Energy Management of Hybrid UAV Based on Reinforcement Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. System Modeling
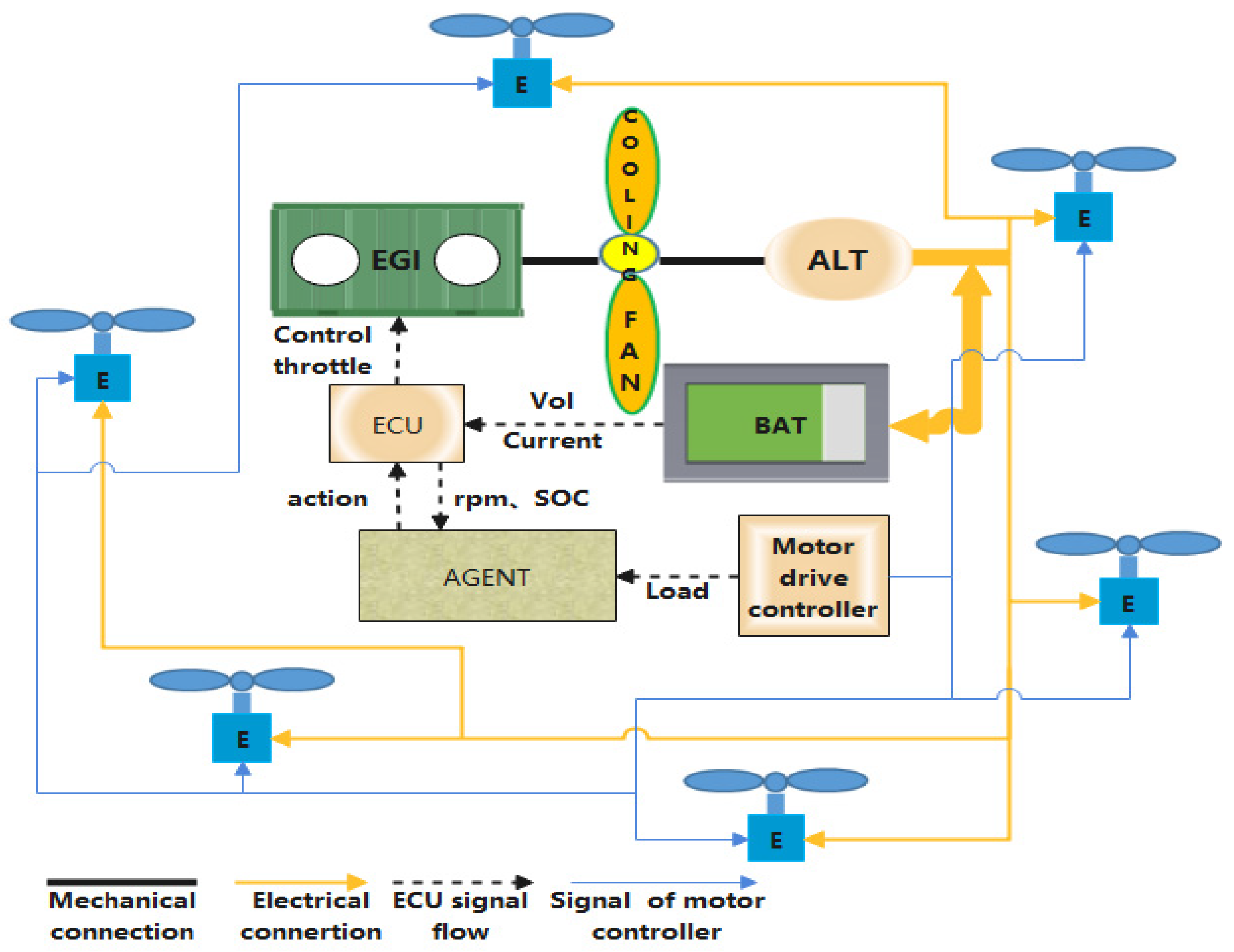
2.1. Hybrid System Modeling
2.2. Internal Combustion Engine Modeling
2.3. Generator Modeling
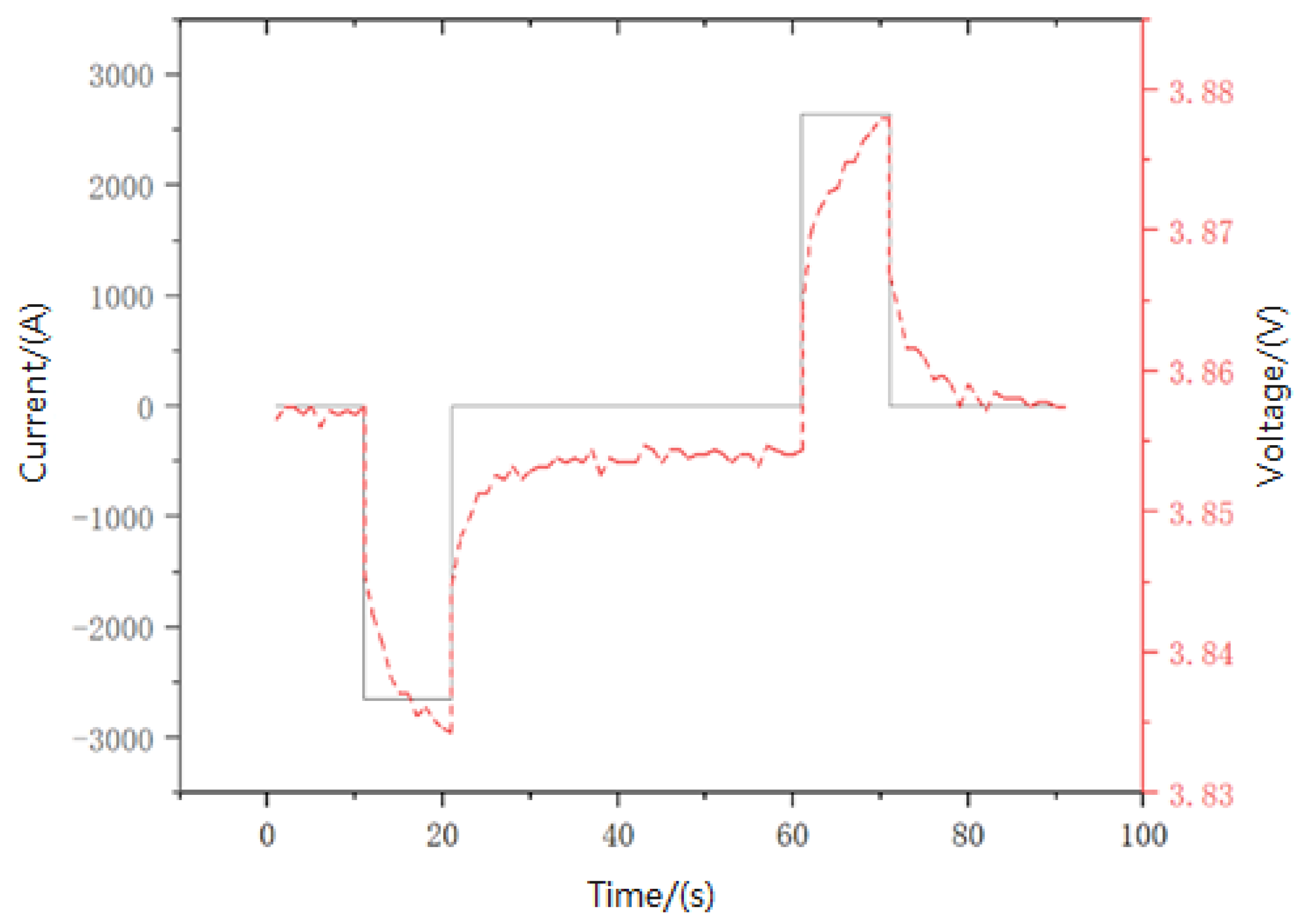
2.4. Energy Storage Device Modeling
2.5. Cooling System Modeling
3. Energy Management Strategy
3.1. Introduction
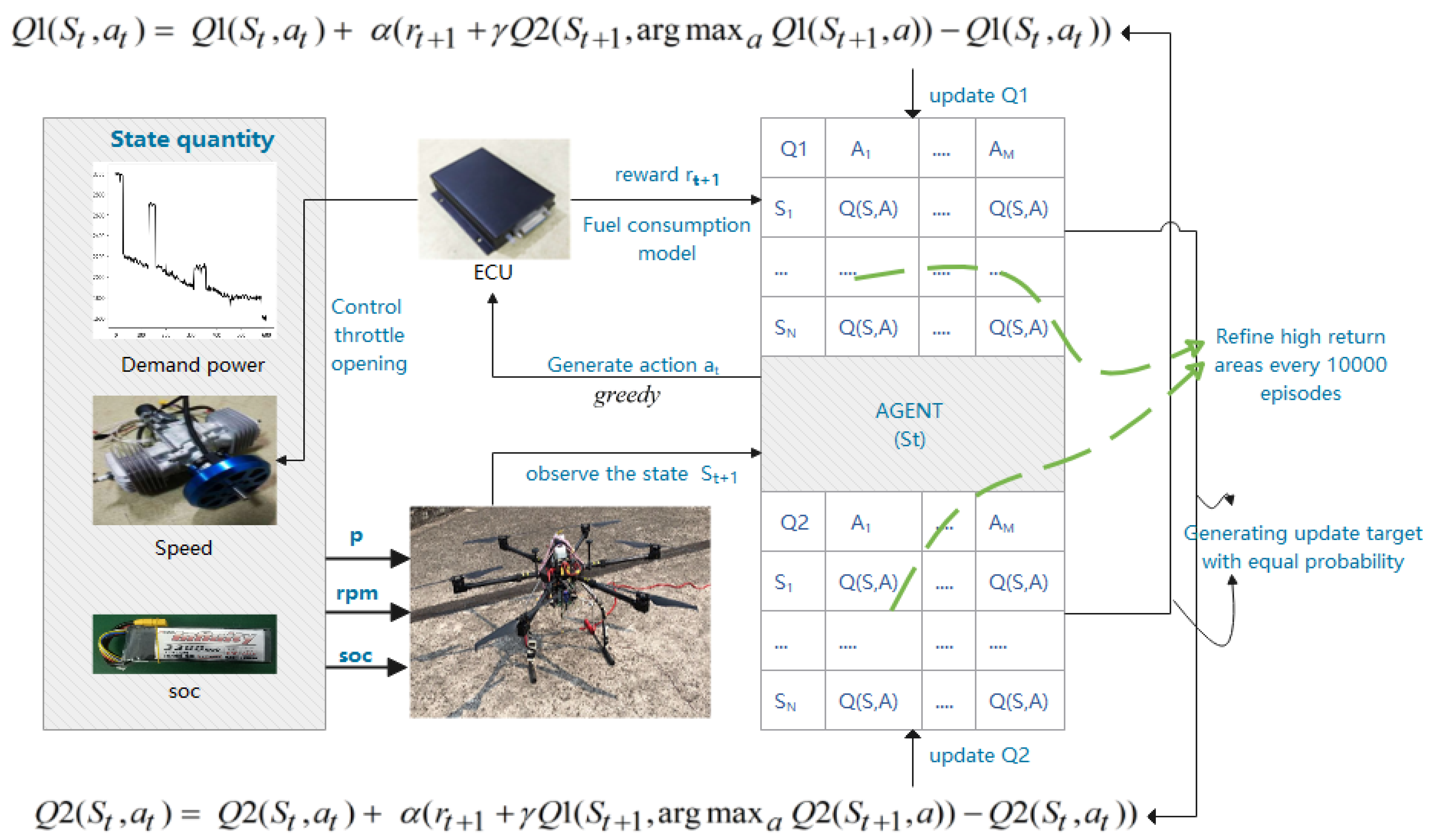
3.2. MDP Action and State Space
3.3. Reward Function
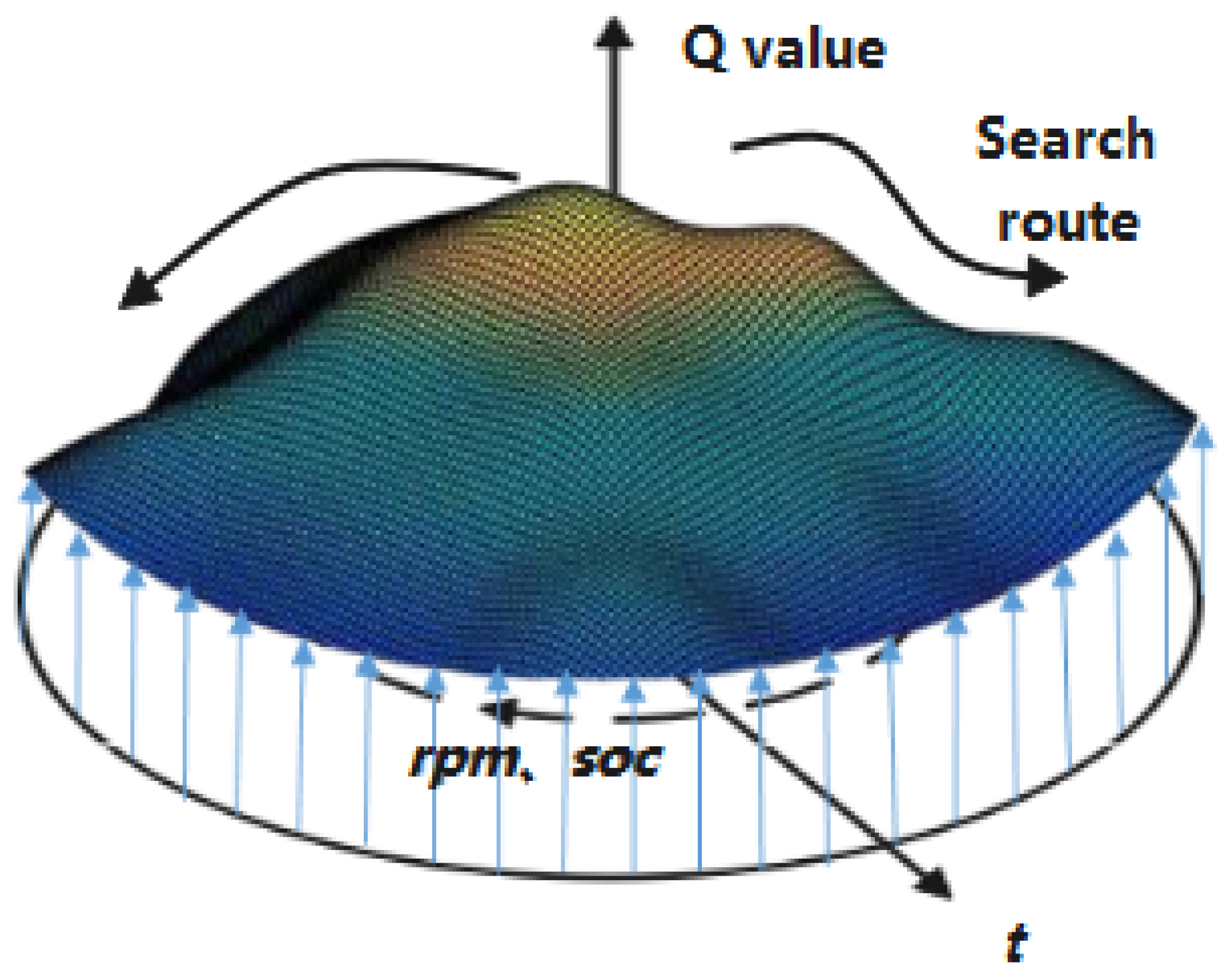
3.4. Theoretical Basis
3.5. Algorithm Improvement and Application
4. Results and Discussion
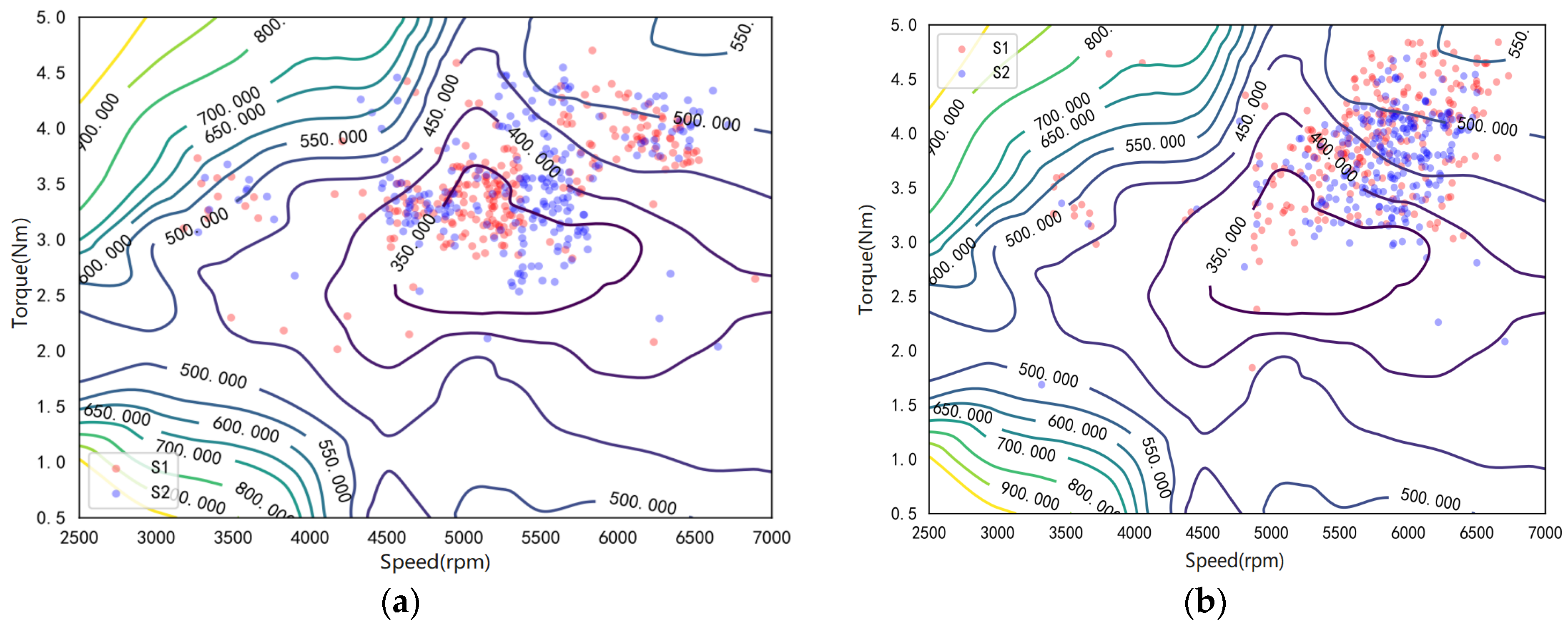
4.1. Convergence Analysis
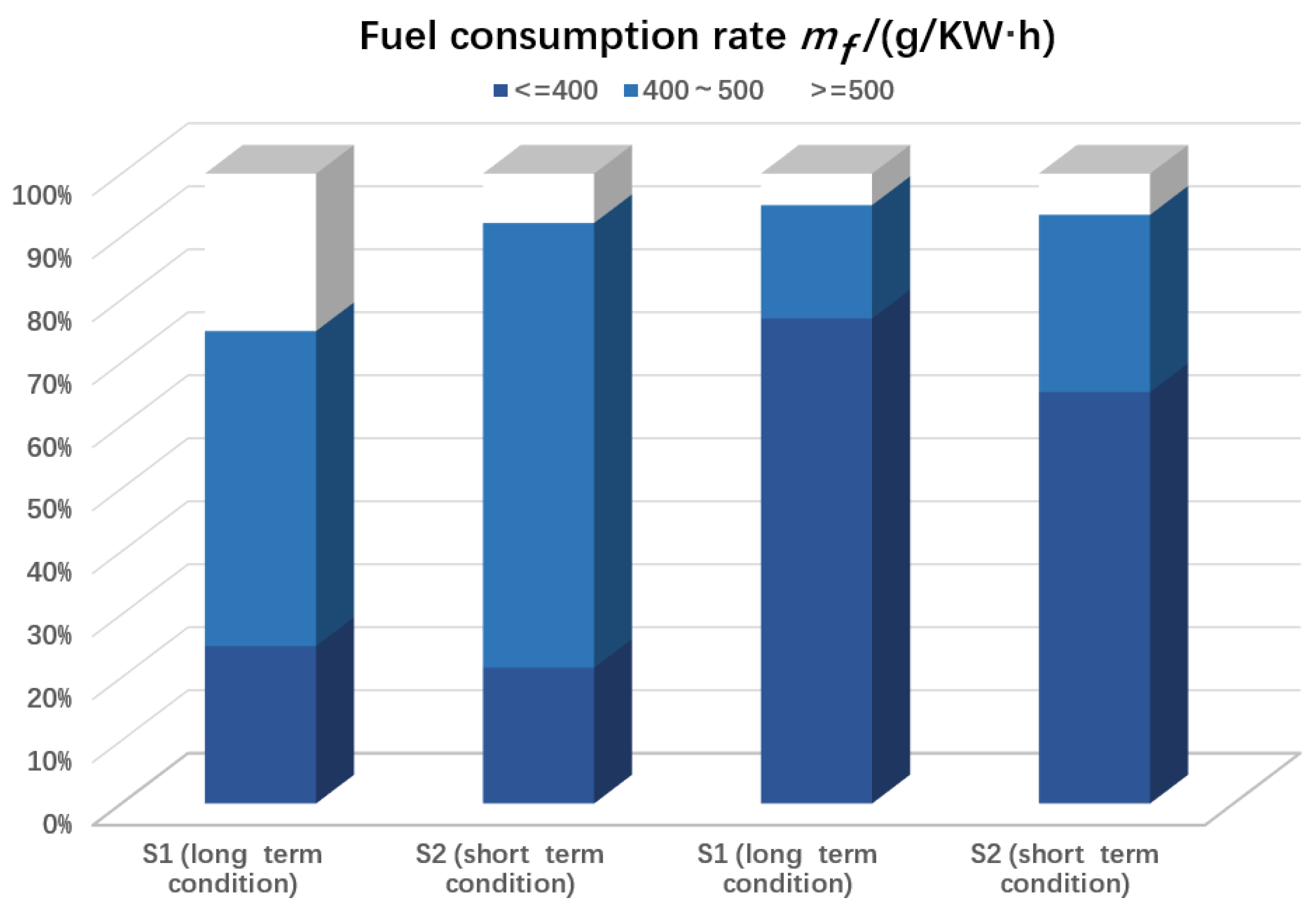
4.2. Economic Analysis
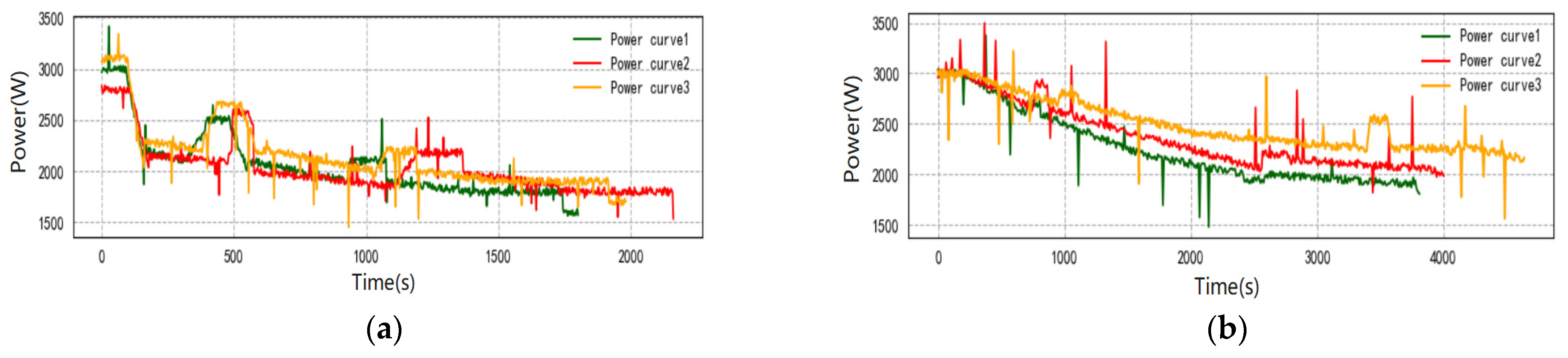
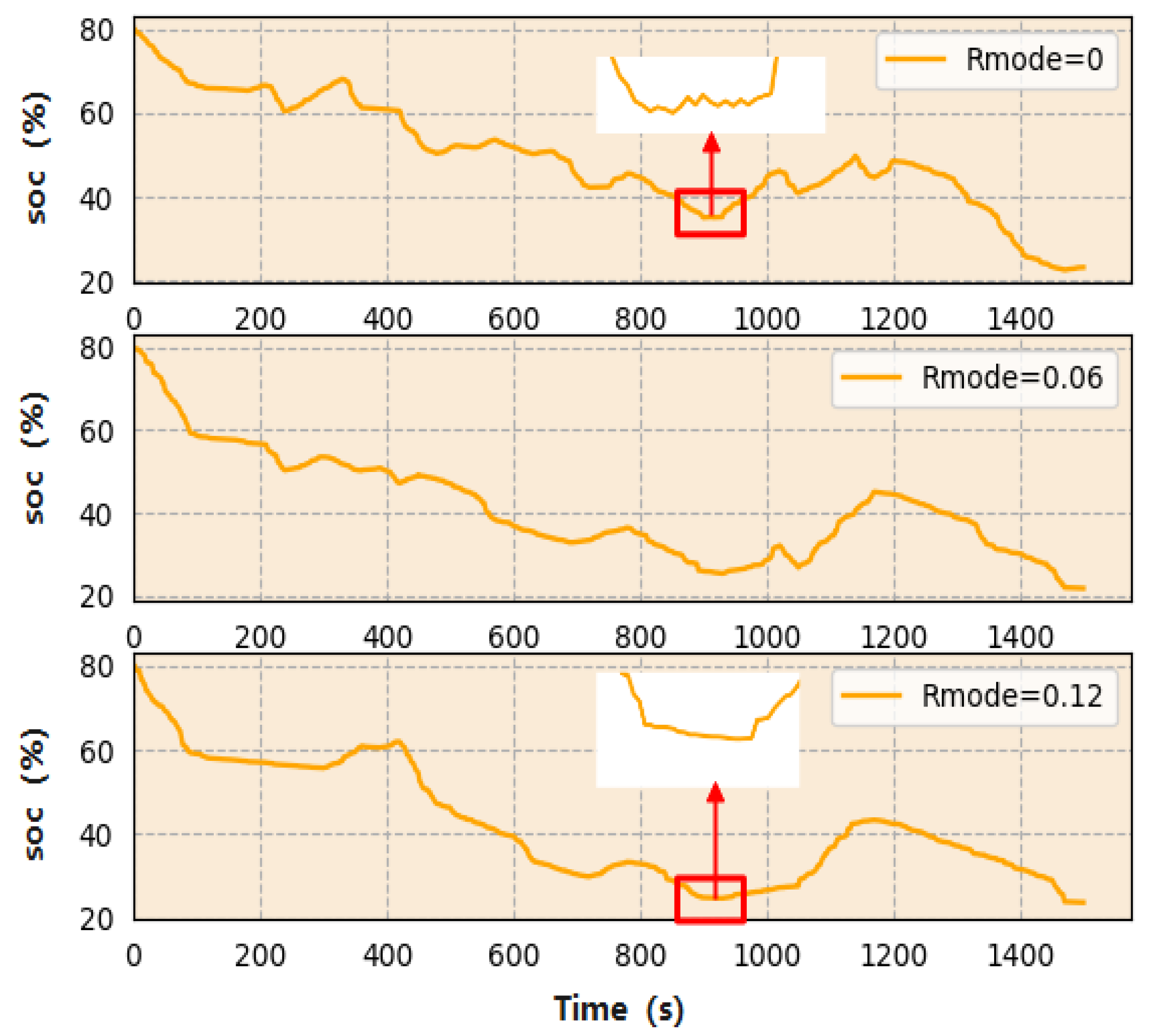
4.3. Charge–Discharge Frequency Analysis
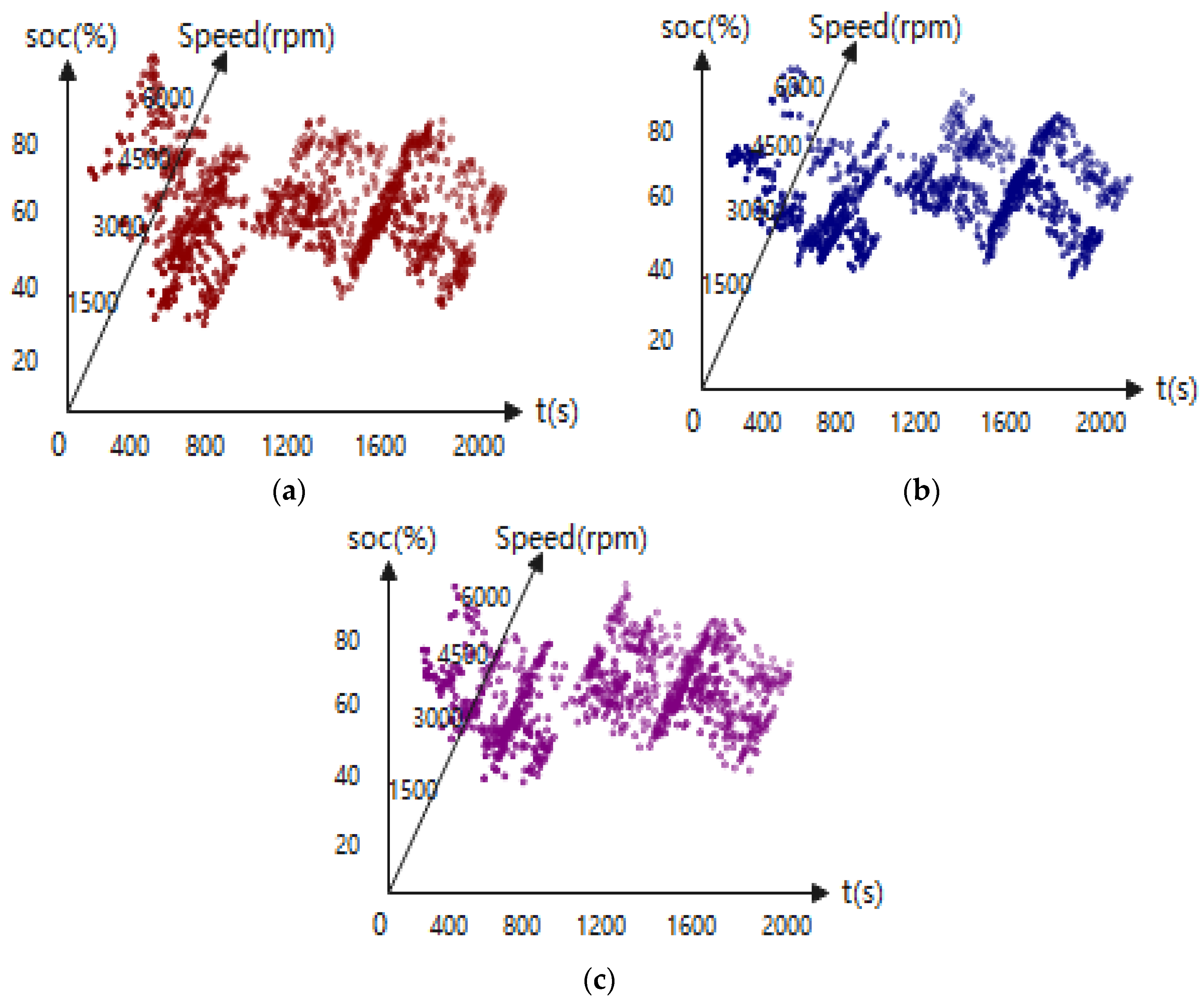
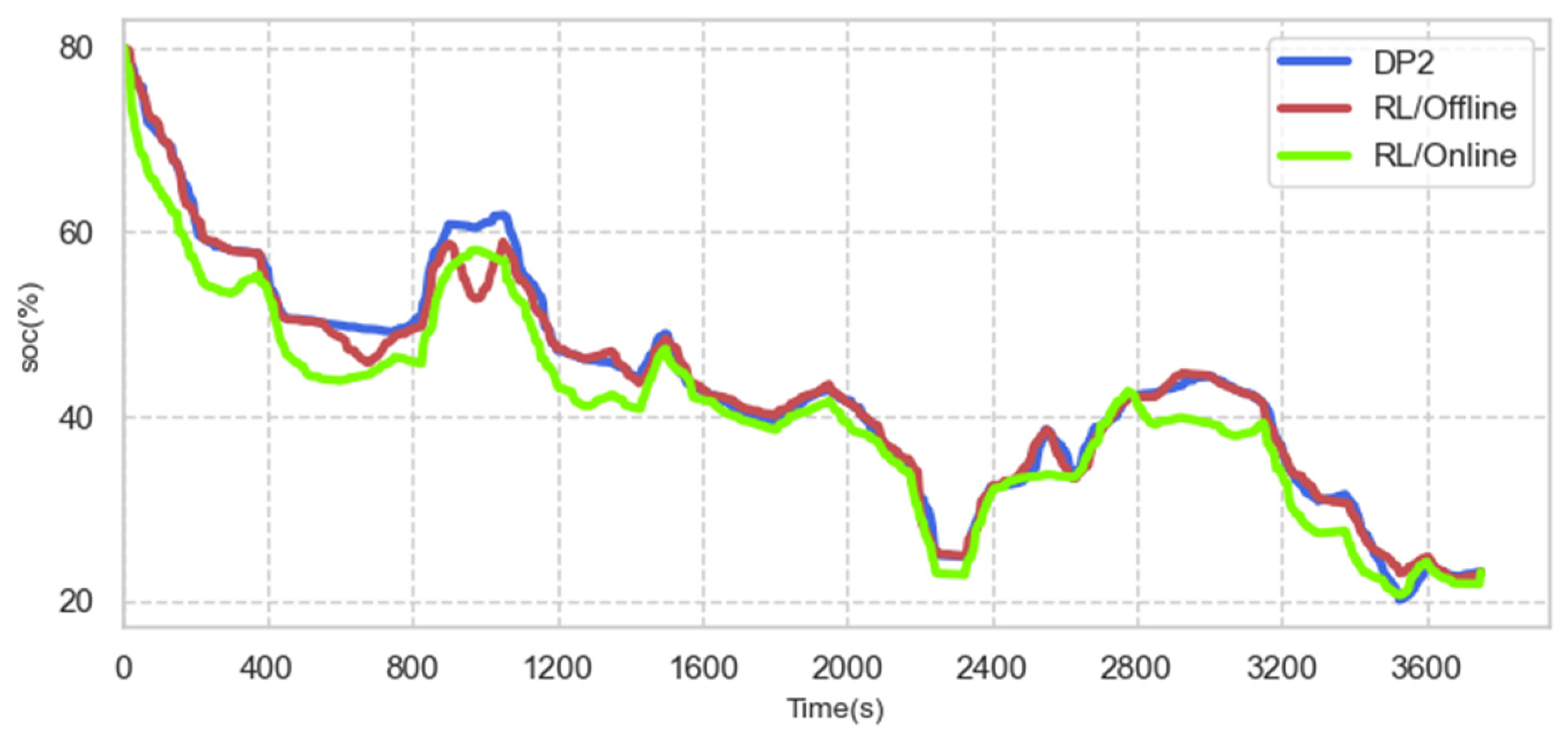
4.4. On-Line Control Analysis
4.5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lei, T.; Min, Z.; Fu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, X. Research on dynamic balance management strategy of hybrid power supply for fuel cell UAV. J. Aeronaut. 2020, 41, 324048. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Fu, Z.; Tao, F.; Zhu, L.; Si, P. Data-driven reinforcement-learning-based hierarchical energy management strategy for fuel cell/battery/ultracapacitor hybrid electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 2020, 455, 227964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Hu, X.; Tang, X.; Lin, X.; Rathod, D.; Filipi, Z. Ensemble Reinforcement Learning-Based Supervisory Control of Hybrid Electric Vehicle for Fuel Economy Improvement. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2020, 6, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, B.; Mellit, A.; Marco, T.; Rabhi, A.; Launay, J.; Naimi, S.E. Energy Management Strategy for parallel Hybrid Electric Vehicle Using Fuzzy Logic. Control Eng. Pract. 2003, 11, 171–177. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; You, S.; Wang, W.; Li, L.; Xiang, C. A Stochastic Predictive Energy Management Strategy for Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles Based on Fast Rolling Optimization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 9659–9670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Pang, Y.; Wu, C.; Yang, X. Energy management strategy optimization of hybrid electric vehicle based on parallel deep reinforcement learning. J. Chongqing Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2020, 34, 62–72. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; He, H.; Khajepour, A.; Wang, H.; Peng, J. Energy management for a power-split hybrid electricbus via deep reinforcement learning with terraininformation. Appl. Energy 2019, 255, 113762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Shi, J.; Chen, H. A comparison study of battery size optimization and an energy management strategy for FCHEVs based on dynamic programming and convex programming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 21858–21872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Hofmann, H.; Li, J.; Han, X.; Ouyang, M. Optimization for a hybrid energystorage system in electric vehicles using dynamic programing approach. Appl. Energy 2015, 139, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Teng, L.; Sun, F.; Peng, H. Comparative study of dynamic programming and pontryagin minimum principle on energy management for a parallel hybridelectric vehicle. Energies 2013, 6, 2305–2318. [Google Scholar]
