Towards a Balanced Sustainability Vision for the Coffee Industry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
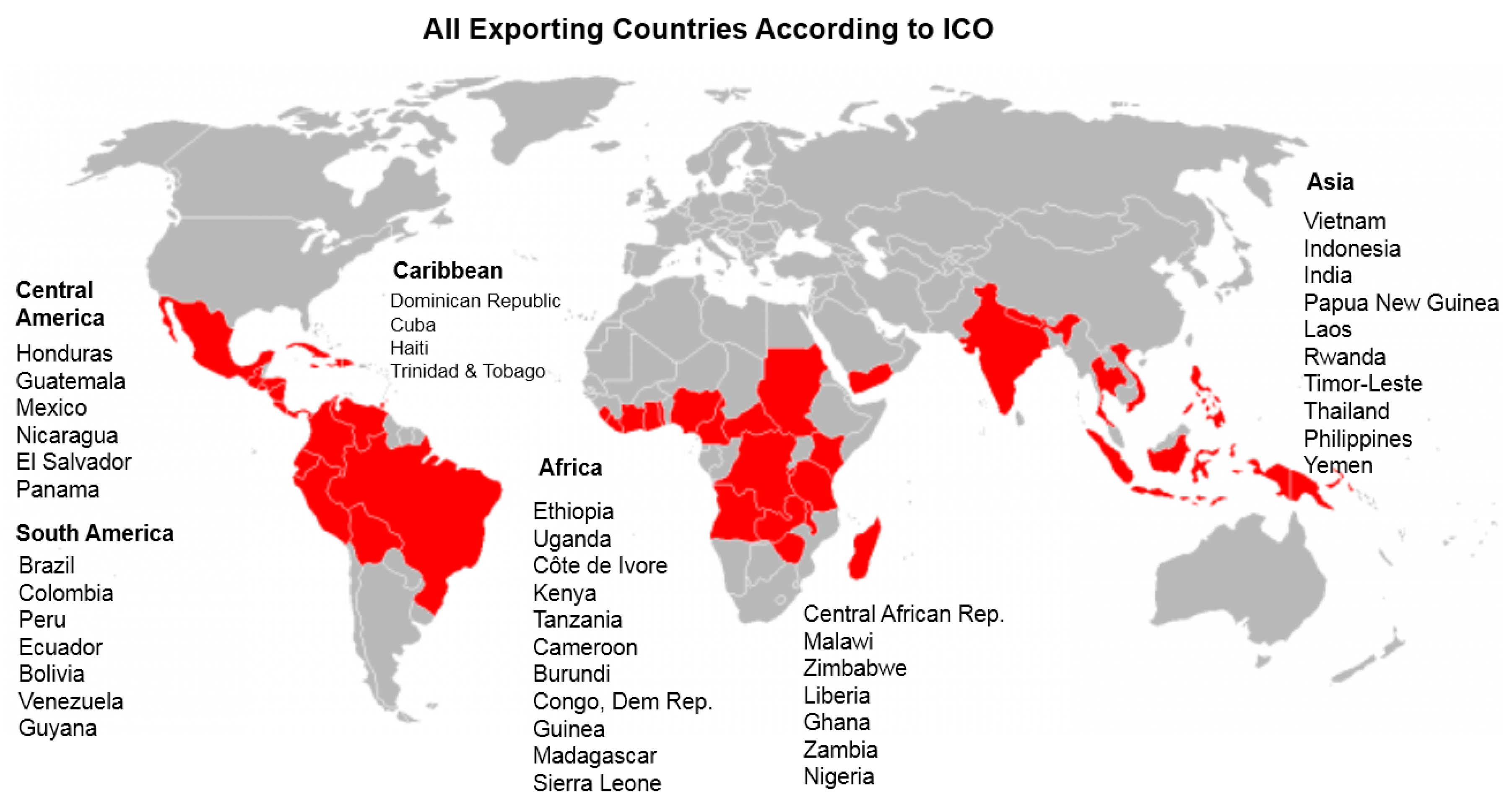
1.1. The Evolving Voluntary Sustainability Standards Landscape
1.2. The Role of Geographical Indications
1.3. A Necessary Debate
2. Voluntary Sustainability Standards and Value Chain Governance
2.1. A Question of Impact
2.2. Growing Pains: VSS Challenges
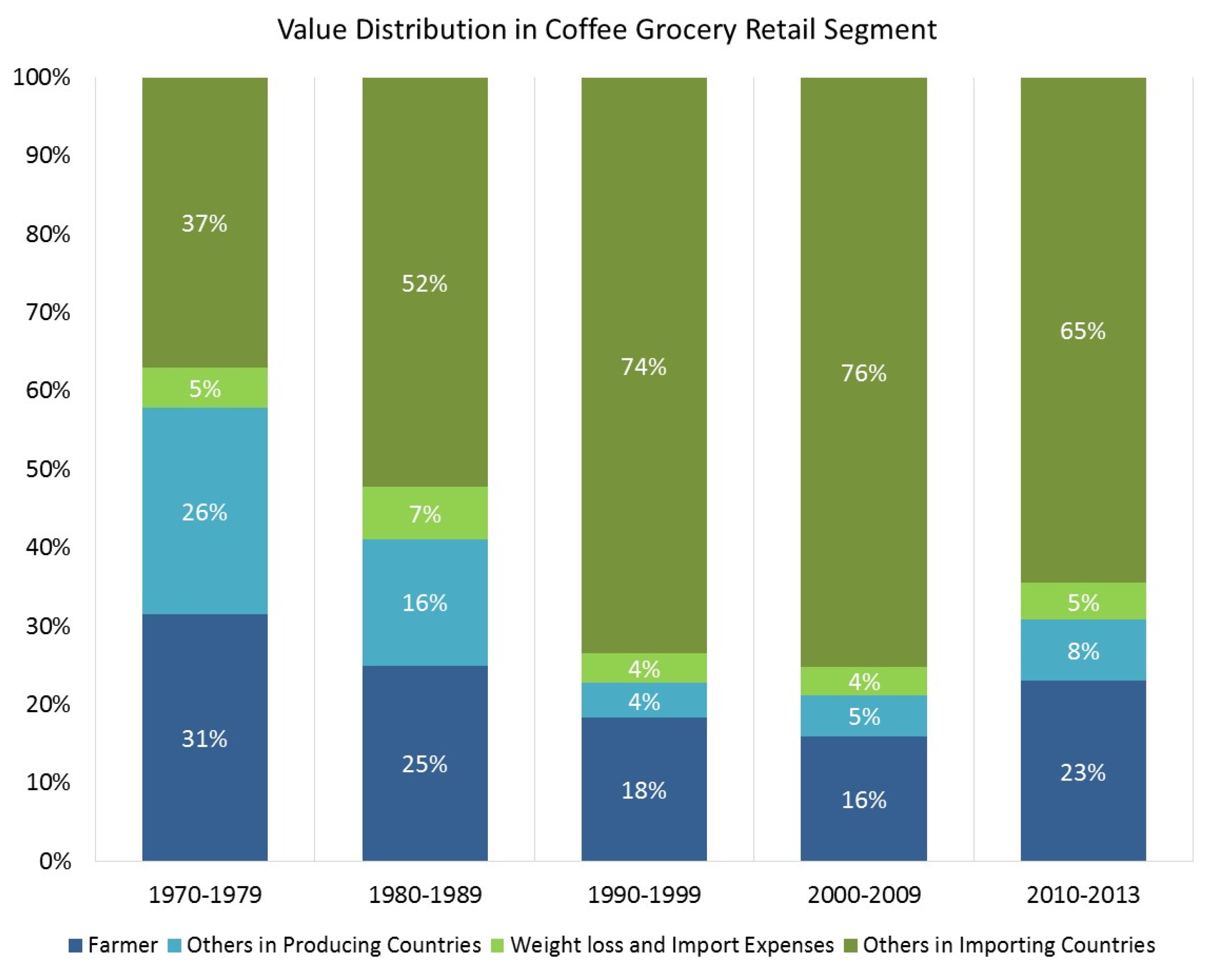
2.3. The North and South Perspective
3. Sustainability Reporting
3.1. A Question of Materiality
3.2. Coffee Brand Reporting
3.3. A Top-Down/Bottom-Up Approach
4. Toward a New and Complementary Sustainability Model
4.1. The Need for a New Model
4.2. The Challenge of Effective Consultation
4.3. Region Specific Sustainability KPIs and Global Priorities
4.4. Benefits for Origins
4.5. A Platform for Fruitful Dialogue
- It is agreed upon and defined with the explicit participation of growers or a collective of growers, reflecting their own challenges and conditions, as well as their priorities in terms of social and natural capital and profitability concerns.
- It is inexorably linked to the origin where those growers live, therefore building upon and complementing the equity of the origin of their coffees. If a collective of growers or a given region demonstrates a firmer commitment to Sustainability KPIs that can be measured in a given geography or community/communities, the equity of such origin in consumer minds and industry buyers can correspondingly improve, as it will be more credible to consumers and stakeholders. In fact, this would lead to GIs in general adopting Sustainability KPIs to complement their own minimum quality policies.
