An End-to-End Robust Video Steganography Model Based on a Multi-Scale Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
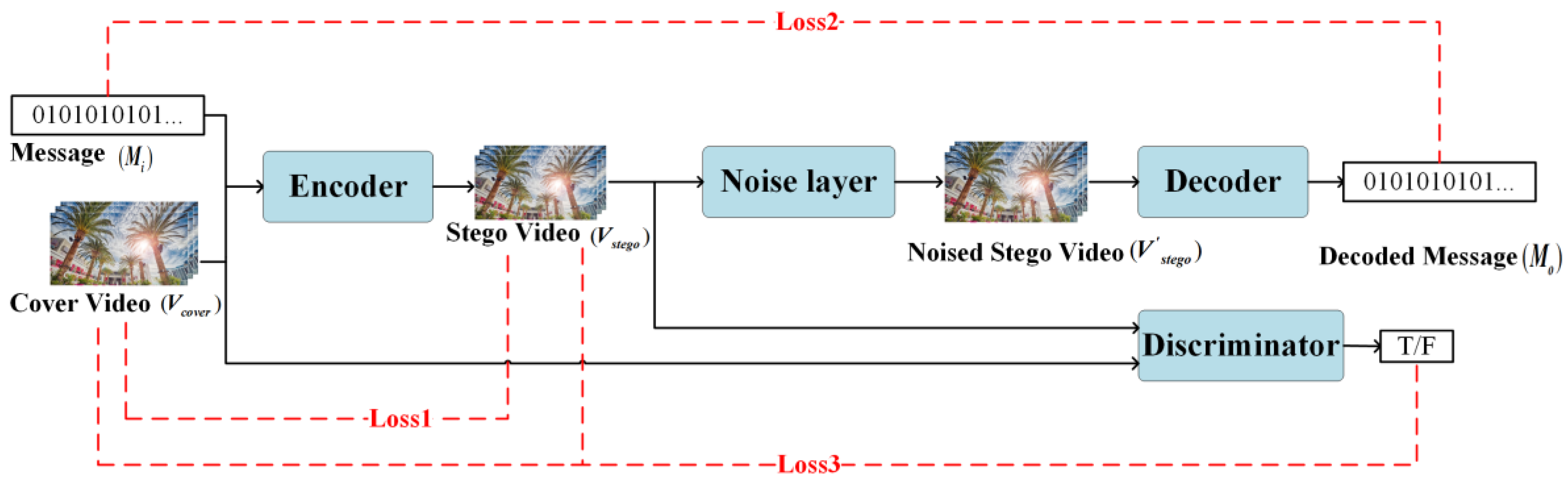
2. Proposed End-to-End Video Steganography Network
2.1. The Architecture of the End-to-End Video Steganography Model
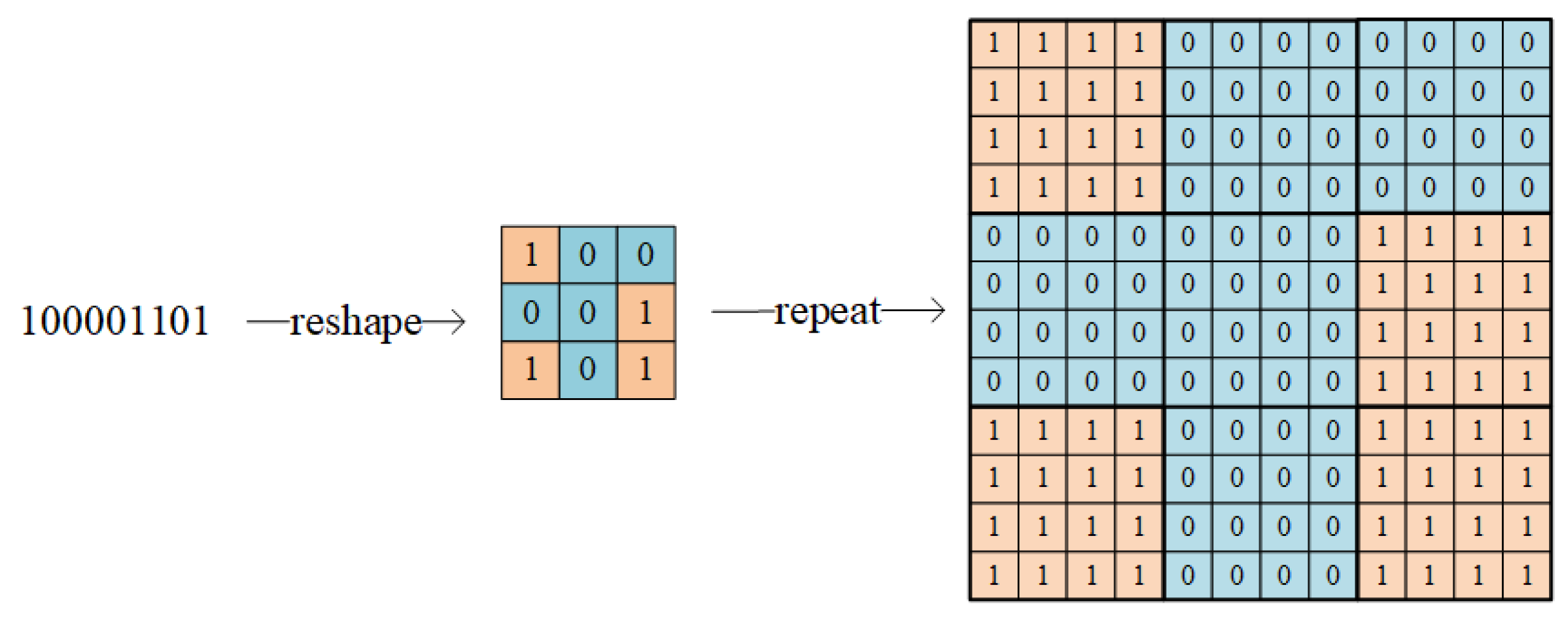
2.1.1. Encoder Network Design
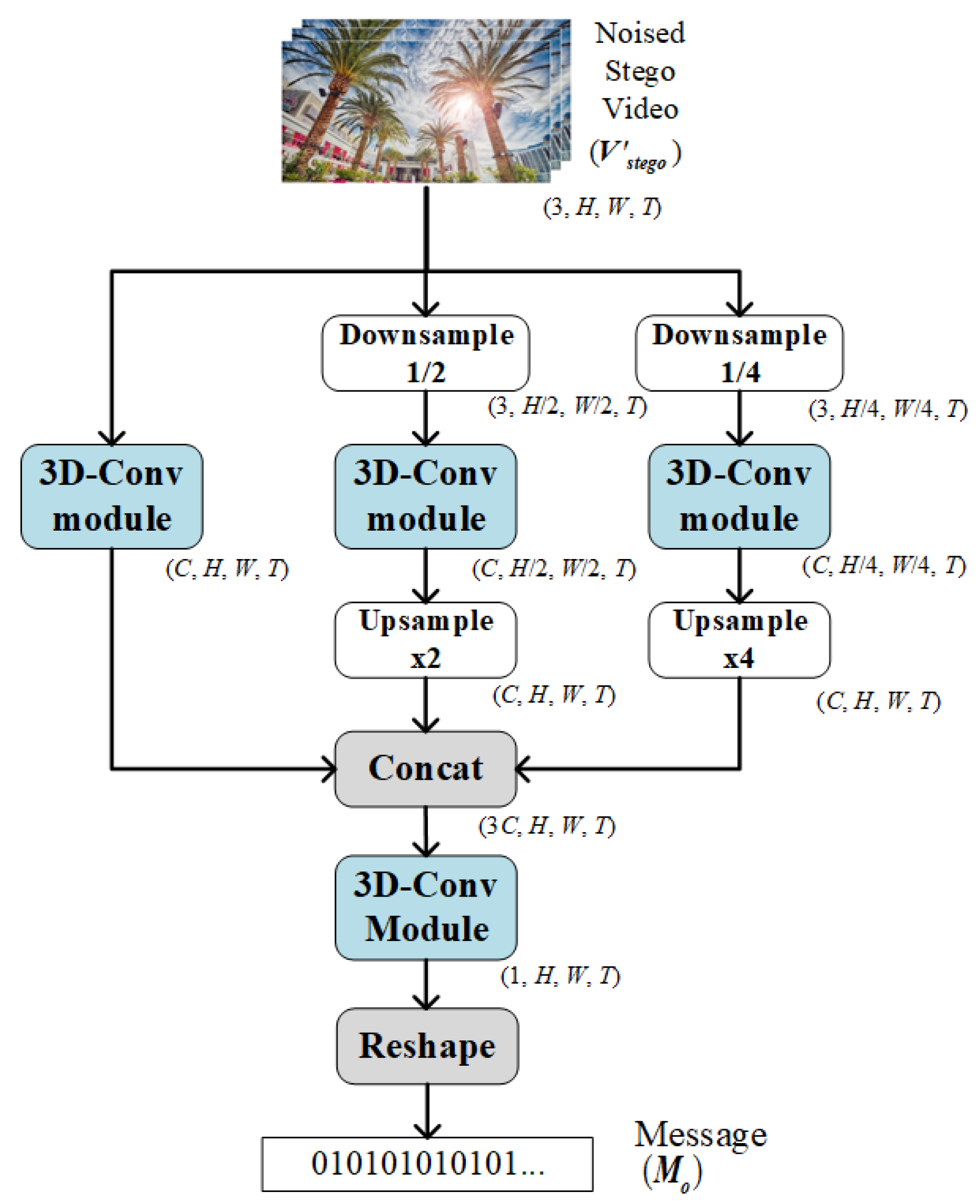
2.1.2. Decoder Network Design
2.1.3. Discriminator Network Design
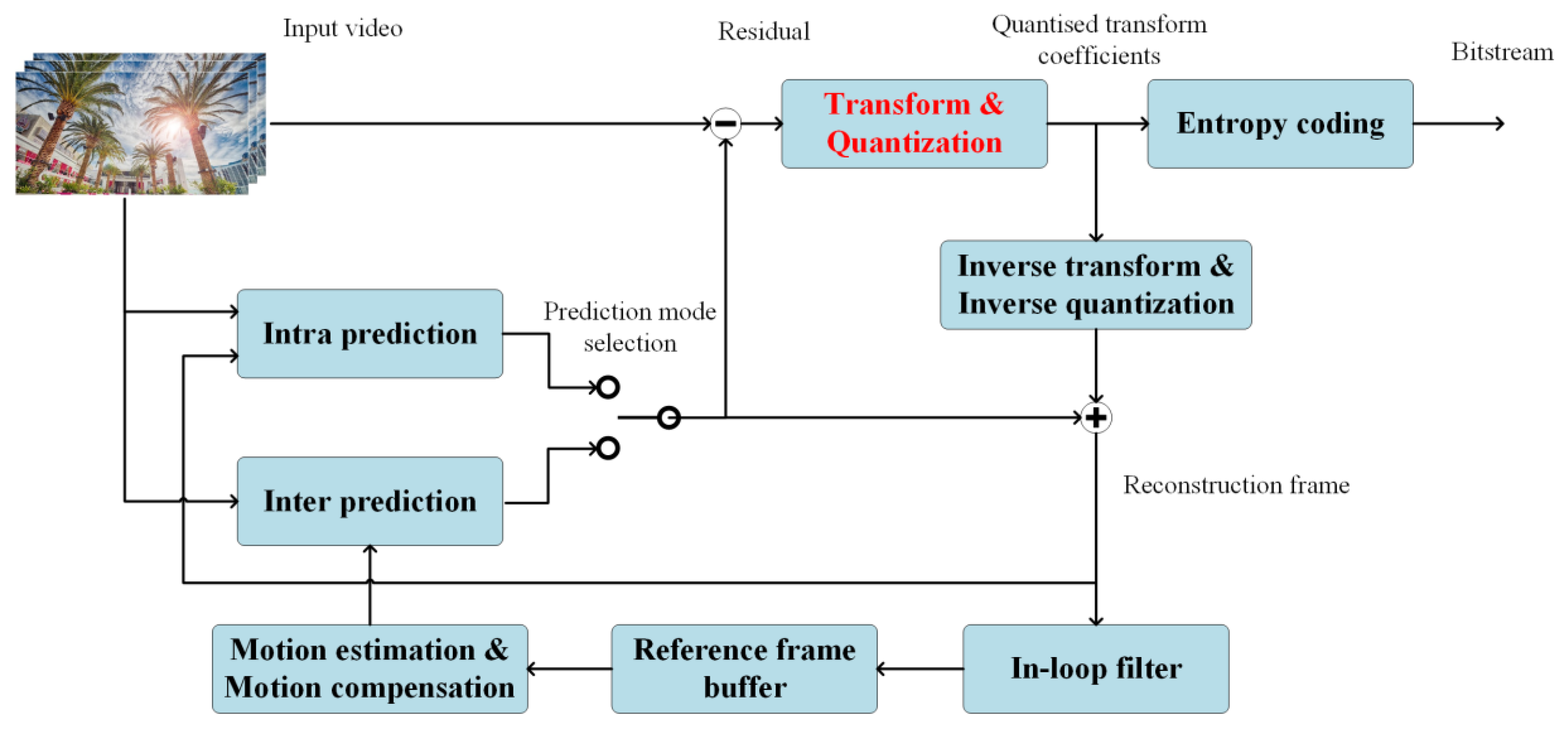
2.1.4. Noise Layer Design
2.2. Loss Function
- Loss1 () which constrains the encoder uses mean square error (MSE) as Equation (5). The purpose of is to make the stego video as similar to the cover video as possible. Note that the loss function compares two videos, so the number of frames T will be calculated in the formula. We have
- Loss2 () uses cross entropy loss to measure the message extraction ability of the decoder. The more consistent the input message and decoded message are, the smaller the . We have
- In Equation (7), and are judgment results from the discriminator for cover video and stego video respectively. The range of and is 0 to 1. If it is greater than 0.5, it means that this video is judged to be a stego video, otherwise this video is judged to be a cover video. Therefore, the smaller the , the stronger the steganalysis ability of the discriminator. We have
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.1. Evaluation Indicators
3.2. Performance of the Proposed Model
