Design and Analysis of Wideband Flexible Self-Isolating MIMO Antennas for Sub-6 GHz 5G and WLAN Smartphone Terminals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
- The antenna is a four-port structure with all the four elements connected to a common ground plane.
- The antenna operates in the entire sub-6 GHz 5G band (3.3 GHz–5 GHz) along with the WLAN band (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz).
- SAR analysis is carried out at two resonant peaks (3.5 and 5.1 GHz) in order to ensure the safe usage of the antenna in mobile terminals.
- Bending analysis is performed, which shows decent performance in terms of MIMO diversity, transmission, and scattering parameters that guarantee the practical usage of the antenna for slim and foldable smartphone devices.
- The antenna has demonstrated high gain (>4 dBi), high inter-elemental isolation (>17.5 dB), and reasonable efficiency (85%) with all the diversity parameters such as ECC, DG, TARC, MEG, and channel capacity meeting the requirements of MIMO antennas. Scattering, transmission, and MIMO parameters matched well under normal as well as bending conditions.
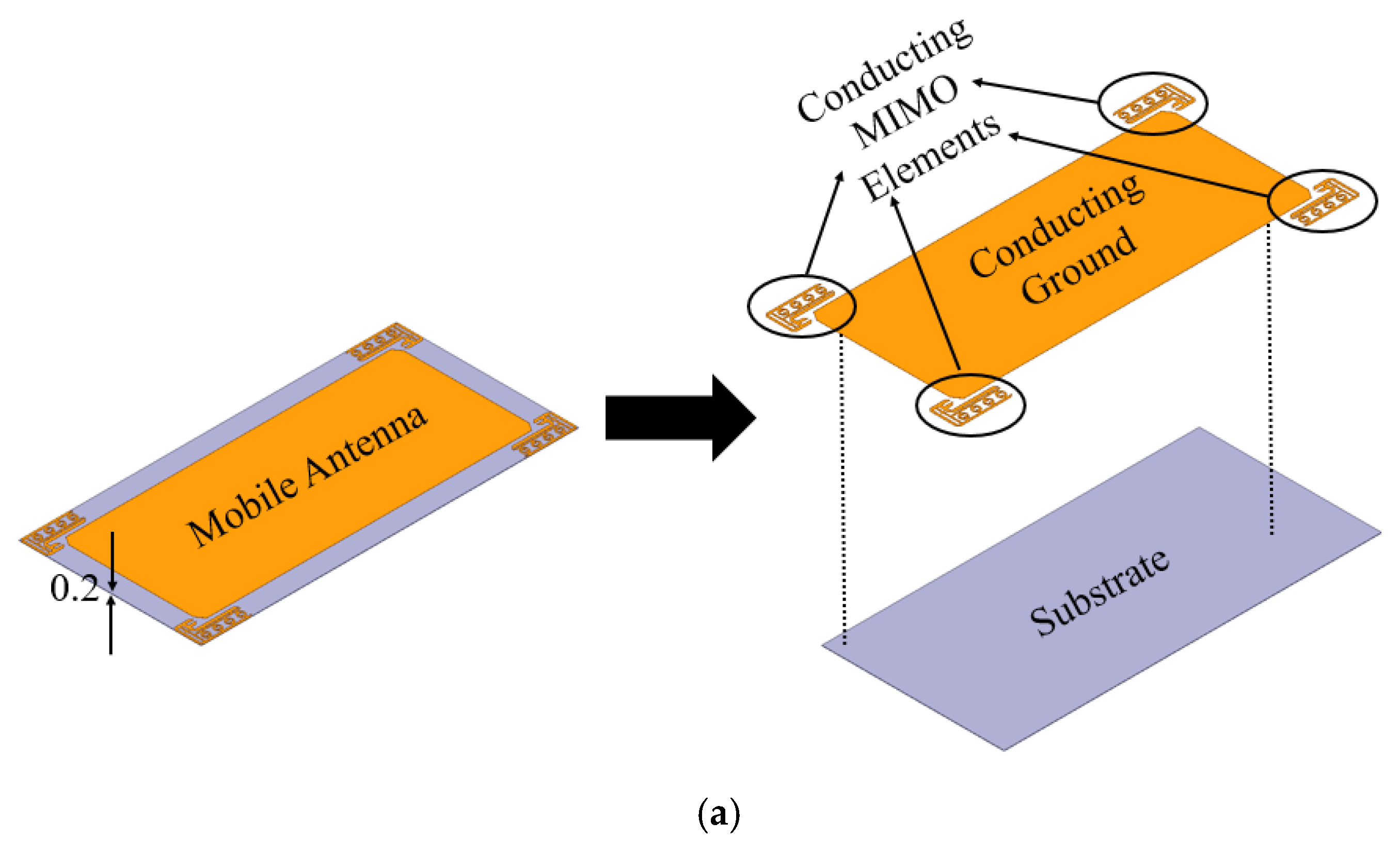
3. Mobile Antenna Design and Geometry
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Reflection Coefficient (dB)
4.2. Transmission Coefficient (dB)
4.3. Surface Current Disctribution (A/m)
4.4. Radiation Pattern (2D)
4.5. Radiation Pattern (3D)
4.6. Gain and Efficiency
5. MIMO Diversity Analysis
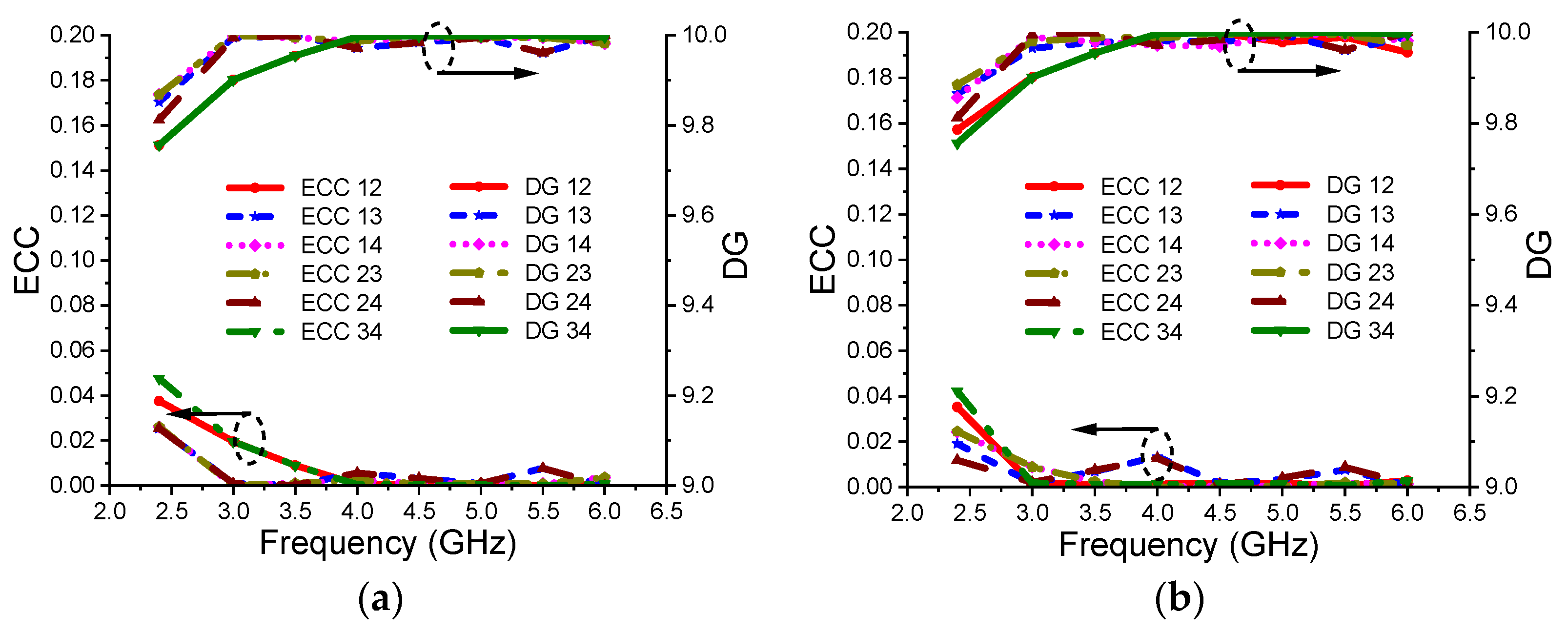
5.1. ECC and DG
5.2. TARC
5.3. MEG
5.4. Channel Capacity
6. Bending Analysis
6.1. Reflection Coefficient
6.2. Transmission Coefficient
6.3. Gain and Efficiency
6.4. ECC and DG
7. Impact on User Due to Smartphone Antenna (SAR Analysis)
7.1. Effect of SAR Analysis on Radiation Pattern (3D)
7.2. Effect of SAR on Human Tissue
8. Performance Comparison of Proposed Antenna
- The antenna in [21] has a lower bandwidth (3.4–3.6 GHz). Additionally, no bending analysis is carried out for any of the antennas.
