Passive Electrical and Optical Methods of Ultra-Short Pulse Expansion for Event Timer-Based TDC in PPM Receiver
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of PPM Technique
3. Electrical and Optical Pulse Expansion Methods
- The full width at half maximum (FWHM) duration of the input pulse is 40–60 ps.
- The bandwidth of the input pulse is at most 25 GHz.
- The FWHM duration of the output pulse is at least 150 ps.
- The rise of the output pulse time is at most 50 ps.
- The fall time of the output pulse is at most 100 ps.
- The ripples and overshoots of the output pulse are at most 10% of pulse amplitude.
- The jitter of the output pulse rising edge is less than 5 ps.
3.1. Electrical Pulse Expansion
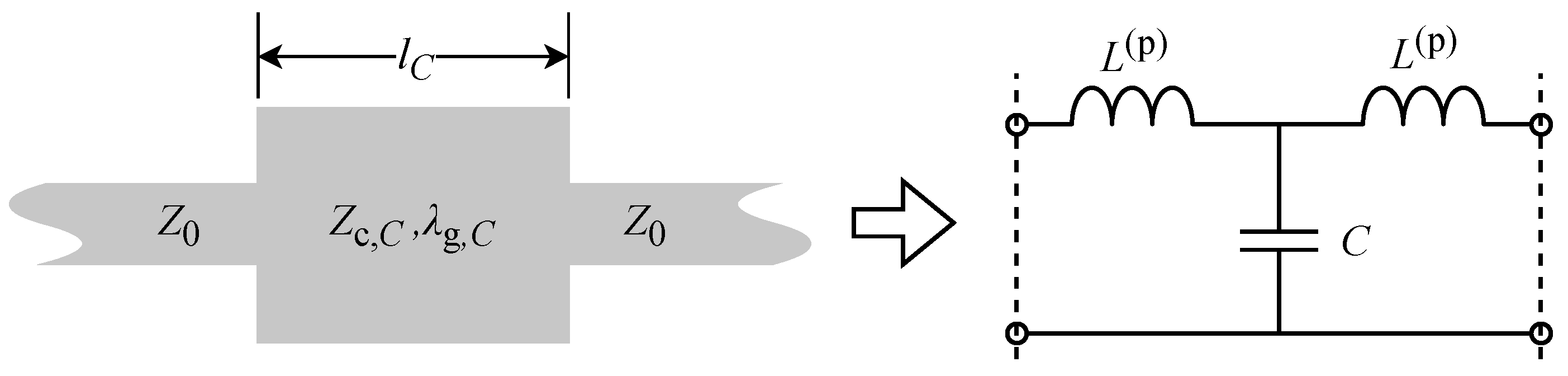
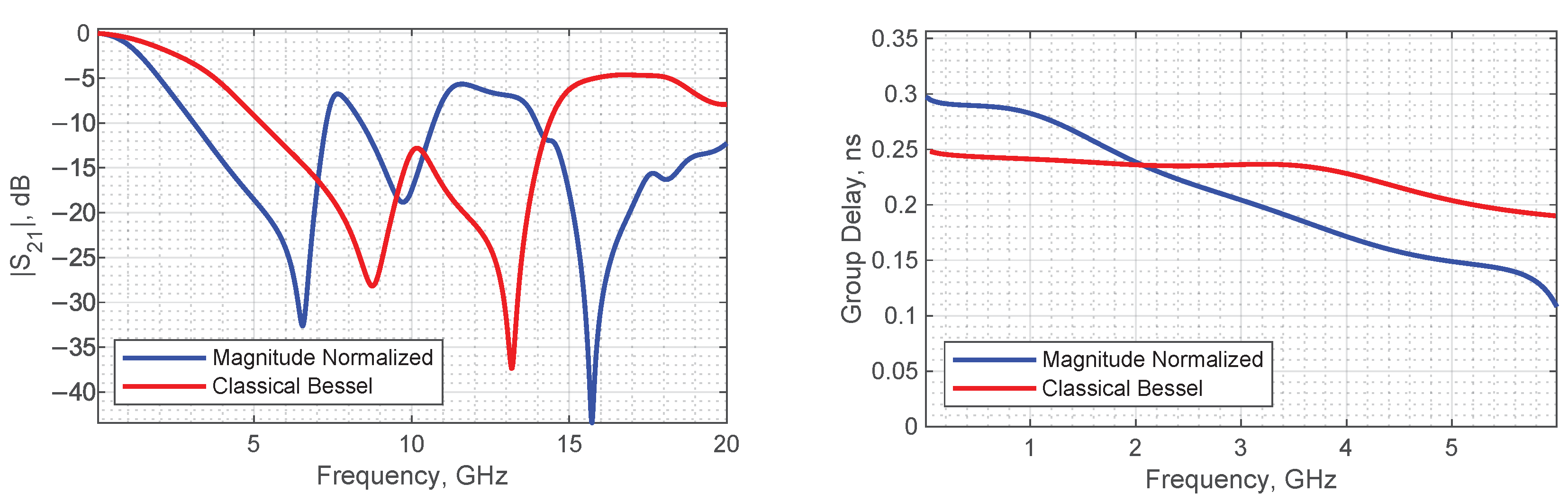
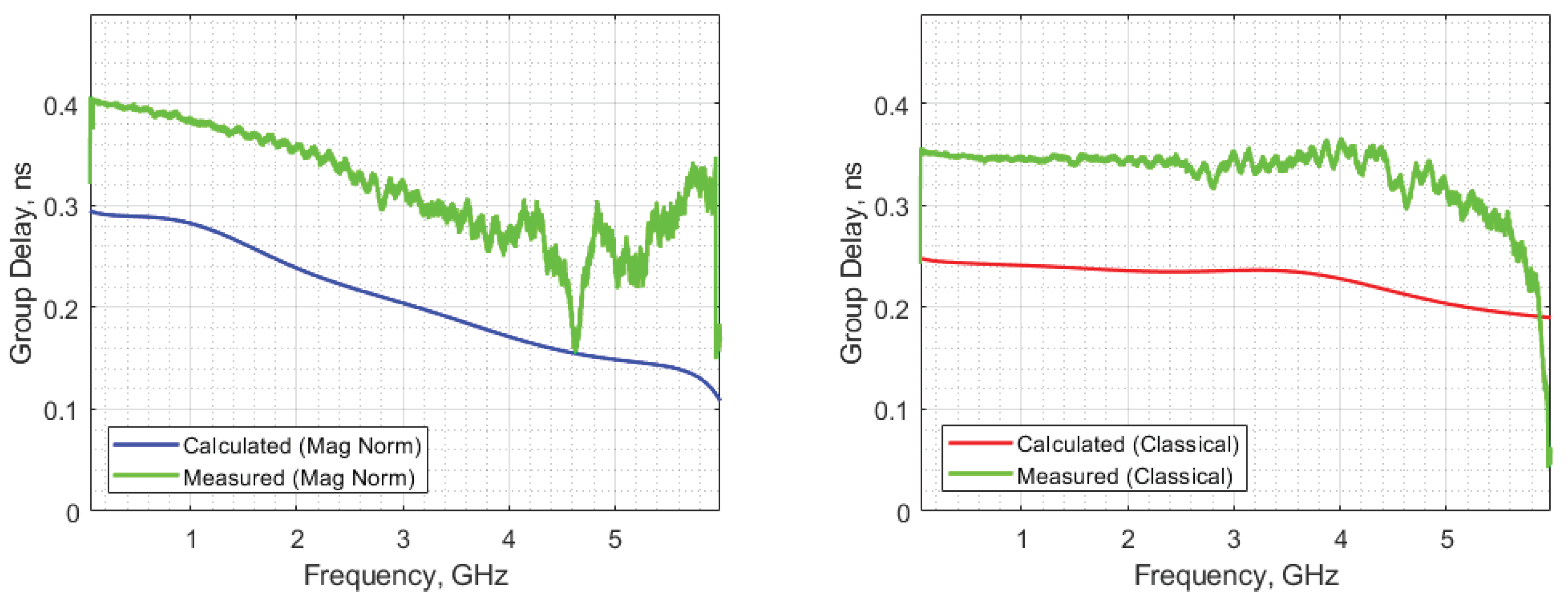
3.1.1. Design of Custom LPFs
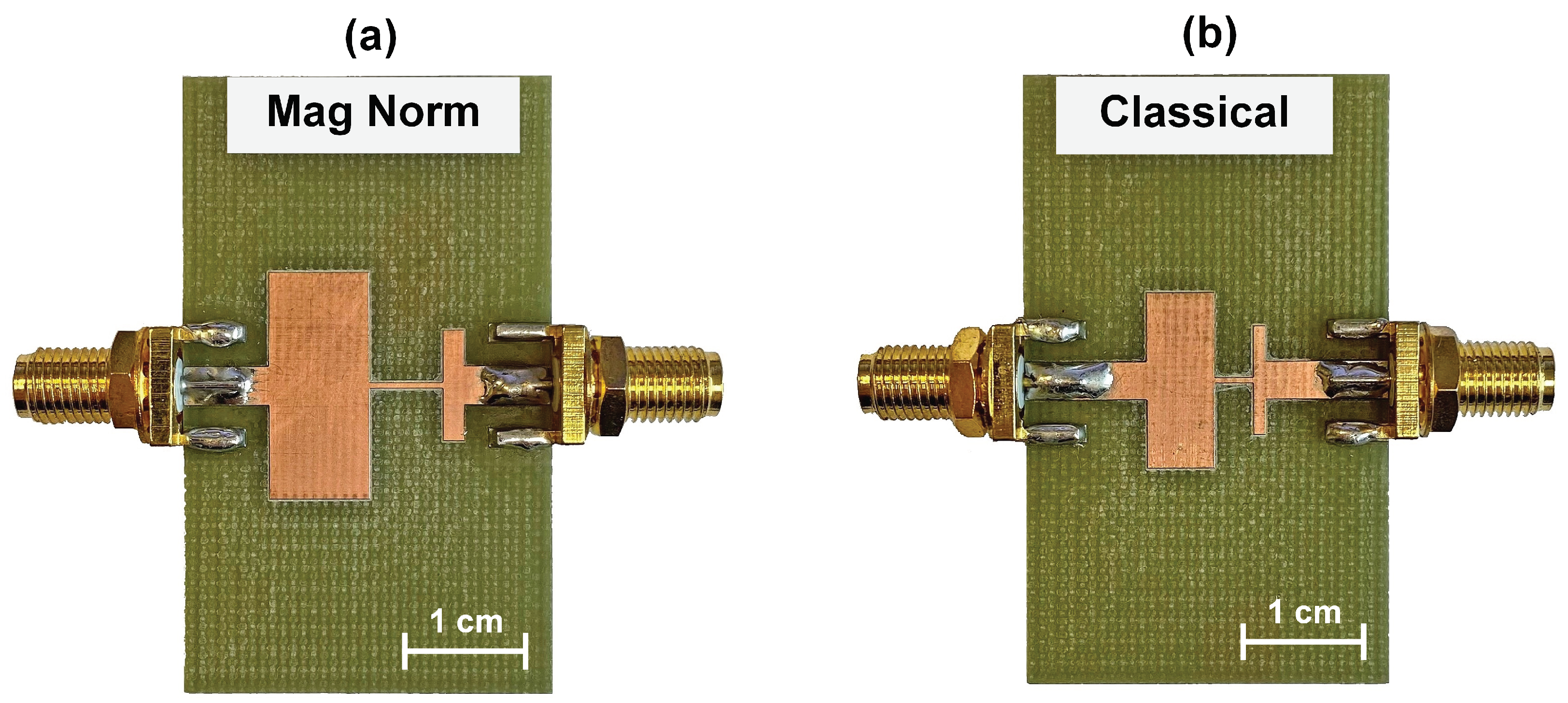
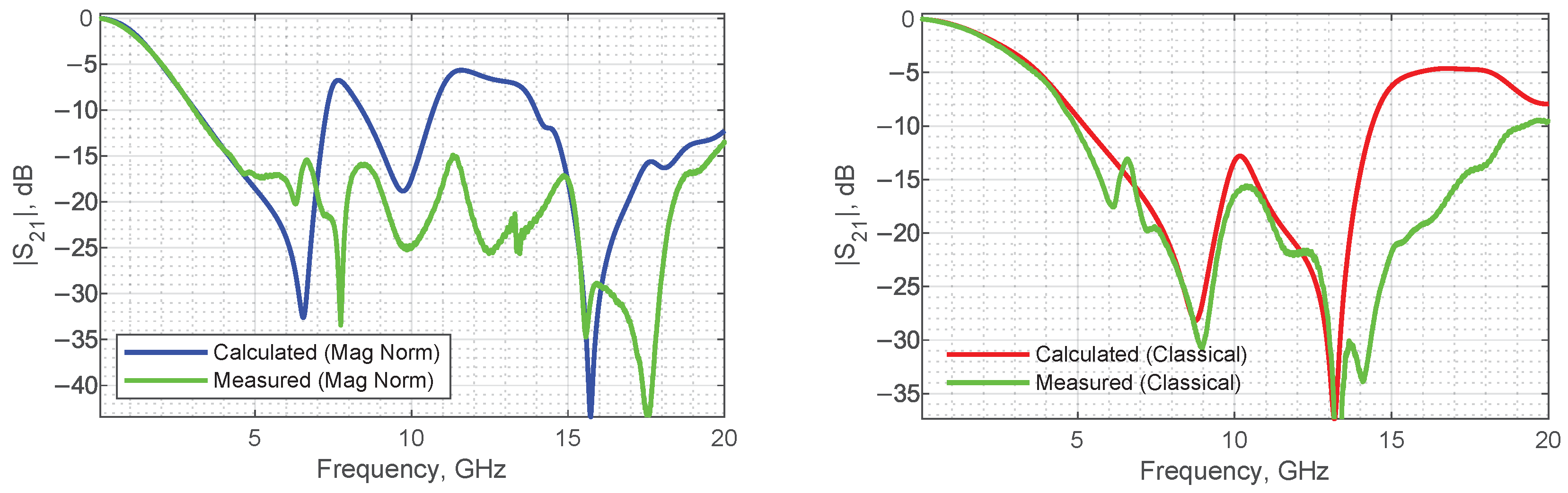
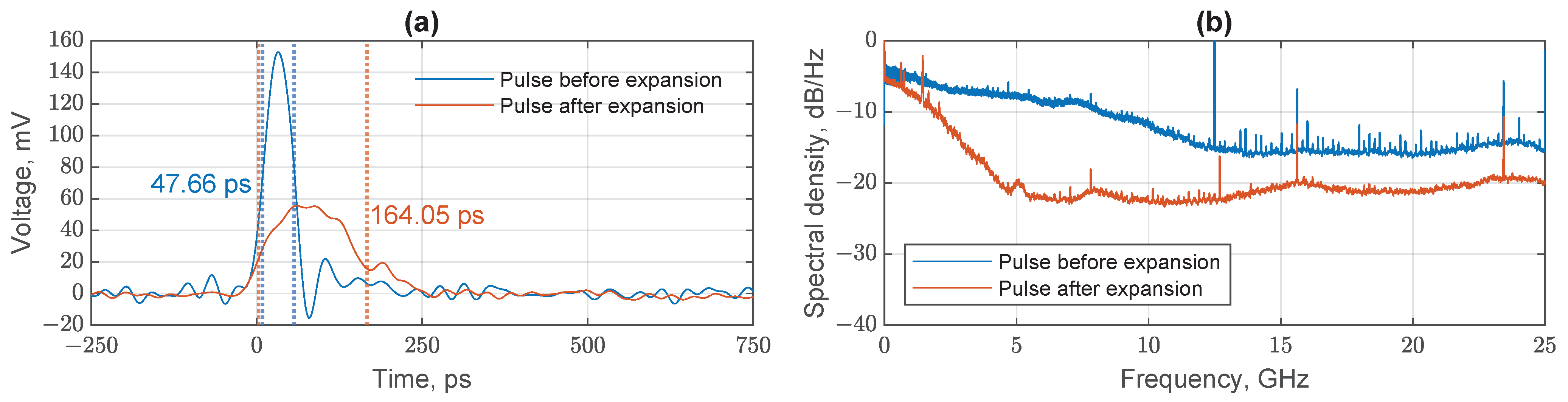
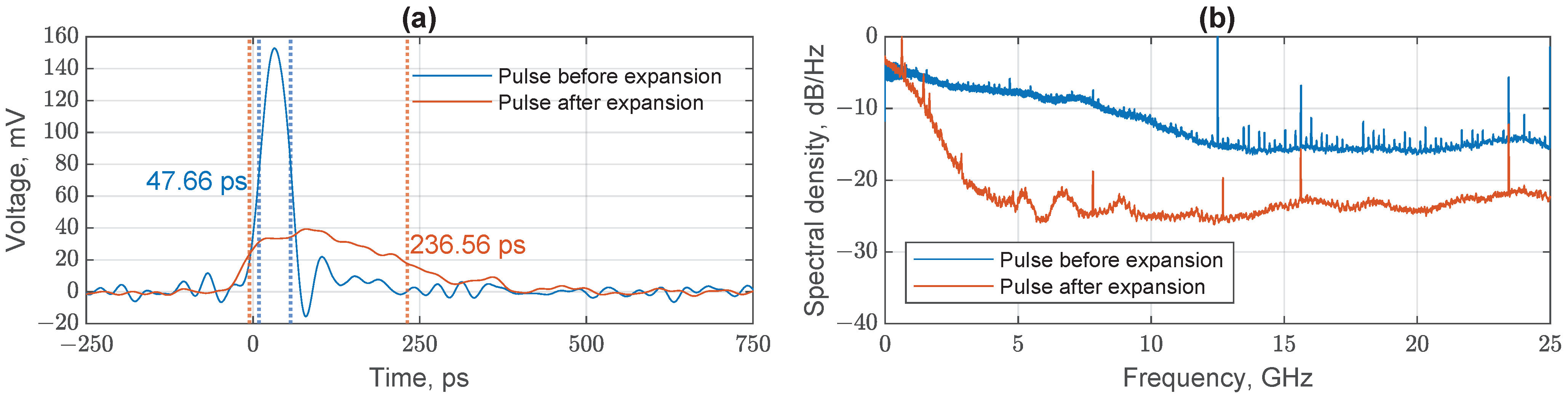
3.1.2. Experimental Electrical Pulse Expansion
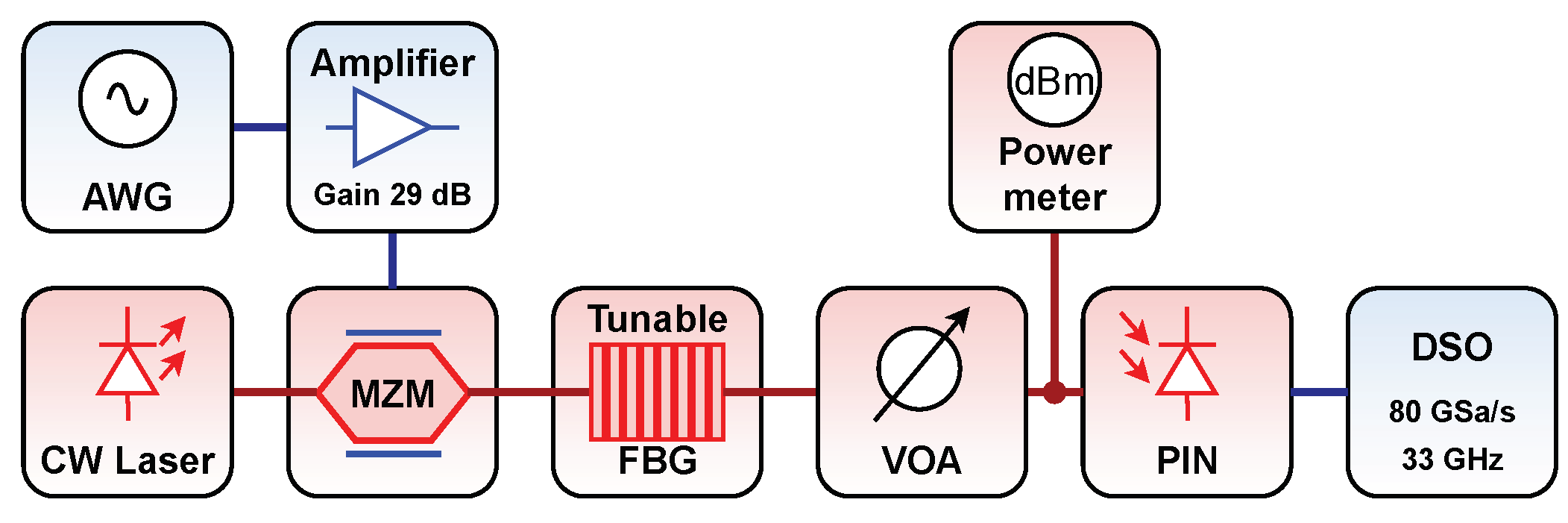
3.2. Optical Pulse Expansion
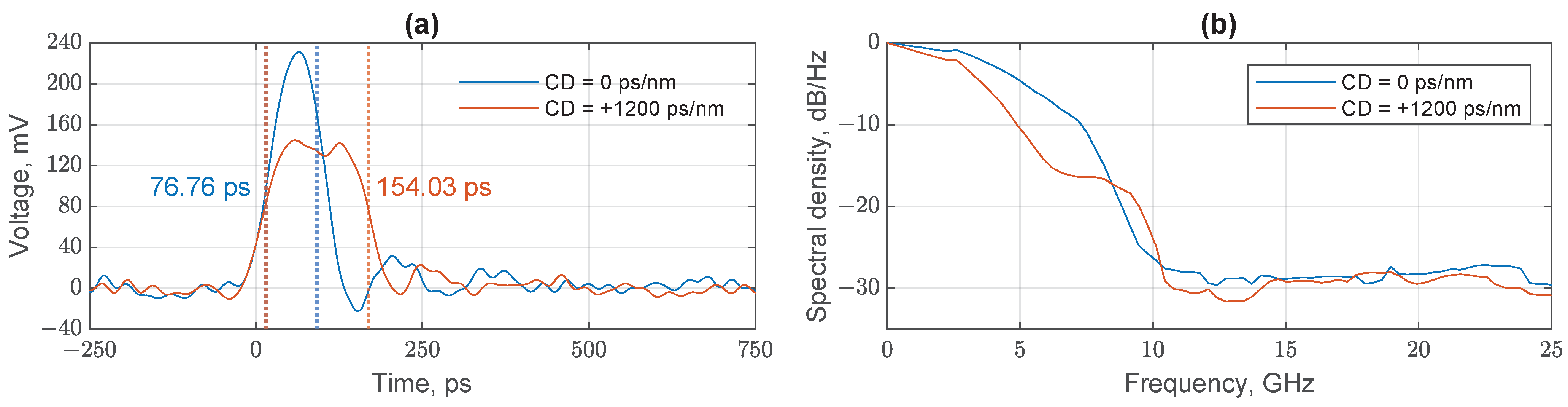
Experimental Optical Pulse Expansion
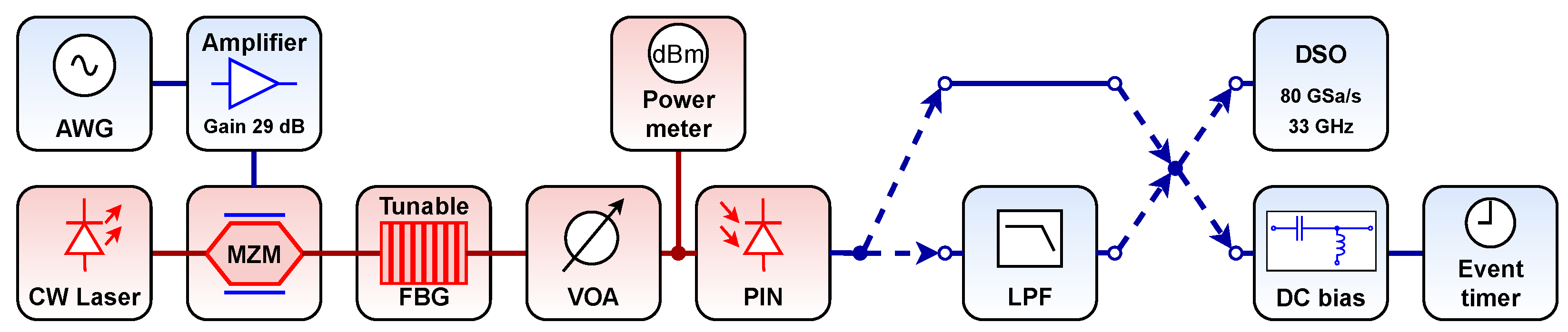
4. Experimental Validation Using PPM Data Transmission
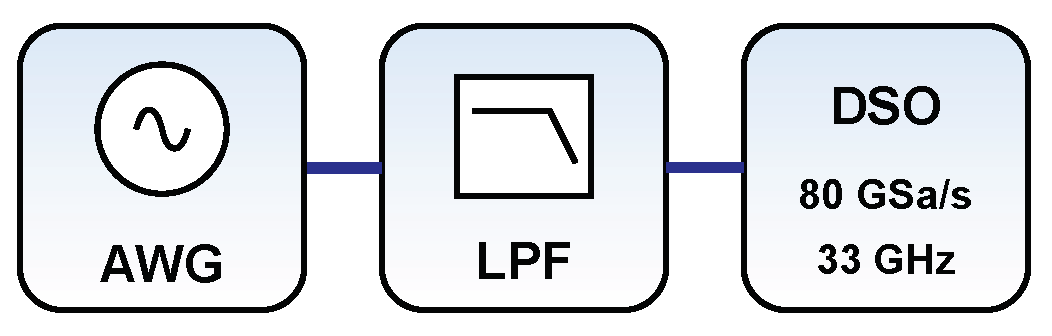
4.1. Experimental Setup
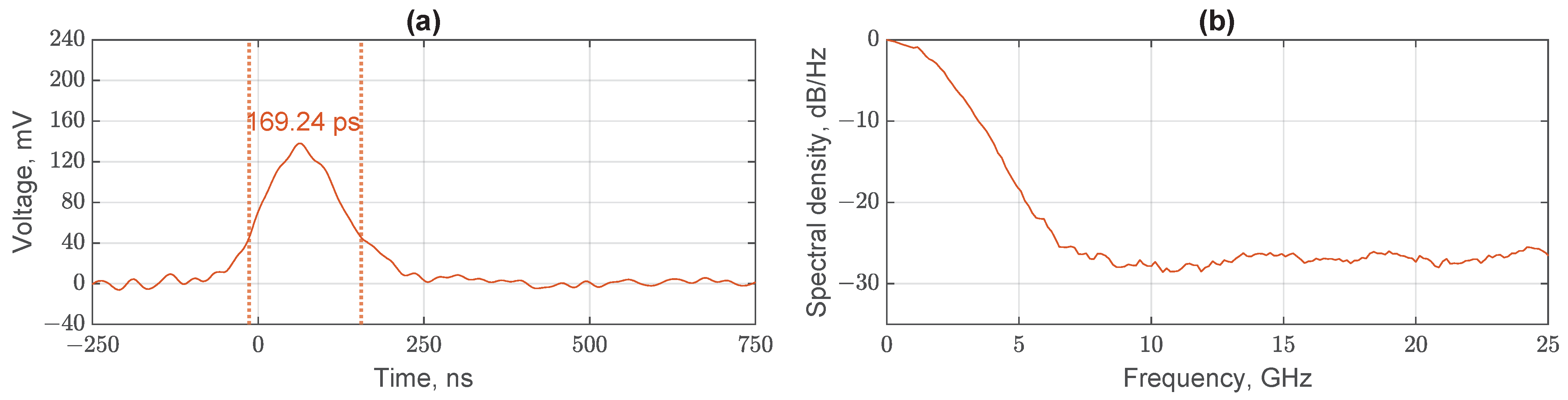
4.2. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APF | all-pass filter |
| ASP | analog signal processing |
| AWG | arbitrary waveform generator |
| BER | bit error ratio |
| CD | chromatic dispersion |
| CW | continuous wave |
| DC | direct current |
| DSO | digital storage oscilloscope |
| DSP | digital signal processing |
| FBG | fiber Bragg grating |
| FEC | forward error correction |
| FFT | fast Fourier transform |
| FWHM | full width at half maximum |
| LPF | low-pass filter |
| MZM | Mach–Zehnder modulator |
| PIN | p-i-n photodiode |
| PPM | pulse-position modulation |
| RF | radio frequency |
| TDC | time-to-digital converter |
| TR-PPM | transmitted reference pulse-position modulation |
| UWB | ultra-wideband |
| VOA | variable optical attenuator |
References
