Dynamic Coupling Coefficient Estimation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 5005–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Onar, O.C.; Chinthavali, M. Primary-Side Power Flow Control of Wireless Power Transfer for Electric Vehicle Charging. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2015, 3, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, F.; Mei, T. Multifrequency Phase-Shifted Control for Multiphase Multiload MCR WPT System to Achieve Targeted Power Distribution and High Misalignment Tolerance. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-S.; Covic, G.; Stielau, O. Power Transfer Capability and Bifurcation Phenomena of Loosely Coupled Inductive Power Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2004, 51, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Cai, T.; Duan, S.; Feng, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X. A General Design Method of Primary Compensation Network for Dynamic WPT System Maintaining Stable Transmission Power. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 8343–8358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Zhang, H.; Hofmann, H.; Su, W.; Mi, C.C. A Dual-Coupled LCC-Compensated IPT System with A Compact Magnetic Coupler. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 6391–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, B.; Li, Q.; Feng, H.; Zhou, X.; He, Z.; Mai, R. Reconfigurable Topology for IPT System Maintaining Stable Transmission Power Over Large Coupling Variation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 4915–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Cai, T.; Duan, S.; Zhang, X.; Hu, H.; Niu, J. A Dual-Side-Detuned Series-Series Compensated Resonant Converter for Wide Charging Region in A Wireless Power Transfer System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 2177–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Cai, T.; Duan, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C. An LCC-Compensated Resonant Converter Optimized for Robust Reaction to Large Coupling Variation in Dynamic Wireless Power Transfer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6591–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Thrimawithana, D.J.; Madawala, U.K.; Hu, A.P. A Push-Pull Parallel Resonant Converter-Based Bidirectional IPT System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 2659–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, B. Angular-Misalignment Insensitive Omnidirectional Wireless Power