Abstract
It is proposed to use a brain emotional learning control (BELC) system that is based on radial basis function (RBF) in order to enhance the performance of the speed control system of a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) and its capacity to remain stable following an unexpected load. First, the shortcomings of the traditional PI control in the PMSM speed-control system are explained. The intelligent control system has excellent learning ability and can effectively improve the control effect. The brain emotional learning control is great for nonlinear system control. Thus, it was utilized as the PMSM speed controller in place of the conventional PI control. The RBF neural network was used to optimize some parameters of BELC. Therefore, the process of adjusting parameters in BELC was simplified and the controller ability to resist disturbances was enhanced. The results showed that the brain-based emotional learning control based on RBF optimization (RBF-based BELC) not only improved the speed-control effect of the PMSM system but also enhanced the stability of the torque and current.
1. Introduction
A PMSM is used in aerospace, electric vehicles, and other sectors because of its simplicity and efficiency [1,2,3]. Motor operation requires a motor controller. A PMSM speed-control system adopts PI, direct torque, model prediction, sliding model [4,5,6,7,8], and other intelligent controls. PI control is a common control method in a PMSM speed-regulating system. When PI control is adopted, the controller parameters are fixed. When there is external disturbance, the control effect is low and it is difficult to meet the requirements of overshoot and speed. Improving the control ability of a PMSM speed-regulating system is an important research topic.
With the emergence of various optimization algorithms, some have been combined with control algorithms. An intelligent control algorithm optimizes controller parameters to improve performance. In [9], fuzzy PI utilizes fuzzy control theory to adjust PI coefficient online so as to improve the anti-disturbance ability of a PMSM speed-regulating system. However, the fuzzy law is complex and steady-state error exists in practical application. In addition, some scholars started with the optimization algorithm and combined particle swarm optimization, locust optimization, and an ant lion optimization algorithm with PI control to optimize PI and fuzzy PI parameters, thus improving the control performance [10,11,12,13,14]. Reference [15] combined the back propagation neural network with PI control for automatic parameter adjustment. However, these methods converge slowly and have errors. In [16], a radial basis neural network corrects PI control parameters, and the convergence rate is fast enough to solve the local optimal problem, but the controller still has problems in stability, speed, and accuracy. In utilizing radial basis neural networks for optimizing controller parameters, Reference [17] employs RBF neural networks to optimize the coefficients of PID controllers to enhance control performance. In a comparable approach within the aerospace industry, Reference [18] incorporates RBF neural networks with PID to resolve the constant tension issue. In [19,20,21], they mainly use RBF neural networks to improve controller control capability by optimizing its parameters when faced with external interference. This technique can also be combined with optimization algorithms to further exploit the parameter search capability of RBF neural networks, where, in the literature, References [22,23] combine particle swarms, fuzzy control theory, and RBF neural networks to achieve rapid optimization of controller parameters and thus improve control performance.
A brain emotional learning model was proposed in [24,25] and gradually applied to nonlinear systems to improve control ability. In [26,27,28], brain emotional learning control (BELC) is implemented in unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) with multi-rotor and induction motor vector control systems, and BELC demonstrates nonlinear control capabilities. BELC is difficult to adjust and improper parameter selection will slow down the learning rate and reduce the stability. Removing the orbitofrontal cortex of BELC simplified its structure but reduced the control effect of BELC [29].
Therefore, this paper proposes a BELC algorithm based on RBF neural network optimization (RBF-based BELC). The RBF network adjusts the coefficient of BELC emotional implication function for self-regulation. The optimized emotional implication function is helpful to the orbitofrontal cortex and amygdala learning. The adjustment of BELC parameters is simplified and the anti-disturbance of the controller is improved. In a PMSM speed-regulating system, the RBF-based BELC is used as the speed controller. The proposed method is superior to PI control and BELC in feasibility and effectiveness.
2. Vector Control System for PMSM
The block diagram of a PMSM speed-control system is shown in Figure 1, which uses a surface-mounted PMSM. The PMSM speed-regulation system adopts vector control, in which the speed regulator and current regulator adopt PI control to form a double closed-loop structure. The system works as follows: The position information collected by the position sensor is calculated to obtain the actual speed of the PMSM. The difference between the given speed nr and the actual speed n is used as the input of the speed PI regulator. The currents id and iq of the dq axis are obtained by coordinate transformation of the collected three-phase currents ia, ib, and ic. Set id* to zero and subtract id as the input to the current regulator 2. The output of the speed PI regulator is iq* and its difference from iq is added to the current regulator 1. The outputs ud and uq of the two current regulators are converted by coordinates as inputs to the SVPWM generator to generate six drive signals that control the inverter to provide drive voltage to the PMSM. For such a closed-loop control system, when the speed fluctuates, the control signal will also change so that the speed is stable near the given value.
