An Accuracy-Improved Fixed-Width Booth Multiplier Enabling Bit-Width Adaptive Truncation Error Compensation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries and Design Issues
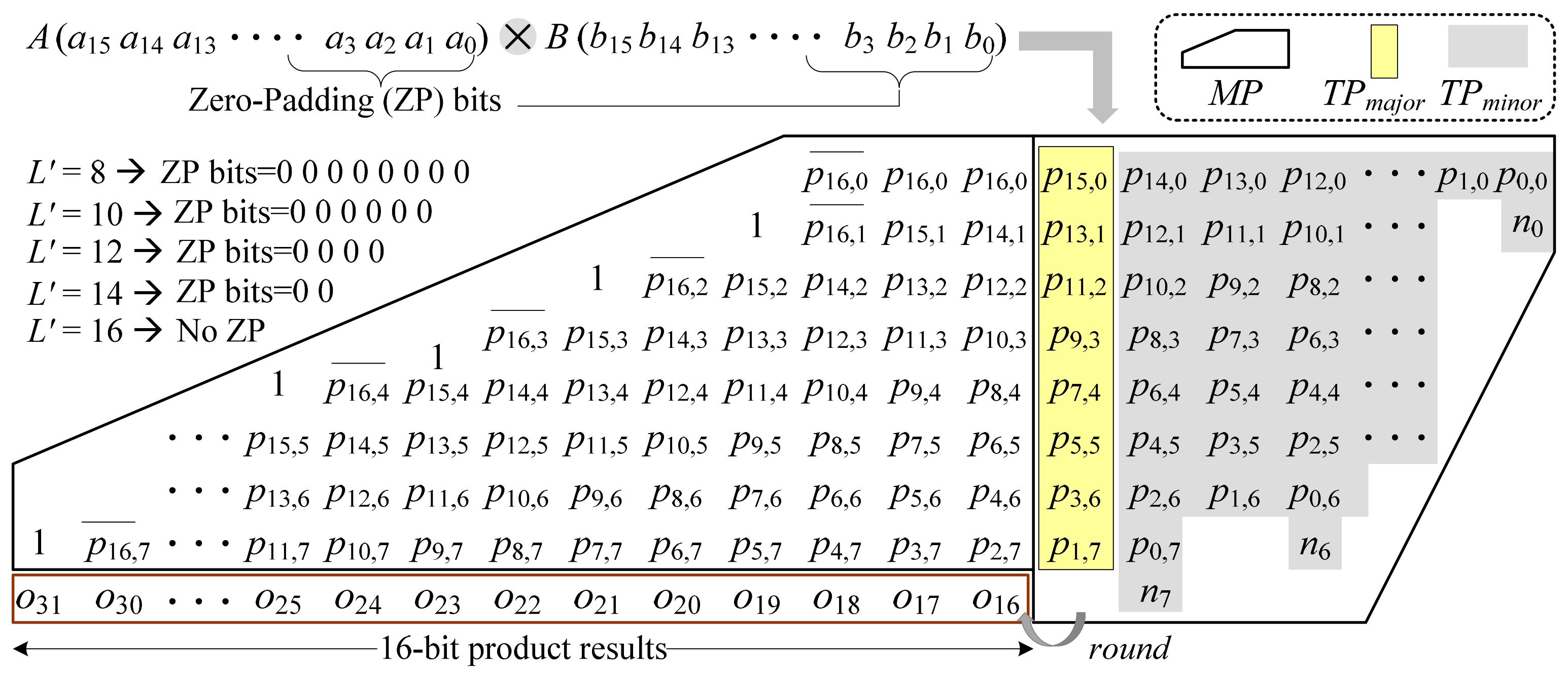
2.1. Fixed-Width Booth Multiplier (FWBM)
2.2. Probability-Based TEC Schemes for FWBMs
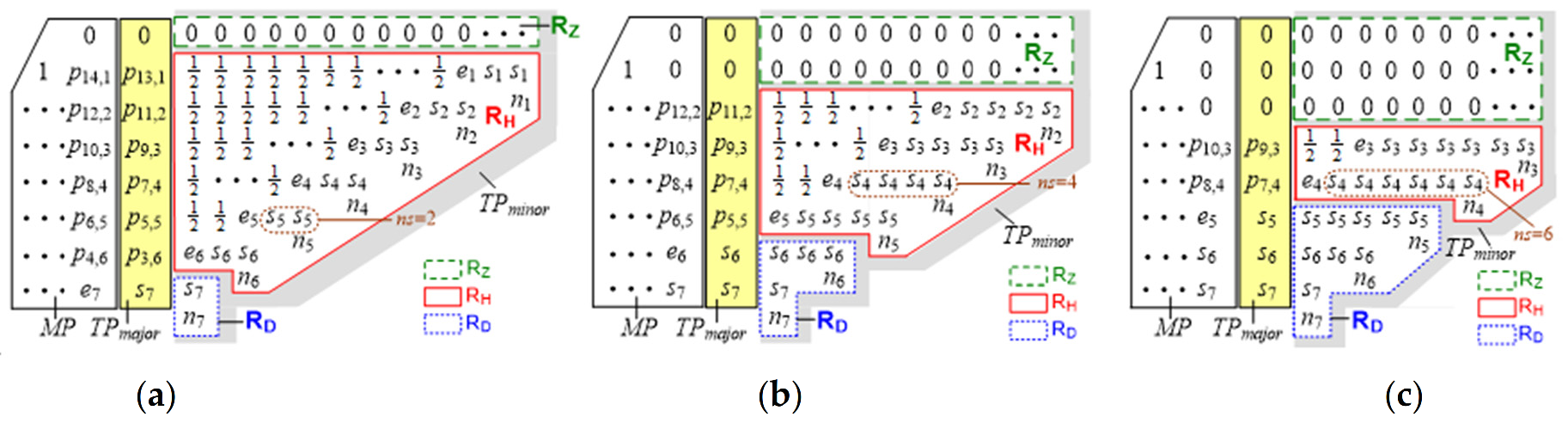
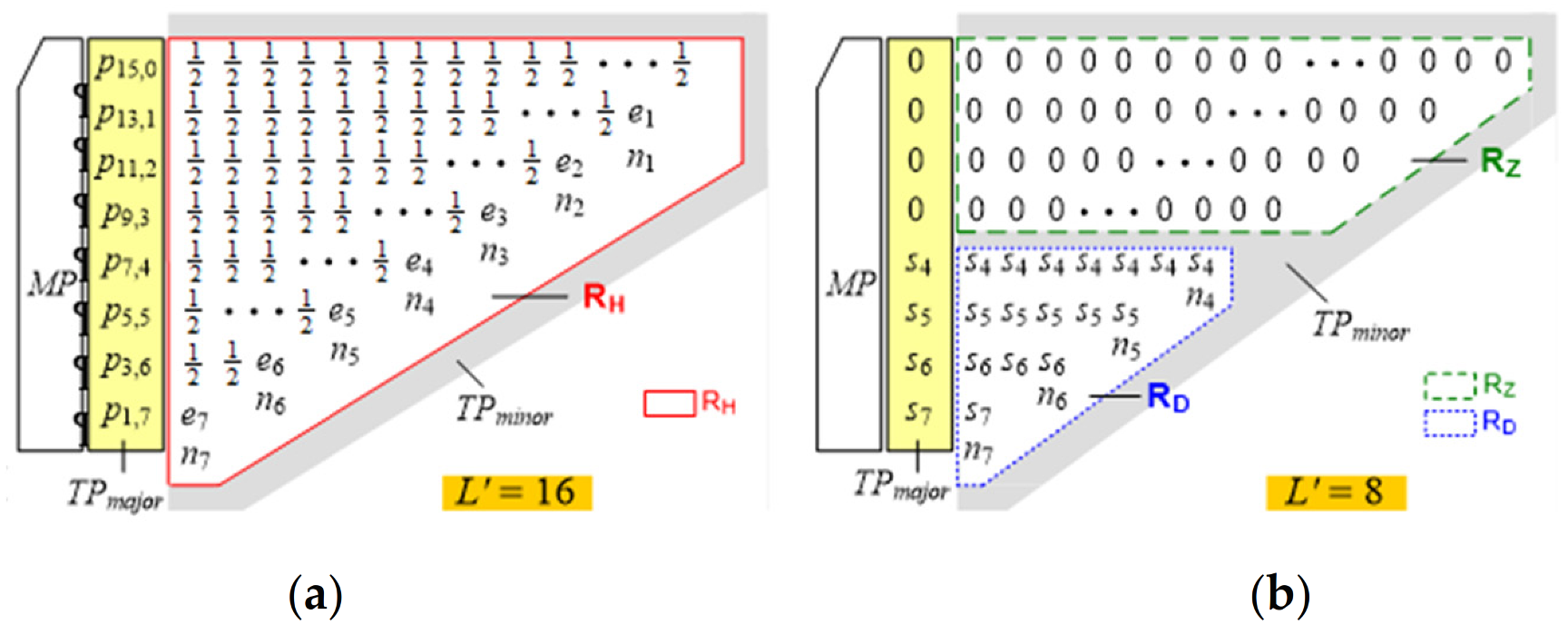
3. Proposed Bit-Width Adaptive TEC (BWATEC) Scheme
3.1. Derivation of Probabilistic Estimation for BWATEC
3.2. BWATEC Synthesis and Operations
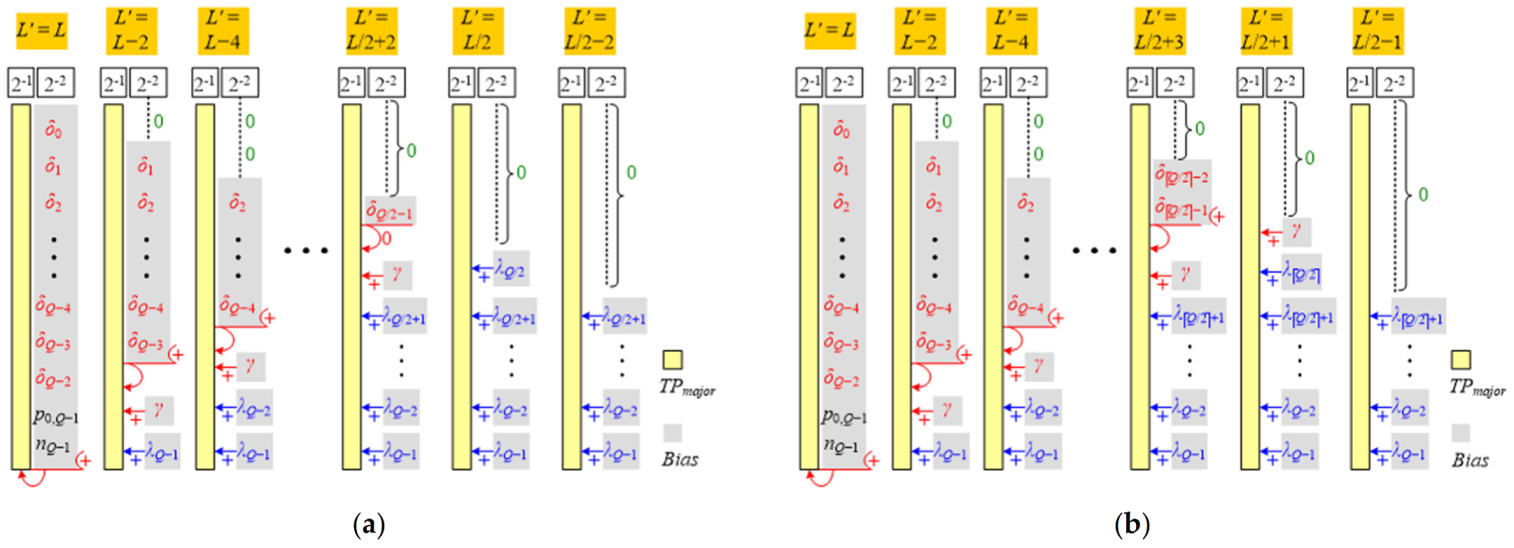
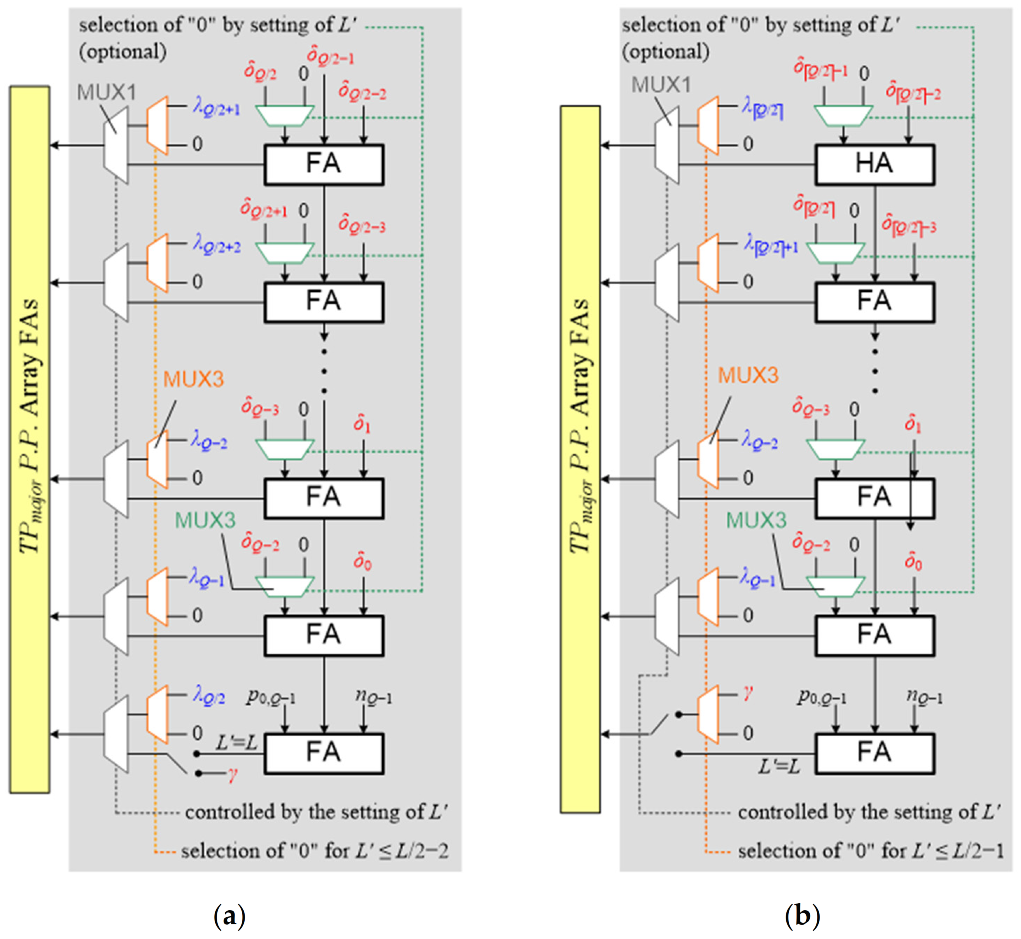
3.3. Design Scalability
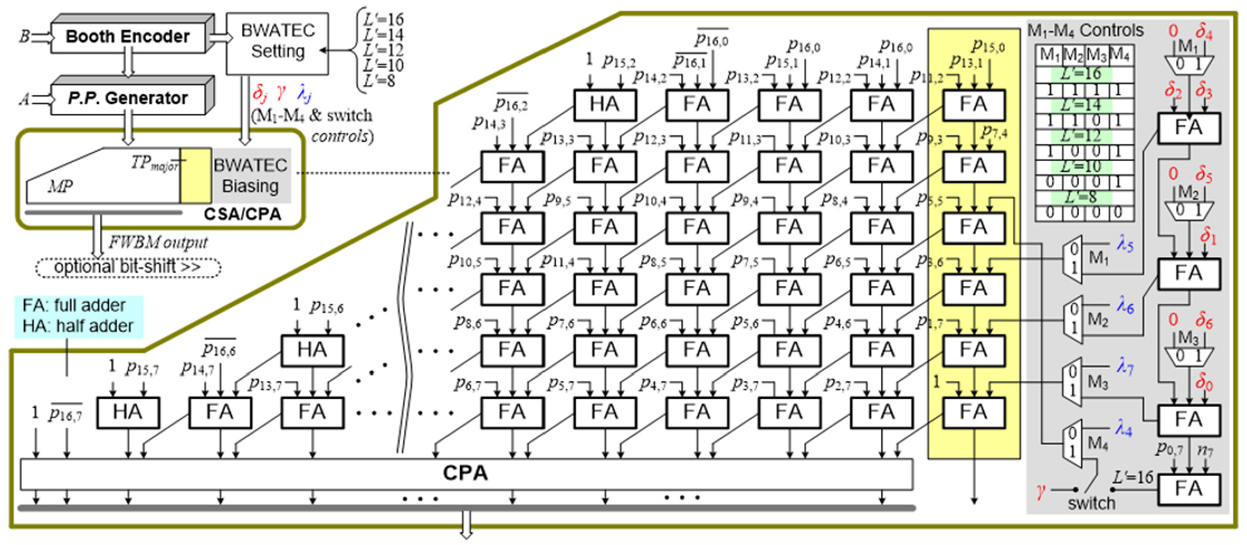
4. Proposed BWATEC-Enabled FWBM Architecture
5. Evaluations and Experiments
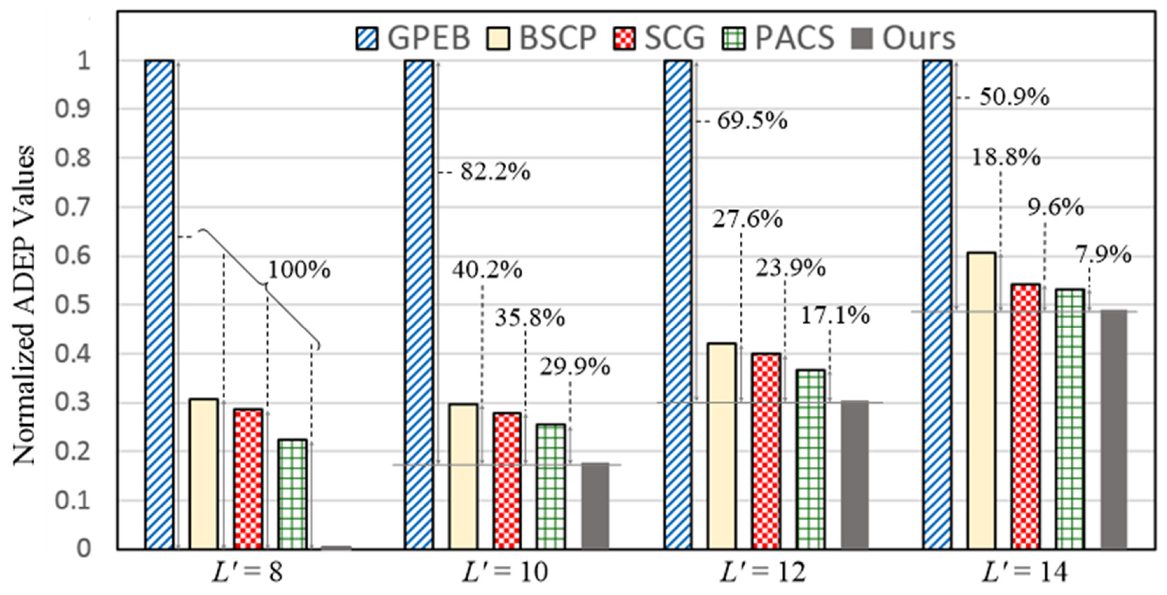
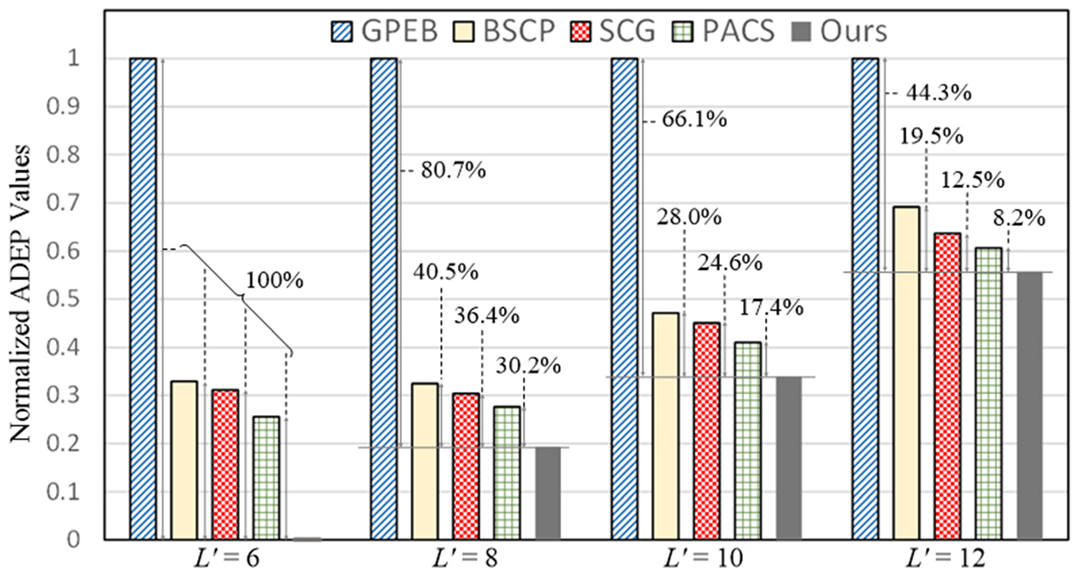
5.1. Evaluations of Accuracy and Hardware Performances
5.2. Design Verification and Experiments
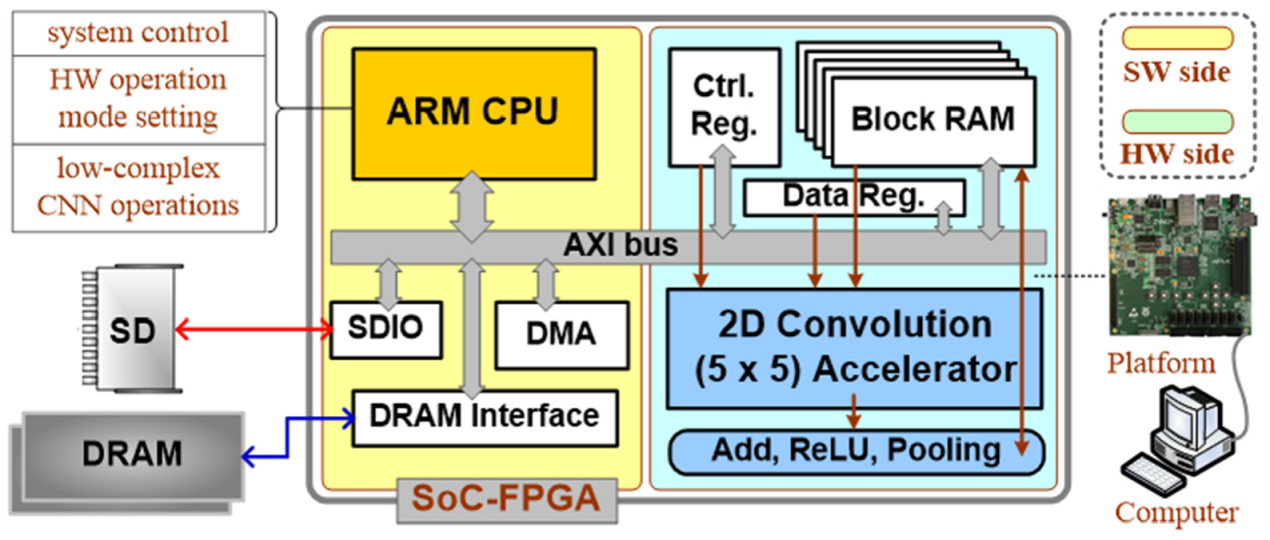
5.2.1. CNN Acceleration Application
5.2.2. SoC-FPGA Implementation
5.2.3. Electrocardiogram Classification Experiment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parhi, K.K. VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems: Design and Implementation, 1st ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.Y.; Park, I.C. Balanced Binary-Tree Decomposition for Area-Efficient Pipelined FFT Processing. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2007, 54, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Lin, J.N.; Hu, H.S.; Jou, S.J. STBC-OFDM Downlink Baseband Receiver for Mobile WMAN. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2013, 21, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.-N.; Han, Y.-S. A High-Accuracy Hardware-Efficient Multiply–Accumulate (MAC) Unit Based on Dual-Mode Truncation Error Compensation for CNNs. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 214716–214731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, L.-D.; Yang, C.-C. Generalized Low-Error Area-Efficient Fixed-Width Multipliers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2005, 52, 1608–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.-H.; Van, L.-D. Power-efficient pipelined reconfigurable fixed-width Baugh-Wooley multipliers. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2009, 58, 1346–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-H.; Satzoda, R.K. A Low Error and High Performance Multiplexer-Based Truncated Multiplier. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2010, 18, 1767–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petra, N.; Caro, D.D.; Garofalo, V.; Napoli, E.; Strollo, A.G.M. Design of Fixed-Width Multipliers with Linear Compensation Function. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2011, 58, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, S.-J.; Tsai, M.-H.; Tsao, Y.-L. Low-error reduced-width Booth multipliers for DSP applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 2003, 50, 1470–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Chang, T.-Y.; Jou, R.-Y. A statistical error-compensated Booth multipliers and its DCT applications. In Proceedings of the TENCON IEEE Region 10 Conference, Fukuoka, Japan, 21–24 November 2010; pp. 1146–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.A.; Van, L.D.; Kuo, S.Y. Adaptive low-error fixed-width Booth multipliers. IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci. 2007, 90, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, J.-P.; Kuang, S.-R.; Liang, S.-C. High-Accuracy Fixed-Width Modified Booth Multipliers for Lossy Applications. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2011, 19, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, S.-R.; Wang, J.-P.; Guo, C.-Y. Modified Booth Multipliers with a Regular Partial Product Array. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs 2009, 56, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-J.; Lee, K.-C.; Chung, J.-G.; Parhi, K.K. Design of low-error fixed-width modified Booth multiplier. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2004, 12, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, T.-B.; Hsiao, S.-F. Low-error carry-free fixed-width multi- pliers with low-cost compensation circuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs 2005, 52, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chang, T.-Y.; Chen, J.-N. A Probabilistic Estimation Bias Circuit for Fixed-Width Booth Multiplier and Its DCT Applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs 2011, 58, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Li, C.-Y.; Chang, T.