Abstract
Clustering is an effective topology control approach that evenly distributes loads across sensor nodes, enhances network scalability, and increases the lifetime in wireless sensor networks. In this paper, we propose a novel energy-efficient weighted cluster head (CH) selection approach that improves the overall performance of the network and increases energy efficiency. An optimization strategy is proposed that emphasizes adjusting the transmission range with the appropriate node density, which increases energy efficiency for intra- and inter-cluster communications to 86% and 97%, respectively. In addition, the implementation of a quantum search algorithm for choosing the CH is explained. Compared to the classical method such as EECS and HEED, the proposed quantum search algorithm has a quadratic speed-up advantage. The classical search algorithm requires N steps to find a specific element in an array of N elements, but instead of using a classical algorithm, Grover’s quantum search algorithm minimizes the complexity to O (). In this work, an energy-efficient cluster head selection approach is illustrated through a classical weighted clustering algorithm, and its implementation is also extended through a quantum weighted search algorithm which is demonstrated by the simulation results.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, wireless sensor networks (WSNs) have attracted a lot of attention, mostly as a result of their diverse applications across a wide range of fields. Many military and civilian applications (for example, intelligent transportation systems) integrate tasks such as detection, classification, plus the localization and tracking of events or targets in sensor fields [1,2,3,4]. Wireless sensor nodes communicate with each other to collect data, process them, and then transmit the sensed data to a base station (BS). Apart from their miscellaneous applications, energy efficiency in a WSN is still a vital issue. Wireless sensor nodes are identified as major energy-consuming sources in WSNs [5,6,7]. Generally, wireless sensors are limited in terms of their size and battery lifetime. In addition, in most cases it is difficult to replace or recharge the sensors, hence, limitations on energy resources in WSNs specify energy consumption is a major problem.
For the efficient conservation of energy in WSNs, various mechanisms have been used by researchers, including single-hop, multi-hop, and cluster-based transmission. Briefly, important parameters such as the distance between the source and the destination, as well as path loss, are inevitable factors in multi-hop transmission [8]. Additionally, the efficiency of multi-hop transmission will be influenced by the correlation between the power costs of receiving and transmitting [9]. If the nodes are communicating with the minimum amount of power necessary to reach the destination, and if that is considered to be the total power transmitted along the path, then single-hop communication [10] would be the most energy-efficient strategy [11]. In the sensor network, there are two different routing protocols: flat routing and hierarchical routing. In the flat routing protocol, the nodes directly communicate with the base station (BS) to send data packets. Therefore, the energy of the nodes rapidly drains out due to direct interaction with the BS. To improve the lifetime and performance, the sensor network must utilize the least amount of energy. For extending the network’s lifespan, scalability, and load balancing, various cluster-based routing methods have developed [12]. The hierarchical routing models provide both single-hop and multi-hop routing through the formation of several clusters by considering CH in the network for improving the performance of WSN. So, cluster head selection is important to handle the limited energy in the best possible way to uplift the network lifetime. However, for efficient data transmission and energy management, clustering is one of the most effective methods in WSNs [13,14,15,16,17,18]. Typically, sensor nodes in networks are organized into several clusters, as shown in Figure 1, and each cluster has a cluster head (CH) that collects information from each member node (sensor) in the cluster and transmits data to the BS.

Figure 1.
Graphical abstract (3D) of clustering architecture in WSN.
There are numerous clustering protocols focused on transmission power control or network topology. EECS, HEED, UCR, EECF, and others are energy-based. LEACH, C-LEACH, I-LEACH, P-LEACH, and PEGASIS are protocols in homogeneous networks. Low-Energy Adaptive Clustering Hierarchy (LEACH) was the first cluster-based hierarchical routing protocol. The probability of selecting the CH in LEACH and LEACH-based clustering networks is a totally random process with no guarantee of the number of CHs, which adversely affects the overall performance of the network [19]. On the other hand, transmission-power-based protocols such as EECS and HEEDS use residual energy as a rudimentary factor, as well as intra-cluster communication cost as a secondary factor. However, multi-hop inter-cluster communications increases the network overhead and costs. To control the network topology, transmission power control has been widely explored by the research community [20,21], but the interactions of transmission power with clustering algorithms are still uninvestigated.
In this paper, we propose a modified CH selection method by assigning an individual weight to each sensor node based on its node degree, the average distance between the CH and its member nodes, as well as this, we assign residual energy as a function of transmission power. As mentioned, our work focuses on a homogeneous, randomly connected network, and our goal is energy-efficient CH selection by controlling the transmission power. Two nodes can communicate directly if their transmission ranges overlap, which signifies the connectivity between them. For multi-hop communications, connectivity is a fundamental property, but because we are concerned with finding the optimum transmission range, we must consider a fully connected network with a minimum node degree (i.e., 1-connectivity). A network with k-connectivity (k ≥ 2) has much better fault tolerance than a network does with only 1-connectivity, but higher connectivity requires more power consumption [22]. Therefore, a fully connected network with a minimum node degree (1-connectivity) is believed, in this paper, to lessen the energy consumption. During intra-cluster communications, each node adjusts its transmission power based on the cluster range or radius, instead of transmitting at maximum power. This ensures that the nodes are restrained from unwanted power usage, which reduces the amount of battery drainage. However, for fast data transmission from the CH to the BS, the maximum amount of transmission power is needed, which resembles single-hop communications. In a communication model, there exist several problems which can be classified into their hardness on different categories. These problems can be categorized into four complexity classes as: P (easy), NP (medium), NP-complete (hard), and NP-hard (hardest). The main concept of the complexity is how efficiently an algorithm can solve a problem [23].
