Abstract
This paper presents a multi-task learning framework, called the dynamic information transfer network (DITN). We mainly focused on improving the pose estimation with the spatial relationship of the adjacent joints. To benefit from the explicit structural knowledge, we constructed two branches with a shared backbone to localize the human joints and bones, respectively. Since related tasks share a high-level representation, we leveraged the bone information to refine the joint localization via dynamic information transfer. In detail, we extracted the dynamic parameters from the bone branch and used them to make the network learn constraint relationships via dynamic convolution. Moreover, attention blocks were added after the information transfer to balance the information across different granularity levels and induce the network to focus on the informative regions. The experimental results demonstrated the effectiveness of the DITN, which achieved 90.8% PCKh@0.5 on MPII and 75.0% AP on COCO. The qualitative results on the MPII and COCO datasets showed that the DITN achieved better performance, especially on heavily occluded or easily confusable joint localization.
1. Introduction
Two-dimensional human pose estimation (HPE) is the task of localizing human joints or parts from monocular images [1,2] or videos [3,4,5]. It has become a significant basis for human action recognition [6], human–computer interaction [7], human parsing [8], animation [9], etc. Classical methods [10,11,12,13] are mainly based on the pictorial structure (PS) framework. They usually adopt vertices indicating joints and edges encoding the connections of adjacent joints to construct skeleton graph models. The spatial relationship of joints, such as the angle and distance, is captured to predict the localization of body joints. Deep learning methods [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21] extract spatial contextual information directly from data. These methods perform well in visual representation; however, they lack the ability to explicitly learn the spatial relationship between joints. Without utilizing a holistic skeleton structure and intrinsic prior knowledge, it is difficult for them to tackle challenges including uncommon body postures and occlusions.
Recent studies [22,23] suggest that spatial dependency can provide contextual cues to help localize body joints in crowded and occluded scenes. Tang et al. [24] proposed a hierarchical compositional framework that exploits the relationships among human joints. Nie et al. [25,26] leveraged bone information from human parsing to assist human pose estimation in a multi-task learning manner. These methods prove the effectiveness of spatial representation learning. The representation in the form of human bones provides more holistic structure information for the precise localization of human joints. For human pose estimation, it is significant to explore the simplicity of the spatial information from different levels and promote information interaction between them.
Inspired by advances in multi-task learning for computer vision tasks [27,28], we present a simple and effective framework, called the dynamic information transfer network (DITN). With implicit constraints from multi-task learning, the localization accuracy of human joints and bones is boosted. Different from previous works, we adopted information interaction across different granularity levels to refine the human pose estimation. Specifically, we constructed the joint prediction branch and the bone prediction branch to localize the human joints (e.g., shoulder, elbow, wrist) and bones (e.g., lower arms, upper arm) of images, respectively. The two branches use the same backbone as they share a common optimal hypothesis class in localization tasks. We took dynamic parameters generated from the bone prediction branch as the convolutional kernel weight to extract specified features in the joint prediction branch by performing dynamic convolution. By conducting information interaction, the two branches learn the corresponding spatial features mutually in the training phase. The bone prediction branch provides explicit spatial information for the joint prediction branch by dynamic information transfer. As shown in Figure 1, the estimated poses from HRNet [19] fail to localize the right elbow due to the occlusion. We used the spatial constraints from the bone predictions to refine the localization of the human joints. Explicit spatial information leads to better results, especially on heavily occluded or easily confusable joints’ localization.

Figure 1.
Illustration of human pose estimation in an occluded scene. (a) The pose estimation from HRNet [19]. (b) Visualization of bone information from our the bone prediction branch. (c) The pose estimation of our method. We observe that the visual-based HRNet fails to localize the right elbow, yet our approach delivers dependable pose estimation by exploiting bone information.
Furthermore, we introduced attention blocks into the DITN to improve the performance of the networks. The channel attention block is incorporated in the dynamic information transfer to balance shared features. The spatial attention block refines the output joint features to benefit joint localization. By combining the DITN and attention blocks, our network can obtain more accurate predictions.
The main contributions of this work are summarized as follows:
- We propose a multi-task learning framework that estimates human joints and bones in an end-to-end trainable manner.
- We propose a dynamic information transfer module (DITM) that exploits transferred bone-based part representations to obtain better pose estimation results.
- We integrated attention blocks into the DITM, which balance the shared feature across different granularity levels and induce the network to focus on important features.
We achieved competitive results on two popular human pose estimation benchmarks, the MPII and COCO datasets. Empirical evaluations proved the effectiveness of the multi-task learning framework with dynamic information transfer.
