Study on the Systematic Design of a Passive Balancing Algorithm Applying Variable Voltage Deviation
Abstract
1. Introduction
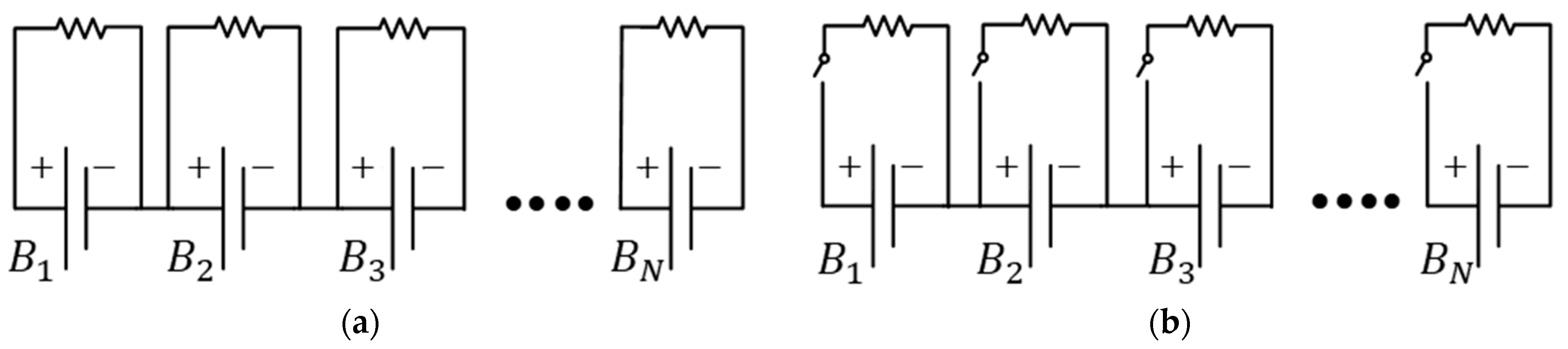
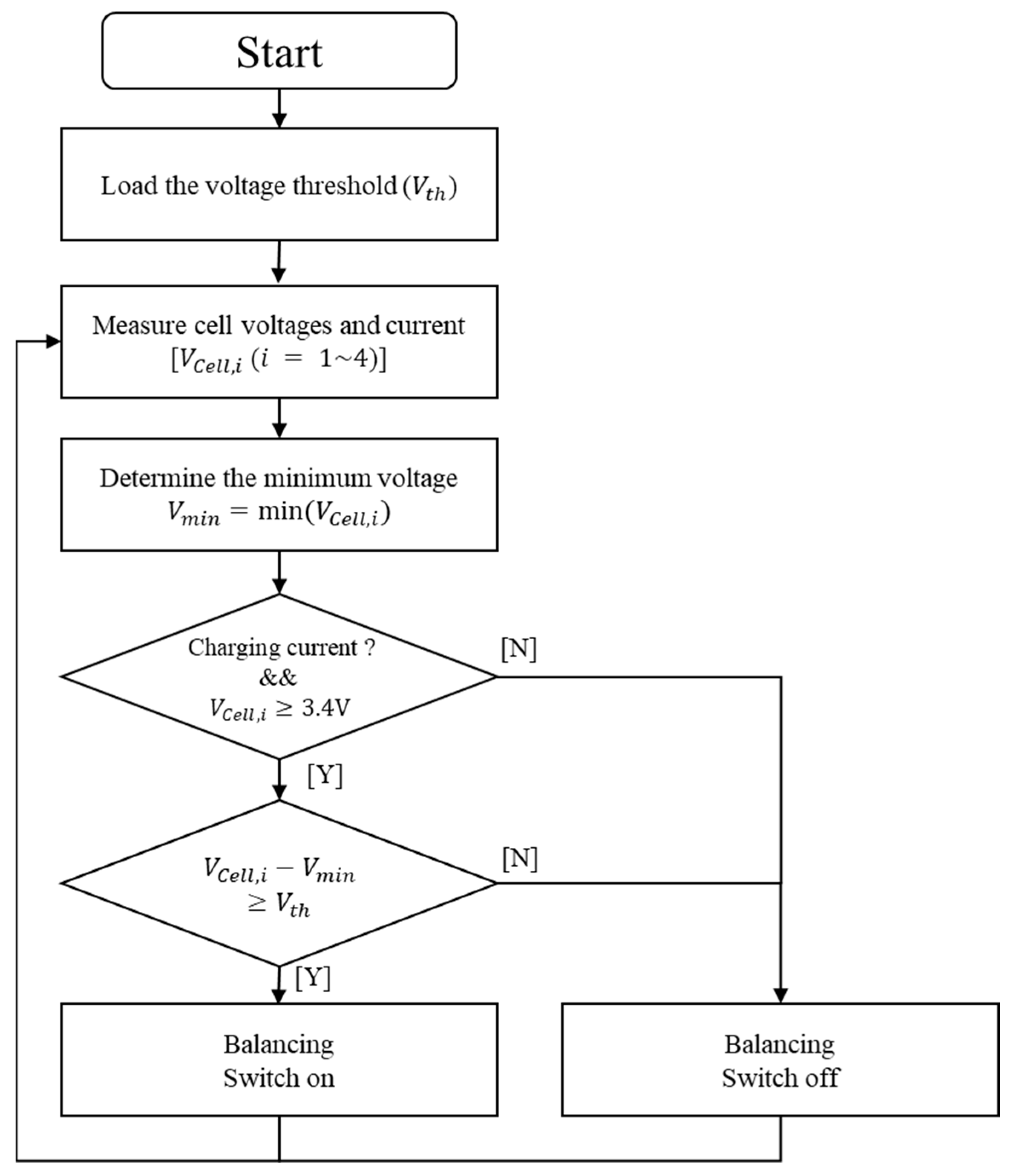
2. Balancing Algorithm Design Methodology
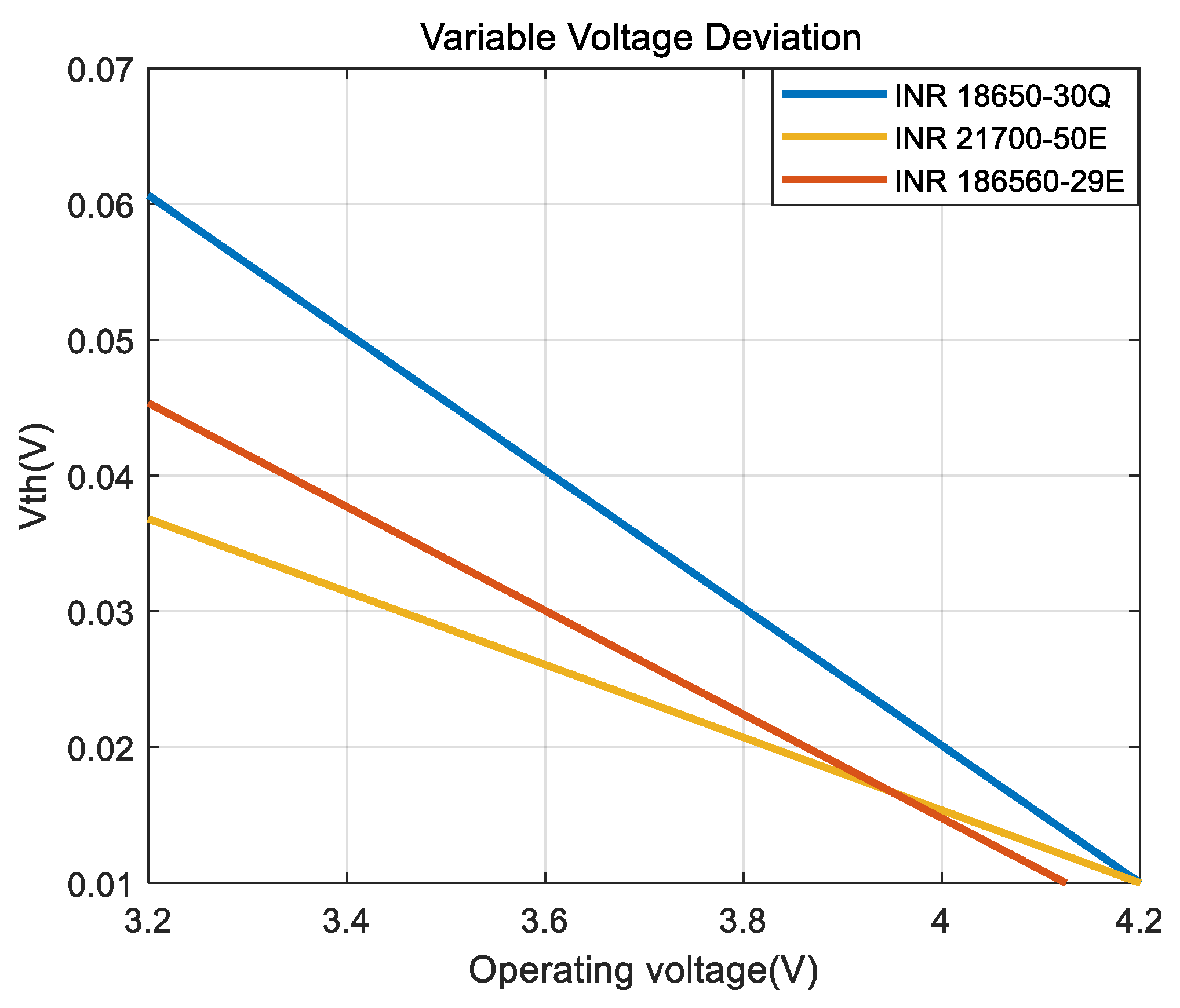
2.1. Balancing Voltage Deviation Determination
2.2. Load Condition Determination for Balancing
3. Performance Analysis of the Proposed Method
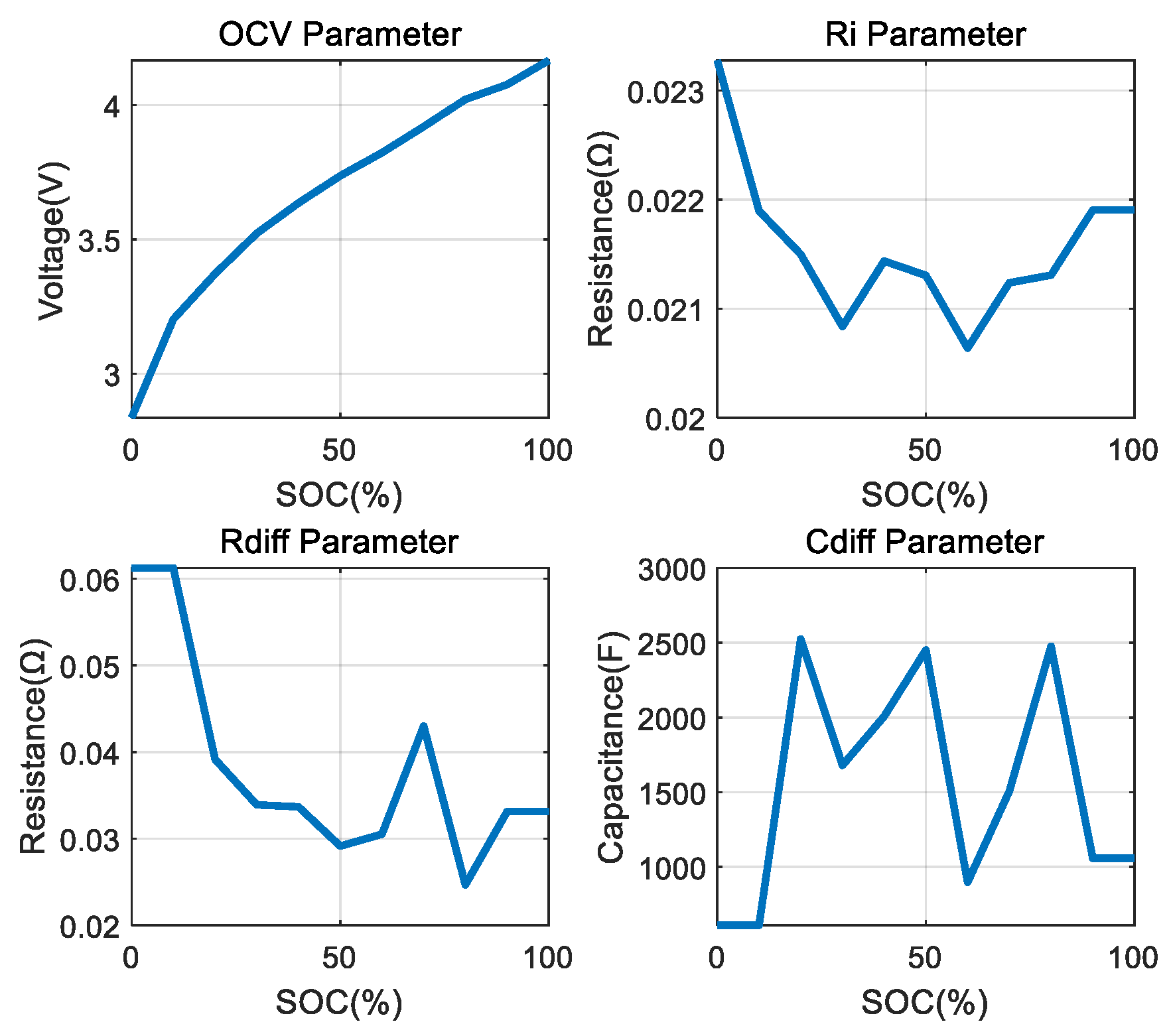
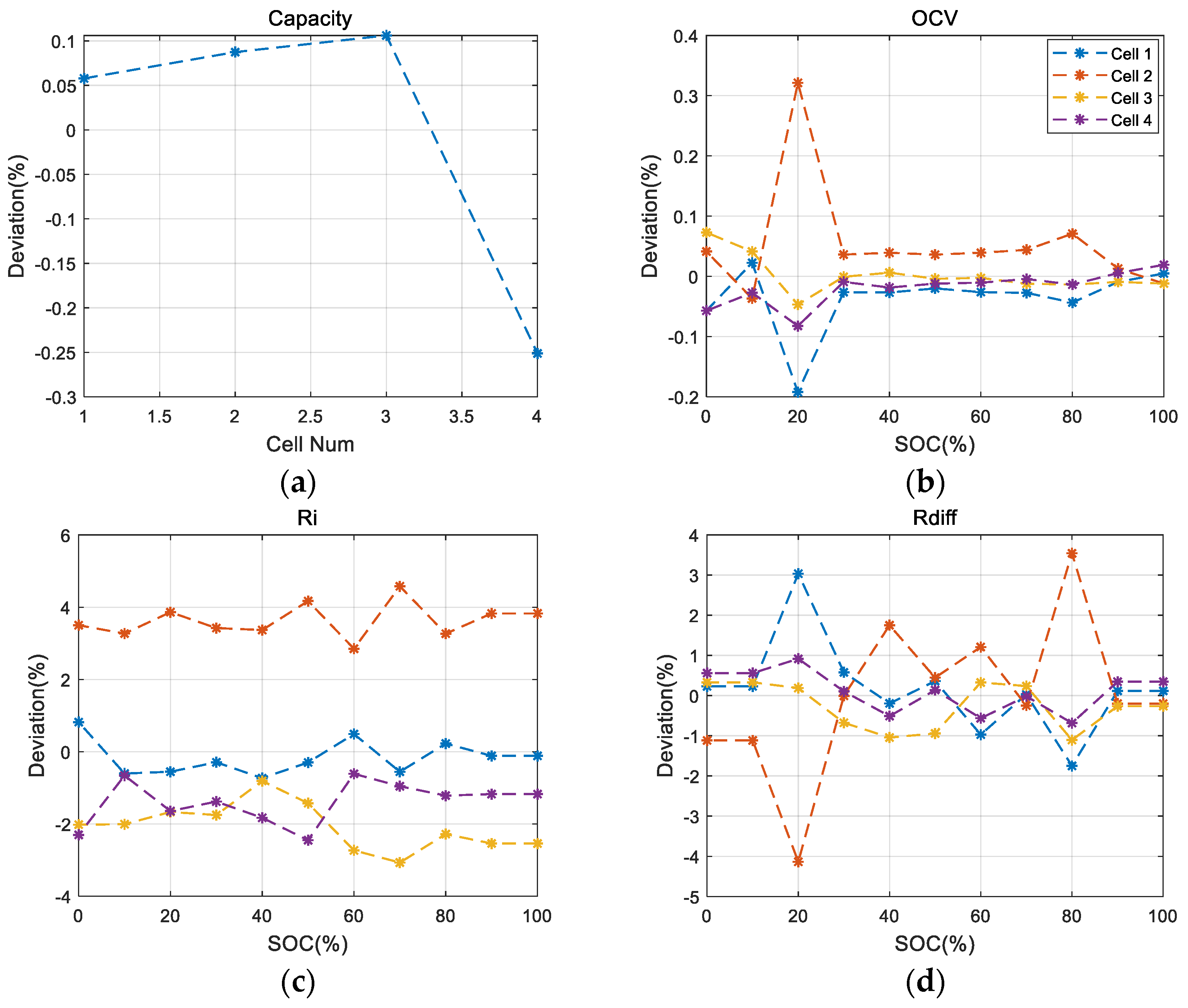
3.1. Performance Analysis According to Parameter Deviation
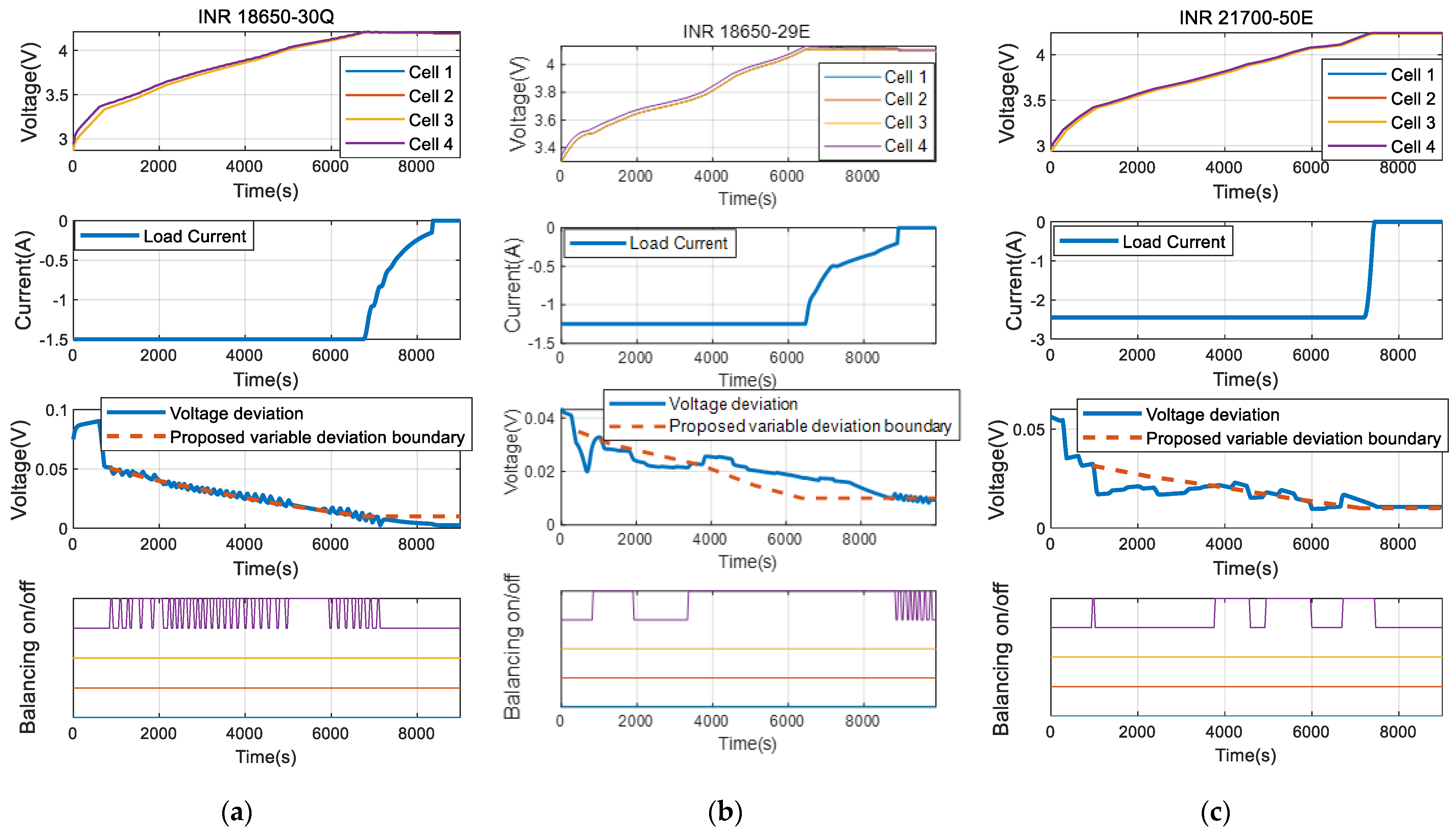
3.2. Performance Analysis According to Battery Cell Type
3.3. Efficiency Analysis of the Proposed Algorithm
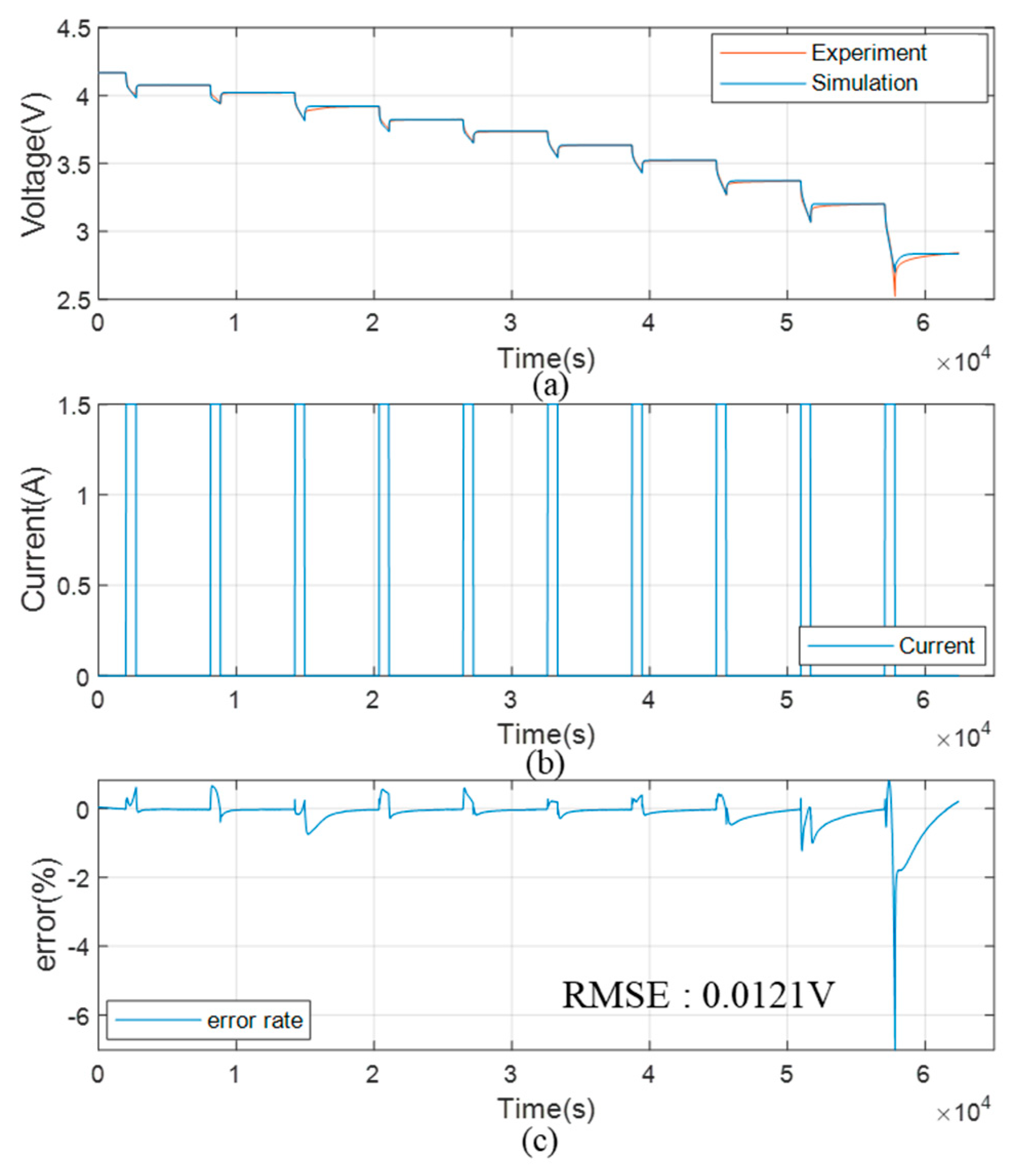
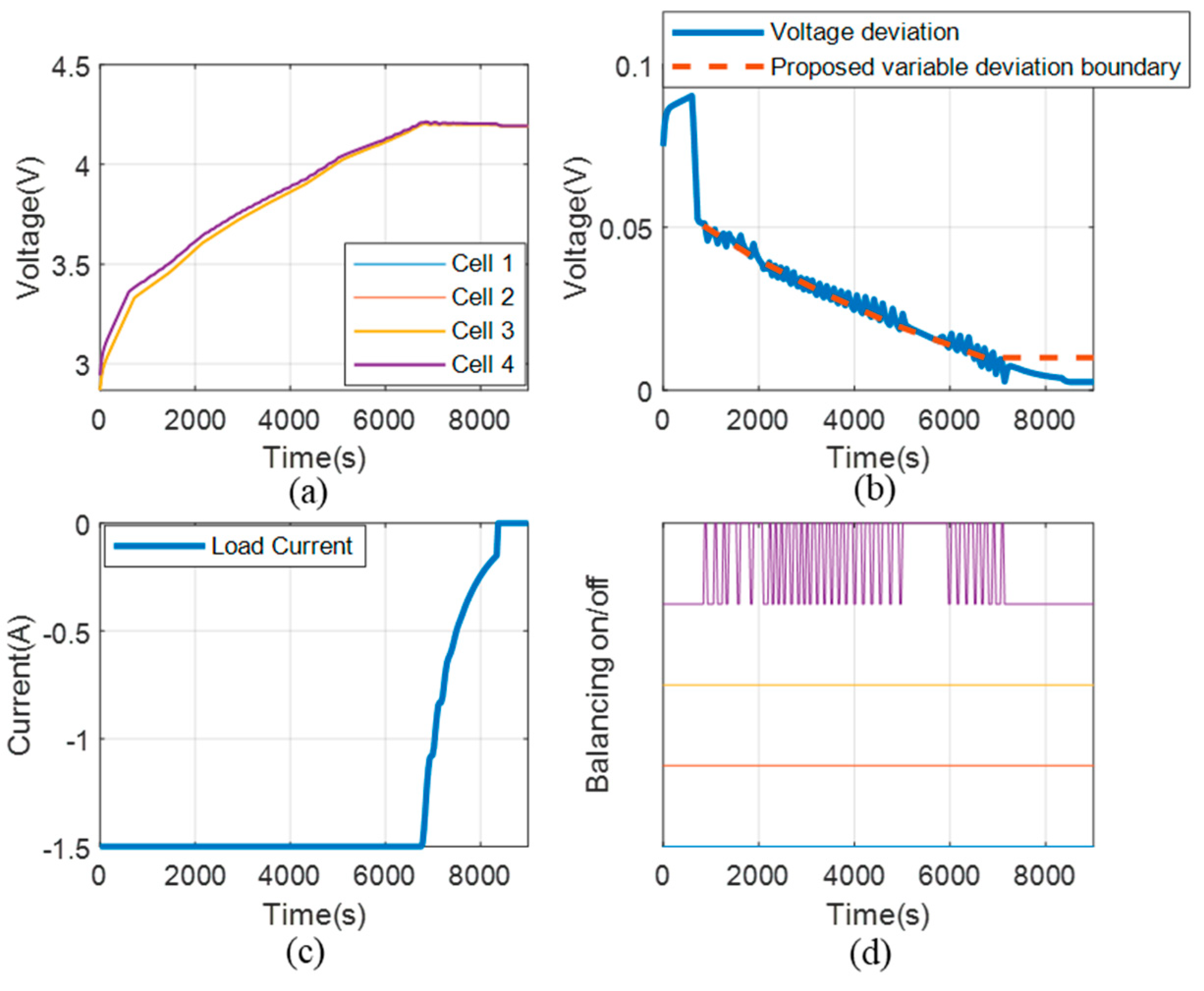
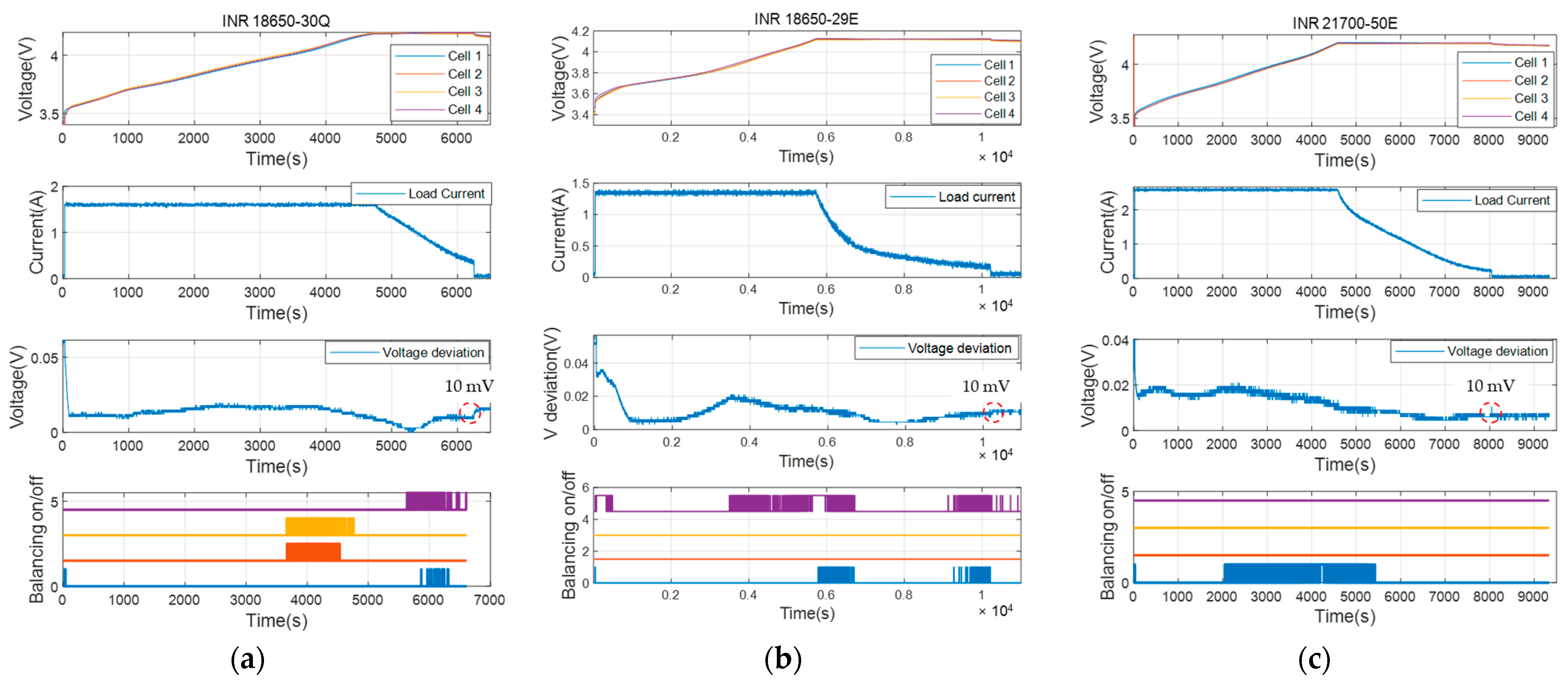
4. Experiment Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
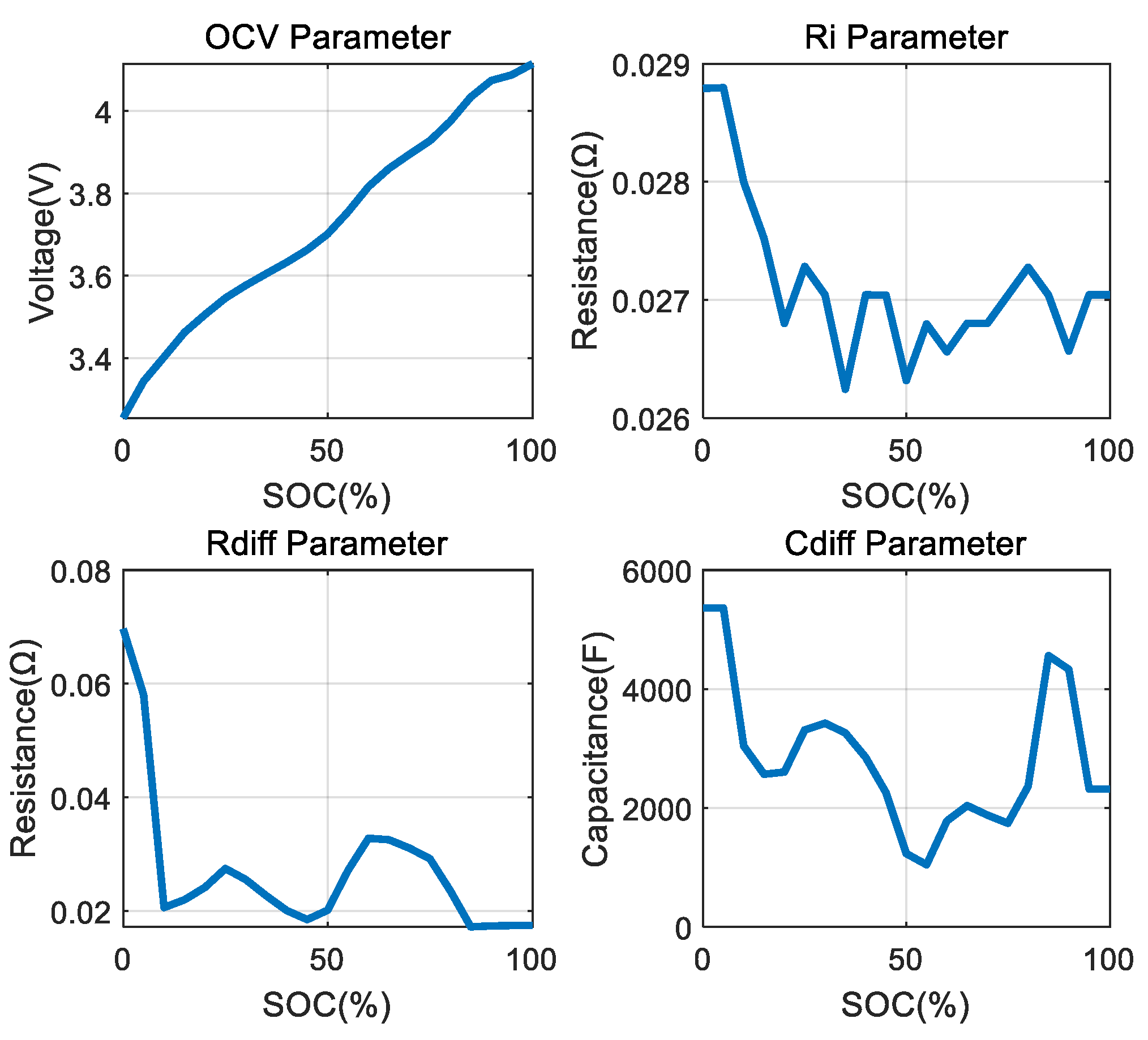
| SOC | OCV (V) | Ri (Ω) | Rdiff (Ω) | Cdiff (F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100% | 4.1682 | 0.0219 | 0.0331 | 1058 |
| 90% | 4.0765 | 0.0219 | 0.0331 | 1058 |
| 80% | 4.0157 | 0.0213 | 0.0247 | 2476 |
| 70% | 3.9168 | 0.0212 | 0.0430 | 1507 |
| 60% | 3.8204 | 0.0206 | 0.0305 | 898 |
| 50% | 3.7336 | 0.0213 | 0.0291 | 2451 |
| 40% | 3.6322 | 0.0214 | 0.0337 | 2007 |
| 30% | 3.5200 | 0.0208 | 0.0339 | 1680 |
| 20% | 3.3513 | 0.0215 | 0.0392 | 2525 |
| 10% | 3.2019 | 0.0219 | 0.0613 | 610 |
| 0% | 2.8277 | 0.0233 | 0.0613 | 610 |