3.2.1. Experimental Results without Noise Layer
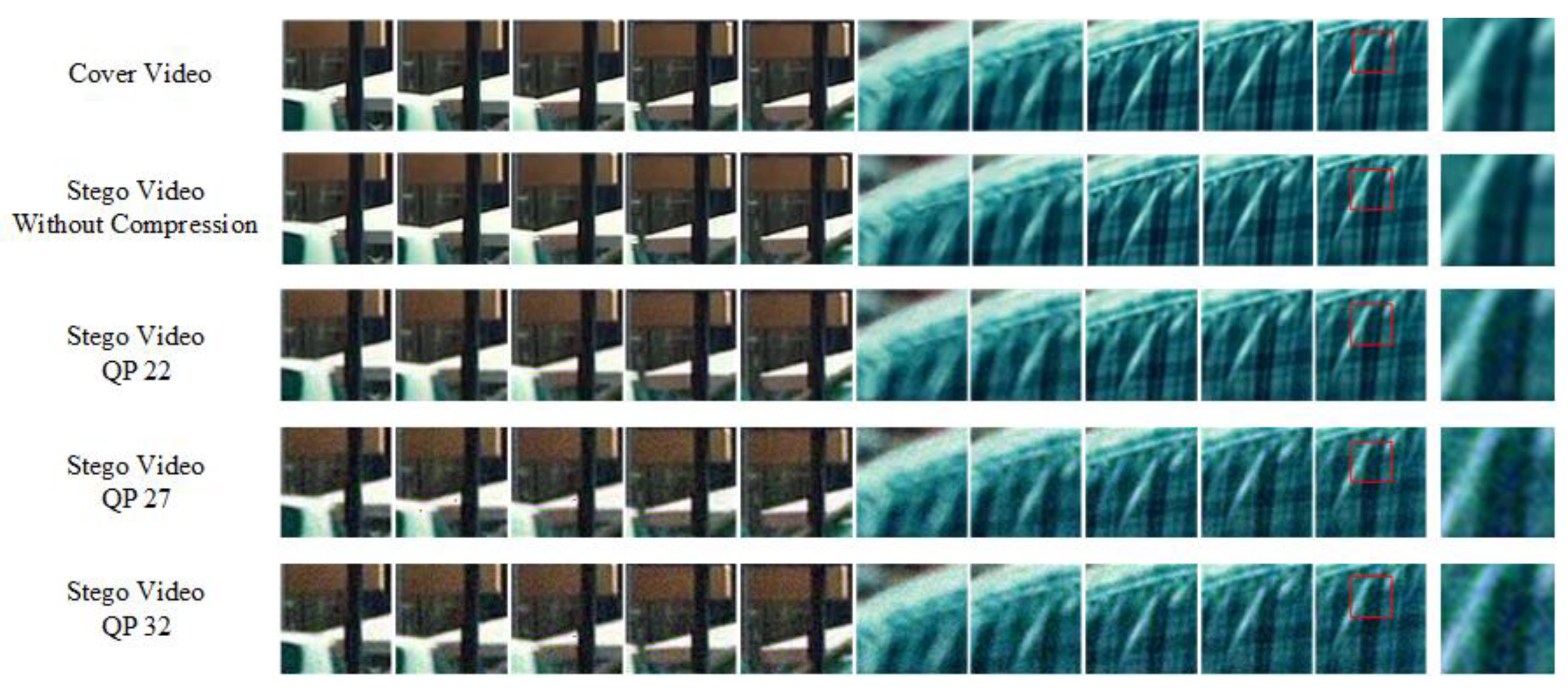
3.2.2. Experimental Results with Noise Layer
3.3. Comparison Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, J.; Kaplan, R.; Johnson, J. HiDDeN: Hiding Data with Deep Networks. Comput. Vis. ECCV 2018, 11219, 682–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluja, S. Hiding images in plain sight: Deep steganography. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 2066–2076. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, J.; Danezis, G. ste-GAN-ography: Generating Steganographic Images via Adversarial Training. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1406.2661. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.A.; Cuesta-Infante, A.; Xu, L. SteganoGAN: High Capacity Image Steganography with GANs. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.03892. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Liao, X.; Liu, J.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, H. Channel Attention Image Steganography with Generative Adversarial Networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 888–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M. Generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, N.; Cheheb, I.; Elharrouss, O.; Al-Maadeed, S.; Bouridane, A. End-to-End Image Steganography Using Deep Convolutional Autoencoders. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 135585–135593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Li, Y.; Chi, L.; Mu, Y. Convolutional Video Steganography with Temporal Residual Modeling. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.02941. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Chang, H. DVMark: A Deep Multiscale Framework for Video Watermarking. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.12734. [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand, T.; Sullivan, G.J.; Bjontegaard, G.; Luthra, A. Overview of the h. 264/avc video coding standard. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2003, 13, 560–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.A.; Xu, L.; Cuesta-Infante, A. Robust Invisible Video Watermarking with Attention. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.01285. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, H.; Li, Z.; Li, F.; Zhang, Z. An End-to-End Video Steganography Network Based on a Coding Unit Mask. Electronics 2022, 11, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhu, D.; Min, X.; Hu, M.; Zhai, G. RIVIE: Robust Inherent Video Information Embedding. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancik, M.; Mildenhall, B.; Ng, R. StegaStamp: Invisible Hyperlinks in Physical Photographs. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2114–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, X. A Novel Two-stage Separable Deep Learning Framework for Practical Blind Watermarking. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Fang, H.; Zhang, W. MBRS: Enhancing Robustness of DNN-based Watermarking by Mini-Batch of Real and Simulated JPEG Compression. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Mou, C.; Hu, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhang, J. Robust Invertible Image Steganography. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 7865–7874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ying, Q.; Zhang, X.; Qian, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, X. Robust Watermarking for Video Forgery Detection with Improved Imperceptibility and Robustness. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.03409. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Gao, Z.; Chen, K.; Hu, M.; Min, X.; Zhai, G.; Yang, X. RIHOOP: Robust Invisible Hyperlinks in Offline and Online Photographs. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 7094–7106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Wang, N.; Chen, T. Empirical evaluation of rectified activations in convolutional network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.00853. [Google Scholar]
- Santurkar, S.; Tsipras, D.; Ilyas, A. How does batch normalization help optimization? arXiv 2019, arXiv:1805.11604. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Laurens, V. Densely Connected Convolutional Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosewarne, C. High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) Test Model 16 (HM 16) Improved Encoder Description Update 6. In Proceedings of the 24th Meeting, Geneva, Switzerland, 30 May–3 