2. Related Work
2.1. Human Pose Estimation
Recent deep learning methods relying on convolutional neural networks have achieved better performance than prior works. Regression-based methods were explored in the early stage of 2D human pose estimation. DeepPose [17] applies the deep convolutional neural network to the human pose estimation task and directly regresses the human joint coordinates. Papandreou et al. [29] introduced a novel aggregation procedure to obtain highly localized keypoint predictions. Sun et al. [30] applied an integral operation that relates and unifies the heat map representation and joint regression, thus avoiding non-differentiable postprocessing and quantization error. Heat map regression methods are easy to implement and have much higher accuracy than traditional coordinate regression. These convolutional neural networks usually adopt the high-to-low and low-to-high frameworks to excavate features on various scales. Newell et al. [16] proposed a stacked hourglass architecture that consolidates features at multiple scales for repeated bottom-up, top-down inference. Yang et al. [31] proposed a pyramid residual module (PRM) to enhance the invariance in the scales of deep convolutional neural networks. Tang et al. [24] demonstrated a sequential architecture that refines joint detection via composing multiple modules. Chen et al. [32] proposed a cascaded pyramid network that integrates and refines different spatial features to handle the “hard” joints. Li et al. [33] adopted a coarse-to-fine supervision strategy and aggregated features across a multi-stage network architecture to achieve better performance. To keep high-resolution features across different stages of the network, Sun et al. [19] proposed a high-resolution network (HRNet) with multi-branch information fusion. We adopted HRNet as our backbone due to its outstanding performance. Besides, our approach exploits inter-level feature fusion to extract more semantic information and refine localization with the assistance of multi-task learning.
2.2. Multi-Task Learning
Multi-task learning (MTL) [27,28,34] in deep neural networks exploits similarities and differences in multiple tasks simultaneously to learn representations by a shared model. Compared with training the models separately, MTL can improve the generalization performance and prediction accuracy for all tasks. In general, MTL can be divided into two categories: hard parameter sharing and soft parameter sharing. Hard parameter sharing is applied by sharing the model weight among all the tasks, and it has different output layers to prevent overfitting. As for the soft parameter sharing scheme, every task has its specific model weights. The weight distance among different tasks is generally regularized to ensure the similarity of the parameters. The hard parameter sharing paradigm is more helpful in these methods, such as [8,25,26,35], which used closely related tasks as auxiliary tasks for MTL. Since human joints and bones share a common optimal hypothesis class, we chose the hard parameter sharing paradigm to share the same hidden space for two localization tasks.
Besides, dynamic transfer [36] is an effective process to provide useful guidance. Bertinetto et al. [37] utilized the dynamic parameter prediction mechanism to fuse specific information in the learning process for one-shot learning. Motivated by this, Nie et al. [25] exploited the dynamic parameters from the human parsing information to extract complementary features for pose estimation. Moreover, Nie et al. [26] introduced a mutual adaptation mechanism by learning mutual guidance information for joint human parsing and pose estimation. Zhou et al. [35] proposed a macro–micro mutual learning mechanism to boost the information interaction between human limbs and joints.
2.3. Attention Mechanism
The attention mechanism helps neural networks pay attention to particular areas in an end-to-end trainable manner. Since the attention model is effective in understanding images, it can be easily incorporated into many computer vision tasks, such as object detection [38], visual recognition [39], object segmentation [40,41,42,43,44,45], and activity recognition [6]. Hu et al. [46] proposed the squeeze-and-excitation network (SENet), which focuses on the relationship among channel features. Woo et al. [47] introduced a convolutional block attention module (CBAM), which exploits spatial and channelwise features to compute complimentary attention. Moreover, Cai et al. [48] combined mixed attention to balance local and global representations for the final prediction.
The recent representative works for 2D human pose estimation are summarized in Table 1. We show the details of recent studies on the network type, the technique of implementation, the datasets used, the evaluation measures, and the highlights. More details of the datasets and evaluation metrics are described in Section 4.

Table 1.
Summary of 2D human pose estimation methods.
Previous studies proposed successful network architectures to improve the qualities of features. Our architecture builds upon the effective HRNet architecture [19] to generate reliable representations. These methods also prove the effectiveness of multi-task learning and the attention mechanism. We combined multi-task learning and the attention mechanism to build an efficient framework. In our work, we chose human bone localization as an auxiliary task for pose estimation. Our method leverages existing pairs of adjacent joints to generate auxiliary labels to avoid extra manual annotations. Compared with [35], we solely transferred the information of the human bones to the human joints through one stage. To filter useless information from related human joints, we applied the channel attention block to the stage of multi-granularity information fusion. We refined the output features via the spatial attention block, which helps the model focus on human body regions.
3. Method
In this section, we first introduce the architecture of the dynamic information transfer network (DITN) and detail its components. The overall pipeline for the proposed DITN model is shown in Figure 2. At the end of the backbone network, we constructed two branches that predict the heat maps for body joints and bones, respectively. The backbone network (Section 3.1) aims to aggregate low-level and high-level representations to achieve a mutual boosting scheme and learn the multi-granularity features for pose estimation. The resultant feature maps from the highest-resolution output are fed to the decoder module (Section 3.2) to generate the features of joints or bones separately. For fine-grained information transfer, we grouped the features so that the pairs of adjacent joint features correspond to the bones. We appended a dynamic information transfer module (DITM) (Section 3.3) after feature grouping. Dynamic information transfer is performed from bone features to joint features. Meanwhile, we introduced attention blocks (Section 3.4), the channel attention block and spatial attention block, into the DITM. The attention blocks control the balance of shared features across different granularities and reweight the features to automatically infer the regions of interest.
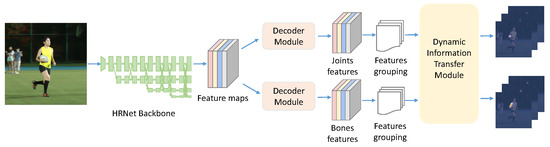
Figure 2.