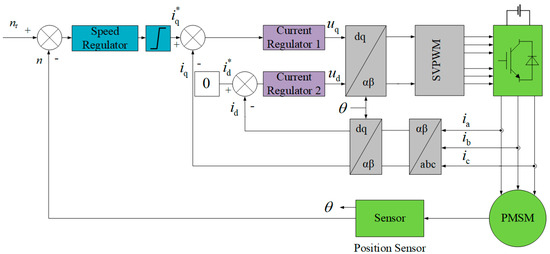
Figure 1.
Block diagram of PMSM vector control system.
The PMSM is highly coupled and nonlinear. In order to facilitate the research, the influence of hysteresis loss and eddy current in the PMSM was disregarded and a mathematical model was developed using a synchronous rotation coordinate system. In a synchronous rotating coordinate system, the equation for the voltage of the PMSM is
The equation for the electromagnetic torque of the PMSM is
where ud, uq, id, iq, Ld, and Lq are, respectively, the stator voltage, inductance, and current of the dq axis, R is the stator resistance, is the rotor electrical angle, and is the flux linkage of the PMSM.
3. Improved Brain Emotional Learning Control
3.1. Conventional BELC
BELC simulates human brain behavior in the process of emotional learning and processes input signals to generate output control signals. The BELC model architecture is shown in Figure 2. The amygdala, sensory cortex, orbitofrontal cortex, and thalamus constitute the BELC. The thalamus receives SI, stimulates the sensory cortex, and regulates the amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex. The amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex learn through REW. The output of the controller E is the amygdala–orbitofrontal cortex difference. The orbitofrontal cortex monitors the amygdala BELC learning process to prevent errors.
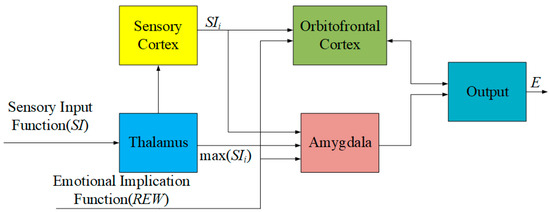
Figure 2.
Brain emotional learning control model.
In the PMSM system, the difference between the given speed and the feedback speed is fed into the brain emotional learning control. Set the speed of the PMSM speed-regulating system as nr, the feedback speed as n, and the input error of brain emotional learning control as e = nr − n.
The sensory input function SI and the emotional implication function REW are
where k1, k2, k3, k4, and k5 are adjustable coefficients.
The thalamus receives the sensory input signal SI and chooses the maximum value of the signal as the thalamic output
The output of each node within the amygdala is
where i = 1, 2, 3, ... and m and Vi are the weights of node Ai.
The regulation rule of the amygdala in the brain’s emotional learning control is to adjust the weight Vi of each node in real time when the output is less than the emotional implication signal and keep the same when the output is greater than the emotional implication signal.
The orbitofrontal cortex receives signals from the sensory cortex and emotional implication signals, and the output of each node in the orbitofrontal cortex is
where Wi is the weight of each node in the orbital cortex.
Similarly, the learning process of the orbitofrontal cortex is realized by adjusting the weights of nodes in the orbitofrontal cortex in real time. The weight adjustment values of Wi are
where β is the learning rate of node weights in the orbitofrontal cortex, is the difference between the output signal from the amygdala that does not pass through the thalamus and the orbitofrontal cortex, and .
The final output of the brain emotional learning control is
The emotional implication function runs through the BELC learning process, and the orbitofrontal cortex supervises the amygdala learning, so as to avoid overlearning and underlearning and regulate the output of the controller. Therefore, the response rate and control precision of BELC can be enhanced by adjusting the emotional implication function.