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kizilkan, Z.B.; Sivri, M.S.; Yazici, I.; Beyca, O.F. Neural Networks and Deep Learning. Bus. Anal. Prof. 2022, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Karjauv, A.; Benz, P. Towards Robust Data Hiding Against (JPEG) Compression: A Pseudo-Differentiable Deep Learning Approach. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2101.00973. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, T.; Chen, B.; Wu, J. Video Enhancement with Task-Oriented Flow. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.09078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.C.; Wang, S.; Quan, Z.Y. Design of MJPEG2000 HD Video Codec. TV Eng. 2005, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Method | Cover Size | BPP | PSNR (dB) | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ours | 5 × 64 × 64 | 1.0 | 43.036 | 1.000 |
| PyraGAN [12] | 256 × 256 | 1.0 | 43.109 | 0.994 |
| QP | Method | PSNR (dB) (before Compression) | PSNR (dB) (after Compression) | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | Ours | 38.493 | 31.894 | 0.976 |
| Ours (no noise layer) | 43.222 | 38.685 | 0.616 | |
| PyraGAN [12] | 42.419 | 39.200 | 0.514 | |
| 27 | Ours | 35.777 | 29.026 | 0.968 |
| Ours (no noise layer) | 43.097 | 38.870 | 0.520 | |
| PyraGAN [12] | 42.419 | 36.356 | 0.504 | |
| 32 | Ours | 32.473 | 27.029 | 0.795 |
| Ours (no noise layer) | 43.036 | 37.010 | 0.520 | |
| PyraGAN [12] | 42.419 | 33.189 | 0.501 |