- Assessing the impact and progress of sustainability indicators that are adapted to defined regions and origins is simpler and provides more ready feedback to reassess policies and evaluate benefits of sustainability investments.
- It reflects a complex reality where, at times, all KPIs may not be positive, without sacrificing the transparency and the commitment to improve upon them in the long term, gaining consumer’s trust.
- It has the benefit of scale, impacting a larger number of growers and not just those that can achieve the standards with less effort. Materiality questions aim to achieve widespread changes to a large number of farms and growers, not limiting itself to those that can more easily access a given certification standard or with the financing to be able to comply with them. This allows for forging alliances to invest resources in commonly agreed priorities rather than parceling available funds in limited initiatives.
- It does not work against the current voluntary standards model. On the contrary, it complements it, supplying a set of sustainability objectives for all coffee growers according to priorities defined by themselves, consulting consumer and industry expectations. At the same time, it does not do away with the existing certification and verification protocols, which aim for laudable objectives for those growers and industry members that see benefit in their use.
- It provides a platform to industry members to communicate to the farming communities their own sustainability challenges and efforts. At the coffee growing and supply chain levels, it allows them to use available resources more effectively with commonly agreed priorities. At industry and brand levels, it provides content and actions that allow communicating to clients and consumers with long-term strategies that include an effective and measurable impact.
