Understanding Frailty: Probabilistic Causality between Components and Their Relationship with Death through a Bayesian Network and Evidence Propagation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Frailty
2.3. Analytic Plan
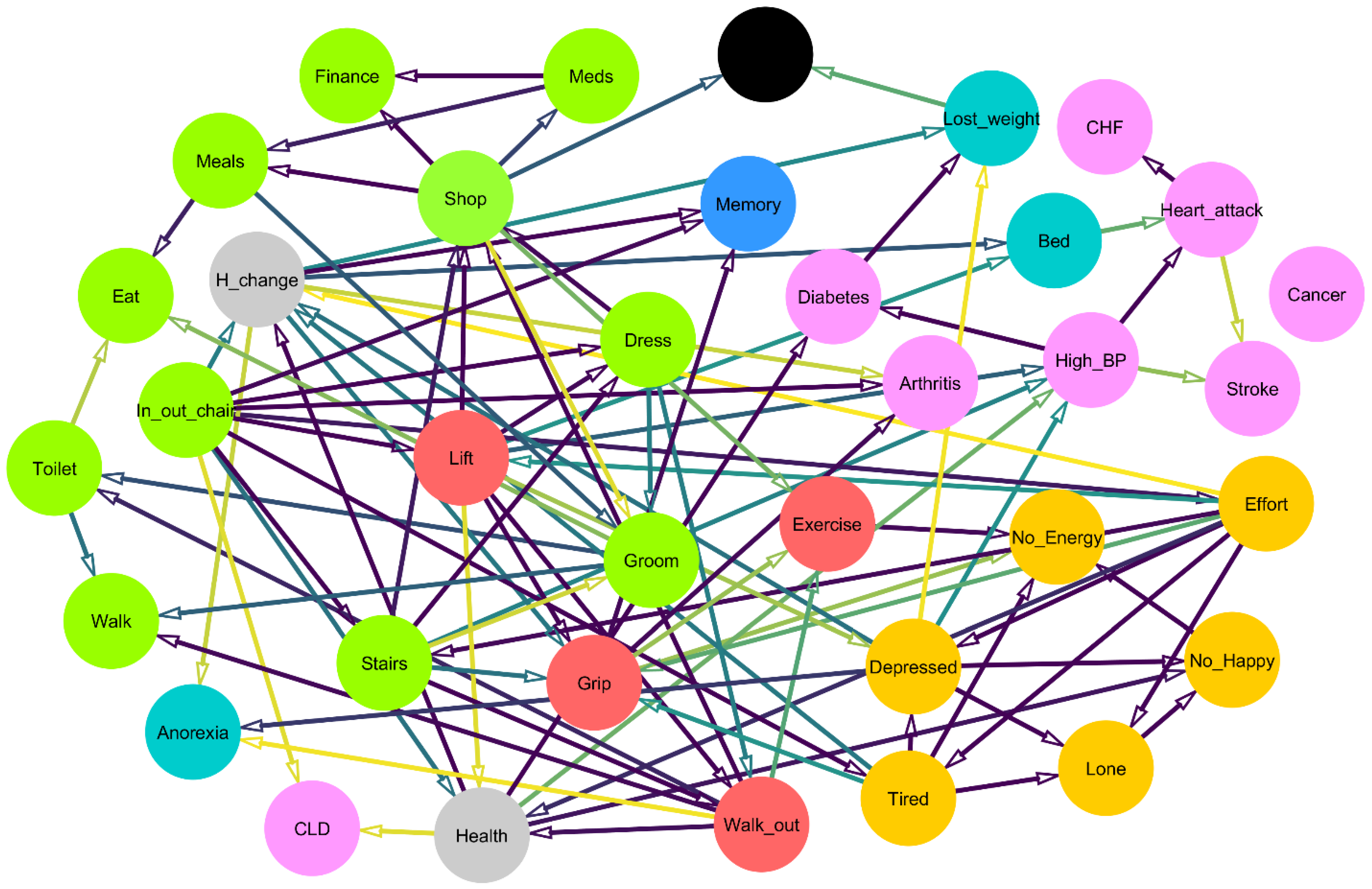
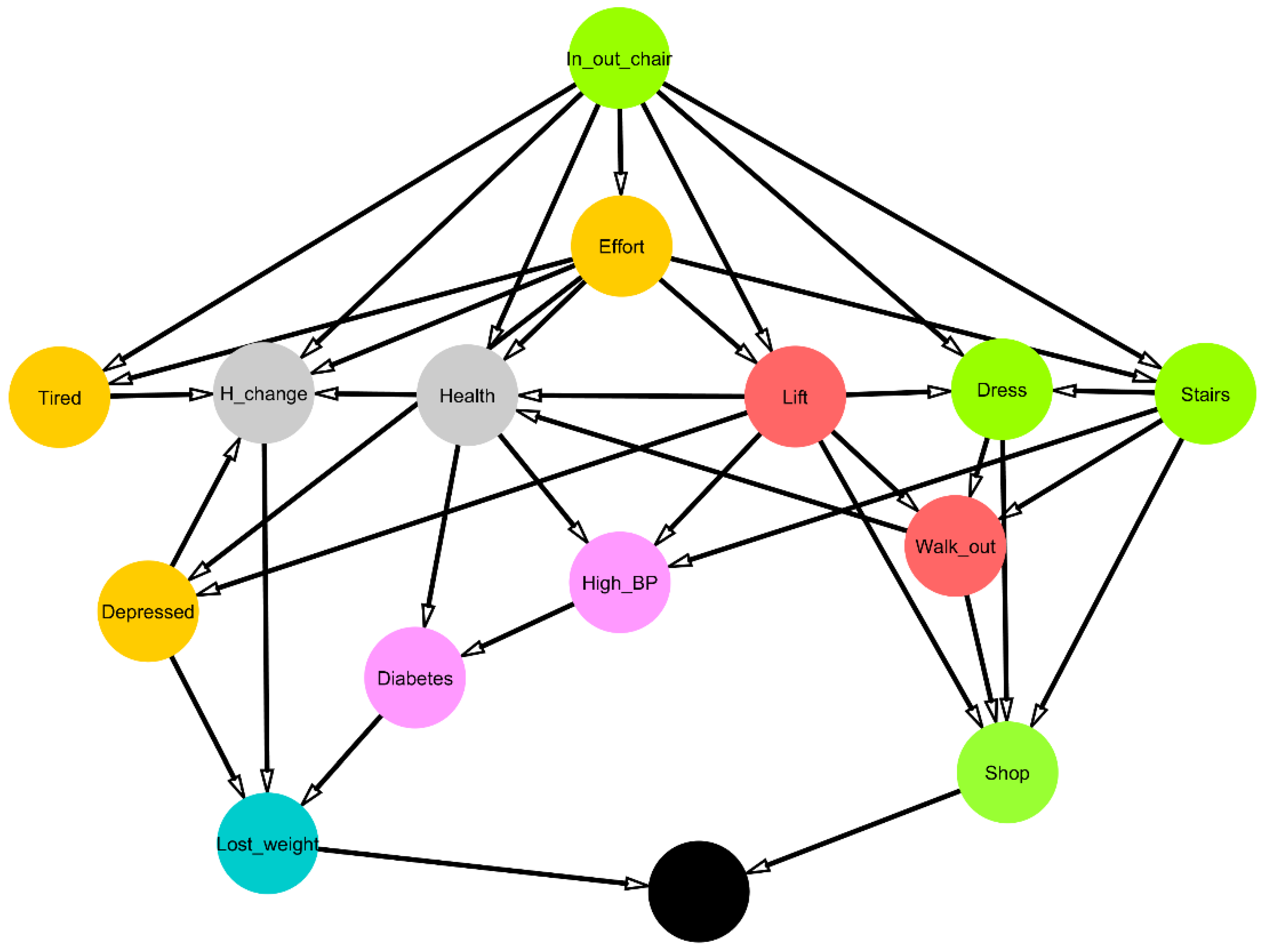
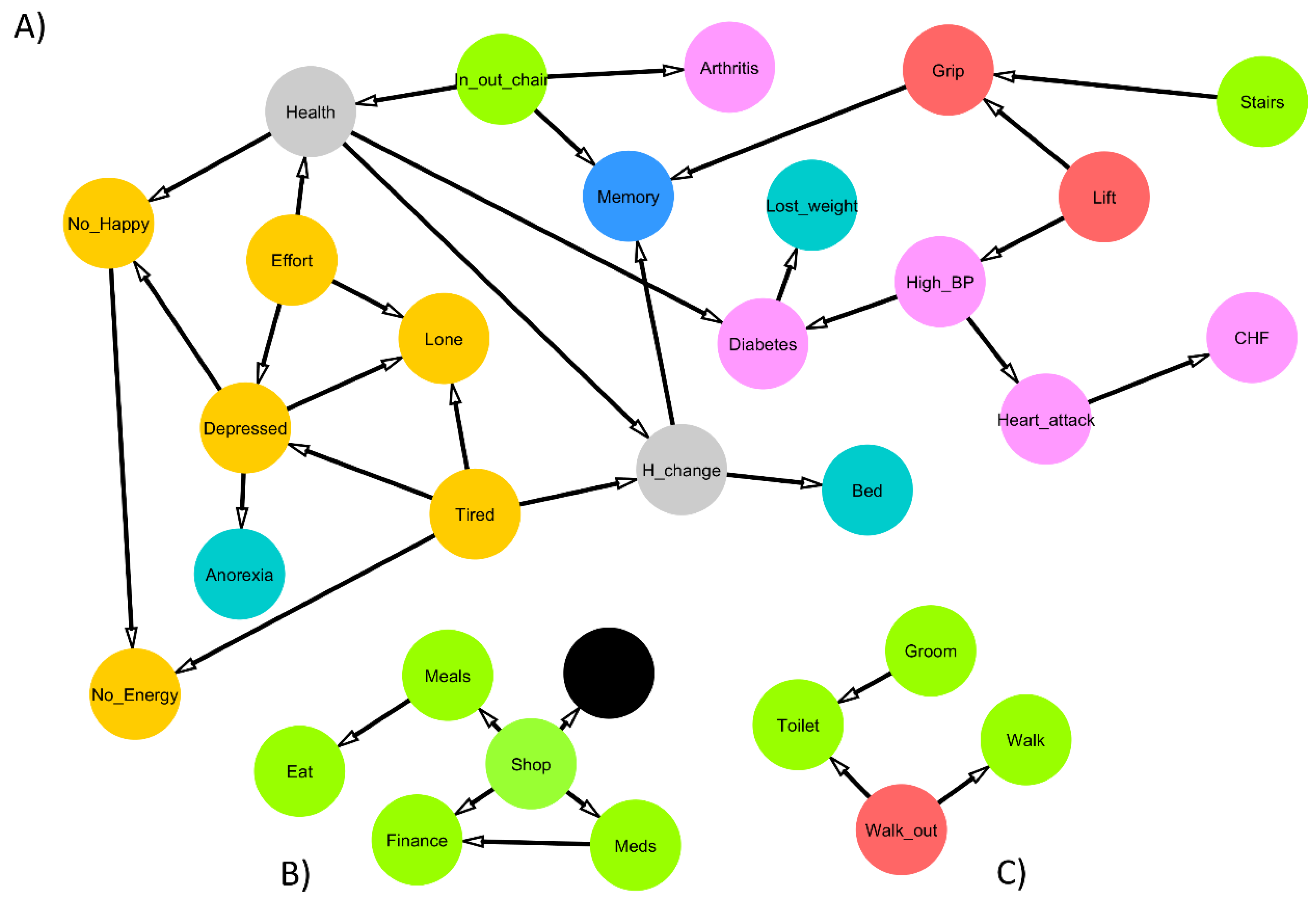
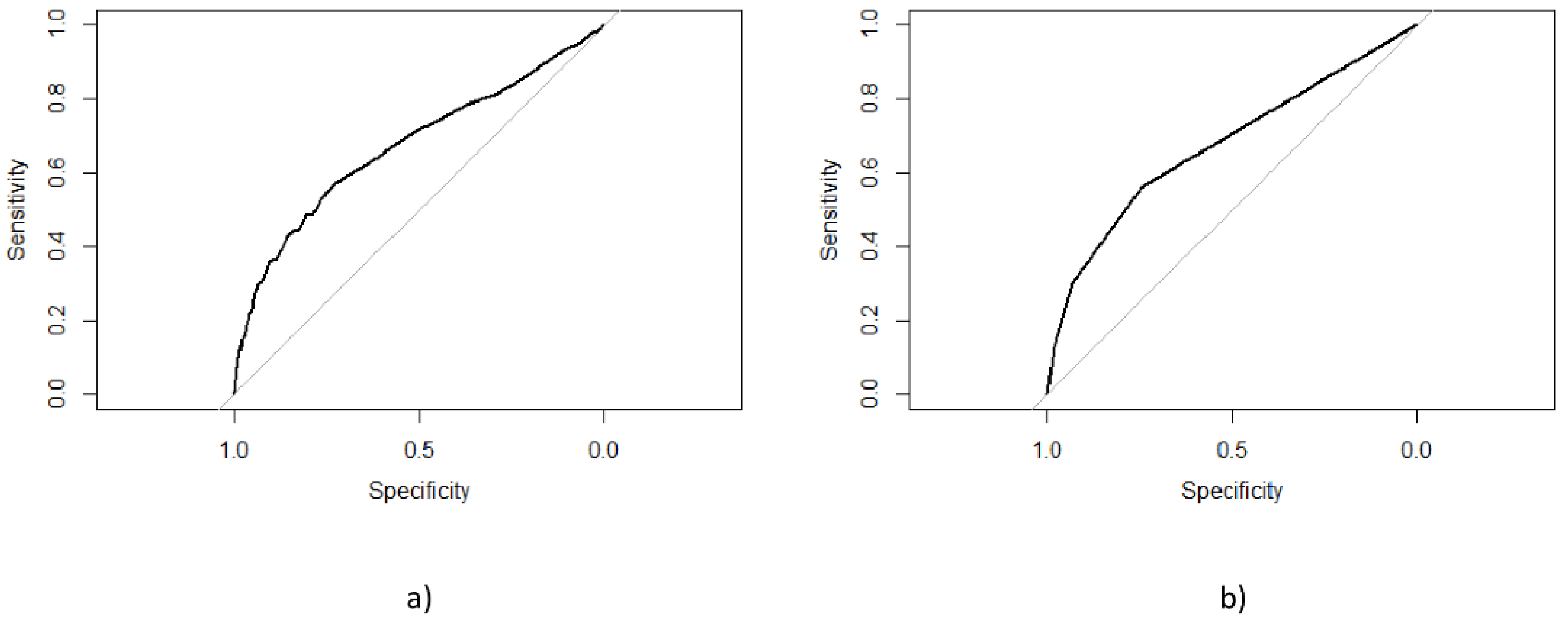
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variable Description (Name) | MHAS Variable | Coding of the Variable | Syntaxis to Generate Variables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Help dressing (Dress) | h13_12 Because of health problems, difficulty dressing self | 1 Yes 2 No 6 Can’t do 7 Doesn’t do 8 RF | Dress = h13_12_d_2 1 Yes if h13_12 = 1|h13_12 = 6|h13_12 = 7 0 No if h13_12 = 2 |
| Help getting in/out of a chair (In_out_chair) | h5_12 Because of health problems, difficulty getting up from chair | 1 Yes 2 No 6 Can’t do 7 Doesn’t do 8 RF | In_out_chair = h5_12_d_2 1 Yes if h5_12 = 1|h5_12 = 6|h5_12 = 7 0 No if h5_12 = 2 |
| Help walking around the room (Walk) | h15a_12 Because of health problems, difficulty walking | 1 Yes 2 No 6 Can’t do 7 Doesn’t do 8 RF 9 DK | Walk = h15d_12_d 1 Yes if (h15a_12 = 1|h15a_12 = 6|h15a_12 = 7) & h15d_12 = 1 0 No if h1_12 = 2 & h4_12 = 2 & h5_12 = 2 & h8_12 = 2 & h9_12 = 2 & h10_12 = 2 & h11_12 = 2 & h12_12 = 2 & h13_12 = 2|h15a_12 = 2|h15d_12 = 2 |
| h15d_12 Someone helps you walk across room | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | ||
| Help eating (Eat) | h17a_12 Because of health problems, difficulty eating or cutting | 1 Yes 2 No 6 Can’t do 7 Doesn’t do 8 RF 9 DK | Eat = h17d_12_d 1 Yes if (h17a_12 = 1|h17a_12 = 6|h17a_12 = 7) & h17d_12 = 1 0 No if h1_12 = 2 & h4_12 = 2 & h5_12 = 2 & h8_12 = 2 & h9_12 = 2 & h10_12 = 2 & h11_12 = 2 & h12_12 = 2 & h13_12 = 2 OR h17a_12 = 2 OR h17d_12 = 2 |
| h17d_12 Does someone help you eat your food? | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | ||
| Help grooming (Groom) | h16a_12 Because of health problems, difficulty bathing | 1 Yes 2 No 6 Can’t do 7 Doesn’t do 8 RF 9 DK | Groom = h16d_12_d 1 Yes if (h16a_12 = 1 | h16a_12 = 6 | h16a_12 = 7) & h16d_12 = 1 0 No if h1_12 = 2 & h4_12 = 2 & h5_12 = 2 & h8_12 = 2 & h9_12 = 2 & h10_12 = 2 & h11_12 = 2 & h12_12 = 2 & h13_12 = 2 OR h16a_12 = 2 OR h16d_12 = 2 |
| h16d_12 Does someone help you to bathe or shower? | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | ||
| Help using toilet (Toilet) | h19a_12 Because of health problems, difficulty going to the bathroom | 1 Yes 2 No 6 Can’t do 7 Doesn’t do 8 RF 9 DK | Toilet = h19d_12_d 1 Yes if (h19a_12 = 1 | h19a_12 = 6 | h19a_12 = 7) & h19d_12 = 1 0 No if h1_12 = 2 & h4_12 = 2 & h5_12 = 2 & h8_12 = 2 & h9_12 = 2 & h10_12 = 2 & h11_12 = 2 & h12_12 = 2 & h13_12 = 2 OR h19a_12 = 2 OR h19d_12 = 2 |
| h19d_12 Does someone help you use the toilet, get on/off? | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | ||
| Help up/down 1 flight of stairs (Stairs) | h6_12 Because of health problems, difficulty with flights of stairs | 1 Yes 2 No 6 Can’t do 7 Doesn’t do 8 RF 9 DK | Stairs = h7_12_d_2 h7_12_d = 1 if h7_12 = 1 h7_12_d = 0 if h6_12 = 2 | h7_12 = 2 1 Yes if h7_12_d = 1 | h7_12 = 6 0 No if h7_12_d = 0 |
| h7_12 Because of health problems, difficulty with 1 flight of stairs | 1 Yes 2 No 6 Can’t do 7 Doesn’t do 8 RF 9 DK | ||
| Help lifting 10 pounds (Lift) | h11_12 Because of health problems, difficulty carrying objects | 1 Yes 2 No 6 Can’t do 7 Doesn’t do 8 RF 9 DK | Lift = h11_12_d_2 1 Yes if h11_12 = 1 | h11_12 = 6 0 No if h11_12 = 2 |
| Help shopping groceries (Shop) | h27a_12 Difficulty shopping | 1 Yes 2 No 6 Can’t do 7 Doesn’t do 8 RF 9 DK | Shop = h27c_12_d_2 h27c_12_d = 1 if h27c_12 = 1 h27c_12_d = 0 if h27a_12 = 2|h27c_12 = 2 1 Yes if h27c_12_d = 1|h27a_12 = 6| h27a_12 = 7 0 No if h27c_12_d = 0 |
| h27c_12 Does anyone help you shop for groceries? | 1 Yes 2 No | ||
| Help with preparing hot meal (Meals) | h26a_12 Difficulty preparing hot food | 1 Yes 2 No 6 Can’t do 7 Doesn’t do 8 RF | Meals = h26c_12_d_2 h26c_12_d = 1 if h26c_12 = 1 h26c_12_d = 0 if h26a_12 = 2 | h26c_12 = 2 1 Yes if h26c_12_d = 1 | h26a_12 = 6 | h26a_12 = 7 0 No if h26c_12_d = 0 |
| h26c_12 Does anyone help you prepare a hot meal? | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | ||
