Performance Analysis of PI and DMRAC Algorithm in Buck–Boost Converter for Voltage Tracking in Electric Vehicle Using Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
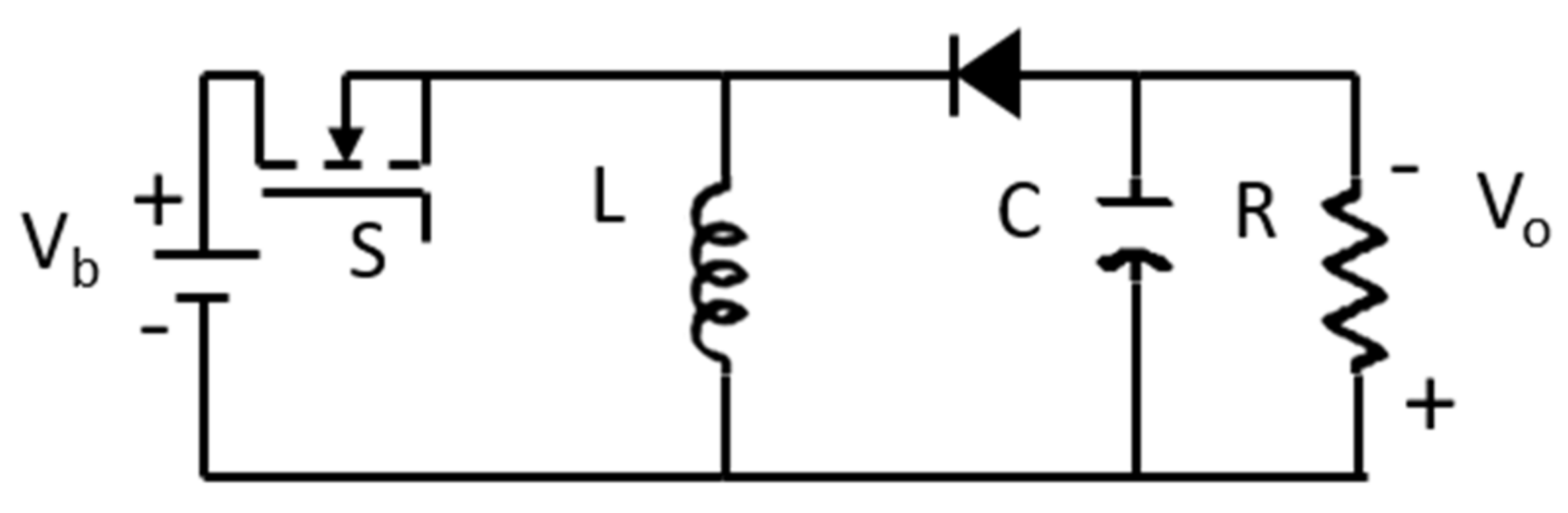