3.2. RBF-Based Brain Emotional Learning Control
The traditional BELC uses the emotional implication function in the learning process, which requires more parameter adjustment. Whether the emotional implication function is appropriate affects the BELC control effect. Because the RBF neural network has a simple structure, fast convergence speed, and no local optimal problem, it can self-adjust the coefficient of the emotional implication function for optimal control.
An input layer, a hidden layer, and an output layer make up the RBF neural network. Each layer is responsible for a different function. In the RBF neural network structure, the RBF takes its input in the form of the vector . The RBF neural network vector of the hidden layer is , where hj is the Gaussian kernel function
where Cj indicates the center vector of the j-th network node while bj denotes the node width
In the equation that was just given, and .
The following expression constitutes the RBF neural network basis width vector
The following represents the weight vector for the RBF neural network
The expression that represents the RBF neural network output layer is
For improving the performance of speed controllers in PMSM speed-control systems, the performance index function of the RBF neural network is
where y(k) is the actual output of the system and ym(k) is the predictive value of the identifier output of the RBF neural network.
The weights W of the RBF neural network, the center vector Cj, and the basis width vector B are updated using the gradient descent method. The weights W are updated as follows
The basis width vector B is updated as
where .
The center vector Cj is updated as follows
where , is the momentum factor, and is the learning rate.
The improved BELC is used as the speed controller of the PMSM speed-regulating system. The block diagram of the system with the BELC optimized by an RBF neural network is illustrated in Figure 3.
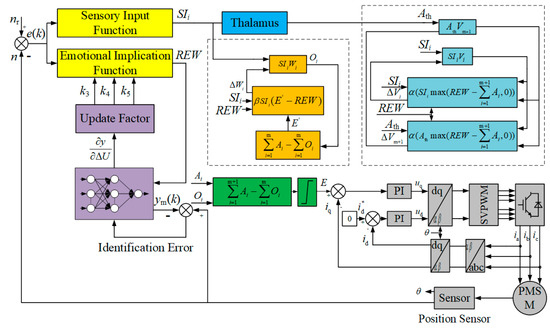
Figure 3.
The block diagram of RBF-optimized brain emotion.
The RBF neural network is used to optimize the parameters of the emotional implication function of the BELC to realize the automatic adjustment of the coefficient of the emotional implication function. According to (3), the emotional implication function is a typical PI structure. The e(k) is the difference between the given value and the system output value, where k represents the k-th moment.
The input of the emotional implication function is e(k), and the input layers of the RBF neural network are
The discretized emotional implication function can be rewritten as
The coefficients of k3, k4, and k5 are adjusted online according to the sensitivity calculated by the RBF neural network.
where .
The PMSM speed-control system employs the RBF-based BELC controller as a speed regulator. Its primary purpose is to improve the speed performance of the PMSM system. The input is the deviation between the required and the actual speed. Following the adaptation of the sensory input function and the emotional implication function, the signal SIi and signal REW are obtained. The SIi and REW signals are acquired following the adjustment of the sensory input and emotional implication functions. Subsequently, these signals undergo supervised learning in accordance with (4)–(10). Finally, the output of the RBF-based BELC controller is obtained as E. The RBF neural network serves the purpose of parameter optimization for the coefficients of the emotional implication functions k3, k4, and k5. In the RBF-based BELC control, the RBF neural network is constructed following (11)–(19), with its inputs being (20)–(22). Additionally, Equations (24) and (25) are used for online tuning of the coefficients of the emotional implication functions k3, k4, and k5, resulting in the optimal output of the RBF-based BELC controller. The aim of this is to improve the control of the PMSM speed by the RBF-based BELC controller.
4. Simulation Verification
To verify the control effect of the BELC optimized by an RBF neural network, the PMSM double closed-loop speed-control system was simulated by MATLAB/Simulink. The simulation results were compared with the conventional BELC and PI. The PMSM parameters used are shown in Table 1. In the system, only the control strategy of the speed regulator was changed, while the current regulator still used PI control. In the simulation of the current PI controller with a typical type I system, according to the calculation, the theoretical value of the current PI controller proportional and integral coefficients, respectively, were 8.433 and 4300 and, after further adjustment, the coefficients of proportional and integral finally were 50 and 4300. In the simulation of a speed ring for speed PI control, the speed ring was controlled by a PI control, which is a typical type II system. The theoretical values of the proportional and integral coefficients of the speed PI controller were calculated to be 0.276 and 138, respectively, and the coefficients of the proportional and integral coefficients were finally 0.4 and 138 after further adjustment. In the simulation experiments of the RBF-based BELC and the BELC, the learning rates of the brain emotional learning control were 0.8 and 0.02, respectively. The coefficients of the sensory input function SI were 3 and 1.8.