| Help taking medication (Meds) | h28a_12 Difficulty taking medications | 1 Yes 2 No 6 Can’t do 7 Doesn’t do 8 RF | Meds = h28c_12_d_2 h28c_12_d = 1 if h28c_12 = 1 h28c_12_d = 0 if h28a_12 = 2 | h28c_12 = 2 1 Yes if h28c_12_d = 1 | h28a_12 = 6 | h28a_12 = 7 0 No if h28c_12_d = 0 |
| h28c_12 Does anyone help you take medications? | 1 Yes 2 No | ||
| Help with finances (Finance) | h29a_12 Difficulty managing money | 1 Yes 2 No 6 Can’t do 7 Doesn’t do 8 RF 9 DK | Finance = h29c_12_d_2 h29c_12_d = 1 if h29c_12 = 1 h29c_12_d = 0 if h29a_12 = 2 | h29c_12 = 2 1 Yes if h29c_12_d = 1 | h29a_12 = 6 | h29a_12 = 7 0 No if h29c_12_d = 0 |
| h29c_12 Does anyone help you manage your money? | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | ||
| Compared to 2 years ago: Unintentional change in weight (Lost_weight) | c64_12 Compared to 2 years ago: respondent’s change in weight | 1 Has increased 5 kilos/more 2 Has decreased 5 kilos/more 3 Has remained more/less the same 8 RF 9 DK | Lost_weight = c64_12_d 1 Yes if c64_12 = 2 & c65_12 = 2 0 No if c64_12 = 1 | c64_12 = 3 |
| c65_12 Compared to 2 years ago: respondent’s change in exercise or diet | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | ||
| Self-rating of health (Health) | c1_12 Global self-reported quality of health | 1 Excellent 2 Very good 3 Good 4 Fair 5 Poor 8 RF 9 DK | Health = c1_12_d 1 Yes if c1_12 = 5 0 No if c1_12 = 1 | c1_12 = 2 | c1_12 = 3 | c1_12 = 4 |
| Compared to 2 years ago: Report your current health (H_change) | c2a_12 Compared to 2 years ago: report your current health | 1 Much better 2 Somewhat better 3 More or less the same 4 Somewhat worse 5 Much worse 9 DK | H_change = c2a_12_d 1 Yes if c2a_12 = 4 | c2a_12 = 5 0 No if c2a_12 = 1 | c2a_12 = 2 | c2a_12 = 3 |
| Last 12 months: Number of days in bed… due to sickness/injury (Bed) | c73_12 Last 12 months: Respondent’s number of days in bed… due to sickness/injury | Bed = c73_12_d 1 Yes if c73_12 >= 1 & c73_12 <= 365 0 No if c73_12 = 0 | |
| Within the past week: Felt tired (Tired) | c49_8_12 Within the past week: Respondent felt tired | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | Tired = c49_8_12_d 1 Yes if c49_8_12 = 1 0 No if c49_8_12 = 2 |
| Difficulty walking a block (Walk_out) | h1_12 Because of health problems, difficulty walking blocks | 1 Yes 2 No 6 Can’t do 7 Doesn’t do 8 RF 9 DK | Walk_out = h3_12_d_2 h3_12_d = 1 if h3_12 = 1 h3_12_d = 0 if h1_12 = 2 | h3_12 = 2 1 Yes if h3_12 = 6 | h3_12 = 7 | h3_12_d = 1 0 No if h3_12_d = 0 |
| h3_12 Because of health problems, difficulty walking a block | 1 Yes 2 No 6 Can’t do 7 Doesn’t do 8 RF 9 DK | ||
| Feel everything is an effort (Effort) | c49_2_12 Within the past week: respondent experienced difficulty performing | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | Effort = c49_2_12_d 1 Yes if c49_2_12 = 1 0 No if c49_2_12 = 2 |
| Feel depressed (Depressed) | c49_1_12 Within the past week: respondent was depressed | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | Depressed = c49_1_12_d 1 Yes if c49_1_12 = 1 0 No if c49_1_12 = 2 |
| Feel happy (No_happy) | c49_4_12 Within the past week: respondent was happy | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | No_happy = c49_4_12_d 1 Yes if c49_4_12 = 2 0 No if c49_4_12 = 1 |
| Feel lonely (Lone) | c49_5_12 Within the past week: respondent was lonely | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | Lone = c49_5_12_d 1 Yes if c49_5_12 = 1 0 No if c49_5_12 = 2 |
| Feel energetic (No_energy) | c49_9_12 Within the past week: respondent was energetic | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | No_energy = c49_9_12_d 1 Yes if c49_9_12 = 2 0 No if c49_9_12 = 1 |
| Hypertension/high blood pressure (High_BP) | c4_12 Has a physician diagnosed hypertension/high blood pressure? | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | High_BP = c4_12_d 1 Yes if c4_12 = 1 0 No if c4_12 = 2 |
| Heart attack (Heart_attack) | c22a_12 Has a physician ever told respondent of a heart attack? | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | Heart_attack = c22a_12_d 1 Yes if c22a_12 = 1 0 No if c22a_12 = 2 |
| Heart failure (CHF) | c25b_12 Has a physician ever told respondent of a heart failure? | 1 Yes 2 No 9 DK | CHF = c25b_12_d 1 Yes if c25b_12 = 1 0 No if c22a_12 = 2 | c25b_12 = 2 |
