Machine Vision-Based Human Action Recognition Using Spatio-Temporal Motion Features (STMF) with Difference Intensity Distance Group Pattern (DIDGP)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Contributions
2.2. Organization
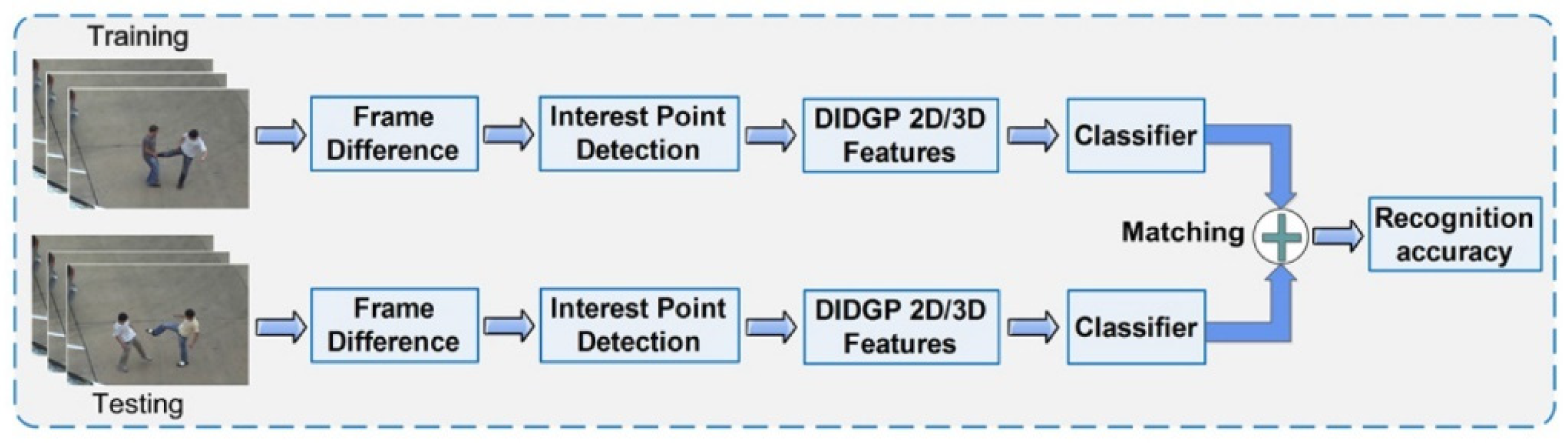
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Identifying Motion by Frame Differencing
3.2. Overview of the Proposed Human Action Recognition Framework
Interest Point Identification
3.3. Feature Extraction Procedure
3.3.1. Distance Relationship Calculation
3.3.2. Distance Group Pattern
3.3.3. Signal Transformation Descriptors
3.4. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3.5. Classification Methods
3.5.1. Support Vector Machines
3.5.2. Random Forest
4. Experimental Setup
4.1. 3D-DIDGP
4.2. 2D-DIDGP
4.3. DCT
4.4. DWT
4.5. Hybrid DWT+DCT
4.6. Dataset
4.7. Evaluation Metrics
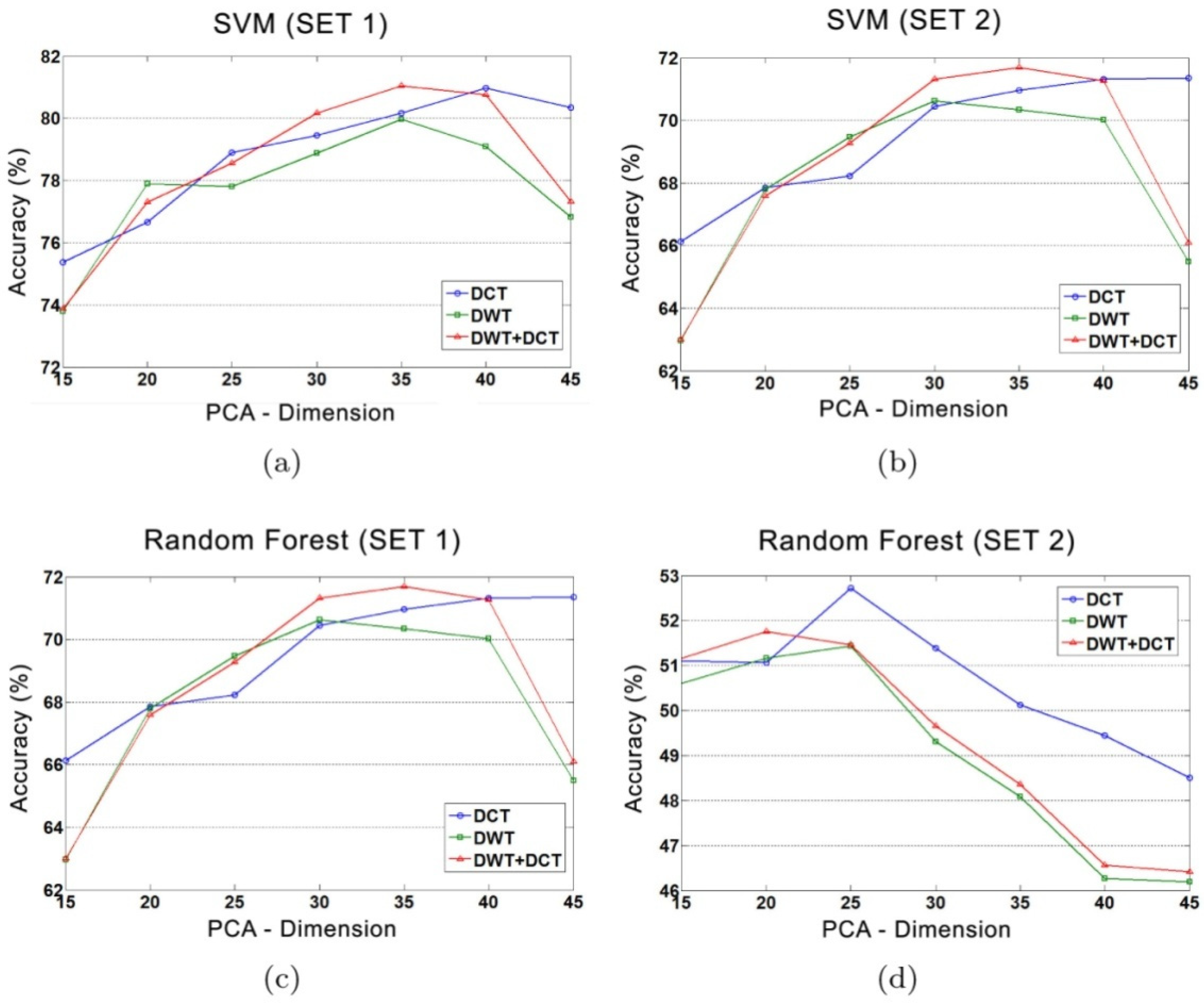
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Transform Based Descriptor
5.2. 2D-DIDGP
5.3. 3D-DIDGP
6. Performance Analysis of Different Methods
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russo, P.; Ticca, S.; Alati, E.; Pirri, F. Learning to See Through a Few Pixels: Multi Streams Network for Extreme Low-Resolution Action Recognition. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 12019–12026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Gao, X. Multi-Scale Mixed Dense Graph Convolution Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 36475–36484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Cho, S.; Kim, D.; Bailo, O.; Park, H.; Hong, S.; Park, J. A Body Part Embedding Model with Datasets for Measuring 2D Human Motion Similarity. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 36547–36558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Guo, L.; Guan, W.; Liu, A.-A.; Ren, T.; Chen, S. A Pairwise Attentive Adversarial Spatiotemporal Network for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Action Recognition-R2. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 30, 767–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunnehru, J.; KalaiselviGeetha, M. Automatic human emotion recognition in surveillance video. In Intelligent Techniques in Signal Processing for Multimedia Security; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 321–342. [Google Scholar]
