Abstract
The Hall sensor is the most commonly used position sensor of the permanent magnet brushless direct current (PMBLDC) motor. Its failure may lead to a decrease in system reliability. Hence, this article proposes a novel methodology for the Hall sensors fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control in PMBLDC motor drives. Initially, the Hall sensor faults are analyzed and classified into three fault types. Taking the Hall signal as the system state and the conducted MOSFETs as the system event, the extended finite state machine (EFSM) of the motor in operation is established. Meanwhile, a motor speed observer based on the super twisting algorithm (STA) is designed to obtain the speed signal of the proposed strategy. On this basis, a real-time Hall sensor fault diagnosis strategy is established by combining the EFSM and the STA speed observer. Moreover, this article proposes a Hall signal reconstruction strategy, which can generate compensated Hall signal to realize fault-tolerant control under single or double Hall sensor faults. Finally, theoretical analysis and experimental results validate the superior effectiveness of the proposed real-time fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control strategy.
1. Introduction
Permanent magnet brushless direct current (PMBLDC) motors have been widely used in various industrial and commercial fields, benefit from the characteristics of high power density, simple structure, and low cost [1,2,3]. During the regular operation of a PMBLDC motor, the control system needs to acquire the position of its rotor in real-time and apply the corresponding voltage vector on its stator winding to produce the required electromagnetic torque by its rotation [4,5,6,7]. Although different sensorless control methods have been proposed in many literatures, there are many limitations in the applications of these approaches, especially in the startup stage and the speed range [8,9,10,11]. Therefore, the PMBLDC motor drives with position sensors are usually preferred in most applications. The Hall sensors have advantages of simplicity and inexpensive, which make them well suited for the position sensors of the PMBLDC motor drives. Hence, the Hall sensors play a considerable important role in the motor drives [12,13,14]. The Hall sensors may fail due to various reasons (such as harsh environments, faulty connections, violent vibration, etc.), which can result in that the feedback signal of the faulty Hall sensor cannot correctly reflect the position of the rotor [15,16]. Once there is a fault in the Hall sensors, the dynamic performance of the motor drives will be significantly reduced or even overcurrent, which can lead to extensive damage to the whole system [17,18,19].
To improve the reliability of the PMBLDC motor drives with Hall sensors, it is essential to realize the fault-tolerant control (FTC) of the Hall sensors faults in motor drives [20,21,22]. In most relevant literatures, the FTC is consists of fault diagnosis and signal reconstruction, and the most essential critical part is the fault diagnosis strategy [23,24,25,26]. Several FTC methods of the Hall sensors faults in PMBLDC motor drives have been proposed in different researches, such as in [27], G. Scelba et al. investigated a fault-tolerant control algorithm to deal with the Hall-effect sensor faults and repercussion on the low-cost vector control drives. The performances of the fault-tolerant control system are discussed along with the theoretical analysis and the experimental results. Based on [27], in [28], the authors explored a much effective methodology for the detection, identification, and compensation of the binary Hall-effect sensor faults in BLDC motor drives. The proposed fault compensation strategy was applied in three states of the art estimation algorithms (the zero-order algorithm, the hybrid observer, and the vector tracking observer). The proposed fault-tolerant control methods in [27,28] both need to convert the Hall signal or the current signal to a rotation vector. Further, the fault detection was realized by detecting the corresponding zero vector. However, these methods result in significant data processing time and low fault diagnosis efficiency.
In [29], Donget et al. put forward three different fault diagnosis methods based on the characteristics of the Hall signal sequence (FD-1, FD-2, and FD-3, respectively) and the corresponding fault signal reconstruction measures were also implemented. Through the theoretical analysis and the comparison of the experimental results of the three fault diagnosis control methods, the author finally adopts the more efficient FD-3 as their fault diagnosis strategy. In [30], an improved fault-tolerant control strategy based on the vector-tracking observer was proposed based on [29], which reduced the transient current and speed dip of the motor during the Hall sensor fault diagnostic process. In most researches, the fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control of the Hall sensor is analyzed separately. The research ideas are basically the same: after the fault of a Hall sensor, first, the fault of the Hall sensor is identified by detecting the specific Hall signal (such as “000” and “111”) or another similar signal sequence; then the faulty sensor can be located by comparing the actual Hall signal with a specific Hall signal sequence; finally, the corresponding fault tolerant control strategy is carried out. However, during the period from the fault of a Hall sensor to the fault tolerant control, the electric drive system may have commutation error or even over-current. Therefore, the control system needs to diagnose the Hall sensor fault as soon as possible and apply the corresponding compensation control strategies, in case of huge damage to the motor drives. Z. Qian et al. in [31] proposed a new fast fault diagnosis (FFD) method for different Hall sensor faults cases by using a high-frequency fast counter for the purpose of diagnosing the fault Hall signal in the shortest time. This research provides us with a good solution for the fast fault diagnosis of Hall sensor fault. Worst of all, there are still some limitations in its working environments. The fast counter plays an essential role during the fault diagnosis, and the threshold coefficient of the fast counter is critical data. In [31], the author only adjusts the threshold coefficient according to the motor speed calculated by the Hall signal, which dramatically limits the dynamic performance and application range of the proposed FTC algorithm. Meanwhile, in order to reduce the performance fluctuation during the Hall sensor faults, we need to analyze the fault diagnosis and fault tolerant control simultaneously instead of separately.
To improve the dynamic performance of the FTC that can be applied in more fields, it is necessary to estimate the motor speed more accurately. In this work, we extend the research of Dong et al. [29,30] and Zhang et al. [31] by proposing a real-time fault diagnosis (RFD) method using an extended finite state machine (EFSM) and super twisting algorithm (STA) based motor speed observer.
Considering the above analysis, this article proposed a real-time fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control strategy for Hall sensors in PMBLDC motor drives. The overall contributions of this paper are summarized as follows:
(1) This article analyzed the cause of the Hall sensor failure in detail. Meanwhile, according to the fault occurring instants, this article classified the possible faults into three types.
(2) This article proposed a superior real-time Hall fault diagnosis strategy, which is learning from the ideal of the EFSM and STA observer.
(3) Directing at the single and double Hall sensor fault, an effective Hall fault-tolerant control strategy is proposed.
(4) The 35-W PMBLDC motor experimental platform verified the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed methodology.
This reminder of this article is structured as follows. Section 2 classifies the Hall fault types according to the cause of failure. In Section 3, a superior real-time Hall sensor fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control strategy are present. Meanwhile, the effectiveness of the proposed scheme is demonstrated by experiments in Section 4. Finally, Section 5; concludes this article and addresses the future work directions.