- Clearly, there is a lot more work on developing a far encompassing sustainability model. However, as the coffee industry considers new paths for sustainability, we advocate for a framework of continuous improvement on clearly defined material topics that take into account the economic challenges of growers. The implied governance of the new model will require that farmer organizations from different regions of the world are able to participate in the co-definition of sustainability priorities that are relevant to their own realities and provide them with economic upgrade opportunities.
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panhuysen, S.; Pierrot, J. Coffee Barometer 2014, Hivos, IUCN Nederland, Oxfam Novi, Solidaridad, WWF, 2014. Available online: https://www.hivos.org/coffee-barometer-2014 (accessed on 11 November 2016).
- NCA (National Coffee Association of USA). 2016 National Coffee Drinking Trends, New York, USA, 2016. Available online: http://www.ncausa.org/Portals/56/PDFs/NCA-Release-NCDT-2016.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2016).
- ECF (European Coffee Federation). Coffee Consumption in Europe, 2016. Available online: http://www.ecf-coffee.org/about-coffee/coffee-consumption-in-europe (accessed on 5 November 2016).
- ICO (International Coffee Organization). Country Data on the Global Coffee Trade. Available online: http://www.ico.org/profiles_e.asp (accessed on 10 October 2016).
- ICO (International Coffee Organization). The Current State of the Global Coffee Trade. Coffee Trade Stats, 2016. Available online: http://www.ico.org/monthly_coffee_trade_stats.asp (accessed on 10 October 2016).
- Daviron, B.; Ponte, S. The Coffee Paradox: Global Markets, Commodity Trade and the Elusive Promise of Development; Zed Books: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, C.L. International commodity agreements: An obituary notice. World Dev. 1996, 24, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muradian, R.; Pelupessy, W. Governing the coffee chain: The role of voluntary regulatory Systems. World Dev. 2005, 33, 2029–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Impact of International Voluntary Standards on Smallholder Market Participation in Developing Countries—A Review of Literature (Agribusiness and Food Industries Series); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; Available online: http://www.fao.org/publications/card/en/c/2858ceb4-4b8f-47af-9ba5-7c4e360bbf2d (accessed on 20 May 2016).
- Deshpande, R.; de Royere, A. Cafe de Colombia; Harvard Business School Case 502-024. Available online: http://www.hbs.edu/faculty/Pages/item.aspx?num=28514 (accessed on 27 March 2017).
- Bacon, C. Confronting the coffee crisis: Can fair trade, organic, and specialty coffees reduce small-scale farmer vulnerability in Northern Nicaragua? World Dev. 2005, 33, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheson-Brown, D. Coffee Oversupply and the Need for Managed-trade Regimes; Edwin Mellen Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pelupessy, W. Smallholders and coffee products. In Smallholders and Markets: Towards a Conducive Environment; Moll, H.A.J., van der Straaij, F., van Tilburg, A., Eds.; Ministry of Foreign Affairs: Hague, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Raynolds, L.T.; Murray, D.; Heller, A. Regulating sustainability in the coffee sector: A comparative analysis of third-party environmental and social certification initiatives. Agric. Hum. Values 2007, 24, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinecke, J.; Manning, S.; von Hagen, O. The emergence of a standards market: Multiplicity of sustainability standards in the global coffee industry. Organ. Stud. 2012, 33, 791–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresser, C.; Tickell, S. Mugged-Poverty in your Cup. Oxfam Research Report. Available online: https://www.oxfamamerica.org/static/oa3/files/mugged-full-report.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2017).
- Bacon, C.; Méndez, E.; Gliessman, S.; Goodman, D.; Fox, J. Confronting the Coffee Crisis—Fair Trade, Sustainable Livelihoods and Ecosystems in Mexico and Central America; MIT University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, F.; Montes, E.; Raine, M. Central America Region Dealing with the Coffee Crisis: Impacts and Strategies. Available online: http://elibrary.worldbank.org/doi/abs/10.1596/1813-9450-2993 (accessed on 27 March 2017).
- Geiger-Oneto, S.; Arnould, E.J. Alternative trade organization and subjective quality of life: The case of Latin American coffee producers. J. Macromark. 2011, 31, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffee, D. Brewing Justice. Fair Trade Coffee, Sustainability, and Survival; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kolk, A. Mainstreaming sustainable coffee. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 21, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolk, A. Linking subsistence activities to global marketing systems. The role of institutions. J. Macromark. 2014, 34, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibovich, J. Conferencia Internacional sobre Agro cadenas y desarrollo sostenible. In Proceedings of the Agri-Chains & Sustainable Development, Montpellier, France, 12–14 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Talbot, J.M. Where does your coffee dollar go? The division of income and surplus along the coffee commodity chain. Stud. Comp. Int. Dev. 1997, 32, 56–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD 2013—OECD Policy Roundtables—Competition Issues in the Food Chain Industry. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/daf/competition/CompetitionIssuesintheFoodChainIndustry.pdf (accessed on 2 January 2017).
- Rueda, X.; Garrett, R.; Lambin, E. Corporate investments in supply chain sustainability: Selecting instruments in the agri-food industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. Coffee Retail Market Share Worldwide in 2014, by Company. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/323254/global-retail-coffee-market-share-by-company/ (accessed on 30 October 2016).
- Potts, J.; Lynch, M.; Wilkings, A.; Huppé, G.; Cunningham, M.; Voora, V. The State of Sustainability Initiatives Review 2014: Standards and the Green Economy. Available online: http://www.iisd.org/library/state-sustainability-initiatives-review-2014-standards-and-green-economy (accessed on 30 October 2016).