The proposed multi-task learning framework. The network employs a convolutional network with shared parameters to extract joint and bone features for each person. By performing feature grouping, the corresponding joint and bone features are sent to the dynamic information transfer module (DITM) to achieve refined pose estimation.
3.1. Feature Extraction
Given an input RGB image of size , we first ran a human detector to extract the human bounding boxes. Then, each of these boxes is cropped from the image and sent to the backbone network. We adopted HRNet as the backbone network, which is a successful architecture for many vision tasks such as pose estimation [19], object detection [49], and semantic segmentation [50]. HRNet starts from a high-resolution convolutional stem and gradually connects high-to-low-resolution subnetworks in parallel. Instead of adopting the high-to-low and low-to-high frameworks to recover the resolution, HRNet maintains a high-resolution pass throughout the whole process. It is an effective way to generate reliable representations by repeatedly receiving the information from the high-resolution subnetwork. With the repeatedly aggregated high-level and low-level representations, multi-resolution spatial features with rich semantics are extracted. We modified the original HRNet by discarding the final heat map regression layer and adding two branches to produce the human joints’ and bones’ prediction.
3.2. Decoder and Grouping
To amplify the valuable features and reduce the noise for specific tasks, we appended two decoder modules at the end of the backbone network. The architecture of the decoder module is shown in Figure 3, which is modified by the basic residual blocks [51]. The number of the input feature channels C is expanded to 2C through a convolution and reduced to C with a convolution. Then, we added the original feature and implemented a convolution on the residual features to generate the corresponding feature maps.
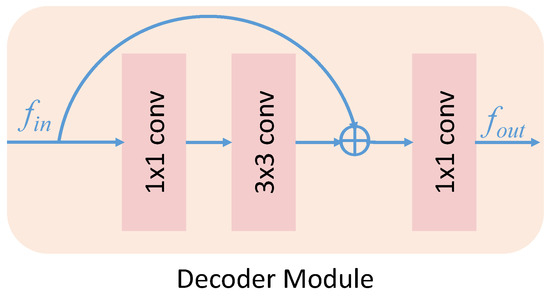
Figure 3.
The architecture of the decoder module.
High-level joint features and bone features are extracted from the decoder module. To perform the fine-grained information transfer in the DITM, we divided the joint features and bone features into b groups by anatomical constraints as follows:
We split and concatenated the tensor into , where N represents the batch size and C, H, and W represent the channel number, height, and width of the feature maps. Concretely, like group , we concatenated the left elbow features and left wrist features in the channel dimension to generate joint features . Then, we expanded the left lower arm features to obtain the bone features for the same channel number with the joint features. Figure 4 shows the body joints linked by the bones, in which the features correspond to the left lower arm features . Other groups follow the same procedure to transfer the information in the dynamic information transfer module.
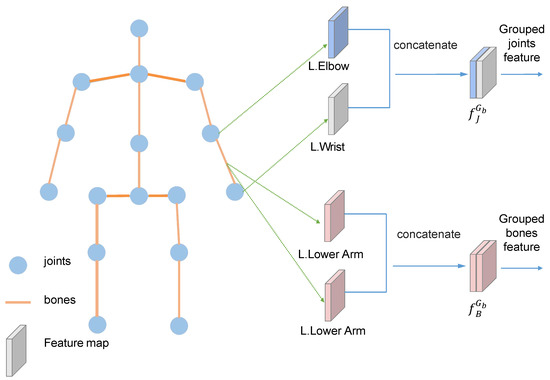
Figure 4.
Illustration of the proposed feature grouping.
The architecture of the DITM is shown in Figure 5. It takes the grouped joint features and bone features as the input for the DITM. Our parameter adapter is a one-shot learner, which processes the bone features to generate the dynamic parameter following [26,37]. The architecture of the parameter adapter is shown in Figure 6a. We exploited a sequence of convolution and max-pooling to reduce the space and time cost of the information transfer. Note that we always applied batch normalization and the ReLU activation function after the convolution. To transfer information adaptively, the dynamic parameter is taken as a convolutional kernel. After being convolved by a standard convolutional layer, the joint features are sent to the adaptive convolution together with the dynamic parameter to generate the bone-induced features :
where represents the convolutional operation and means dividing the features or into the B group. represents the adaptive convolutional operation, which replaces the static convolutional kernel with the dynamic convolution parameter . represents the parameter adapter, which predicts convolution parameter . It is a more efficient way to capture and consolidate information than using hand-crafted features.
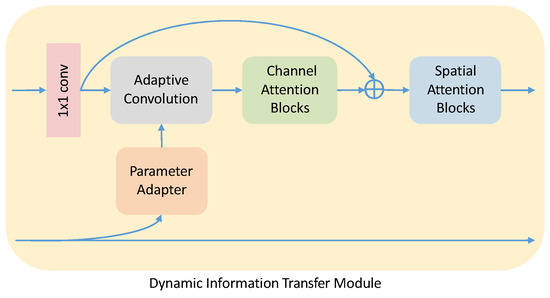
Figure 5.
The architecture of the dynamic information transfer module.
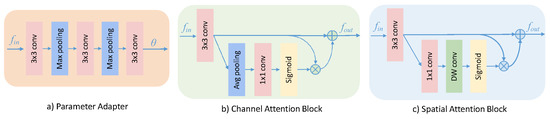
Figure 6.