2. Ideal Hall Signal and Hall Sensor Fault Types
The structure of the PMBLDC motor drives is shown in Figure 1a, which comprises a PMBLDC motor with three Hall sensors, a voltage-source inventor, and a motor control system [32,33]. The three Hall sensors A, B, and C are fixed at the stator. When the rotor turns to different positions, the Hall sensors will output different Hall signal , , and . The rotor positions are divided into six sectors by the different Hall signal with an interval angel of rad, as shown in Figure 1b.
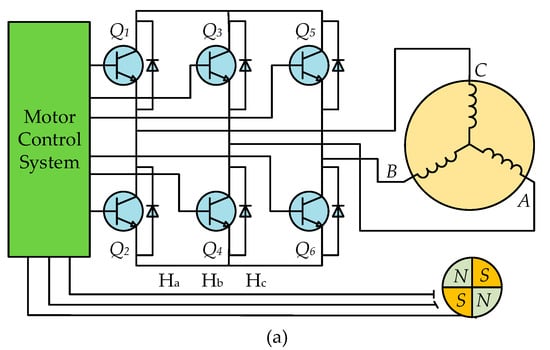
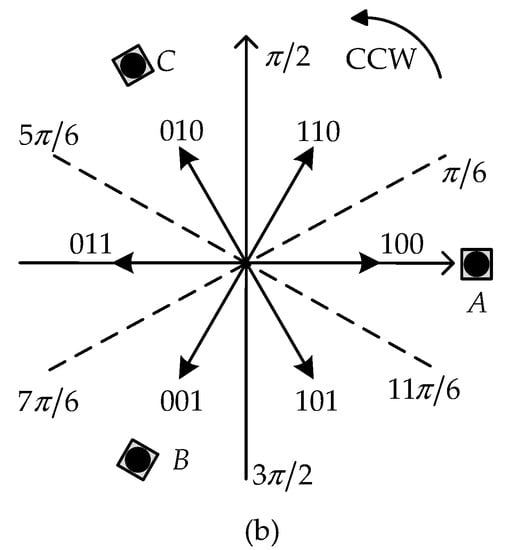
Figure 1.
The Permanent magnet brushless direct current (PMBLDC) motor drive and Hall sensors: (a) the structure of PMBLDC motor drives; (b) the simplified view of the Hall sensors in the PMBLDC drives.
When the rotor turns from a sector to the next sector, there will be an edge signal in the corresponding Hall signal. Without loss of generality, the edge signal of (i = a, b, c) is signed with :
According to the analysis in [20], Hall sensors may fail due to many reasons, which will lead to the loss of the rotor position information contained in the Hall signal. Like Zhang et al. [22], we just consider the situation of one or two Hall sensors failure in this study. Because when all the three Hall sensors are invalid, only the sensorless control method can be used to maintain the operation of the motor. In the control system, the Hall signal is treated as a digital signal of “0” or “1”. For all the Hall sensors failure types, the signal from the faulty Hall sensor is assumed to be a constant value of either “0” or “1”.
For simplicity, we define the fault states of Hall sensors for the single and double faults (as shown in Table 1), where Fi = 1 indicates a fault in Hall signal (i = a, b, c). Furthermore, to realize the fault detection of Hall sensors in the shortest possible time, we choose to analyze the Hall sensor faults based on the different fault occurring sectors. When the motor is rotating CCW (counter-clockwise), and there are no faults in the Hall sensors, the three regular commutation Hall signal , , and in six sectors are depicted in Figure 2 (lower panel). Without loss of generality in fault analysis, a single fault in Hall Sensor A at six different sectors are adopted to demonstrate the fault occurring instants, and the fault signal of Hall Sensor A is marked with , as shown in Figure 2 (upper panel).

Table 1.
Hall sensor fault.
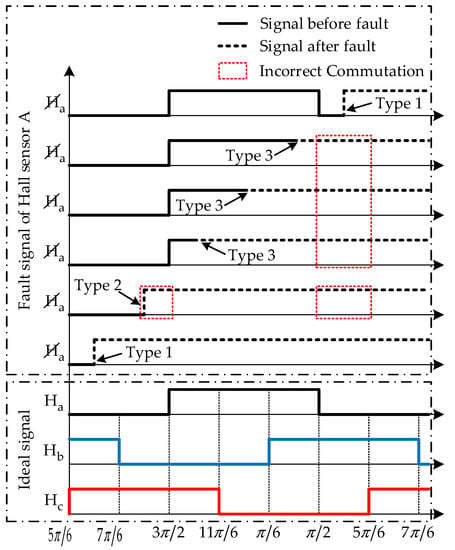
Figure 2.
Examples of faults in Hall Sensor A at six different sectors (Signal changes to “1”).
In Figure 2 (lower panel), during the normal operations, it can be found that the Hall signal , , and changes according to the sequence 011→001→101→100→110→010→011 for CCW and an opposite sequence for CW rotation. In fault situations, the signal from Hall Sensor A does not change anymore, which results in different Hall signal sequences. These Hall sensor faults in Figure 2 can be classified into three fault types, defined as Types 1–3.
Fault Type 1: Abnormal Hall signal change appears when the Hall sensor fault occurs. For example, when the fault in Hall Sensor A occurs at the sector , there is an abnormal Hall signal change of 011→111, while the normal one is 011→001; when the fault occurs at the sector , the abnormal Hall signal change is 010→110, while the normal one is 010→011.
Fault Type 2: Hall signal change appears in advance when the Hall sensor fault occurs. For example, when the fault in Hall Sensor A occurs at the sector , there is a normal Hall signal change of 001→101, but the Hall signal change is earlier than the normal one.
Fault Type 3: No Hall signal change appears when the Hall sensor fault occurs. For example, when the fault in Hall Sensor A occurs at the sector , and , there is no Hall signal change appears.
As presented in [20], the fault sensor is identified by detecting the corresponding fault Hall state and Hall transition sequences. Using the fault diagnosis methods in [20], the Type 1 fault can be detected in real-time. However, for the Type 2 and Type 3 fault, there is a common limitation in these fault diagnosis methods: it needs some time for the fault diagnosis system to detect the corresponding abnormal Hall signal sequence from the occurrence of the Hall sensor faults to the completion of the fault detection. During this period, the motor commutation still relies on the fault Hall signal, which will lead to an incorrect commutation in some sectors, as shown in Figure 2. Furthermore, these incorrect commutations may cause the motor to be unable to maintain the normal operation and eventually lead to massive damage to the motor drive system. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a real-time fault diagnosis (RFD) method for the Hall sensor failure in the PMBLDC motor.
3. Realization of Control Strategy
3.1. Finite State Machine and Definition of Signals
The finite state machine (FSM) is a mathematical model, which is usually used to describe the running process of a control system [34,35]. There are four basic components in a traditional basic FSM: state, transition, action, and event [36,37]. For a certain basic FSM, it can be defined as an ordered set of five elements, as shown in (2):
where S is the finite state set of the system and , C is the input set of the system and , is the state transition rules of the system, is the initial state of the system and , O is the output set of the system and .
