Abstract
In this paper, a feasibility study of a microwave antenna-based sensor is proposed for in vitro experiments for monitoring blood glucose levels. The proposed device consists of a square-ring incorporated within a fully textile monopole antenna to absorb and sense different glucose concentrations, covering patients with different diabetic conditions. The designed antenna-sensor is optimized to operate at 2.4 GHz. The sensing principle is based on the resonance frequency shift of the reflection response of the antenna-based sensor under different glucose levels. The experiments were carried out with blood mimicking by means of aqueous solutions, using D(+)- glucose/water in different concentrations for various diabetic conditions of type-2 diabetes. The performance of the embroidered antenna-based sensor is characterized and validated using a convenient setup for in vitro measurements. The results demonstrated the ability of the proposed antenna-based sensor to cover all the glucose levels of the diabetes range, including hypoglycemia (10–70 mg/dL), normoglycemia (80–110 mg/dL) and hyperglycemia (130–190 mg/dL) with a sensitivity of 350 kHz/(mg/dL). Besides its ability to detect different glucose concentrations of various diabetic conditions, the proposed antenna-sensor presents diverse features such as a simplistic design, compact size, wearability and low cost. The proposed textile device demonstrates a proof of concept for efficient in vitro blood glucose level measurements and diagnostics of diabetes.
1. Introduction
Human beings suffer from several diseases related to genetic or lifestyle factors. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the most common illnesses increasingly expanding among humankind, and it is a critical worldwide health problem due to the increase of diabetes patients and the lack of treatment [1]. Diabetes is caused by the malfunction of the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate the level of blood glucose, and it also helps introduce glucose molecules into cells for storage or energy production [2]. This illness can cause many complications in the human body including stroke, kidney failure, heart attacks and peripheral arterial disease. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 422 million people worldwide have diabetes, particularly in low-and middle-income countries, and the number will increase to 592 million in 2035 [3]. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), the diabetes is categorized into three main categories as Type-1 diabetes, Type-2 diabetes and gestational diabetes (GDM). The Type-2 is the most common among diabetics and accounts for around 90% of all diabetes cases [4,5]. The blood glucose level is classified into three categories: Hypoglycemia, Normoglycemia and Hyperglycemia [6]. The first one is typically defined as a blood glucose level less than 70 mg/dL. The primary signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia include shivering, accelerated heartbeat, dizziness and others [7]. When the patients feel any of these symptoms, they should consume food or drinks high in sugar until their blood glucose levels reach the normal range. The second one is the state of having a normal level of blood glucose and it encompasses the range of 80 to 110 mg/dL. The last category, called hyperglycemia, was defined by WHO as a blood glucose level greater than 120 mg/dL and it is considered one of the most dangerous conditions for diabetic patients because it causes more complications such as nerve damage, cardiovascular disease, feet problems and eye diseases [8]. Therefore, diabetics have to check their blood glucose levels regularly to reduce the danger of additional illness.
In the literature, there are various techniques developed for glucose monitoring levels including Raman spectroscopy [9,10], electrochemistry [11], reverse iontophoresis (RI) [12] and optical [13], on which the researchers have been working to measure blood glucose levels. Microwave sensing is considered as a promising technique for monitoring blood glucose levels due to the miniaturization of the involved electronic systems, ease of handing, cost-effectiveness and quick response time [14]. The operation principle in most of the microwave sensors is based on detecting the variations in the dielectric properties of different concentrations of blood glucose on the sensing area. The changes in dielectric properties of the liquid under test in the sensing area are perceived and explained by the sensing parameters (resonance frequency and/or amplitude) of a readout device. To enhance the sensitivity and generate high-accuracy measurement results, the liquid under test should be placed in the zone of a high intensity electric field.
Recently, antennas operating as sensors established a growing demand for monitoring blood glucose levels [15]. Several studies have been reported in the literature using antenna-based sensors to detect blood glucose levels [16,17,18]. In [16], a microstrip patch antenna-sensor was developed to monitor blood glucose levels in an in vitro experiment. The glucose concentration ranged from 0 to 400 mg/dL, and the antenna-based sensor demonstrated a sensitivity of 25 kHz/(mg/dL). A planar inverted-F antenna (PIFA) was used as a sensor to test three diabetic conditions [17]. The antenna-sensor was optimized to operate at 530 MHz. A resonance frequency shift of 3.54 kHz/(mg/dL) was observed according to the change of glucose concentration. All the devices mentioned above used conventional electronic rigid substrates. Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are implemented by means of commercial substrates that are not suitable for electronic textile applications.