- Flexible structure, high gain, high inter-elemental isolation, and reasonable efficiency with all the diversity parameters such as ECC, DG, TARC, MEG, and channel capacity meeting the requirements of the MIMO antenna make the proposed antenna a good contender for future mobile devices. Scattering, transmission, and MIMO parameters matched well under normal as well as bending conditions.
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sim, C.-Y.-D.; Chen, H.-D.; Kulkarni, J.; Lo, J.-J.; Hsuan, Y.-C. Recent Designs to Achieving Wideband MIMO Antenna for 5G NR Sub-6GHz Smartphone Applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Osaka, Japan, 25–28 January 2021; pp. 417–418. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, I.; Tang, X.; Shaukat, K.; Sarwar, M.U.; Alam, T.M.; Hameed, I.A.; Saleem, M.A. V2X-Based Mobile Localization in 3D Wireless Sensor Network. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.; Upadhyaya, T.; Patel, J.; Patel, R.; Palandoken, M. Flexible CPW fed transparent antenna for WLAN and sub-6 GHz 5G applications. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2020, 62, 2090–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishteyaq, I.; Khalid, M. Multiple input multiple output (MIMO) and fifth generation (5G): An indispensable technology for sub-6 GHz and millimeter wave future generation mobile terminal applications. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Dong, G.; Cai, Q.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, G. Dual-band MIMO antenna for 5G/WLAN mobile terminals. Micromachines 2021, 12, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, J.; Dhabre, S.; Kulkarni, S.; Sim, C.-Y.D.; Gangwar, R.K.; Cengiz, K. Six-Port Symmetrical CPW-Fed MIMO Antenna for Futuristic Smartphone Devices. In Proceeding of the 2021 6th International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT), Maharashtra, India, 2–4 April 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, K.; Kumar, S.; Kanaujia, B.K.; Dwari, S. Design and packaging of ultra-wideband multiple input-multiple-output/ diversity antenna for wireless applications. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput. Aided Eng. 2020, 30, e22357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, K.R.; Jibran, Z.A.P.; Singh, C.; Sharma, S.K. 4-Port MIMO Antenna Using Common Radiator on a Flexible Substrate for Sub-1GHz, Sub-6GHz 5G NR, and Wi-Fi 6 Applications. IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag. 2021, 2, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zhengwei, D.; Wang, Y. Eight-band antenna for full-screen metal frame LTE mobile phones. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 67, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, R.; Alreshaid, A.T.; Podilchak, S.K.; Sharawi, M.S. Compact 4G MIMO Antenna Integrated with a 5G Array for Current and Future Mobile Handsets. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2017, 11, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, Y.-J. Ceramic Based Small LTE MIMO Handset Antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 61, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-Q.; Sun, Y.-T.; Zhou, Q.-Q.; Ban, Y.-L.; Li, Y.-X.; Ang, S.S. Reconfigurable MIMO antenna for integrated-metal-rimmed smartphone applications. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 21223–21228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, M.; Wen, H.; Wang, J. Compact quadruple band MIMO antenna for 5G mobile applications. In Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP 2018), London, UK, 9–13 April 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.W.; Jang, B. A tunable MIMO antenna with dual-port structure for mobile phones. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 34113–34120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Xin, L. Wideband MIMO antenna with small ground clearance for mobile terminals. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2019, 13, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.Y.; Lin, X.Q.; Qiang, Q.Y.Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B. Structure-shared planar UWB MIMO antenna with high isolation for mobile platform. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 67, 2735–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.; Hussain, R.; Hammi, O.; Sharawi, M.S. An L-shaped 4-element monopole MIMO antenna system with enhanced isolation for mobile applications. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2016, 58, 2587–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Gupta, V.R. Design and development of low-profile MIMO antenna for 5G new radio smartphone applications. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 111, 1695–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Yang, S.-R.; Ban, Y.-L.; Qiang, Y.-F.; Guo, J.; Yu, Z.-F. Four-feed reconfigurable MIMO antenna for metal-frame smartphone applications. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2018, 12, 1477–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Haigang, F.; Yue, L.; Zhijun, Z. Tightly arranged orthogonal mode antenna for 5G MIMO mobile terminal. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2018, 60, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Haigang, F.; Yue, L.; Zhijun, Z. Compact 5G MIMO mobile phone antennas with tightly arranged orthogonal-mode pairs. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 6364–6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Di, L.; Xin, L. Tightly arranged four-element MIMO antennas for 5G mobile terminals. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 6353–6361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattha, H.T. 4-port 2-element MIMO antenna for 5G portable applications. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 96516–96520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Hui, L.; Sheng, B.Q.; Zhu, L. A compact 4-element MIMO antenna for terminal devices. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2020, 62, 2930–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricardo, G.-V.; Hildeberto, J.-A. Compact UWB uniplanar four-port MIMO antenna array with rejecting band. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 2543–2547. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Ansari, A.Q.; Kanaujia, B.K.; Kishor, J. A novel ITI-shaped isolation structure placed between two-port CPW-fed dual-band MIMO antenna for high isolation. Int. J. Electron. Commun. AEU 2019, 104, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Liu, B.; Cui, Y.; Hu, W. High-isolation eight-element MIMO array for 5G smartphone applications. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 34104–34112. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, G.; Jain, P.; Awasthi, Y. High diversity gain super-wideband single band-notch MIMO antenna for multiple wireless applications. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2020, 14, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.; Palandoken, M.; Kulkarni, J.; Byun, G.; Nguyen, T.K. Wideband Flexible/Transparent Connected-Ground MIMO Antennas for Sub-6 GHz 5G and WLAN Applications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 147003–147015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






