In engineering applications, a state transition diagram is usually used in FSM design, representing the transition condition and process of the system more vividly. The basic FSM is shown in Figure 3.
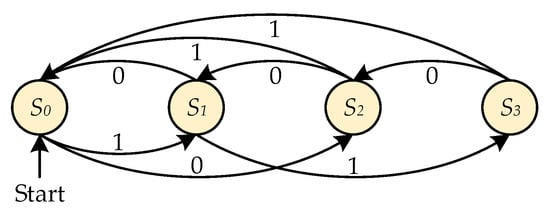
Figure 3.
State transition diagram of a basic finite state machine (FSM).
According to the above analysis, it can be found that the second state of a basic FSM is determined by the current state, the system event, and the transition function. Meanwhile, it can only transfer between the finite states. Similarly, during the working process of the PMBLDC motor drive, different MOSFETs need to be conducted according to the rotation direction of the motor and the different rotor positions. Therefore, the concept of the FSM can be combined with the PMBLDC motor drives, with the Hall signal as the system state and the conducted MOSFETs as the system event. The six normal Hall signals and two fault Hall signals are marked with , as shown in Table 2. The different conducted MOSFETs are marked with , as shown in Table 3.

Table 2.
System states of the FSM.

Table 3.
System events of the FSM.
Then the finite state set of the proposed PMBLDC motor drive system is . The input set of the system is . The initial state is , as the rotor could be in any sector in the initial state. The output set is .
When there are no faults in the three Hall sensor, the 12 transition functions of the system can be derived from the operation of the motor drive and expressed as:
The corresponding normal FSM of the PMBLDC motor drives is shown in Figure 4. Using the proposed FSM in Figure 4, the Type 1 Hall sensor fault can be detected whenever it happens, as an abnormal state transition function appeared when the Hall sensor fails. Take the case of Hall sensor faults in Figure 2, when the fault in Hall Sensor A occurs at sector and , there are abnormal state transition functions of and , while the normal state transition functions are and .
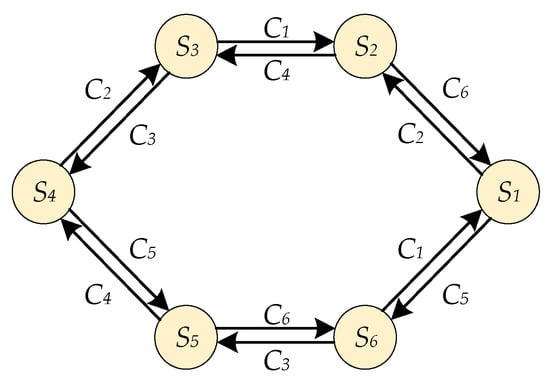
Figure 4.
Normal FSM of the PMBLDC motor drive.
However, for the Type 2 and 3 Hall sensor faults, the proposed FSM in Figure 4 cannot finish the fault detection in real-time, as there are no abnormal state transition functions appeared when the Hall sensor fails.
For the three fault types, the Type 1 fault can be represented by a logical failure, and the Type 2 and 3 faults can be described by a timing failure. It can be found that there are only logic constraints in the basic FSM in Figure 4, that is why it cannot detect the Type 2 and 3 Hall sensor faults in time, and the similar problem comes to the fault diagnosis methods in the other researches.
Therefore, both the logic constraints and time constraints are essential to realize the RFD of the Hall sensor faults, and the following definitions about time zone are introduced [38,39].
Definition 1.

Time zone. The range of the global clock L in the proposed FSM model is described as . If the global clock L is divided into k sub zones , then each of the time point in the sub zones can be represented by , in which . So that the set of can be used as the time zone division for the time constraint , as shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5.
Time zone division.
From the above definition of the time zone division, the time constraint of can be divided into three sub time zones of , and .
Definition 2.
Valid time zone. In the proposed FSM in Figure 4, the state transition events set is C, then in events set . In the time zone division in Figure 5 , which means that is a sub time zone of the global clock L. If the system event occurs in and the state transition could be triggered by , the time zone is called a valid time zone for the system event .
Definition 3.
Invalid time zone. In contrast with the valid time zone, if the system event occurs in and the state transition could not be triggered by , the time zone is called an invalid time zone for the system event .
In some real-time systems, the state transition is constrained by the system state variables. Meanwhile, the time constraint of these state variables can also be used as the boundary condition of the system state transition. Based on the definitions of time zone, the basic FSM can be extended with a time constraint, which can be used as the judgment of whether the system state transition is normal. A state transition with both time and variable constraints is shown in Figure 6.
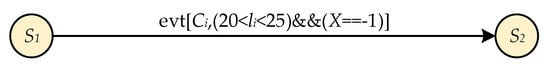
Figure 6.
A state transition with variable constraint and time constraint.
In Figure 6, and are two system states, is a system input. There are two boundary conditions in the state transition: variable constraint and time constraint . When the system inputs is , the state transition from to holds true only when the system variable occurs in the valid time zone . When the system variable occurs in the invalid time zone or , or system variables other than appear in the time zone , the state transition from to is false.
When it comes to the PMBLDC motor drive in Figure 1, the system operation is similar to the state transition with variable constraint and time constraint:
Assuming that the system state (Hall signal) is , and the system input (conducted MOSFETs) is , then the next system state can be obtained from the transition function as . If all the three Hall sensors are normal, a corresponding edge signal will be detected when the state transition from to is completed. Therefore, the appearance of the edge signal can be treated as the variable constraint of the transition from to and signed with . The appearance time of the edge signal can be used as the time constraint of the transition from to and signed with .
Then the proposed FSM of the PMBLDC motor drive in Figure 4 can be extended to an extended finite state machine (EFSM) with variable constraints and time constraints. The relation between the variable constraint and the edge signal of the Hall sensors is shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Variable Constraints of the EFSM.
Subsequently, the 12 new transition functions of the EFSM are expressed as:
Based on the above definitions and the basic FSM in Figure 4, the normal EFSM of the PMBLDC motor drive can be established, as shown in Figure 7.
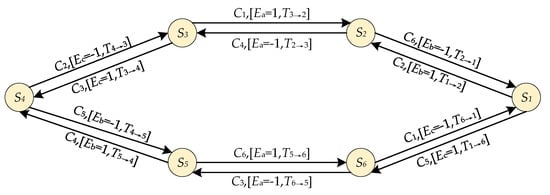
Figure 7.
Normal extended finite state machine (EFSM) of the PMBLDC motor drive.