- Cui, S.; Goldsmith, A.; Bahai, A. Energy-Efficiency of MIMO and Cooperative MIMO Techniques in Sensor Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2004, 22, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavami, M.; Michael, L.B.; Kohno, R. Ultra Wideband Signals and Systems in Communication Engineering; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.; Miao, M. Design of CMOS RFIC Ultra-Wideband Impulse Transmitters and Receivers; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrakasan, A.P.; Lee, F.S.; Wentzloff, D.D.; Sze, V.; Ginsburg, B.P.; Mercier, P.P.; Daly, D.C.; Blazquez, R. Low-Power Impulse UWB Architectures and Circuits. Proc. IEEE 2009, 97, 332–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, H.S.; Beyer, J.W.; Grieser, T.J.; Polkinghorn, F.A. A Multichannel Microwave Radio Relay System. Trans. Am. Inst. Electr. Eng. 1946, 65, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamkins, J. Pulse Position Modulation; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Liu, Z.; Meng, S.; Zhao, Y. Research on the Pulse-position Modulation in the Digital Communication System. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Wireless Communications and Smart Grid (ICWCSG), Hangzhou, China, 13–15 August 2021; pp. 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, L. Simulation on the design of digital pulse position modulation system. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Networks, Information, and Communication Engineering (NNICE 2022), Qingdao, China, 25–27 March 2022; Tiwari, R., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proakis, J.; Salehi, M. Digital Communications, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill Higher Education: Columbus, OH, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Karp, S.; Gagliardi, R. The Design of a Pulse-Position Modulated Optical Communication System. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1969, 17, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, M.; Li-ying, T.; Siyuan, Y. Technologies and applications of free-space optical communication and space optical information network. J. Commun. Inf. Netw. 2016, 1, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Ghassemlooy, Z. Pulse time modulation techniques for optical communications: A review. IEE Proc. Optoelectron. 1993, 140, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, R.; Khatun, S.; Ali, B.M.; Abduallah, M.K. Ultra Wide Band (UWB) Ad-hoc Networks: Review and Trends. J. Comput. Sci. 2005, 1, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulse Position Modulation: Block Diagram, Circuit, Working, Generation with PWM & Its Applications. Available online: https://www.elprocus.com/pulse-position-modulation/ (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Green, R.J. Comparison of pulse position modulation and pulse width modulation for application in optical communications. Opt. Eng. 2007, 46, 065001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai-ping, H.; Yang-Yu, F.; Yuan-Kui, L.; Meng, J.; Bo, B.; Qing-Gui, T. A differential pulse position width modulation for optical wireless communication. In Proceedings of the 2009 4th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Xi’an, China, 25–27 May 2009; pp. 1773–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacko, D.; Kéïta, A.A. Techniques of Modulation: Pulse Amplitude Modulation, Pulse Width Modulation, Pulse Position Modulation. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2017, 7, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Jahid, A.; Alsharif, M.H.; Hall, T.J. A contemporary survey on free space optical communication: Potentials, technical challenges, recent advances and research direction. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2022, 200, 103311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Chen, G.; Tang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y. Research and Simulation of PPM Modulation and Demodulation System on Spatial Wireless Optical Communication. In Proceedings of the 2010 Symposium on Photonics and Optoelectronics, Chengdu, China, 19–21 June 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Yu, Z. The Research Process, Application, and the Future Development of Pulse-Position Modulation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2384, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urkowitz, H. Energy detection of unknown deterministic signals. Proc. IEEE 1967, 55, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillard, G. Pulse-Position Modulation Based on Energy Detection. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1973, AES-9, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, S.S.; Youssif, A.; Ghouz, H.H.M. Performance Analysis and Evaluation of TH-PPM and TH-BPSK under Dynamic Channel Environment. Int. J. Future Comput. Commun. 2012, 1, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munirathinam, R.; Aboltins, A.; Pikulins, D.; Grizans, J. Chaotic Non-Coherent Pulse Position Modulation Based Ultra- Wideband Communication System. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Microwave Theory and Techniques in Wireless Communications (MTTW), Riga, Latvia, 7–8 October 2021; pp. 