| SOC | OCV (V) | Ri (Ω) | Rdiff (Ω) | Cdiff (F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100% | 4.1146 | 0.0270 | 0.0174 | 2318 |
| 90% | 4.0737 | 0.0266 | 0.0174 | 4330 |
| 80% | 3.9748 | 0.0273 | 0.0236 | 2366 |
| 70% | 3.8945 | 0.0268 | 0.0311 | 1878 |
| 60% | 3.8161 | 0.0266 | 0.0328 | 1780 |
| 50% | 3.7010 | 0.0263 | 0.0201 | 1232 |
| 40% | 3.6322 | 0.0270 | 0.0201 | 2849 |
| 30% | 3.5764 | 0.0270 | 0.0255 | 3425 |
| 20% | 3.5051 | 0.0268 | 0.0242 | 2603 |
| 10% | 3.4022 | 0.0280 | 0.0206 | 3039 |
| 0% | 3.2543 | 0.0288 | 0.0696 | 5361 |
| SOC | OCV (V) | Ri (Ω) | Rdiff (Ω) | Cdiff (F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100% | 4.1794 | 0.0281 | 0.0187 | 1616 |
| 90% | 4.0842 | 0.0276 | 0.0164 | 3237 |
| 80% | 4.0253 | 0.0274 | 0.0201 | 2924 |
| 70% | 3.9215 | 0.0274 | 0.0243 | 2113 |
| 60% | 3.8275 | 0.0276 | 0.0194 | 1506 |
| 50% | 3.7342 | 0.0272 | 0.0181 | 3108 |
| 40% | 3.6542 | 0.0275 | 0.0240 | 3359 |
| 30% | 3.5677 | 0.0276 | 0.0220 | 3219 |
| 20% | 3.4608 | 0.0283 | 0.0189 | 3556 |
| 10% | 3.3036 | 0.0289 | 0.0377 | 1648 |
| 0% | 2.9362 | 0.0323 | 0.0582 | 1215 |
| Parameters | Values | |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Cell Model | OCV | Table A1 for INR 18650-30Q Table A2 for INR 18650-29E Table A3 for INR 21700-50E |
| Ri | ||
| Rdiff | ||
| Cdiff | ||
| Cn | 3.0 Ah for INR 18650-30Q 2.66 Ah for INR 18650-29E 4.83 Ah for INR 21700-50E | |
| CC-CV Cycler | CC 1.5 A, CV 4.2 V (cutoff current 150 mA) for INR 18650-30Q CC 1.25 A, CV 4.125 V (cutoff current 62.5 mA) for INR 18650-29E CC 2.5 A, CV 4.2 V (cutoff current 98 mA) for INR 21700-50E | |