Hierarchical clustering algorithms are based on classical algorithms in which several clusters are formed [24,25]. If the number of clusters and the total number of elements are represented by k and n, respectively, then the time complexity of a hierarchical algorithm is O(kn2). This time complexity represents time complexity that is similar to that of NP-hard (non-deterministic polynomial) problems [26]. Hence, CH selection is generally recognized as an NP-hard optimization problem [27,28], and its time complexity is equivalent to O(kn2) if the clustering problem is solved by a classical approach. As a result, the CH selection procedure is also time consuming. Therefore, the main challenge is to overcome time complexity, which incurs huge computational and data processing times. In order to improve on the time complexity problem, quantum algorithms can play significant roles. Recently, CH selection was proposed via the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA) [29]. The QAOA structure is classified into two parts: parameterization and classical optimization. A parameterized quantum circuit consists of building a Hamiltonian problem where the proper optimization of the parameters is essential [30]. In a parameterized quantum circuit, the components of the circuit are demonstrated by and the output state . The Quantum Max Cut problem solved by the QAOA needs to optimize the circuit parameters efficiently [31]. The main problem of the QAOA algorithm is that it considers each qubit (qi) as an individual node, which unintentionally limits it from forming clusters in the whole network. For instance, IBM’s 127-qubit Eagle is the biggest quantum computer, yet it has only 127 qubits. Consequently, the highest number of network nodes that can be used is only 127. For a larger network (>127), the above-mentioned algorithm is impractical. To overcome this issue, we present a new CH selection technique based on the Quantum Search Algorithm (QSA) using weighted targets [32,33]. The platform of the QSA is related to Grover’s search algorithm. According to Panchi et al. [34], the probability of obtaining each search target is equal in the traditional quantum search algorithm. In order to resolve this problem, they proposed a weighted target-based quantum search algorithm where the probability of finding each target resembles the corresponding weight coefficient, and it is constituted as a quantum superposition state. If all the sensor nodes are assigned by an individual weight, then it is possible to apply the weighted-based QSA algorithm to select the appropriate cluster head. In addition, we apply this algorithm to select a CH, which efficiently improves the time complexity compared to that of the classical approach. This weighted approach to Grover’s search algorithm has time complexity O (), where n is the number of search items or, in our case, the total number of sensor nodes in the whole network. As mentioned above, it is necessary to have individual weights for each search item in the weighted Grover’s search algorithm, and on that account, we also propose a weight-based algorithm that is similar to the classical approach. Moreover, we compare the CH selections between the classical and quantum search algorithms. Our proposed CH selection via the Grover’s Quantum Weighted Search Algorithm (QWSA) represented the nodes as qubit states, allowing it to cover numerous networks with a limited number of qubits. In our knowledge, this is one of the pioneering works of cluster head selection through Grover’s Quantum Weighted Search Algorithm.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 briefly summarizes the previous clustering algorithms. Section 3 describes the system model, including the network models and energy models. Section 4 demonstrates the detailed approach to CH selection based on weights, a mathematical representation of the quantum weighted search algorithm (QWSA), and its implementation in CH selection. Section 5 presents a performance evaluation of the proposed classical and quantum algorithms, along with results and a discussion. Section 6 concludes the paper and briefly describes the future work and the limitations of this research.
2. Related Work
Among the clustering algorithms, the energy-efficient clustering scheme (EECS) [20] was proposed for effective topology control in wireless sensor networks. Under this protocol, the nodes select a CH at the minimum distance for cluster formation. The CH selection procedure is based on the probability of a certain threshold value between 0 and 1, which is a random process that is similar to the that of the LEACH protocol [35]. A candidate node that is going to become a CH needs to ensure that its residual energy is within radio range . This radio range is inversely proportional to the square root of , which is the optimal range of the CH. Under EECS, the optimal range selection equation is taken from the LEACH protocol, and there is no relation to transmission power for . Therefore, the control of optimum transmission power in the whole network is somehow overlooked. To resolve this problem, the selection of an optimal number of cluster heads is proposed in this work, while managing optimum transmission power. On the other hand, in the EECS cluster formation phase, a complex cost function for distance prioritizes only the cluster-head-to-BS distance, which eventually increases the overhead and time complexity in the whole network. The total control of the given overhead complexity is O(N), and to overcome this, we propose a quantum algorithm for CH selection where the overhead complexity is reduced to O ().
Power-Efficient Gathering in Sensor Information Systems (PEGASIS) [36] is an improvement over the LEACH protocol. The fundamental idea behind PEGASIS is for each node to communicate with and send data to its immediate neighbors, while they take turns acting as the leader, transmitting to the BS. The nodes arrange themselves into a chain by using a greedy algorithm. The data transmission is direct between the leader and the BS within a fixed transmission range. However, an adjustment of the transmission power level in the whole network is not discussed.
Energy-efficient unequal clustering (EEUC) [37] was proposed for multi-hop routing. This clustering technique is based on competition range as a function of the distance to the BS. As the node moves farther from the base station, its competition range becomes narrower. Consequently, reduced cluster sizes are anticipated for the clusters that are closer to the base station. Although this protocol is efficient in intra-cluster communication, inter-cluster communication increases the energy overhead complexity O(N) due to multi-hop routing.
Energy-Efficient Cluster Formation (EECF) [38] is known for being a distributed clustering protocol that considers the node degree and residual energy for cluster head selection. There is no mention of re-adjusting the transmission power level during each round, but a fixed transmission range for at least one cluster head cannot guarantee efficient communications. Like EECS, EECF has a worst-case algorithmic complexity of O(N) at each node.
The Hybrid Energy-Efficient Distributed (HEED) [8] protocol considers CH selection based on the ratio of the estimated current residual energy in a sensor node and its maximum energy. Transmission power level control can be optimized by setting one specific cluster power level for intra- and inter-cluster communications. The connectivity requirement setting cluster range Rt ~ (where n is the total number of nodes) is for a unit square region in intra-cluster communications. However, the probability of connectivity in the whole network does not consider any specific limit on the transmission range, and no detailed explanation is given. Node density () and node degree (d) play essential roles in establishing connectivity in the network, but under the HEED protocol, it is somewhat questionable to not consider those parameters. To resolve this issue, we studied minimum network connectivity where at least one node in the network can connect to achieve the optimum transmission power level depending upon node density. Another important point is to consider the time complexity, which is O(N) per node under this protocol. To the best of our knowledge, there is still no classical algorithm that can improve on this time complexity.
Researchers in quantum computing have been researching quantum algorithms that can outperform classical algorithms. Due to the advancements in quantum hardware and the inherent features of quantum entanglement, quantum computing has demonstrated promising advantages over classical counterparts in a wide range of applications [38]. Grover’s quantum search algorithm has been extensively studied over the past few decades, including theoretical explanations of the algorithm’s effectiveness and its utilization in a variety of problem domains. Quantum computing using Grover’s search algorithm performs a database search, and it quadratically outperforms the classical counterparts in terms of time. Classical NP-hard tasks can be performed on quantum computers in polynomial time, showing a tremendous increase in speed over that of the classical computers [39].
