Maximum Versoria Criterion Algorithm with Adaptive Radius in Active Impulse Noise Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. ANC System and Algorithm Review
2.1. ANC Model
2.2. Algorithm Review
3. Proposed Algorithm
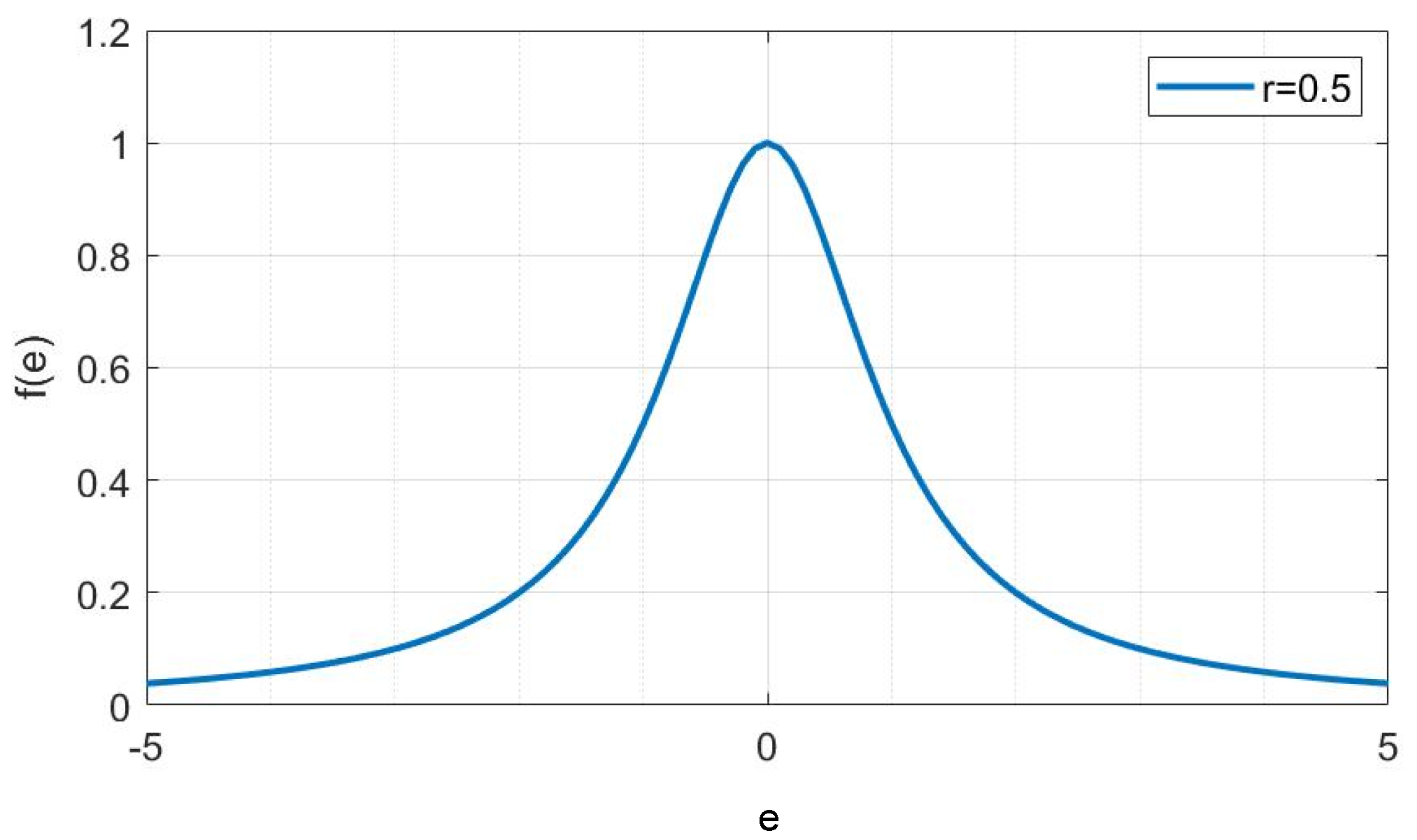
3.1. Derivation of the FxRMVC Algorithm
3.2. Stability of FxRMVC Algorithm
3.3. Adaptive Radius Strategy
3.4. Computational Complexity
4. Simulations
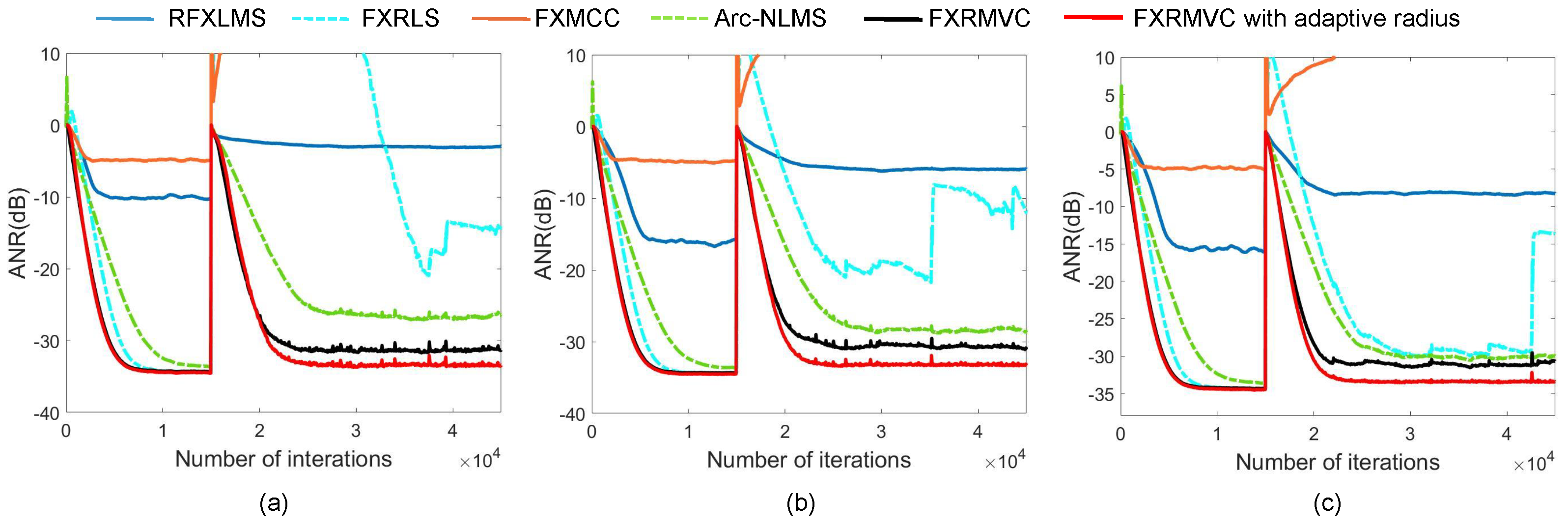
4.1. Effect of Sliding Window Size
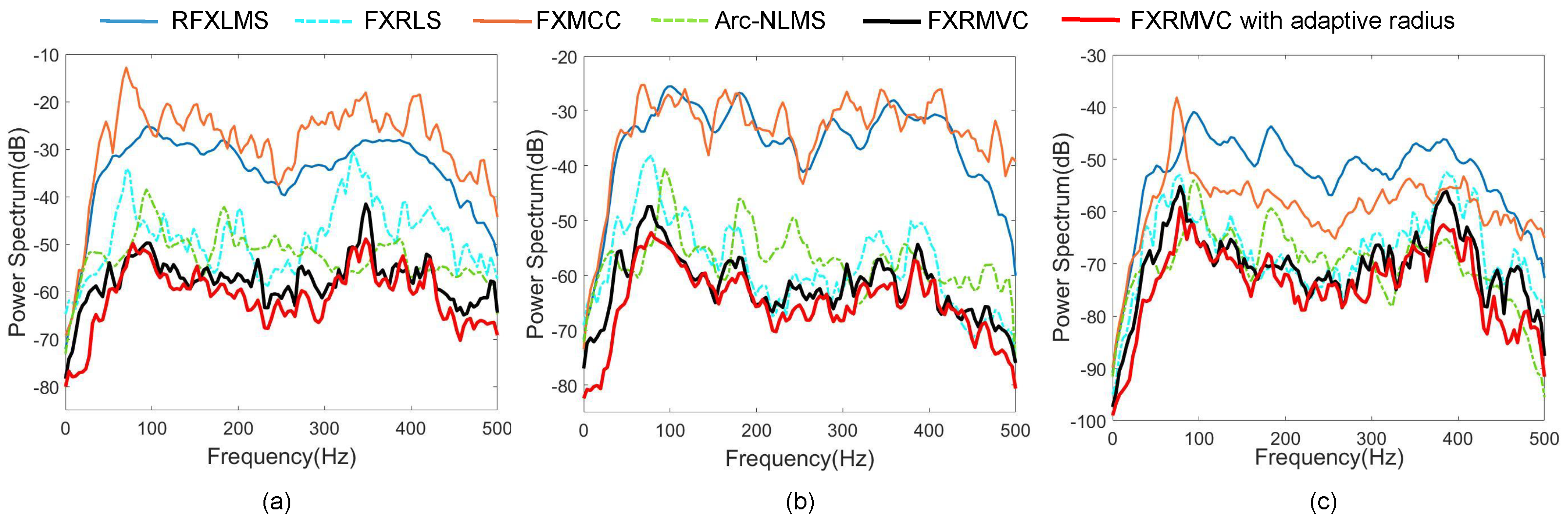
4.2. Alpha-Stable Noise
4.3. Mixture of Impulse and Gaussian Noise
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuo, S.M.; Kuo, K.; Gan, W.S. Active noise control: Open problems and challenges. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Green Circuits and Systems, Shanghai, China, 21–23 June 2010; pp. 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, S.M.; Morgan, D.R. Active Noise Control Systems; Wiley Publishing House: New York, NY, USA, 1996; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Qiu, X. Active impulsive noise control algorithm with post adaptive filter coefficient filtering. IET Signal Process. 2013, 7, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, R.; Zhou, Z.; Hsu, Y.-C. Adaptive filtering of stable processes for active attenuation of impulsive noise. In Proceedings of the 1995 International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Detroit, MI, USA, 9–12 May 1995; Volume 5, pp. 2983–2986. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Kuo, S.M.; Meng, G. Adaptive algorithm for active control of impulsive noise. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 291, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.T.; Mitsuhashi, W. Improving performance of FxLMS algorithm for active noise control of impulsive noise. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 327, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; He, H.; Qiu, X. An active impulsive noise control algorithm with logarithmic transformation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2010, 19, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, Y. Active control of impulsive noise with symmetric α-stable distribution based on an improved step-size normalized adaptive algorithm. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 56, 320–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayin, M.O.; Vanli, N.D.; Kozat, S.S. A novel family of adaptive filtering algorithms based on the logarithmic cost. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 4411–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, I.; Park, P.; Newcomb, R.W. A normalized least mean squares algorithm with a step-size scaler against impulsive measurement noise. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2013, 60, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Lin, Y.; Shi, L. A normalized least mean square algorithm based on the arctangent cost function robust against impulsive interference. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 35, 3040–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Pokharel, P.P.; Principe, J.C. Correntropy: Properties and applications in non-Gaussian signal processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2007, 55, 5286–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Sparse SM-NLMS algorithm based on correntropy criterion. Electron. Lett. 2016, 52, 1461–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Ning, X.; Wang, S. Mixture complex correntropy for adaptive filter. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2018, 66, 1476–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Shi, W.; Han, X.; Chen, B. Blocked maximum correntropy criterion algorithm for cluster-sparse system identifications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2019, 66, 1915–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Qu, H.; Gui, G.; Xu, L.; Zhao, J.; Chen, B. Maximum correntropy criterion based sparse adaptive filtering algorithms for robust channel estimation under non-Gaussian environments. J. Frankl. Inst. 2015, 352, 2708–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, X.; Chen, B. Robust generalized maximum correntropy criterion algorithms for active noise control. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio, Speech Lang. Process. 2020, 28, 1282–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.; Zeb, A.; Sheikh, S.A. Robust adaptive algorithm for active control of impulsive noise. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2016, 2016, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jabeen, F.; Mirza, A.; Zeb, A.; Imran, M.; Afzal, F.; Maqbool, A. FxRLS Algorithms Based Active Control of Impulsive Noise With Online Secondary Path Modeling. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 117471–117485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.-B.; Hou, X.-G.; Wu, Z.-G. Variable Step Adaptive Filtering LMS Algorithm Based on Tongue-Like Curve. J. Data Acquis. Process. 2004, 3, 282–285. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S. Maximum versoria criterion-based robust adaptive filtering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2017, 64, 1252–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Xue, W. A Kernel Recursive Maximum Versoria-Like Criterion Algorithm for Nonlinear Channel Equalization. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nithin, V.G.; Ganapati, P. A robust filtered-s LMS algorithm for nonlinear active noise control. Appl. Acoust. 2012, 73, 836–841. [Google Scholar]
- Kurian, N.C.; Patel, K.; George, N.V. Robust active noise control: An information theoretic learning approach. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 117, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belge, M.; Miller, E.L. A sliding window RLS-like adaptive algorithm for filtering alpha-stable noise. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2000, 7, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhao, H. Active impulsive noise control using maximum correntropy with adaptive kernel size. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 87, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrouz, F.