It can be found that there are both logic constraints and time constraints in the established EFSM in Figure 7. Then the fault detection of the Hall sensors can be realized by detecting the logical states of the variable constraints and solving the time constraints of the state transition. When it comes to the logical states of the variable constraint, i.e., the logical state of the edge signal, it’s easy to obtain the corresponding variable constraint from the current system state and input event. However, the time constraint of the state transition is related to the real-time speed of the motor, which means it cannot be obtained directly.
Thus, we need to establish a speed observer, which will be used to estimate the motor speed in real-time and obtain the valid time zone of the state transition.
3.2. Proposed RFD Method and Fault Analysis
According to the mathematical model of the PMBLDC motor drive, the dynamic equation of speed and current in normal operation can be expressed as:
where, is the motor speed, is the inertia moment, is the viscous damping coefficient, is the electromagnetic torque, is the load torque, is the armature current, is the stator inductance, is the stator resistance, is the back electromotive force, is the armature voltage, is the torque constant, is the back electromotive force constant.
During the fault detection, the motor speed is necessary to solve the time constraints of the state transition. Next, a motor speed observer based on the super twisting algorithm (STA) is designed with the angular speed of the motor as the observation [40].
The differential equation of the estimated armature current can be expressed as:
where is the armature current estimation error, is a robust term based on the super twisting algorithm.
The robust term is described as:
From Equations (5) and (7), the differential equation of the armature current estimation error can be expressed as:
Here, the two disturbance terms in (9) are represented by and , in which and . Then the differential term of can be expressed as:
In and , terms , , , , and are all constants, terms , and are all bounded variables.
Therefore, there exist two constants and that make Equation (11) holds true.
Taking and into Equation (9), we can get (12):
Based on the above analysis, if the coefficients , and satisfy the following Equation (13), the armature current estimation error will converge to zero in finite time [41].
Consequently, the convergence and stability of the proposed sliding surface in the STA observer can be ensured similar to [41]. After the sliding mode is established, the estimated speed can be expressed as Equation (14):
Then the estimated speed can be expressed as Equation (14):
As there is observation error between the estimated speed and actual speed, an error threshold is set. When the motor drive system is working, the threshold value is always greater than the residual value between the estimated speed and actual speed , as shown in (15):
To facilitate the subsequent description, a virtual reference variable is introduced into the control system, as described in (16):
where is the rotation angle (electrical angle) of the motor in each commutation cycle, t is the current time of the motor drive system, is the initial time of the motor drive system in the commutation cycle.
Assumed that the initial state of the motor drive system at, and the system input is . Then the next state after can be calculated by using the transition functions in Equation (4), which is signed with . The corresponding variable constraint of the transition from to is signed with , and the valid time zone of is signed with . According to the definitions of the EFSM, only when the edge signal corresponding to occurs in the time range , the state transition from to is normal.
In order to analyze the time zone division in the process of state transition intuitively, the relationship among the three signals of the motor estimated speed , the error threshold and virtual reference variable is expressed in Figure 8.
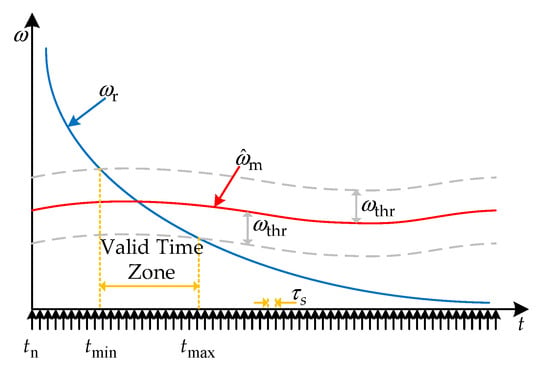
Figure 8.
The valid time zone for the system state transition.
In Figure 8, according to the relationship among , and , the time zone can be divided into three parts as follows:
(1) Invalid time zone . In this interval, keeps decreasing and gradually approaches , but is always greater than . Meanwhile, the error is always greater than the set error threshold .
(2) Valid time zone . The error between and is always less than the set error threshold in this interval.
(3) Invalid time zone . After time exceeds , the decreasing is always less than . Moreover, the error between and is always greater than the set error threshold .
According to the signal curve in Figure 8 and the above analysis, the time zone division can be summarized as shown in Equation (17):
The proposed STA observer is used to divide the time zone of the variable constraint condition during the state transition process and solve the problem of the time variable constraint condition in the extended finite state machine. The above workflow based on the FSM-STA Hall sensor fault diagnosis algorithm is summarized, and its implementation logic is shown in Figure 9.
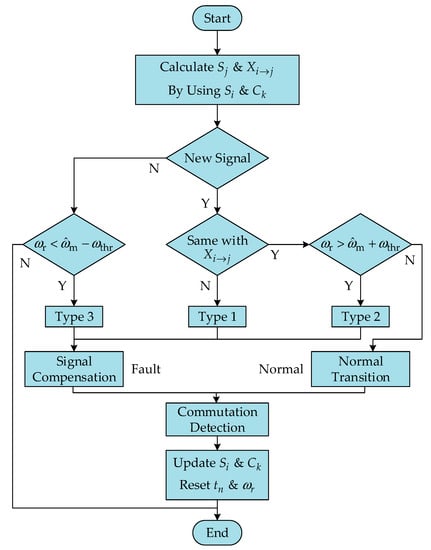
Figure 9.
Fault diagnosis logic based on FSM-STA.
When the fault diagnosis system is working, to ensure that the faulty sensor signal is detected and identified in the shortest time, the control system will sample and compare the state transition of the motor drive system in each control cycle. If a state transition process is regarded as a fault signal, the control system records the fault information and carries out the corresponding signal compensation control. Oppositely, if no fault signal is detected, the system is detected to be running normally and proceed to the logic decision of the following control cycle.
Taking the failure of a single Hall sensor as an example, the fault diagnosis system will have different detection results for three different types of Hall sensor failures:
(1) Fault Type 1: When a new jump edge signal is detected in the current commutation period, which is not the signal corresponding to the current variable constraint condition , it indicates that the Hall sensor with jump edge signal faults with abnormal state transition behavior.
(2) Fault Type 2: When a new jump edge signal is detected in the current commutation period occurring at this time , which corresponds to the current variable constraint condition , but at this time, it indicates that the variable constraint condition does not occur in the effective time region. Then, it can be known that the Hall sensor with jump edge signal faults with advance state transition behavior.
(3) Fault Type 3: It is supposed that a new edge signal is not detected until the current commutation cycle . In that case, it indicates that the state transition behavior of the system is not completed in the effective time zone. Therefore, it can be observed that the Hall sensor that should have the edge signal has a Fault Type 3.