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariat, M.; Ferdosizadeh, M.; Abdoli, M.J.; Makouei, B.; Yazdanpanah, A.; Marvasti, F. Comparison Between Several Methods of PPM Demodulation Based on Iterative Techniques. In Telecommunications and Networking-ICT 2004; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushchik, M.; Rulkov, N.; Larson, L.; Tsimring, L.; Abarbanel, H.; Yao, K.; Volkovskii, A. Chaotic pulse position modulation: A robust method of communicating with chaos. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2000, 4, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisz, J. Review of methods for time interval measurements with picosecond resolution. Metrologia 2003, 41, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjoubfar, A.; Churkin, D.V.; Barland, S.; Broderick, N.; Turitsyn, S.K.; Jalali, B. Time stretch and its applications. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, R.; Botteron, C.; Farine, P.A. A novel low complexity data demodulation algorithm for pulse position modulation. Digit. Signal Process. 2012, 22, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Clerckx, B. Wireless Information and Power Transfer for IoT: Pulse Position Modulation, Integrated Receiver, and Experimental Validation. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 12378–12394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Event Timer A033-ET. Available online: https://eventechsite.com/products/a033-et/ (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Eventech Stream Time Tagger. Available online: https://eventechsite.com/products/ (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Barrett, T.W. History of Ultra Wideband Communications and Radar: Part I, UWB Communications. Microw. J. 2001, 44, 22–56. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, T.W. History of Ultra Wideband Communications and Radar: Part II, UWB Radars and Sensors. Microw. J. 2001, 44, 22–52. [Google Scholar]
- O’Meara, T.R. The Synthesis of Band-Pass, All-Pass Time Delay Networks with Graphical Approximation Techniques; Research Report No. 114; Hughes Aircraft Company: Culver City, LA, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Zverev, A.I. Handbook of Filter Synthesis; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffswell, R.A. A Microstrip Line Stretcher. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2003, 41, 1330–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputi, W.J. Stretch: A Time-Transformation Technique. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1971, AES-7, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M.; Yamada, G.; Miyatake, H. Pulse Stretching Circuit and Method. U.S. Patent No. US20130141148A1, 8 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, B.; Kopa, A.; Fu, Z.; Apsel, A.B. An integrated Ku-band nanosecond time-stretching system using improved dispersive delay line (DDL). In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 12th Topical Meeting on Silicon Monolithic Integrated Circuits in RF Systems, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 16–18 January 2012; pp. 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, G.; Tarricone, L. Negative Group Velocity in a Split Ring Resonator-Coupled Microstrip Line. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2009, 94, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regalia, P.; Mitra, S.; Vaidyanathan, P. The digital all-pass filter: A versatile signal processing building block. Proc. IEEE 1988, 76, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caloz, C.; Gupta, S.; Zhang, Q.; Nikfal, B. Analog Signal Processing: A Possible Alternative or Complement to Dominantly Digital Radio Schemes. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2013, 14, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamien, M.B.; Maundy, B.J.; Belostotski, L.; Elwakil, A.S. Synthesis of Wideband High-Quality Factor Delay- Tunable Fully Differential All-Pass Filters. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2020, 68, 4348–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de França Ferreira, J.A.; Avignon-Meseldzija, E.; Ferreira, P.M.; Bénabès, P. Design and Synthesis of Arbitrary Group Delay Filters for Integrated Analog Signal Processing. In Proceedings of the 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), Bordeaux, France, 9–12 December 2018; pp. 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gupta, S.; Caloz, C. Synthesis of Narrowband Reflection-Type Phasers With Arbitrary Prescribed Group Delay. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2012, 60, 2394–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sounas, D.L.; Caloz, C. Synthesis of Cross-Coupled Reduced-Order Dispersive Delay Structures (DDSs) With Arbitrary Group Delay and Controlled Magnitude. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Parsa, A.; Perret, E.; Snyder, R.V.; Wenzel, R.J.; Caloz, C. Group-Delay Engineered Noncommensurate Transmission Line All-Pass Network for Analog Signal Processing. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2010, 58, 2392–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avignon-Meseldzija, E.; Anastasov, J.; Milic, D. A linear group delay filter with tunable positive slope for analog signal processing. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2021, 49, 1307–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, I.; Krishnapura, N. Expansion and Compression of Analog Pulses by Bandwidth Scaling of Continuous-Time Filters. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2018, 65, 2703–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pactitis, S.A. Active Filters: Theory and Design; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher, C. Microwave Active Filters Based on Transversal and Recursive Principles. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1985, 33, 1350–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Law, C.L.; Jiang, J. A Novel 3–5 GHz Active Matched Filter for Impulse Radio Ultra-Wideband. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Components Lett. 2009, 19, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarjar, M.; el Ouazzani, N.P. Three branch microwave channelized active bandpass filter. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Communications (WINCOM), Fez, Morocco, 29 October–1 November 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Garcia, R.; Sanchez-Soriano, M.A.; Tam, K.W.; Xue, Q. Flexible Filters: Reconfigurable-Bandwidth Bandpass Planar Filters with Ultralarge Tuning Ratio. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2014, 15, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovjova, T.; Semenako, J.; Prigunovs, D.; Ortiz, D.; Spolitis, S.; Aboltins, A. Picosecond Pulse Expansion Using The Low-Pass Filter in Event Timer-Based PPM Communication System. In Proceedings of the 2022 Workshop on Microwave Theory and Techniques in Wireless Communications (MTTW), Riga, Latvia, 5–7 October 2022; pp. 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, W. Delay networks having maximally flat frequency characteristics. Proc. IEE-Part III Radio Commun. Eng. 1949, 96, 487–490. [Google Scholar]
