Inhibition of Melanogenesis via Passive Immune Targeted Alpha-MSH Binder Polypeptide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents, Chemicals and Standards
2.2. Configuring the Phage Display Variant Hagfish VLRB Library
2.2.1. Screening for VLRB (α-MSH Target Binding Polypeptide)
2.2.2. Phage ELISA
2.2.3. Expression and Purification of α-MSH Target Binding Polypeptide
2.3. Anti-Whitening Effect of α-MSH-Specific Targeted Protein
2.3.1. Cell Culture and Morphological Change
2.3.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.3.3. In Vitro Tyrosinase Inhibition Assay
2.3.4. Intracellular and Extracellular Melanin Content
2.3.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phage Library Screening for α-MSH Antigen
3.2. Expression, Purification, and Antigen Binding of α-MSH Target Binding Polypeptide
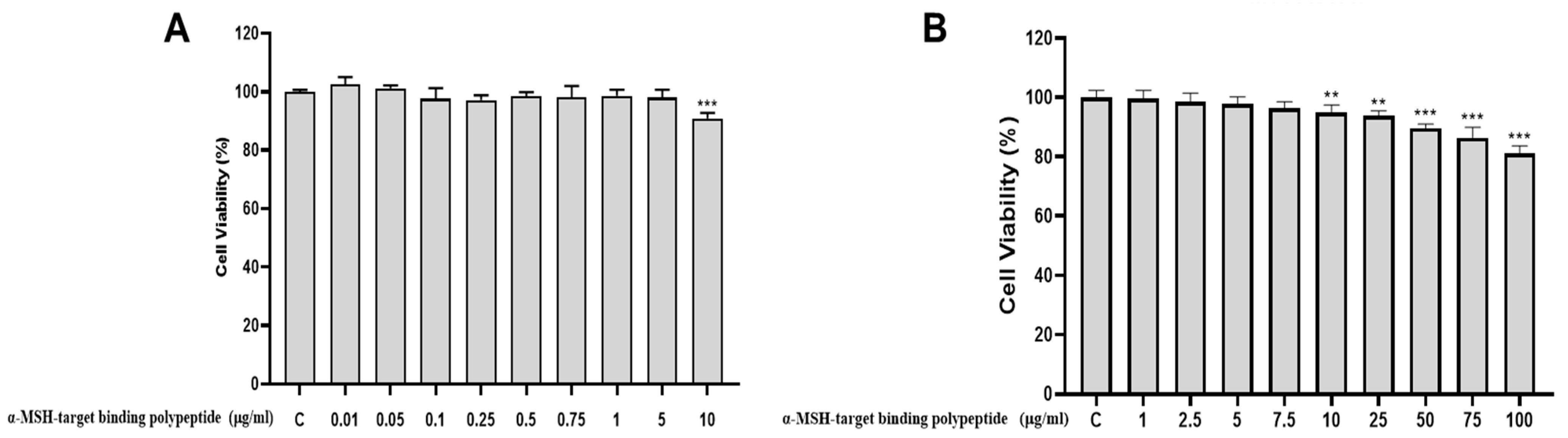
3.3. The Cytotoxicity of α-MSH Target Binding Polypeptide on the HaCaT Cell
3.4. The Cytotoxicity of Arbutin on the B16F10
3.5. The Cytotoxicity of α-MSH-Target Binding Polypeptide on the B16F10
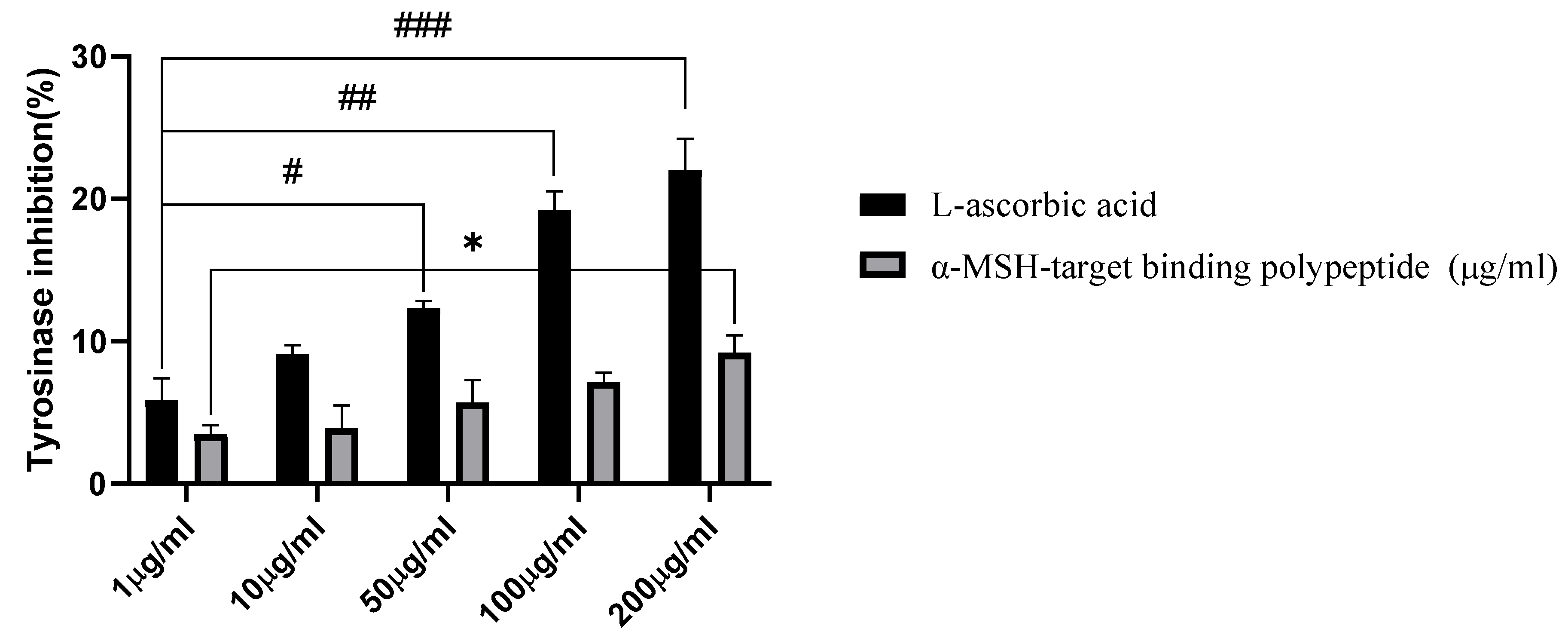
3.6. Tyrosinase Inhibition Activity
3.7. Determination of Intracellular and Extracellular Melanin Content
3.8. Cell Morphological Change
3.9. Effect of α-MSH Target Binding Polypeptide on the Expression of Melanogenic Proteins in B16F10 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dall’Olmo, L.; Papa, N.; Surdo, N.C.; Marigo, I.; Mocellin, S. Alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH): Biology, clinical relevance and implication in melanoma. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thody, A.J. Alpha-MSH and the regulation of melanocyte function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 885, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.-H.; Xu, L.; Xiong, M.; Qu, M. Role of α-MSH-MC1R-cAMP Signaling Pathway in Regulating the Melanin Synthesis in Silky Fowl. J. Cell. Signal. 2018, 3, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, M.; Ali, A.; Kaushik, N.; Choi, E. Perspective in Pigmentation Disorders. In Comprehensive Clinical Plasma Medicine: Cold Physical Plasma for Medical Application; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 363–400. [Google Scholar]
- Snyman, M.; Walsdorf, R.E.; Wix, S.N.; Gill, J.G. The metabolism of melanin synthesis—From melanocytes to melanoma. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2024, 37, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandorkar, N.; Tambe, S.; Amin, P.; Madankar, C. Alpha Arbutin as a Skin Lightening Agent: A Review. Int. J. Pharm. Res. 2021, 13, 3502–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Seo, S.H.; Lee, B.G.; Lee, Y.S. Identification of tyrosinase inhibitors from Glycyrrhiza uralensis. Planta Medica 2005, 71, 785–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanadi, R.M.; Deshmukh, R.S. The effect of Vitamin C on melanin pigmentation—A systematic review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. JOMFP 2020, 24, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakozaki, T.; Minwalla, L.; Zhuang, J.; Chhoa, M.; Matsubara, A.; Miyamoto, K.; Greatens, A.; Hillebrand, G.G.; Bissett, D.L.; Boissy, R.E. The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. Br. J. Dermatol. 2002, 147, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.-F.; Chen, Y.-S.; Lin, Y.-J.; Tai, T.