Two-Neuron Based Memristive Hopfield Neural Network with Synaptic Crosstalk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Simplest Hyperbolic Memristive Synapse-Coupled HNN
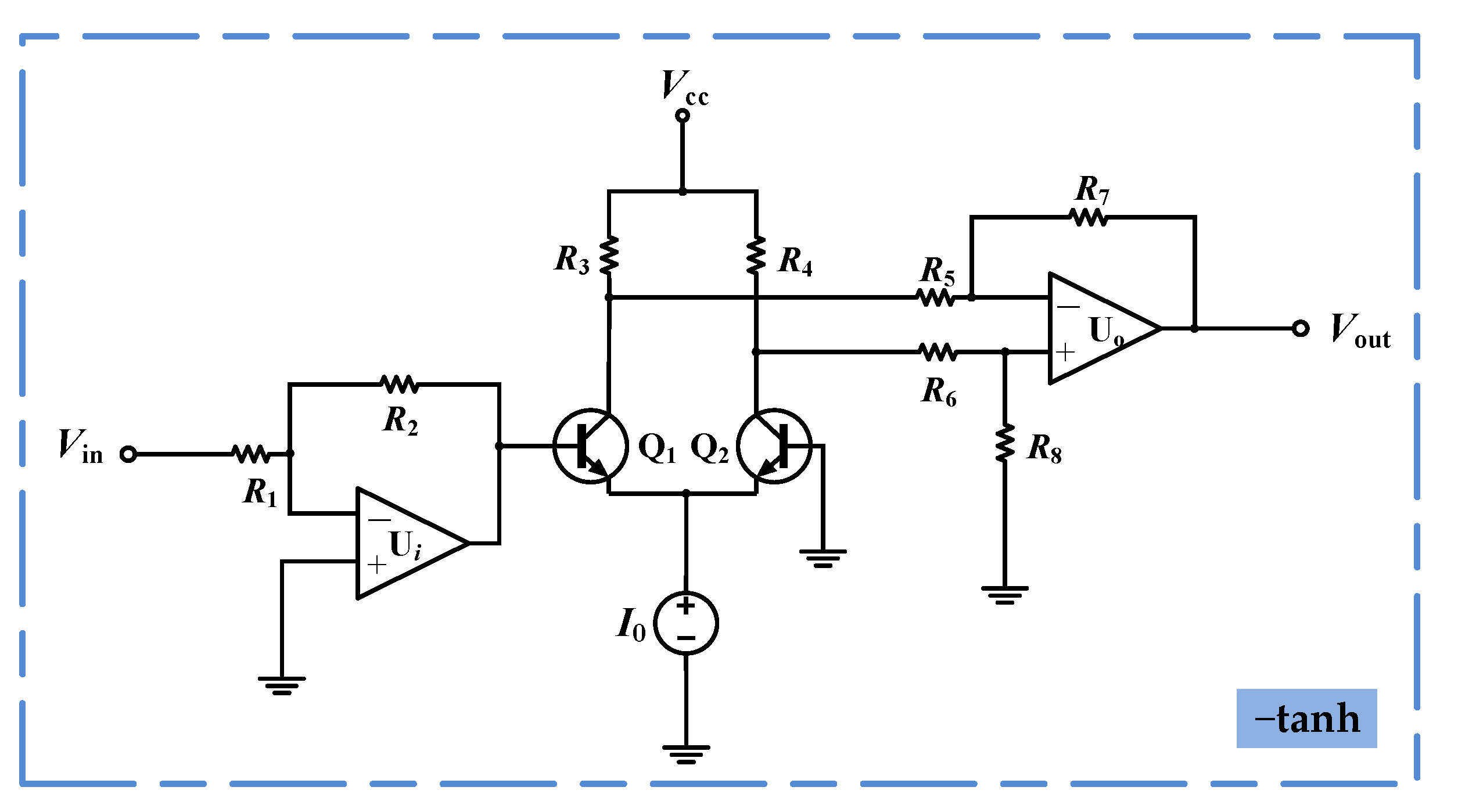
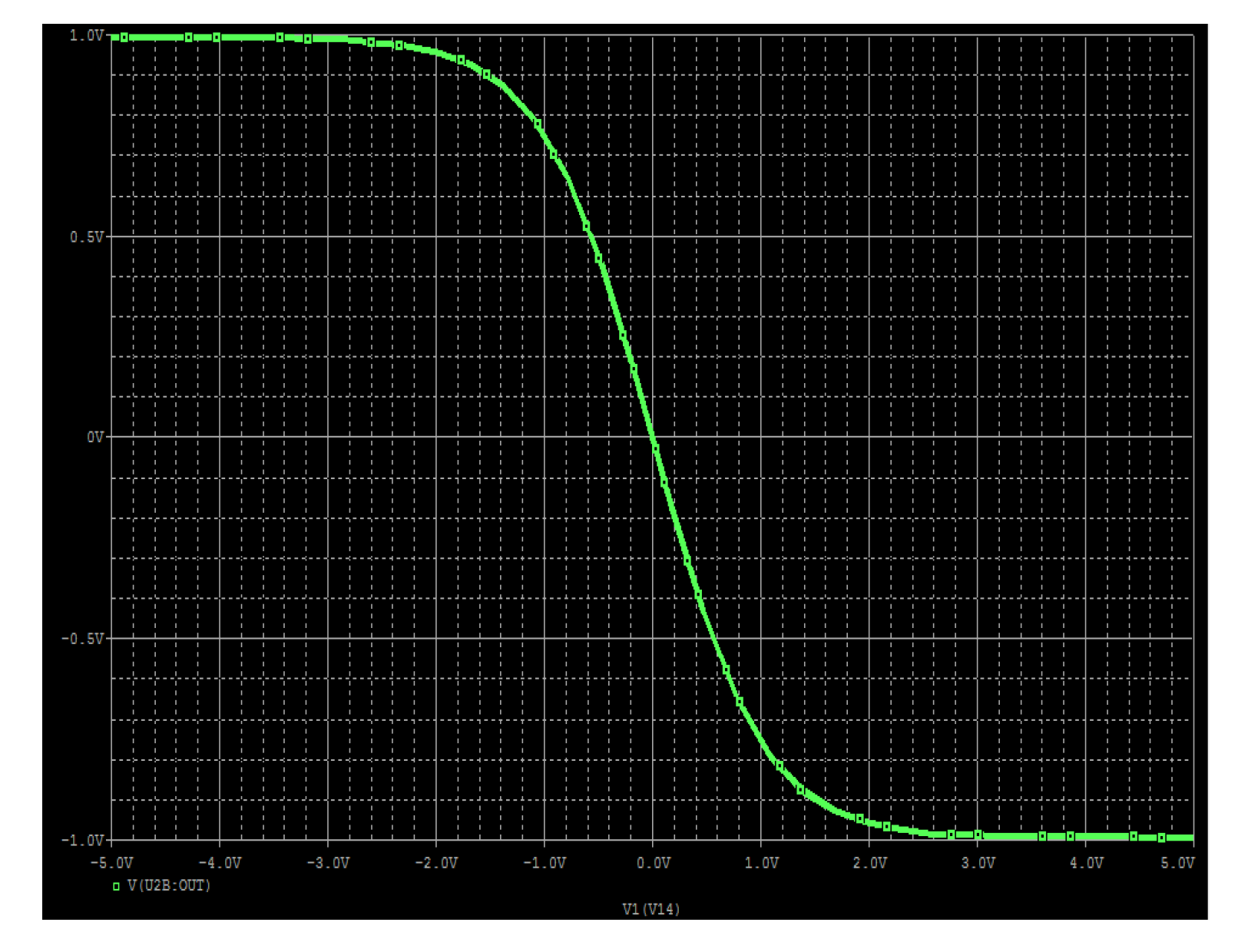
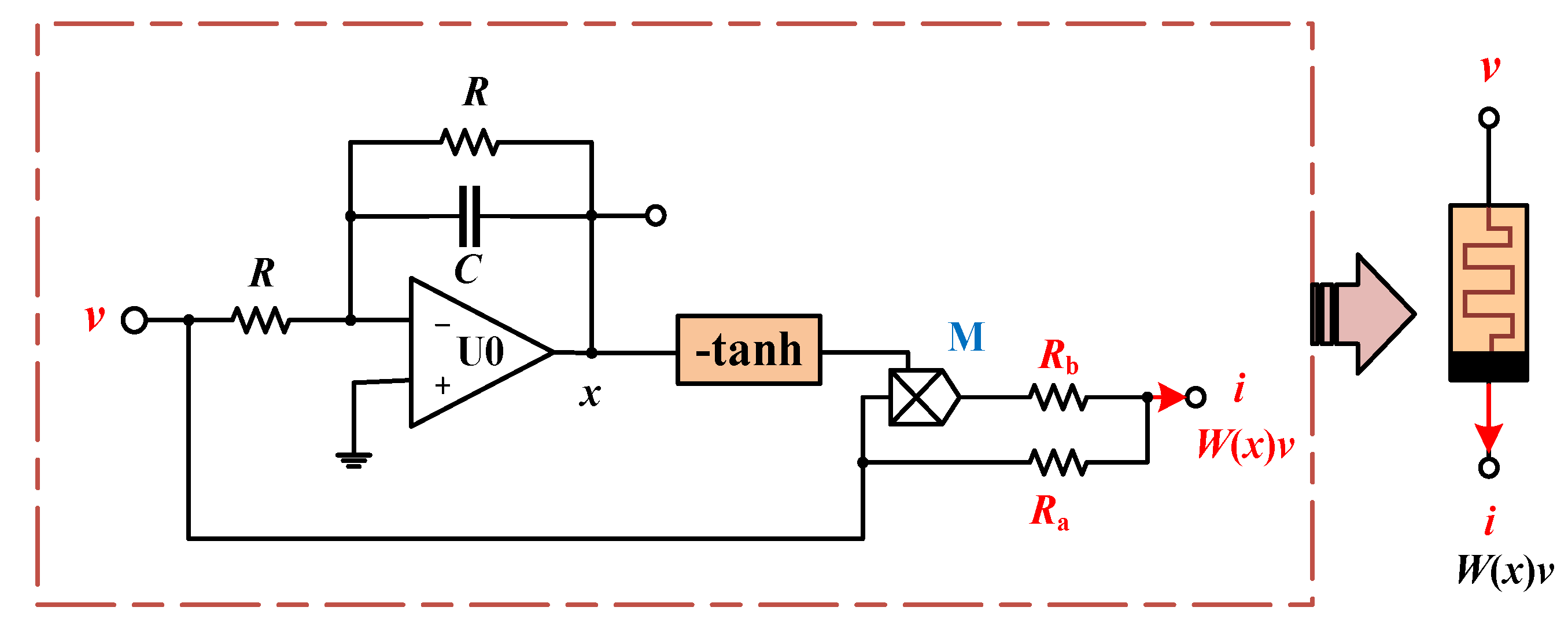
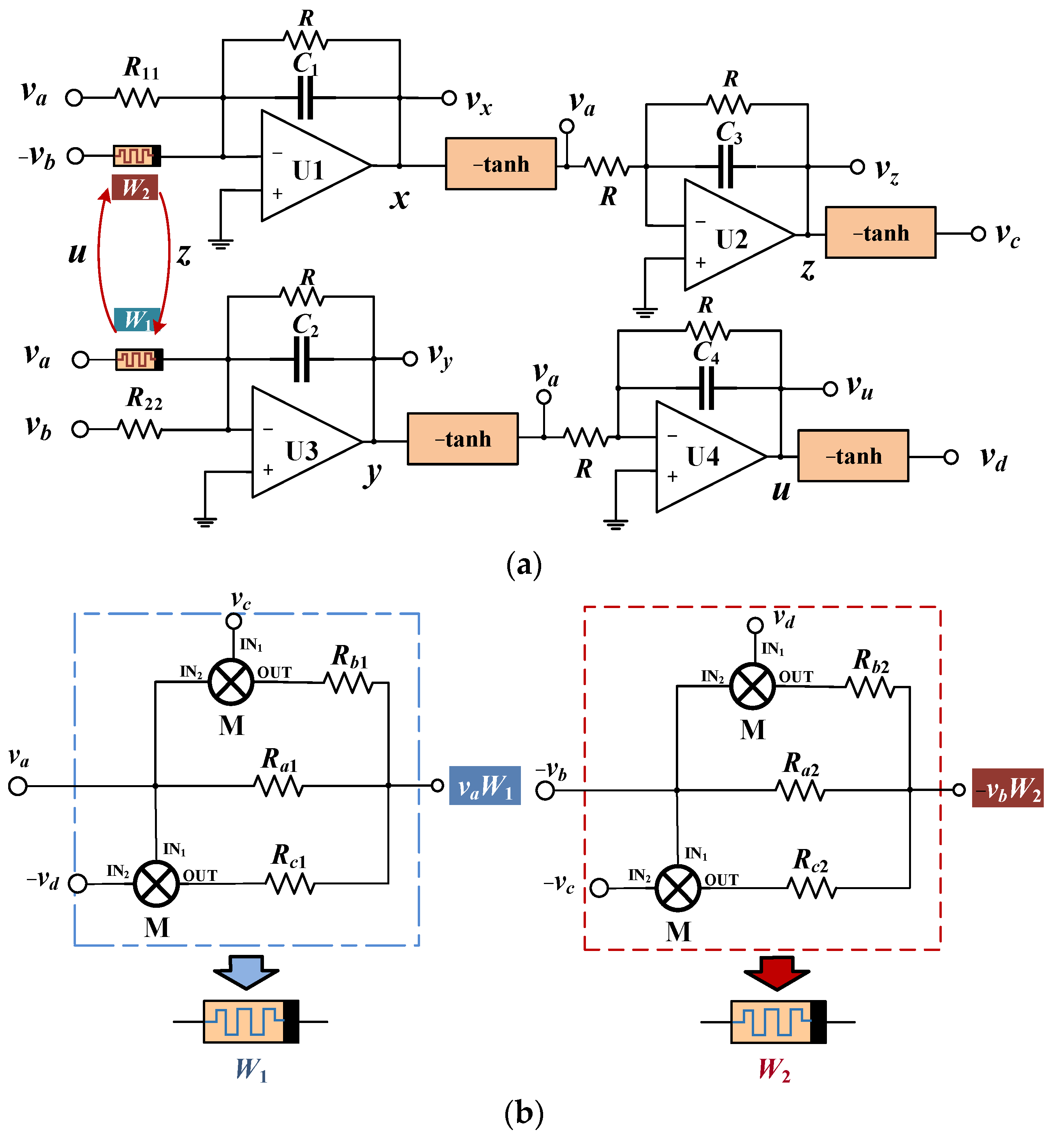
2.1. Hyperbolic Memristive Synapse Emulator
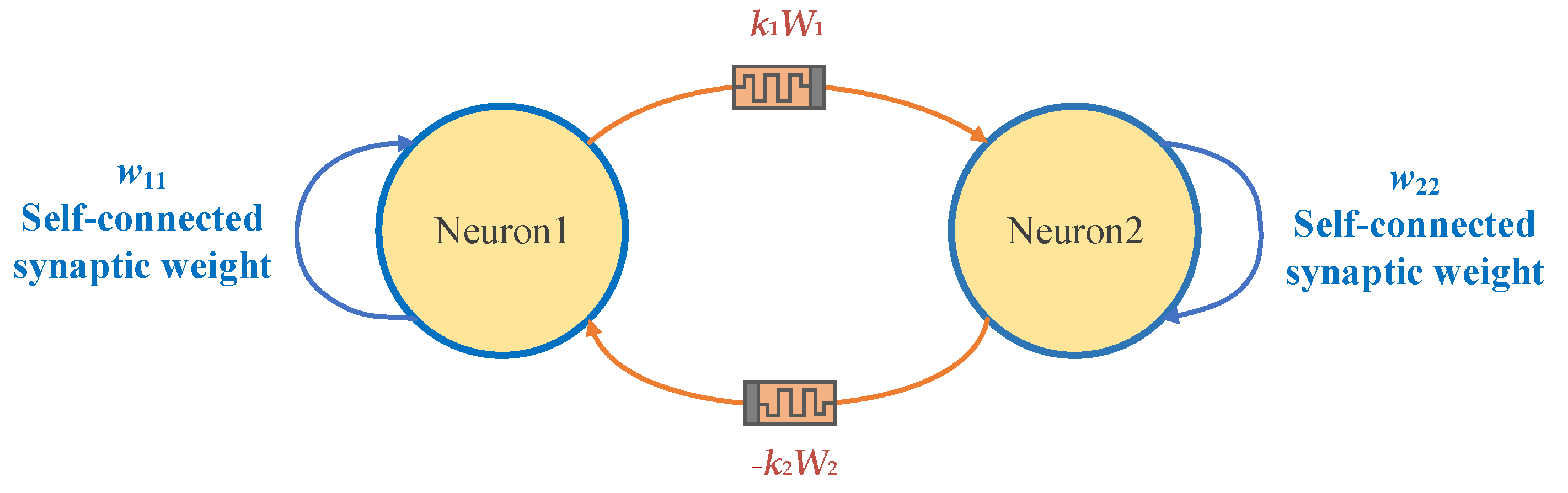
2.2. Two Neurons-Based HNN Model
3. Dissipativity and Stability of HNN
3.1. Dissipativity Analyses
3.2. Stability Analyses
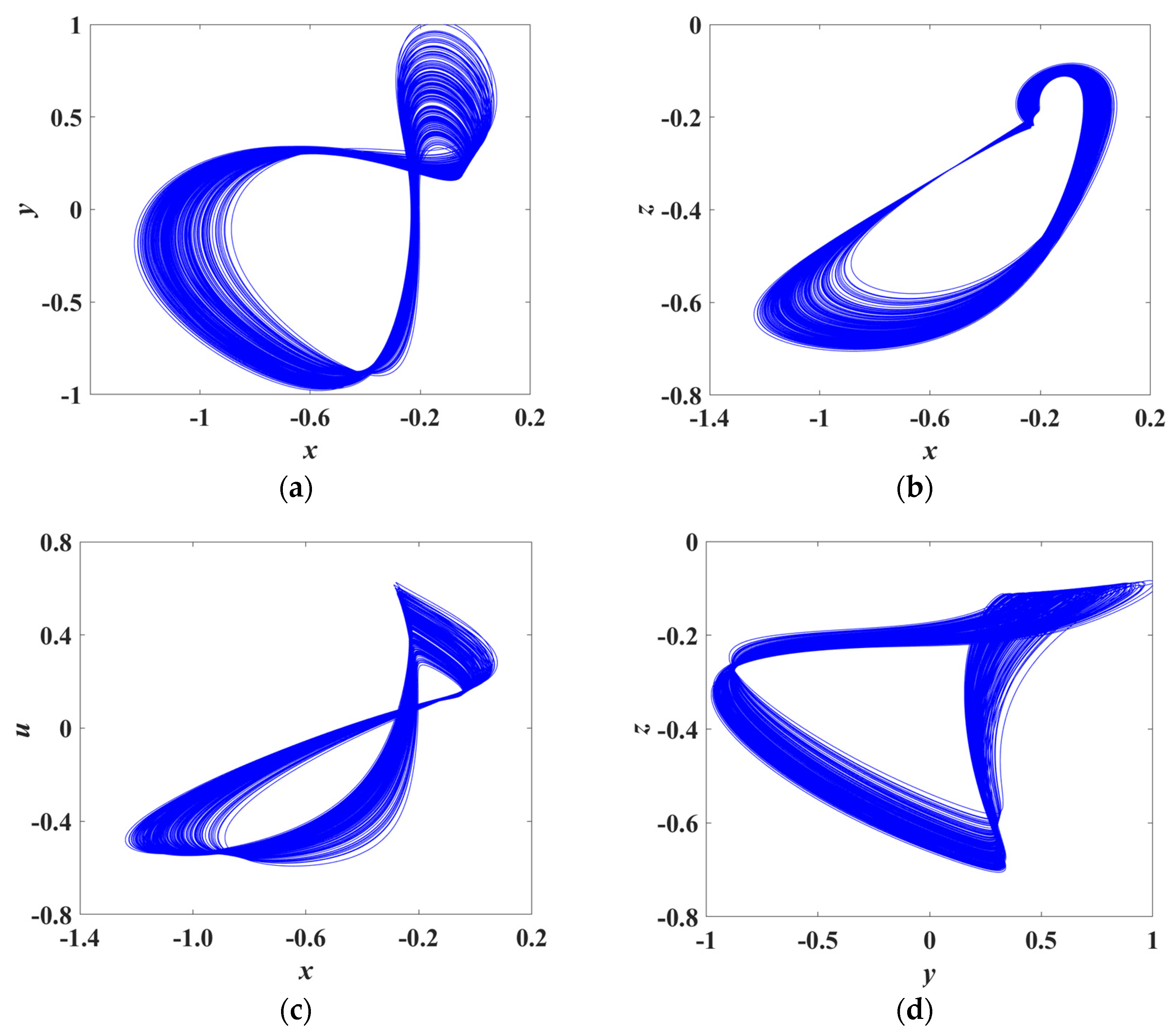
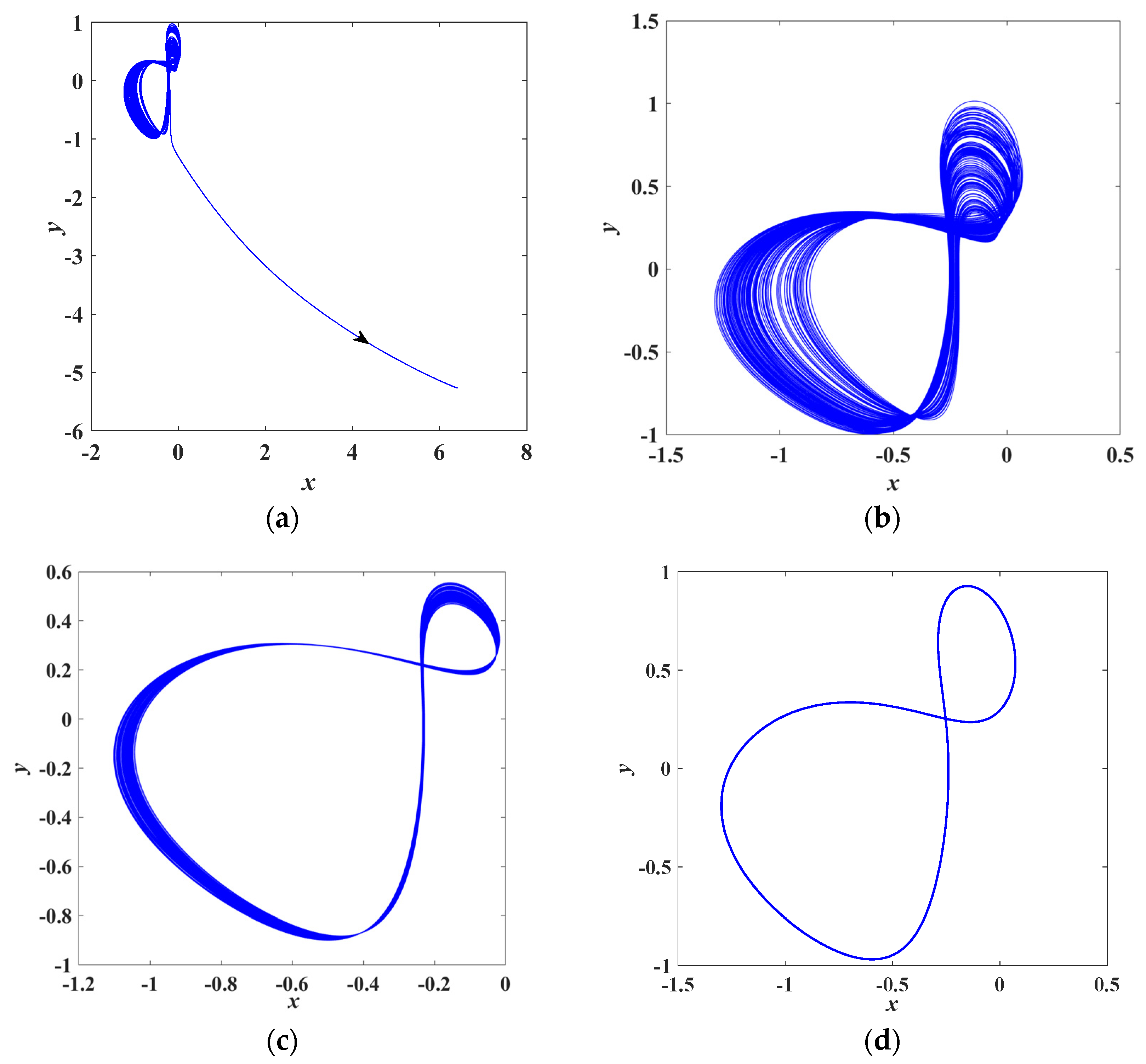
3.3. Chaotic Behaviors
4. Dynamics Varying with Parameters
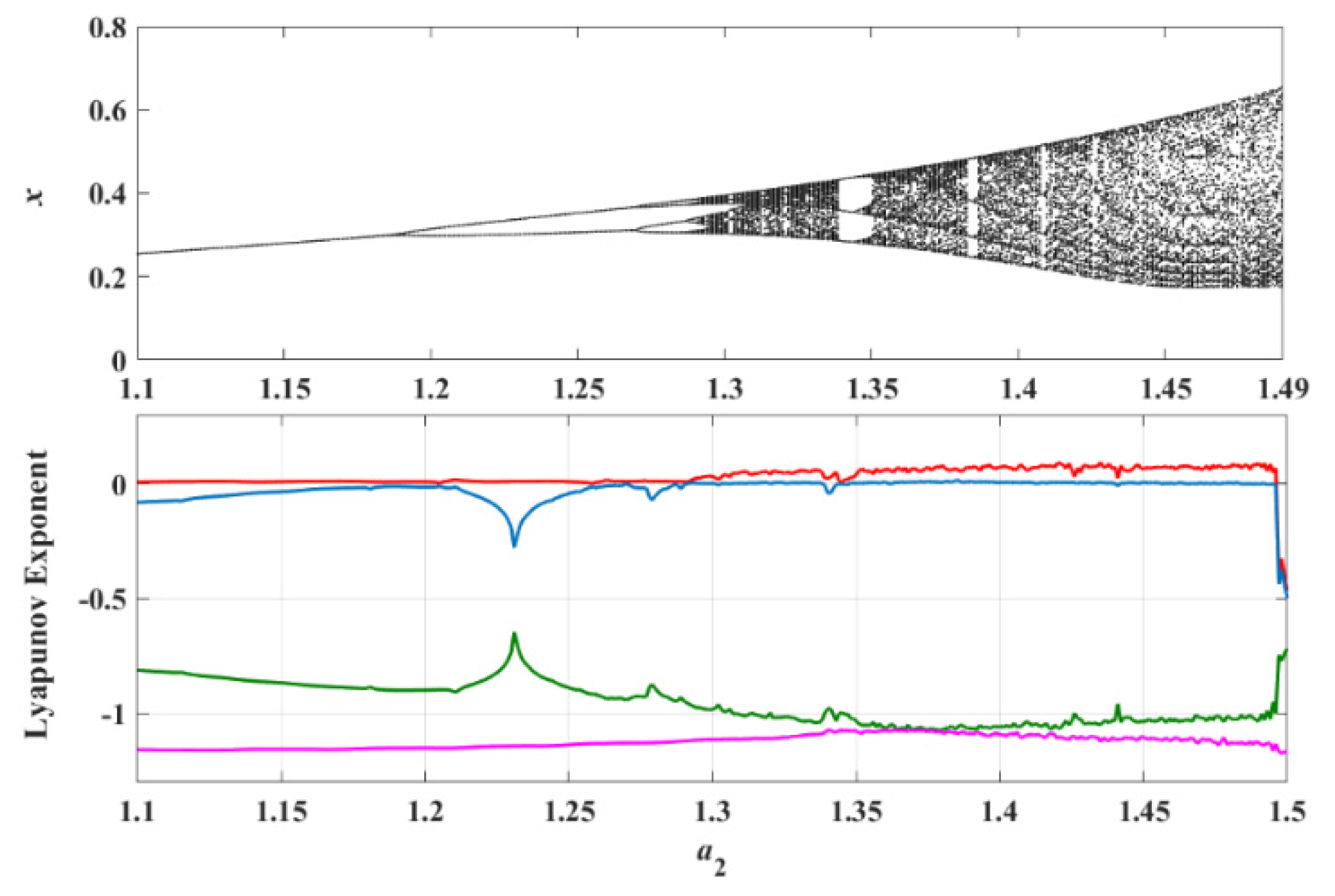
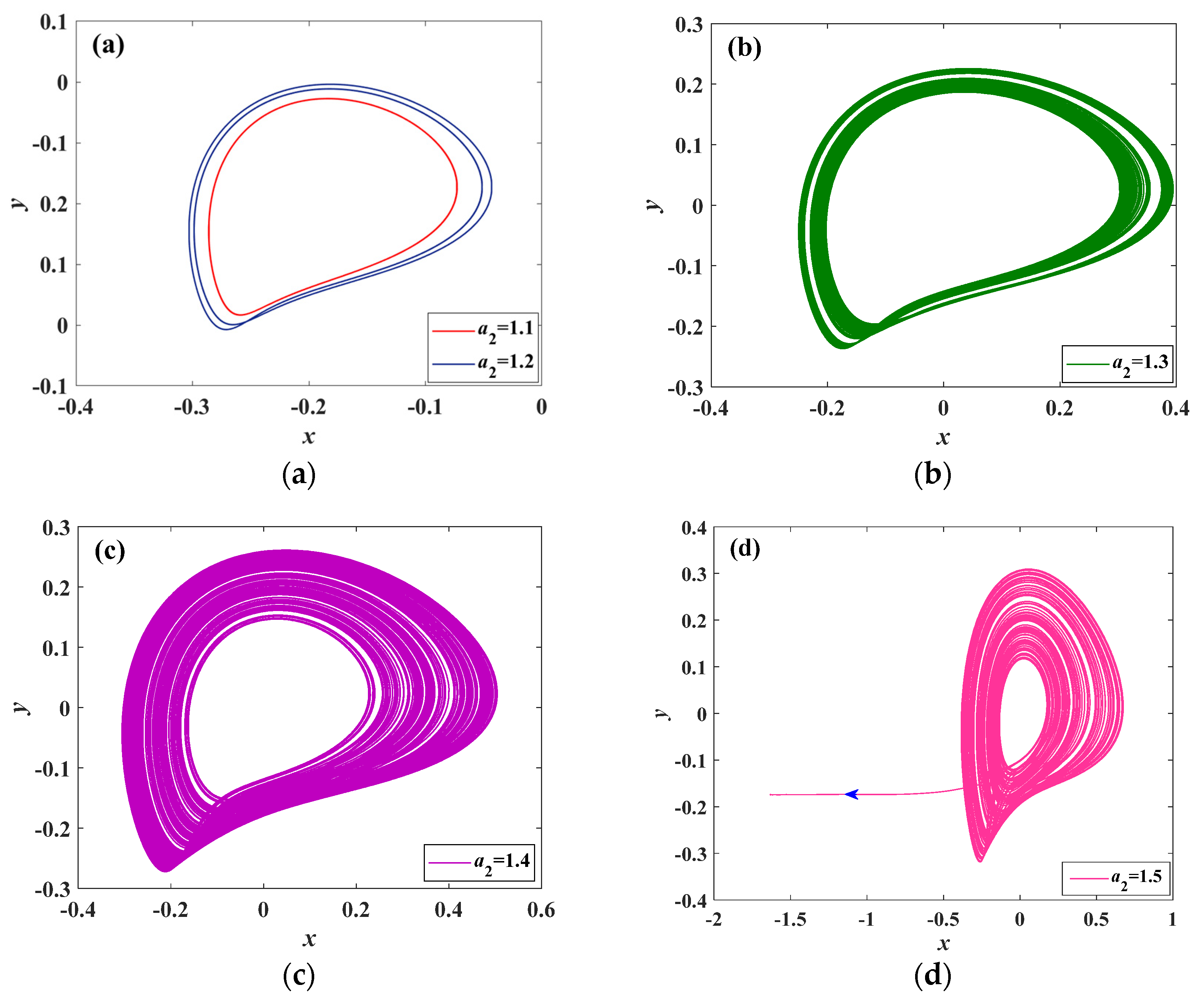
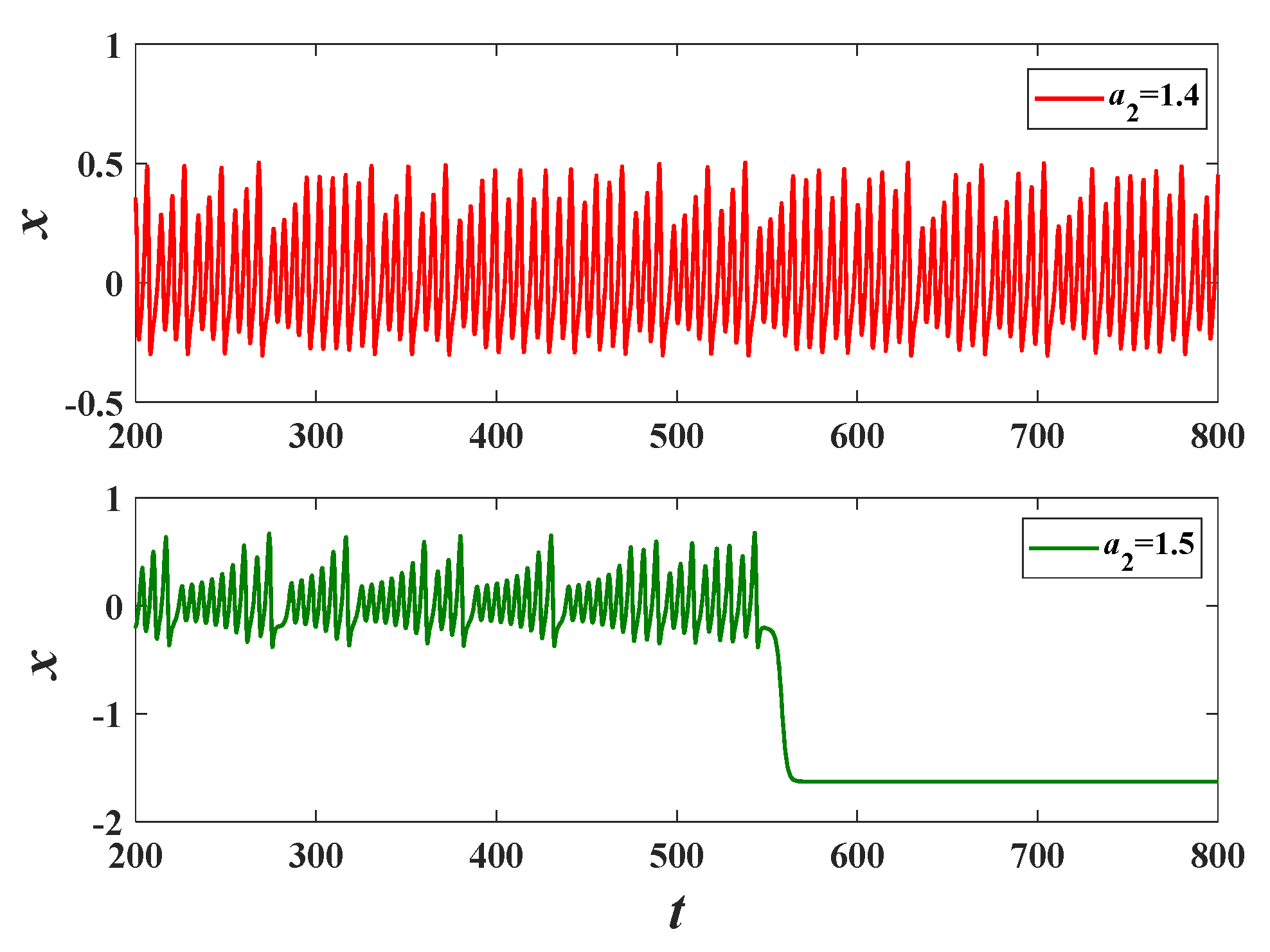
4.1. Influence of Memristive Parameter a2 on Dynamics
4.2. Influence of Crosstalk Parameter c2 on Dynamics
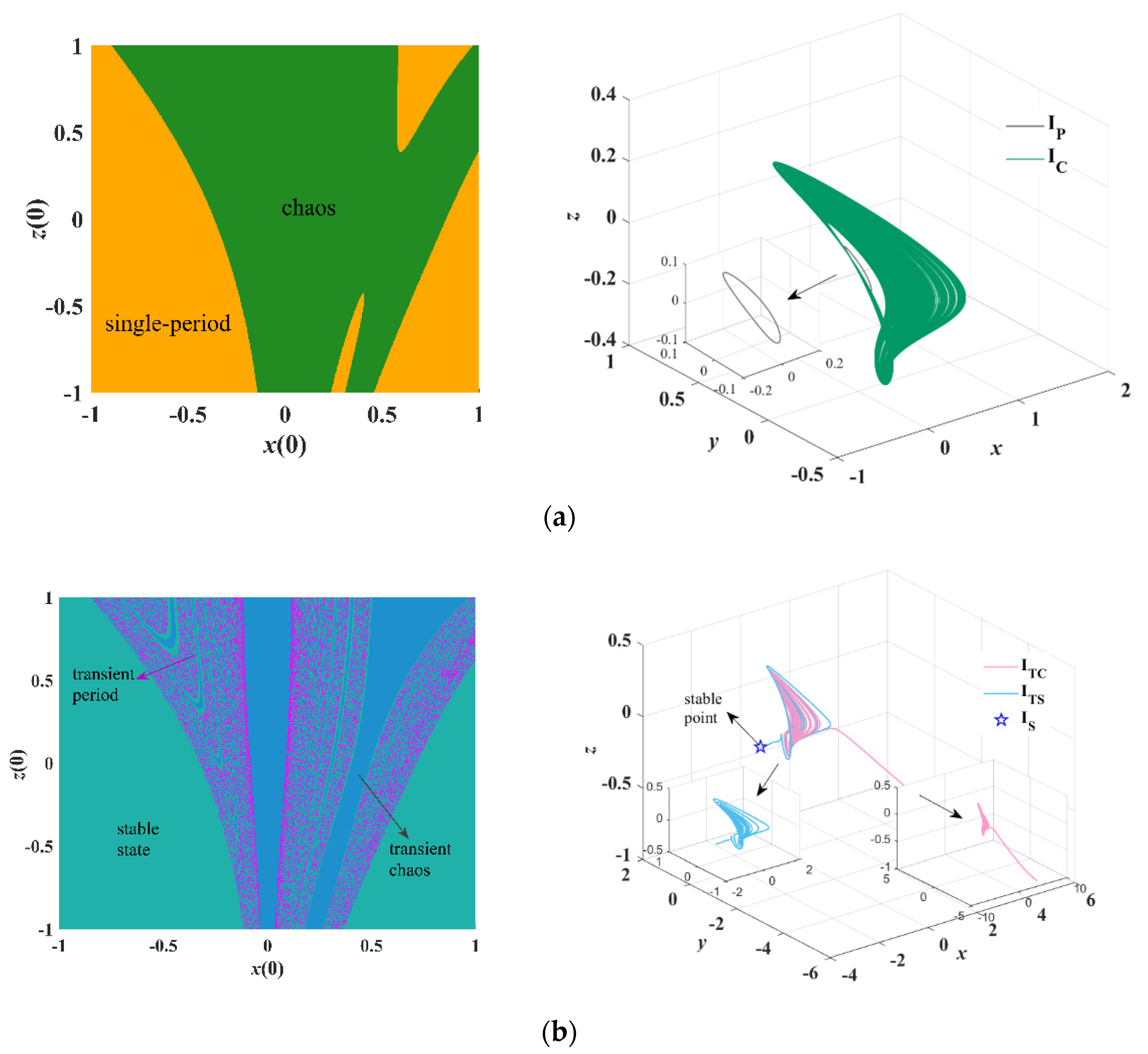
5. Sensitivity of Initial Conditions and Coexisting Behaviors
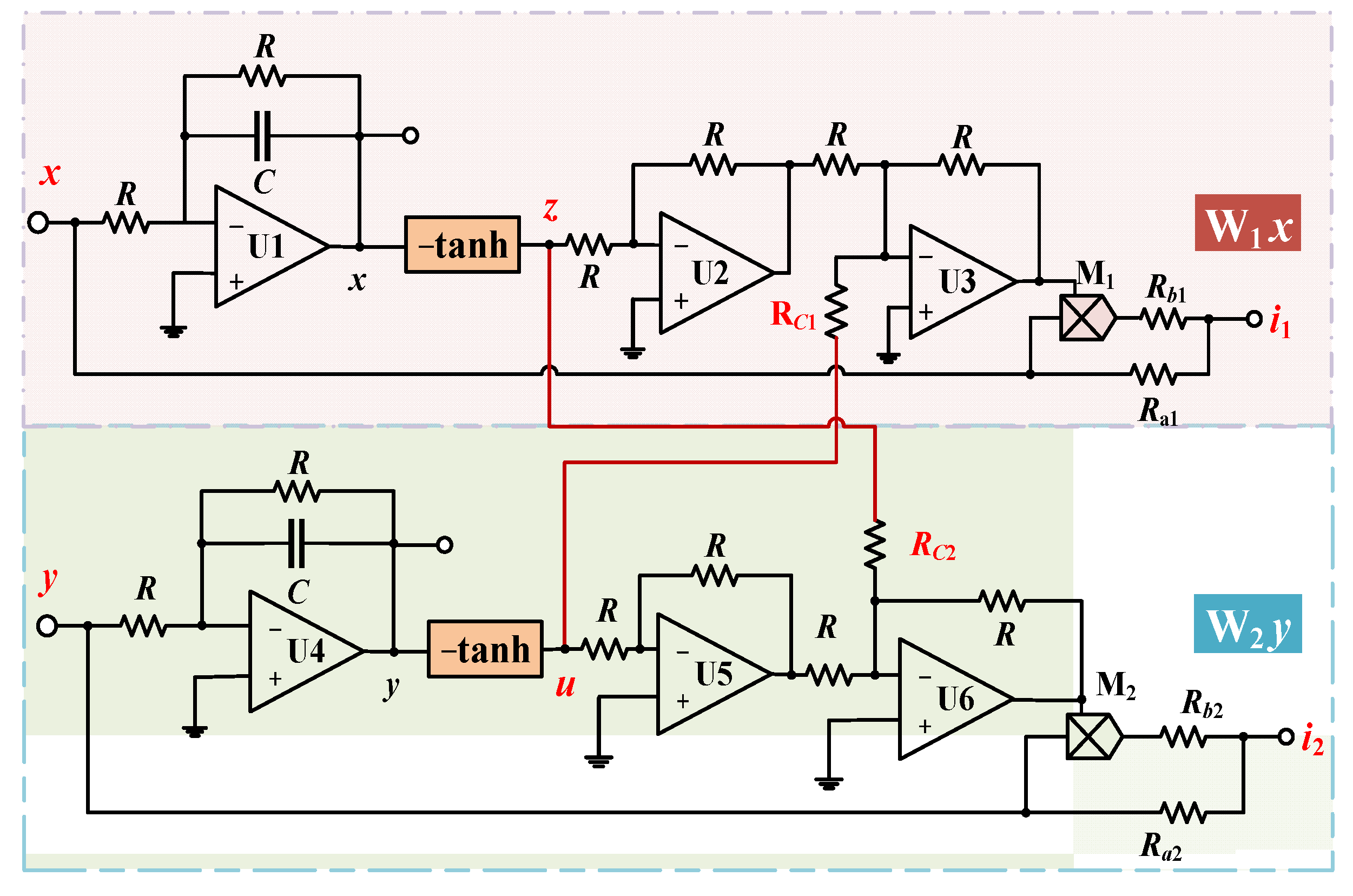
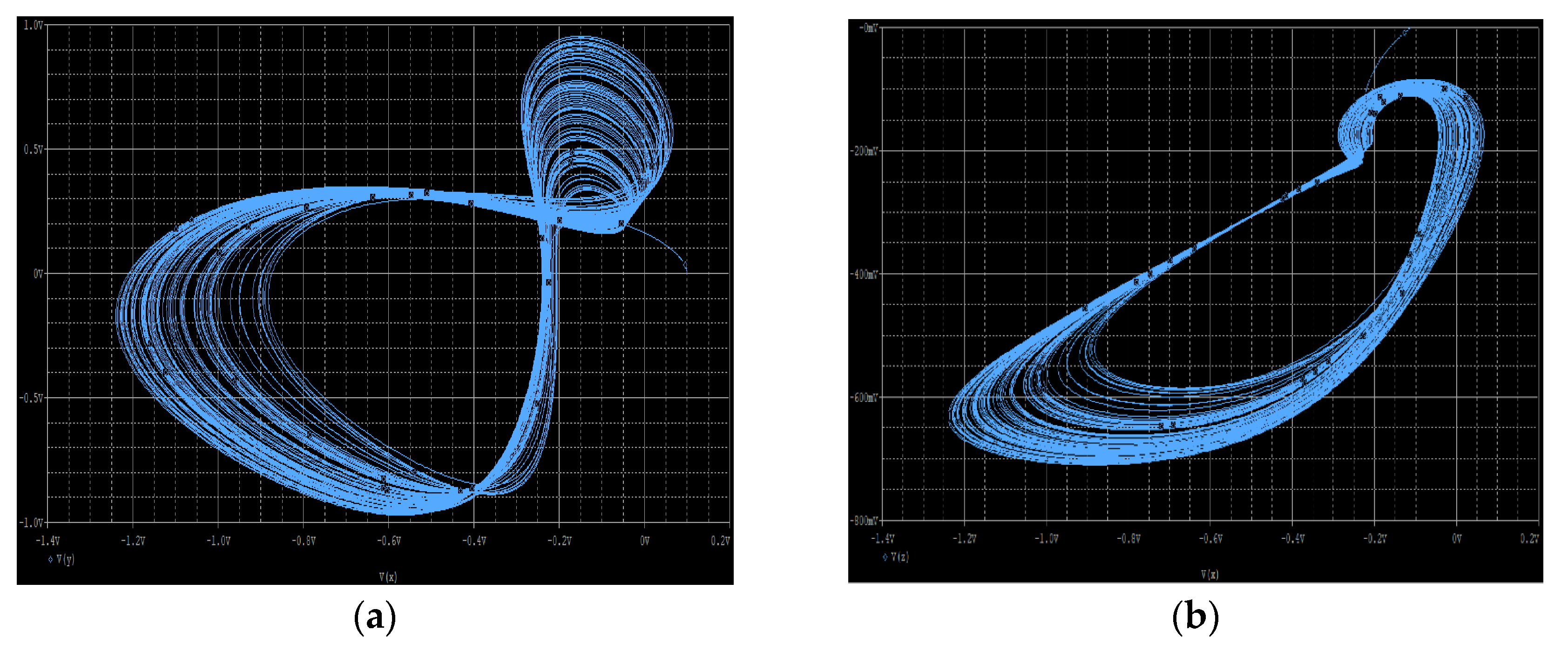