- García-Cardona, J. Value-Added Initiatives: Distributional Impacts on the Global Value Chain for Colombia’s Coffee. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Development Studies, University of Sussex, Brighton, UK, August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mutersbaugh, T. Serve and certify: Paradoxes of service work in organic coffee certification. In Confronting the Coffee Crisis: Fair Trade, Sustainable Livelihoods and Ecosystems in Mexico and Central America; Bacon, C.M., Mendez, V.E., Gliessman, S.R., Goodman, D., Fox, J.A., Eds.; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; London, UK, 2008; pp. 261–288. [Google Scholar]
- Giovannucci, D. Food and Agriculture: The future of sustainability; A strategic input to the Sustainable Development in the 21st Century (SD21) Project; United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Division for Sustainable Development: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, J. Global Value Chain in the Agrifood Sector. Available online: https://www.unido.org/fileadmin/user_media/Publications/Pub_free/Global_value_chains_in_the_agrifood_sector.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2017).
- Humphrey, J. Policy Implications of Trends in Agribusiness. Eur. J. Dev. Res. 2006, 18, 572–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagal, M.; Belletti, G.; Marescotti, A.; Onori, G. Study on the Potential of Marketing of Kenyan Coffee as Geographic Indication. REDD SA: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2013. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/agriculture/external-studies/2013/gis-acp-countries/case-study-coffee-kenya_en.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2016).
- Samper, L.F.; Giovanucci, D. ¿Cómo una institución local aprovecha un gobierno efectivo y una nueva tecnología para promover Indicaciones Geográficas globalmente competitivas en Colombia? Ensayos sobre Economía Cafetera No. 30; Federación Nacional de Cafeteros de Colombia: Bogotá, Colombia, 2014; pp. 73–83. [Google Scholar]
- Barjolle, D.; Chappuis, J.M.; Sylvander, B. From individual competitiveness to collective effectiveness: A study on cheese with protected designations of origin; EAAE: Appeldoorn, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Giovannucci, D.; Barham, E.; Pirog, R. Defining and marketing “local” foods: Geographical indications for US products. J. World Intellect. Prop. 2010, 13, 94–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, W.D. GI Joe—Coffee, Location, and Regulatory Accountability. Available online: http://heinonline.org/HOL/LandingPage?handle=hein.journals/nylr85&div=56&id=&page= (accessed on 27 March 2017).
- Marescotti, A.; Belletti, B. Differentiation Strategies in Coffee Global Value Chains through Reference to Territorial Origin in Latin American Countries. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Giovanni_Belletti/publication/303909147_Differentiation_strategies_in_coffee_global_value_chains_through_reference_to_territorial_origin_in_Latin_American_countries/links/582eb36008ae138f1c02d26b.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2017).
- Quiñones-Ruiz, X.F.; Penker, M.; Vogl, C.R.; Samper-Gartner, L.F. Can origin labels re-shape relationships along international supply chains? Int. J. Commons 2015, 9, 419–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuber, R. Geographical indications of origin as a tool of product differentiation: The case of coffee. J. Int. Food Agribus. Mark. 2010, 22, 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICO (International Coffee Organization). Assessing the Economic Sustainability of Coffee Growing, 2016. Available online: http://www.ico.org/documents/cy2015-16/icc-117-6e-economic-sustainability.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2016).
- Gereffi, G. The organization of buyer-driven global commodity chains: How U.S. retailers shape overseas production networks. In Commodity Chains and Global Capitalism; Gereffi, G., Korzeniewicz, M., Westport, T.C., Eds.; Praeger Publishers: Wesport, CT, USA, 1994; pp. 95–122. [Google Scholar]
- Gereffi, G. Global production systems and Third World development. In Global Change, Regional Response: The New International Context of Development; Stallings, B., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hillocks, R.J. Coffee: Is it still a viable cash crop for small holders in Africa? Outlook Agric. 2001, 30, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponte, S. Behind the coffee crisis. Econ. Political Wkly. 2001, 36, 4410–4417. [Google Scholar]
- Gereffi, G.; Humphrey, J.; Sturgeon, T. The governance of global value chains. Rev. Int. Political Econ. 2005, 12, 78–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, X.; Lambin, E.R. Linking globalization to local land uses: How eco-consumers and gourmands are changing the Colombian coffee landscapes. World Dev. 2013, 41, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponte, S. The ‘Latte Revolution’? Regulation, Markets and Consumption in the Global Coffee Chain; Centre for Development Research, Copenhagen, Denmark, World Development: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 30, pp. 1099–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Reardon, T.; Codron, M.; Busch, L. Global Change in Agrifood Grades and Standards: Agribusiness Strategic Responses in Developing Countries. Int. Food Agribus. Manag. Rev. 2001, 2, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anholt, S. Branding New Justice; Elsevier: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dolan, C.; Humphrey, J. Changing governance patterns in the trade in fresh vegetables between Africa and the United Kingdom. Environ. Plan. 2004, 36, 491–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, J. Shaping Value Chains for Development: Global Value Chains in Agribusiness; Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ) GmbH: Eschborn, Germany, 2005; p. 70. [Google Scholar]