| Stroke (Stroke) | c26_12 Ever/last 2 years: has a physician told respondent of a stroke? | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | Stroke = c26_12_d 1 Yes if c26_12 = 1 0 No if c26_12 = 2 |
| Cancer (in the last 10 years) (Cancer) | c12_12 Has a physician diagnosed respondent cancer (last 10 years)? | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | Cancer = c12_12_d 1 Yes if c12_12 = 1 last 10 years 0 No if c12_12 = 2 last 10 years |
| Diabetes (Diabetes) | c6_12 Has a physician diagnosed respondent with diabetes? | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | Diabetes = c6_12_d 1 Yes if c6_12 = 1 0 No if c6_12 = 2 |
| Arthritis/rheumatism (Arthritis) | c32_12 Has a physician diagnosed respondent with arthritis/rheumatism? | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | Arthritis = c32_12_d 1 Yes if c32_12 = 1 0 No if c32_12 = 2 |
| Respiratory illness (CLD) | c19_12 Has a physician diagnosed respondent with respiratory illness? | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | CLD = c19_12_d 1 Yes if c19_12 = 1 0 No if c19_12 = 2 |
| Compared to 2 years ago: respondent reports his/her memory quality (Memory) | e1b_12 Compared to 2 years ago: respondent reports his/her memory quality | 1 Better 2 About the same 3 Worse 8 RF 9 DK | Memory = e1b_12_d 1 Yes if e1b_12 = 3 0 No if e1b_12 <= 2 |
| Respondent’s dominant hand strength (Grip) | c69a_12 Respondent’s dominant hand strength | 1 Very strong 2 Somewhat strong 3 Somewhat weak 4 Very weak 8 RF 9 DK | Grip = c69a_12_d 1 Yes if c69a_12 = 3 | c69a_12 = 4 0 No if c69a_12 <= 2 |
| Anorexia: Last 2 years: Loss of appetite (Anorexia) | c70_12 Last 2 years: Respondent’s loss of appetite | 1 Often 2 Sometimes 3 Rarely 8 RF 9 DK | Anorexia = c70_12_d 1 Yes if c70_12 = 1 0 No if c70_12 = 2 | c70_12 = 3 |
| Exercise: Last 2 years: Exercise or hard physical work >= 3 times a week (Exercise) | c50b_12 Last 2 years: Respondent’s exercise or hard physical work >= 3 times a week | 1 Yes 2 No 8 RF 9 DK | Exercise = c50b_12_d 1 Yes if c50b_12 = 2 0 No if c50b_12 = 1 |
| Died between 2012 and 2015 (Dead) | fallecido_15 Died between 2012 and 2015 | 1 Yes 0 No | Dead 1 Yes if fallecido_15 = 1 0 No if fallecido_15 = 0 |
| * Filter participants aged 50 or more years old Variable for age 2012 is age_12, then age_12_cat = 1 if age_12 >= 50, age_12_cat = 0 if age_12 < 50 Filter: age_12_cat = 1 | |||
| ** Eliminate second or third wives or husbands Variable for subject identification is np, np = 10 original subject, np = 20 original spouse Filter: np = 10 | np = 20 | |||
| *** The following variables have the same coding: h1_12 Because of health problems, difficulty walking blocks h4_12 Because of health problems, difficulty staying seated h5_12 Because of health problems, difficulty getting up from chair h8_12 Because of health problems, difficulty sitting up h9_12 Because of health problems, difficulty lifting arms h10_12 Because of health problems, difficulty pushing or pulling h11_12 Because of health problems, difficulty carrying objects h12_12 Because of health problems, difficulty picking up a coin h13_12 Because of health problems, difficulty dressing self | 1 Yes 2 No 6 Can’t do 7 Doesn’t do 8 RF 9 DK | ||
Appendix B
| Arc from | Arc to | Strength (Presence) | Strength (Direction) | Arcs with Greatest Strength (Value = 1 if Presence and Direction >= 0.8) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depressed | Anorexia | 0.91 | 1.00 | 1 |
| Depressed | Lone | 1.00 | 0.94 | 1 |
| Depressed | No_Happy | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1 |
| Diabetes | Lost_weight | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1 |
| Effort | Depressed | 1.00 | 0.85 | 1 |
| Effort | Health | 0.93 | 0.85 | 1 |
| Effort | Lone | 1.00 | 0.94 | 1 |
| Grip | Arthritis | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1 |
| Grip | Memory | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1 |
| Groom | Toilet | 0.87 | 0.91 | 1 |
| H_change | Bed | 0.86 | 1.00 | 1 |
| H_change | Memory | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1 |
| Health | Diabetes | 1.00 | 0.96 | 1 |
| Health | H_change | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1 |
| Health | No_Happy | 0.97 | 0.91 | 1 |
| Heart_attack | CHF | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1 |