Table 1.
PMSM parameters.
The simulation time was set at 0.4 s and the speed was set at 800 rpm under no-load condition. The no-load speed waveforms under the RBF-based BELC, BELC, and PI control are illustrated in Figure 4.
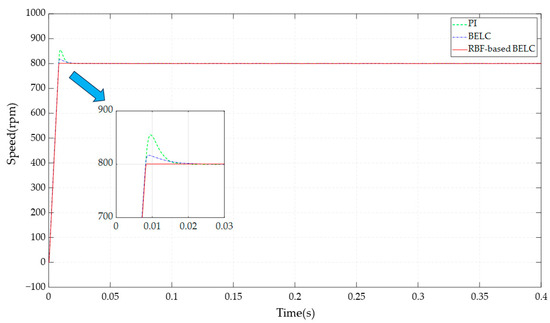
Figure 4.
Comparison of speed under three control strategies.
It can be seen that the trend of the engine speed increase was basically the same under the three control methods due to the limiting treatment of the speed controller output. However, there was an overshoot in the speed under PI control and BELC control, in which the overshoot in the speed was 55 rpm under PI control and 17 rpm under BELC control. In comparison, there was no overshoot in the speed under the RBF-based BELC control; at the same time, the shortest time to reach the given speed was 0.0085 s. The speed of the motor reached the given speed in 0.0085 s. The speed of the motor reached the given speed in 0.0085 s under both PI control and BELC control, and the speed was 0.0085 s. The speed under PI control and BELC control was 0.018 s and 0.022 s, respectively. On this basis, the load was suddenly added at 0.2 s; the speed waveforms of the three control strategies are shown in Figure 5.
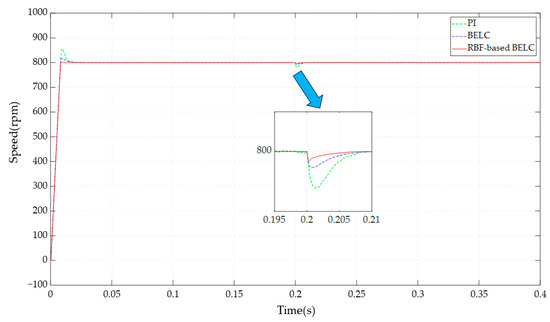
Figure 5.
Comparison of speed under sudden loading.
After a sudden increase in torque, the speed decreased for all three control methods and eventually returned to the given speed. The simulation results showed that PI control had a speed drop of 19 rpm, followed by BELC control with a drop of 8 RPM and, finally, the RBF-based BELC control with a drop of 5 rpm. Additionally, the speed recovery time was evaluated in terms of the shortest time taken for the speed to recover, which was achieved by the RBF-based BELC control method at 0.0071 s. The recovery times for speed in both PI and BELC control were 0.0086 s and 0.0093 s, respectively, exhibiting a near-similar result. In summary, the RBF-based BELC outperformed the other two methods in terms of speed overshoot during PMSM speed initiation and the extent of motor speed drop and recovery time after sudden load application.
The current waveforms are shown in Figure 6. Figure 6a–c respectively correspond to the three-phase current waveforms under PI, BELC, and RBF-based BELC.