Illustration of the proposed parameter adapter, channel attention block, and spatial attention block.
3.3. Dynamic Information Transfer Module
The bone-induced features by the adaptive convolution are fed into the channel attention block to generate residual features. Our network regards after the convolutional operation as the original information and fuses it with the output features of the channel attention block to generate the refined features . In particular, the feature fusion with the channel attention block makes the network ignore the bias parameters in the adaptive convolutional operation. Then, the features are sent to a spatial attention module to generate joint heat maps:
where are the final joint heat maps and represent the bone-induced features. and represent the channel attention block and spatial attention block, which are detailed in Section 3.4. As for the bone prediction branch, the bone heat maps are directly generated from the decoder module.
3.4. Attention Blocks
To make the network pay attention to particular areas, we inserted the channel attention block and the spatial attention block into the dynamic information transfer module. The architectures of the channel attention block and the spatial attention block are illustrated in Figure 6b,c. The channel attention block aims to generate a channel attention map, which drives the network to focus on the meaningful channel information. The first component of this block is a convolution to excavate information as a residual feature. Inspired by SENet [46], we aggregated the spatial information using a global average pooling, a convolution, and a sigmoid activation to obtain a set of channel weights. The final features are obtained via conducting sum and elementwise multiplication with residual features. Define the input features of the channel attention block as and the output features as . The channel attention block is formulated as Equation (4):
where represents the convolution, represents the convolution, represents the global average pooling, represents the sigmoid activation function, and ⊙ represents the elementwise multiplication. We expected the network to benefit from the correctly induced features and to diminish the negative impacts of ambiguous information. Therefore, we utilized the channel attention block to exchange the information through adaptive channel weighting.
To utilize the spatial relationship of the features, the spatial attention block induces the network to focus on the informative part for target localization. Similar to our channel attention block, a convolution is implemented to extract the residual features. Then, we used a convolution, a depthwise convolution, and a sigmoid activation to obtain a spatial attention map. The sum and elementwise multiplication with residual features are conducted in the final component. Define the input features of the spatial attention block as and the output features as . The spatial attention block can be formulated as Equation (5):
where represents the depthwise convolution. The larger convolutional kernel used in the spatial attention block not only obtains a larger receptive field, but also obtains more global features. A previous study [47] showed the comparison of different convolutional kernel sizes, showing that adopting a larger kernel size generates better accuracy. This implies that a broad view (i.e., large receptive field) is needed to decide on spatially important regions. CBAM [47] uses average pooling in the spatial attention, which generates the spatial attention map at each pixel by aggregating all the channel information. However, our spatial attention block aims at learning the spatial information about specific human joints. The depthwise convolution breaks the filters and feature maps into different channels. It convolves the corresponding feature map with the corresponding channel and then stacks them back. In this way, the spatial features of different joints can be adaptively learned.
Background pixels occupy the greater part of the heat maps, and only the smaller part of the heat maps indicates the foreground pixels. This is the common challenging foreground–background imbalance problem in pose estimation. The attention blocks drive the network to focus on the human body regions highlighted by the attention maps. Our network pays attention to localizing each body joint based on the well-defined human body region without considering the background. Therefore, our network tackles the imbalance problem and improves the localization performance with the attention blocks.
3.5. Loss Function
A straightforward idea is to jointly train the network with two kinds of losses: the focal L2 loss [52] for the joint prediction branch and the smooth L1 loss [53] for the bone prediction branch. After dynamic information transfer, the joint prediction branch generates the heat maps , one for each joint, with each pixel of these heat maps indicating the probability of containing a joint. The bone prediction branch simultaneously generates the heat maps , one for each bone with each pixel of these heat maps indicating the probability of being a human bone. Previous methods [4,14,18,19] adopted a mean-squared error (MSE) loss function, between the predicted heat map and the ground-truth heat map . To pay more attention to the occluded and “hard” keypoints, online hard keypoint mining (OHKM) [32] is proposed to backpropagate the gradients of the K maximum keypoint losses. In our work, we adopted the focal L2 loss, which balances the foreground and background and helps the network learn the “hard” keypoints adaptively. The joint prediction branch loss function is computed as Equation (6):
in which
where J is the number of body joints, W is the horizontal location, and H is the vertical location. The ground-truth heat maps are generated by applying a Gaussian kernel to each joint’s location. denotes a pixel-weight-adaptive function that can help the network handle the “hard” keypoints. is a hyper-parameter, which controls the weight for easy examples and hard examples in the focal loss. The higher the value of , the lower the loss for easy examples is, so we could turn the attention of the model more towards hard examples. In our work, we set to obtain more accuracy following [52]. The hyper-parameter was set to 0.01 to filter areas that have a low confidence of being body joints following [52].
The focal L2 loss is sensitive to outliers, which is difficult for the highly differentiated bone heat maps’ prediction. To prevent exploding gradients, the smooth L1 loss was adopted for the bone heat maps’ regression. The bone prediction branch loss function is written as Equation (8):
in which
where B is the number of body bones and the confidence maps are weighted by the perpendicular distance from a pixel to a line of two joints. To balance the conflicts between the two branches, a hyper-parameter is multiplied on . Specifically, we improved the localization ability of the network by jointly updating two losses. The overall loss function is:
where denotes the weight of the bone loss .