3. System Model
3.1. Network Model
The following properties are used to simplify the network model, with a few reasonable assumptions.
- ✓
- The sensor nodes and the base station are assumed to be stationary once they are deployed in the environment.
- ✓
- The base station is aware of each sensor node’s location.
- ✓
- A sensor node determines its neighbor node(s) within a specific distance.
- ✓
- All sensor nodes are homogeneous in terms of their energy and processing capabilities.
- ✓
- The basic component of intra- and inter-cluster communications is the single hop.
- ✓
- Communication is symmetric, and a sensor node can compute the approximate distance based on the received signal strength if transmission power is given.
- ✓
- Two nodes can communicate with each other via wireless link if they are within range.
- ✓
- The base station is not limited in terms of energy, memory, and computing power.
- ✓
- The sensor nodes are eligible to determine their own power levels via the standard system call [40].
Considering a set of n network nodes, each node is independently and randomly placed in a two-dimensional simulation area (A). A uniform random distribution is used such that for a large network (n) and a large area (A), we can define a constant node density, = , which denotes the expected number of nodes per unit area. A radio link model is assumed in which each node has a specific transmission range to represent wireless communications between the nodes. If two nodes are within range of one another, they can directly communicate through a wireless link. To establish connectivity in the whole network, a necessary condition is that each node has at least one neighbor node () [9]. If the node degree is defined by d(n), then the minimum node degree of a network is denoted as:
Therefore, a node is considered to be isolated if d = 0. From the definition of a k-connected network, each node pair has at least k mutually independent path(s) (k = 1, 2, 3…), and the probability of that network is indicated with P(k-con). In our analysis, we consider k = 1 to represent the probability of a 1-connected network, P(1-con), so a network is steadily connected if P(1-con) ≥ 0.95 [41]. Because we are interested in finding the optimum transmission power for the whole network, it is dependent on the distributed node density () and the contemplated node degree (). If no node is isolated, then the transmission range (r0) can be represented as a function of node density and probable node degree, as proposed by Bettstetter [22].
The transmission range of each node is denoted with . By adding to both sides of Equation (2), we can determine the transmission range as follows [22]:
The significance of this equation is demonstrated by the following example.
Example 1:
Consider a network of totally deployed sensor nodes, n = 100, in a square area, A = 100 m × 100 m, which yields a node density of = .
If the probability of connectivity is P = 0.94, then the transmission range can be calculated with Equation (3):
If the transmission range = 15 m, then Figure 2a depicts two nodes that are isolated. In order to connect at least one of those nodes, the transmission range needs to be modified. For this reason, the probability of connectivity needs to be p (0.95) to reconnect the nodes. Here, we consider p = 0.99. Therefore, the modified transmission range will be:
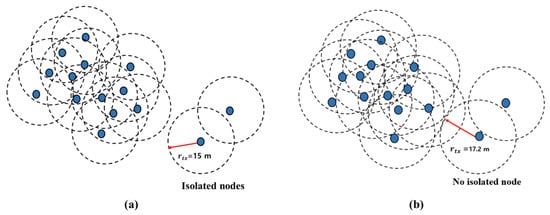
Figure 2.
(a) Isolated nodes are found. (b) By increasing transmission range , connections are established in the whole network, and no isolated nodes are observed.
After increasing the transmission range to 17.12 m, as shown in Figure 2b, the whole network is connected. Therefore, the node degree and the node density are considered in designing an adjustment model of the transmission range to establish an energy-efficient network with full reachability.
3.2. Energy Model
We used a simplified energy model shown in [15] for radio hardware energy dissipation transmitting an -bit message () with distance d as follows:
All parameter descriptions are in Table 1.

Table 1.
The energy model’s parameters and their descriptions.
When receiving data, the radio expends the following [35]:
Additionally, the energy dissipated by the cluster head during a single frame is:
Assuming that there are N nodes which are distributed uniformly, if there are k clusters, then on the average number of nodes per cluster, m = . Each CH dissipates energy by receiving signals from the nodes, collecting the signals, and transmitting the gathered signals to the BS. The energy required in each non-cluster-head node can be expressed by [35]:
4. Proposed Clustering Algorithm
4.1. Expected Number of Clusters
Before the selection of the CH, it is necessary to define the expected number of clusters in the network. Using the following computation and connectivity model, we analytically estimate the expected number of clusters (). Let us assume there are N nodes which are distributed uniformly in area A. The nodes are stationary, and therefore, the density is constant. The transmission area of a sensor node can be assumed to be = , where is the transmission range of the sensor node (from Equation (3)). As mentioned before, transmission range depends on node connectivity and density, and using these two assumptions, the expected number of clusters, , is computed as = . An illustrative example is given to clarify the above assumptions: nodes n = 100, and area A = 100 m × 100 m. Because the nodes are stationary, the node density m−2. From Example 1, we already found that our expected transmission range is 17.12 m. The transmission area of one sensor node will be = = [3.1416 × (17.12)2] = 921 m2. Now, we must calculate the expected number of clusters by dividing the entire sensing area through the obtained transmission area:
4.2. CH Selection Approach (Classical)
Based on the preceding assumptions, in this work, an algorithm called the classical weighted clustering algorithm (CWCA) is proposed to efficiently combine the necessary parameters, such as the node degree, node-to-node average distance, and current residual energy, with certain weighting factors being chosen according to the network system. In wireless networks, for instance, power regulation is crucial, and hence, the weight of the corresponding parameter might be larger. The adaptability from altering the weighted variables enables us to apply this proposed method across different networks. A predefined value/threshold for node degree needs to be set in the clusters to ensure that the cluster heads are not encumbered and that throughput is achieved by optimizing the number of member nodes of each cluster head (the node degree). In addition, the battery power of a sensor node needs to be effectively utilized within a particular transmission range; for instance, communication between the nodes will use less power if they are close to one another. Since a CH is responsible for additional tasks, it uses more battery power than an ordinary node does. It can interact more smoothly with the neighbors within the transmission range and those located closer to it. Due to signal attenuation, communication between the nodes and the CH becomes challenging as the distance increases. According to [42], this has been considered for wireless ad hoc networks, so we modified it, and we propose it for our algorithm. Considering all the above preliminaries, the CH selection procedure consists of the following steps.