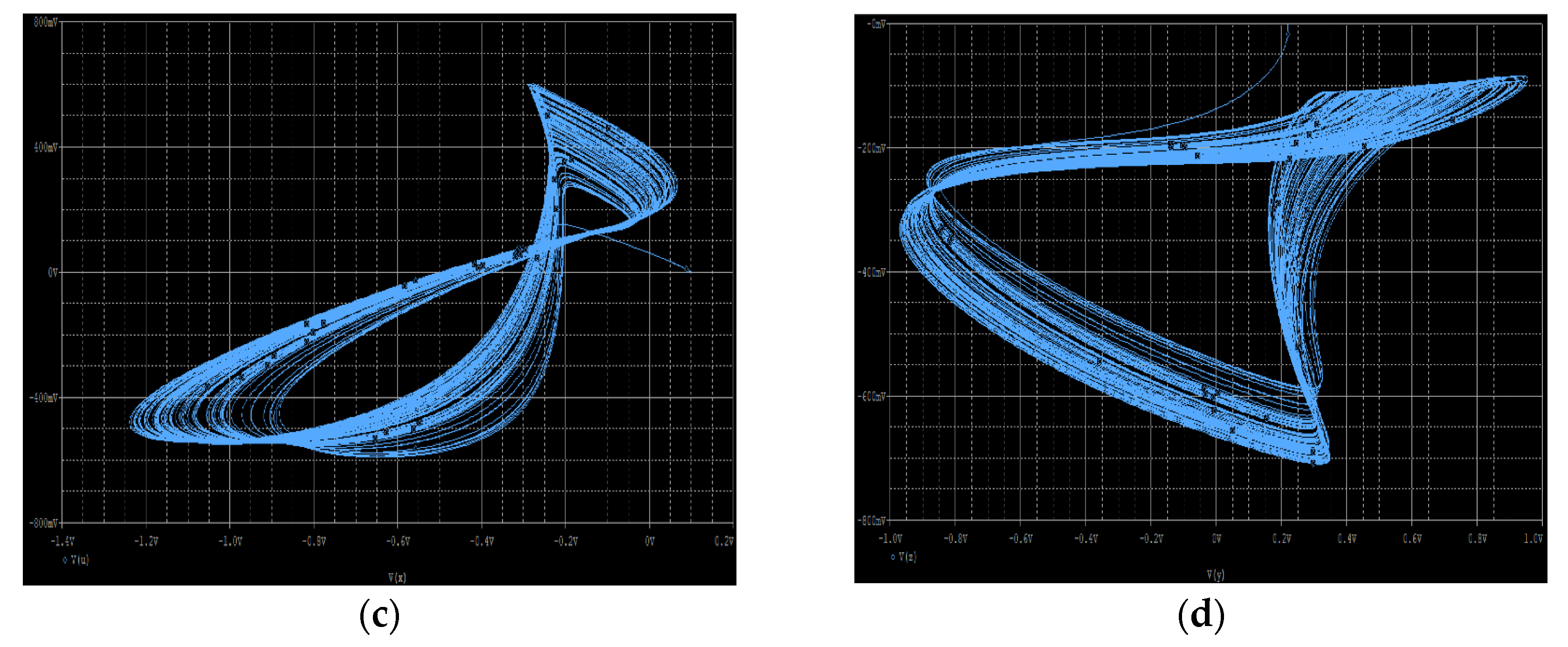
6. Circuit Simulation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawahara, M.; Kato-Negishi, M.; Tanaka, K. Cross talk between neurometals and amyloidogenic proteins at the synapse and the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Metallomics 2017, 9, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L.O. Memristor—The missing circuit element. IEEE Tran. Circuit Theory 1971, 18, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strukov, D.B.; Snider, G.S.; Stewart, D.R.; Williams, R.S. The missing memristor found. Nature 2008, 453, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Harkin, J.; McDaid, L.; Luo, Y. An memristor-based synapse implementation using BCM learning rule. Neurocomputing 2021, 423, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.F.; Feng, G.; Duan, S.; Liu, L. A memristive multilayer cellular neural network with applications to image processing. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 28, 1889–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.K.; Lai, C.S.; Qi, D.L.; Xu, Z.; Li, C.Y.; Duan, S.K. A general memristor-based