- Thalapathiraj, S.; Baskaran, B.; Arunnehru, J. Novel approach for texture feature extraction and classification of satellite images using modified Hilbert matrix. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2112, 020154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeslund, T.B.; Hilton, A.; Krüger, V. A survey of advances in vision-based human motion capture and analysis. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2006, 104, 90–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turaga, P.; Chellappa, R.; Subrahmanian, V.S.; Udrea, O. Machine Recognition of Human Activities: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2008, 18, 1473–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poppe, R. Vision-based human motion analysis: An overview. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2007, 108, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe, R. A survey on vision-based human action recognition. Image Vis. Comput. 2010, 28, 976–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinland, D.; Ronfard, R.; Boyer, E. A survey of vision-based methods for action representation, segmentation and recognition. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2011, 115, 224–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hur, T.; Bang, J.; Huynh-The, T.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.-I.; Lee, S. Iss2Image: A Novel Signal-Encoding Technique for CNN-Based Human Activity Recognition. Sensors 2018, 18, 3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cruciani, F.; Vafeiadis, A.; Nugent, C.; Cleland, I.; McCullagh, P.; Votis, K.; Giakoumis, D.; Tzovaras, D.; Chen, L.; Hamzaoui, R. Feature learning for Human Activity Recognition using Convolutional Neural Networks. CCF Trans. Pervasive Comput. Interact. 2020, 2, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arunnehru, J.; Chamundeeswari, G.; Bharathi, S.P. Human Action Recognition using 3D Convolutional Neural Networks with 3D Motion Cuboids in Surveillance Videos. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 133, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaijayanthi, S.; Arunnehru, J. Synthesis approach for emotion recognition from cepstral and pitch coefficients using machine learning. In International Conference on Communication, Computing and Electronics Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 515–528. [Google Scholar]
- Laptev, I. On space-time interest points. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2005, 64, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollar, P.; Rabaud, V.; Cottrell, G.; Belongie, S. Behavior recognition via sparse spatio-temporal features. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Workshop on Visual Surveillance and Performance Evaluation of Tracking and Surveillance, Beijing, China, 15–16 October 2005; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Foroosh, H. View-invariant action recognition using fundamental ratios. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan, P.; Singh, V.K.; Nevatia, R. Learning 3D action models from a few 2D videos for view invariant action recognition. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 2006–2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sabzmeydani, P.; Mori, G. Semi-latent dirichlet allocation: A hierarchical model for human action recognition. In Human Motion–Understanding, Modeling, Capture and Animation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 240–254. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, A.; Mori, G. Action recognition by learning mid-level motion features. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Elgammal, A.; Shet, V.; Yacoob, Y.; Davis, L. Learning dynamics for exemplar-based gesture recognition. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Proceedings, Madison, WI, USA, 18–20 June 2003; Volume 1, pp. 571–578. [Google Scholar]
- Thurau, C.; Hlavac, V. Pose primitive based human action recognition in videos or still images. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Schuldt, C.; Laptev, I.; Caputo, B. Recognizing human actions: A local svm approach. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, ICPR 2004, Cambridge, UK, 26 August 2004; Volume 3, pp. 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Shechtman, E.; Irani, M. Space-time behavior based correlation. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 405–412. [Google Scholar]
- Laptev, I.; Marszalek, M.; Schmid, C.; Rozenfeld, B. Learning realistic human actions from movies. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gorelick, L.; Blank, M.; Shechtman, E.; Irani, M.; Basri, R. Actions as space-time shapes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 2247–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuehne, H.; Jhuang, H.; Garrote, E.; Poggio, T.; Serre, T. Hmdb: A large video database for human motion recognition. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 2556–2563. [Google Scholar]
- Marszalek, M.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. Actions in context. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 2929–2936. [Google Scholar]
- Ryoo, M.S.; Aggarwal, J.K. UT-Interaction Dataset, ICPR Contest on Semantic Description of Human Activities (SDHA). 2010. Available online: https://cvrc.ece.utexas.edu/SDHA2010/Human_Interaction.html (accessed on 17 July 2022).