-Y. Area-Effective and Power-Efficient Fixed-Width Booth Multipliers Using Generalized Probabilistic Estimation Bias. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2011, 1, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Chang, T.-Y. A High-Accuracy Adaptive Conditional Probability Estimator for Fixed-Width Booth Multipliers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2012, 59, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H. An Accuracy-Adjustment Fixed-Width Booth Multiplier Based on Multilevel Conditional Probability. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2015, 23, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.-Q.; Chen, Y.-H.; Jou, S.-J. High-Accuracy Fixed-Width Booth Multipliers Based on Probability and Simulation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2015, 62, 2052–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H. Improvement of Accuracy of Fixed-Width Booth Multipliers Using Data Scaling Technology. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs 2021, 68, 1018–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, Y. A Low-Error Energy-Efficient Fixed-Width Booth Multiplier with Sign-Digit-Based Conditional Probability Estimation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2018, 65, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oklobdzija, V.G.; Villeger, D.; Liu, S.S. A method for speed optimized partial product reduction and generation of fast parallel multipliers using an algorithmic approach. IEEE Trans. Comput. 1996, 45, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chang, C.-H. A New Redundant Binary Booth Encoding for Fast 2n-Bit Multiplier Design. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2009, 56, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X. MALOC: A Fully Pipelined FPGA Accelerator for Convolutional Neural Networks with All Layers Mapped on Chip. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2018, 37, 2601–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J. FPGA Acceleration of CNNs-Based Malware Traffic Classification. Electronics 2020, 9, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moons, B.; Verhelst, M. An Energy-Efficient Precision-Scalable ConvNet Processor in 40-nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camus, V.; Mei, L.; Enz, C.; Verhelst, M. Review and Benchmarking of Precision-Scalable Multiply-Accumulate Unit Architectures for Embedded Neural-Network Processing. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2019, 9, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Fu, Y.; Song, W.; Cheng, K.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, L. An Efficient Streaming Accelerator for Low Bit-Width Convolutional Neural Networks. Electronics 2019, 8, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Krishna, T.; Emer, J.S.; Sze, V. Eyeriss: An Energy-Efficient Reconfigurable Accelerator for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Du, Y.; Li, Y.; Su, J.; Kuan, Y.-C.; Liu, C.-C.; Chang, M.