-H.; Chen, A.-N.; Huang, C.-H.; Lin, C.-C. Study of Hydroquinone Mediated Cytotoxicity and Hypopigmentation Effects from UVB-Irradiated Arbutin and DeoxyArbutin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Du, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Kong, L.; Xu, Q.; Ma, H.; Sun, Y. New opportunities and challenges of natural products research: When target identification meets single-cell multiomics. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 4011–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaivi, L.; Turabi, K.; Aich, J.; Devarajan, S.; Unni, D.; Garse, S. In Silico Approaches in the Repurposing of Bioactive Natural Products for Drug Discovery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 125–147. [Google Scholar]
- Majtan, J.; Bucekova, M.; Jesenak, M. Natural Products and Skin Diseases. Molecules 2021, 26, 4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, T.; McCurley, N.; Sutoh, Y.; Schorpp, M.; Kasahara, M.; Cooper, M.D. VLR-Based Adaptive Immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Rast, J.P.; Li, J.; Kadota, M.; Donald, J.A.; Kuraku, S.; Hirano, M.; Cooper, M.D. Evolution of variable lymphocyte receptor B antibody loci in jawless vertebrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2116522118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehm, T.; Hirano, M.; Holland, S.J.; Das, S.; Schorpp, M.; Cooper, M.D. Evolution of Alternative Adaptive Immune Systems in Vertebrates. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrin, B.R.; Alder, M.N.; Roux, K.H.; Sina, C.; Ehrhardt, G.R.A.; Boydston, J.A.; Turnbough, C.L.; Cooper, M.D. Structure and specificity of lamprey monoclonal antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2040–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alder, M.N.; Rogozin, I.B.; Iyer, L.M.; Glazko, G.V.; Cooper, M.D.; Pancer, Z. Diversity and Function of Adaptive Immune Receptors in a Jawless Vertebrate. Science 2005, 310, 1970–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, E.A.; Shusta, E.V. The variable lymphocyte receptor as an antibody alternative. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 52, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirimanapong, W.; Thaijongrak, P.; Sudpraseart, C.; Bela-ong, D.B.; Rodelas-Angelia, A.J.D.; Angelia, M.R.N.; Hong, S.; Kim, J.; Thompson, K.D.; Jung, T.S. Passive immunoprophylaxis with Ccombodies against Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Pacific white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 154, 109973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, K.M.A.; Hansen, J.D.; Herrin, B.R.; Amemiya, C.T. Generation of Lamprey Monoclonal Antibodies (Lampribodies) Using the Phage Display System. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-H. A Review of Current Research on Natural Skin Whitening Products. Asian J. Beauty Cosmetol. 2018, 16, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillbro, J.M.; Olsson, M.J. The melanogenesis and mechanisms of skin-lightening agents—Existing and new approaches. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2011, 33, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macrini, D.; Suffredini, I.; Varella, A.; Younes, R.; Ohara, M. Extracts from Amazonian plants have inhibitory activity against tyrosinase: An in vitro evaluation. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 45, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoi, J.; Abe, E.; Suda, T.; Kuroki, T. Regulation of melanin synthesis of B16 mouse melanoma cells by 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and retinoic acid. Cancer Res. 1985, 45, 1474–1478. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maranduca, M.A.; Branisteanu, D.; Serban, D.N.; Branisteanu, D.C.; Stoleriu, G.; Manolache, N.; Serban, I.L. Synthesis and physiological implications of melanic pigments. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4183–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videira, I.F.; Moura, D.F.; Magina, S. Mechanisms regulating melanogenesis. An. Bras. De Dermatol. 2013, 88, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, Active and passive immunity, vaccine types, excipients and licensing. Occup. Med. 2007, 57, 552–556. [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, L. Advances in targeting cell surface signalling molecules for immune modulation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.-M.; Hwang, Y.-C.; Liu, I.J.; Lee, C.-C.; Tsai, H.-Z.; Li, H.-J.; Wu, H.-C. Development of therapeutic antibodies for the treatment of diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sockolov, M.E.; Alikhan, A.; Zargari, O. Non-psoriatic dermatologic uses of monoclonal antibody therapy. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2009, 20, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, M.S.; McGonigle, P.; Hornby, P.J. The pharmacology and therapeutic applications of monoclonal antibodies. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2019, 7, e00535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, W.J. Adverse side-effects to biological agents. Allergy 2006, 61, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, J.B. Mechanisms of adverse drug reactions to biologics. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2010, 196, 453–474. [Google Scholar]







| α-MSH Target Binding Polypeptide Plant | MW (kDa) | Concentration (mg/mL) | Volume | Kd (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSH | 32.26 | 1.53 | 0.70 | 0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, S.-H.; Kim, H.-H.; Rodelas-Angelia, A.J.D.; Angelia, M.R.N.; Bhosale, P.B.; Kim, E.-H.; Jung, T.-S.; Ahn, M.-J.; Kim, G.-S. Inhibition of Melanogenesis via Passive Immune Targeted Alpha-MSH Binder Polypeptide. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12010012
Jeong S-H, Kim H-H, Rodelas-Angelia AJD, Angelia MRN, Bhosale PB, Kim E-H, Jung T-S, Ahn M-J, Kim G-S. Inhibition of Melanogenesis via Passive Immune Targeted Alpha-MSH Binder Polypeptide. Cosmetics. 2025; 12(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Se-Hyo, Hun-Hwan Kim, Abigail Joy D. Rodelas-Angelia, Mark Rickard N. Angelia, Pritam Bhagwan Bhosale, Eun-Hye Kim, Tae-Sung Jung, Mee-Jung Ahn, and Gon-Sup Kim. 2025. "Inhibition of Melanogenesis via Passive Immune Targeted Alpha-MSH Binder Polypeptide" Cosmetics 12, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12010012
APA StyleJeong, S.-H., Kim, H.-H., Rodelas-Angelia, A. J. D., Angelia, M. R. N., Bhosale, P. B., Kim, E.-H., Jung, T.-S., Ahn, M.-J., & Kim, G.-S. (2025). Inhibition of Melanogenesis via Passive Immune Targeted Alpha-MSH Binder Polypeptide. Cosmetics, 12(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12010012