- Mini-Circuits. Low Pass Filter SLP-2400+. Available online: https://www.minicircuits.com/pdfs/SLP-2400+.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Hammerstad, E.O. Equations for Microstrip Circuit Design. In Proceedings of the 1975 5th European Microwave Conference, Hamburg, Germany, 1–4 September 1975; pp. 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerstad, E.; Jensen, O. Accurate Models for Microstrip Computer-Aided Design. In Proceedings of the 1980 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave symposium Digest, Washington, DC, USA, 28–30 May 1980; pp. 407–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschning, M.; Jansen, R. Accurate Wide-Range Design Equations for the Frequency-Dependent Characteristic of Parallel Coupled Microstrip Lines. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1984, 32, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschning, M.; Jansen, R.; Koster, N. Accurate model for open end effect of microstrip lines. Electron. Lett. 1981, 17, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.S.; Lancaster, M.J. Microstrip Filters for RF/Microwave Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, C. Bessel Filters, Polynomials, Poles and Circuit Elements. 2003. Available online: http://www.crbond.com/papers/bsf2.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Paschotta, R. Pulse Stretchers. Available online: https://www.rp-photonics.com/pulse_stretchers.html (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Steed, R. Modelling of Optical Pulse Stretching Using Circulating Cavities. 2015. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/272292773_Modelling_of_Optical_Pulse_Stretching_using_Circulating_Cavities?channel=doi&linkId=54e0db5d0cf24d184b0e92cd&showFulltext=true (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Ulyanov, I.; Przhiialkovskii, D.V.; Butov, O.V. Point-by-point inscription of chirped apodized fiber Bragg gratings for application as ultrashort pulse stretchers. Results Phys. 2022, 32, 105101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, A.P.; Kiefer, J. Polarization-controlled optical ring cavity (PORC) tunable pulse stretcher. Opt. Commun. 2016, 372, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraceno, C. Pulse Stretching and Compressing Using Grating Pairs. Photonics and Ultrafast Laser Science, Ibsen Photonics A/S, 2017. Available online: https://ibsen.com/wp-content/uploads/White-paper-Pulse-stretching-and-compressing-using-grating-pairs_v1-2.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Luo, X.; Giannakis, G.B. Achievable rates of transmitted-reference ultra-wideband radio with PPM. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2006, 54, 1536–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolitis, S.; Prigunovs, D.; Migla, S.; Ortiz, D.; Selis, O.; Sics, P.E.; Ostrovskis, A.; Solovjova, T.; Semenjako, J.; Aboltins, A. Demonstration of 512-TR-PPM Fiber Optical Transmission Link. In Proceedings of the 2023 Photonics & Electromagnetics Research Symposium (PIERS), Prague, Czech Republic, 3–6 July 2023; pp. 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
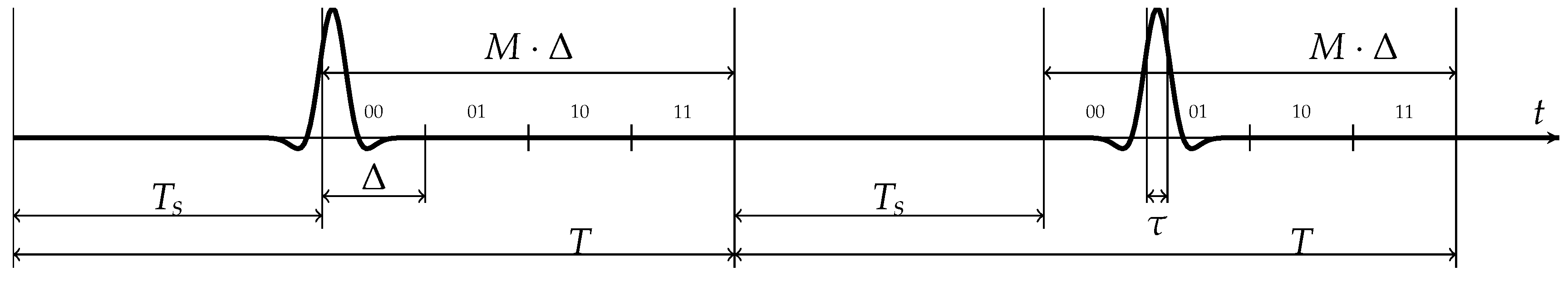
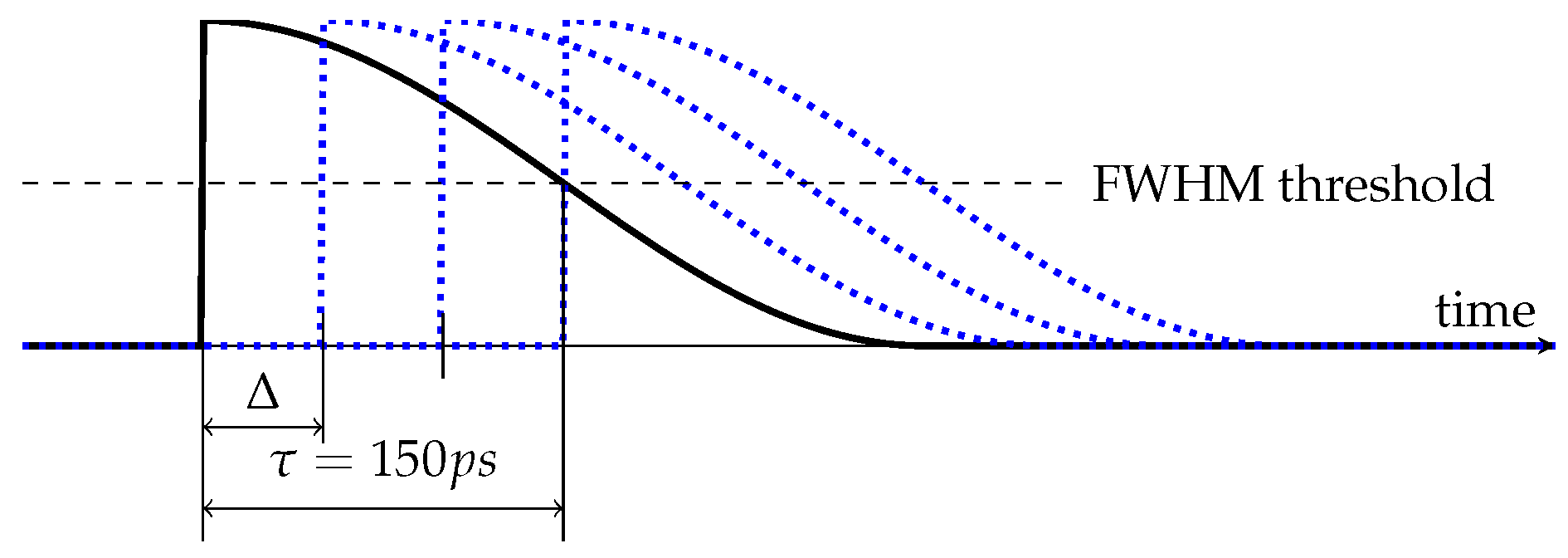
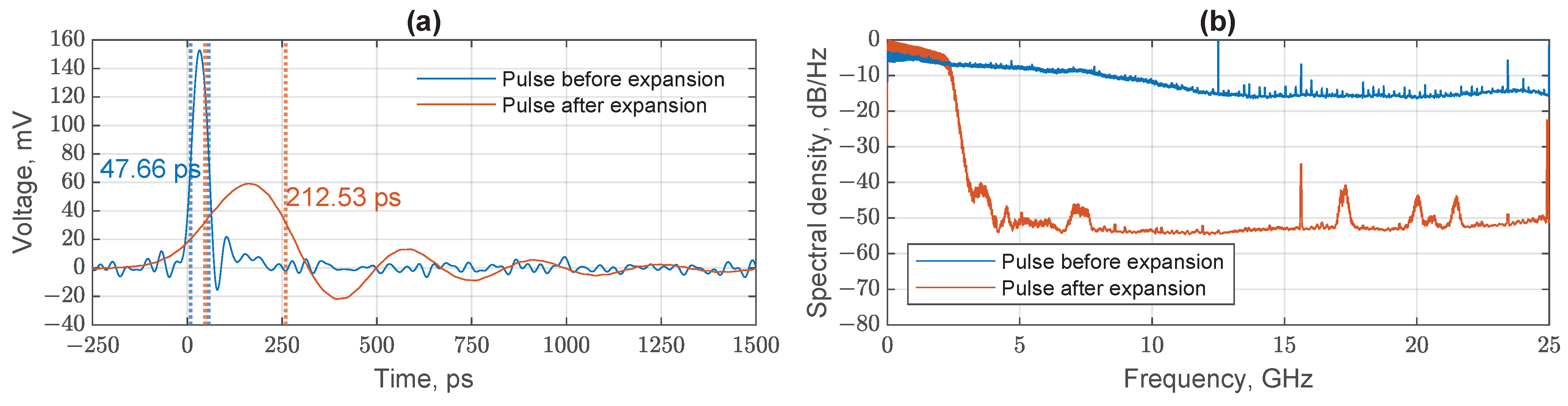
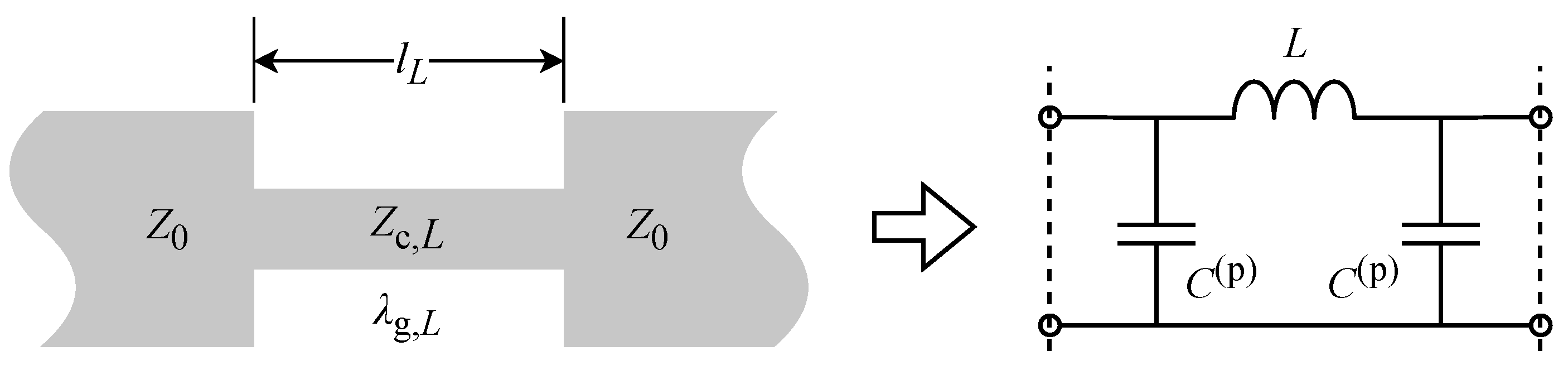
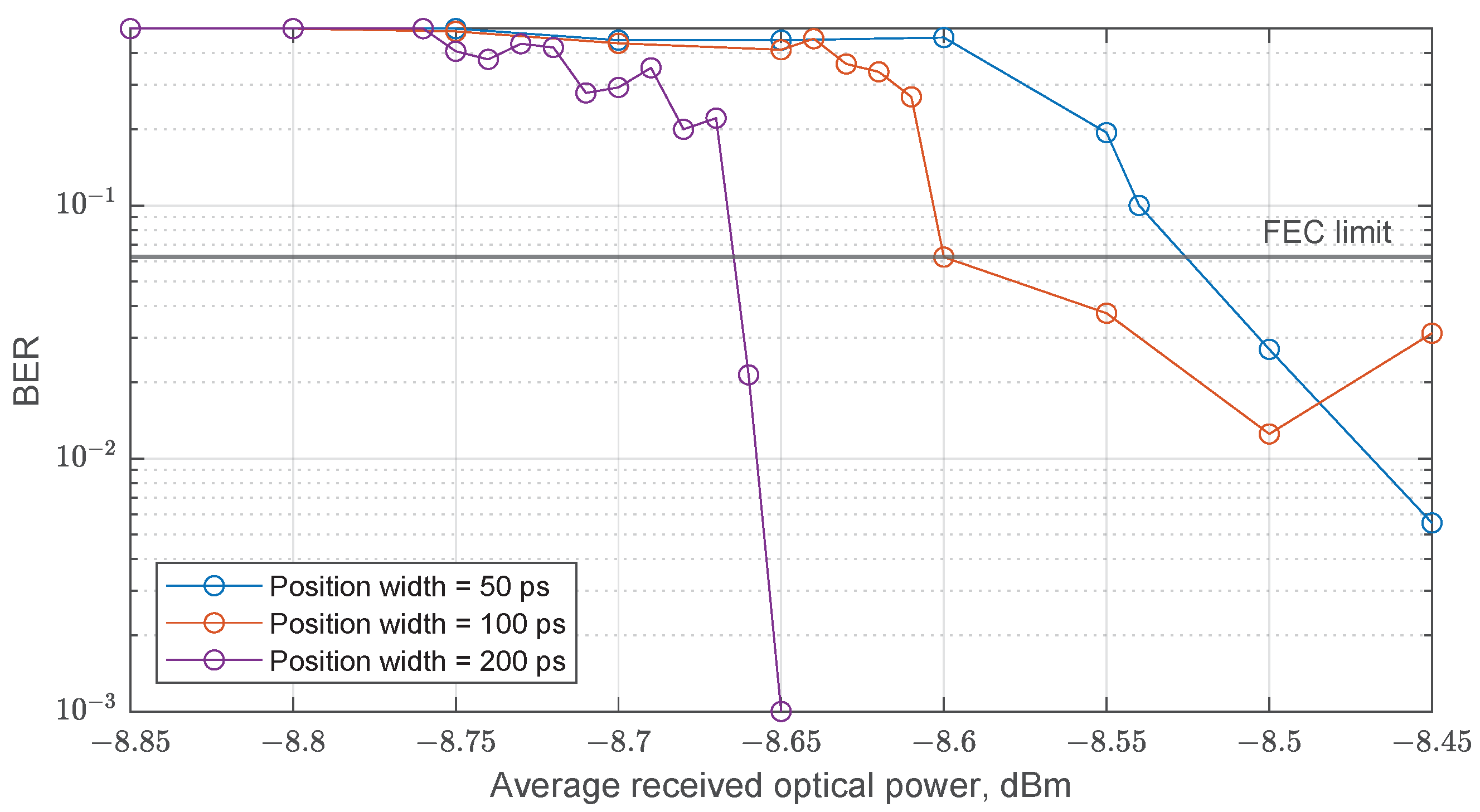
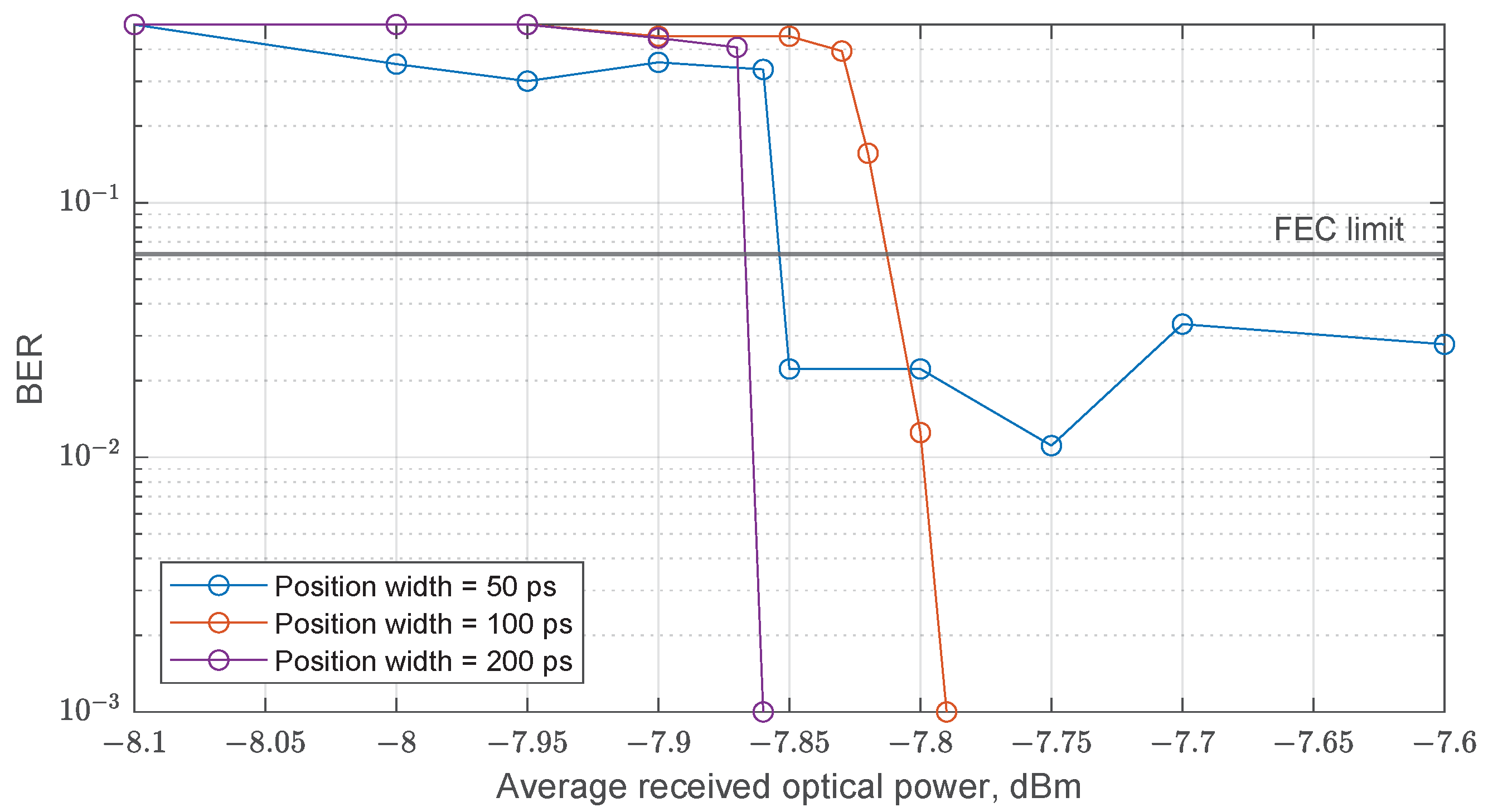
| Number of Positions, N | Position Width , ps | Pulse Width , ps | Expansion Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 512 | 50 | 50 | Optical |
| 256 | 100 | 50 | Optical |
| 128 | 200 | 50 | Optical |
| 512 | 50 | 50 | Electrical |
| 256 | 100 | 50 | Electrical |
| 128 | 200 | 50 | Electrical |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aboltins, A.; Solovjova, T.; Semenako, J.; Kusnins, R.; Migla, S.; Sics, P.E.; Selis, O.; Tihomorskis, N.; Prigunovs, D.; Ostrovskis, A.; et al. Passive Electrical and Optical Methods of Ultra-Short Pulse Expansion for Event Timer-Based TDC in PPM Receiver. Electronics 2023, 12, 4634. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224634
Aboltins A, Solovjova T, Semenako J, Kusnins R, Migla S, Sics PE, Selis O, Tihomorskis N, Prigunovs D, Ostrovskis A, et al. Passive Electrical and Optical Methods of Ultra-Short Pulse Expansion for Event Timer-Based TDC in PPM Receiver. Electronics. 2023; 12(22):4634. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224634
Chicago/Turabian StyleAboltins, Arturs, Tatjana Solovjova, Janis Semenako, Romans Kusnins, Sandis Migla, Pauls Eriks Sics, Oskars Selis, Nikolajs Tihomorskis, Dmitrijs Prigunovs, Armands Ostrovskis, and et al. 2023. "Passive Electrical and Optical Methods of Ultra-Short Pulse Expansion for Event Timer-Based TDC in PPM Receiver" Electronics 12, no. 22: 4634. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224634
APA StyleAboltins, A., Solovjova, T., Semenako, J., Kusnins, R., Migla, S., Sics, P. E., Selis, O., Tihomorskis, N., Prigunovs, D., Ostrovskis, A., & Spolitis, S. (2023). Passive Electrical and Optical Methods of Ultra-Short Pulse Expansion for Event Timer-Based TDC in PPM Receiver. Electronics, 12(22), 4634. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224634