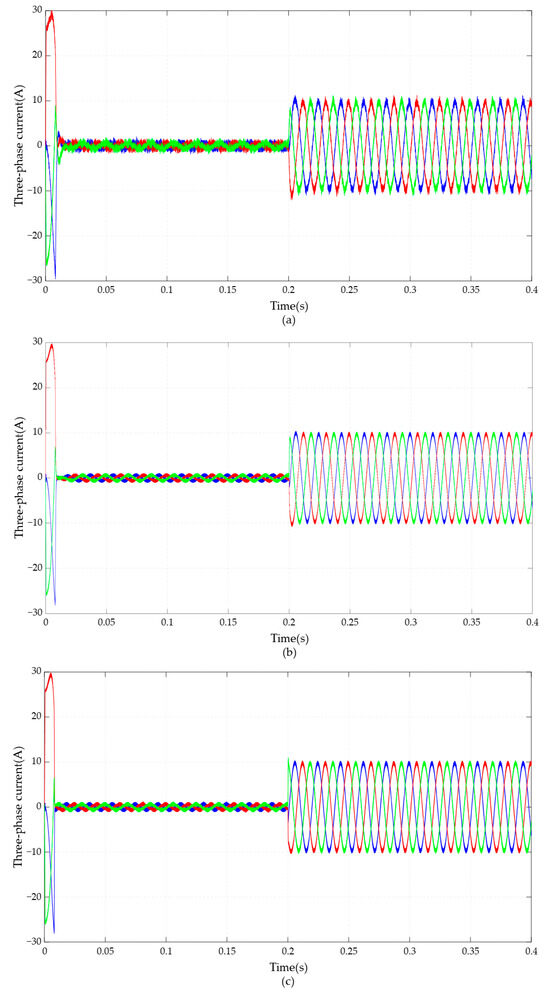
Figure 6.
Comparison of current under three control strategies: (a) PI, (b) BELC, (c) RBF-based BELC.
It can be clearly seen from Figure 6 that for the current waveform under all three control methods, when PI control was used for all current controllers, the stability of the three-phase current waveform of the PMSM was worst when the speed controller was PI controlled, while the current stability was best with the RBF-based BELC control.
Figure 7 depicts the PMSM torque comparison of the three control methods.
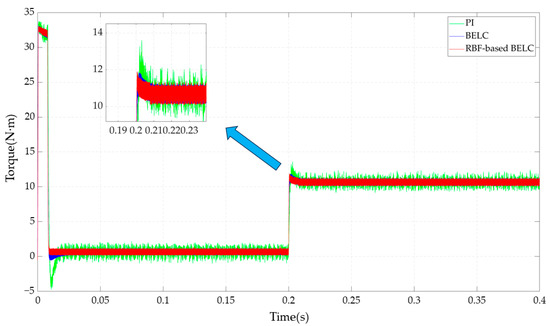
Figure 7.
Comparison of torque under sudden loading.
Figure 7 illustrates that the motor torque waveform of the PMSM speed-control system abruptly rose at 0.2 s after sudden loading. The largest torque rise was obtained under PI control, while the torque rise under the RBF-based BELC control was similar to that under BELC control. However, the time required for torque to stabilize was shortest under the RBF-based BELC control. Moreover, after stabilization, PMSM torque under the RBF-based BELC control exhibited the greatest stability.
The simulation results showed that the control performance of the PMSM system in the RBF-based BELC was better than that of BELC and PI control. In order to more intuitively compare the performance of the three controllers, the corresponding indexes measured quantitatively are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Comparison of quantitative indexes.
It is clear from Table 2 that the control performance of the RBF-based BELC was better than that of the other two methods.
5. Experimental Verification
5.1. Experimental Setup
As seen in Figure 8, an experimental platform for a PMSM speed-regulating system based on the RBF-based BELC was created to confirm the accuracy of the suggested control theory. This experiment was based on the SP2000 rapid prototype controller, which takes the DSP28335 as the control core, and combines MATLAB and Simulink automatic code-generation technology. In Simulink, a simulation model of a PMSM controlled by the RBF-based BELC was built, communication modules such as ADC and DAC were set up, and a C program to control the PMSM was automatically generated and downloaded to DSP. The PMSM parameters were the same as those shown in Table 1

Figure 8.
PMSM experimental platform with SP2000.
5.2. Comparative Performance Test of Speed Control
Figure 9 shows the no-load speed waveforms under PI, BELC, and RBF-based BELC, respectively.
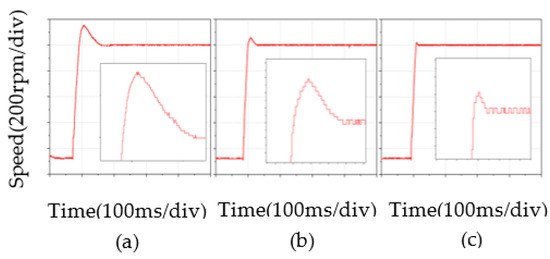
Figure 9.
Speed comparison of no-load: (a) PI, (b) BELC, (c) RBF-based BELC.