Wearable electronic textiles have grown rapidly in recent years for various research fields such as communication, sensing, information and medical [19]. Electronic textiles (e-textiles) could be developed on common clothes which are lighter and more comfortable than those implemented on PCBs, and they can also easily adapt to rapid changes in the computational and sensing conditions of any application. Recently, textile materials have been getting more attention due to their special characteristics including low weight, integration level, softness and flexibility [20].
In the current study, a textile embroidered monopole antenna-based sensor is proposed for monitoring blood glucose levels for in vitro experiment. The designed antenna-sensor was optimized to operate at 2.4 GHz. Different glucose concentrations were prepared to cover diabetes patients with Hypoglycemia, Normoglycemia and Hyperglycemia. The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 details the methodology of the antenna-sensor design as well as the preparation of the blood mimicking aqueous solutions. Section 3 presents the results of the proposed antenna-based sensor for three diabetic conditions. A comparison of different techniques for detecting glucose concentration using microwave sensors is presented in Section 4. Finally, Section 5 exhibits the main conclusions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antenna-Sensor Design
To design an antenna-sensor and perform a realistic simulation, the substrate-related parameters have to be defined. For textile materials, it is essential to determine the permittivity and the losses of the substrates. A split-post dielectric resonator (SPDR) was used to characterize the dielectric parameters of the textile substrate by means of the resonance method. Felt was chosen as a substrate due to its low loss tangent and low cost in comparison with other fabrics. The experimental dielectric constant and loss tangent of the felt fabric were and . Furthermore, an electronic outside micrometer was used to measure the thickness (h = 0.7 mm) of the felt substrate. The fabric material corresponds to a non-woven structure with a 100% polyester (PES) composition. The conductive antenna-sensor layer is embroidered by means of a commercial conductive yarn (Shieldex 117/17 dtex 2-ply) made of 99% pure silver-plated nylon yarn 140/17 dtex with a linear resistance 30 Ω/cm.
The design of the proposed antenna-based sensor mainly consisted of a square ring (radiation part) and a partial ground plane. This antenna-sensor is designed to operate at 2.4 GHz. The embroidered textile monopole antenna-sensor was fabricated using a Singer Futura XL embroidery machine. The manufacturing embroidery process is depicted in Figure 1. Starting with the simulated design of the antenna-sensor using the commercial CST Studio Suite 3D full electromagnetic simulator 2019, the geometry of the proposed antenna-sensor as well as the sensing area are presented in Figure 1a. A parametric study was performed by means of a geometric tuning process on various parameters such as length and width of the substrate and square-ring of the proposed antenna-sensor in order to obtain better insight into the physical behavior of the antenna and to optimize its behavior at 2.4 GHz. The list of the optimized geometrical parameters are detailed in Table 1. The desired design layout was digitized, converting the antenna-sensor shape into the path that the needle was going to follow in the embroidery machine. After importing the file which contained the identification of the desired geometry into the embroidery machine in digital format, the computerized embroidery process was implemented to embroider the conductive part of the design. A needle with the conductive yarn was threaded through the substrate material and interwoven with a bobbin assistant yarn to form the stitch (Figure 1b). The stitches appeared the same on the top and bottom of the felt substrate. A satin fill stitch pattern was selected and implemented because it was well-suited to a narrow shape. This fact ensures the required resolution for the antenna dimensions. The final embroidered prototype of the textile antenna-sensor is shown in Figure 1c.
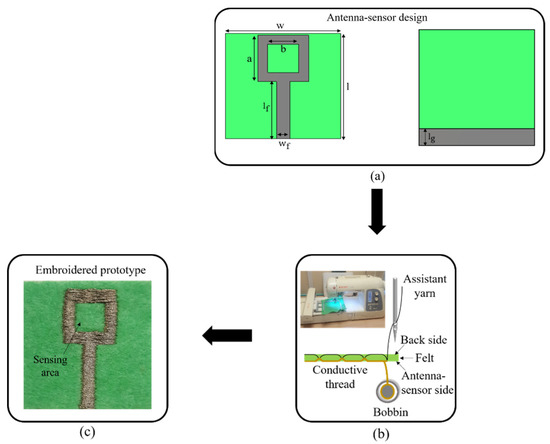
Figure 1.
