Application of Feature Pyramid Network and Feature Fusion Single Shot Multibox Detector for Real-Time Prostate Capsule Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
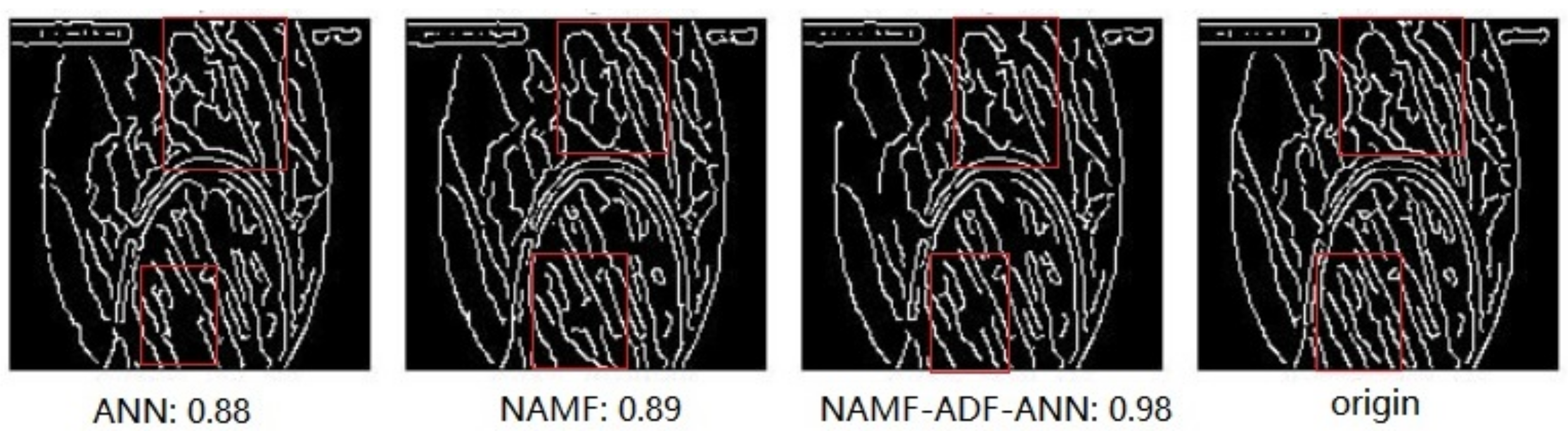
- To reduce the impact of salt and pepper noise on the object detection network, a salt and pepper noise reduction method based on edge feature preservation is proposed. Compared with fourteen other methods, this method has the highest peak signal-to-noise ratio. The proposed image denoising methods can improve the mAP of Faster R-CNN, YOLOv4, TOOD, SSD, and FSSD.
- (2)
- Based on FPN and FSSD, a multistage bidirectional feature fusion network called FFSSD is proposed. Compared with other algorithms such as Faster R-CNN, YOLOv4, TOOD, SSD, FSSD, OWOD, Foveabox, Sparse R-CNN, and Efficientdet, the proposed algorithm has the highest mAP on the prostate capsule detection task.
2. Materials and Methods
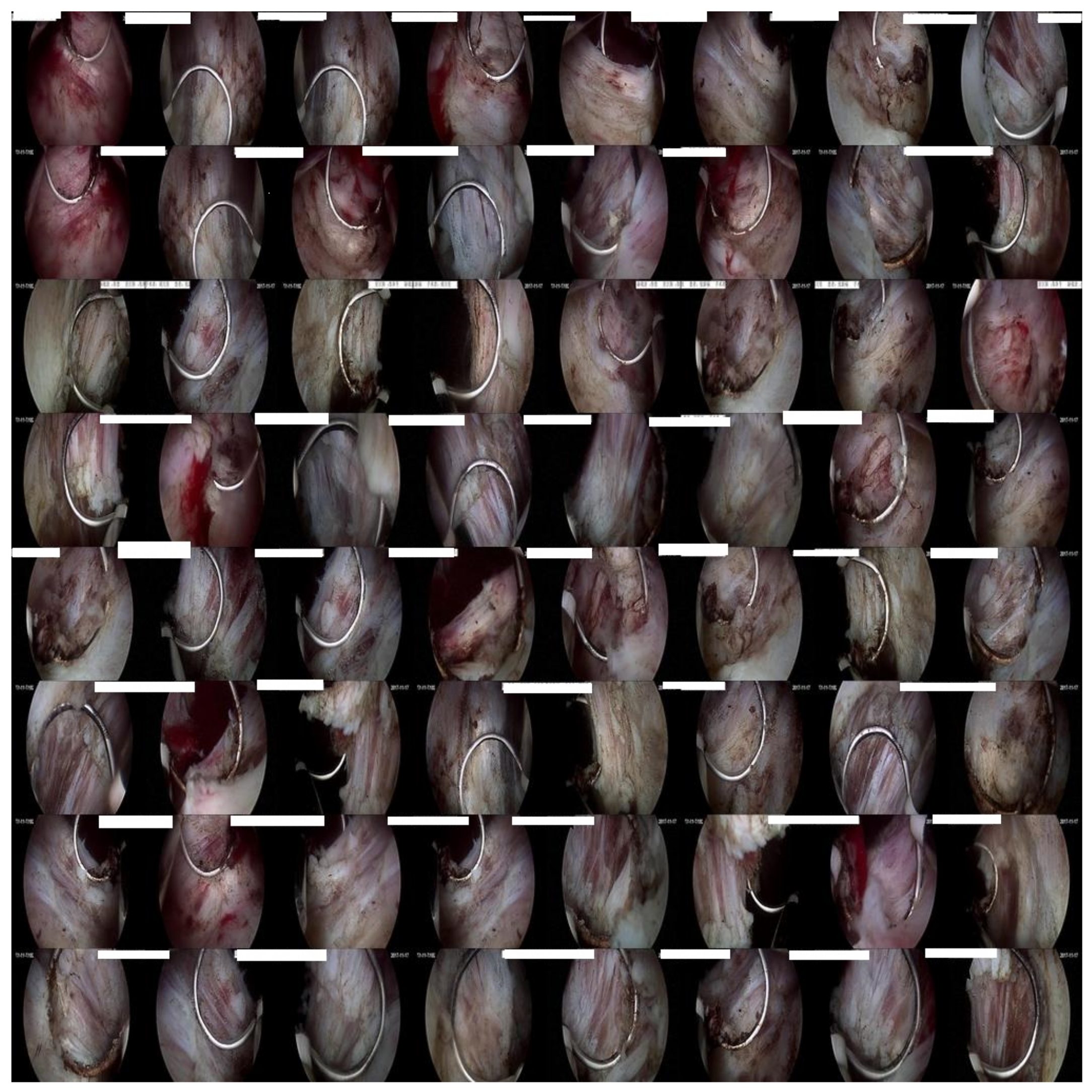
2.1. Dataset
| Algorithm 1: CF algorithm |
| Input: Noisy_img v, noisy level x |
| Output:, , R, |
| 1: Function u = compose(v, z) |
| 2: Initialize d = {}, p = ones(0,6), s = ones(0,6), R = 0, = 0, D = {2,6} |
| 3: set = AMF(v,x) |
| 4: set = NAMF(v,x) |
| 5: set = ANN(v,x) |
| 6: set = RUN_ADF(,,0) |
| 7: set = RUN_ADF(,,0) |
| 8: set = RUN_ADF(,,0) |
| 9: MAX = PSNR( |
| 10: for all |
| 11: = PSNR(,o) |