- Step 1: Within transmission range, find the neighbors of each node, s, which define their node degree, , as follows:where represents the degree of each sensor node s; S = the set of sensor nodes; n = the neighbors of sensor node s; = the transmission range of sensor node s.
- Step 2: Evaluate the degree difference,, for every node.where = the current node degree of the sensor node, and = the expected or predefined node degree.
- Step 3: Compute the sum of the distances of the member nodes within the transmission range, and find the average distance, :Average distance = .
- Step 4: Compute the residual energy to find the node with the highest energy level:where (s) = the residual energy of node s, and (s) = the initial energy of node s.
- Step 5: Calculate combined weight, , for each node s which might become a CH. The lowest weighted node will be chosen as CH:where , , and are the weight factors for the corresponding system parameters. The node with the minimum weight will be selected as the cluster head, so:
The first component, , or the node degree difference, is the important factor for a CH in order to control several nodes in its cluster. This also ensures that the CH is not overloaded, and the efficiency of the system is retained at the intended level. The second component , is mainly related to energy consumption because more power is required to communicate over a larger distance. It is important to find the node which is located at the center of a cluster. The last component, , contemplates a sensor node’s available battery power. The CH battery drainage will occur quickly compared to that which occurs in other nodes. Within the transmission range, each node compares its energy level with the other nodes. The node with the highest energy level has an increased probability of becoming the CH. Overall, this term is dependent on the node’s starting power along with the power needed over time based on the network traffic. The flowchart for the proposed cluster head selection is presented in Figure 3.
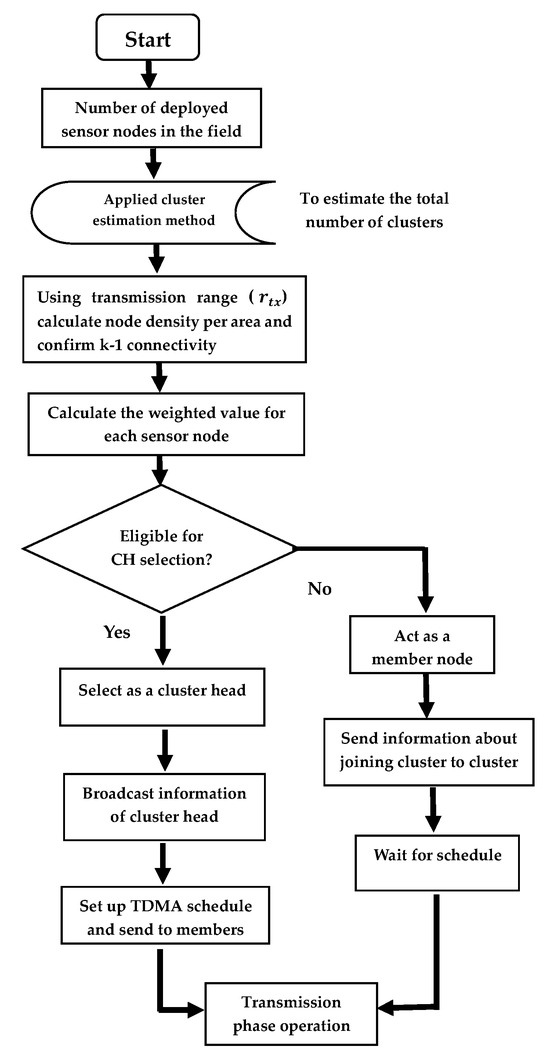
Figure 3.
Flowchart of cluster head selection and cluster formation in the CWCA algorithm.
An Illustrative Example
In our proposed classical weighted algorithm, we assume that 15 nodes are initially deployed in an area 50 m × 50 m, as shown in Figure 4a. The red arrow shows each node’s transmission range (), which is equal for all of the nodes, and the dotted circles represent the transmission area (). Figure 4b identifies the neighbor(s) of sensor nodes within the transmission range . For instance, node 11 has only one neighbor within the transmission range , whereas node 10 and node 2 have five and three neighbor nodes, respectively. Therefore, in Table 2, the current node degree is calculated according to Figure 4b. The degree difference is important and needs to be set, otherwise, some clusters will be heavily loaded, and others will be lightly loaded. To quantitatively determine the well-balanced clusters in our algorithm, we use the following expression for degree difference:
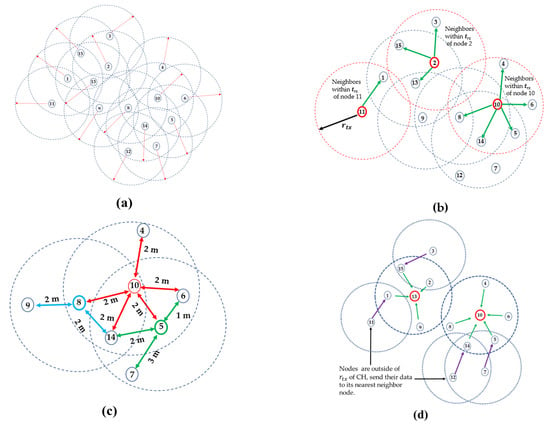
Figure 4.
(a) Initial deployment of sensor nodes; (b) identification of neighbor nodes, (c) an example of the node-to-node distance calculation; (d) identification of the cluster head using the CWCA.

Table 2.
Calculation of CH selection parameters, and implementation of the CWCA.
In this example, the total number of nodes n = 15, the area A = 50 m × 50 m, and the node density m−2 = 0.006 m−2. Hence, no node is isolated, based on Figure 4a, and the probability of connectivity will be 99%. Now, we can determine that our expected transmission range from Equation (3) is 20 m. Therefore, the transmission area of each sensor node (AS = ) will be 1256 m2. The expected number of clusters () for area A can be computed as = 2. From Equation (15), we calculate the expected node degree difference () as 6.5~7. The sum of the distances, , for each sensor node is shown in Figure 4c, where the unit distance was chosen randomly. To ensure that the probable location of the CH is in the center, we consider the average distance, , instead of taking the sum of . Because long-distance communication consumes more energy, minimizes the intra-cluster communication energy consumption. In the next step, we calculate residual energy for the candidate cluster heads. Now, in the final step, the minimum weighted node will be selected as the CH.