Embroidery process of the proposed antenna-sensor: (a) Antenna-sensor design; (b) Pattern embroidery; (c) Embroidered prototype.

Table 1.
Geometrical parameters of the proposed antenna-sensor.
2.2. Samples Preparation and Test Setup
The entire human blood consists of glucose and other components, as well as water which accounts for a major proportion of its volume. Therefore, it can be predicted that the dielectric properties of the blood are related to the properties of aqueous glucose solutions. To imitate the blood behavior for in vitro experiments, several aqueous glucose concentrations were prepared by mixing distilled water and D(+)- glucose powder for various diabetic conditions of type-2 diabetes.. The glucose/water solutions were prepared to verify the functionality of the proposed antenna-based sensor.
The glucose/water solutions were prepared to cover diabetes patients for three states concerning glucose concentration level ():
- Hypoglycemia: 70 mg/dL.
- Normoglycemia: 80 110 mg/dL.
- Hyperglycemia: 120 mg/dL.
To test the antenna-sensor response for different concentration at each diabetic condition, three sets of samples were prepared. Each set consisted of four newly embroidered antenna-sensors for a specific state of the diabetes patients. A photograph of the measurement setup is shown in Figure 2. A digital micropipette device was used to drop a specific volume of each concentration on the sensing area. To reduce the measurement errors due to uncertainty in the solution volume, a minimum volume considered of was selected for testing different glucose concentrations. The antenna-sensor was connected to an N9916A FieldFox microwave analyzer operating as a vector network analyzer (VNA) for recording data of the return loss for the in vitro experiment. Throughout the experiment, the controlled environmental conditions were maintained. Absorbed solutions in the sensing area (square ring) with various concentrations of glucose alter the dielectric properties of the substrate and therefore reflection measurements are expected to change accordingly.
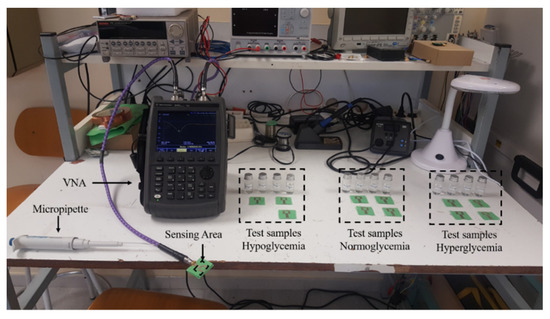
Figure 2.
Test setup for verification of the antenna-sensor performance.
3. Results
In order to verify the accuracy of the fabrication technique of the antenna-sensor design, 12 antenna-sensors (same as presented in Figure 1a) were fabricated for testing and validation. All the fabricated antenna-sensors were tested in free space by measuring the return loss. The return loss of the simulated and measured device are compared in Figure 3. We presented five samples (S1, S2, S3, S4 and S5) as an example to emphasize consistency of our antenna-sensor output. The measured return loss of five fabricated antenna-sensors presented a slight deflection between measured and simulated results due to manufacturing tolerance. The simulated return loss reaches −24 dB at resonance frequency 2.4 GHz.
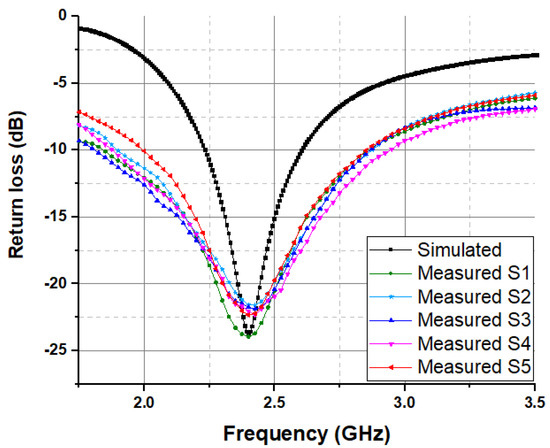
Figure 3.