According to the above analysis and the fault diagnosis logic in Figure 9, the fault diagnosis algorithm is designed after integrating the established finite state machine with the motor speed observer based on the STA. The proposed fault diagnosis strategy can effectively distinguish the Hall signal when the motor speed changes direction from the Hall signal when the sensor fails and complete the Hall sensor fault diagnosis and identification task.
3.3. Signal Reconstruction and Fault-Tolerant Control
After the fault diagnosis is completed, the control system also needs to perform fault-tolerant control on the faulty sensor. Hence, the operational stability of the motor drive system can be maintained under fault conditions.
In the fault-tolerant control of the Hall sensor, the rotor rotating angle of the motor should be estimated in real-time. Then the compensation signal of the fault sensor should be generated by the estimation signal, which can be used as the reference signal for motor commutation control of the control system. Through the STA motor speed observer established above, the output motor can be used to estimate the speed . The rotation angle of the motor rotor can be estimated in the form of integral. The estimated value of the motor rotation angle can be expressed as:
The initial time of the motor drive system in the current commutation cycle is denoted as , the initial state is denoted as , and the subsequent state of the system is driven by the system input events .
Suppose that the ideal time for the state to appear is . Then, when the motor rotor runs in the commutation interval, the ideal average speed of the motor can be expressed as:
Since the state variable is related to the running state of the motor drive system and cannot be accurately calculated, the actual value of the ideal time when the state appears cannot be obtained. Therefore, the motor estimated speed signal from the STA observer is used instead of the state quantity as the average speed of the motor during the commutation interval. Based on this, the estimated value of the ideal time can be derived according to Equations (15) and (16), as shown in Equation (20).
Simultaneously, to improve the operation stability of the drive system, the accuracy of the estimated state transition time must be enhanced as much as possible. Therefore, the actual speed of the motor in the previous commutation interval is taken as the initial value of the integral in Equation (20) during each calculation, as shown in Equation (21):
Through Equations (20) and (21), the estimation value of state existence time can be calculated. Then, combining with the normal state transition, compensating Hall signals of the corresponding Hall sensors can be generated according to different fault conditions and used as reference signals in the commutation control of the motor. Similarly, for the fault-tolerant control in the subsequent motor operation cycle, the fault Hall sensor signals that need to compensate can be updated and replaced in real-time by updating the commutation time and the motor estimated speed .
4. Experimental Verification
4.1. Experimental Platform
To validate the efficacy of the proposed fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control strategy, experimental tests are conducted based on a 35-W PMBLDC motor prototype. The overall structure of the proposed real-time fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control system for Hall sensors in PMBLDCM drives is shown in Figure 10.
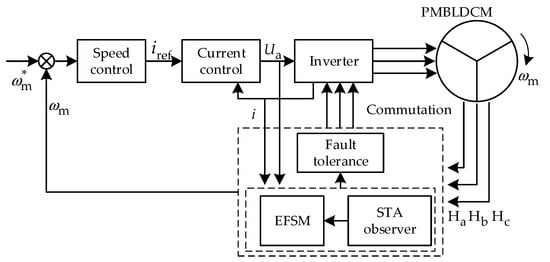
Figure 10.
The overall structure of the control system.
The experimental setup is built, as displayed in Figure 11. The details of the controller are as follows: the digital signal processor (DSP) TMS320F28335 (Texas Instruments, Dallas, TX, USA) is selected as the core control unit; the IR2136s 3-phase bridge driver (Infineon, New bieberg, Germany) is selected as the gate driver; the three-phase inverter consists of the N-channel MOSFET transistor IRFR4615 (Infineon, New bieberg, Germany) with a switching frequency of 5 kHz. In the experiments, the speed and torque signal are measured by the sensor (JN-DN). The currents are detected by Allegro current sensors (ACS712ELCTR-05B-T (Allegro MicroSystems, Manchester, NH, USA)). The time interval of Hall state monitoring is 0.1 ms. The main parameters of the motor are indicated in Table 5.
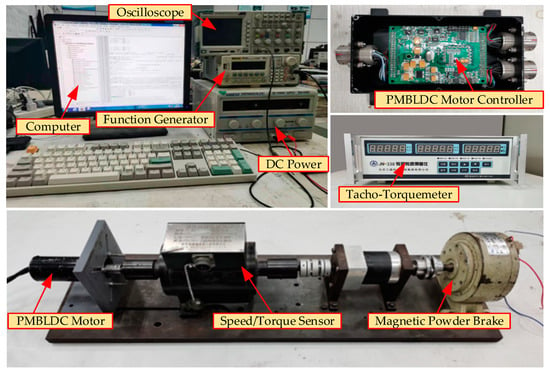
Figure 11.
Experimental Platform.

Table 5.
Main parameters of the PMBLDC motor.
The parameters of the STA observer are selected as follows: , , .
4.2. STA Observer Experimental Results
Experiments verify the estimation performance of the proposed STA observer. Meanwhile, the motor speed range is set from 600 rpm to 1200 rpm.
As shown in Figure 12, the estimated current can effectively reflect the actual current, and the maximum error between the actual speed and estimated speed is about 20 rpm. Accordingly, the fault diagnosis threshold during the fault diagnosis process is set to 40 rpm.
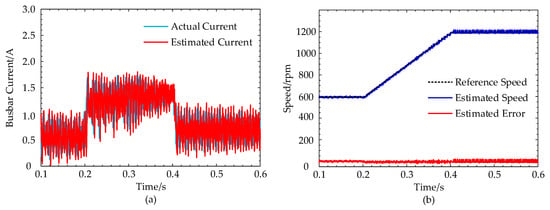
Figure 12.
STA observer experimental results: (a) estimated and actual current curves; (b) reference and estimated speed curves.
4.3. Fault Diagnosis Experimental Results
The proposed Hall fault diagnosis strategy is signed with M1. To evaluate the effectiveness and superiority of the strategy, a comparative experiment with the fault diagnosis method M2 in [29] is carried out.
Experimental conditions: (1) The controller will run the PMBLDC motor to 200 rpm under the premise of the normal hall signal. When the motor speed reaches 200 rpm and the system enters the steady state, the experimental data will start to be recorded. (2) The motor speed will be increased to 1200 rpm from 0.2 s to 0.4 s. The three different Hall fault types will be simulated in the motor speed increase, and the corresponding fault diagnosis experiments will be analyzed. (3) It is an effective method to realize the simulation of the Hall fault that switching the input signal of the I/O port from the Hall signal to the high level signal. (4) The Hall signal changes according to the sequence 011→001→101→100→110→010→011. (5) The reconstructed signal is output from the I/O port.
(1) Fault Type 1 diagnosis experiments: The I/O ports of the DSP are utilized to monitor the Hall signals. When the Hall state change to 010, the I/O port obtaining the Hall signal will maintain the high level to simulate fault type 1. At the same time, M1 and M2 are adopted to realize the Hall fault diagnosis experiment.