-C.F. A Reconfigurable Streaming Deep Convolutional Neural Network Accelerator for Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2018, 65, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.; Cha, S.; Rho, D.; Park, I. DSIP: A Scalable Inference Accelerator for Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2018, 53, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wu, Y.; Ni, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wen, H.; Zou, Y. DoReFa-Net: Training Low Bitwidth Convolutional Neural Networks with Low Bitwidth Gradients. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.06160. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.06160v2 (accessed on 11 October 2021).
- Park, E.; Ahn, J.; Yoo, S. Weighted-Entropy-Based Quantization for Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Yoo, H.J. DNPU: An 8.1 TOPS/W reconfigurable CNN-RNN processor for general-purpose deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Int. Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–9 February 2017; pp. 240–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, A.; Tagliavini, G.; Conti, F.; Rossi, D.; Benini, L. XpulpNN: Accelerating Quantized Neural Networks on RISC-V Processors Through ISA Extensions. In Proceedings of the Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Grenoble, France, 9–13 March 2020; pp. 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, C.; Kang, S.; Shin, D.; Kim, S.; Yoo, H. UNPU: An Energy-Efficient Deep Neural Network Accelerator with Fully Variable Weight Bit Precision. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2019, 54, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Virupakshappa, K.; Vitor Silva Pinto, E.; Oruklu, E. Hardware/Software Co-Design of a Traffic Sign Recognition System Using Zynq FPGAs. Electronics 2015, 4, 1062–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Han, S.; Yao, S.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yang, H. Software-Hardware Codesign for Efficient Neural Network Acceleration. IEEE Micro 2017, 37, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moini, S.; Alizadeh, B.; Emad, M.; Ebrahimpour, R. A Resource-Limited Hardware Accelerator for Convolutional Neural Networks in Embedded Vision Applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2017, 64, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, G.B.; Mark, R.G. The impact of the MIT-BIH arrhythmia database. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2001, 20, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, T.J.; Nguyen, H.M.; Kang, D.; Kim, D.; Kim, D.; Kim, Y.-H. ECG arrhythmia classification using a 2-D convolutional neural network. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.06812. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.06812 (accessed on 11 October 2021).
- Wu, Y.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; Zha, X.; Yuan, S. A Comparison of 1-D and 2-D Deep Convolutional Neural Networks in ECG Classification. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.07088. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.07088 (accessed on 11 October 2021).
