A Hierarchical Estimation Method for Road Friction Coefficient Combining Single-Step Moving Horizon Estimation and Inverse Tire Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Literature | Method | Features |
|---|---|---|
| [13,14,15,16,20,21] | Slip-slope curves or friction coefficient-slip curves | 1. Computationally inexpensive. 2. Large excitations are usually required to achieve accurate identification results. 3. Sensitive to changes in tire parameters. |
| [17,18] | Longitudinal dynamics models | 1. Large excitations are usually required to achieve accurate identification results. 2. Sensitive to changes in tire parameters. |
| [22,23,26] | Tire self-aligning torque model | 1. High sensitivity to RFC. 2. Modeling of suspension and steering systems is required. 3. Low practicability. |
| [24,25] | Lateral dynamics model | 1. High sensitivity to RFC. 2. High practicability. |
| Literature | Method | Features |
|---|---|---|
| [11,13,17,18,22,26,28] | Kalman filter and its variant | 1. Applicable to linear and unconstrained systems subject to normal distribution. 2. Computationally inexpensive. |
| [27,30] | Particle filter | 1. Applicable to non-Gaussian and non-linear systems. 2. Particle degeneracy and the curse of dimensionality problems exist. |
| [9,25,28,29,30,32] | Moving horizon estimation | 1. Applicable to linear or non-linear, constrained or unconstrained systems. 2. High computational costs |
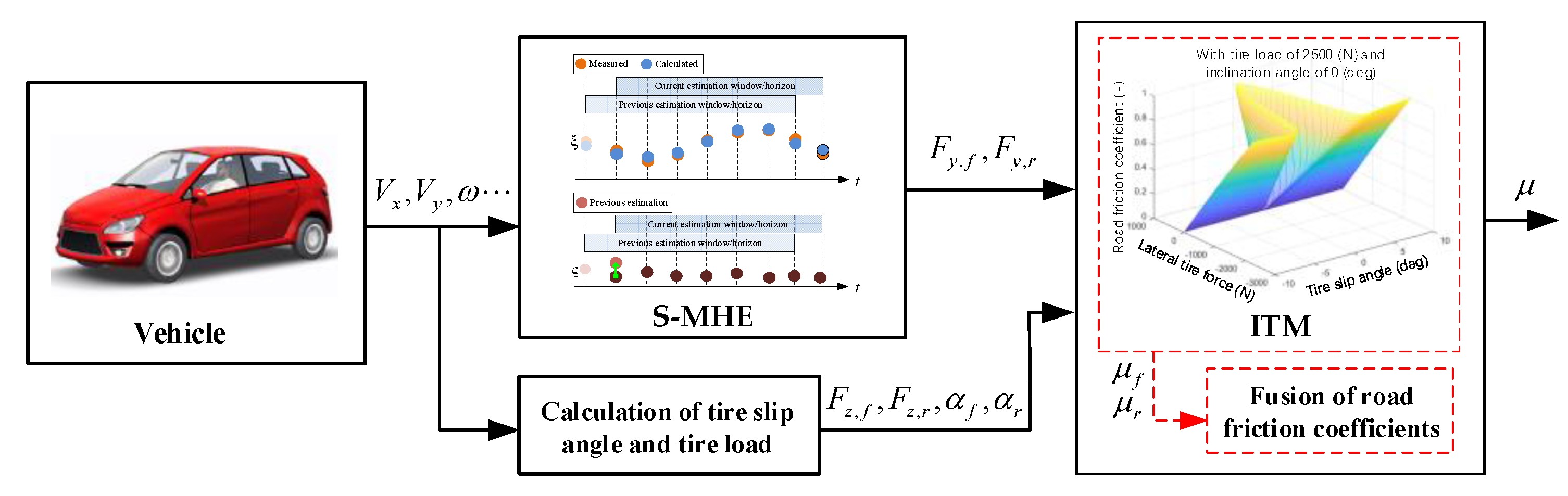
2. Overall Structure of Hierarchical Estimation Method