Return loss of simulated and measured for the proposed antenna-sensor.
All the measured results of the embroidered antenna-sensor have a resonant frequency of 2.4 GHz and exhibited a small declination in the amplitude of the return loss due to embroidery fabrication tolerance.
RF Response of the Glucose Level
The radio frequency (RF) microwave sensing of the glucose level relies on the resonance concept of the antenna-sensor. The main principle is based on the detection of the change in the RF signal induced by different concentrations of the glucose/water solutions, which present different dielectric properties. 12 measurements are performed to verify the functionality of the proposed antenna-sensor for several diabetic conditions. The measurement setup of the antenna-sensors is shown in Figure 2. Three sets of samples are prepared, with each set dedicated to one of the diabetic conditions. The initial testing was performed for four antenna-sensors to cover diabetes patients with hypoglycemia (10–70 mg/dL) within in vitro experiments. A second test was implemented for the glucose-based aqueous solution range from 80 to 110 mg/dL of four new fabricated antenna-sensors to cover diabetes patients with normoglycemia. Finally, the last four new microwave antenna-sensors were tested to reach the indicated concentrations for hyperglycemia (130–190 mg/dL) diabetic condition. All samples were tested with a fixed-volume micropipette and the return loss was immediately recorded after the solution was dropped on the sensing area.
When the textile antenna-sensor absorbs certain solutions, the electrical properties such as the resonance frequency are expected to change, since the overall permittivity of the textile substrate was modified. Therefore, the frequency shift was considered as the principal sensing parameter of the proposed antenna-sensor. The square ring was selected as the sensing area to apply a drop of by micropipette of different concentrations, which can generate a detectable shift in the resonance frequency. Different glucose/water solutions correspond to different dielectric properties. Therefore, this alteration in dielectric properties produced a shift in the resonance frequency. The return loss response of the antenna-sensor was recorded for each of the indicated concentrations for different diabetic conditions. Figure 4 illustrates the measured return loss of the proposed antenna-sensor for three diabetic conditions with a zoom-in zone of the main resonance points. The distilled water was considered as a reference sample. Due to the higher constant dielectric of the distilled water, the resonance frequency in the air shifted by 100 MHz. We observed that the resonance frequency of the antenna-based sensor for each diabetic condition shifts up when increasing the concentration of the glucose/water solutions. The electromagnetic interaction between the antenna-based sensor and glucose with a different dielectric constant was the main cause of the change in resonance frequency.
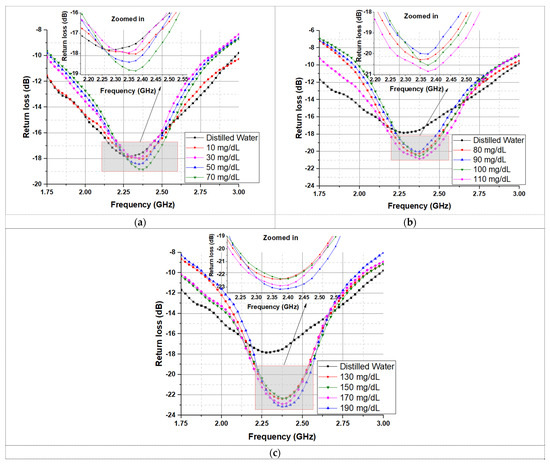
Figure 4.
The measured return loss of the proposed antenna-based sensor of three diabetic conditions: (a) Hypoglycemia; (b) Normoglycemia; and (c) Hyperglycemia.
The behavior of the proposed device can be understood as an antenna-based sensor whose resonance frequency was altered by absorbing different glucose/water concentrations for each diabetic condition. This device can help to distinguish the glucose levels in diabetes patients. After recording the antenna-sensor performance results, a linear regression analysis was applied to evaluate the resonance frequency with various concentrations of glucose/water solutions for each diabetic condition. Figure 5 presents the applied linear regression of the resonance frequency shift for the three diabetic conditions. It can be observed that the results show a good linear relationship between different glucose concentrations and the resonance frequency shift. The obtained results reveal a correlation coefficient ( of 0.96 between the indicated concentrations and the resonance frequency shift.