- Ponte, S.; Gibbon, P. Quality standards, conventions and the governance of global value chains. Econ. Soc. 2005, 34, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, J. Alternative Trade Initiatives and Income Predictability: Theory and Evidence from the Coffee Sector; International Institute for Sustainable Development: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2007; p. 33. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffee, S.; Henson, S.; Diaz-Rios, L. Making the Grade: Smallholder Farmers, Emerging Standards, and Development Assistance Programs in Africa–A Research Program Synthesis; Report No. 62324-AFR; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lewin, B.D.; Giovannucci, D.; Varangis, P. Coffee Markets: New Paradigms in Global Supply and Demand; Agriculture and Rural Development Discussion Paper 3; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- García, C.; Mejía, N.; Zarate, C.; Ochoa, G.; Mora, J.C.; Castellanos, J.F. Costos y Beneficios de la Implementación de Estándares Voluntarios de Sostenibilidad en Café: Un Estudio de caso en Colombia; CRECE: Manizales, Colombia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, S.; Chan-Kang, C. Is small beautiful? Farm size, productivity, and poverty in Asian agriculture. Agric. Econ. 2005, 32, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, J.; Marsden, T.; Banks, J. Quality, nature, and embeddedness: Some theoretical considerations in the context of the food sector. Econ. Geogr. 2000, 76, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynolds, L.T. Re-embedding global agriculture: The international organic and fair trade movements. Agric. Hum. Values 2000, 17, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Ploeg, J.D.; Renting, H. Behind the “Redux”: A rejoinder to David Goodman. Sociol. Rural. 2004, 44, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Ploeg, J.D.; Renting, H.; Brunori, G.; Knickel, K.; Mannion, J.; Marsden, T.; De Roest, K.; Sevilla-Guzmán, E.; Ventura, F. Rural development: From practices and policies towards theory. Sociol. Rural. 2000, 40, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramley, C.; Biénabe, E. Why the need to consider GIs in the South? In Developing Geographical Indications in the South; Bramley, C., Bienabe, E., Kirsten, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Marsden, T.; Banks, J.; Bristow, G. Food supply chain approaches: Exploring their role in rural development. Sociol. Rural. 2000, 40, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuchelt, T.D.; Zeller, M. Profits and poverty: Certification’s troubled link for Nicaragua’s organic and fairtrade coffee producers. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, G.; von Hagen, O. The Impacts of Private Standards on Producers in Developing Countries; Literature Review Series on the Impact of Private Standards; Part II. No. ID 2184273. Available online: http://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=2184273 (accessed on 24 May 2016).
- Teuber, R. Geographical Indications of Origin as a Tool of product Differentiation—The Case of Coffee. In Proceedings of the 105th Seminar “International Marketing and International Trade of Quality Food Products”, Bologna, Italy, 8–10 March 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Linton, A. A niche for sustainability? Fair labor and environmentally sound practices in the specialty coffee industry. Globalizations 2008, 5, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilson, J. Global Private Regulations and Value-Chain Restructuring in Indonesian Smallholder Coffee Systems. World Dev. 2008, 36, 1607–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynolds, L. Mainstreaming Fair Trade Coffee: From Partnership to Traceability. World Dev. 2009, 37, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampe, M. Leveraging the Vertical: The Contested Dynamics of Sustainability Standards and Labour in Global Production Networks. Br. J. Ind. Relat. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannucci, D.; Potts, J. Seeking Sustainability: COSA Preliminary Analysis of Sustainability Initiatives in the Coffee Sector. Committee on Sustainability Assessment: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2008. Available online: http://www.iisd.org/pdf/2008/seeking_sustainability.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2016).
- COSA (Committee on Sustainability Assessment). The COSA Measuring Sustainability Report: Coffee and Cocoa in 12 Countries; COSA: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dragusanu, R.; Giovannucci, D.; Nunn, N. The economics of fair trade. J. Econ. Perspect. 2014, 28, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, C.; García, J.; Ochoa, G.; Mora, J.C.; Castellanos, J.F. Impact Evaluation of Utz Certifies Coffee Program in Colombia; Centro de Estudios Regionales Cafeteros y Empresariales: Manizales, Colombia, 2014; p. 51. [Google Scholar]
- CRECE’s Monitoring & Evaluation study on the Nespresso AAA Sustainable Quality Program in Colombia. C. d. E.R. C. y. Empresariales; CRECE: Manizales, Columbia, 2013; Volume 1, p. 2.
- Thomas, M.; Baer, E.; Semroc, B.; Sonenshine, J. C.A.F.E. Practices Result Assessment 2011—Conservation International. Available online: http://www.conservation.org/publications/Documents/2011_2012_tarbucks_CAFE_Practices_Results_Assessment.pdf (accessed on 2 January 2017).
- Standards and Sustainability in the Coffee Sector: A Global Value Chain Approach; May 2004 United Nations Conference on Trade and Development and IISD. Available online: http://www.iisd.org/pdf/2004/sci_coffee_standards.pdf (accessed on 2 January 2017).