Transfer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 2755–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.; Li, Q.; He, Z.; Mai, R.; Lai, J.-S. A Hybrid Inductive Power Transfer System with Misalignment Tolerance Using Quadruple-D Quadrature Pads. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 6039–6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Pei, Y.; Xu, D.G. A Novel Unsymmetrical Coupling Structure Based on Concentrated Magnetic Flux for High-Misalignment IPT Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 3110–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, J.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Sun, M.; Xu, D. High-Misalignment-Tolerant IPT Systems with Solenoid and Double-D Pads. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 3527–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Thrimawithana, D.J.; Madawala, U.K.; Hu, A.P.; Mi, C.C. A Misalignment-Tolerant Series-Hybrid Wireless EV Charging System with Integrated Magnetics. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Thrimawithana, D.J.; Madawala, U.K. Hybrid Bidirectional Wireless EV Charging System Tolerant to Pad Misalignment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 7079–7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Yao, Y.; Wang, D.; Wong, S.-C.; Tse, C.K. A Family of Hybrid IPT Topologies with Near Load-Independent Output and High Tolerance to Pad Misalignment. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 6867–6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, B.; Kou, Z.; He, Z.; Cao, G.; Mai, R. Hybrid and Reconfigurable IPT Systems with High-Misalignment Tolerance for Constant-Current and Constant-Voltage Battery Charging. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8259–8269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

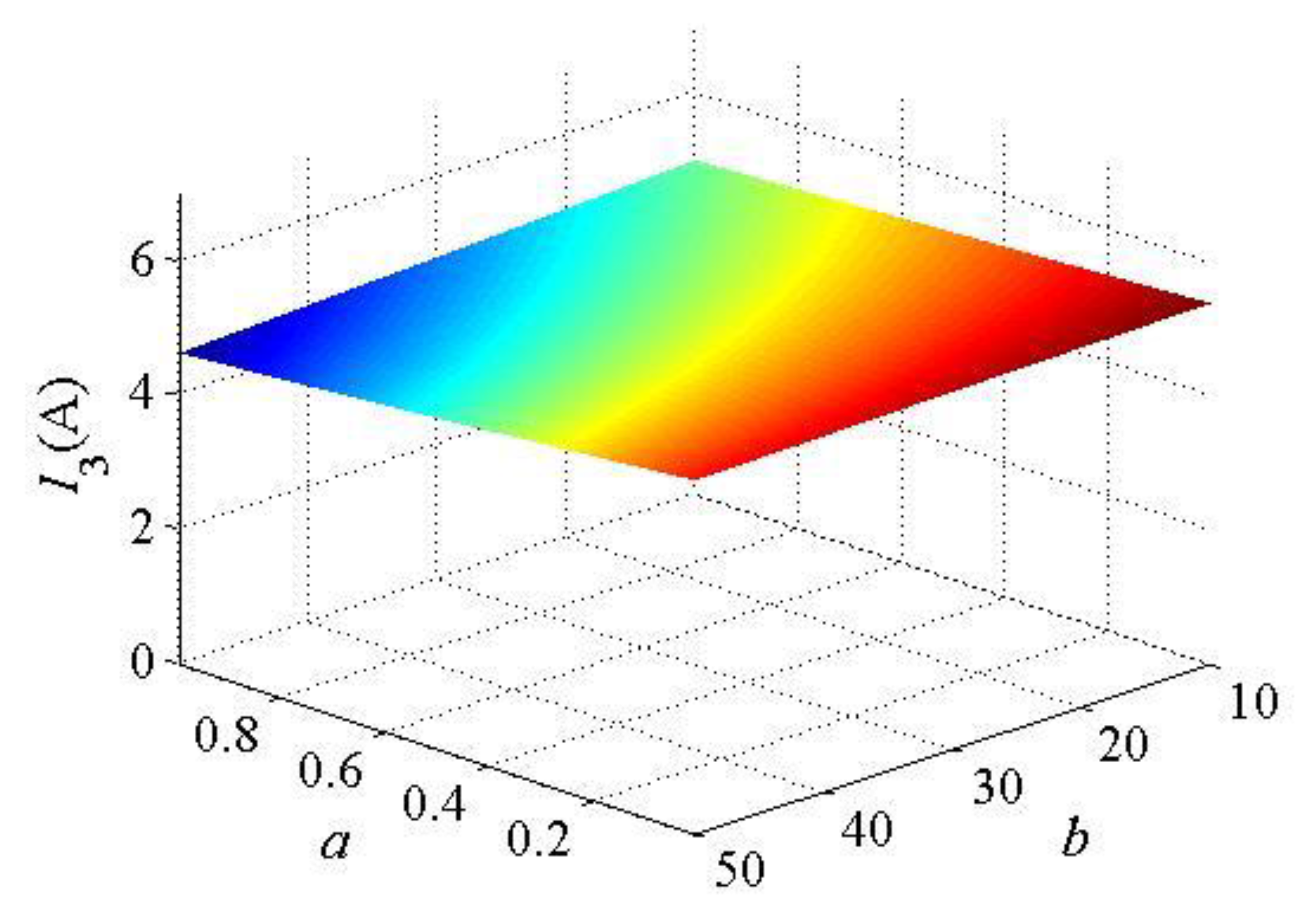
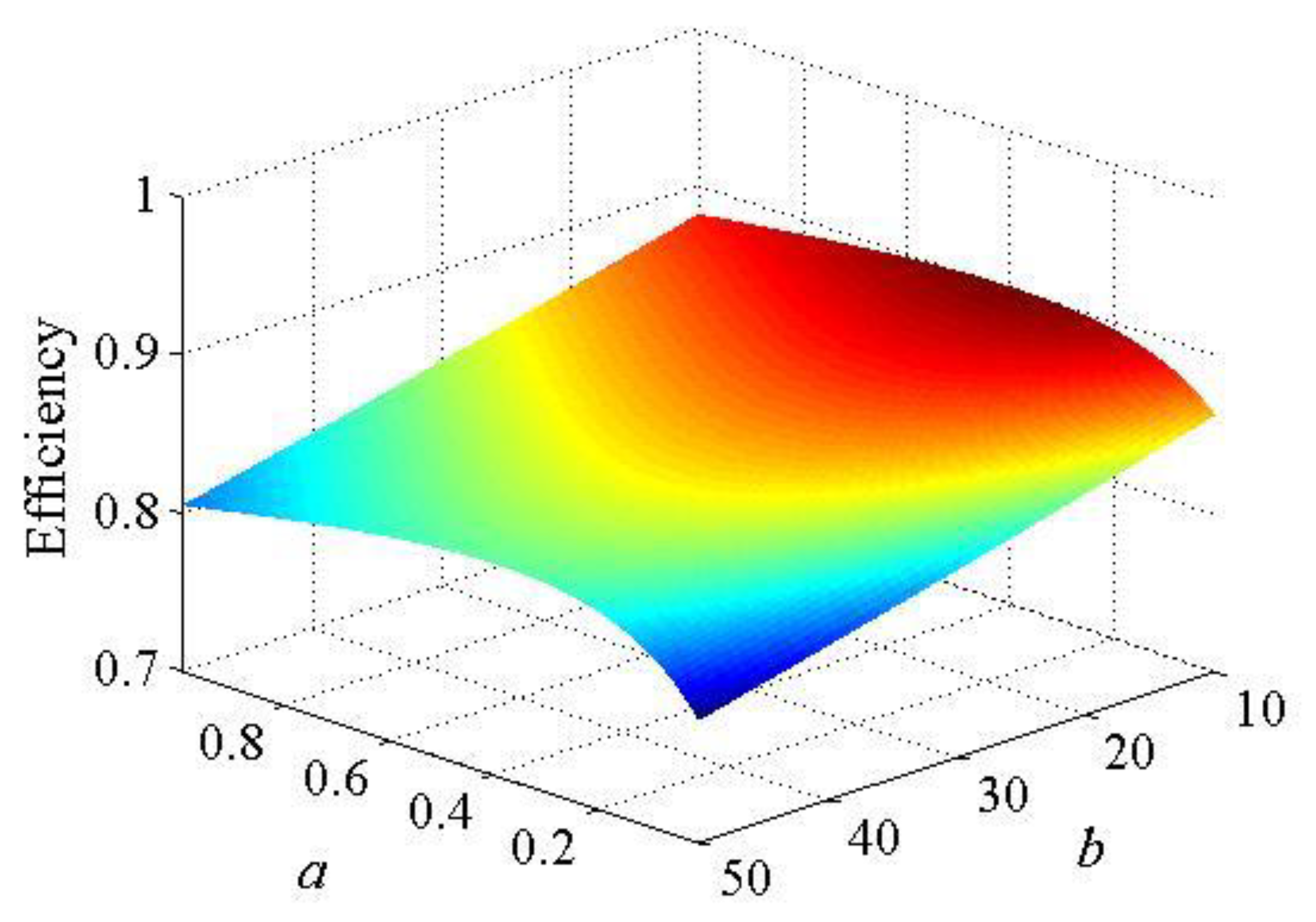
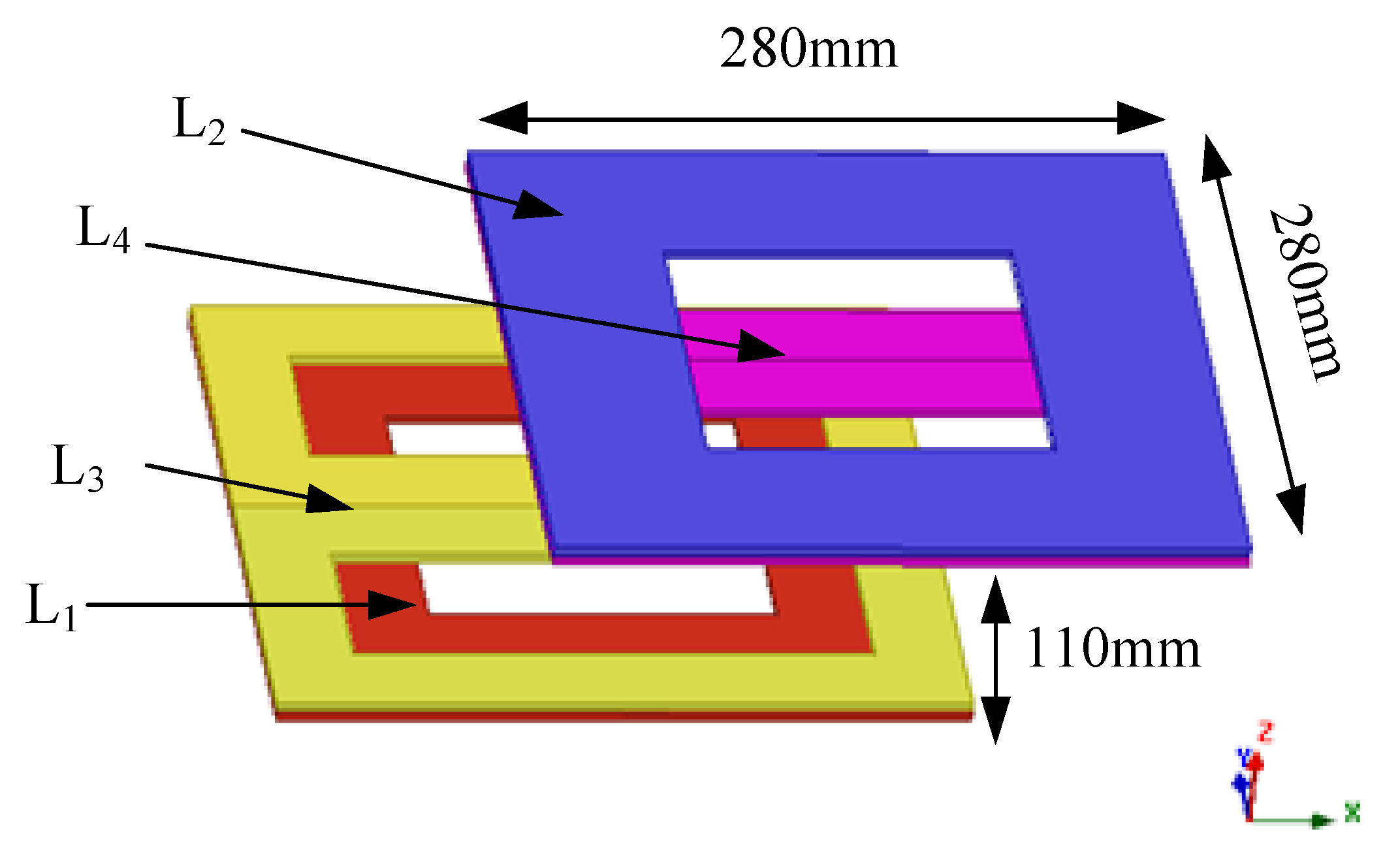
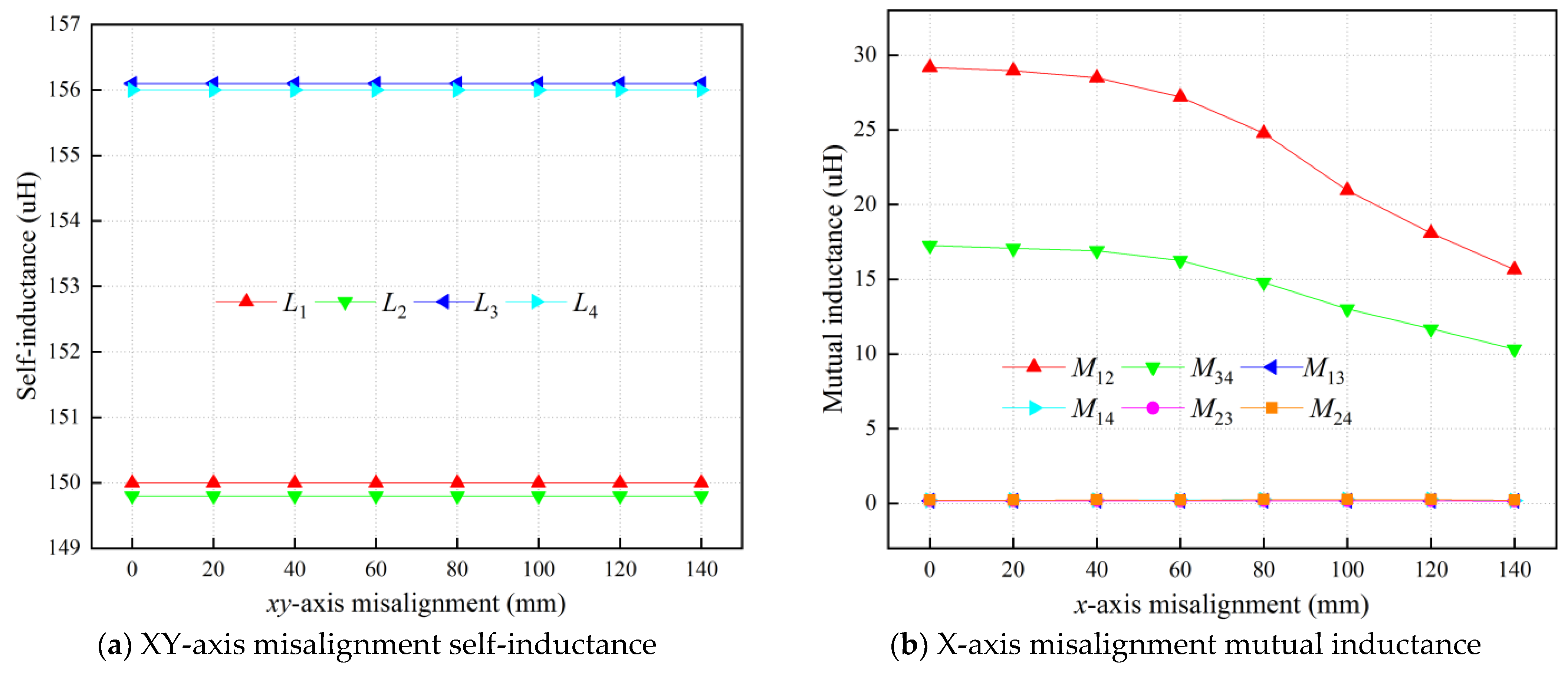
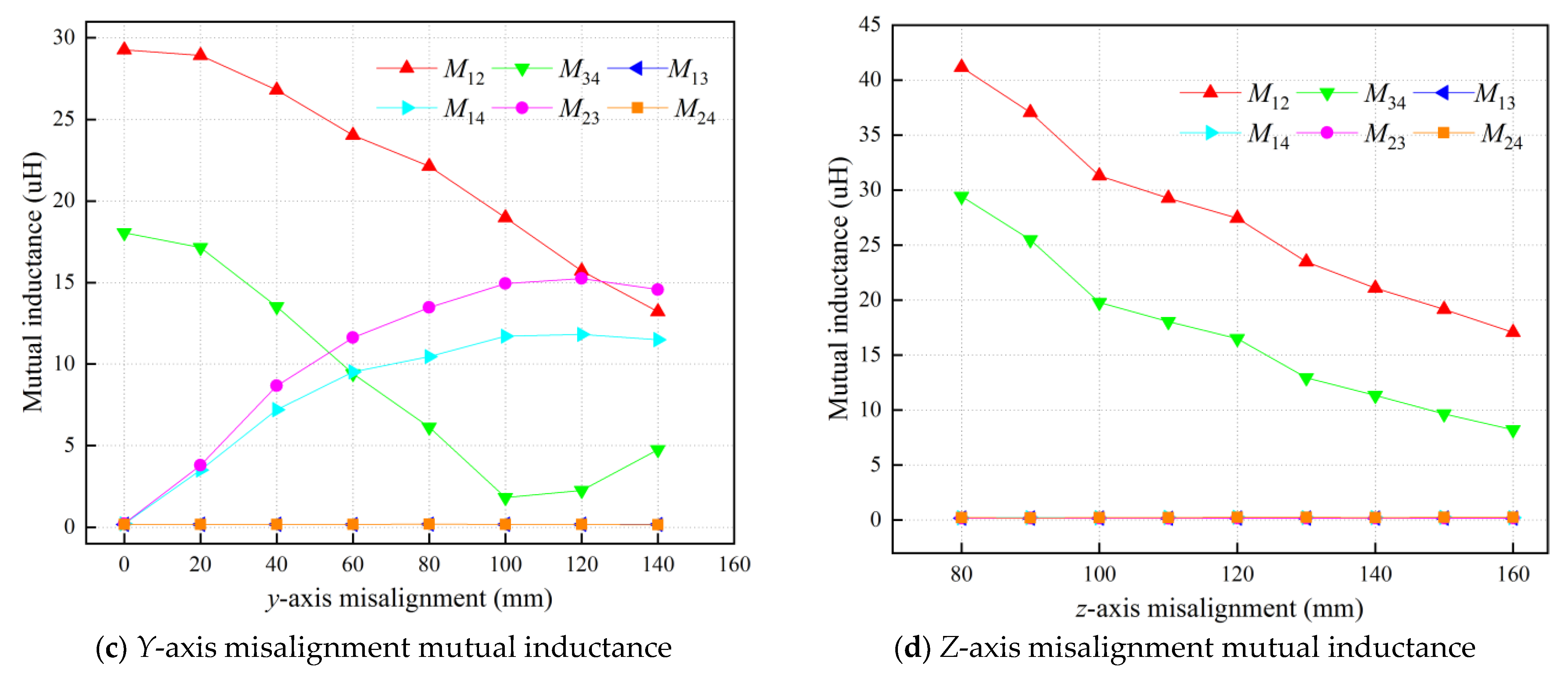
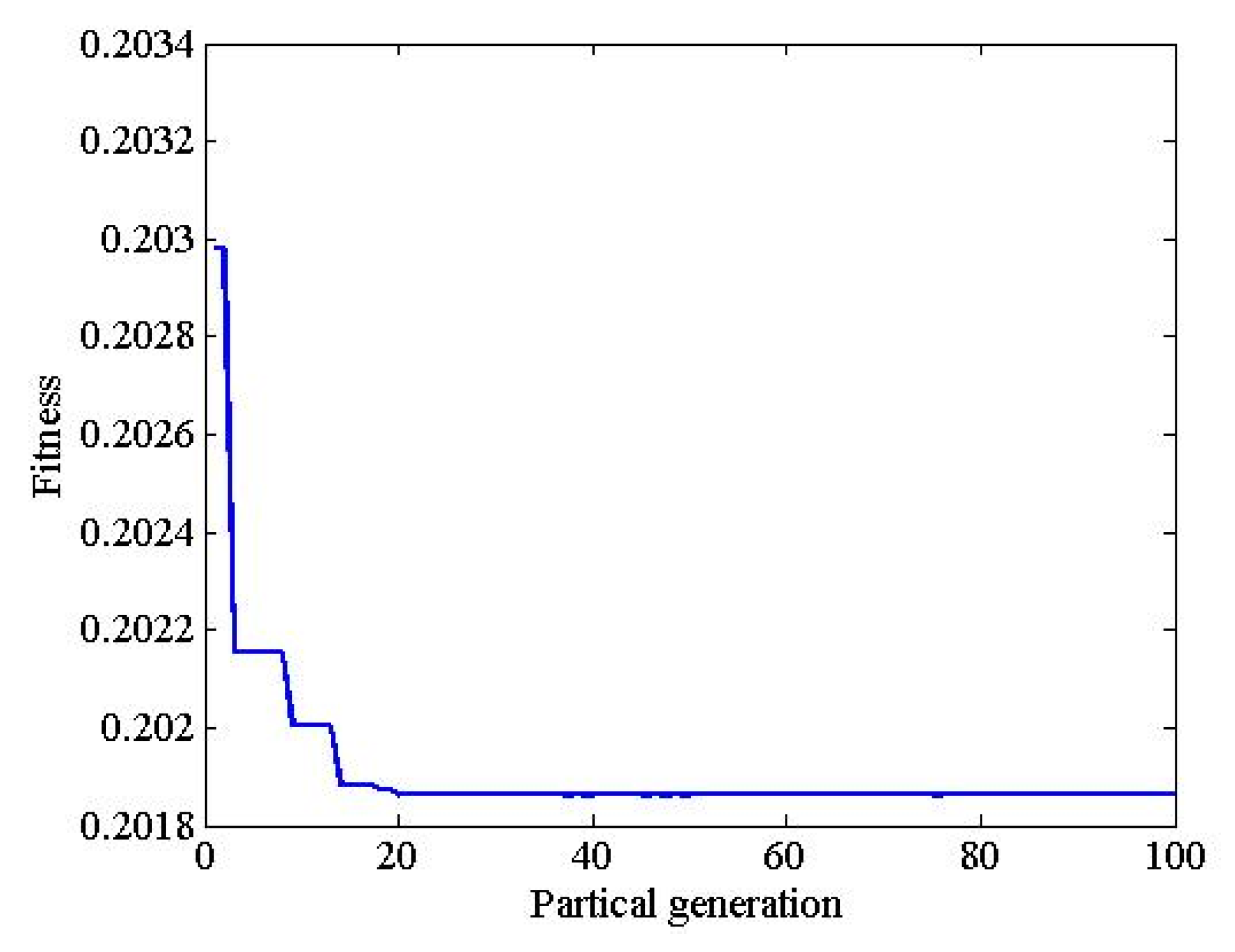
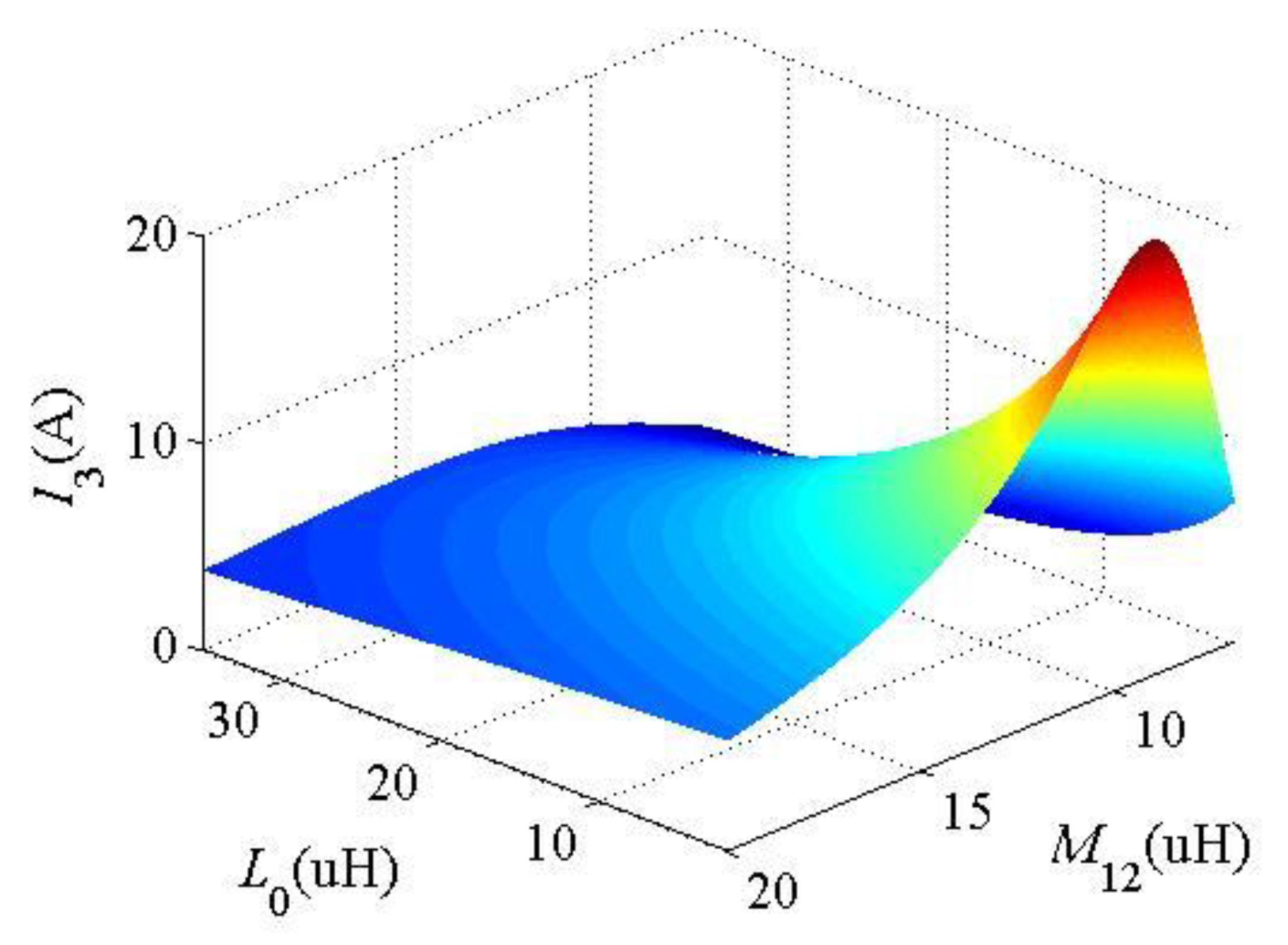
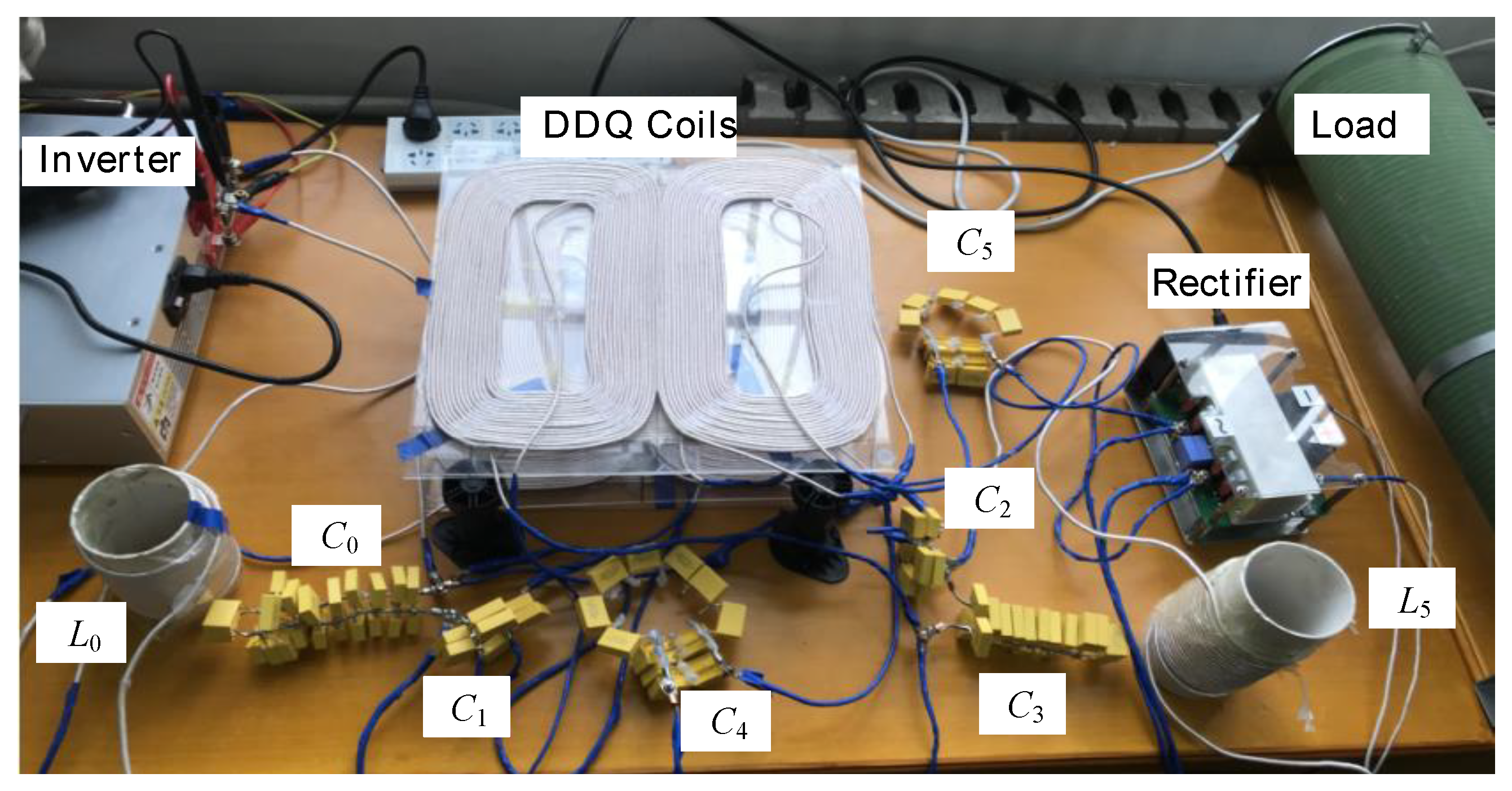



| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| f | 85 kHz | C5 | 26.5 nF |
| L0 | 16.1 uH | E | 70 V |
| L1 | 150.1 uH | a | 0.52 |
| L2 | 149.8 uH | b | 2.17 uH |
| L3 | 156.1 uH | RL | 5–10 Ω |
| L4 | 156.0 uH | R0 | 0.06 Ω |
| L5 | 16.1 uH | R1 | 0.42 Ω |
| C0 | 220.2 nF | R2 | 0.42 Ω |
| C1 | 26.6 nF | R3 | 0.41 Ω |
| C2 | 220.1 nF | R4 | 0.41 Ω |
| C3 | 22.5 nF | R5 | 0.07 Ω |