- Saadatnejad, S.; Oveisi, M.; Hashemi, M. LSTM-Based ECG Classification for Continuous Monitoring on Personal Wearable Devices. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| FWBM | Fixed-Width Booth Multiplier |
|---|---|
| TEC | Truncation error compensation |
| BWATEC | Bit-width adaptive truncation error compensation |
| P.P. | Partial products |
| MP/TP | Main part/truncation part |
| MSC | Most significant column |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| HW/SW | Hardware/software |
| SoC-FPGA | System-on-chip field-programmable gate array |
| ZP | Zero-Padding |
| RZ/RH/RD | Zero region/hybrid region/deterministic-only region |
| ADEP | Area-delay-error product |
| (0 0 0)/(1 1 1) | 0 | 0 | |
| (0 0 1)/(0 1 0) | 1 | 0 | |
| (1 0 1)/(1 1 0) | −1 | 1 | |
| (0 1 1) | 2 | 0 | |
| (1 0 0) | −2 | 1 |
| P.P. Values | Values | |
|---|---|---|
| dj = 0 | (all P.P. = 0) | zero |
| dj = 1 | (nj = 0; sj = 0; ej = 1/2) | |
| dj = −1 | (nj = 1; sj = 1; ej = 1/2) | |
| dj = 2 | (nj = 0; sj = 0; ej = 0) | |
| dj = −2 | (nj = 1; sj = 1; ej = 1) |
| MP/TPmajor HW Resources | BWATEC Biasing HW Resources | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #FA/HA | #FA/HA | #MUX1 | #MUX2 | #MUX3 | |
| L = 2n (even n) | |||||
| L = 2n (odd n) | 1 | ||||
| PT | BSCP | PACS | GPEB | SCG | Ours | DT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy Performance (L′ = 16)–SNR (dB) | |||||||
| SNR | 85.56 | 81.91 | 81.83 | 79.34 | 81.84 | 81.87 | 64.84 |
| Hardware Performances—Area (µm2)/Delay (ns)/Power (mW) | |||||||
| Area | 2294 | 1330 | 1301 | 1249 | 1325 | 1312 | 1098 |
| Delay | 3.62 | 3.25 | 3.24 | 3.20 | 3.24 | 3.27 | 2.96 |
| Power | 1075 | 615.1 | 585.2 | 562.3 | 612.9 | 591.0 | 486.4 |
| BSCP | PACS | GPEB | SCG | Ours | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADEP (%) | 59.80% | 59.35% | 100% | 60.32% | 59.71% |
| BSCP | PACS | GPEB | SCG | Ours | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L′ = 14 | 80.62 | 81.06 | 78.10 | 81.04 | 81.69 |
| L′ = 12 | 80.77 | 81.25 | 76.67 | 80.96 | 82.12 |
| L′ = 10 | 81.01 | 81.57 | 75.40 | 81.28 | 83.18 |
| L′ = 8 | 80.14 | 81.36 | 74.65 | 80.38 | Inf. |
| LUT Util. | LUTRAM Util. | FF Util. | BRAM Util. | GOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6786 | 62 | 2572 | 12.5 | 2.55 |
| Layers | Input Feature Map Size | Input Channel No. | Kernel Size | Output SNR (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | 128 × 128 | 1 | − | − |
| 1st Convolution | 128 × 128 | 1 | 5 × 5 | 34.37 |
| 1st Max. Pooling | 128 × 128 | 4 | 2 × 2 | 35.14 |
| 2nd Convolution | 64 × 64 | 4 | 5 × 5 | 29.48 |
| 2nd Max. Pooling | 64 × 64 | 8 | 2 × 2 | 29.86 |
| FC | 32 × 32 | 8 | − | − |
| BSCP | PACS | GPEB | SCG | Ours | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LUT Util. | 5225 | 4907 | 4459 | 5206 | 4957 |
| Prediction→ | Abnormal | Normal | Metrics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Label↓ | ||||
| Abnormal | 27,577 (TP) | 705 (FN) | 97.5% (Sen.) | |
| Normal | 2266 (FP) | 35,316 (TN) | 94.0% (Spc.) | |
| Metrics | 95.5%(Acc.) | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, S.-N.; Liao, J.-C.; Chiu, C.-K.; Ku, P.-T.; Chen, Y.-S. An Accuracy-Improved Fixed-Width Booth Multiplier Enabling Bit-Width Adaptive Truncation Error Compensation. Electronics 2021, 10, 2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202511
Tang S-N, Liao J-C, Chiu C-K, Ku P-T, Chen Y-S. An Accuracy-Improved Fixed-Width Booth Multiplier Enabling Bit-Width Adaptive Truncation Error Compensation. Electronics. 2021; 10(20):2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202511
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Song-Nien, Jen-Chien Liao, Chen-Kai Chiu, Pei-Tong Ku, and Yen-Shuo Chen. 2021. "An Accuracy-Improved Fixed-Width Booth Multiplier Enabling Bit-Width Adaptive Truncation Error Compensation" Electronics 10, no. 20: 2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202511
APA StyleTang, S.-N., Liao, J.-C., Chiu, C.-K., Ku, P.-T., & Chen, Y.-S. (2021). An Accuracy-Improved Fixed-Width Booth Multiplier Enabling Bit-Width Adaptive Truncation Error Compensation. Electronics, 10(20), 2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202511