The weighting factors which are assumed in order to calculate total weights in Table 2 are = 0.7, = 0.2, and = 0.1 [42]. We note that weighting factors are chosen randomly, such that + + = 1. This is basically used to normalize the appropriate combination of weighting factors, such as the degree difference, the distance from neighboring nodes, and the energy usage. By adjusting the weighting factors, the combination of various eligibility requirements can be set in a suitable way. In our example, node degree has the highest priority as a result, so the weight w1 = 0.7 is chosen to represent the node degree. In this experiment, each node begins with only 1 J of energy. Therefore, the energy ratio is one, as depicted in Table 2 for all of the nodes. From Table 2, the lowest weighted nodes, which are node no. 10 and node no. 13, will be selected as the cluster heads. It is worth mentioning that no two cluster heads are adjacent neighbors. We found that all member nodes of each cluster are quite close to the desired node degree set earlier: . Figure 4d clearly identifies the CHs and the member nodes. The member nodes that are outside of the selected cluster head’s transmission range (nodes 11, 3, 12, and 7) will send their data to the nearest neighbor node within the transmission range.
4.3. CH Selection Approach (Quantum)
Before conducting CH selection through QSA, we must discuss the basics of the weighted Grover’s search algorithm. We want to search for one specific item in a search space that consists of N elements. For instance, we assume N = 2n, which states that the index of the search items can be kept to n bits. Additionally, the search problem has exactly M solutions within the range of 1 The algorithm starts with the state: . The algorithm starts with state which can be transformed into a superposition state via Walsh–Hadamard transformation [34]:
where are the marked states, and the set is Q = . If these marked states have weighted coefficients, which are denoted as , ……. , they must satisfy , , as the denoted degree of significance of each search item. From [34], it can be written as:
Based on Equation (17), the Oracle operator can be stated as follows:
After assigning the weight coefficients in Equation (16), it can be represented by the following expression:
Now multiplying Equation (18) with Equation (19), which gives system state using Oracle operator O and it can be represented as follows:
The iterative equation can be constructed from [43], and the first sub-step of the superposition becomes:
The second sub-step of the equation is:
Now, after inserting the value of into Equation (22), we obtain:
The term above can be written with the following assumptions:
The parameters of Equation (24) are obtained as follows:
V = 1
If is equal to the superposition state, , after some iterations, then the success probability should be equal to one, which means . The success probability can be illustrated after t Grover iterations, as follows [44]:
where CI means integer closest to the real number.
In terms of security perspective, the quantum algorithm is more reliable than the classical algorithm is [45,46]. Quantum algorithms are superior to their classical analogues when the input exists in a superposition state. In our case, all of the node information is encrypted in the superposition state which ensures high degree of security [47].
An Illustrative Example of the Quantum Approach
In our proposed quantum weighted algorithm, as mentioned before, the limitations on the number of qubits are the main obstacles in quantum computing systems. Therefore, we only used an n = 4 qubit system to simulate the performance of our proposed quantum algorithm. Before approaching the quantum part, it is worth mentioning that in some previous research of clustering algorithms, such as EECS, all of the nodes need to send a message to the BS, and the CH needs to send at least three messages, which heavily increases the overhead complexity. Under HEED, a CH probably generates at least N iterations, which is a similar range of time complexity: O(N). Our main approach to implementing a quantum algorithm for CH selection is to reduce the time and overhead complexity. In a quantum computing system, CH selection can be achieved from one to two iterations using Grover’s weighted search algorithm, which reduces overhead complexity to O ().
The above-mentioned nodes, N = 16 = 24, can be formed into a superposition state with four qubits. Therefore, the initial state can be written from Equation (16):
where , represent node 1, node 2, node 3, … node 16, respectively. Our probable CHs are node 10 and node 13 which is the marked state. Grover’s algorithm will search for this marked state within one iteration, which can be proven by the mathematical formulation and IBM’s QISKIT quantum simulation.
In the classical CWCA algorithm, the nodes with the lowest weights, node 10 and node 13, will be eligible for CH selection. However, in a quantum algorithm, the highest weighted node will be selected as the CH. Therefore, to select the CH in the quantum approach, all of the nodes’ corresponding weights need to be inverted, which is called inversion about the mean. In this process, the nodes’ average weights will be calculated, and then, each node’s corresponding weight is subtracted from two times the average value. By this process, we obtain new values for the nodes. From Table 3, we can see that the lowest weight nodes become the highest weighted ones. The target that needs to be found must be the node that has the highest weight under Grover’s search algorithm. Using the traditional search algorithm, the complexity is linear, but Grover’s search algorithm will predict comparatively better complexity. In terms of function, the above expression becomes:

Table 3.
Our quantum algorithm based on weighted target parameters, and its implementation.
Since, Grover’s algorithm based on weighted targets requires
it means the sum of all of the search target node weights should be one. To obtain the sum value of one, it is necessary to normalize the corresponding weight values. Normalization can be performed via the following formula:
where n is the number of candidate nodes. From Table 3, we can see that our candidate nodes are 10 and 13. The sum of their inverted weights is 3.55. As a result, when the normalized weights of node 10 (=0.51) and node13 (=0.49) are added together, they equals one. As mentioned earlier, Equation (16) represents the initial state of the nodes. Our marked state is constructed as follows:
Now, the iteration steps can be found with Equation (28) by applying the original Grover’s algorithm, which comes from [48]:
where m = number of candidate nodes/CH nodes, and N = total number of maximum nodes.
Table 4 shows that when comparing both iteration values, Equation (28) depicts a value that is closer to two. Therefore, it can be stated that the targets from Grover’s weighted search algorithm are more perfect than the original Grover’s search algorithm ones are.

Table 4.
Iterations for finding the target nodes.
5. Performance Evaluation
5.1. Classical Approach
First, we discuss the classical clustering performance evaluation. We are interested in optimizing the transmission range, which depends highly on node density. In a WSN, the nodes are stationary after deployment, but it is necessary to deploy sensor nodes wisely because, in our network model, we introduce the network connectivity equation as a function of the transmission range, which is related to node density and the number of sensor nodes in each cluster.