pulse coupled neural network with variable linking coefficient for multi-focus image fusion. Neurocomputing 2018, 308, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.M.; Wang, G.Y.; Han, C.Y.; Shen, Y.R.; Liang, Y. A memristive neural network model with associative memory for modeling affections. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 61614–61622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfield, J.J. Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 2554–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Trojovský, P. Teamwork optimization algorithm: A new optimization approach for function minimization/maximization. Sensors 2021, 21, 4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasihmuddin, M.S.M.; Mansor, M.A.; Basir, M.F.M.; Sathasivam, S. Discrete mutation Hopfield neural network in propositional satisfiability. Mathematics 2019, 7, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citko, W.; Sienko, W. Inpainted image reconstruction using an extended Hopfield neural network based machine learning system. Sensors 2022, 22, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazuhair, M.M.; Jamaludin, S.Z.M.; Zamri, N.E.; Kasihmuddin, M.S.M.; Mansor, M.A.; Always, A.; Karim, S.A. Novel Hopfield neural network model with election algorithm for random 3 satisfiability. Processes 2021, 9, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Manzano, C.; Segura-Navarrete, A.; Martinez-Araneda, C.; Vidal-Castro, C. Explainable Hopfield neural networks using an automatic video-generation system. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njitacke, Z.T.; Isaac, S.D.; Kengne, J.; Negou, A.N.; Leutcho, G.D. Extremely rich dynamics from hyperchaotic Hopfield neural network: Hysteretic dynamics, parallel bifurcation branches, coexistence of multiple stable states and its analog circuit implementation. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2020, 229, 1133–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Bao, H.; Chen, M.; Bao, B. Coexisting multi-stable patterns in memristor synapse-coupled Hopfield neural network with two neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 2019, 95, 3385–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xiao, X.; Yang, Q.