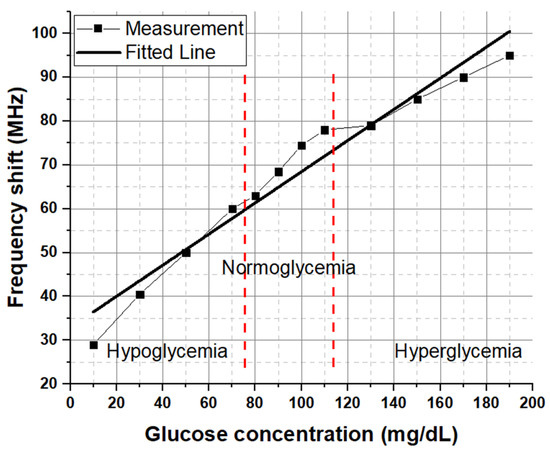
Figure 5.
Linear correlation for the frequency shift as a function of glucose concentration in different diabetic conditions.
4. Discussion
This paper exhibits proof of how RF signals may be used to differentiate various glucose concentrations, covering diabetic patients with hypoglycemia, normoglycemia and hyperglycemia within in vitro experiments. The main concept is based on the absorption of different glucose/water solutions by the textile substrate on the sensing area. Therefore, the resonance frequency of the antenna-based sensor changes due to the variation in dielectric properties of different glucose concentrations inside the sensing area. Furthermore, the microwave measurements of the proposed antenna-sensor succeed to distinguish different glucose concentrations for the three diabetic conditions. In order to demonstrate the performance of our device, a comparison of the proposed antenna-sensor with previous works is listed in Table 2. It can be observed to have excellent sensor sensitivity and a reasonable measurement range of glucose concentrations. The sensing parameter is based on the resonance frequency of reflection response in some of the microwave sensors, while others used the resonance frequency of the transmission response variations for sensing. The sensitivity (S) was defined by the resonant frequency shift that the sensor can achieve for a unit change in glucose concentration. The proposed antenna-sensor offers higher sensitivity in comparison with microwave sensors reported in the literature which are based on various sensing mechanisms. Moreover, the area of the proposed antenna-sensor is competitive in comparison with the reported works. All of the techniques reported in Table 2 used rigid substrates. Therefore, the proposed work is a novel approach for monitoring blood glucose levels based on a textile antenna.

Table 2.
Comparisons of different techniques for detecting glucose concentration using microwave sensors.
5. Conclusions
In this article, a textile monopole antenna-based sensor was presented for the monitoring of glycemia level for diabetes. The performance of the antenna-sensor was practically validated. The measured results of the return loss in free space presented a good agreement with the simulation at 2.4 GHz. The proposed antenna-sensor was tested on in vitro experiments to verify the functionality of the microwave glucose antenna-sensor. A blood mimicking aqueous solution was prepared for different concentrations to cover diabetes patients with hypoglycemia, normoglycemia and hyperglycemia relevant to type-2 diabetes. The sensing method is based on the absorption of different glucose concentrations by textiles on the sensing area. The textile antenna-based sensor uses reflection measurement to monitor the glucose level change in the resonant frequency. The detection of different glucose/water solutions is based on the variation of the dielectric properties of the sensing area which produce a significant shift in the resonant frequency. A linear regression was applied to the resonant frequency shift and a good correlation can be clearly seen between glucose concentration and the frequency shift. The results demonstrate the capability of the proposed device to cover all the glucose levels of diabetes, hypoglycemia, normoglycemia and hyperglycemia, with a sensitivity of 350 kHz/(mg/dL). The proposed antenna-sensor presents a higher sensitivity compared to existing microwave sensors reported in the literature; together with other features such as simple design, low cost and miniature size, it can therefore be used as a preliminary screening for monitoring blood glucose levels.
Author Contributions
M.E.G. conducted the research and writing; I.G. and R.F.-G. supervised and reviewed the work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Spanish Government-MINECO under Projects TEC2016-79465-R.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Whiting, D.R.; Guariguata, L.; Weil, C.; Shaw, J. IDF diabetes atlas: Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 94, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Diabetes Federation. Available online: https://www.idf.org/aboutdiabetes/what-is-diabetes.html (accessed on 21 May 2021).