| High_BP | Diabetes | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1 |
| High_BP | Heart_attack | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1 |
| In_out_chair | Arthritis | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1 |
| In_out_chair | Health | 0.81 | 0.90 | 1 |
| In_out_chair | Memory | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1 |
| Lift | Grip | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1 |
| Lift | High_BP | 0.84 | 0.99 | 1 |
| Meals | Eat | 0.95 | 0.98 | 1 |
| Meds | Finance | 1.00 | 0.94 | 1 |
| No_Happy | No_Energy | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1 |
| Shop | Dead | 0.85 | 1.00 | 1 |
| Shop | Finance | 1.00 | 0.97 | 1 |
| Shop | Meals | 1.00 | 0.84 | 1 |
| Shop | Meds | 0.89 | 0.89 | 1 |
| Stairs | Grip | 0.81 | 0.98 | 1 |
| Tired | Depressed | 1.00 | 0.84 | 1 |
| Tired | H_change | 0.80 | 0.95 | 1 |
| Tired | Lone | 1.00 | 0.94 | 1 |
| Tired | No_Energy | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1 |
| Walk_out | Toilet | 0.94 | 0.98 | 1 |
| Walk_out | Walk | 0.99 | 0.95 | 1 |
| Bed | Heart_attack | 0.68 | 1.00 | 0 |
| Depressed | H_change | 0.81 | 0.62 | 0 |
| Depressed | High_BP | 0.76 | 0.99 | 0 |
| Depressed | Lost_weight | 0.52 | 1.00 | 0 |
| Dress | Groom | 0.79 | 0.89 | 0 |
| Dress | Shop | 0.99 | 0.55 | 0 |
| Dress | Walk_out | 0.79 | 0.65 | 0 |
| Effort | Grip | 0.69 | 0.97 | 0 |
| Effort | H_change | 0.51 | 0.97 | 0 |
| Effort | Lift | 0.75 | 0.47 | 0 |
| Effort | Stairs | 0.99 | 0.50 | 0 |
| Effort | Tired | 1.00 | 0.51 | 0 |
| Exercise | No_Energy | 0.99 | 0.77 | 0 |
| Grip | Exercise | 0.62 | 1.00 | 0 |
| Grip | No_Energy | 0.62 | 0.90 | 0 |
| Groom | Eat | 0.64 | 0.98 | 0 |
| Groom | Walk | 0.84 | 0.54 | 0 |
| H_change | Anorexia | 0.57 | 1.00 | 0 |
| H_change | Arthritis | 0.57 | 1.00 | 0 |
| H_change | Grip | 0.80 | 0.78 | 0 |
| H_change | Lost_weight | 0.77 | 1.00 | 0 |
| Health | CLD | 0.54 | 0.98 | 0 |
| Health | High_BP | 0.67 | 1.00 | 0 |
| Heart_attack | Stroke | 0.57 | 0.64 | 0 |
| High_BP | Stroke | 0.63 | 1.00 | 0 |
| In_out_chair | CLD | 0.54 | 0.95 | 0 |
| In_out_chair | Dress | 1.00 | 0.67 | 0 |
| In_out_chair | Effort | 0.96 | 0.52 | 0 |
| In_out_chair | H_change | 0.79 | 0.99 | 0 |
| In_out_chair | Lift | 1.00 | 0.60 | 0 |
| In_out_chair | Stairs | 1.00 | 0.53 | 0 |
| In_out_chair | Tired | 1.00 | 0.54 | 0 |
| Lift | Bed | 0.75 | 0.99 | 0 |
| Lift | Depressed | 0.61 | 0.62 | 0 |
| Lift | Dress | 0.99 | 0.64 | 0 |
| Lift | Health | 0.54 | 0.84 | 0 |
| Lift | Shop | 1.00 | 0.70 | 0 |
| Lift | Walk_out | 1.00 | 0.69 | 0 |
| Lone | No_Happy | 1.00 | 0.51 | 0 |
| Lost_weight | Dead | 0.69 | 1.00 | 0 |
| Meals | Groom | 0.85 | 0.58 | 0 |
| Meds | Meals | 0.95 | 0.19 | 0 |
| Shop | Exercise | 0.66 | 0.94 | 0 |
| Shop | Groom | 0.54 | 0.86 | 0 |
| Stairs | Dress | 1.00 | 0.67 | 0 |
| Stairs | Groom | 0.56 | 0.92 | 0 |
| Stairs | High_BP | 0.78 | 0.99 | 0 |
| Stairs | Shop | 0.96 | 0.69 | 0 |
| Stairs | Walk_out | 1.00 | 0.70 | 0 |
| Tired | Grip | 0.75 | 0.96 | 0 |
| Toilet | Eat | 0.59 | 0.98 | 0 |
| Toilet | Walk | 0.81 | 0.17 | 0 |
| Walk_out | Anorexia | 0.52 | 1.00 | 0 |
| Walk_out | Exercise | 0.70 | 0.93 | 0 |
| Walk_out | Health | 0.98 | 0.75 | 0 |
| Walk_out | Shop | 1.00 | 0.65 | 0 |
References
- Clegg, A.; Young, J.; Iliffe, S.; Rikkert, M.O.; Rockwood, K. Frailty in elderly people. Lancet 2013, 381, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baztán, J.J.; De La Puente, M.; Socorro, A. Frailty, functional decline and mortality in hospitalized older adults. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2017, 17, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockwood, K.; Hogan, D.; Macknight, C. Conceptualisation and Measurement of Frailty in Elderly People. Drugs Aging 2000, 17, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, S.D.; Mitnitski, A.; Gahbauer, E.A.; Gill, T.M.; Rockwood, K. A standard procedure for creating a frailty index. BMC Geriatr. 2008, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockwood, K.; Mitnitski, A. Frailty in Relation to the Accumulation of Deficits. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2007, 62, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwood, K.; Andrew, M.; Mitnitski, A. A Comparison of Two Approaches to Measuring Frailty in Elderly People. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2007, 62, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockwood, K.; Song, X.; MacKnight, C.; Bergman, H.; Hogan, D.B.; McDowell, I.; Mitnitski, A. A global clinical measure of fitness and frailty in elderly people. CMAJ 2005, 173, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachmann, R.; Stelmach-Mardas, M.; Bergmann, M.M.; Bernigau, W.; Weber, D.; Pischon, T.; Boeing, H. The accumulation of deficits approach to describe frailty. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theou, O.; Rockwood, M.R.; Mitnitski, A.; Rockwood, K. Disability and co-morbidity in relation to frailty: How much do they overlap? Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2012, 55, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitnitski, A.B.; Rutenberg, A.D.; Farrell, S.; Rockwood, K. Aging, frailty and complex networks. Biogerontology 2017, 18, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, S.G.; Mitnitski, A.B.; Rockwood, K.; Rutenberg, A.D. Network model of human aging: Frailty limits and information measures. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 94, 052409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, S.G.; Mitnitski, A.B.; Theou, O.; Rockwood, K.; Rutenberg, A.D. Probing the network structure of health deficits in human aging. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 98, 032302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutenberg, A.D.; Mitnitski, A.B.; Farrell, S.G.; Rockwood, K. Unifying aging and frailty through complex dynamical networks. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 107, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneja, S.; Mitnitski, A.B.; Rockwood, K.; Rutenberg, A.D. Dynamical network model for age-related health deficits and mortality. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 93, 022309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Peña, C.; Ramírez-Aldana, R.; Parra-Rodriguez, L.; Gomez-Verjan, J.C.; Pérez-Zepeda, M.U.; Gutiérrez-Robledo, L.M. Network analysis of frailty and aging: Empirical data from the Mexican Health and Aging Study. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 128, 110747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.; Michaels-Obregon, A.; Palloni, A. Cohort Profile: The Mexican Health and Aging Study (MHAS). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritzen, S.L. Graphical Models; Oxford Statistical Science Series; The Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bondy, J.A.; Murty, U.S.R. Graph Theory with Applications; The Macmillan Press Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Højsgaard, S.; Edwards, D.; Lauritzen, S. Graphical Models with R; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-1-4614-2298-3. [Google Scholar]
- Nagarajan, R.; Scutari, M.; Lèbre, S. Bayesian Networks in R: With Applications in Systems Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4614-6445-7. [Google Scholar]
- Cowell, R.G.; Dawid, P.; Lauritzen, S.L.; Spiegelhalter, D.J. Probabilistic Networks and Expert Systems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1999; ISBN 0-387-98767-3. [Google Scholar]
- Pearl, J. Fusion, propagation, and structuring in belief networks. Artif. Intell. 1986, 29, 241–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scutari, M. Learning Bayesian Networks with the Bnlearn R Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 35, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Müller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idler, E.L.; Benyamini, Y. Self-Rated Health and Mortality: A Review of Twenty-Seven Community Studies. J. Health Soc. Behav. 1997, 38, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idler, E.L.; Russell, L.B.; Davis, D. Survival, Functional Limitations, and Self-rated Health in the NHANES I Epidemiologic Follow-up Study, 1992. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 152, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKenbach, J.P.; Simon, J.G.; Looman, C.W.; Joung, I.M. Self-assessed health and mortality: Could psychosocial factors explain the association? Int. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 31, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuorisalmi, M.; Lintonen, T.; Jylhä, M. Global self-rated health data from a longitudinal study predicted mortality better than comparative self-rated health in old age. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2005, 58, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobbens, R.J. Associations of ADL and IADL disability with physical and mental dimensions of quality of life in people aged 75 years and older. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sien, N.Y.; Jung, H. Assessment of the Six Activities of Daily Living in Adults. Singap. Fam Physician 2012, 38, 26–36. [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney, F.I.; Barthel, D.W. Functional evaluation: The Barthel Index. Md. State Med. J. 1965, 14, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.; Vanclay, F.; Cooper, B. Improving the sensitivity of the Barthel Index for stroke rehabilitation. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1989, 42, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granger, C.V.; Hamilton, B.B.; Keith, R.A.; Zielezny, M.; Sherwin, F.S. Advances in functional assessment for medical rehabilitation. Top. Geriatr. Rehabil. 1986, 1, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jylhä, M. What is self-rated health and why does it predict mortality? Towards a unified conceptual model. Soc. Sci. Med. 2009, 69, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossey, J.M.; Shapiro, E. Self-rated health: A predictor of mortality among the elderly. Am. J. Public Health 1982, 72, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhme, S.; Renneberg, B. Predicting Self-Rated Health in Diabetes and Chronic Heart Failure—A Multiple Mediation Model. Front. Public Health 2015, 3, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, M.E.Y.; Barrera, V.H.; Cordero, X.F.; Gil de Miguel, A.; Pérez, M.R.; Andres, A.L.-D.; Jiménez-García, R. Self-perception of health status, mental health and quality of life among adults with diabetes residing in a metropolitan area. Diabetes Metab. 2010, 36, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.Y.; Mak, K.K.; Thomas, G.N.; Schooling, M.; Fielding, R.; Janus, E.D.; Lam, T.H. The relation of chronic cardiovascular diseases and diabetes mellitus to perceived health, and the moderating effects of sex and age. Soc. Sci. Med. 2007, 65, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamrozik, K. Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: A meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet 2002, 360, 1903–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowling, C.B.; Davis, B.R.; Luciano, A.; Simpson, L.M.; Sloane, R.; Pieper, C.F.; Einhorn, P.T.; Oparil, S.; Muntner, P. Sustained blood pressure control and coronary heart disease, stroke, heart failure, and mortality: An observational analysis of allhat. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2019, 21, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. A Global Brief on Hypertension: Silent Killer, Global Public Health Crisis: World Health Day 2013; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation—IHME GBD Compare Data Visualization. 2019. Available online: http://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare/ (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Almeida, O.P.; Tamai, S. Congestive heart failure and cognitive functioning amongst older adults. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2001, 59, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Ovbiagele, B.; Feng, W. Diabetes and Stroke: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Pharmaceuticals and Outcomes. Am. J. Med Sci. 2016, 351, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, K.; Tarr, J.M.; Ahmad, S.I.; Kohner, E.M.; Chibber, R. Introduction to Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes 2013, 771, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emdin, C.A.; Anderson, S.G.; Woodward, M.; Rahimi, K. Usual Blood Pressure and Risk of New-Onset Diabetes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Zhou, T.; Heianza, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, M.; Fonseca, V.A.; Qi, L. Type 2 Diabetes and Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Pan, A.; Wu, J.H.; Zhao, F.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Pan, X.-F.; Yang, C.