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y. Memristor-based Hopfield Network Circuit for Recognition and Sequencing Application. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2021, 134, 1536984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njitacke, Z.T.; Kengne, J.; Fotsin, H.B. A plethora of behaviors in a memristor based Hopfield neural networks (HNNs). Int. J. Dyn. Control 2019, 7, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Qian, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y. Coexisting behaviors of asymmetric attractors in hyperbolic-type memristor based Hopfield neural network. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Yu, D.; Hu, Y.; Yu, S.S.; Ye, Z. Dynamic behaviors of hyperbolic-type memristor-based Hopfield neural network considering synaptic crosstalk. Chaos 2020, 30, 033108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfield, J.J. Neurons with graded response have collective computational properties like those of 2-state neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 3088–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, P.C. A new proof of the Routh-Hurwitz stability criterion using the second method of lyapunov. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1962, 58, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margielewicz, J.; Gaska, D.; Opasiak, T.; Litak, G. Multiple solutions and transient chaos in a nonlinear flexible coupling model. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2021, 43, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.S.; Xu, Q. Chaos and transient chaos in simple Hopfield neural networks. Neurocomputing 2005, 69, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Y.; Huang, R. Transiently chaotic simulated annealing based on intrinsic nonlinearity of memristors for efficient solution of optimization problems. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba9901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1963, 20, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faradja, P.; Qi, G. Analysis of multistability, hidden chaos and transient chaos in brushless DC motor. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 132, 1884–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Equilibria | Eigenvalues | Stability |