| C4 | 22.5 nF |
| Proposed in | Ref. [12] | Ref. [15] | Ref. [28] | Ref. [29] | Ref. [30] | This Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control strategy | Additional DC–DC | pulse frequency modulation | No | No | No | No |
| Number of Component | 5 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 12 | 8 |
| Coupling coils | BPs | Multi-phase coils | DDs | DDQs | DDQs | DDQs |
| output characteristic | CV | CV | CC | CV | CC-CV | CV |
| Parameter optimization | / | / | / | Complex | Complex | Easy |
| Wireless communication | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Operate without secondary side | / | / | No | Yes | No | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, Z.; Li, J.; Tong, X. A Misalignment-Insensitive Hybrid IPT System with Constant Current Output Based on Parameter Optimization. Electronics 2023, 12, 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12051138
Gong Z, Li J, Tong X. A Misalignment-Insensitive Hybrid IPT System with Constant Current Output Based on Parameter Optimization. Electronics. 2023; 12(5):1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12051138
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Zhaowei, Jingang Li, and Xiangqian Tong. 2023. "A Misalignment-Insensitive Hybrid IPT System with Constant Current Output Based on Parameter Optimization" Electronics 12, no. 5: 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12051138
APA StyleGong, Z., Li, J., & Tong, X. (2023). A Misalignment-Insensitive Hybrid IPT System with Constant Current Output Based on Parameter Optimization. Electronics, 12(5), 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12051138