| 12: = COMPUTE_FOM(,o) |
| 13: IF( > ) |
| 14: { = ; R = k} |
| 15: end for |
| 16: return , , R, |
- (1)
- The image with noise is denoised by AMF, NAMF, and ANN.
- (2)
- Anisotropic diffusion fusion is used to combine the image denoising results of AMF, NAMF, and ANN in pairs.
- (3)
- The noise reduction results of the three algorithms and the pin-two fusion results of the three algorithms are combined, then the maximum value of the combination according to the PSNR is used to obtain the final image denoising cascade optimization results.
2.2. The Proposed Network
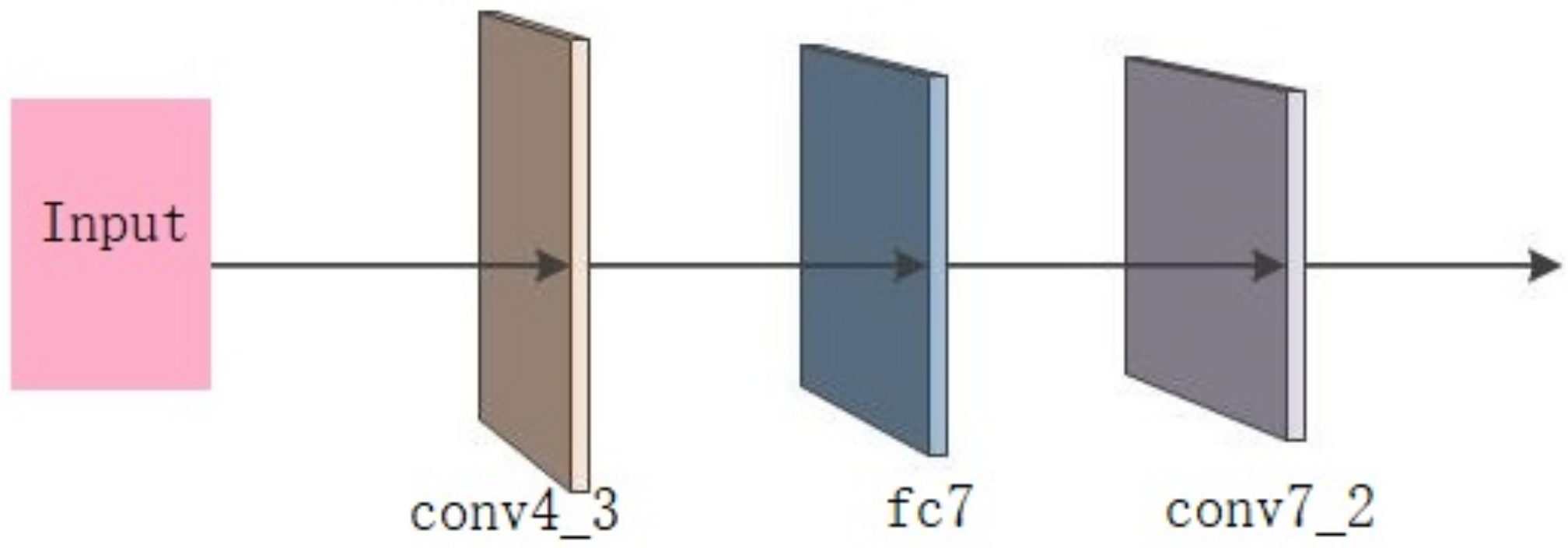
2.2.1. First Feature Forward Propagation
2.2.2. Reverse Feature Propagation
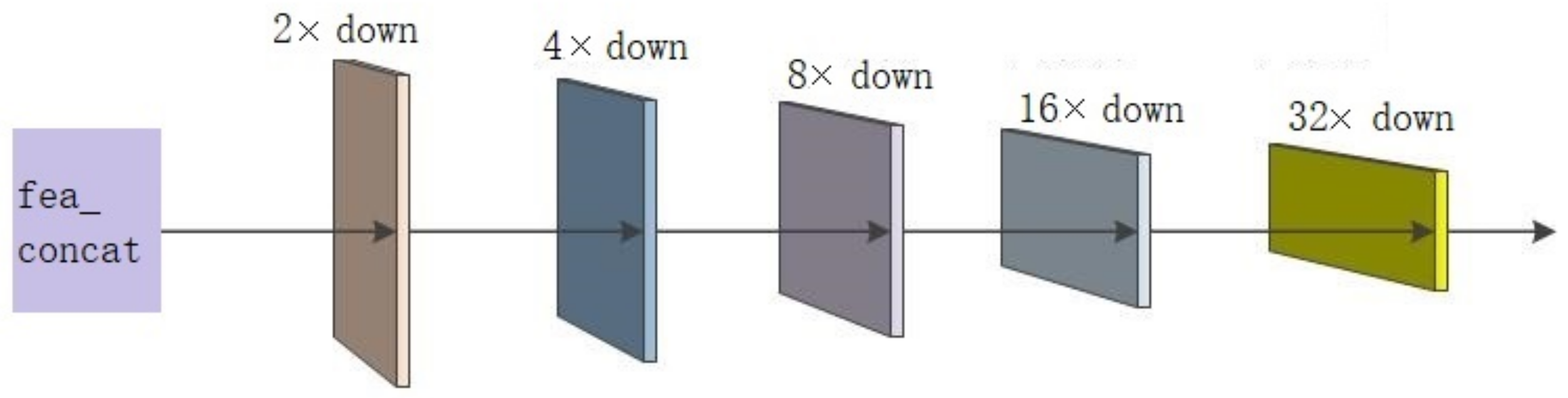
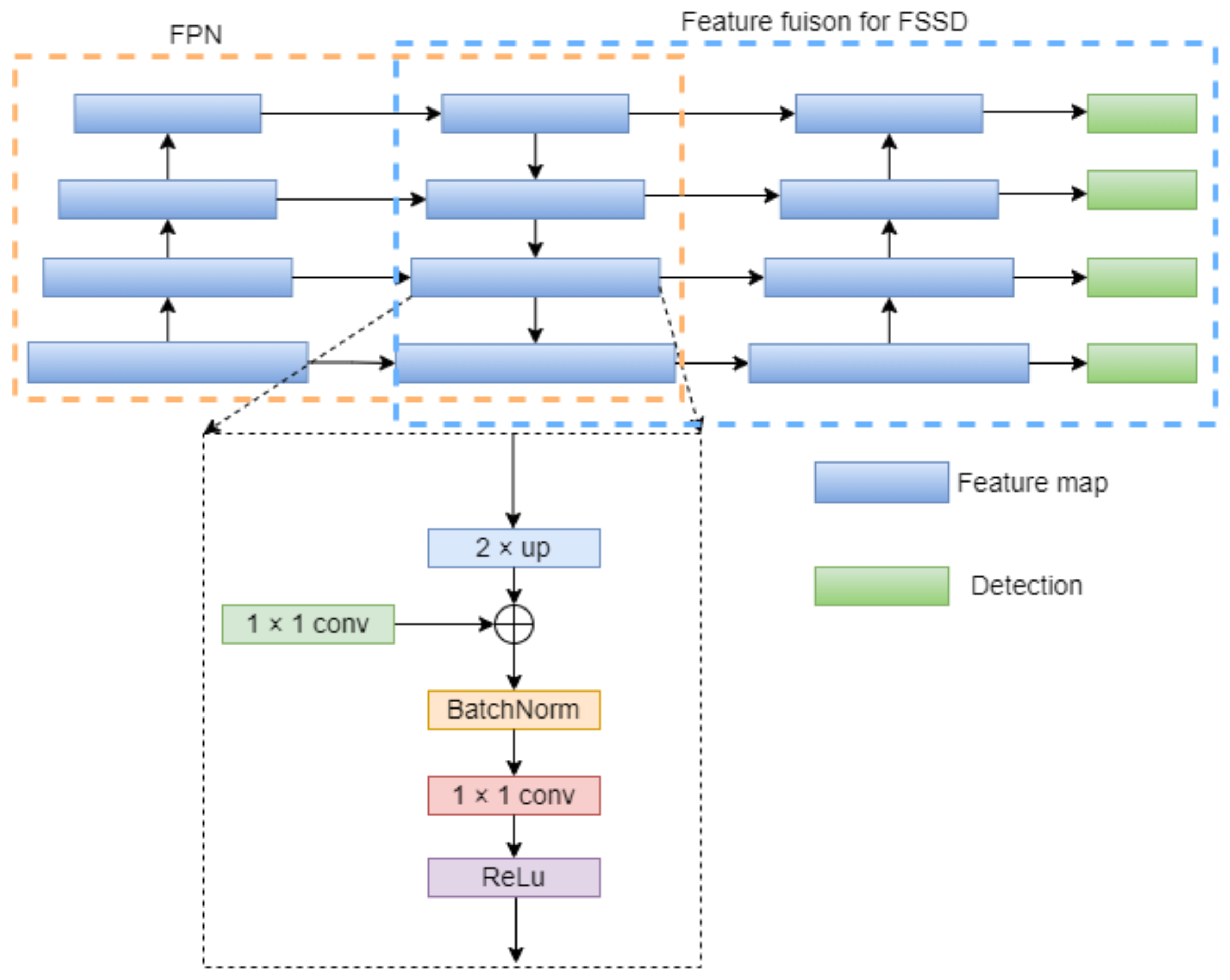
2.2.3. New Feature Pyramid Network
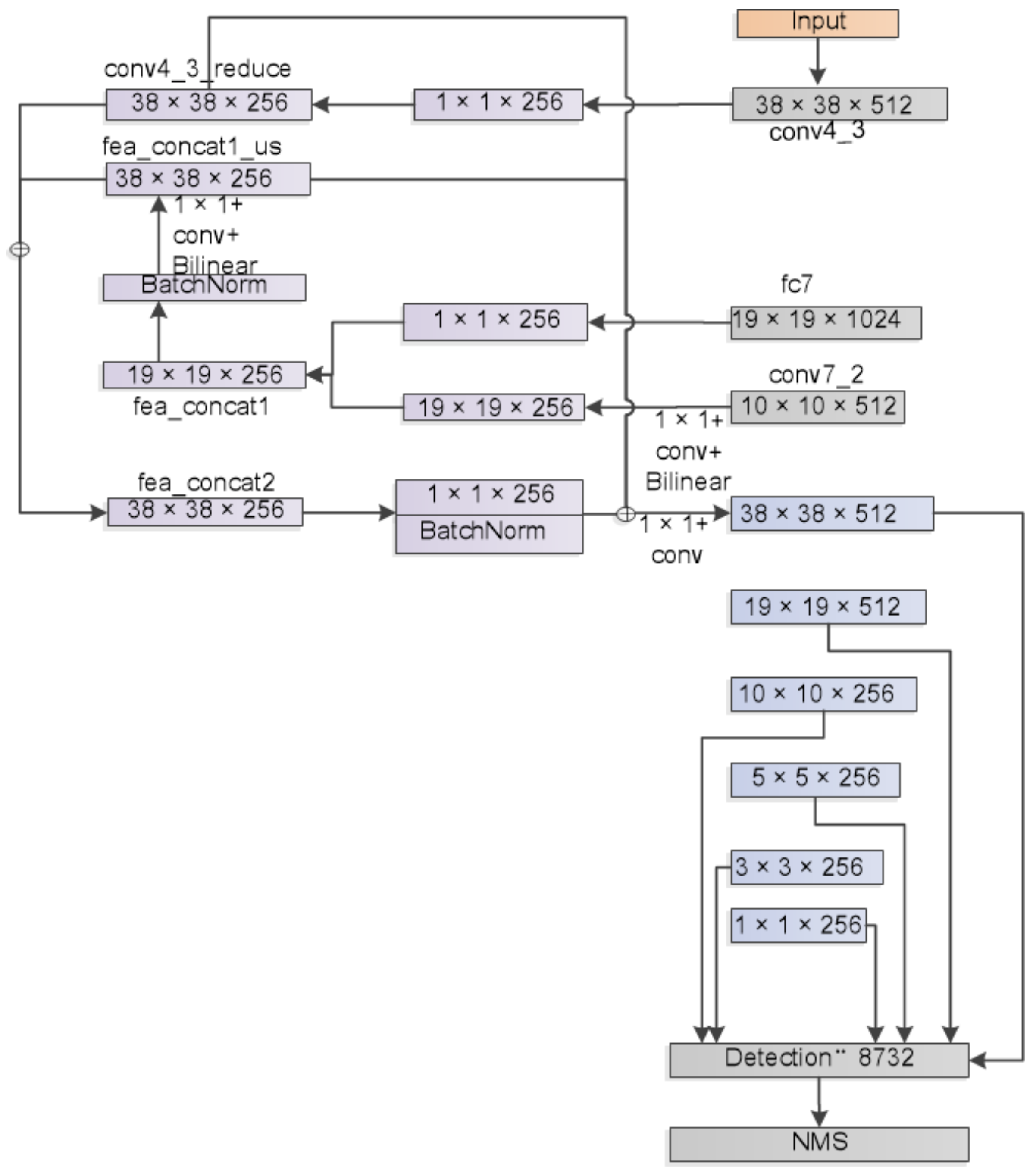
2.2.4. FFSSD Network
3. Results
3.1. Criteria for Evaluation
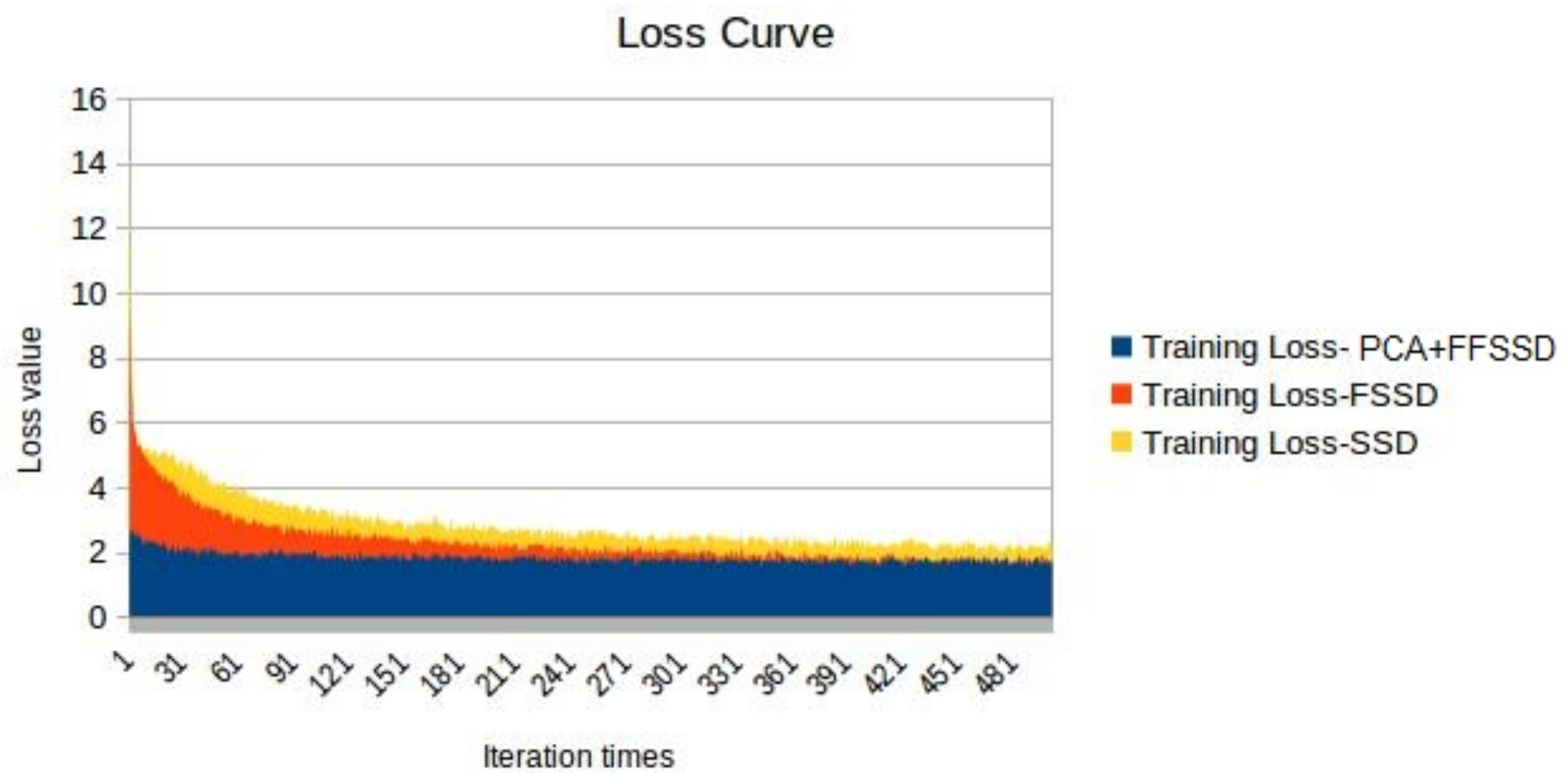
3.1.1. mAP and Loss
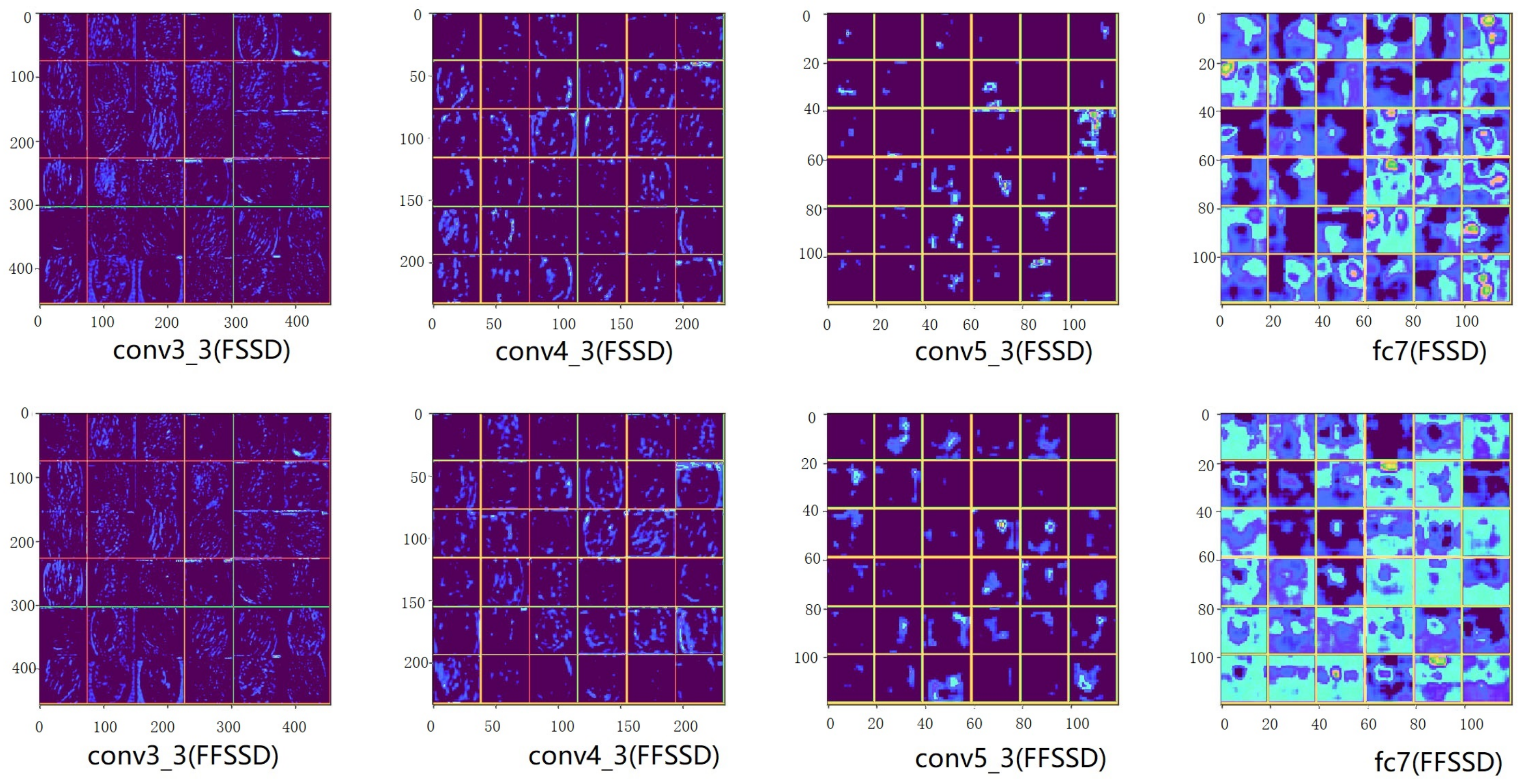
3.1.2. Feature Visualization
3.1.3. Speed and Precision Comparison
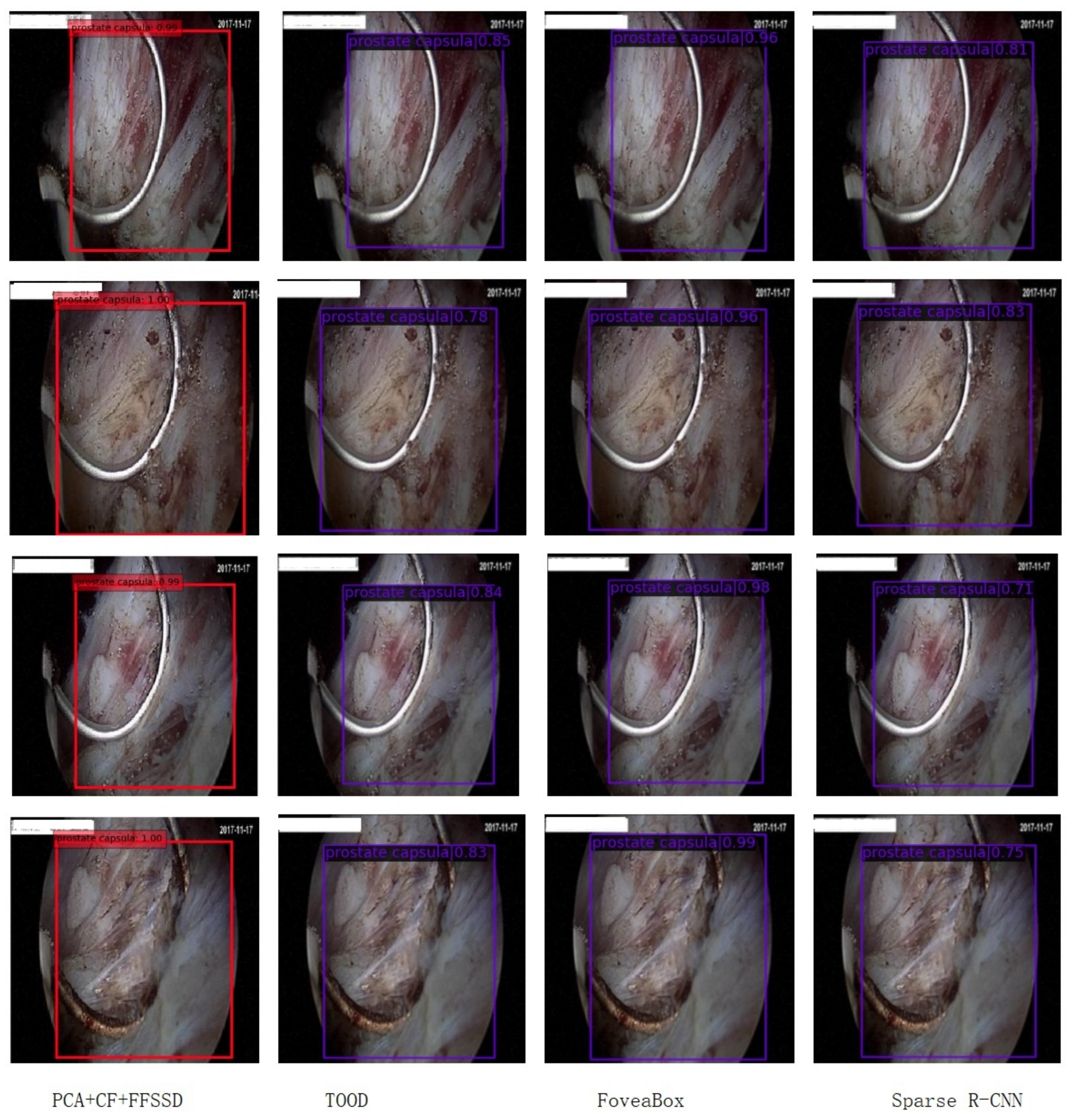
3.1.4. Detection Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papageorgiou, C.; Poggio, T. A Trainable System for Object Detection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2000, 38, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, P.A.; Jones, M.J. Rapid Object Detection using a Boosted Cascade of Simple Features. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2001, Kauai, HI, USA, 8–14 December 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of Oriented Gradients for Human Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, F. FSSD: Feature Fusion Single Shot Multibox Detector. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.00960. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cao, L.; Akin, O.; Tian, Y. 3DFPN-HS2: 3D Feature Pyramid Network Based High Sensitivity and Specificity Pulmonary Nodule Detection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Shenzhen, China, 13–17 October 2019; pp. 513–521. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, Y.; Kong, T.; Xu, C.; Zhan, W.; Tomizuka, M.; Li, L.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, C. Sparse R-CNN: End-to-End Object Detection With Learnable Proposals. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.y. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, T.; Sun, F.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, J. FoveaBox: Beyound Anchor-Based Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 7398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Zhong, Y.; Gao, Y.; Scott, M.R.; Huang, W. TOOD: Task-aligned One-stage Object Detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.07755. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, K.; Khan, S.; Khan, F.; Balasubramanian, V. Towards Open World Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Pang, R.; Le, Q.V. EfficientDet: Scalable and Efficient Object Detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.09070. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, G.; Sun, L. IPG-Net: Image Pyramid Guidance Network for Object Detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.00632. [Google Scholar]
- Bakkouri, I.; Karim, A. Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system based on multi-layer feature fusion network for skin lesion recognition in dermoscopy images. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 20483–20518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haekal, M.; Septiawan, R.R.; Haryanto, F.; Arif, I. A comparison on the use of Perlin-noise and Gaussian noise based augmentation on X-ray classification of lung cancer patient. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1951, 012064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Cheng, J. Classification and detection of COVID-19 X-Ray images based on DenseNet and VGG16 feature fusion. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2022, 77, 103772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, H.; Khatami, F.; Aghamir, S. U-shape incision on prostate capsule: New intraperitoneal laparoscopic technique in simple prostatectomy: A case report. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 69, 102787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weizer, A.; Shah, R.; Lee, C.; Gilbert, S.; Daignault, S.; Montie, J.; Wood, D. Evaluation of the prostate peripheral zone/capsule in patients undergoing radical cystoprostatectomy: Defining risk with prostate capsule sparing cystectomy. Urol. Oncol. 2007, 25, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, R.Y. An Adaptive Algorithm to Identify Ambiguous Prostate Capsule Boundary Lines for Three-Dimensional Reconstruction and Quantitation. Ph.D. Thesis, Old Dominion University, Norfolk, VA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Holder, K.G.; Galvan, B.; Knight, A.S.; Ha, F.; Riese, W. Possible clinical implications of prostate capsule thickness and glandular epithelial cell density in benign prostate hyperplasia. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2021, 62, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.S. Two-Dimensional Signal and Image Processing; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, H.; Haddad, R.A. Adaptive median filters: New algorithms and results. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1995, 4, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wu, H.R. Adaptive impulse detection using center-weighted median filters. IEEE Signal Process Lett. 2001, 8, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Tan, J. A Universal Impulse Noise Filter with an Impulse Detector and Nonlocal Means. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2014, 33, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Tan, J.; Gan, K. Non-local Means Image Denoising Algorithm Based on Edge Detection. In Proceedings of the 2014 5th International Conference on Digital Home (ICDH), Guangzhou, China, 28–30 November 2014; pp. 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, H. NAMF: A Nonlocal Adaptive Mean Filter for Removal of Salt-and-Pepper Noise. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 4127679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, D.N.H.; Thanh, L.T.; Hien, N.N.; Prasath, S. Adaptive total variation L1 regularization for salt and pepper image denoising. Optik 2020, 208, 163677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Ding, T.; Qiao, S.; Meng, F.; Wang, S.; Li, P.; Wang, X. A novel YOLOv3-arch model for identifying cholelithiasis and classifying gallstones on CT images. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, B. ANN Based Removal for Salt and Pepper Noise. In Proceedings of the Global Conference on Engineering Research, Online, 2–5 June 2021; pp. 558–566. [Google Scholar]