-X. Association between Higher Blood Pressure and Risk of Diabetes Mellitus in Middle-Aged and Elderly Chinese Adults. Diabetes Metab. J. 2020, 44, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, B.; De Faria, A.P.; Ritter, A.M.V.; Yugar, L.B.T.; Ferreira-Melo, S.E.; Amorim, R.; Modolo, R.; Fattori, A.; Yugar-Toledo, J.C.; Coca, A.; et al. Glycated hemoglobin correlates with arterial stiffness and endothelial dysfunction in patients with resistant hypertension and uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2018, 20, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E.; Cushman, W.C. Diabetes and hypertension: The bad companions. Lancet 2012, 380, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conen, D.; Ridker, P.M.; Mora, S.; Buring, J.E.; Glynn, R.J. Blood pressure and risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus: The Women’s Health Study. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 2937–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, T.; Tsumura, K.; Suematsu, C.; Endo, G.; Fujii, S.; Okada, K. High normal blood pressure, hypertension, and the risk of type 2 diabetes in Japanese men. The Osaka Health Survey. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 1683–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alibhai, S.M.; Greenwood, C.; Payette, H. An approach to the management of unintentional weight loss in elderly people. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2005, 172, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stajkovic, S.; Aitken, E.M.; Holroyd-Leduc, J. Unintentional weight loss in older adults. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2011, 183, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payette, H.; Coulombe, C.; Boutier, V.; Gray-Donald, K. Weight Loss and Mortality Among Free-Living Frail Elders: A Prospective Study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 1999, 54, M440–M445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tully, C.L.; Snowdon, D.A. Weight Change and Physical Function in Older Women: Findings from the Nun Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1995, 43, 1394–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reise, S.P.; Henson, J.M. A Discussion of Modern Versus Traditional Psychometrics As Applied to Personality Assessment Scales. J. Pers. Assess. 2003, 81, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrory, S.; Shenkin, S.; Austin, E.; Starr, J.M. Lawton IADL scale in dementia: Can item response theory make it more informative? Age Ageing 2014, 43, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempen, G.; Myers, A.; Powell, L. Hierarchical structure in ADL and IADL: Analytical assumptions and applications for clinicians and researchers. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1995, 48, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieo, R.; Watson, R.; Deary, I.J.; Starr, J.M. A Revised Activities of Daily Living/Instrumental Activities of Daily Living Instrument Increases Interpretive Power: Theoretical Application for Functional Tasks Exercise. Gerontology 2010, 56, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suurmeijer, T.P.; Doeglas, D.M.; Moum, T.; Briançon, S.; Krol, B.; Sanderman, R.; Guillemin, F.; Bjelle, A.; Heuvel, W.J.V.D. The Groningen Activity Restriction Scale for measuring disability: Its utility in international comparisons. Am. J. Public Health 1994, 84, 1270–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, G.; Iliffe, S.; Walters, K. Frailty index as a predictor of mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing 2018, 47, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veld, L.P.M.O.H.; Beurskens, A.J.H.M.; de Vet, H.C.W.; van Kuijk, S.M.J.; Hajema, K.; Kempen, G.I.J.M.; van Rossum, E. The ability of four frailty screening instruments to predict mortality, hospitalization and dependency in (instrumental) activities of daily living. Eur. J. Ageing 2019, 16, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stow, D.; Matthews, F.; Barclay, S.; Iliffe, S.; Clegg, A.; De Biase, S.; Robinson, L.; Hanratty, B. Evaluating frailty scores to predict mortality in older adults using data from population based electronic health records: Case control study. Age Ageing 2018, 47, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mexican Health and Aging Study. Available online: http://www.mhasweb.org/ (accessed on 6 July 2022).