-B. Adaptive Filters: Theroy and Applications; John Wiley & Sons Publishing House: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sayed, A.H. Fundamentals of Adaptive Filtering; John Wiley & Sons Publishing House: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamasco, M.; Della Rossa, F.; Piroddi, L. Active noise control with on-line estimation of non-Gaussian noise characteristics. J. Sound Vib. 2012, 331, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navia-Vazquez, A.; Arenas-Garcia, J. Combination of recursive least p-norm algorithms for robust adaptive filtering in alpha-stable noise. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 60, 1478–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Initialization: , , |
| FxRMVC algorithm:length of filter L, , , r |
| FxRMVC algorithm with adaptive radius: |
| 1:; |
| 2:; |
| 3:; |
| 4:; |
| 5:; |
| 6:; |
| 7:; |
| 8:; |
| 9:; |
| 10:; |
| Algorithms | Multiplications | Additions/Subtractions | Divisions |
|---|---|---|---|
| FxMCC | - | ||
| RFxLMS | 1 | ||
| Arc-NLMS | 2 | ||
| FxRLS | 1 | ||
| FxRMVC | 2 | ||
| FxRMVC with adaptive radius | 2 |
| Algorithms | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| FxMCC | |||
| RFxLMS | |||
| Arc-NLMS | |||
| FxRLS | |||
| FxRMVC | , , | ||
| FxRMVC with adaptive radius | , , |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, N.; Li, C.; Yu, L.; Yu, P.; Yao, T. Maximum Versoria Criterion Algorithm with Adaptive Radius in Active Impulse Noise Control. Electronics 2022, 11, 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11142178
Peng N, Li C, Yu L, Yu P, Yao T. Maximum Versoria Criterion Algorithm with Adaptive Radius in Active Impulse Noise Control. Electronics. 2022; 11(14):2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11142178
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Nuomeng, Chen Li, Linghao Yu, Ping Yu, and Tiannan Yao. 2022. "Maximum Versoria Criterion Algorithm with Adaptive Radius in Active Impulse Noise Control" Electronics 11, no. 14: 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11142178
APA StylePeng, N., Li, C., Yu, L., Yu, P., & Yao, T. (2022). Maximum Versoria Criterion Algorithm with Adaptive Radius in Active Impulse Noise Control. Electronics, 11(14), 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11142178