|---|---|---|
| P0 (0, 0, 0, 0) | 0.5000 ± 0.8944i, −1.0000, −1.0000 | unstable |
| P1 (−1.7, −0.238, −0.935, 0.234) | −0.0760 ± 1.6875i, −1.2437, −0.5887 | stable |
| P2 (−0.186, −1.116, −0.184, −0.806) | 1.6461, −0.6511 ± 0.2767i, −2.6779 | unstable |
| P3 (1.737, −0.149, 0.940, −0.148) | 2.3973, −2.4408, −1.1678, −0.7158 | unstable |
| Color | Characteristics | Types | Initial Values |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Single-period attractor | IP | (−0.1, 0, 0.1, 0) |
 | Single-scroll chaos | IC | (0.1, 0, −0.1, 0) |
 | Transient chaos | ITC | (−0.2, 0, 0.2, 0) |
 | Transient periodic attractor | ITS | (0.2, 0, −0.3, 0) |
 | Point attractor | IS | (0.2, 0, −0.2, 0) |
 | Double-scroll chaos | IIC | (1, 0, −4, 0) |
 | Double-periodic attractor | IIP | (2.5, 0, 2, 0) |
 | Point attractor | IIS | (−1.5, 0, −1, 0) |
 | Point attractor | IIIS | (1.5, 0, 0.5, 0, 0) |
| Symbol | Parameter Values | Symbol | Parameter Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| R | 10 kΩ | Rb1 = R/b1 | 250 kΩ |
| C | 1 μF | Ra2 = R/a2 | 9.52 kΩ |
| R11 = R/W11 | 8.06 kΩ | Rb2 = R/b2 | 333.33 kΩ |
| R22 = R/W22 | 13.33 kΩ | Rc1 = R/c1 | 1.8 kΩ |
| Ra1 = R/a1 | 10 kΩ | Rc2 = R/c2 | 1.69 kΩ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, R.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, G. Two-Neuron Based Memristive Hopfield Neural Network with Synaptic Crosstalk. Electronics 2022, 11, 3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11193034
Qiu R, Dong Y, Jiang X, Wang G. Two-Neuron Based Memristive Hopfield Neural Network with Synaptic Crosstalk. Electronics. 2022; 11(19):3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11193034
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Rong, Yujiao Dong, Xin Jiang, and Guangyi Wang. 2022. "Two-Neuron Based Memristive Hopfield Neural Network with Synaptic Crosstalk" Electronics 11, no. 19: 3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11193034
APA StyleQiu, R., Dong, Y., Jiang, X., & Wang, G. (2022). Two-Neuron Based Memristive Hopfield Neural Network with Synaptic Crosstalk. Electronics, 11(19), 3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11193034