As shown in Figure 13a, the Hall signal fault occurred at t = 335 ms, and the Hall state changed from 010 to 110. Compared to M1 with M2 in Figure 13b, the proposed strategy M1 can immediately diagnose the fault. Meanwhile, when the Hall fault is detected, the output level signal of the fault diagnosis I/O port is converted from low to high. However, M2 did not reflect fault information until t = 336 ms. The strategy M2 took 1 ms longer than M1.
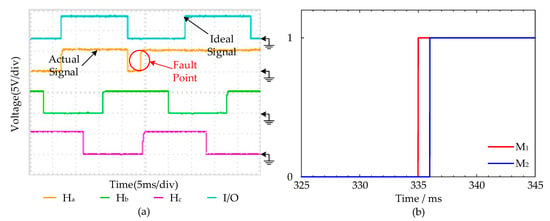
Figure 13.
Hall Fault Type 1 diagnosis experimental results: (a) The Hall signal curves at Fault Type 1 and the ideal Hall signal curves. (b) The fault diagnosis experimental curves of M1 and M2.
(2) Hall Fault Type 2 diagnosis experiments: Similarly, when the I/O ports acquire the Hall state of 001, the Hall Fault Type 2 will be assumed. It can be seen from Figure 14 that the fault occurred at t = 362 ms, and the proposed fault diagnosis strategy M1 can detect the diagnosis instantly after the appearance of the fault. On the contrary, the strategy M2 detected the Hall Fault Type 2 until the Hall signal jump from low level to the high level, and this strategy caused a wasted of 6.7 ms. Hence, the proposed fault diagnosis strategy M1 can diagnose the Hall fault faster than the method M2.
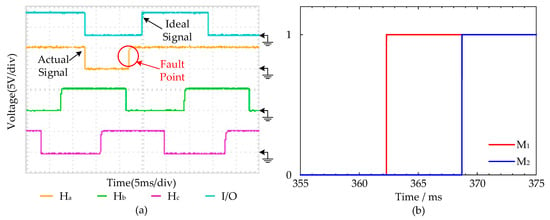
Figure 14.
Hall Fault Type 2 diagnosis experimental results: (a) The Hall signal curves at Fault Type 2 and the ideal Hall signal curves. (b) The fault diagnosis experimental curves of M1 and M2.
(3) Hall Fault Type 3 diagnosis experiments: When the I/O ports detect the Hall state of 001 at t = 372 ms, the Hall signal will maintain the high level to simulate the Hall Fault Type 3. Figure 15 shows the comparative experimental results under the Hall Fault Type 3. On account of no Hall signal change appears when the Hall sensor fault occurs, the proposed fault diagnosis strategy M1 cannot detect the fault immediately. However, strategy M1 diagnoses the fault signal in 375.2 ms, which is 1.3 ms faster than strategy M2.
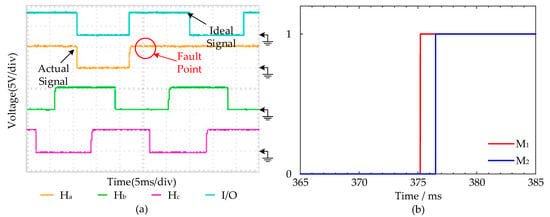
Figure 15.
Hall Fault Type 3 diagnosis experimental results: (a) The Hall signal curves at Fault Type 3 and the ideal Hall signal curves. (b) The fault diagnosis experimental curves of M1 and M2.
Based on the above fault diagnosis experimental results, the comparison of fault diagnosis results between M1 and M2 are summarized in Table 6. It can be found that the proposed fault diagnosis strategy is equipped with the superior fault diagnosis performance compared with Method 2.

Table 6.
Comparison of fault diagnosis results between M1 and M2.
4.4. Fault-Tolerant Control Experimental Results
After the Hall fault was diagnosed, it is necessary to reconstruct the fault signal and generate the compensated signal to realize fault-tolerant control. The experiments are carried out to verify the validity of the proposed Hall fault-tolerant control strategy.
4.4.1. Fault-Tolerant Control at Load Constant
Experimental conditions: (1) The same with the fault diagnosis experiments, the fault-tolerant control experiments also drive the PMBLDC motor to 200 rpm. Then the controller will drive the motor from 200 rpm to 1200 rpm in 0.2 s. (2) The single and double Hall fault-tolerant control experiments will be verified in the process of motor speed increase. (3) Relevant experimental dates are stored by the RS422 communication protocol.
(1) Single Hall fault-tolerant control experimental results: As seen from Figure 16a, the experiment assumes the fault of the Hall signal Ha occurs at t = 0.27 s. Meanwhile, when the fault is diagnosed, the Hall signal reconstruction strategy can ensure the regular operation of the motor. As seen in Figure 16a, the ideal signal can replace the original normal Hall signal. Figure 16b,c showed that the motor speed fluctuated when the fault occurred, and the fluctuation range is 25 rpm. Fortunately, the motor is always in a stable state under the proposed strategy. From Figure 16d, the instantaneous current at the fault point is 2.25 A. The control strategy quickly stabilizes the current after a failure, and it is challenging to find the difference of operation state before and after Hall failure after stability. The experimental results show that the proposed fault-tolerant strategy can rapidly recover the drive system from the fault in a single Hall fault case.
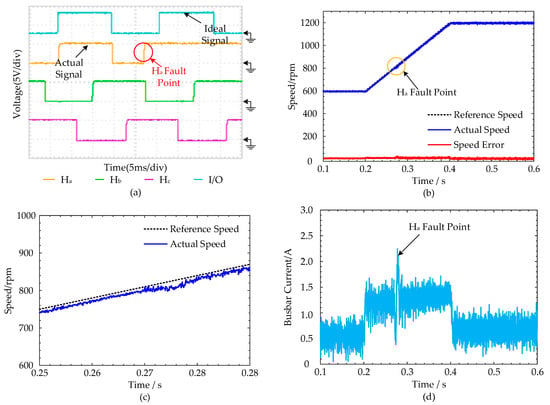
Figure 16.
Single Hall fault-tolerant control experimental results: (a) The Hall signal curves of the motor; (b) the speed curves of the motor; (c) the detail speed curves at the fault point; (d) the busbar current of the motor.
(2) Double Hall fault-tolerant control experimental results: Figure 17a shows that the Hall signal Ha and Hb failed at t = 0.3 s and t = 0.32 s, respectively. It is apparent that the double Hall signal fault occurred at t = 0.32 s. As shown in Figure 16b, the motor speed fluctuated within the fluctuation range of 30 rpm. The detailed speed curves at the fault point can be seen in Figure 17c. The busbar current curve is shown in Figure 17d. To all appearances, the maximum instantaneous current is 2.11 A at the double Hall fault point. After adopting the fault-tolerant control strategy proposed in this paper, the motor speed and current of the system tend to be stable. Hence, we can know that the fault-tolerant control can effectively troubleshoot the double Hall fault problem.