- Djama, M.; Fouilleux, E.; Vagneron, I. Standard-setting, certifying and benchmarking: A governmentality approach to sustainability standards in the agro-food sector. In Governing Through Standards: Origins, Drivers and Limitations; Ponte, S., Gibbon, P., Vestergaard, J., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: Basingstoke, UK, 2011; pp. 184–209. [Google Scholar]
- Reina, M.; Silva, G.; Samper, L.F.; Fernández, M. Juan Valdez: La Estrategia Detrás de la Marca; Ediciones B: Bogota, Colombia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Neilson, J. Institutions, the governance of quality and on-farm value retention for Indonesian specialty coffee. Singap. J. Trop. Geogr. 2007, 28, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FNC (Federación Nacional de Cafeteros de Colombia). CEO report to National Coffee Growers Congress 2015–2014, 2015. Available online: https://www.federaciondecafeteros.org/particulares/es/quienes_somos/publicaciones/ (accessed on 30 October 2016).
- Simons, L. Changing the Food Game: Market Transformation Strategies for Sustainable Agriculture; Greenleaf Publishing Limited: Sheffield, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schouten, G.; Bitzer, V. The emergence of Southern standards in agricultural value chains. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 120, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannucci, D.; Scherr, S.; Nierenberg, D.; Hebebrand, C.; Shapiro, J.; Milder, J.; Wheeler, K. Food and Agriculture: The Future of Sustainability. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/agriculture_and_food_the_future_of_sustainability_web.pdf (accessed on 29 October 2016).
- Ponte, S.; Cheyns, E. Voluntary standards, expert knowledge and the governance of sustainability networks. Glob. Netw. 2013, 13, 459–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, D.; Kalfagianni, A.; Havinga, T. Actors in private food governance: The legitimacy of retail standards and multistakeholder initiatives with civil society participation. Agric. Hum. Values 2011, 28, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattenberg, P. Private Governance and the South: Lessons from Global Forest Politics. Third World Q. 2006, 27, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheyns, E. Multi-stakeholder initiatives for sustainable agriculture: Limits of the “inclusiveness” paradigm. In Governing Through Standards: Origins, Drivers and Limitations; Ponte, S., Gibbon, P., Vestergaard, J., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: Basingstoke, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hospes, O. Marking the success or end of global multi-stakeholder governance? The rise of national sustainability standards in Indonesia and Brazil for palm oil and soy. Agric. Hum. Values 2014, 31, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.M.; Fischlein, M. Rival private governance networks: Competing to define the rules of sustainability performance. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2010, 20, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FlorVerde Sustainable_Flowers (2016). Available online: http://www.florverde.org/ (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- Cerrado Mineiro (2017). Cerrado Mineiro Region Designation of Origin Official Production Process. Available online: http://www.cafedocerrado.org/index.php?pg=denominacaodeorigem#group2 (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- FNC—Federacion de Cafeteros (2016). Además de sinónimo de calidad, Café de Colombia será 100% sostenible. Available online: https://www.federaciondecafeteros.org/particulares/es/sala_de_prensa/detalle/ademas_de_sinonimo_de_calidad_cafe_de_colombia_sera_100_sostenible/ (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- Eccles, R.G.; Ioannou, I.; Serafeim, G. The Impact of Corporate Sustainability on Organizational Processes and Performance. Available online: http://www.hbs.edu/faculty/Publication%20Files/SSRN-id1964011_6791edac-7daa-4603-a220-4a0c6c7a3f7a.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2016).
- Sustainable Brands. 22 Research Studies Proving the ROI of Sustainability, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016. Available online: http://e.sustainablebrands.com/resources-report-22-research-studies-proving-the-roi-of-sustainability.html?_ga=1.77425757.974955321.1467725336&iesrc=ctr (accessed on 2 November 2016).
- Morgan, S. Understanding the Performance of Sustainable Investment Strategies. Available online: http://www.morganstanley.com/sustainableinvesting/pdf/sustainable-reality.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2016).
- Khan, M.; Serafeim, G.; Yoon, A. Corporate Sustainability: First Evidence on Materiality. Harvard Business School Working Paper 15-073, 2015. Available online: http://hbswk.hbs.edu/item/corporate-sustainability-first-evidence-on-materiality (accessed on 27 March 2017).
- WBCSD (World Business Council for Sustainable Development); UNEP FI (United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative). Translating ESG into Sustainable Business Value: Key Insights for Companies and Investors. Available online: http://www.unepfi.org/fileadmin/documents/translatingESG.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2016).
- Williams, F. Green Giants. How Smart Companies Turn Sustainability into Billion-Dollar Business; Amacom: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zadek, S. The Path to Corporate Responsibility; Harvard Business Review 82 (December), 2004. Available online: https://hbr.org/2004/12/the-path-to-corporate-responsibility (accessed on 2 January 2017).
- Deloitte. The 2016 Deloitte Millennial Survey: Winning over the Next Generation of Leaders. Available online: https://www2.deloitte.com/global/en/pages/about-deloitte/articles/millennialsurvey.html (accessed on 30 October 2016).
- Nielsen. The Sustainability Imperative. New Insights on Consumer Expectations, 2015. Available online: http://www.nielsen.com/content/dam/nielsenglobal/dk/docs/global-sustainability-report-oct-2015.pdf (accessed on 29 October 2016).
- Gidwani, B. The Link between Brand Value and Sustainability. Available online: http://brandfinance.com/images/upload/the_link_between_brand_value_and_sustainability.pdf (accessed on 29 October 2016).
- Roberts, K. Lovemarks the Future beyond Brands; Powerhouse Books: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Edmans, A.; Li, L.; Zhang, C. Employee Satisfaction, Labor Market Flexibility, and Stock Returns around the World. Available online: http://e.sustainablebrands.com/resources-report-22-research-studies-proving-the-roi-of-sustainability.html?_ga=1.77425757.974955321.1467725336&iesrc=ctr (accessed on 2 November 2016).