| Deficit Description (Name) | n = 10,983 Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| Help dressing (Dress) | 983 (8.95) |
| Help getting in/out of a chair (In_out_chair) | 3264 (29.72) |
| Help walking around the room (Help_Walk) | 160 (1.46) |
| Help eating (Eat) | 101 (0.92) |
| Help grooming (Groom) | 150 (1.37) |
| Help using toilet (Toilet) | 128 (1.17) |
| Help up/down one flight of stairs (Stairs) | 2594 (23.62) |
| Help lifting 10 pounds (Lift) | 2557 (23.28) |
| Help shopping groceries (Shop) | 865 (7.88) |
| Help with preparing a hot meal (Meals) | 630 (5.74) |
| Help taking medication (Meds) | 162 (1.48) |
| Help with finances (Finance) | 169 (1.54) |
| Lost five kilos or more of weight in the last two years (Lost_weight) | 2375 (21.62) |
| Poor/regular self-rated health (Health) | 1315 (11.97) |
| Compared to 2 years ago much worse or worse self-rated health (H_change) | 3149 (28.67) |
| Spent one day or more in bed due to sickness or injury (Bed) | 1941 (17.67) |
| Within the past week: Felt tired (Tired) | 6402 (58.29) |
| Difficulty walking a block (Walk_out) | 1353 (12.32) |
| Feel everything is an effort (Effort) | 3810 (34.69) |
| Feel depressed (Depressed) | 3705 (33.73) |
| Not feeling happy (No_Happy) | 2187 (19.91) |
| Feel lonely (Lone) | 3196 (29.10) |
| Feel without energy (No_Energy) | 5639 (51.34) |
| Hypertension/high blood pressure (High_BP) | 4727 (43.04) |
| Heart attack (Heart_attack) | 378 (3.44) |
| Heart failure (CHF) | 207 (1.88) |
| Stroke (Stroke) | 203 (1.85) |
| Cancer (in the last 10 years) (Cancer) | 227 (2.07) |
| Diabetes (Diabetes) | 2394 (21.80) |
| Arthritis or rheumatism (Arthritis) | 1490 (13.57) |
| Respiratory illness (CLD) | 639 (5.82) |
| Worse memory quality compared to two years ago (Memory) | 2342 (21.32) |
| Weak dominant hand strength (Grip) | 2566 (23.36) |
| Loss of appetite in the last 2 years (Anorexia) | 515 (4.69) |
| Not doing exercise or hard physical work at least3 times a week (Exercise) | 6647 (60.52) |
| Died between 2012 and 2015 (Dead) | 574 (5.23) |
| Deficit | Indegree + Outdegree | Outdegree | Indegree |
|---|---|---|---|
| H_change | 11 | 6 | 5 |
| In_out_chair | 10 | 10 | 0 |
| Lift | 10 | 8 | 2 |
| Shop | 10 | 6 | 4 |
| Health | 9 | 5 | 4 |
| Walk_out | 9 | 6 | 3 |
| Effort | 9 | 8 | 1 |
| Depressed | 9 | 6 | 3 |
| Grip | 9 | 4 | 5 |
| Stairs | 8 | 6 | 2 |
| Groom | 7 | 3 | 4 |
| Tired | 7 | 5 | 2 |
| High_BP | 7 | 3 | 4 |
| Dress | 6 | 3 | 3 |
| Toilet | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Meals | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Lost_weight | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| No_Happy | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| Lone | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| No_Energy | 4 | 0 | 4 |
| Heart_attack | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Exercise | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| Walk | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Eat | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Meds | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Bed | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Diabetes | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Arthritis | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Memory | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Anorexia | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Finance | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Stroke | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| CLD | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Dead | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| CHF | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Cancer | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramírez-Aldana, R.; Gomez-Verjan, J.C.; García-Peña, C.; Gutiérrez-Robledo, L.M.; Parra-Rodríguez, L. Understanding Frailty: Probabilistic Causality between Components and Their Relationship with Death through a Bayesian Network and Evidence Propagation. Electronics 2022, 11, 3001. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11193001
Ramírez-Aldana R, Gomez-Verjan JC, García-Peña C, Gutiérrez-Robledo LM, Parra-Rodríguez L. Understanding Frailty: Probabilistic Causality between Components and Their Relationship with Death through a Bayesian Network and Evidence Propagation. Electronics. 2022; 11(19):3001. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11193001
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamírez-Aldana, Ricardo, Juan Carlos Gomez-Verjan, Carmen García-Peña, Luis Miguel Gutiérrez-Robledo, and Lorena Parra-Rodríguez. 2022. "Understanding Frailty: Probabilistic Causality between Components and Their Relationship with Death through a Bayesian Network and Evidence Propagation" Electronics 11, no. 19: 3001. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11193001
APA StyleRamírez-Aldana, R., Gomez-Verjan, J. C., García-Peña, C., Gutiérrez-Robledo, L. M., & Parra-Rodríguez, L. (2022). Understanding Frailty: Probabilistic Causality between Components and Their Relationship with Death through a Bayesian Network and Evidence Propagation. Electronics, 11(19), 3001. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11193001