| Passive Balancing Model | Ideal Switch and balancing resistor (30 Ω) | |
References
- Ren, D.; Hsu, H.; Li, R.; Feng, X.; Guo, D.; Han, X.; He, X.; Gao, S.; Hou, J.; Li, Y.; et al. A comparative investigation of aging effects on thermal runaway behavior of lithium-ion batteries. ETransportation 2019, 2, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Jiang, M.; Tao, P.; Song, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Deng, T.; Shang, W. Temperature effect and thermal impact in lithium-ion batteries: A review. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2018, 28, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, A.; Santhanagopalan, S.; Kim, G.H. Addressing the Impact of Temperature Extremes on Large Format Li-Ion Batteries for Vehicle Applications (Presentation); No. NREL/PR-5400-58145; National Renewable Energy Lab (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Petri, A.M.; Petreuș, D. Balancing and SOC Estimation in a Battery Management System for Electric Vehicle. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2021 44th International Spring Seminar on Electronics Technology (ISSE), Bautzen, Germany, 5–9 May 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kutkut, N.H.; Divan, D.M. Dynamic equalization techniques for series battery stacks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelec’96-International Telecommunications Energy Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 6–10 October 1996; pp. 514–521. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Jeon, S.; Lee, H.; Bae, S. Comparison on cell balancing methods for energy storage applications. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 92316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.A.; Hasan, M.K.; Mahmud, M.; Motakabber, S.M.A.; Ibrahimya, M.I.; Islam, S. A review: Energy storage system and balancing circuits for electric vehicle application. IET Power Electron. 2021, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omariba, Z.B.; Zhang, L.; Sun, D. Review of battery cell balancing methodologies for optimizing battery pack performance in electric vehicles. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 129335–129352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Schofield, N.; Emadi, A. Battery balancing methods: A comprehensive review. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Harbin, China, 3–5 September 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul-jabbar, T.A.; Kersten, A.; Mashayekh, A.; Obed, A.A.; Abid, A.J.; Kuder, M. Efficient Battery Cell Balancing Methods for Low-Voltage Applications: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference in Power Engineering Application (ICPEA), Shah Alam, Malaysia, 7–8 March 2022; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Y.; Zhou, S.; Cui, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Xu, X.; Ling, H.; Yang, S. A comprehensive review on inconsistency and equalization technology of lithium-ion battery for electric vehicles. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 11059–11087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelkar, A.; Dasari, Y.; Williamson, S.S. A comprehensive review of power electronics enabled active battery cell balancing for smart energy management. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Smart Grid and Renewable Energy (PESGRE2020), Cochin, India, 2–4 January 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Daowd, M.; Omar, N.; Van Den Bossche, P.; Van Mierlo, J. Passive and active battery balancing comparison based on MATLAB simulation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 6–9 September 2011; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hemavathi, S. Overview of cell balancing methods for Li-ion battery technology. Energy Storage 2020, 203, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, S.W.; Schneider, P.J. A review of cell equalization methods for lithium ion and lithium polymer battery systems. SAE Tech. Pap. 2001, 2001, 01–0959. [Google Scholar]
- Bayati, M.; Abedi, M.; Farahmandrad, M.; Gharehpetian, G.B.; Tehrani, K. Important technical considerations in design of battery chargers of electric vehicles. Energies 2021, 14, 5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvonasundari, D.; Deepa, K. Optimized passive cell balancing for fast charging in electric vehicle. IETE J. Res. 2021, 69, 2089–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraisamy, T.; Kaliyaperumal, D. Adaptive passive balancing in battery management system for e-mobility. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 10752–10764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, K.; Nugroho, A.; Kaleg, S. Passive balancing battery management system using MOSFET internal resistance as balancing resistor. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2017 International Conference on Sustainable Energy Engineering and Application (ICSEEA), Jakarta, Indonesia, 23–24 October 2017; pp. 151–155. [Google Scholar]
- Kıvrak, S.; Özer, T.; Oğuz, Y.; Erken, E.B. Battery management system implementation with the passive control method using MOSFET as a load. Meas. Control 2020, 53, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizpuru, I.; Iraola, U.; Canales, J.M.; Echeverria, M.; Gil, I. Passive balancing design for Li-ion battery packs based on single cell experimental tests for a CCCV charging mode. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2013 International Conference on Clean Electrical Power (ICCEP), Alghero, Italy, 11–13 June 2013; pp. 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, J.; Luo, G.; Ricco, M.; Swierczynski, M.; Stroe, D.I.; Teodorescu, R. Overview of lithium-ion battery modeling methods for state-of-charge estimation in electrical vehicles. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windarko, N.A.; Choi, J.H. SOC estimation based on OCV for NiMH batteries using an improved takacs model. J. Power Electron. 2010, 10, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miniguano, H.; Barrado, A.; Lázaro, A.; Zumel, P.; Fernández, C. General parameter identification procedure and comparative study of Li-Ion battery models. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 69, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, H.; Ning, Z.; Mu, Z.; Sun, C. Comparative research on RC equivalent circuit models for lithium-ion batteries of electric vehicles. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Boukhnifer, M.; Diallo, D. On-line model-based short circuit diagnosis of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicle application. In Proceedings of the IEEE IECON 2019-45th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 October 2019; Volume 1, pp. 6022–6027. [Google Scholar]





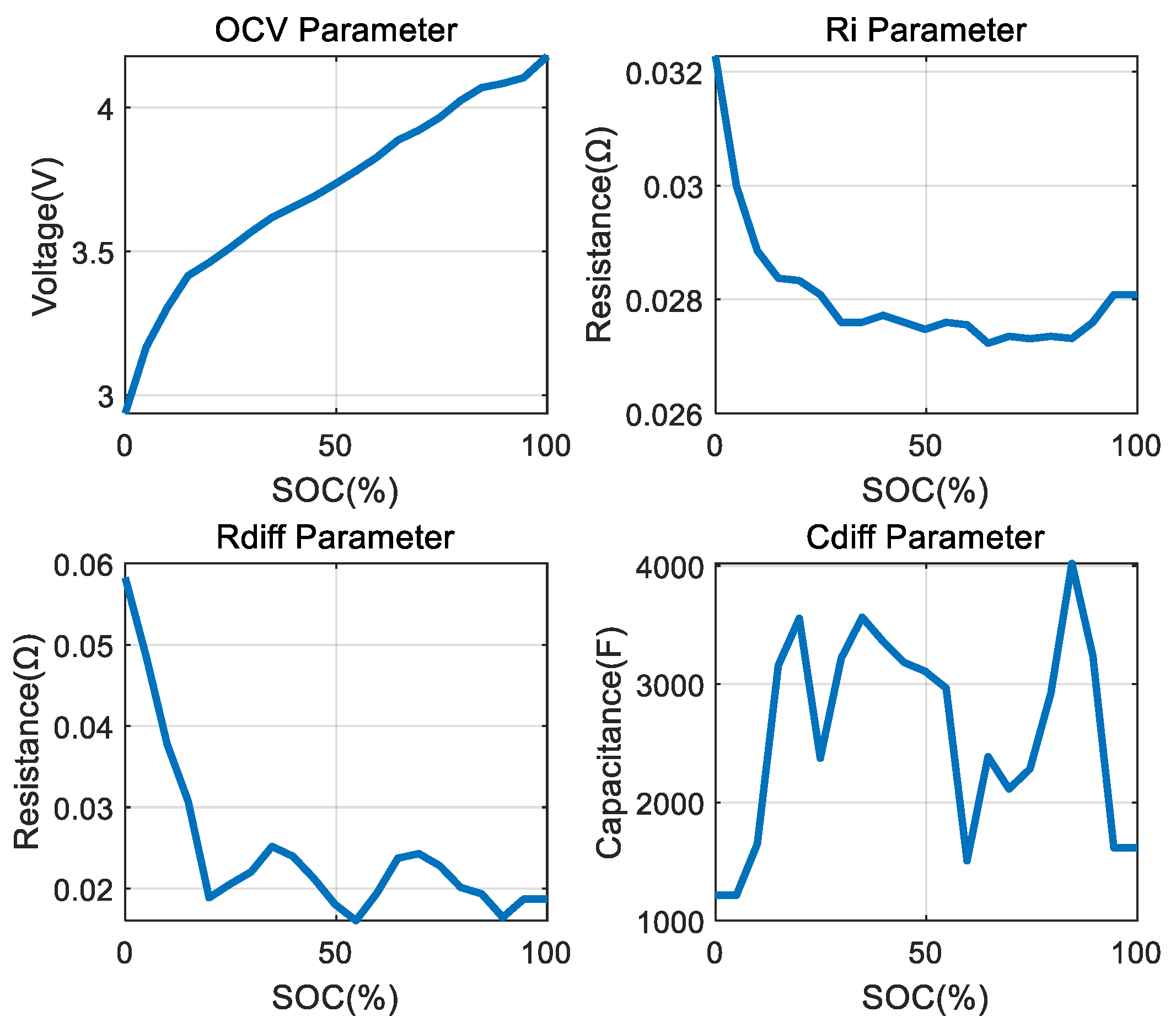


| Balancing Algorithm | Current Condition | Voltage Condition | Voltage Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|
| D. Thiruvonasundari [17] | Charge | above 3.3 V | 25 mV |
| D. Thiruvonasundari [18] | Charge | above 3.9 V | 30 mV |
| K. Ismail [19] | Charge | above 3.55–3.6 V | 50 mV |
| S. Kivrak [20] | Charge | whole range | 50 mV |
| Parameter | Initial Condition | |
|---|---|---|
| Cell #1, #2, #4 | Cell #3 | |
| SOC | 100% | 97% |
| Cn | 100% (3.0 Ah) | 99% |
| OCV | OCV parameter of Figure 5 | +0.05% compared to other cells |
| Ri/Rdiff | Ri, Rdiff/Cdiff parameters of Figure 5 | +10% compared to other cells |
| Balancing Condition | Balancing Loss Energy during 1-CC/CV Cycle |
|---|---|
| Discharging | 0.24 Wh |
| Rest | 0.53 Wh |
| Charging | 0.22 Wh |
| Battery Type | Parameter | Initial Condition | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell #1, #2, #3 | Cell #4 | ||
| Module #1 with INR 18650-30Q | SOC | 0% | 1.4% |
| Cn | 100% (3.0 Ah) | 99% | |