- Di Somma, M. Will Customers Forgive Your Brand? Brand Management. Available online: http://www.brandingstrategyinsider.com/2016/04/will-customers-forgive-your-brand.html#.VxfCQ_nhDIU (accessed on 29 October 2016).
- Brat, I.; Ģasparro, A. El origen de los ingredientes se vuelve una prioridad para las empresas de alimentos. Available online: http://lat.wsj.com/articles/SB10889846692453914051504581605452927620170 (accessed on 30 October 2016).
- Mainwaring, S. We First: How Brands and Consumers Use Social Media to Build a Better World; St Martins Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- The Economist. Consumer goods. Invasion of the Bottle Snatchers: Smaller Rivals Are Assaulting the World’s Biggest Brands, 2016. Available online: http://www.economist.com/news/business/21701798-smaller-rivals-are-assaulting-worlds-biggest-brands-invasion-bottle-snatchers (accessed on 30 October 2016).
- Centre for Corporate Governance 2017—Materiality Tracker. Available online: www.materialitytracker.net (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- KPMG International. Sustainable Insight. The Essentials of Materiality Assessment, 2016. Available online: https://www.kpmg.com/Global/en/IssuesAndInsights/ArticlesPublications/Documents/materiality-assessment.pdf (accessed on 29 October 2016).
- GRI (Global Reporting Initiative). G4 Sustainability Reporting Guidelines, 2016. Available online: https://www.globalreporting.org/information/g4/Pages/default.aspx (accessed on 25 October 2016).
- SASB (Sustainability Accounting Standards Board). Food Retailers & Distributors, 2015. Available online: http://www.sasb.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/CN0401_Food-Retailers-Distributors_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2016).
- Brow, S.; Jong, M.; Levy, D.L. Building institutions based on information disclosure: Lessons from GRI’s sustainability reporting. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federación Nacional de Cafeteros. Sostenibilidad en Acción 1927–2010; Urueña, M., Pinzón, N., Rodríguez, A., Samper, L.F., Eds.; Federación Nacional de Cafeteros de Colombia: Bogotá, Colombia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Corporate Sustainability Report–Responsible Sourcing. Available online: http://corporateresponsibility.jmsmucker.com/sourcing/commodity.html (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- Global Responsibility Report. Available online: http://globalassets.starbucks.com/assets/ee8121c1a6554399b554d126228d52ed.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- McDonalds Journey towards Sourcing Sustainable Coffee—October 2016. Available online: http://corporate.mcdonalds.com/content/dam/AboutMcDonalds/2.0/pdfs/sustainability/McDonalds_2016_Coffee_Sustainability_Report.pdf?1 (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- Farmer Brothers (2016)—2015 Sustainability Report—Procurement Practices. Available online: http://www.farmerbros.com/media//FB-2015-Procurement.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- JacobsDouweEgberts (2017)—Corporate Responsibility at the Source. Available online: https://www.jacobsdouweegberts.com/CR/source/ (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- Keurig-Green Mountain (2016). Keurig Green Mountain Sustainability Report 2015. Available online: http://www.keuriggreenmountain.com/~/media/Sustainability/PDF/ReportsDisclosures/KeurigSustainabilityReport_2015.ashx (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- Nestle (2015). Nestlé in Society Creating Shared Value and Meeting Our Commitments 2015. Available online: http://www.nestle.com/asset-library/documents/library/documents/corporate_social_responsibility/nestle-csv-full-report-2015-en.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- Lavazza (2016). Lavazza 2015 Sustainability Report. Available online: http://www.lavazza.com/csa/lavazza-world/sustainability-report/ (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- Lee, J.; Gereffi, G.; Beauvais, J. Global value chains and agrifood standards: Challenges and possibilities for smallholders in developing countries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 199, 12326–12331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conservation International 2017—Sustainable Coffee Challenge. Available online: http://www.conservation.org/stories/sustainable-coffee-challenge/pages/about-the-challenge.aspx (accessed on 10 February 2017).
- ISEAL. Assessing the Impacts of Social and Environmental Standards Systems v 2.0. ISEAL; Code of Good Practice; 2014. Available online: http://www.isealalliance.org/sites/default/files/ISEAL_Impacts_Code_v2_Dec_2014.pdf (accessed on 4 April 2017).
- ISEAL. The ISEAL Stakeholders’ Workshop; Joint Statement, 2011. Available online: http://www.isealalliance.org/online-community/news/historic-joint-statement-fairtrade-sanrainforest-alliance-utz-certified (accessed on 10 February 2017).
- World Cocoa Foundation 2016—Cocoa Action. Available online: http://www.worldcocoafoundation.org/about-wcf/cocoaaction/ (accessed on 10 February 2017).
- GCP 2017. The Global Coffee Platform. Available online: http://www.globalcoffeeplatform.org/ (accessed on 10 February 2017).