2. Modelling of a Buck–Boost Converter
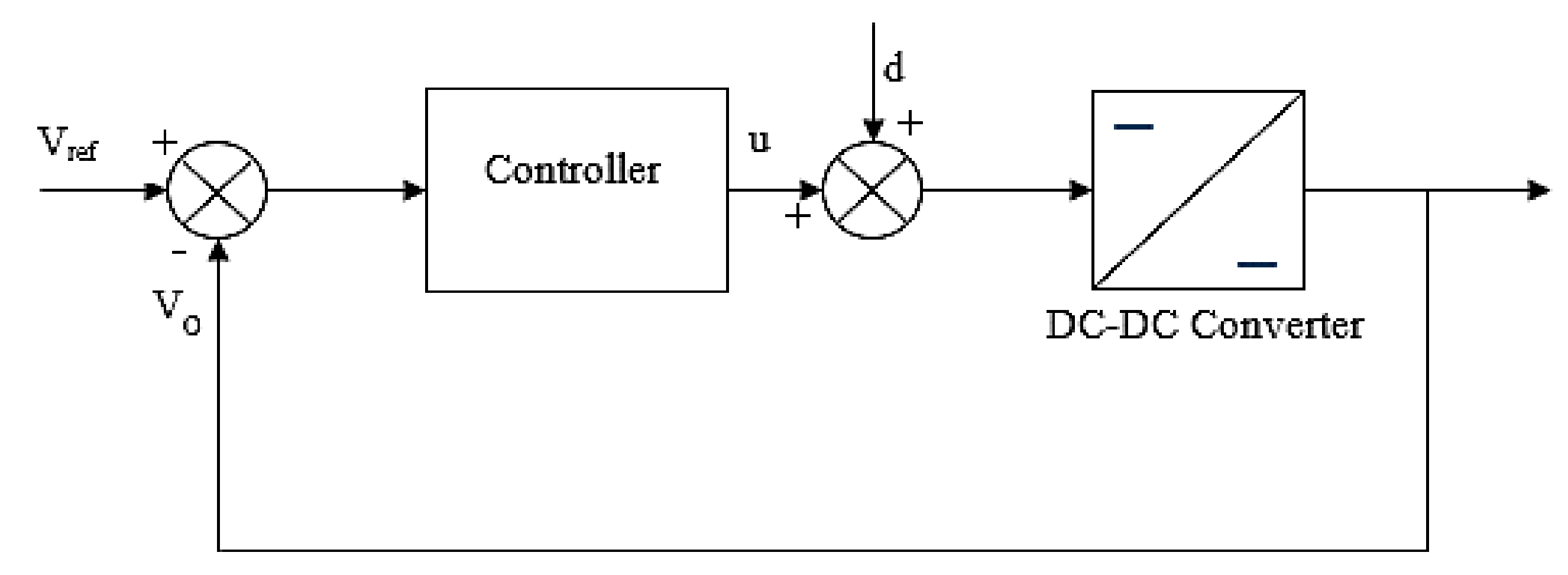
3. Controller Design
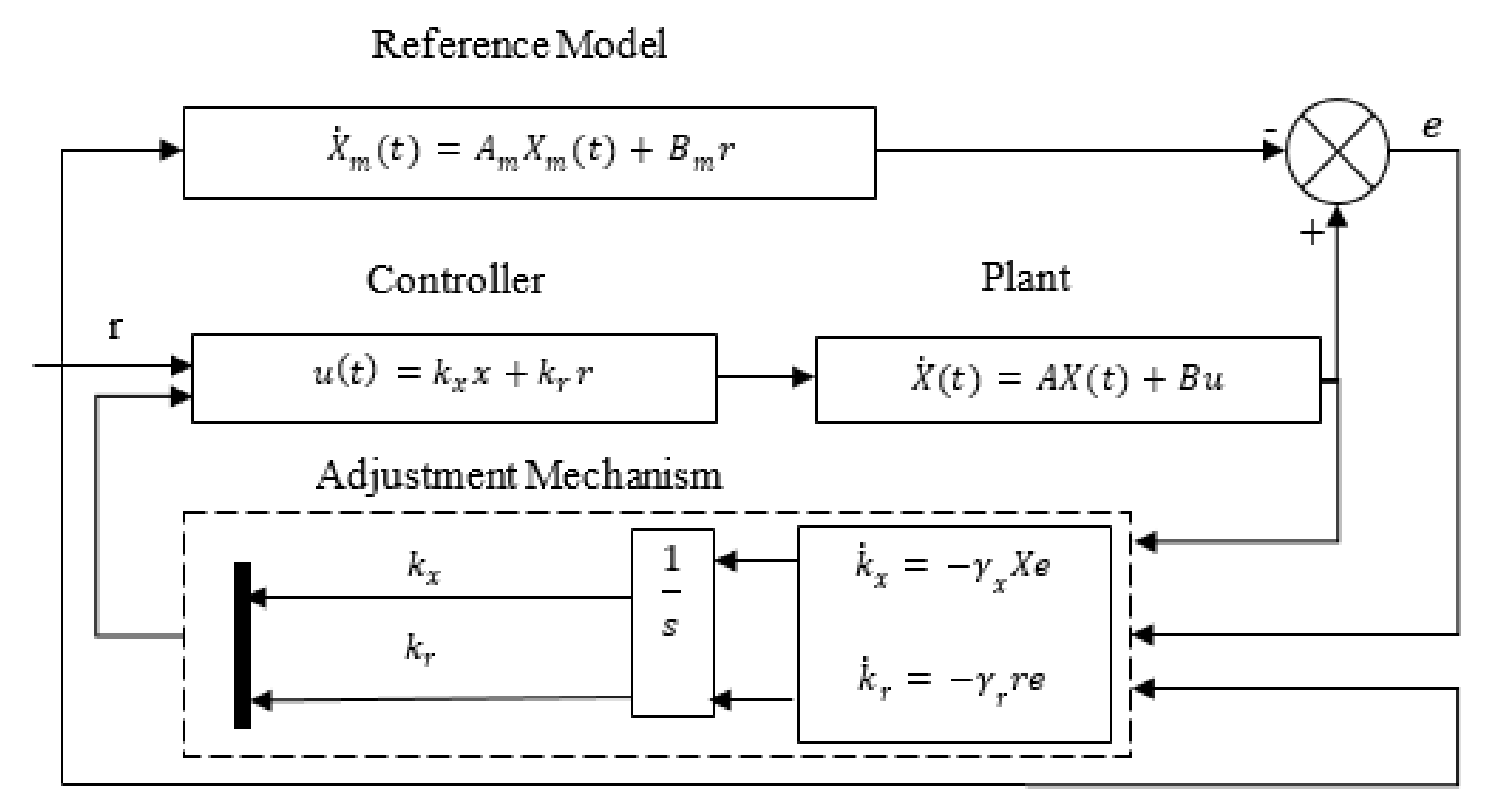
3.1. DMRAC Design
3.2. PI Controller Design
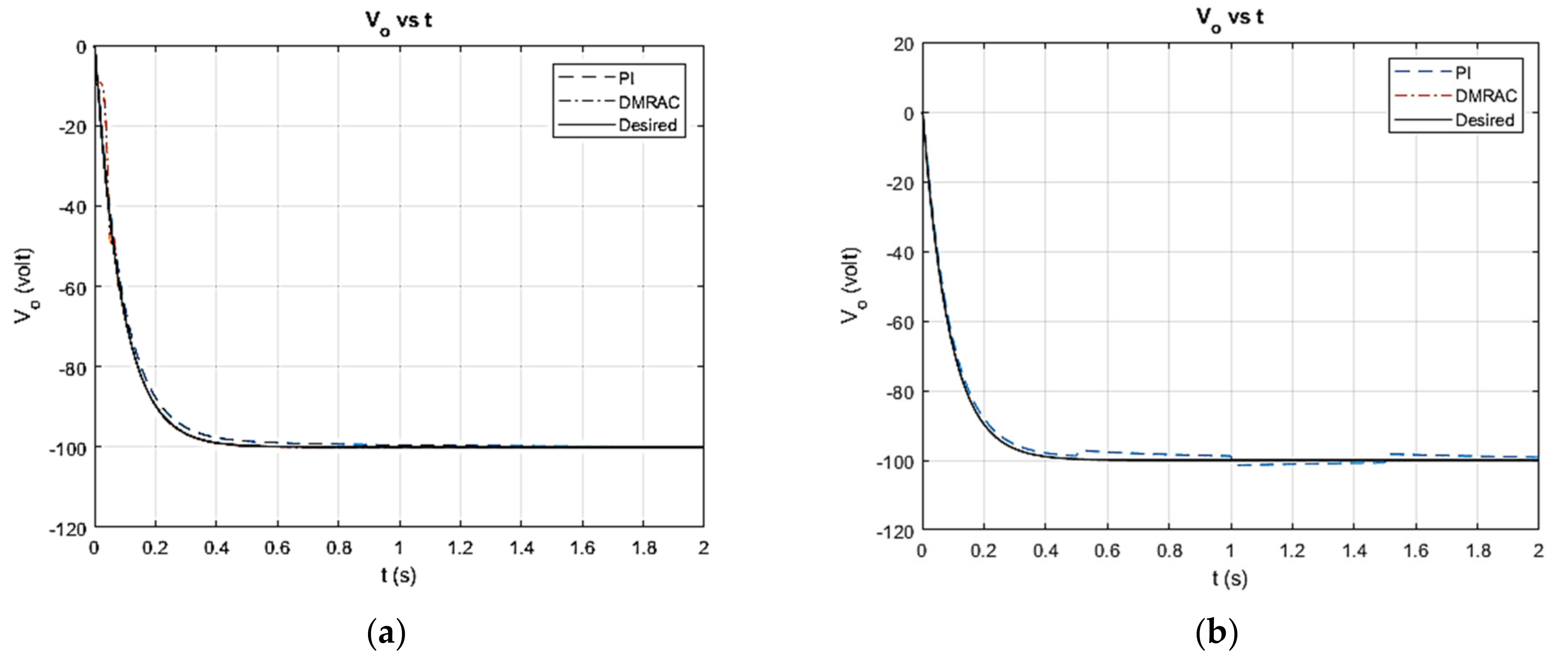