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/diabetes#tab=tab_3 (accessed on 21 May 2021).
- Nathan, D.M.; DCCT/Edic Research Group. The diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study at 30 years: Overview. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, L.; Chang, S.J.; Chen, C.-J.; Liu, J.-T. Non-Invasive Blood Glucose Monitoring Technology: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Diabetes Federation Guideline Development Group. Global guideline for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 104, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.-W.; Park, S.; Lee, Y.-H.; Balkau, B.; Yi, J.-J. Fasting Glucose and All-Cause Mortality by Age in Diabetes: A Prospective Cohort Study. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, C.H.; Litwin, S.E. Hyperglycemia and adverse outcomes in acute coronary syndromes: Is serum glucose the provocateur or innocent bystander? Diabetes 2014, 63, 2209–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stuart, D.A.; Yuen, J.M.; Shah, N.; Lyandres, O.; Yonzon, C.R.; Glucksberg, M.R.; Walsh, J.T.; Van Duyne, R.P. In Vivo Glucose Measurement by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 7211–7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zang, H.; Sun, H.; Jiao, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, T.C.-Y.; Meng, Y. A Noninvasive Accurate Measurement of Blood Glucose Levels with Raman Spectroscopy of Blood in Microvessels. Molecules 2019, 24, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Ren, Z.; Pang, H. Nitrogen-Doped Carbon–Copper Nanohybrids as Electrocatalysts in H2O2 and Glucose Sensing. ChemElectroChem 2014, 1, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, R.O.; Tamada, J.A.; Tierney, M.J. Glucose monitoring by reverse iontophoresis. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2002, 18, S49–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, M.-S.; Duerkop, A.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Optical methods for sensing glucose. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4805–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, T.; Wang, C.; Kim, N.-Y. Quantitative detection of glucose level based on radiofrequency patch biosensor combined with volume-fixed structures. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gharbi, M.; Fernández-García, R.; Ahyoud, S.; Gil, I. A Review of Flexible Wearable Antenna Sensors: Design, Fabrication Methods, and Applications. Materials 2020, 13, 3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, K.; Anand, S. Demonstration of Microstrip Sensor for the Feasibility Study of Non-invasive Blood-Glucose Sensing. MAPAN 2020, 36, 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Khadase, R.; Nandgaonkar, A. Design of Implantable MSA for Glucose Monitoring. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing 2016 (ICCASP 2016), Lonere, India, 26–27 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Cano-Garcia, H.; Sotiriou, I.; Lipscombe, O.; Gouzouasis, I.; Koutsoupidou, M.; Palikaras, G.; Mackenzie, R.; Reeve, T.; Kosmas, P.; et al. A Glucose Sensing System Based on Transmission Measurements at Millimetre Waves using Micro strip Patch Antennas. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonçalves, C.; Ferreira da Silva, A.; Gomes, J.; Simoes, R. Wearable e-textile technologies: A review on sensors, actuators and control elements. Inventions 2018, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvado, R.; Loss, C.; Gonçalves, R.; Pinho, P. Textile Materials for the Design of Wearable Antennas: A Survey. Sensors 2012, 12, 15841–15857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennarelli, G.; Romeo, S.; Scarfi, M.R.; Soldovieri, F. A Microwave Resonant Sensor for Concentration Measurements of Liquid Solutions. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.E.; Shaker, G.; Safavi-Naeini, S.; Ngo, K.; Shubair, R.M.; Alquie, G.; Deshours, F.; Kokabi, H. Multiple-Cell Microfluidic Dielectric Resonator for Liquid Sensing Applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 6094–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govind, G.; Akhtar, M.J. Metamaterial-inspired microwave microfluidic sensor for glucose monitoring in aqueous solutions. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 11900–11907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Uttamchandani, D. A Microwave Dielectric Biosensor Based on Suspended Distributed MEMS Transmission Lines. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 9, 1825–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turgul, V.; Kale, I. Simulating the Effects of Skin Thickness and Fingerprints to Highlight Problems with Non-Invasive RF Blood Glucose Sensing from Fingertips. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 7553–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).