4. Experiments
We evaluated our method on two standard human pose estimation benchmarks: the MPII human pose dataset (MPII) [54] and Common Objects in Context (COCO) [55].
4.1. Experiments on MPII Dataset
4.1.1. Dataset and Evaluation Metric
The MPII dataset is a large-scale benchmark for human pose estimation with rich annotations. It contains about images of full-body poses collected from daily human activities. There are over person instances annotated with up to 16 visible joint locations, among which human instances were used for training, instances for validation, and the others for testing.
Our models were evaluated using the standard evaluation metric of the MPII dataset: head-normalized percentage of correct keypoints (PCKh). We adopted the PCKh@ evaluation measure, which refers to the matching threshold as of the head diameter.
4.1.2. Implementation
We trained our models with the input image size of and a batch size of 32. The size of the generated feature maps is , which is typically smaller than the input image. Data augmentation was adopted with random rotation , random scaling , and flipping. The AdamW optimizer [56] was used for training. We used and for the momentum and weight decay parameters. The initial learning rate was , which was decayed by a factor of 10 at Epoch 130 and Epoch 160, respectively. We trained the model on the MPII dataset for 210 epochs. In the loss function (Equation (8)), we set for the balance between joint loss and bone loss. We used the provided person boxes from the MPII dataset as the detected person boxes. The results were evaluated on the validation split proposed in [57]. Following [16,18,32], we computed the heat map by averaging the heat maps of the original and flipped images. The final predicted localization is calculated by adjusting the highest response value with a quarter offset in the direction from the highest heat value to the second one following [19].
4.1.3. Results
Figure 7 shows the qualitative results to visually illustrate the effectiveness of our approach in pose estimation. HRNet does not accurately estimate the joints in the first row of Figure 7 due to truncation in the camera view, similar parts, and occlusion. The images of the second row are shown with our results refined via dynamic information transfer. Not only did we have fewer false positives, but also we gave joints that partially occlude each other more reasonable inferences. We further show the qualitative results on more real-world scenes in Figure 8. This suggests that our model can achieve satisfying results in many real-world scenes.

Figure 7.
Qualitative comparison on the MPII dataset. HRNet (first row) often fails on overlapping and occluded joints in cluttered scenes. Our approach (second row) overcomes these limitations with dynamic information transfer.
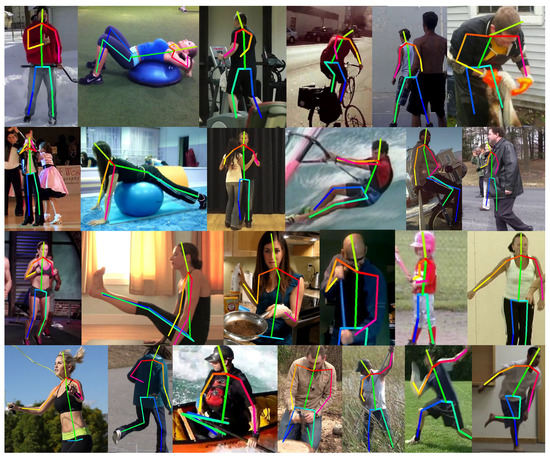

Figure 8.
Sample results on the MPII dataset.
Figure 9 depicts the PCKh@0.5 score curves of our approach and HRNet [19] during training. We can clearly see that our method exhibits higher training and validation accuracy. This shows that the DITN has a greater ability to exactly localize the keypoints compared to HRNet. Moreover, we can find that our multi-task learning framework converges much faster than the base HRNet. Table 2 shows the overall PCKh@ results on the MPII validation set. We adopted HRNet-W32 as the main backbone. Our approach achieved PKCh@ scores, which outperformed the base HRNet and stacked hourglass extensions [16,31]. Compared with HRNet, the proposed approach achieved improvements on the elbow and hip. Our approach surpassed HRNet by PCKh@ scores and surpassed the macro–micro mutual learning [35] by PCKh@ scores. The results above verify the effectiveness of our approach.
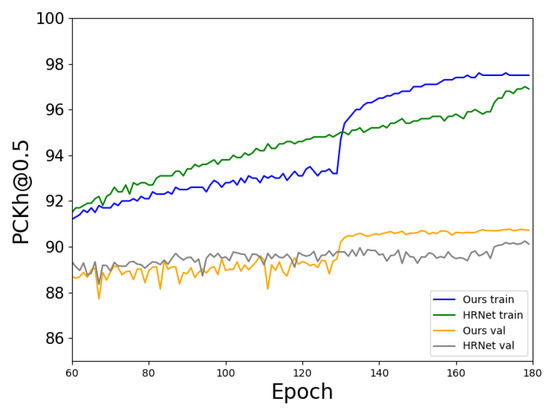
Figure 9.
PCKh@0.5 score curves of our approach and HRNet on the MPII dataset.

Table 2.
Performance comparisons on the MPII validation set (PCKh).
4.2. Experiments on COCO Dataset
4.2.1. Dataset and Evaluation Metric
We validated our model on the COCO 2017 dataset, which has many challenging images in the wild. It contains about images of full-body poses and over person samples. Each person instance is labeled with 17 visible joints. We trained our network on the COCO keypoint detection training set, which has images and labeled person instances. The experimental results were evaluated on the validation subset, which contains images, and the test-dev subset with images.