The experimental waveform in Figure 8 shows that the speed under PI control took a long time to stabilize. The speed overshoot was about 154 rpm, which was much higher than the overshoot under BELC and RBF-based BELC. The RBF-based BELC took slightly less time to stabilize than the BELC. The RBF-based BELC had a speed overshoot of 22 rpm, while the BELC had a speed overshoot of 58 rpm and the RBF-based BELC had a lower speed overshoot than the BELC.
Figure 10 shows three speed waveforms controlled under sudden loading, in which (a), (b), and (c) are PI, BELC, and RBF-based BELC, respectively. According to the test results, under unexpected load changes, the speed controlled by PI dropped to about 32 rpm and it took the longest to recover to the specified speed. The speed was reduced by 20 rpm with the BELC and 14 rpm with the RBF-based BELC, and it took the shortest time to return to the specified speed. Compared with the three control methods, the speed regulation with the RBF-based BELC had a better control effect when the speed returned to the specified speed after a sudden load change.
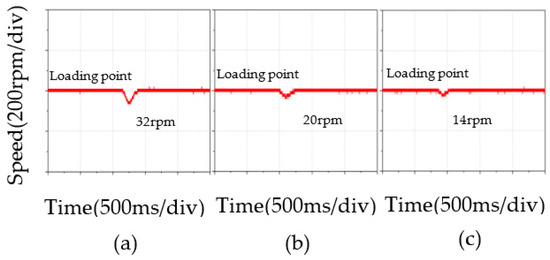
Figure 10.
Speed comparison under sudden loading: (a) PI, (b) BELC, (c) RBF-based BELC.
In Figure 11, the speed waveform under PI, BELC, and RBF-based BELC changed abruptly from load to no-load. PI had the highest speed overshoot of the three control strategies, surpassing BELC and RBF-based BELC. The RBF-based BELC had the smallest overshoot and the fastest recovery rate. For PMSM speed regulation, RBF-based BELC was better than the other two control strategies in terms of response speed and stability.
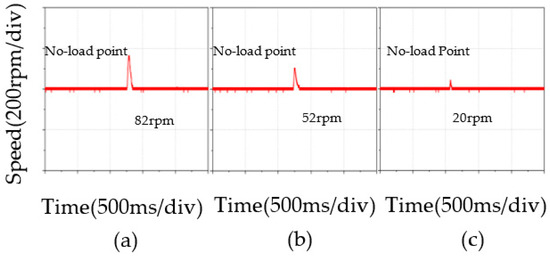
Figure 11.
Speed comparison under abrupt no-load: (a) PI, (b) BELC, (c) RBF-based BELC.
Table 3 shows the comparison results, which more directly reflect the excellent control performance of the RBF-based BELC on PMSM speed.

Table 3.
Quantitative comparison of speed results.
5.3. Comparative Performance Test of Torque Control
Figure 12 shows the torque waveforms of the three control strategies under sudden loading. Figure 11a–c show torque waveforms for PI, BELC, and RBF-based BELC. The torque of the PMSM began to rise after adding a sudden load.
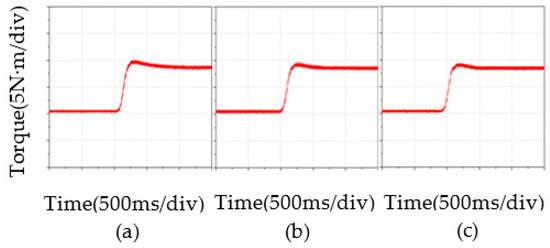
Figure 12.
Comparison of torque results: (a) PI, (b) BELC, (c) RBF-based BELC.
The experimental results showed that the torque under PI control increase was the greatest and the stabilization time was the longest. Second, BELC had less torque overshoot than PI and stabilized faster. The torque overshoot of the RBF-based BELC was the smallest of the three, and the arrival stabilization time was the shortest. The waveform after torque stabilization was the best of the three control strategies. The RBF-based BELC improved torque control and reduced disturbance caused by sudden loads.
5.4. Comparative Performance Test of Current Control
Figure 13 shows the experimental waveforms of current under the three control strategies, in which Figure 12a–c are a-phase waveforms of a PMSM under PI control, BELC, and RBF-based BELC.