From Table 5, we can see that the relationship between the expected number of clusters and the transmission range is reciprocal. The transmission range needs to be higher if the expected number of clusters decreases. If we can change the network area, for example A = 100 m × 100 m in Table 5, and if the number of nodes is 100, the node density will be 0.01 m−2, which is an increase from the previous node density. According to the calculation, the transmission range has decreased from 34 m to 17 m, but the number of clusters remains the same. This illustration, along with data from Table 5, demonstrates how the transmission range will decrease as node density increases. Figure 5a shows the relationship between total number of sensor node and transmission range. When the number of clusters increases, transmission range decreases that is depicted in Figure 5b.

Table 5.
Transmission range for a fixed network area and different node densities. (Probability of connectivity is 0.99).
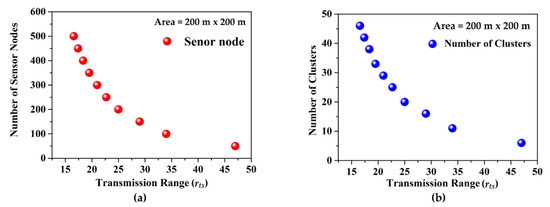
Figure 5.
(a) The relationship between the number of sensor node and transmission range. And (b) the number of clusters and transmission range.
In a practical sense, the selection of the optimum number of clusters should be energy efficient and consume low level of power. In order to select energy-efficient cluster heads, it is essential to calculate the energy consumption between the CH and its member nodes, which is referred to as intra-cluster communications, and between the CH and the BS, which is inter-cluster communications. In the next step, we must characterize intra- and inter-cluster energy consumption, and determine how much energy is saved for different cluster formations through the energy model discussed in Section 3.2. It is worth depicting how, in a cluster, the node consuming the most energy is the CH because it needs to gather information from its member nodes, aggregate their data, and then send them directly to the BS (in our model, we assume that there is single-hop communication with the BS). For this reason, we show the energy dissipation of each member node and the CH separately. In our energy calculation, the power levels of data from the Berkeley CC2420 chip set [49] are used. Before starting the computation, some parameters (showed in Table 6) need to be set (, and , per signal) from [35].

Table 6.
Computation parameters and values.
We consider that one cluster has eight member nodes which need to send one packet of data to the corresponding CH. Therefore, each member node’s transmission energy per packet can be calculated from Equation (8): 43.2 μJ/packet (distance to the CH, = 20 m). In intra-cluster communications, the CH receives a total of eight packets from its member nodes, which consumes 3200 μJ, as calculated from Equation (6). The total energy consumption of intra-cluster communications is shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
Energy calculation of intra-cluster communications.
Table 7 clearly shows that as the number of clusters increases, energy consumption decreases, just as energy savings increase in the network. The next step for energy consumption is from the CH to the BS, (inter-cluster energy consumption). From Equation (7), CH energy consumption can be calculated. The total inter-cluster energy consumption is shown in Table 8.

Table 8.
Energy calculations for inter-cluster communications.
We note that the transmission power level should be at a maximum value for inter-cluster communications. From Table 8, we can see that very low inter-cluster transmission energy is required if the number of clusters increases. Therefore, in both intra- and inter-cluster communications, energy savings is at the highest level when the cluster size increases.
5.2. Quantum Approach (IBM’s Quantum Simulator Results and Discussions)
The second phase of the performance evaluation shows the results from the CH selection formulated using Grover’s weighted search algorithm in IBM’s quantum simulator (QISKIT). In the initialization of this algorithm, the quantum states and are set to an equal superposition state, which can be achieved by implementing a Hadamard gate (H) for each qubit. For this simulation, the algorithm needs five qubits, where one qubit () represents an ancilla/auxiliary qubit that is initialized to state by applying a NOT (X) gate, as shown in Figure 6a. After the implementation of the Hadamard gate (H), the amplitude can be represented by . The next step is to build an Oracle to mark the state. This Oracle can be made by a CZ gate which is a combination of a Hadamard gate and a controlled X (CNOT) gate for a two-qubit system. Our required target states are and , which represent node 10 and node 13. Therefore, to build an Oracle with four qubits, we need to use a quadruple-controlled (cccc-X) gate that can be constructed using a Multi-Controlled Toffoli (MCT) gate, as shown in Figure 6b. Then, we build the circuit by creating a superposition of all of the states, and the final (ancilla) qubit needs to be placed in the state (negative), as required.
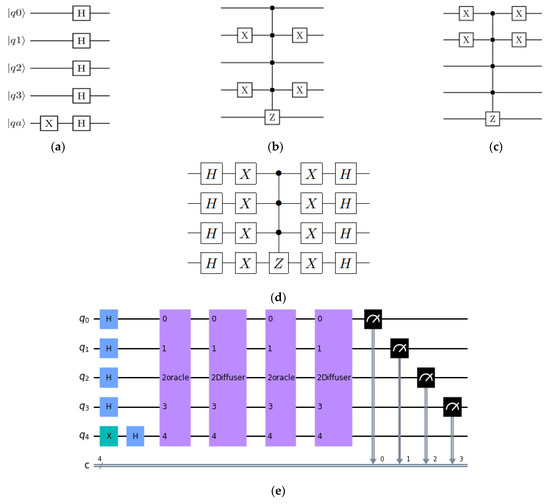
Figure 6.
(a) Initialization of the quantum circuit; (b,c) represent Oracle marked states and , (Note: the #1100 element is marked as (lsb to msb)); (d) the diffusion operator to invert the mean; (e) the complete quantum circuit ready to run on a simulator or quantum system to find the target element with high probability.
The next stage in Grover’s algorithm is related to implementing a diffuser, which is also called the amplification stage, which inverts the average of the amplitudes. This can be accomplished using the formula HRH, in which H is the Hadamard transform, and R is a phase shift transform [39]. The amplitudes of the N possible states associated with the newly decreased mean are inverted by a diffuser. The target state’s negative phase is reversed by this inversion, which also contributes to differentiating the target from the other states. The last and final step is the measurement of the qubits. After conducting this measurement, the qubits are not in the superposition state, and they collapse to give the outcome of one of the possible states.
The execution of the proposed quantum algorithm is performed on IBM’s QasmSimulator, with the results being shown in Figure 7. The marked states are found within () = 2 iterations with 1024 shots, as shown in Figure 7a. If we increase the number of shots to 8192, then the probability of finding the states remains the same at the highest values of the two states.