| OCV | OCV parameter of Figure 5 | +0.05% compared to other cells | |
| Ri/Rdiff | Ri, Rdiff/Cdiff parameters of Figure 5 | +10% compared to other cells | |
| Module #2 with INR 18650-29E | SOC | 0% | 1.4% |
| Cn | 100% (2.66 Ah) | 99% | |
| OCV | OCV parameter of Figure 12 | +0.05% compared to other cells | |
| Ri/Rdiff | Ri, Rdiff/Cdiff parameters of Figure 12 | +8% compared to other cells | |
| Module #3 with INR 21700-50E | SOC | 0% | 1% |
| Cn | 100% (4.83 Ah) | 99% | |
| OCV | OCV parameter of Figure 13 | +0.02% compared to other cells | |
| Ri/Rdiff | Ri, Rdiff/Cdiff parameters of Figure 13 | +8% compared to other cells | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, H.; Lee, S. Study on the Systematic Design of a Passive Balancing Algorithm Applying Variable Voltage Deviation. Electronics 2023, 12, 2587. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122587
Song H, Lee S. Study on the Systematic Design of a Passive Balancing Algorithm Applying Variable Voltage Deviation. Electronics. 2023; 12(12):2587. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122587
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Heewook, and Seongjun Lee. 2023. "Study on the Systematic Design of a Passive Balancing Algorithm Applying Variable Voltage Deviation" Electronics 12, no. 12: 2587. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122587
APA StyleSong, H., & Lee, S. (2023). Study on the Systematic Design of a Passive Balancing Algorithm Applying Variable Voltage Deviation. Electronics, 12(12), 2587. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122587