- Francesco, P.; Petronilla, F. Design of an Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy-Based Control in Relation to the Passenger Number for a Fuel Cell Tram Propulsion. Energies 2020, 13, 4010. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Tan, H.; Peng, J.; Zhang, H.; He, H. Deep reinforcement learning of energy management with continuous control strategy and traffic information for a series-parallel plug-in hybrid electric bus. Appl. Energy 2019, 247, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Niu, L.; Shi, H.; Li, X.; Dou, H.; Pei, Z. Energy management optimization strategy of extended range electric vehicle. J. Anhui Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 37, 258–266. [Google Scholar]
- Gen, W.; Lou, D.; Zhang, T. Multi objective energy management strategy of hybrid electric vehicle based on particle swarm optimization. J. Tongji Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 48, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, S. Research on Energy Management Strategy and Power Cell Optimization of Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Jilin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Murphey, Y.L. Optimal Power Management Based on Q-Learning and Neuro-Dynamic Programming for Plug in Hybrid Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 31, 1942–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Chen, Z.; Kiliaris, L.; Kuang, M.L.; Masrur, M.A.; Phillips, A.M.; Murphey, Y.L. Intelligent vehicle power control based on machine learning of optimal control parameters and prediction of road type and traffic congestion. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2009, 58, 4741–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Rathod, D.; Zhang, D. Parametric study on reinforcement learning optimized energy management strategy for a hybrid electric vehicle. Appl. Energy 2020, 259, 114200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; He, H.; Wu, J.; Peng, J.; Li, Y. Energy management based on reinforcement learning with double deep Q-Learning for a hybrid electric tracked vehicle. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Wu, G.; Boriboonsomsin, K.; Barth, M.J.; Gonder, J. Data-Driven Reinforcement Learning-Based Real-Time Energy Management System for Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles. Transp. Res. Rec. 2016, 2572, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, M.; Yang, W.; Song, D.; Kosuda, M.; Szabo, S.; Lipovsky, P.; Kasaei, A. Research on Energy Management of Hybrid Unmanned Aerial Vehicles to Improve Energy-Saving and Emission Reduction Performance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boukoberine, M.N.; Zhou, Z.B.; Benbouzid, M. A critical review on unmanned aerial vehicles power supply and energy management: Solutions, strategies, and prospects. Appl. Energy 2019, 255, 113823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arum, S.C.; Grace, D.; Mitchell, P.D.; Zakaria, M.D.; Morozs, N. Energy Management of Solar-Powered Aircraft-Based High Altitude Platform for Wireless Communications. Electronics 2020, 9, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, T.; Yang, Z.; Lin, Z.C.; Zhang, X.B. State of art on energy management strategy for hybrid-powered unmanned aerial vehicle. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2019, 32, 1488–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.A.; Powell, B.K. Modeling of an internal combustion engine for control analysis. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 1998, 8, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, J.; Wang, B.; Luk, P.C.K. An improved Thevenin model of lithium-ion battery with high accuracy for electric vehicles. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.C.; Hauser, K. Artificial intelligence framework for simulating clinical decision-making: A Markov decision process approach. Artif. Intell. Med. 2013, 57, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, C.C., III. A survey of solution techniques for the partially observed Markov decision process. Ann. Oper. Res. 1991, 32, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cipriano, L.E.; Goldhaber-Fiebert, J.D.; Liu, S.; Weber, T.A. Optimal Information Collection Policies in a Markov Decision Process Framework. Med. Decis. Mak. 2018, 38, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.Y.; Jahromi, M.J.; Luo, H.; Sharma, H.; Jain, R. Model-free Reinforcement Learning in Infinite-horizon Average-reward Markov Decision Processes. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Shanghai, China, 13–18 July 2020; Volume 119, pp. 10170–10180. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.H.; Li, T.H.S.; Lin, C.J. Backward Q-Learning: The combination of Sarsa algorithm and Q-Learning. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2013, 26, 2184–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Li, L.; Zheng, S.; Li, Y.; Situ, H. Variational quantum compiling with double Q-Learning. New J. Phys. 2021, 23, 033002–033016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, B.; Yang, C. Online Markov Chain-based energy management for a hybrid tracked vehicle with speedy Q-Learning. Energy 2018, 160, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Zhang, H. Nonparametric Approximate Generalized strategy iterative reinforcement learning algorithm based on state clustering. Control Decis. Mak. 2017, 32, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Wal, J. Discounted Markov games: Generalized policy iteration method. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1978, 25, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
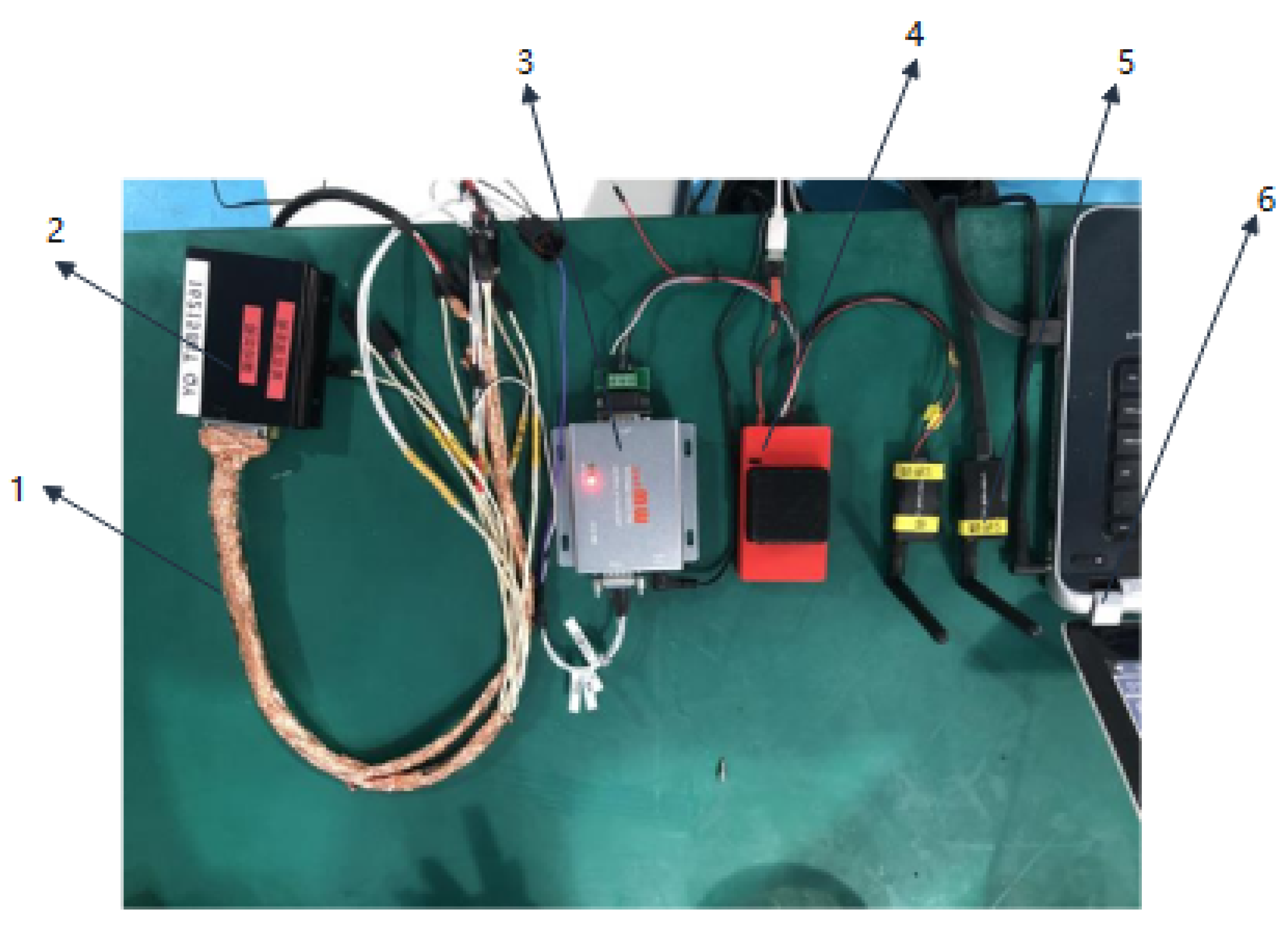












| Device | Item | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Engine | Cylinders | 2 |
| Rated torque | 4.6 Nm | |
| Power rating | 2.8 Kw | |
| Rated speed | 2000–7200 rpm | |
| Alternator | Power rating | 2.7 Kw |
| Phase resistance | 0.3 Ω | |
| D-axis inductance | 0.09 mH | |
| Q-axis inductance | 0.09 mH | |
| Battery | Type | Li-Po Graphene |
| Capacity | 5.2 Ah | |
| Voltage (single cell) | 4.2 V |
| Inputs: 5-D table; Discount factor ; Learning rate ; Exploration probability Outputs: near global optimal strategy |
| 01: Initialize Q1 list and Q2 list arbitrarily; 02: for each MDP trajectory: 03: for each discrete time step t = 0:T~1: 04: observe the state : 05: if temp0 (a random number between 0 and 1) > : 06: ; 07: else: 08: = randomly choose an action; 09: Take action and observe the next state and ; 10: If temp1 (a random number between 0 and 1) <= 0.5: 11: ; 12: else: 13: ; 14: ; |