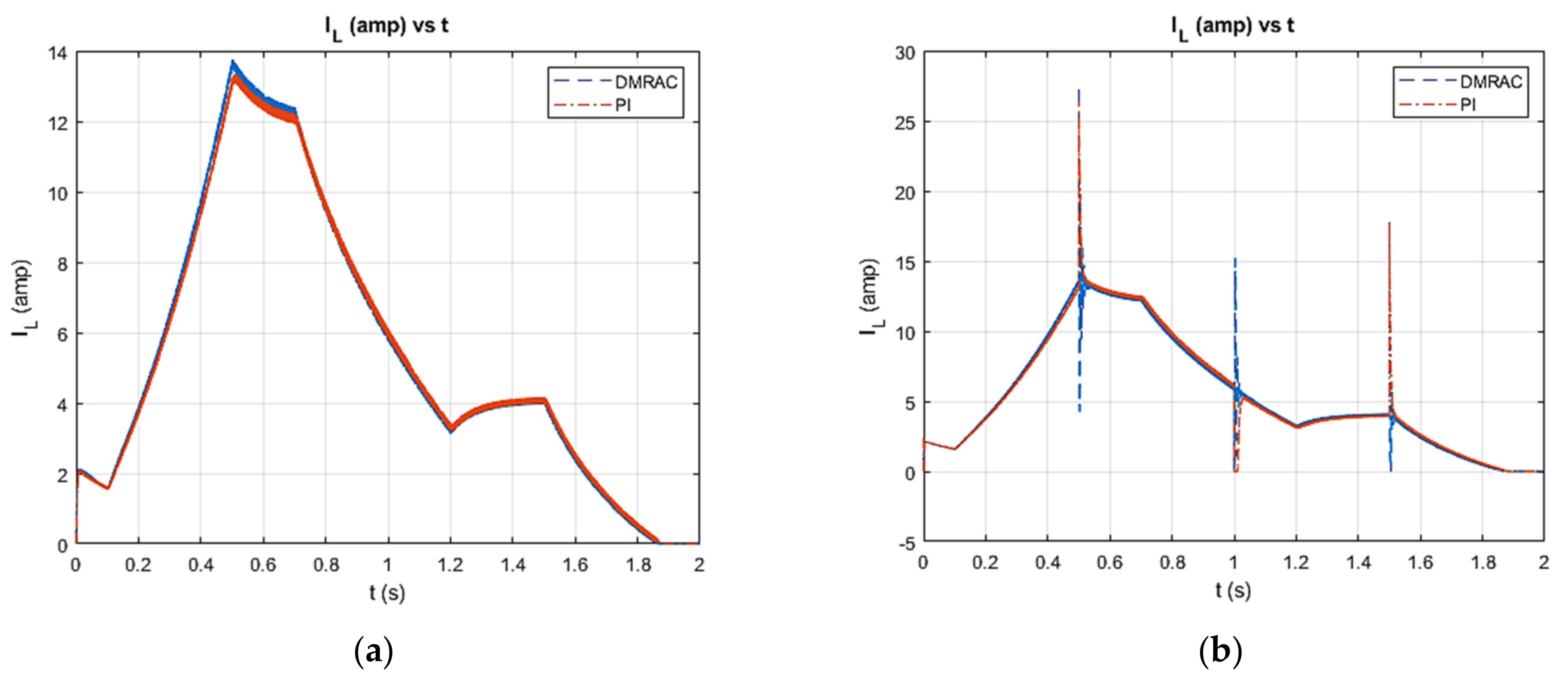
4. Simulated Results
5. Discussion
- (i)
- At the time of writing, the proposed method was not integrated with the electrical vehicle, representing a challenge to confidently assess the performance of our methods.
- (ii)
- The experimental results are presented in terms of Simulink simulations, which may produce different results, while considering various factors, such as voltage, resistance and so on.