| Compression Standard | Method | Cover Size | Length of Message (Bits) | BPP | PSNR (dB) (before Compression) | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H.264 (CRF = 22) | DVMark [9] | 8 × 128 × 128 | 96 | 0.000732 | 36.50 | 0.980 |
| Ours | 8 × 128 × 128 | 100 | 0.000763 | 42.25 | 0.990 | |
| H.264 (CRF = 23) | Jia’s [13] | 400 × 400 | 100 | 0.000625 | 40.28 | 0.977 |
| Ours | 5 × 400 × 400 | 5×100 | 0.000625 | 41.10 | 0.998 | |
| MJPEG | RIVAGAN [11] | 8 × 128 × 128 | 256 | 0.001953 | 42.05 | 0.992 |
| Ours | 8 × 128 × 128 | 256 | 0.001963 | 45.19 | 0.994 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J. An End-to-End Robust Video Steganography Model Based on a Multi-Scale Neural Network. Electronics 2022, 11, 4102. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11244102
Xu S, Li Z, Zhang Z, Liu J. An End-to-End Robust Video Steganography Model Based on a Multi-Scale Neural Network. Electronics. 2022; 11(24):4102. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11244102
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Shutong, Zhaohong Li, Zhenzhen Zhang, and Junhui Liu. 2022. "An End-to-End Robust Video Steganography Model Based on a Multi-Scale Neural Network" Electronics 11, no. 24: 4102. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11244102
APA StyleXu, S., Li, Z., Zhang, Z., & Liu, J. (2022). An End-to-End Robust Video Steganography Model Based on a Multi-Scale Neural Network. Electronics, 11(24), 4102. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11244102