For the COCO dataset, we adopted a standard evaluation metric that is based on object keypoint similarity (OKS):
where denotes the Euclidean distance between the detected keypoint and the ground-truth, s represents the scale of the object, controls the falloff for keypoint i, and is the visibility of keypoint i. We report the standard OKS-induced AP (the mean of the average precision scores at OKS = 0.50, 0.55,..., 0.90, 0.95), (average precision at OKS = 0.50), (average precision at OKS = 0.75), for medium objects, for large objects, and AR (the mean of recall scores at OKS = 0.50, 0.55, …, 0.90, 0.95).
4.2.2. Implementation
We trained our model with an input image size of . Data augmentation and the training strategy were adopted the same as for the experiments on the MPII dataset. We used the detected person boxes provided by [18] for both the validation set and test-dev set.
4.2.3. Results
We report the results of our method and other state-of-the-art methods on the COCO validation 2017 dataset in Table 3. Our network achieved AP scores, outperforming other methods with the same input size (). From the results, we can see that our method was 0.6% higher than the total result of the baseline HRNet [19] at AP with almost the same model size and a marginal increase in GFLOPs (+0.16). Compared with HRNet [19], we also found that the gain of the results mainly came from medium persons (+1.3). This means that the dynamic information transfer brings more spatial information for small-scale persons. Besides, our method was 0.7% higher than macro–micro mutual learning [35] with only 41% GFLOPs. Table 4 reports the final keypoint detection results of our approach on the COCO test-dev 2017 dataset. Our approach achieved AP without the use of additional training data. Moreover, our models have fewer parameters and computational complexity than the others. Compared with the recently proposed attention-based method [48], our approach achieved improvements of on AP. Compared with the macro–micro method [35], our approach performed much better with less computation.

Table 3.
Comparisons on the COCO validation set. Pretrain = pretraining the backbone on the ImageNet classification task. OHKM = online hard keypoint mining [32].

Table 4.
Comparisons on the COCO test-dev set.
Figure 10 shows some pose estimation results obtained by our approach on the COCO dataset. Our method is not constrained to single-person pose estimation and can be applied to multi-person pose estimation. We can note that our model can achieve promising results across different datasets.
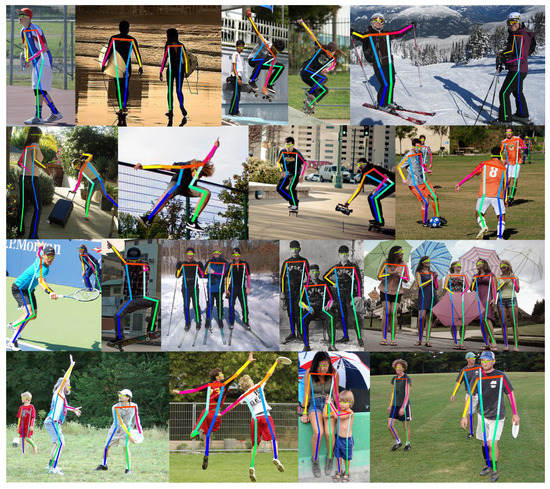

Figure 10.
Sample results on the COCO dataset.
4.3. Ablation Study
4.3.1. Network Design
In this section, we evaluate the model performance with different components of our approach. Table 5 demonstrates the results of each component that contributes to the final performance. Our baseline was the HRNet model; it reached PKCh@ scores on the MPII validation set. “MTL” indicates the multi-task learning with the decode module. We can see that the performance was improved by with MTL compared to the HRNet baseline. The “DITM” indicates the dynamic information transfer module without the “CAB” (channel attention block) and “SAB” (spatial attention block). The improvement of adding the DITM over the baseline reached and proves the effectiveness of dynamic information transfer across different granularity levels. Explicit spatial information leads to better localization accuracy of human joints. Besides, combining the CAB or the SAB with the DITM achieved and improvement, respectively. The combination of the CAB and the SAB improved the performance largely, which surpassed the baseline by . Our attention blocks make a trade-off between spatial and channel representations in the output features and benefit from the combination. This kind of combination confirms that cooperation between the DITN and attention blocks benefits the information exchange across different levels.

Table 5.
Ablation study of each component in our framework.
4.3.2. Loss Function
Gaussian response heat maps have many background pixels and only a few foreground pixels. In the training phase, too many “easy” samples (simply recognized keypoints and background pixels) inhibit the network from learning the “hard” samples (occluded keypoints and foreground pixels). To deal with the problem of imbalanced data, we used the focal L2 loss to replace the original mean-squared error (MSE) loss. We compare different loss functions in Table 6. This study was conducted on the ResNet-50 backbone. For our model trained with the MSE loss, the PCKh scores were , while for our model trained with the focal L2 loss, the PCKh scores decreased to . The reason might be that the bone branch may bring in some ambiguous information. The focal L2 loss is sensitive to outliers, which is difficult for bone pixel regression. We used the smooth L1 loss for the bone pixel regression to guide the network to learn robust features. We can observe that using the focal L2 loss for the joint prediction branch and the smooth L1 loss for the bone prediction branch achieved PCKh scores. The improvement reached about PCKh scores and verifies the effectiveness of the combination of the focal L2 loss and smooth L1 loss.