- Waltisberg, D.; Yao, A.; Gall, J.; van Gool, L. Variations of a hough-voting action recognition system. In Recognizing Patterns in Signals, Speech, Images and Videos; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 306–312. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Wu, X.; Peng, Q.; Qi, X.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, Y. Exploring dense trajectory feature and encoding methods for human interaction recognition. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Internet Multimedia Computing and Service, ACM, New York, NY, USA, 17–19 August 2013; pp. 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/The-Discrete-Cosine-Transform-(-DCT-)-%3A-Theory-and-Khayam/a99022c31741b797c609fde38286882e85a86d59 (accessed on 17 July 2022).
- Cody, M.A. The fast wavelet transform beyond fourier transforms. Dr. Dobb’s J. 1992, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.; Chang, S.-F. Transform features for texture classification and discrimination in large image databases. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Image Processing, Austin, TX, USA, 13–16 November 1994; Volume 3, pp. 407–411. [Google Scholar]
- Climer, S.; Bhatia, S.K. Image database indexing using JPEG coefficients. Pattern Recognit. 2002, 35, 2479–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Audicana, M.; Saleta, J.L.; Catalan, R.G.; Garcia, R. Fusion of multispectral and panchromatic images using improved ihs and pca mergers based on wavelet decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajczyk, K.; Schmid, C. Scale & affine invariant interest point detectors. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 63–86. [Google Scholar]
- Koornwinder, T.H. Wavelets: An Elementary Treatment of Theory and Applications; World Scientific: Singapore, 1993; Volume 1, ISBN 9789814503747. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, K. On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1901, 2, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hotelling, H. Analysis of a complex of statistical variables into principal components. J. Educ. Psychol. 1993, 24, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristianini, N.; Shawe-Taylor, J. An Introduction to Support Vector Machines and Other Kernel-Based Learning Meth-Ods; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, T. Machine Learning; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 0070428077. [Google Scholar]
- Vapnik, V.N. An overview of statistical learning theory. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1999, 10, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-J. Libsvm: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2011, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arunnehru, J.; Davi, A.K.N.; Sharan, R.R.; Nambiar, P.G. Human Pose Estimation and Activity Classification Using Machine Learning Approach. In International Conference on Soft Computing and Signal Processing; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 113–123. [Google Scholar]
- Arunnehru, J.; Kumar, A.; Verma, J.P. Early Prediction of Brain Tumor Classification Using Convolution Neural Networks. In International Conference on Computational Intelligence, Security and Internet of Things; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Poonkodi, M.; Vadivu, G. Action recognition using correlation of temporal difference frame (ctdf)—an algorithmic approach. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 12, 7107–7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Wang, C.; Ju, Z. A New Framework of Human Interaction Recognition Based on Multiple Stage Probability Fusion. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uddin, A.; Joolee, J.B.; Alam, A.; Lee, Y.-K. Human Action Recognition Using Adaptive Local Motion Descriptor in Spark. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 21157–21167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Xu, C.; Feng, Z.; Ma, X. Affective interaction recognition using spatio-temporal features and context. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2016, 144, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chang, M.-C.; Ge, W.; Chen, T. Spatio-Temporal Phrases for Activity Recognition. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2012; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 707–721. [Google Scholar]
- Vahdat, A.; Gao, B.; Ranjbar, M.; Mori, G. A discriminative key pose sequence model for recognizing human interactions. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops), Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 1729–1736. [Google Scholar]
- Motiian, S.; Feng, K.; Bharthavarapu, H.; Sharlemin, S.; Doretto, G. Pairwise Kernels for Human Interaction Recognition. In Advances in Visual Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 210–221. [Google Scholar]
- Ryoo, M.S.; Chen, C.-C.; Aggarwal, J.K.; Roy-Chowdhury, A. An Overview of Contest on Semantic Description of Human Activities (SDHA) 2010. In Recognizing Patterns in Signals, Speech, Images and Videos; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 270–285. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, A.; Gall, J.; Van Gool, L. A Hough transform-based voting framework for action recognition. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 2061–2068. [Google Scholar]












| Types of Kernel Inner Product Kernel |
|---|
| Linear |
| Polynomial |
| Radial Basis Function |
| Sigmoid |
| Actual Values | Positive | Negative | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted Values | |||
| Positive | TP | FP | |
| Negative | FN | TN | |
| A | B | C | D | E | F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 92.66 | 1.68 | 1.68 | 1.22 | 0.61 | 2.14 |
| B | 1.21 | 91.68 | 2.05 | 1.57 | 0.72 | 2.77 |
| C | 2.23 | 2.75 | 88.73 | 1.83 | 1.83 | 2.62 |
| D | 2.48 | 3.73 | 1.45 | 90.06 | 1.04 | 1.24 |
| E | 2.61 | 2.43 | 2.43 | 0.93 | 84.89 | 6.72 |
| F | 1.57 | 3.13 | 1.72 | 0.63 | 1.72 | 91.22 |
| A | B | C | D | E | F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 90.06 | 5.25 | 0.55 | 0.14 | 1.52 | 2.49 |
| B | 2.78 | 89.52 | 1.26 | 0.76 | 1.89 | 3.79 |
| C | 3.37 | 4.16 | 85.94 | 0.59 | 1.39 | 4.55 |
| D | 1.99 | 1.99 | 2.33 | 83.72 | 2.66 | 7.31 |
| E | 2.73 | 4.92 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 85.79 | 5.83 |
| F | 1.69 | 3.38 | 1.52 | 0.34 | 2.54 | 90.52 |
| A | B | C | D | E | F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 90.83 | 4.59 | 1.99 | 0.61 | 0.92 | 1.07 |
| B | 2.90 | 90.83 | 2.65 | 0.60 | 0.97 | 2.05 |
| C | 2.23 | 3.93 | 89.91 | 0.92 | 0.79 | 2.23 |
| D | 5.18 | 4.97 | 2.69 | 85.09 | 0.62 | 1.45 |
| E | 2.61 | 8.02 | 1.87 | 1.68 | 81.90 | 3.92 |
| F | 2.04 | 6.11 | 2.66 | 0.31 | 0.47 | 88.40 |
| A | B | C | D | E | F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 90.19 | 6.35 | 1.10 | 0.00 | 1.24 | 1.10 |
| B | 6.06 | 88.51 | 1.01 | 0.13 | 1.64 | 2.65 |
| C | 3.17 | 6.93 | 80.00 | 0.79 | 3.76 | 5.35 |
| D | 2.99 | 3.32 | 1.99 | 84.72 | 1.99 | 4.98 |
| E | 1.09 | 6.74 | 0.73 | 0.18 | 86.70 | 4.55 |
| F | 1.52 | 6.09 | 2.03 | 0.51 | 2.88 | 86.97 |
| A | B | C | D | E | F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 94.66 | 0.76 | 1.27 | 1.02 | 2.29 | 0.00 |
| B | 0.21 | 95.47 | 1.03 | 0.41 | 2.88 | 0.00 |