- Van der Vossen, H.A.M. A critical analysis of the agronomic and economic sustainability of organic coffee production. Exp. Agric. 2005, 41, 449–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avelino, J.; Zelaya, H.; Merlo, A.; Pineda, A.; Ordoñez, M.; Savary, S. The intensity of a coffee rust epidemic is dependent on production situations. Ecol. Model. 2006, 197, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Bravo, D.F.; Virginio-Filho, E.M.; Avelino, J. Shade is conducive to coffee rust as compared to full sun exposure under standardized fruit load conditions. Crop Prot. 2012, 38, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheserek, J.J.; Gichimu, B.M. Drought and heat tolerance in coffee: A review. Int. Res. J. Agric. Sci. Soil Sci. 2012, 2, 498–501. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio de Cultura. Paisaje Cultural Cafetero: un paisaje cultural productivo en permanente desarrollo. In Coffee Cultural Landscape: A Productive Cultural Landscape in Continuous Development; Ministerio de Cultura: Bogotá, Colombia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio de Cultura. Federación Nacional de Cafeteros de Colombia. Guía para la incorporación del Paisaje Cultural Cafetero en la revisión y ajuste de los planes de ordenamiento territorial (POT, PBOT y EOT). In Guide for the Incorporation of the Coffee Cultural Landscape in the Revision and Adjustment of Territorial Planning Plans (POT, PBOT y EOT); Ministerio de Cultura: Bogotá, Colombia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Federación Nacional de Cafeteros (2012). Coffee Cultural Landscape official Website. Available online: http://paisajeculturalcafetero.org.co/ (accessed on 2 January 2017).
- Departamento Nacional de Planeación (2014). Documento Conpes 3803. Available online: http://paisajeculturalcafetero.org.co/static/files/Conpes1.pdf (accessed on 2 January 2017).
- Ryan, J.; Silvanto, S. The World Heritage List: The making and management of a brand. Place Brand. Public Dipl. 2009, 5, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.; Silvanto, S. A brand for all the nations. Mark. Intell. Plan. 2011, 29, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samper, L.F. Branding Geographical Indications: Building Denominations of Origin That Connect with Consumers; World Symposium on Geographical Indications/World Intellectual Property Organization: Lima, Peru, 2012; pp. 85–87. [Google Scholar]
- Rincón Cardona, F. La Caficultura como Patrimonio Cultural, Social y Productivo. Paisaje Cultural Cafetero de Colombia: cinco años como Patrimonio Mundial Gestiones Interinstitucionales en el Marco del Plan de Manejo del Paisaje Cultural Cafetero Entre 2011 y Diciembre 2015 (Coffee as a Cultural, Social and Productive Heritage. Cultural Landscape Cafetero de Colombia: Five Years as World Heritage Site. Inter-Institutional Management within the Framework of the Management Plan of the Colombia’s Coffee Cultural Landscape between 2011 and December 2015); Ministerio de Cultura/Federación Nacional de Cafeteros: Manizales, Colombia, 2016.
- Samper, L.F. Paisaje Cultural Cafetero: Una apuesta por la sostenibilidad (Coffee Cultural Landscape: An initiative for Sustainability). In La Caficultura Como Patrimonio Cultural, Social y Productivo. Paisaje Cultural Cafetero de Colombia: Cinco años Como Patrimonio Mundial Gestiones Interinstitucionales en el Marco del Plan de Manejo del Paisaje Cultural Cafetero entre 2011 y Diciembre 2015; Rincón Cardona, F., Ed.; Ministerio de Cultura/Federación Nacional de Cafeteros: Manizales, Colombia, 2016; pp. 137–147. [Google Scholar]
- Kinni, T. Exploit What You Do Best; Harvard Management: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Imagine Chicago (2009). Available online: http://www.imaginechicago.org/inquiry.html (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- Federación Nacional de Cafeteros (2016). Gremio Cafetero Reafirma Rumbo Hacia Rentabilidad del Productor. Available online: https://www.federaciondecafeteros.org/particulares/es/sala_de_prensa/detalle/gremio_cafetero_reafirma_rumbo_hacia_rentabilidad_del_productor/ (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- Hoffmann-Riem, H.; Biber-Klemm, S.; Grossenbacher-Mansuy, W.; Hirsch Hadorn, G.; Joye, D.; Pohl, C.; Wiesmann, U.; Zemp, E. Idea of the handbook. In Handbook of Transdisciplinary Research; Hirsch Hadorn, G., Hoffmann-Riem, H., Biber-Klemm, S., Grossenbacher-Mansuy, W., Joye, D., Pohl, C., Wiesmann, U., Zemp, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Berstein, H.J. Transdisciplinarity: A review of its origins, development, and current issues. J. Res. Pract. 2015, 11, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). Sustainability Assessment of Food and Agric. Systems Guidelines (SAFA). Available online: http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/nr/sustainability_pathways/docs/SAFA_Indicators_final_19122013.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2016).

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samper, L.F.; Quiñones-Ruiz, X.F. Towards a Balanced Sustainability Vision for the Coffee Industry. Resources 2017, 6, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources6020017
Samper LF, Quiñones-Ruiz XF. Towards a Balanced Sustainability Vision for the Coffee Industry. Resources. 2017; 6(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources6020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamper, Luis F., and Xiomara F. Quiñones-Ruiz. 2017. "Towards a Balanced Sustainability Vision for the Coffee Industry" Resources 6, no. 2: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources6020017
APA StyleSamper, L. F., & Quiñones-Ruiz, X. F. (2017). Towards a Balanced Sustainability Vision for the Coffee Industry. Resources, 6(2), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources6020017