Table 6.
Ablation study of different loss functions.
The hyper-parameter was set to balance the conflicts between joint loss and bone loss. We study the impact of the hyper-parameters in Table 7. We found that setting achieved the highest performance among all variations. This setting ensures that the balance of joint loss and bone loss should be addressed properly.

Table 7.
Ablation study on the hyper-parameter .
5. Discussion
Our proposed dynamic information transfer network architecture explores how to refine body joint localization with the spatial relationship of adjacent joints. The advantages of our study are three-fold. First, we conducted inference of the human pose in a compositional model, which is composed of the joint and bone branches to benefit from the spatial dependency. The bone information has more spatial constraints, which can mitigate the inconsistencies (even some errors) in joint localization. Second, our method leverages the existing pairs of adjacent joints to generate auxiliary bone labels to avoid extra manual annotations. Finally, we improved the localization ability of the network by adding the attention blocks. The attention blocks balance the shared feature across different granularity levels and drive the network to focus on the human body regions.
For clarity, the main network architectures of the proposed models are presented in Table 8. Our framework uses the same backbone for joint estimation and bone location prediction. With the feature-sharing mechanism, our model only brings a small computational cost (+0.19GFLOPs) and model parameter (+0.1M) overhead for HRNet. The computational superiority of our proposed modules is of great value.

Table 8.
Main architectural details of the networks. IC denotes the number of input channels for a layer; OC is the number of output channels; Nums indicates the number of layers; K is the kennel size; S is the stride size; P is the padding size; BN (Y/N) indicates if batch normalization is applied; ReLU (Y/N) indicates if the ReLU activation is used.
There are some limitations in our work. For the source images with complex scenes as shown in Figure 11, it is insufficient to use the spatial correspondences extracted from human bone features as guidance. In crowded scenes, many joints from other human instances generate mistaken bone predictions, which misleads the network to learn unrealistic cases. Besides, our framework with the attention mechanism can focus on human body regions, but cannot cope well with the invisible joints in the image.

Figure 11.
Failure cases caused by (left) overlapping people, (middle) cluttered background, and (right) severe occlusion.
In this paper, we focused on predicting the pose of a single person assuming the location and scale of the person are provided in the form of a bounding box. Our method can be extended to multi-person pose estimation in a bottom-up manner. The proposed dynamic information transfer module can fuse multi-granularity feature information to boost the joint location. However, joint grouping can be a big challenge. In the future, we plan to extend our work on multi-person pose estimation and explore the way of applying dynamic information transfer for joint grouping.
6. Conclusions
This paper presented a dynamic information transfer network (DITN) that jointly localizes human joints and bones. The DITN was designed to share features across different granularity levels in a multi-task learning scheme. Our approach exploits bone information to assist human pose estimation through dynamic information transfer. Moreover, attention blocks were integrated into our network to balance the shared feature and induce the network to focus on the human body region to refine body joint localization. The extensive experimental results showed that the spatial dependency of human joints is the key ingredient for human pose estimation. The proposed DITN shows advantages over previous studies in model performances and the simplicity of information transfer. The DITN achieved competitive results on two benchmarks, COCO and MPII. We believe that the dynamic transfer module with an attention mechanism can be applied to other tasks.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Y.L.; software, Y.L.; validation, J.S., Y.L., and Q.S.; formal analysis, Y.L.; investigation, Q.S., Y.L., and J.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.L., Q.S., J.S., and F.Y.; visualization, Y.L.; supervision, Q.S.; funding acquisition, Q.S. and F.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by The Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (F2019201451). This work is also supported by the Science and Technology Project of Hebei Education Department (ZD2019131).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dantone, M.; Gall, J.; Leistner, C.; Van Gool, L. Body parts dependent joint regressors for human pose estimation in still images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 2131–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.E.; Ramakrishna, V.; Kanade, T.; Sheikh, Y. Convolutional pose machines. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4724–4732. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.; Di, H.; Lu, Y.; Lv, F.; Tian, X. Video pose estimation with global motion cues. Neurocomputing 2017, 219, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tighe, J.; Modolo, D. Combining detection and tracking for human pose estimation in videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11088–11096. [Google Scholar]
- Bazarevsky, V.; Grishchenko, I.; Raveendran, K.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, F.; Grundmann, M. Blazepose: On-device real-time body pose tracking. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.10204. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, L.; Dai, Y.; Cheng, X.; Chen, H.; He, M. Skeleton based action recognition using translation-scale invariant image mapping and multi-scale deep CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo Workshops, Michigan, WI, USA, 21–25 May 2017; pp. 601–604. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.S.; Cao, J.; Tai, Y.W.; Lu, C. Pairwise body-part attention for recognizing human-object interactions. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 51–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, W.; Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Gool, L.V. Differentiable multi-granularity human representation learning for instance-aware human semantic parsing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 1622–1631. [Google Scholar]
- Barmpoutis, A. Tensor body: Real-time reconstruction of the human body and avatar synthesis from RGB-D. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 43, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felzenszwalb, P.F.; Huttenlocher, D.P. Pictorial structures for object recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2005, 61, 55–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompson, J.J.; Jain, A.; LeCun, Y.; Bregler, C. Joint training of a convolutional network and a graphical model for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the Advances in neural information processing systems, Montreal, CA, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 1799–1807. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Savarese, S. Articulated part-based model for joint object detection and pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Washington, DC, USA, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 723–730. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yuille, A. Articulated pose estimation by a graphical model with image dependent pairwise relations. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1407.3399. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Hidalgo, G.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.E.; Sheikh, Y. OpenPose: Realtime multi-person 2D pose estimation using Part Affinity Fields. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insafutdinov, E.; Pishchulin, L.; Andres, B.; Andriluka, M.; Schiele, B. Deepercut: A deeper, stronger, and faster multi-person pose estimation model. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 34–50. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A.; Yang, K.; Deng, J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 483–499. [Google Scholar]