| C | 2.22 | 0.49 | 92.84 | 0.74 | 3.46 | 0.25 |
| D | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| E | 0.65 | 0.86 | 1.29 | 0.22 | 96.77 | 0.22 |
| F | 0.46 | 0.23 | 0.92 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 98.16 |
| A | B | C | D | E | F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 91.51 | 0.63 | 0.94 | 0.63 | 1.57 | 4.72 |
| B | 1.33 | 88.67 | 1.67 | 0.67 | 3.33 | 4.33 |
| C | 1.37 | 2.73 | 82.24 | 0.55 | 2.46 | 10.66 |
| D | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| E | 0.68 | 0.46 | 0.91 | 1.14 | 93.15 | 3.65 |
| F | 1.57 | 0.79 | 0.26 | 0.00 | 0.79 | 96.59 |
| A | B | C | D | E | F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 89.57 | 2.54 | 5.34 | 0.51 | 1.27 | 0.76 |
| B | 1.03 | 93.21 | 3.50 | 0.41 | 1.23 | 0.62 |
| C | 7.16 | 7.16 | 79.01 | 0.99 | 2.72 | 2.96 |
| D | 0.00 | 0.62 | 0.00 | 99.38 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| E | 0.86 | 1.72 | 2.15 | 0.86 | 91.83 | 2.58 |
| F | 1.84 | 1.84 | 2.53 | 0.00 | 1.61 | 92.18 |
| A | B | C | D | E | F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 77.67 | 2.20 | 1.26 | 0.63 | 8.81 | 9.43 |
| B | 6.33 | 67.67 | 2.33 | 0.33 | 14.67 | 8.67 |
| C | 3.28 | 3.28 | 75.96 | 0.82 | 13.11 | 3.55 |
| D | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| E | 1.14 | 1.37 | 3.65 | 0.68 | 89.50 | 3.65 |
| F | 2.62 | 2.36 | 2.36 | 0.00 | 7.87 | 84.78 |
| Method | Year | Set 1 | Set 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed | - | 96.32 | 92.03 |
| Poonkodi et at. [49] | 2020 | 96.08 | 89.3 |
| Xiao-Fei et al. [50] | 2017 | 94 | - |
| Uddin et al. [51] | 2017 | 91.67 | - |
| Liang et al. [52] | 2016 | 92.3 | - |
| Zhang et al. [53] | 2012 | 95 | 90 |
| Xiaojiang et al. [32] | 2013 | 94.5 | 91.7 |
| Vahdat et al. [54] | 2011 | 93 | 90 |
| Motiian et al. [55] | 2013 | 91.8 | 87.87 |
| Waltisberg et al. [31] | 2010 | 88 | 77 |
| Ryoo et al. [56] | 2010 | 85 | 70 |
| Angela et al. [57] | 2012 | 77 | 73 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arunnehru, J.; Thalapathiraj, S.; Dhanasekar, R.; Vijayaraja, L.; Kannadasan, R.; Khan, A.A.; Haq, M.A.; Alshehri, M.; Alwanain, M.I.; Keshta, I. Machine Vision-Based Human Action Recognition Using Spatio-Temporal Motion Features (STMF) with Difference Intensity Distance Group Pattern (DIDGP). Electronics 2022, 11, 2363. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11152363
Arunnehru J, Thalapathiraj S, Dhanasekar R, Vijayaraja L, Kannadasan R, Khan AA, Haq MA, Alshehri M, Alwanain MI, Keshta I. Machine Vision-Based Human Action Recognition Using Spatio-Temporal Motion Features (STMF) with Difference Intensity Distance Group Pattern (DIDGP). Electronics. 2022; 11(15):2363. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11152363
Chicago/Turabian StyleArunnehru, Jawaharlalnehru, Sambandham Thalapathiraj, Ravikumar Dhanasekar, Loganathan Vijayaraja, Raju Kannadasan, Arfat Ahmad Khan, Mohd Anul Haq, Mohammed Alshehri, Mohamed Ibrahim Alwanain, and Ismail Keshta. 2022. "Machine Vision-Based Human Action Recognition Using Spatio-Temporal Motion Features (STMF) with Difference Intensity Distance Group Pattern (DIDGP)" Electronics 11, no. 15: 2363. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11152363
APA StyleArunnehru, J., Thalapathiraj, S., Dhanasekar, R., Vijayaraja, L., Kannadasan, R., Khan, A. A., Haq, M. A., Alshehri, M., Alwanain, M. I., & Keshta, I. (2022). Machine Vision-Based Human Action Recognition Using Spatio-Temporal Motion Features (STMF) with Difference Intensity Distance Group Pattern (DIDGP). Electronics, 11(15), 2363. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11152363