| Inputs: 5-D table; Discount factor ; Learning rate ; Exploration probability Outputs: near global optimal strategy |
| 01: Initialize and arbitrarily; Chain = Episodes = 0; Rewards = [−1000]; 02: for each MDP trajectory: 03: reward = 0; 04: If Chain/40,000 = = 10,000: 05: ; 06: for each time step t = 1~T: 07: observe the state : 08: if temp (= random(0,1)) > : 09: ; 10: else: 11: at = randomly choose an action; 12: Take action and observe the next state and ; reward = reward + ; 13: If temp (= random(0,1)) <= 0.5: 14: ; 15: else: 16: ; 17: ; 18: If ε = 1 and reward/Reward [Episodes] < 0.9: 19: Refine high Q table, = 0; 20: Rewards.append (reward), Episodes = Episodes + 1; 21: Chain = Chain + 1 |
| Training Progress (×400 Trajectories) | 100–110 | 200–210 | 300–310 | 400–410 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuel consumption | average/variance | average/variance | average/variance | average/variance |
| Q Learning | 418.4 g/4007.7 | 340.6 g/813.1 | 301.6 g/237.1 | 296.4 g/16.1 |
| Double Q Learning | 355.4 g/1104.3 | 298.6 g/51.9 | 294.7 g/56.4 | 290.2 g/8.7 |
| Proposed double Q Learning | 320.4 g/137.1 | 275.9 g/5.2 | 263.2 g/1.8 | 262.3 g/0.6 |
| Long Time Trajectory 1 | Long Time Trajectory 2 | Long Time Trajectory 3 | Short Time Trajectory 1 | Short Time Trajectory 2 | Short Time Trajectory 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1/g | 935.57 | 966.48 | 1291.71 | 388.88 | 517.21 | 451.07 |
| S2/g | 879.63 | 914.66 | 1235.05 | 409.45 | 552.67 | 491.02 |
| S1/S2 | 106.36% | 105.67% | 104.59% | 94.59% | 93.58% | 91.86% |