3. Vehicle and Tire Dynamics Models
4. Design of Estimators
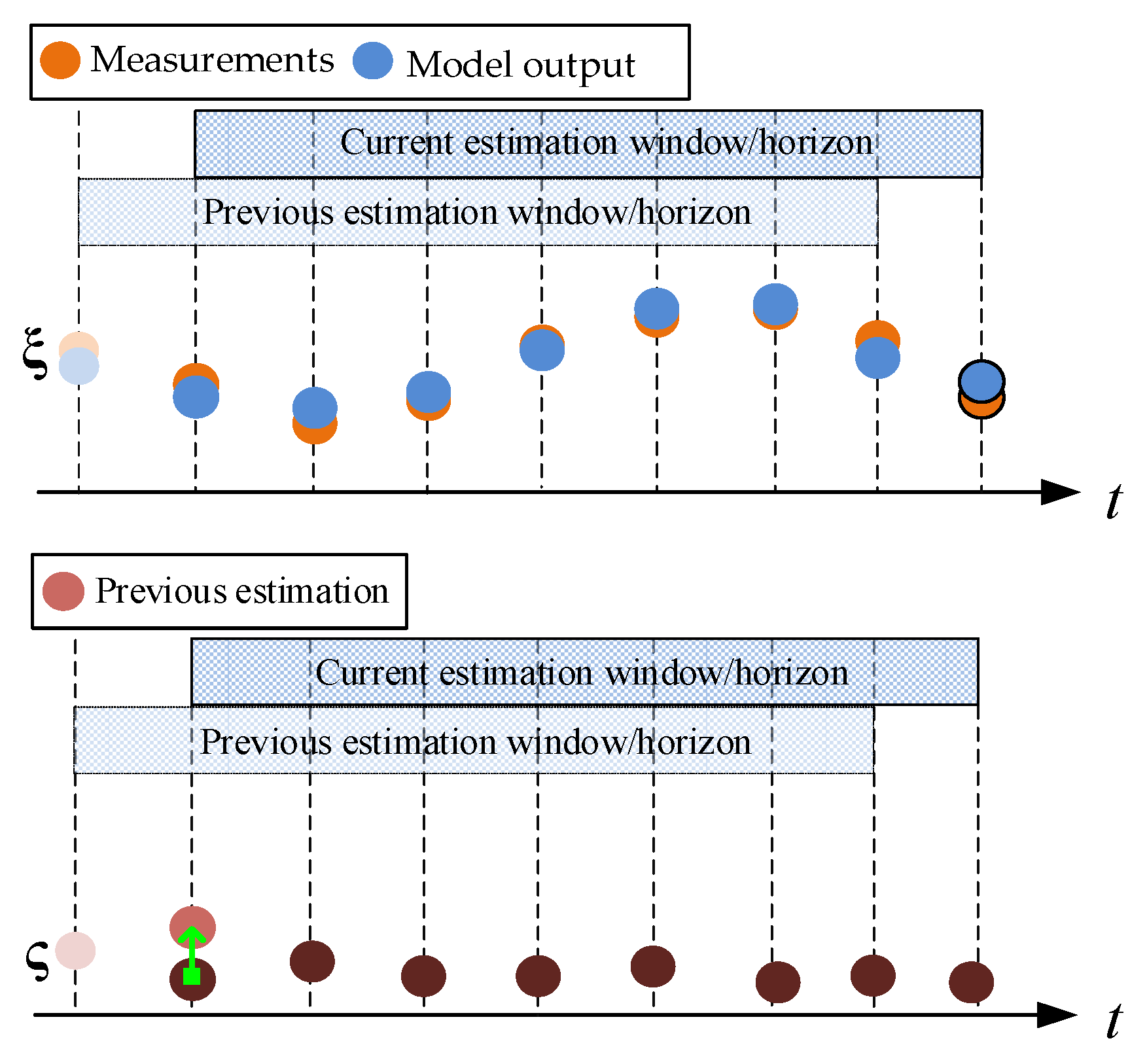
4.1. MHE-Based RFC Estimator
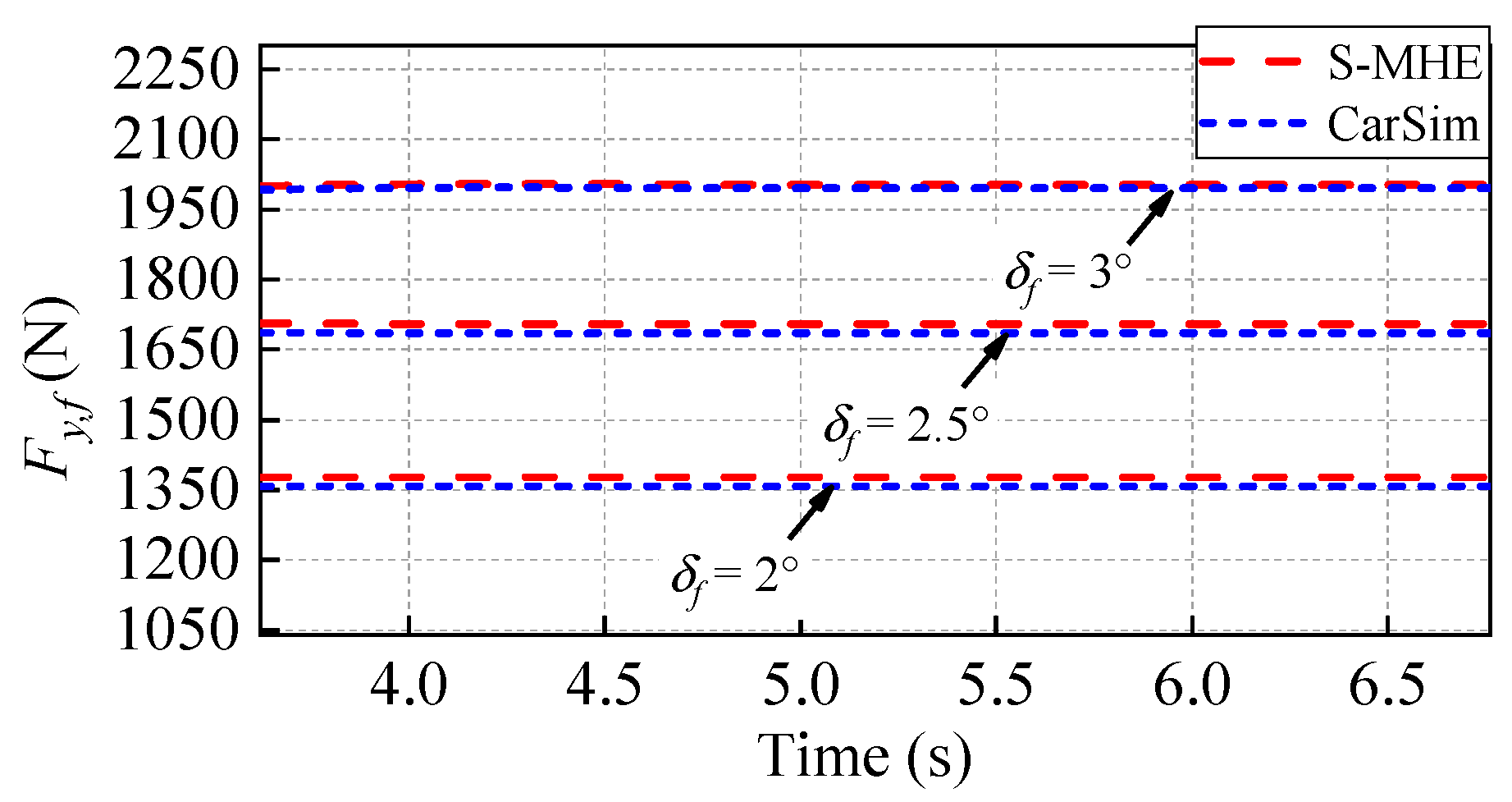
4.2. S-MHE-Based Tire Force Estimator
4.3. ITM-Based RFC Estimator
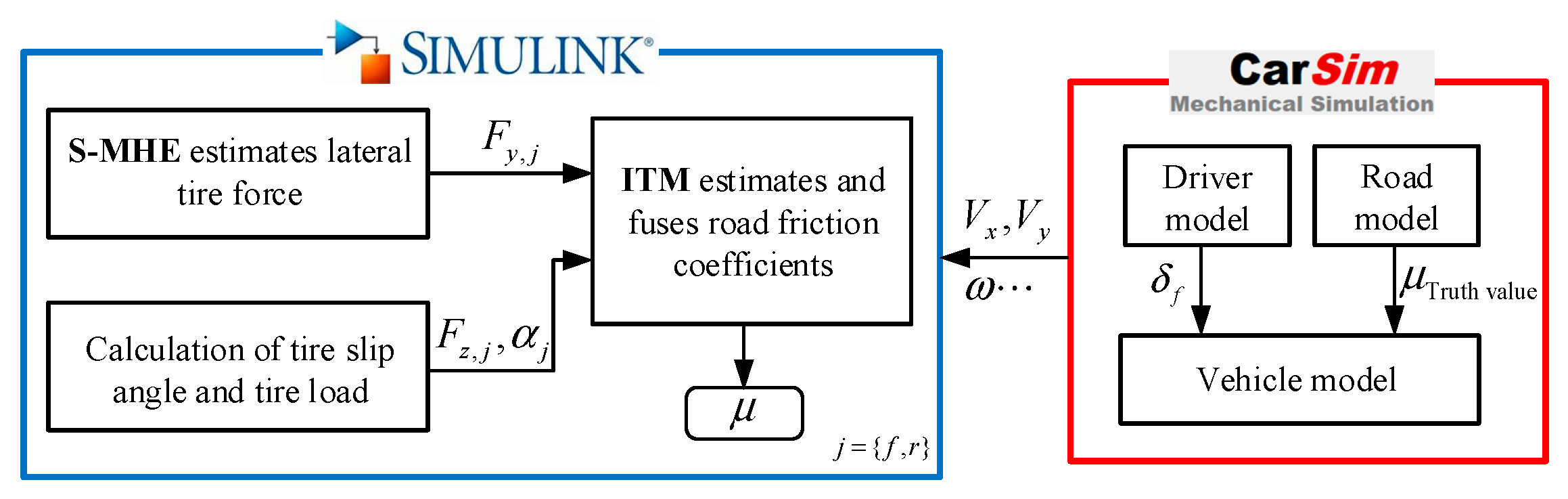
5. Simulation Test
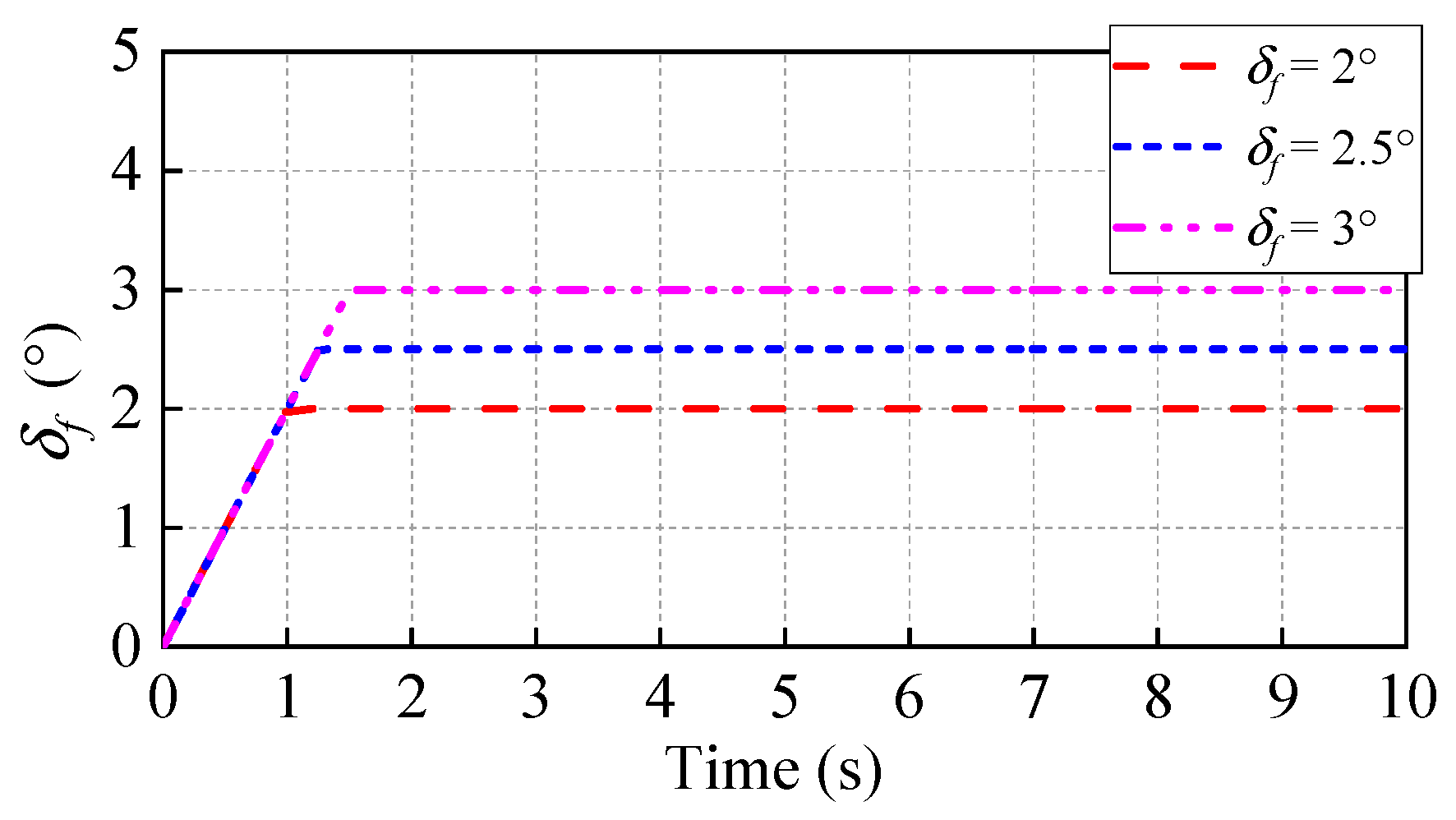
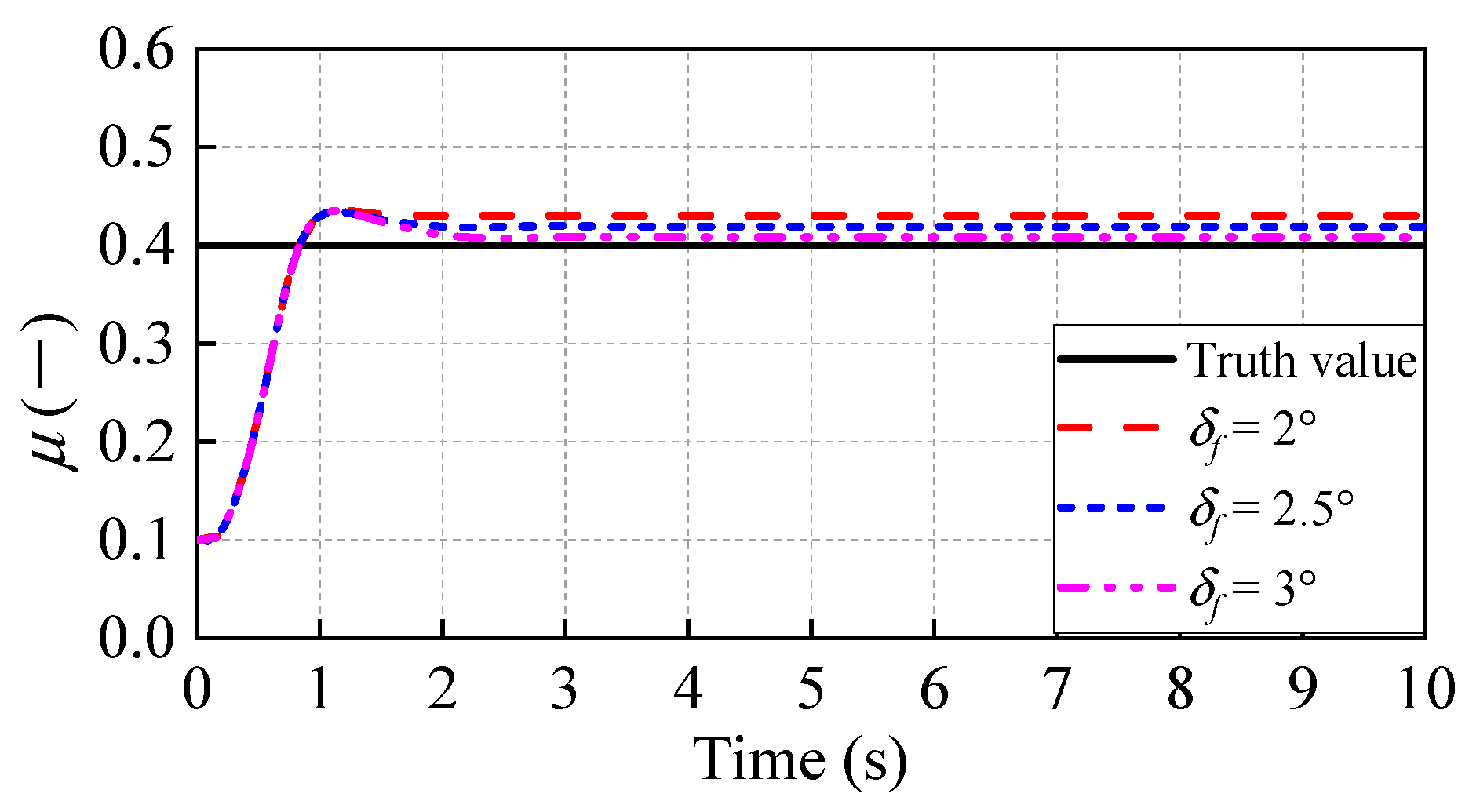
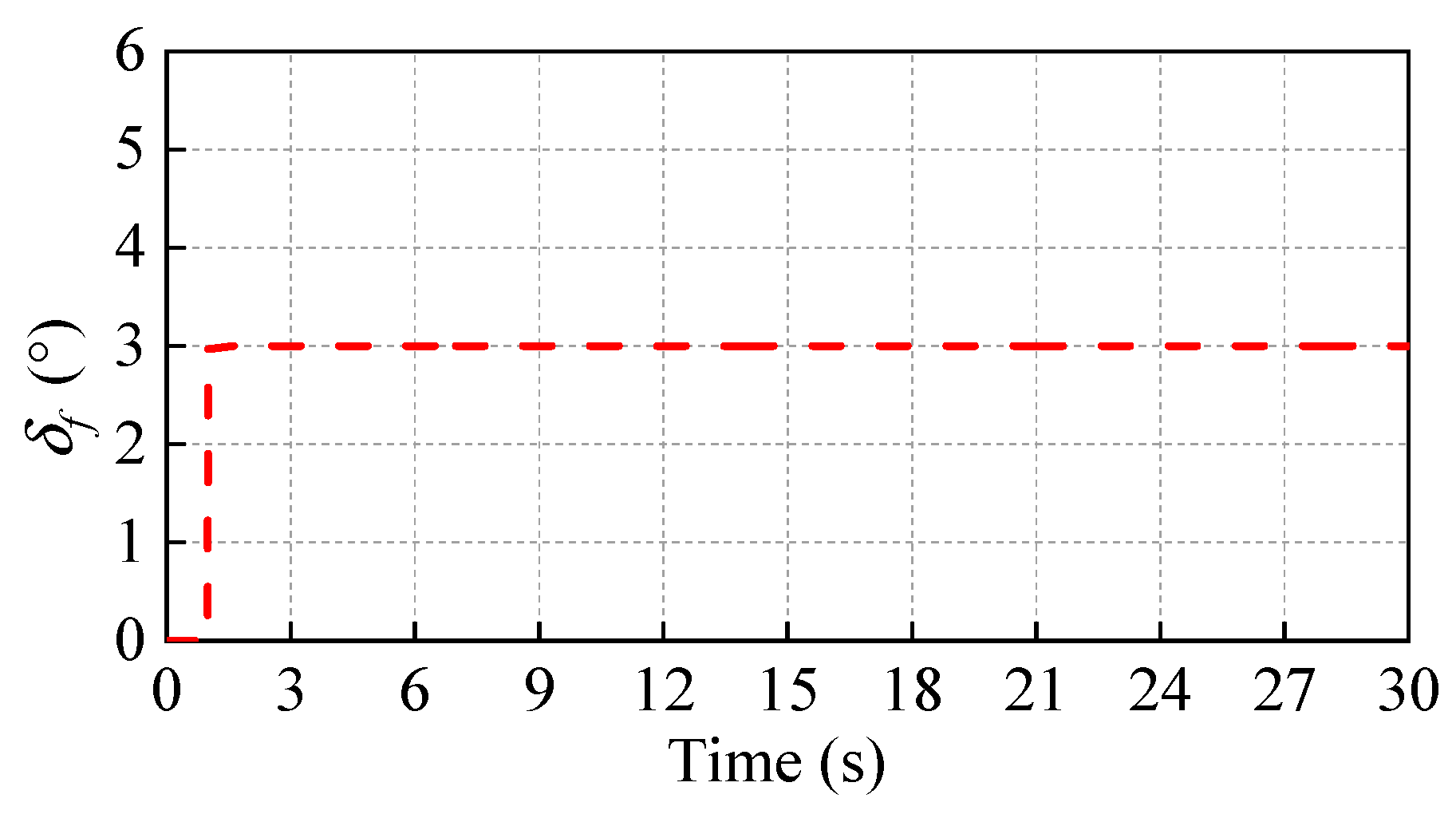
5.1. Test under Different Steering Inputs
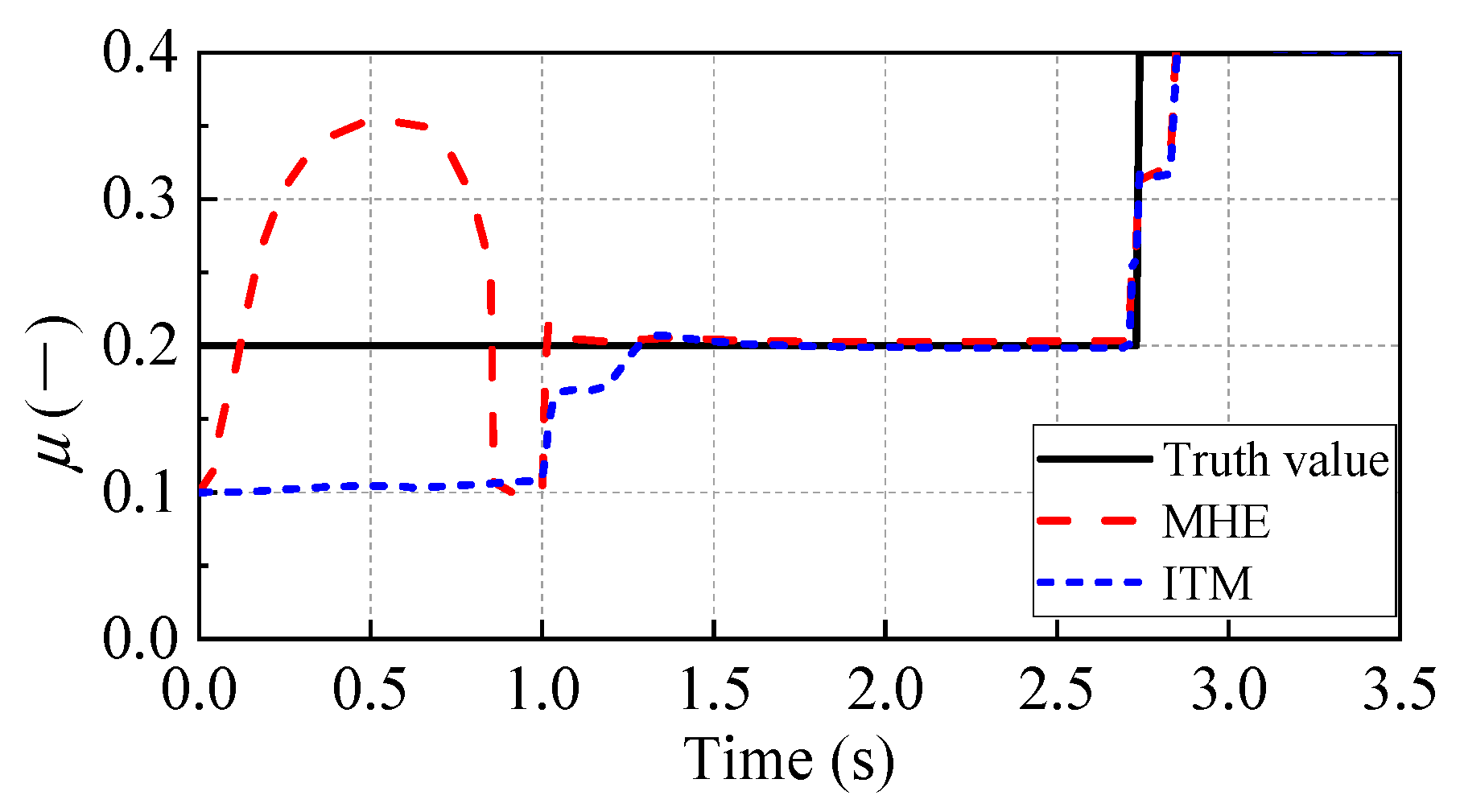
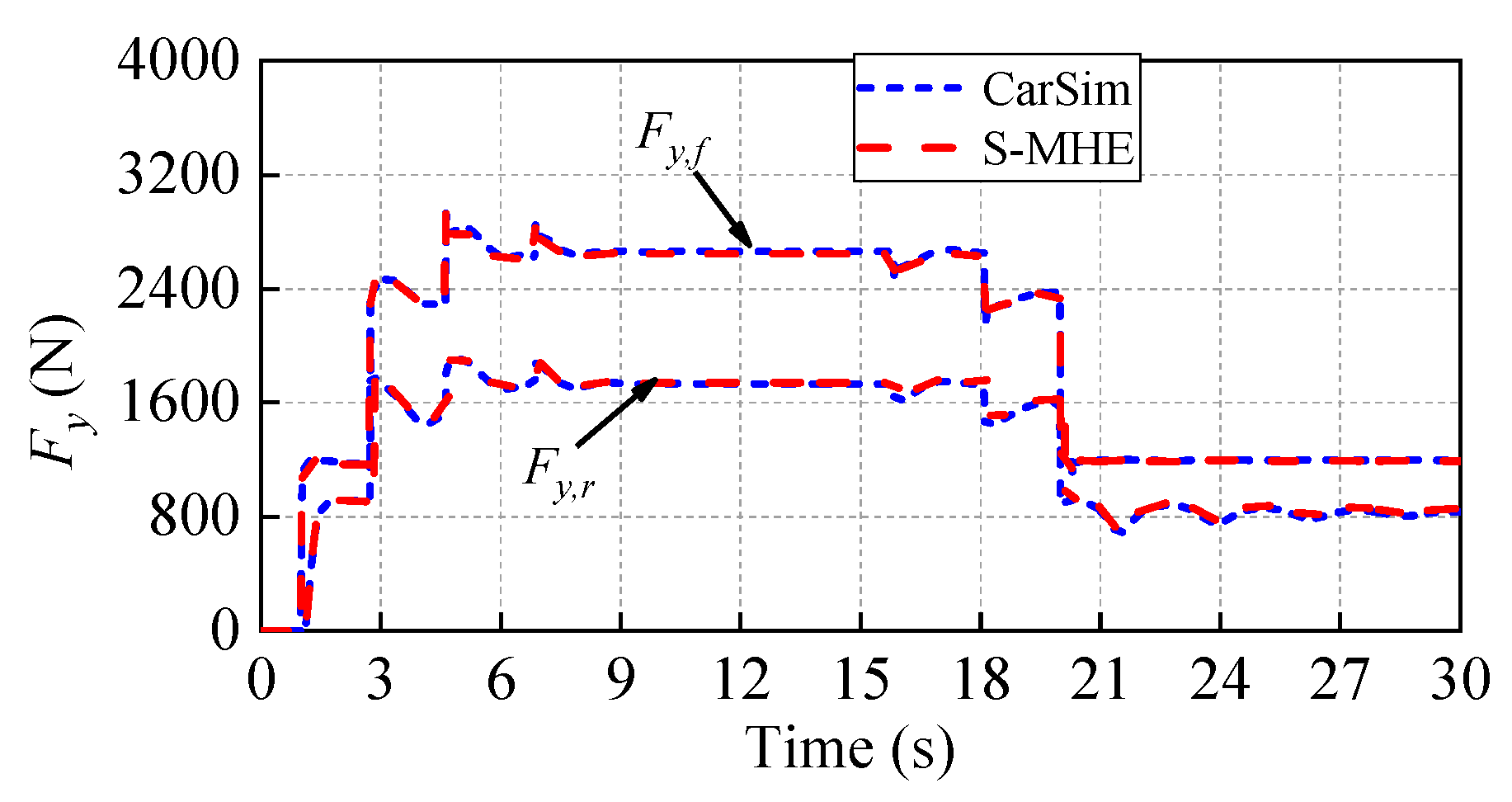
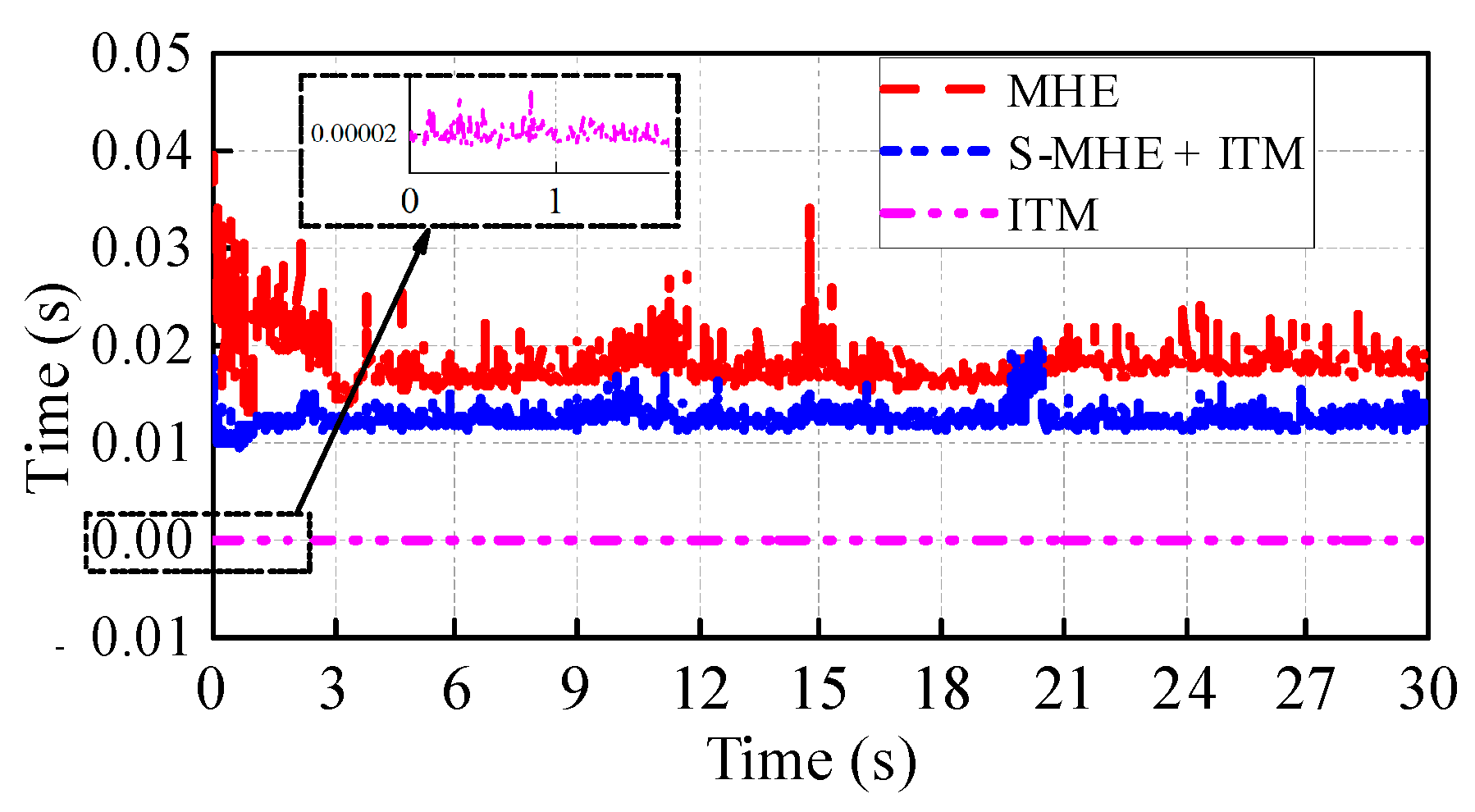
5.2. Test under the Road with Step Change of RFC
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, F.R.; Huang, H.L.; Schwebel, D.C.; Chan, A.H.; Hu, G.Q. Global road traffic injury statistics: Challenges, mechanisms and solutions. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2020, 23, 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisano, P.A.; Goodwin, L.C.; Rossetti, M.A. US highway crashes in adverse road weather conditions. In Proceedings of the 24th Conference on International Interactive Information and Processing Systems for Meteorology, Oceanography and Hydrology, New Orleans, LA, USA, 20 January 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky, H.; Hakkert, A.S. Risk of a road accident in rainy weather. Accid. Anal. Prev. 1988, 20, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaleghian, S.; Emami, A.; Taheri, S. A technical survey on tire-road friction estimation. Friction 2017, 5, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumaa, B.A.; Abdulhassan, A.M.; Abdulhassan, A.M. Advanced driver assistance system (ADAS): A review of systems and technologies. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Eng. Technol. (IJARCET) 2019, 8, 231–234. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Wang, G.; Chen, G.; Chen, H.; Zhang, B. Tire State Stiffness Prediction for Improving Path Tracking Control during Emergency Collision Avoidance. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 179658–179669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, L.; Meng, Y.; Gu, Q.; Bai, G. Integrated Path Tracking Control of Steering and Differential Braking Based on Tire Force Distribution. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2022, 20, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, M.; Kanarachos, S.; Blundell, M. Road Friction Virtual Sensing: A Review of Estimation Techniques with Emphasis on Low Excitation Approaches. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, L.; Meng, Y.; Wang, S.; Gu, Q.; Bai, G. MHE-Based Friction Coefficient Estimation and Compensation Method for Path Tracking Control. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 25th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Macau, China, 8–12 October 2022; pp. 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, B. Path Planning and Path Tracking for Collision Avoidance of Autonomous Ground Vehicles. IEEE Syst. J. 2021, 16, 3658–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lv, C.; Yan, Y.; Peng, P.; Wang, F.; Xu, L.; Yin, G. An Integrated Scheme for Coefficient Estimation of Tire–Road Friction With Mass Parameter Mismatch Under Complex Driving Scenarios. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 13337–13347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, F.; Dong, H.; Yan, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, C.; Yin, G. Tire Road Friction Coefficient Estimation: Review and Research Perspectives. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 35, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, F. Slip-based tire-road friction estimation. Automatica 1997, 33, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Hedrick, K.; Yi, K. Real-Time Slip-Based Estimation of Maximum Tire–Road Friction Coefficient. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2004, 9, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamani, R.; Phanomchoeng, G.; Piyabongkarn, D.; Lew, J.Y. Algorithms for Real-Time Estimation of Individual Wheel Tire-Road Friction Coefficients. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2011, 17, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Wang, B.; Lu, P.; Xu, L. Identification of maximum road friction coefficient and optimal slip ratio based on road type recognition. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2014, 27, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enisz, K.; Szalay, I.; Kohlrusz, G.; Fodor, D. Tyre–road friction coefficient estimation based on the discrete-time extended Kalman filter. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2015, 229, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, L.R. Nonlinear tire force estimation and road friction identification: Simulation and experiments. Automatica 1997, 33, 1819–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Bruzelius, F.; Casselgren, J.; Hjort, M.; Löfving, S.; Olsson, G.; Rönnberg, J.; Sjödahl, M.; Solyom, S.; Svendenius, J.; et al. Road Friction Estimation Part II; Intelligent Vehicle Safety Systems (IVSS) Project Report; IVSS/Swedish Road Administration: Borlange, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, S.; Uchanski, M.; Hedrick, K. Estimation of the Maximum Tire-Road Friction Coefficient. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. 2003, 125, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrieux, A.; Vandanjon, P.O.; Lengellé, R.; Chabanon, C. New results on the relation between tyre–road longitudinal stiffness and maximum available grip for motor car. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2010, 48, 1511–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Lv, C.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Yang, Y.; Ji, X. Estimation of Road Adhesion Coefficient Based on Tire Aligning Torque Distribution. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. 2018, 140, 051010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu YH, J.; Laws, S.M.; Gerdes, J.C. Estimation of tire slip angle and friction limits using steering torque. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2009, 18, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yu, Z.; Neubeck, J.; Wiedemann, J. Sideslip angle estimation based on input–output linearisation with tire–road friction adaptation. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2010, 48, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Cui, G. Collision Avoidance Control by steering based on Moving Horizon Estimation Control. In Proceedings of the 2020 4th CAA International Conference on Vehicular Control and Intelligence (CVCI), Hangzhou, China, 8–20 December 2020; pp. 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Luque, P.; Mántaras, D.A.; Fidalgo, E.; Álvarez, J.; Riva, P.; Girón, P.; Compadre, D.; Ferran, J. Tyre–road grip coefficient assessment—Part II: Online estimation using instrumented vehicle, extended Kalman filter, and neural network. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2013, 51, 1872–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Li, T.; Yang, Y.Y.; Ji, X.W.; Wu, J. Estimation of tire-road friction coefficient based on combined APF-IEKF and iteration algorithm. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 88, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseltine, E.L.; Rawlings, J.B. Critical evaluation of extended Kalman filtering and moving-horizon estimation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 2451–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H. The estimation of vehicle speed and tire-road adhesion coefficient using moving horizon strategy. Automot. Eng. 2009, 31, 520–525. [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings, J.B.; Bakshi, B.R. Particle filtering and moving horizon estimation. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2006, 30, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinen, S. Sensor Data Fusion Based Estimation of Tyre-Road Friction to Enhance Collision Avoidance; Tampere University of Technology: Tampere, Suomi, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zanon, M.; Frasch, J.V.; Diehl, M. Nonlinear moving horizon estimation for combined state and friction coefficient estimation in autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the 2013 European Control Conference (ECC), Zurich, Switzerland, 17–19 July 2013; pp. 4130–4135. [Google Scholar]
- Pacejka, H. Tire and Vehicle Dynamics, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Science: Burlington, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]














| Symbol | Description | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vx | Longitudinal speed | Front steering angle | |
| Vy | Lateral speed | Fy,f | Lateral tire force on the front tire |
| Vehicle yaw rate | Fy,r | Lateral tire force on the rear tire | |
| Front tire slip angle | lf | Distance between front axle and CoG | |
| Rear tire slip angle | lr | Distance between rear axle and CoG |
| Symbol | Value | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.29 | 1.72 | ||
| −0.9 | 0.22 | ||
| 0.18 | 0.0035 | ||
| −4.5 | −0.003 | ||
| −1.07 | 0.045 | ||
| 0.68 | 0.045 | ||
| −0.63 | −0.03 | ||
| −12.35 | −0.174 | ||
| −12.95 | −0.45 | ||