- Toshev, A.; Szegedy, C. Deeppose: Human pose estimation via deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1653–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, B.; Wu, H.; Wei, Y. Simple baselines for human pose estimation and tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 466–481. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5693–5703. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Bao, Q.; Sun, Y.; Mei, T. Recent advances of monocular 2d and 3d human pose estimation: A deep learning perspective. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurtsever, M.M.E.; Eken, S. BabyPose: Real-time decoding of baby’s non-verbal communication using 2D video-based pose estimation. IEEE Sensors J. 2022, 22, 13776–13784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Sun, X.; Wei, Y. Compositional human pose regression. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2018, 176–177, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ouyang, H.; Liu, S.; Qi, X.; Shen, X.; Yang, R.; Jia, J. Human pose estimation with spatial contextual information. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.01760. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Yu, P.; Wu, Y. Deeply learned compositional models for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 190–206. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, X.; Feng, J.; Zuo, Y.; Yan, S. Human pose estimation with parsing induced learner. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 2100–2108. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, X.; Feng, J.; Yan, S. Mutual learning to adapt for joint human parsing and pose estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 502–517. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, X. Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM international conference on Multimedia, Seoul, Korea, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 274–282. [Google Scholar]
- Papandreou, G.; Zhu, T.; Kanazawa, N.; Toshev, A.; Tompson, J.; Bre- gler, C.; Murphy, K. Towards accurate multi-person pose estimation in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4903–4911. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Xiao, B.; Wei, F.; Liang, S.; Wei, Y. Integral human pose regression. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 529–545. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Li, S.; Ouyang, W.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Learning feature pyramids for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1290–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, G.; Sun, J. Cascaded pyramid network for multi-person pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7103–7112. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Yin, B.; Peng, Q.; Du, Y.; Xiao, T.; Yu, G.; Lu, H.; Wei, Y.; Sun, J. Rethinking on multi-Stage networks for human pose estimation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.00148. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.; Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Hospedales, T.; Xiang, T. Robust person re-identification by modelling feature uncertainty. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 22 October–2 November 2019; pp. 552–561. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, Y.; Cao, C.; Chu, Y.; Wang, J.; Lu, H. Macro-micro mutual learning inside compositional model for human pose estimation. Neurocomputing 2021, 449, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrbach, M.; Stark, M.; Schiele, B. Evaluating knowledge transfer and zero-shot learning in a large-scale setting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 1641–1648. [Google Scholar]
- Bertinetto, L.; Henriques, J.F.; Valmadre, J.; Torr, P.; Vedaldi, A. Learning feed-forward one-shot learners. In Proceedings of the Advances in neural information processing systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016; pp. 523–531. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, J.; Wei, Y. Relation networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3588–3597. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, P.; Song, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Qiao, Y. Uniformer: Unifying convolution and self-attention for visual recognition. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.09450. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Song, H.; Zhao, S.; Shen, J.; Zhao, S.; Hoi, S.C.H.; Ling, H. Learning unsupervised video object segmentation through visual attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3064–3074. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Tao, R.; Shen, J. Matnet: Motion-attentive transition network for zero-shot video object segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 8326–8338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Li, L.; Bredell, G.; Li, J.; Unkelbach, J.; Konukoglu, E. Volumetric memory network for interactive medical image segmentation. Med Image Anal. 2023, 83, 1361–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Qi, S.; Wang, W.; Shen, J.; Zhu, S.C. Cascaded parsing of human-object interaction recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2021, 44, 2827–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Feng, C.M.; Li, J.; Shao, L. Group-Wise Learning for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 2021, 31, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, W.; Konukoglu, E.; Van Gool, L. Rethinking semantic segmentation: A prototype view. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 2582–2593. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Z.; Yin, B.; Du, A.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, E.; Sun, J. Learning delicate local representations for multi-person pose estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 455–472. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Sun, K.; Cheng, T.; Jiang, B.; Deng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Mu, Y.; Tan, M.; Wang, X.; et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for visual recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2020, 43, 3349–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Object-contextual representations for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 173–190. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Su, W.; Wang, Z. Simple pose: Rethinking and improving a bottom-up approach for multi-person pose estimation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 11354–11361. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Andriluka, M.; Pishchulin, L.; Gehler, P.; Schiele, B. 2D Human Pose Estimation: New Benchmark and State of the Art Analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 3686–3693. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Fixing weight decay regularization in adam. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.05101. [Google Scholar]
- Tompson, J.; Goroshin, R.; Jain, A.; LeCun, Y.; Bregler, C. Efficient object localization using convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 6–10 June 2015; pp. 648–656. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).