- (iii)
- During this study, we did not compare our proposed model with the currently used DC–DC converters for electrical vehicles, as our proposed methods were in the development stage, while many of the existing algorithms are implemented in real-world scenarios. Thus, a reliable performance comparison would be expected once our proposed method is implemented with an electrical vehicle.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| C | Capacitor |
| Duty cycle | |
| Inductor current | |
| R | Resistance |
| VC | Capacitor voltage |
| Vb | Battery voltage |
| Adaptation gain rate |
References
- Emadi, A.; Lee, Y.J.; Rajashekara, K. Power electronics and motor drives in electric, hybrid electric, and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 2237–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, R.; Bibeau, E.; Filizadeh, S. On conversion of hybrid electric vehicles to plug-in. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2010, 59, 2016–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Tolbert, L. Bi-directional power management and fault tolerant feature in a 5-kW multilevel dc–dc converter with modular architecture. IET Power Electron. 2009, 2, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, Z.; Williamson, S.S. Power-electronics-based solutions for plug-in hybrid electric vehicle energy storage and management systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 57, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, R.-J.; Shih, L.-C. Design of voltage tracking control for DC–DC boost converter via total sliding-mode technique. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 2502–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici, I.; Yaylaci, E.K. Fast and robust voltage control of DC–DC boost converter by using fast terminal sliding mode controller. IET Power Electron. 2016, 9, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizami, T.K.; Mahanta, C. An intelligent adaptive control of DC–DC buck converters. J. Frankl. Inst. 2016, 353, 2588–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, E.; Ayas, M.S.; Altas, I.H. A PSO optimized fractional-order PID controller for a PV system with DC-DC boost converter. In Proceedings of the 2014 16th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference and Exposition, Antalya, Turkey, 21–24 September 2014; pp. 477–481. [Google Scholar]
- Adnan, M.F.; Oninda, M.A.M.; Nishat, M.M.; Islam, N. Design and Simulation of a DC-DC Boost Converter with PID Controller for enhanced Performance. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2017, 6, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Po, L.; Ruiyu, L.; Tianying, S.; Jingrui, Z.; Zheng, F. Composite adaptive model predictive control for DC–DC boost converters. IET Power Electron. 2018, 11, 1706–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, B.M.; Sreeja, K. A Review of sliding mode control of DC-DC converters. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2015, 2, 1382–1386. [Google Scholar]
- Utkin, V. Sliding mode control of DC/DC converters. J. Frankl. Inst. 2013, 350, 2146–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccarelli, F.; Lauria, D. Sliding-mode control of bidirectional dc-dc converter for supercapacitor energy storage applications. In Proceedings of the SPEEDAM 2010, Pisa, Italy, 14–16 June 2010; pp. 1119–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.; Deekshitha, K.; Singh, S.; Fulwani, D. Sliding mode control of a bidirectional DC/DC converter with constant power load. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE First International Conference on DC Microgrids (ICDCM), Atlanta, Georgia, 7–10 June 2015; pp. 287–292. [Google Scholar]
- Albiol-Tendillo, L.; Vidal-Idiarte, E.; Maixé-Altés, J.; Bosque-Moncusí, J.; Valderrama-Blavi, H. Design and control of a bidirectional DC/DC converter for an Electric Vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2012 15th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (EPE/PEMC), Novi Sad, Serbia, 4–6 September 2012; pp. LS4d. 2-1–LS4d. 2-5. [Google Scholar]
- Massaoudi, Y.; Elleuch, D.; Gaubert, J.P.; Mehdi, D.; Damak, T. A new backstepping sliding mode controller applied to a dc-dc boost converter. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2016, 7, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbaha, N.; Zidani, F.; Nait-Said, M.-S.; Zouzou, S.E.; Boukebbous, S.; Ammar, H. dSPACE Validation of Improved Backstepping Optimal Energy Control for Photovoltaic Systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 6th International Renewable and Sustainable Energy Conference (IRSEC), Rabat, Morocco, 5–8 December 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Saadatmand, S.; Shamsi, P.; Ferdowsi, M. The Heuristic Dynamic Programming Approach in Boost Converters. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Texas Power and Energy Conference (TPEC), College Station, TX, USA, 6–7 February 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Abjadi, N.; Goudarzian, A.; Markadeh, G.R.A.; Valipour, Z. Reduced-Order Backstepping Controller for POESLL DC–DC Converter Based on Pulse Width Modulation. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. 2019, 43, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.-K.; Zhao, J.; Ma, D. Adaptive backstepping sliding mode nonlinear control for buck DC/DC switched power converter. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation, Roma, Italy, 17–20 October 2007; pp. 1198–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Sureshkumar, R.; Ganeshkumar, S. Comparative study of Proportional Integral and Backstepping Controller for Buck Converter. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Trends in Electrical and Computer Technology, Nagercoil, India, 23–24 March 2011; pp. 375–379. [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarty, A.; Mahanta, C. Backstepping Enhanced Adaptive Second Order Sliding Mode Controller to compensate Actuator. In Proceedings of the India Conference (INDICON), Pune, India, 11–13 December 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Åström, K.J.; Wittenmark, B. Adaptive Control; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ardhenta, L.; Subroto, R.K. Application of direct MRAC in PI controller for DC-DC boost converter. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2020, 11, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyu, K.-K.; Yang, M.-J.; Chen, Y.-M.; Lin, Y.-F. Model reference adaptive control design for a shunt active-power-filter system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djebbri, S.; Ladaci, S.; Metatla, A.; Balaska, H. Robust MRAC Supervision of a Multi-source Renewable Energy System Using Fractional-Order Integrals. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Electrical Sciences and Technologies in Maghreb (CISTEM), Algiers, Algeria, 29–31 October 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, V.F.; Monteiro, J.; Silva, J.F. Dual 3-Phase Bridge Multilevel Inverters for AC Drives with Voltage Sag Ride-through Capability. Energies 2019, 12, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalakshmi, S.; T Raja, S.R. Time domain based digital controller for buck-boost converter. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2014, 9, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lai, C.-M.; Cheng, Y.-H.; Hsieh, M.-H.; Lin, Y.-C. Development of a bidirectional DC/DC converter with dual-battery energy storage for hybrid electric vehicle system. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 67, 1036–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellur, D.M.; Kazimierczuk, M.K. DC-DC converters for electric vehicle applications. In Proceedings of the 2007 Electrical Insulation Conference and Electrical Manufacturing Expo, Nashville, TN, USA, 22–24 October 2007; pp. 286–293. [Google Scholar]
- Devi Vidhya, S.; Balaji, M. Hybrid fuzzy PI controlled multi-input DC/DC converter for electric vehicle application. Automatika 2020, 61, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.A. Adaptive control. In Control Theory Tutorial; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.; Okasha, M.; Sulaeman, E. A model predictive control (MPC) approach on unit quaternion orientation based quadrotor for trajectory tracking. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2019, 17, 2819–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Properties | Values |
|---|---|
| Inductance, L | 5 × 10−4 H |
| Capacitance, C | 9200 × 10−6 F |
| Capacitor initial voltage, VC | 10 V |
| Resistance, R | 25 Ω |
| Switching frequency | 50 kHz |
| Battery nominal voltage | 48 V |
| Battery rated capacity | 14 Ah |
| Battery initial SOC | 95% |
| Battery response time | 0.3 s |
| Properties | Values |
|---|---|
| Rate of adaptation = 2 = 2 | Proportional gain, = 5 |
| Initial gain = 11 = 11 | Integral gain, = 8 |
| Properties | RMSE Along Controllers | |
|---|---|---|
| DMRAC (%) | PI (%) | |
| Constant voltage | 0.0005 | 0.6723 |
| Constant voltage with disturbance | 0.0003 | 0.8477 |
| Variable voltage | 0.0310 | 0.5149 |
| Variable voltage with disturbance | 0.0321 | 0.1661 |
| Characteristics | Controllers | |
|---|---|---|
| DMRAC | PI | |
| Settling time (s) | 0.3436 | 0.4122 |
| Overshoot (%) | 0.0007 | 0.0003 |
| Rise time (s) | 0.1921 | 0.2060 |
| Peak time (s) | 1.9840 | 2.0000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, M.; Abdul Ghaffar, A.F.; Sulaeman, E.; Ahsan, M.M.; Kouzani, A.Z.; Mahmud, M.A.P. Performance Analysis of PI and DMRAC Algorithm in Buck–Boost Converter for Voltage Tracking in Electric Vehicle Using Simulation. Electronics 2021, 10, 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202516
Islam M, Abdul Ghaffar AF, Sulaeman E, Ahsan MM, Kouzani AZ, Mahmud MAP. Performance Analysis of PI and DMRAC Algorithm in Buck–Boost Converter for Voltage Tracking in Electric Vehicle Using Simulation. Electronics. 2021; 10(20):2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202516
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Maidul, Alia Farhana Abdul Ghaffar, Erwin Sulaeman, Md Manjurul Ahsan, Abbas Z. Kouzani, and M. A. Parvez Mahmud. 2021. "Performance Analysis of PI and DMRAC Algorithm in Buck–Boost Converter for Voltage Tracking in Electric Vehicle Using Simulation" Electronics 10, no. 20: 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202516
APA StyleIslam, M., Abdul Ghaffar, A. F., Sulaeman, E., Ahsan, M. M., Kouzani, A. Z., & Mahmud, M. A. P. (2021). Performance Analysis of PI and DMRAC Algorithm in Buck–Boost Converter for Voltage Tracking in Electric Vehicle Using Simulation. Electronics, 10(20), 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202516