| 1 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 1 | ||
| 2 | 0 | ||
| 1 | 0 | ||
| 1 | 4100 |
| Symbol | Description | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| m | 1231 kg | lf | 1.04 m |
| Iz | 2031.4 kg⋅m2 | lr | 1.56 m |
| N | 10 | [14,000;14,000] | |
| [1400;1400] | [0.1;0.1] | ||
| 500 | [1;1] | ||
| 1 | [0;0] | ||
| 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, G.; Bai, G.; Meng, Y.; Liu, L.; Gu, Q.; Ma, Z. A Hierarchical Estimation Method for Road Friction Coefficient Combining Single-Step Moving Horizon Estimation and Inverse Tire Model. Electronics 2023, 12, 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12030525
Wang G, Bai G, Meng Y, Liu L, Gu Q, Ma Z. A Hierarchical Estimation Method for Road Friction Coefficient Combining Single-Step Moving Horizon Estimation and Inverse Tire Model. Electronics. 2023; 12(3):525. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12030525
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Guodong, Guoxing Bai, Yu Meng, Li Liu, Qing Gu, and Zhiping Ma. 2023. "A Hierarchical Estimation Method for Road Friction Coefficient Combining Single-Step Moving Horizon Estimation and Inverse Tire Model" Electronics 12, no. 3: 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12030525
APA StyleWang, G., Bai, G., Meng, Y., Liu, L., Gu, Q., & Ma, Z. (2023). A Hierarchical Estimation Method for Road Friction Coefficient Combining Single-Step Moving Horizon Estimation and Inverse Tire Model. Electronics, 12(3), 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12030525