| Frequency (GHz) | MEGAnt-1/2 (dB) | MEG Ant-1/3 (dB) | MEG Ant-1/4 (dB) | MEG Ant-2/3 (dB) | MEG Ant-2/4 (dB) | MEG Ant-3/4 (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.5 | −3.01 | −3.01 | −3.01 | −3.01 | −3.01 | −3.01 |
| 5.1 | −3.01 | −3.01 | −3.01 | −3.01 | −3.01 | −3.01 |
| Ref | Year | Size (mm3) | Flexible | No. of Ports | Frequency Band (GHz) | Gain (dBi) | Efficiency (%) | Isolation | ECC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [9] | 2018 | 142 × 79 × 7.5 | No | 1 | (698–960 MHz) and (1.710–2.690 GHz) | -- | 42 | -- | -- |
| [10] | 2017 | 60 × 100 × 0.965 | No | 2 | 1.870–2.530 GHz 28 GHz | 4, 8 | 75 | 14 | ~0.18 |
| [11] | 2012 | 110 × 45 × 5 | No | 2 | 698 –960 and 1.710–2.690 GHz | 0–5/2–7 | 20–70/40 | 10 | ~0.4/0.03 |
| [12] | 2017 | 145 × 72 × 0.8 | No | 2 | 824–960 MHz, 1.710–2.690 GHz | −0.32–1.4 i/1.6–4.8 | 59–72 | 17 | 0.02/0.4 |
| [13] | 2018 | 136 × 68 × 6 | No | 2 | 3.5–3.9 GHz, 2.3–2.5 GHz, 3.3–3.5 GHz and 4.25–4.45 GHz | -- | 50 | 10 | ~0.2 |
| [14] | 2019 | 60 × 100 × 1 | No | 2 | 2.5–3.6 GHz | −4.9–−1.9 | -- | 10 | 0.16 |
| [15] | 2019 | 65 × 130 × 1 | No | 2 | 1710–2690 MHz | -- | 60–80 | 19 | <0.005 |
| [16] | 2018 | 110 × 120 × 0.508 | Semi | 2 | 3 to 10 | 2.6 | -- | 38 | ~0.0002 |
| [17] | 2016 | 100 × 60 × 0.8 | No | 4 | 2017 and 2265 MHz | 4.27 | 70 | 10 | ~0.18 |
| [18] | 2020 | 120 × 65 × 1.6 | No | 4 | N77 (3.3–4.2 GHz), n78 band (3.3–3.8 GHz) and n79 band (4.4–5 GHz), | 2,4,4.71 | -- | 18.8 | <0.018 |
| [19] | 2018 | 160 × 85 × 0.8 | No | 4 | 824–960 MHz/ 1710–2690 MHz) Reconfigurable | -- | 70 | 10 | ~0.2 |
| [20] | 2018 | 153 × 77 × 1 | No | 4 | 3.3–3.6 GHz | -- | 64.2 | 10 | ~0.11 |
| [21] | 2018 | 150 × 73 × 0.8 | No | 4 | 3.4–3.6 | -- | 51–74 | 20 | <0.06 |
| [22] | 2019 | 140 × 70 × 0.8 | No | 4 | 3400–3600 MHz | -- | 51 | 11.6 | -- |
| [23] | 2019 | 50 × 100 × 4.5 | No | 4 | 2.7–3.6 GHz | 3 | 80–90 | −25 dB | -- |
| [24] | 2020 | 39 × 30 × 1 | No | 4 | 5.15–5.85 GHz | 2.8 | >70 | 20 | <0.02 |
| [25] | 2019 | 38.3 × 38.3 × 0.8 | No | 4 | 3–13.2 GHz | 0.5–6.3 | 72–97 | 17 | 0.02 |
| Proposed | 70 × 145 × 0.2 | Yes | 4 | 2.37–5.85 GHz | 4–5.5 | 85 | 17.5 | <0.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kulkarni, J.; Alharbi, A.G.; Desai, A.; Sim, C.-Y.-D.; Poddar, A. Design and Analysis of Wideband Flexible Self-Isolating MIMO Antennas for Sub-6 GHz 5G and WLAN Smartphone Terminals. Electronics 2021, 10, 3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10233031
Kulkarni J, Alharbi AG, Desai A, Sim C-Y-D, Poddar A. Design and Analysis of Wideband Flexible Self-Isolating MIMO Antennas for Sub-6 GHz 5G and WLAN Smartphone Terminals. Electronics. 2021; 10(23):3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10233031
Chicago/Turabian StyleKulkarni, Jayshri, Abdullah G. Alharbi, Arpan Desai, Chow-Yen-Desmond Sim, and Ajay Poddar. 2021. "Design and Analysis of Wideband Flexible Self-Isolating MIMO Antennas for Sub-6 GHz 5G and WLAN Smartphone Terminals" Electronics 10, no. 23: 3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10233031
APA StyleKulkarni, J., Alharbi, A. G., Desai, A., Sim, C.-Y.-D., & Poddar, A. (2021). Design and Analysis of Wideband Flexible Self-Isolating MIMO Antennas for Sub-6 GHz 5G and WLAN Smartphone Terminals. Electronics, 10(23), 3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10233031