| Model | Backbone Network | mAP | img/s |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSD | VGG16 | 71.90% | 0.027 |
| FSSD | VGG16 | 73.82% | 0.037 |
| FSSD+FPN | VGG16 | 75.45% | 0.046 |
| PCA+FFSSD | VGG16 | 82.39% | 0.046 |
| Model | Backbone Network | mAP | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN [7] | VGG16 | 62.67% | 5 (K40) |
| Faster R-CNN [7] | ResNet 50+FPN | 74.41% | - |
| PCA+CF+Faster R-CNN (ours) | ResNet 50+FPN | 77.10% | - |
| SSD [5] | VGG16 | 71.90% | 46 |
| SSD [5] | ResNet-101 [5] | 74.39% | 15 (NVIDIA GTX 1070) |
| PCA+CF+SSD (ours) | VGG16 | 77.30% | 46 |
| EfficientDet-D0 [14] | B0 | 53.38% | 97 (Telsa v100) |
| EfficientDet-D1 [14] | B1 | 56.58% | 74 (Telsa v100) |
| EfficientDet-D2 [14] | B2 | 59.23% | 57 (Telsa v100) |
| EfficientDet-D3 [14] | B3 | 61.14% | 35 (Telsa v100) |
| EfficientDet-D4 [14] | B4 | 58.81% | 23 (Telsa v100) |
| EfficientDet-D5 [14] | B5 | 58.09% | 10 (Telsa v100) |
| EfficientDet-D7 [14] | B6 | 78.37% | — |
| FSSD [6] | VGG16 | 73.82% | 65.8 (NVIDIA 1080Ti) |
| PCA+CF+FSSD (ours) | VGG16 | 75.58% | 65.8 (NVIDIA 1080Ti) |
| FoveaBox [11] | ResNet50+FPN | 81.10% | 25 (NVIDIA RTX 2060) |
| TOOD [12] | ResNet50+FPN | 73.08% | 20 (NVIDIA RTX 2060) |
| PCA+CF+TOOD (ours) | ResNet50+FPN | 76.50% | 20 (NVIDIA RTX 2060) |
| YOLOv4 [10] | CSPDarknet-53 | 70.29% | 45 (NVIDIA RTX 2060) |