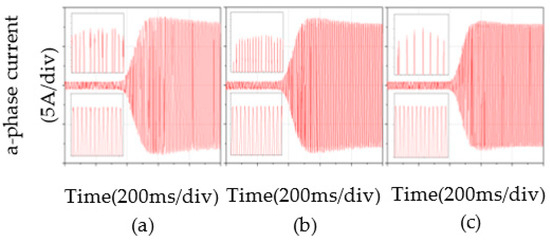
Figure 13.
Comparison of a-phase current: (a) PI, (b) BELC, (c) RBF-based BELC.
Compared with the three control strategies, the current of the PMSM changed after loading the motor and remained stable over time. The peak of a-phase current with PI was 8.8 A under sudden loading. BELC and PI controls had the same peak and stable a-phase current values. As shown in Figure 14, the waveform with BELC was more stable and the current stabilized faster. Under the control of the RBF-based BELC, the peak of a-phase current was 8.3 A and the stable current was 8 A. The RBF-based BELC had the smallest current rise and the fastest stabilization time under sudden loading. The RBF-based BELC improved the current stability and speed-regulating effect of the PMSM.
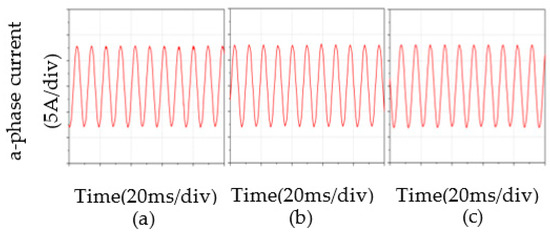
Figure 14.
Comparison of a-phase current after stabilization: (a) PI, (b) BELC, (c) RBF-based BELC.
6. Conclusions
To enhance system performance, we suggest utilizing the brain emotional learning control technique, rooted in RBF neural network optimization, to configure the governor of the PMSM governor system. The empirical findings from simulations and experiments demonstrate that the optimized PMSM governor system employing an RBF neural network outperforms the conventional system, as evidenced by the waveforms generated from the final simulation. While all three speed controllers limit the outputs and display comparable start-up times, the PMSM speed remains stable under the RBF-based BELC control without overshooting. Furthermore, the PMSM speed under the RBF-based BELC control experiences the least decrease in speed while also displaying the shortest recovery time following the sudden application of a load during operation. The RBF neural network enhances the efficiency of the BELC by optimizing its emotion-cueing function, which, in turn, improves the controller’s robustness and anti-interference capability. Additionally, the RBF neural network optimizes the PMSM governor system’s performance. During the PMSM regulation experiments, the RBF-based BELC system replaced the PI control, resulting in a reduction in the speed overshoot by 16.5% before stabilization and 2.25% after sudden loading. Technical abbreviations like PMSM, RBF, and BELC have been defined upon initial use, and there is a clear sense of logical progression in the text. The chosen academic register due to the avoidance of biased or emotional language ensures that the text is suitably objective. Furthermore, the desired speed was achieved in a shorter period. Upon comparing the PMSM with PI control to the PMSM with RBF-based BELC control, it is evident that the latter provides superior torque and current performance. Furthermore, the suggested RBF-derived BELC control approach exhibits exceptional control precision and anti-interference proficiency.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, funding acquisition, W.L.; methodology, B.L.; hardware, B.L. and S.L.; software, B.L. and H.X.; validation, W.L. and B.L.; investigation, W.L.; writing—original draft preparation, B.L.; writing—review and editing, W.L. and B.L.; experiment, B.L.; supervision, W.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52075134).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kuruppu, S.S. Open-Loop Self-Calibration of Position Sensor Offset in SM-PMSM Drive Systems. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 7502007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.D.; Lai, C.Y.; Kar, N.C. An Analytical Solution to Optimal Stator Current Design for PMSM Torque Ripple Minimization with Minimal Machine Losses. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 7655–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercorelli, P. Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors for Track Applications. Electronics 2023, 12, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Fan, M.D.; Yang, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhu, Z.K.; Garcia, C.; Rodriguez, J. Tolerant Sequential Model Predictive Direct Torque Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Drives. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2020, 6, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.X.; Luo, Y.X.; Fu, W.N.; Zhang, X.D. An Indirect Reference Vector-Based Model Predictive Control for a Three-Phase PMSM Motor. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 29435–29445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sousy, F.F.M.; Alenizi, F.A.F. Optimal Adaptive Super-Twisting Sliding-Mode Control Using Online Actor-Critic Neural Networks for Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 82508–82534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Zhao, R.; Xiao, R.; Liu, Z. Zero Common-Mode Voltage Model Predictive Torque Control Based on Virtual Voltage Vectors for the Dual Three-Phase PMSM Drive. Electronics 2022, 11, 3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Hu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Han, F.; Wang, X. New Sliding Mode Control Based on Tracking Differentiator and RBF Neural Network. Electronics 2022, 11, 3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, Z.Q. Fuzzy Logic Speed Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine and Feedback Voltage Ripple Reduction in Flux-Weakening Operation Region. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, C.I.; Nicola, M.; Selișteanu, D. Sensorless Control of PMSM Based on Backstepping-PSO-Type Controller and ESO-Type Observer Using Real-Time Hardware. Electronics 2021, 10, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazelan, A.M.; Osman, M.K.; Salim, N.A.; Samat, A.A.A.; Ahmad, K.A. PSO-Based PI Controller for Speed Sensorless Control of PMSM. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1019, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.Q.; Yang, H.L. Intelligent Control for PMSM Based on Online PSO Considering Parameters Change. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Symposium on Application of Materials Science and Energy Materials (SAMSE 2017), Shanghai, China, 28–29 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Du, T.; Zeng, G.H.; Huang, B. PMSM Vector Control Based on Grasshopper Optimization Algorithm Variable Universe Fuzzy PI. Mod. Manuf. Eng. 2021, 487, 1–5+11. [Google Scholar]
- Soundirarrajan, N.; Srinivasan, K. Performance Evaluation of Ant Lion Optimizer–Based PID Controller for Speed Control of PMSM. J. Test. Eval. 2021, 49, 1104–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Wang, T.; Li, D.; Zhao, R.Y. Design of Motor Speed PID Controller Based on BP Neural Network. Equip. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 311, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.L.; Pang, H.; Li, X.C.; Wu, Y.P.; Song, X.F. Research on Speed Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on RBF Neural Network Tuning PID. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2264, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Song, M.; Yu, P.; Li, J. Research of RBF-PID Control in Maglev System. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ju, C.; Xue, X.; Zhang, J. A New Force Control Method by Combining Traditional PID Control with Radial Basis Function Neural Network for a Spacecraft Low-Gravity Simulation System. Aerospace 2023, 10, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C. An ADRC Parameters Self-Tuning Controller Based on RBF Neural Network for Multi-Color Register System. Machines 2023, 11, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q. Multi-Motor Cooperative Control Strategy for Speed Synchronous Control of Construction Platform. Electronics 2022, 11, 4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Tu, Z.; Ai, J. Research on Aerial Autonomous Docking and Landing Technology of Dual Multi-Rotor UAV. Sensors 2022, 22, 9066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.; Lei, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M. Networked Control System Based on PSO-RBF Neural Network Time-Delay Prediction Model. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xue, L.; Li, Y.; Cao, L.; Chen, C. A Novel Fuzzy Controller for Visible-Light Camera Using RBF-ANN: Enhanced Positioning and Autofocusing. Sensors 2022, 22, 8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorashadizadeh, S.; Zadeh, S.M.H.; Koohestani, M.R.; Shekofteh, S.; Erkaya, S. Robust Model-Free Control of a Class of Uncertain Nonlinear Systems Using BELBIC: Stability Analysis and Experimental Validation. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2019, 41, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qutubuddin, M.; Gibo, T.K.; Bapi, R.S.; Narri, Y. Brain Affective System Inspired Control Architecture: An Application to Nonlinear System. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 86565–86580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giernacki, W. Minimum Energy Control of Quadrotor UAV: Synthesis and Performance Analysis of Control System with Neurobiologically Inspired Intelligent Controller (BELBIC). Energies 2022, 15, 7566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameshkumar, N.; Rahman, M.A.M.J.Z. Hybrid BELBIC based PV Powered Vector Controlled Induction Motor Drive. Asian J. Res. Social Sci. Humanities. 2016, 6, 994–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affan, M.; Uddin, R. Brain Emotional Learning and Adaptive Model Predictive Controller for Induction Motor Drive: A New Cascaded Vector Control Topology. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2021, 19, 3122–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.G.; Sheng, Y.B.; Yang, D.L.; Hu, L.K. Simplified emotion-based design of D-STATCOM controller. Electr. Mach. Control 2014, 18, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).