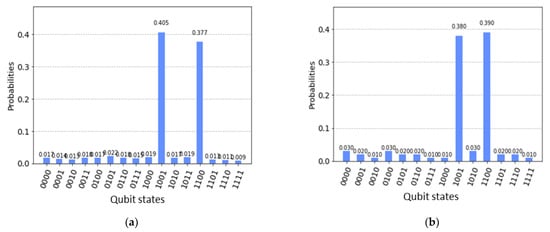
Figure 7.
(a) QasmSimulator results when the number of shots = 1024, and (b) when the number of shots = 8192.
The above results indicate that for the two states, and , the probabilities are 40% and 37%, respectively, which means if we run the algorithm every time, the two states will have the highest probability. Within two iterations, we will reach our probable destination. There are negligible discrepancies between the theoretical values of the iterations and the simulation results because if we increase the iteration values in the simulator, then the probability of success will increase by around 10%, but we can still obtain the same state with the same results. Therefore, we can state that with the two single Grover’s operator, the desired results can be found. The maximum number of iterations for this experiment is O (), where N = 16 nodes. However, here, we can see that within two iterations, we can find our target state. If we increase the number of iterations () of Grover’s operator, the algorithmic success probability (ASP) will be high. In the classical algorithm, in order to find the search state, we need to check each value (in the worst case) for the required time complexity O(N). For time complexity, the quantum algorithm surpasses the classical algorithm in terms of the CH selection procedure. In sum, this reduction in time will improve the overall performance of the network by decreasing the end-to-end delay and power consumption.
6. Conclusions and Future Lines of Research
This paper introduced an optimization approach for a WSN-based hierarchical network with the focus on topology control as a function of the transmission range and power. A new approach to cluster head selection (in both classical and quantum computing) attributed to transmission power will help to establish an energy-efficient network. The factors (the node degree, average distance between nodes, and energy consumption) which are essential for CH selection and proposed for the CWCA algorithm are scalable in terms of weight. MATLAB simulations of the classical algorithm show that around 86% and 97% of the energy efficiency is achievable in the whole network for intra- and inter-cluster communications, respectively. On the other hand, by reducing the time complexity and with a faster search for CH selection, an improved weighted target-based quantum search algorithm was proposed. By implementing the QWSA algorithm, the cluster head can be selected within two iteration steps, which is a favorable agreement between the mathematic approach and the QISKIT simulation result.
A probable limitation of the CWCA technique is that it requires a computationally expensive system when taking into account a large number of cluster heads. It will also be necessary to evaluate the end-to-end reliability and the delay in the sensor data. In addition, it is essential to ensure security in the cluster head selection process such as identify selfish and duplicate nodes. Future research directions will focus on implementing the proposed QWSA algorithm in significant networking systems. Now, the performance is bounded because of the limited number of qubits. For instances, if we increase the number of qubits by two times, we can easily implement this algorithm for about 256 () nodes, and increasing it by three times the number of qubits in the simulation can cover up to 4096 () nodes in the whole network.
We also demonstrated that qubit selection can have a significant impact on how the quantum algorithms are implemented, and researchers will need to pay attention to this when they are trying to accurately implement algorithms in the future. IBM and other experts in quantum computing are continuously enhancing and introducing new quantum devices. In the future, it will be essential to follow the development of these new and advanced devices to gain a sense of how rapidly quantum computing technology is progressing.
Author Contributions
K.R. obtained the analytical results and wrote the paper; M.-K.K. supervised creation of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the 2022 Research Fund of the University of Ulsan.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest related to the publication of this paper.
References
- Maraiya, K.; Kant, K.; Gupta, N. Application Based Study on Wireless Sensor Network. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2011, 21, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, M.; Habib, S.; Javed, A.R.; Rizwan, M.; Srivastava, G.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Lin, J.C.W. Applications of Wireless Sensor Networks and Internet of Things Frameworks in the Industry Revolution 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, F.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Yang, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, D. WSNEAP: An Efficient Authentication Protocol For IIoT-Oriented Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2022, 22, 7413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deverajan, G.; Ramakrishnan, S. Selfish Node Detection Based on Evidence by Trust Authority and Selfish Replica Allocation in DANET. Int. J. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2016, 9, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunathan, V.; Schurgers, C.; Park, S.; Srivastava, M.B. Energy-Aware Wireless Microsensor Networks. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2002, 19, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, T.M.; Samal, U.C.; Mohapatra, S.K.; Khan, M.S.; Appasani, B.; Bizon, N.; Thounthong, P. Energy-Efficient Routing Protocols for Wireless Sensor Networks: Architectures, Strategies, and Performance. Electronics 2022, 11, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, S.; Sennan, S.; Ramasubbareddy, S.; Deverajan, G. Communication Trust and Energy-Aware Routing Protocol for WSN Using D-S Theory. Int. J. Grid High Perform. Comput. 2021, 13, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibreel, F.; Tuyishimire, E.; Daabo, M.I. An Enhanced Heterogeneous Gateway-Based Energy-Aware Multi-Hop Routing Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks. Information 2022, 13, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwieger, K.; Fettweis, G. Multi-Hop Transmission: Benefits and Deficits. In 2. Fachgesprach der GI/ITG Fachgruppe KuVS “Drahtlose Sensornetze” 26./27. Februar 2004 Universitat Karlsruhe (TH); Institute of Telematics, University of Karlsruhe: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M. An Efficient Hole Recovery Method in Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 24th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT), Pyeongchang-gun, Republic of Korea, 13–16 February 2022; pp. 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedor, S.; Collier, M. On the Problem of Energy Efficiency of Multi-Hop vs One-Hop Routing in Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops (AINAW’07), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 21–23 May 2007; Volume 1, pp. 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabet, M.; Naji, H.R. A Decentralized Energy Efficient Hierarchical Cluster-Based Routing Algorithm for Wireless Sensor Networks. AEU—Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2015, 69, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shagari, N.M.; Bin Salleh, R.; Ahmedy, I.; Idris, M.Y.I.; Murtaza, G.; Ali, U.; Modi, S. A Two-Step Clustering to Minimize Redundant Transmission in Wireless Sensor Network Using Sleep-Awake Mechanism. Wirel. Networks 2022, 28, 2077–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakhov, V.; Koo, I. An Efficient Clustering Protocol for Cognitive Radio Sensor Networks. Electronics 2021, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, P.; Chauhan, S. Clustering Protocols in Wireless Sensor Network: A Survey, Classification, Issues, and Future Directions. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2021, 40, 100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, P.; Subramani, N.; Alotaibi, Y.; Alghamdi, S.; Khalaf, O.I.; Ulaganathan, S. Improved Metaheuristics-Based Clustering with Multihop Routing Protocol for Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2022, 22, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Ran, F.; Li, J.; Yan, L.; Shen, H.; Li, A. A Novel Adaptive Cluster Based Routing Protocol for Energy-Harvesting Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2022, 22, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnasamy, L.; Dhanaraj, R.K.; Ganesh Gopal, D.; Reddy Gadekallu, T.; Aboudaif, M.K.; Abouel Nasr, E. A Heuristic Angular Clustering Framework for Secured Statistical Data Aggregation in Sensor Networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Lai, G. Low-Energy Clustering Protocol for Query-Based Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 9135–9145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Li, C.; Chen, G.; Wu, J. An Energy Efficient Clustering Scheme in Wireless Sensor Networks. Ad-Hoc Sens. Wirel. Networks 2007, 3, 99–119. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.H.; Tsai, M.J. A Comment on “HEED: A Hybrid, Energy-Efficient, Distributed Clustering Approach for Ad Hoc Sensor Networks”. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2006, 5, 1471–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettstetter, C. On the Minimum Node Degree and Connectivity of a Wireless Multihop Network. In Proceedings of the 3rd ACM International Symposium on Mobile ad Hoc Networking & Computing, Lausanne, Switzerland, 9–11 June 2002; p. 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Complexity of Data Collection, Aggregation, and Selection for Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2011, 60, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.G.; Chakrabarti, A. Chapter 11—A Novel Graph Clustering Algorithm Based on Discrete-Time Quantum Random Walk. In Quantum Inspired Computational Intelligence; Bhattacharyya, S., Maulik, U., Dutta, P., Eds.; Morgan Kaufmann: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 361–389. ISBN 978-0-12-804409-4. [Google Scholar]
- Manuel, A.J.; Deverajan, G.G.; Patan, R.; Gandomi, A.H. Optimization of Routing-Based Clustering Approaches in Wireless Sensor Network: Review and Open Research Issues. Electronics 2020, 9, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinberg, J.; Tardos, E. Algorithmic Design. In Kleinberg 2006 Algorithm; Pearson Education: Noida, India, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ushakov, A.V.; Vasilyev, I. A Parallel Heuristic for a K-Medoids Clustering Problem with Unfixed Number of Clusters. In Proceedings of the 2019 42nd International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.M.; Amgoth, T.; Pandey, H.M. Particle Swarm Optimization Based Energy Efficient Clustering and Sink Mobility in Heterogeneous Wireless Sensor Network. Ad Hoc Networks 2020, 106, 102237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Oh, S.; Kim, J. Energy-Efficient Cluster Head Selection via Quantum Approximate Optimization. Electronics 2020, 9, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E. Optimizing Quantum Circuit Parameters via SDP. arXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba-Diez, J.; González-Marcos, A.; Ordieres-Meré, J.B. Improvement of Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm for Max–Cut Problems. Sensors 2022, 22, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, P.R.; Korepin, V.E. A Review on Quantum Search Algorithms; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 16, ISBN 1112801717687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.; Tseng, T. Lecture 04: Grover’s Algorithm. In Quantum Computation and Information (15-859BB); Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Panchi, L.; Shiyong, L. Grover Quantum Searching Algorithm Based on Weighted Targets. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2008, 19, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinzelman, W.B.; Chandrakasan, A.P.; Balakrishnan, H. An Application-Specific Protocol Architecture for Wireless Microsensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2002, 1, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, S.; Raghavendra, C.S. PEGASIS: Power-Efficient Gathering in Sensor Information Systems. IEEE Aerosp. Conf. Proc. 2002, 3, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ye, M.; Chen, G.; Wu, J. An Energy-Efficient Unequal Clustering Mechanism for Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mobile Adhoc and Sensor Systems Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 7 November 2005; Volume 2005, pp. 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, R.; Soni, S.K.; Nath, V. Energy Efficient Cluster Head Formation in Wireless Sensor Network. Microsyst. Technol. 2018, 24, 4775–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, L.K. A Fast Quantum Mechanical Algorithm for Database Search. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, STOC ’96, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 22–24 May 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Andersen, M.P.; Chen, K.; Kumar, S.; Zhao, W.J.; Ma, K.; Culler, D.E. System Architecture Directions for Post-SoC/32-Bit Networked Sensors. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Shenzhen, China, 4–7 November 2018; pp. 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettstetter, C. On the Connectivity of Wireless Multihop Networks with Homogeneous and Inhomogeneous Range Assignment. IEEE Veh. Technol. Conf. 2002, 56, 1706–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasai, K.; Ghimire, S. Selection of Weighting Factors in Weighted Clustering Algorithm in MANET. Lect. Notes Eng. Comput. Sci. 2016, 2225, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Ezhov, A.A.; Nifanova, A.V.; Ventura, D. Quantum Associative Memory with Distributed Queries. Inf. Sci. 2000, 128, 271–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushnag, A.; Alessa, A.; Li, M.; Elleithy, K. Directed Diffusion Based on Weighted Grover’s Quantum Algorithm (DWGQ). In Proceedings of the 2015 Long Island Systems, Applications and Technology, Farmingdale, NY, USA, 1 May 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasse, J.-F.; Bonnetain, X.; Kirshanova, E.; Schrottenloher, A.; Song, F. Quantum Algorithms for Attacking Hardness Assumptions in Classical and Post-Quantum Cryptography. IET Inf. Secur. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peelam, M.S.; Johari, R. Enhancing Security Using Quantum Computing (ESUQC). In Proceedings of the Machine Learning, Advances in Computing, Renewable Energy and Communication; Tomar, A., Malik, H., Kumar, P., Iqbal, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Chamoli, A.; Bhandari, C.M. Grover’s Algorithm Based Multi-Qubit Secret Sharing Scheme. arXiv 2007, preprint. arXiv:0707.1042. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, Y.; Kang, Y.; Heo, J. Quantum Search Algorithm for Weighted Solutions. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 16209–16224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieee, G.; Transceiver, Z.R.F. Cc2420: Single-Chip 2.4 GHz IEEE 802.15.4 Compliant and ZigBeeTM Ready RF Transceiver; Texas Instruments: Dallas, TX, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).