| PCA+CF+YOLOv4 (ours) | CSPDarknet-53 | 72.47% | 45 (NVIDIA RTX 2060) |
| Sparse R-CNN [9] | ResNet50+FPN | 75.68% | 17 (NVIDIA RTX 2060) |
| OWOD [13] | ResNet-50 | 71.30% | 62 (NVIDIA RTX 2060) |
| PCA+CF+FFSSD (ours) | VGG16 | 83.58% | 27 (NVIDIA GTX 1070) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, S.; Wang, X.; Guo, C. Application of Feature Pyramid Network and Feature Fusion Single Shot Multibox Detector for Real-Time Prostate Capsule Detection. Electronics 2023, 12, 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12041060
Wu S, Wang X, Guo C. Application of Feature Pyramid Network and Feature Fusion Single Shot Multibox Detector for Real-Time Prostate Capsule Detection. Electronics. 2023; 12(4):1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12041060
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Shixiao, Xinghuan Wang, and Chengcheng Guo. 2023. "Application of Feature Pyramid Network and Feature Fusion Single Shot Multibox Detector for Real-Time Prostate Capsule Detection" Electronics 12, no. 4: 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12041060
APA StyleWu, S., Wang, X., & Guo, C. (2023). Application of Feature Pyramid Network and Feature Fusion Single Shot Multibox Detector for Real-Time Prostate Capsule Detection. Electronics, 12(4), 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12041060