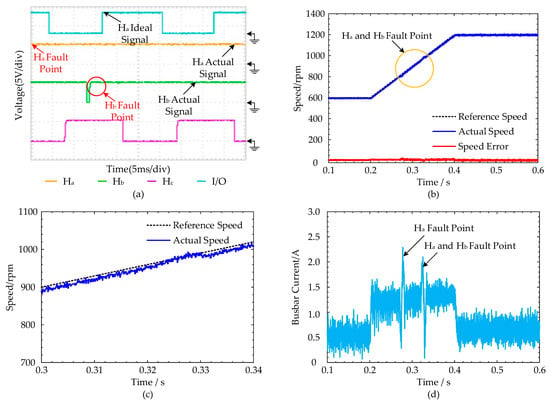
Figure 17.
Double Hall fault-tolerant control experimental results: (a) the Hall signal curves of the motor; (b) the speed curves of the motor; (c) the detail speed curves at the fault point; (d) the busbar current of the motor.
4.4.2. Fault-Tolerant Control at Load Variation
Experimental conditions: At the load variation experiments, the control system drives the PMBLDC motor to 1200 rpm. When the running time is 0.3 s, the motor load will increase from 0.05 N·m to 0.1 N·m. Meanwhile, the control system will simulate the failure of at t = 0.4 s.
Hall fault-tolerant control experimental results at load variation: As shown in Figure 18b,d, the load variation occurred at t = 0.3 s. And the current has also significantly fluctuated, which is a normal phenomenon. Subsequently, the faulted at t = 0.4 s, and the current fluctuated abnormally. After the fault occurred, Figure 18c shows that the fault-tolerant control method can ensure stable operation of the PMBLDC motor with a slight increase of speed error. Hence, we can know that the fault-tolerant control can be adopted in the load variation condition.
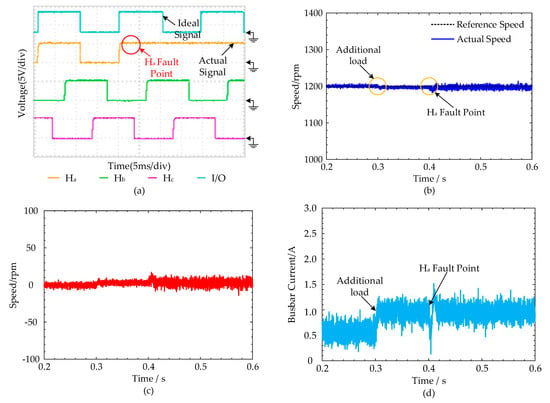
Figure 18.
Fault-tolerant control experimental results at load variation: (a) the Hall signal curves of the motor; (b) the speed curves of the motor; (c) the speed error curve at the fault point; (d) the busbar current of the motor.
The experiment results demonstrated that the proposed fault-tolerant control strategy can reconstruct the Hall signal in case of the single or double Hall failure and make the drive system restore the stable operation rapidly. Meanwhile, the large current fluctuations are inexistent, and the reliability of the drive system is enhanced.
5. Conclusions
This paper focuses on the real-time fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control strategy for Hall sensors in PMBLDC motor drives. Firstly, the Hall sensor faults are classified into three types based on the different sectors of the rotor when the fault occurs in Section 2. In Section 3, a real-time fault diagnosis strategy based on the EFSM and STA speed observer is proposed for the Hall sensor failure of the PMBLDC motor. Meanwhile, the Hall signal compensation controller is also present in Section 3, designed to realize the fault-tolerant control. The proposed method is simple to be implemented in engineering.
Furthermore, a 35-W PMBLDC motor experimental platform is set up in Section 4. According to the experimental results, the proposed fault diagnosis takes less time to diagnose the Hall fault than the method in [29]. Further, the proposed fault-tolerant control strategy can ensure the stable operation of the motor under Hall sensor failure situations with failures of single or double Hall sensors.
Finally, with the application background of the electric brake system, the proposed method will be applied to the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) brake system in future works. The successful application of the strategy is of great significance to improve the operational reliability of UAVs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Z. and H.L.; methodology, X.Z. and Y.Z.; software, Y.Z.; validation, X.Z. and Y.Z.; formal analysis, Y.Z. and S.R.; investigation, S.R.; resources, H.L.; data curation, X.Z. and Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z., S.R. and H.E.; writing—review and editing, Y.Z.; visualization, X.Z.; supervision, H.L.; project administration, H.L.; funding acquisition, H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant Number 51777170 and the National Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province, Grant Number 2020JM-151.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| Notation | Physical significance |
| Hall signals of the Hall Sensors A, B and C | |
| Edge signals of the Hall signals | |
| Fault states of the Hall Sensors A, B and C | |
| System states of the FSM | |
| System events of the FSM | |
| Variable constraint of the FSM | |
| Time constraint of the FSM | |
| Motor speed | |
| Inertia moment | |
| Viscous damping coefficient | |
| Electromagnetic torque | |
| Load torque | |
| Armature current | |
| Stator inductance | |
| Stator resistance | |
| Back electromotive force | |
| Armature voltage | |
| Torque constant | |
| Back electromotive force constant | |
| Estimated current | |
| Estimated current error | |
| Coefficient of the STA observer | |
| Disturbance terms | |
| Estimated speed | |
| Residual value | |
| Error threshold | |
| Virtual reference speed |
References
- Park, Y.; Fernandez, D.; Lee, S.B.; Hyun, D.; Jeong, M.; Kommuri, S.K.; Cho, C.; Reigosa, D.; Briz, F. On-line detection of rotor eccentricity for PMSMs based on hall-effect field sensor measurements. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1–5 October 2017; pp. 4678–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Lin, H.; Li, B.Q. Sliding-Mode Clamping Force Control of Electromechanical Brake System Based on Enhanced Reaching Law. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 19506–19515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommuri, S.K.; Rath, J.J.; Veluvolu, K.C.; Defoort, M.; Soh, Y.C. Decoupled current control and sensor fault detection with second-order sliding mode for induction motor. IET Contr. Theory Appl. 2015, 9, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffo, A.; Wrobel, R.; Mellor, P.; Holliday, D.; Sangha, P.; Dinu, A.; Holme, M. The effect of magnetic saturation on sensorless control of a brushless permanent magnet motor under AC and DC excitation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 17–22 September 2011; pp. 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.X.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Practical Issues in Sensorless Control of PM Brushless Machines Using Third-Harmonic Back-EMF. In Proceedings of the CES/IEEE 5th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference, Shanghai, China, 14–16 August 2006; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Deng, Z.Q.; Wang, X.L.; Ling, X.; Cao, X. Position Sensorless Control Based on Coordinate Transformation for Brushless DC Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 2365–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tu, Y.F.; Wang, T. Sensor-Less Control for Brushless DC Motors Based on Hybrid Sliding Mode Observer. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation (2014 ICICTA’07), Changsha, China, 25–26 October 2014; pp. 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, G.; Ertugrul, N. Wide Speed Range Sensorless Operation of Brushless Permanent-Magnet Motor Using Flux Linkage Increment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4052–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.T.; Zheng, S.Q.; Ren, H.L. Self-Correction of Commutation Point for High-Speed Sensorless BLDC Motor With Low Inductance and Nonideal Back EMF. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Zhou, X.Y.; Bai, G.C.; Wang, K.; Zhu, L.Q. Adaptive Commutation Error Compensation Strategy Based on a Flux Linkage Function for Sensorless Brushless DC Motor Drives in a Wide Speed Range. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 3752–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darba, A.; De Belie, F.; Melkebeek, J.A. A Back-EMF Threshold Self-Sensing Method to Detect the Commutation Instants in BLDC Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 6064–6075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.L.; Patton, R.J. A new strategy for integration of fault estimation within fault-tolerant control. Automatica 2016, 69, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berriri, H.; Naouar, M.W.; Slama-Belkhodja, I. Easy and Fast Sensor Fault Detection and Isolation Algorithm for Electrical Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrad, A.; Hilairet, M.; Diallo, D. Design of a Fault-Tolerant Controller Based on Observers for a PMSM Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 1416–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giulii Capponi, F.; De Donato, G.; Del Ferraro, L.; Honorati, O.; Harke, M.C.; Lorenz, R.D. AC brushless drive with low-resolution Hall-effect sensors for surface-mounted PM Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 42, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.T.; Li, W.Z.; Ren, H.L. Fault-Tolerant Inverter for High-Speed Low-Inductance BLDC Drives in Aerospace Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 2452–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, G.H.B.; Zhang, X.; Vilathgamuwa, D.M. A Sensor Fault Detection and Isolation Method in Interior Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives Based on an Extended Kalman Filter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 3485–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.C.; Li, W.Z.; Li, H.T.; Xu, X.B. Online Inverter Fault Diagnosis of Buck-Converter BLDC Motor Combinations. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 2674–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M.A.; Ahmed, M.S.; Darwish, R.R.; Bassiuny, A.M. Improved fuzzy Luenberger observer-based fault detection for BLDC motor. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Engineering & Systems (2015 ICCESS’10), Cairo, Egypt, 23–24 December 2015; pp. 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmi, T.; Baitie, H.E.; Masmoudi, A. An approach to diagnose and remediate failures of Hall Effect sensors in BLDC motors. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Sustainable Mobility Applications, Renewables and Technology (SMART), Kuwait City, Kuwait, 23–25 November 2015; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakori, A.; Ektesabi, M. A simple fault tolerant control system for Hall Effect sensors failure of BLDC motor. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (2013 ICIEA’08), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 19–21 June 2013; pp. 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sova, V.; Chalupa, J.; Grepl, R. Fault tolerant BLDC motor control for hall sensors failure. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Automation and Computing, (2015, ICAC’21), Glasgow, UK, 11–12 September 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Lee, K.; Lee, W. Observer-Based Phase-Shift Fault Detection Using Adaptive Threshold for Rotor Position Sensor of Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machine Drives in Electromechanical Brake. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 1964–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Li, J.; Ouyang, M.; Gu, J.; Feng, X.; Lu, D. Rule-based fault diagnosis of hall sensors and fault-tolerant control of PMSM. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2013, 26, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, W.X.; Yang, J.F. Fault diagnosis of low-cost hall-effect sensors used in controlling permanent magnet synchronous motor. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (2016 ICEMS’19), Chiba, Japan, 13–16 November 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, H.; Thakar, U.; Joshi, V.; Rathod, K.; Kurulkar, P. Hall sensor fault detection and fault tolerant control of PMSM drive system. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Instrumentation and Control (ICIC), Pune, India, 28–30 May 2015; pp. 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scelba, G.; De Donato, G.; Scarcella, G.; Giulii Capponi, F.; Bonaccorso, F. Fault-Tolerant Rotor Position and Velocity Estimation Using Binary Hall-Effect Sensors for Low-Cost Vector Control Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3403–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scelba, G.; De Donato, G.; Pulvirenti, M.; Giulii Capponi, F.; Scarcella, G. Hall-Effect Sensor Fault Detection, Identification, and Compensation in Brushless DC Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 1542–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.H.; Jatskevich, J.; Huang, Y.W.; Chapariha, M.; Liu, J.L. Fault Diagnosis and Signal Reconstruction of Hall Sensors in Brushless Permanent Magnet Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 31, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.H.; Huang, Y.W.; Jatskevich, J.; Liu, J.L. Improved Fault-Tolerant Control for Brushless Permanent Magnet Motor Drives With Defective Hall Sensors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 31, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Feng, M. Fast Fault Diagnosis Method for Hall Sensors in Brushless DC Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 2585–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.X.; Li, J.; Qu, R.H.; Ye, D.L.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, R. Post-fault model predictive control of asymmetrical six-phase permanent magnet machine with improved mathematical model. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference (IEMDC), Miami, FL, USA, 21–24 May 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.T.; Hur, J. Detection Technique for Stator Inter-Turn Faults in BLDC Motors Based on Third-Harmonic Components of Line Currents. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezernik, K.; Horvat, R.; Harnik, J. Finite-State Machine Motion Controller: Servo Drives. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2012, 6, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Maleh, A.H. Finite state machine-based fault tolerance technique with enhanced area and power of synthesised sequential circuits. IET Comput. Digit. Tech. 2017, 11, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.Y.; Huang, L.S.; Gao, G.; Wang, G.H.; Wang, Z.J.; Chen, X.J. Design of Real-Time Control in Poloidal Field Power Supply Based on Finite-State Machine. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2019, 47, 1878–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Vargas, I.; Senhadji-Navarro, R. Finite State Machines With Input Multiplexing: A Performance Study. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2015, 34, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.F.; Liu, B.; Ni, H.Y. Real-time embedded software testing method based on extended finite state machine. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2012, 23, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hierons, R. Controllable Testing from Nondeterministic Finite State Machines with Multiple Ports. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2011, 60, 1818–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommuri, S.K.; Rath, J.J.; Veluvolu, K.C. Sliding-Mode-Based Observer–Controller Structure for Fault-Resilient Control in DC Servomotors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.A.; Osorio, M. Strict Lyapunov Functions for the Super-Twisting Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2012, 57, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).