| DP1 | DP2 | RL | RULE-BSED | DP1-DP2/RL(%) | RULE-BSED/RL(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Offline | Offline | Offline/Actual | Offline | |||
| State and action accuracy | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.005 | |||
| Fuel consumption under training condition A (short-time) | 467.31 g | 427.28 g | 440.78 g/- | 545.97 g | 106.02/96.94 | 123.87 |
| Fuel consumption under training condition B (long-time) | 982.34 g | 879.10 g | 937.80 g/- | 1083.03 g | 104.74/93.74 | 115.49 |
| Fuel consumption under strange condition A (short-time) | 455.98 g | 418.32 g | 447.32 g/429.82 g | 557.52 g | 101.84/93.51 | 124.64 |
| Fuel consumption under strange condition B (long-time) | 1142.57 g | 1036.38 g | 1140.51 g/1092.76 g | 1329.72 g | 100.18/90.87 | 116.58 |
| Average calculation cost | 18.6 h | 74.3 h | 37.0 h |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, J.; Yan, Z.; Wu, L. Energy Management of Hybrid UAV Based on Reinforcement Learning. Electronics 2021, 10, 1929. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10161929
Shen H, Zhang Y, Mao J, Yan Z, Wu L. Energy Management of Hybrid UAV Based on Reinforcement Learning. Electronics. 2021; 10(16):1929. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10161929
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Huan, Yao Zhang, Jianguo Mao, Zhiwei Yan, and Linwei Wu. 2021. "Energy Management of Hybrid UAV Based on Reinforcement Learning" Electronics 10, no. 16: 1929. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10161929
APA StyleShen, H., Zhang, Y., Mao, J., Yan, Z., & Wu, L. (2021). Energy Management of Hybrid UAV Based on Reinforcement Learning. Electronics, 10(16), 1929. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10161929





