A Socio-Ecological Approach to GIS Least-Cost Modelling for Regional Mining Infrastructure Planning: A Case Study from South-East Sulawesi, Indonesia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
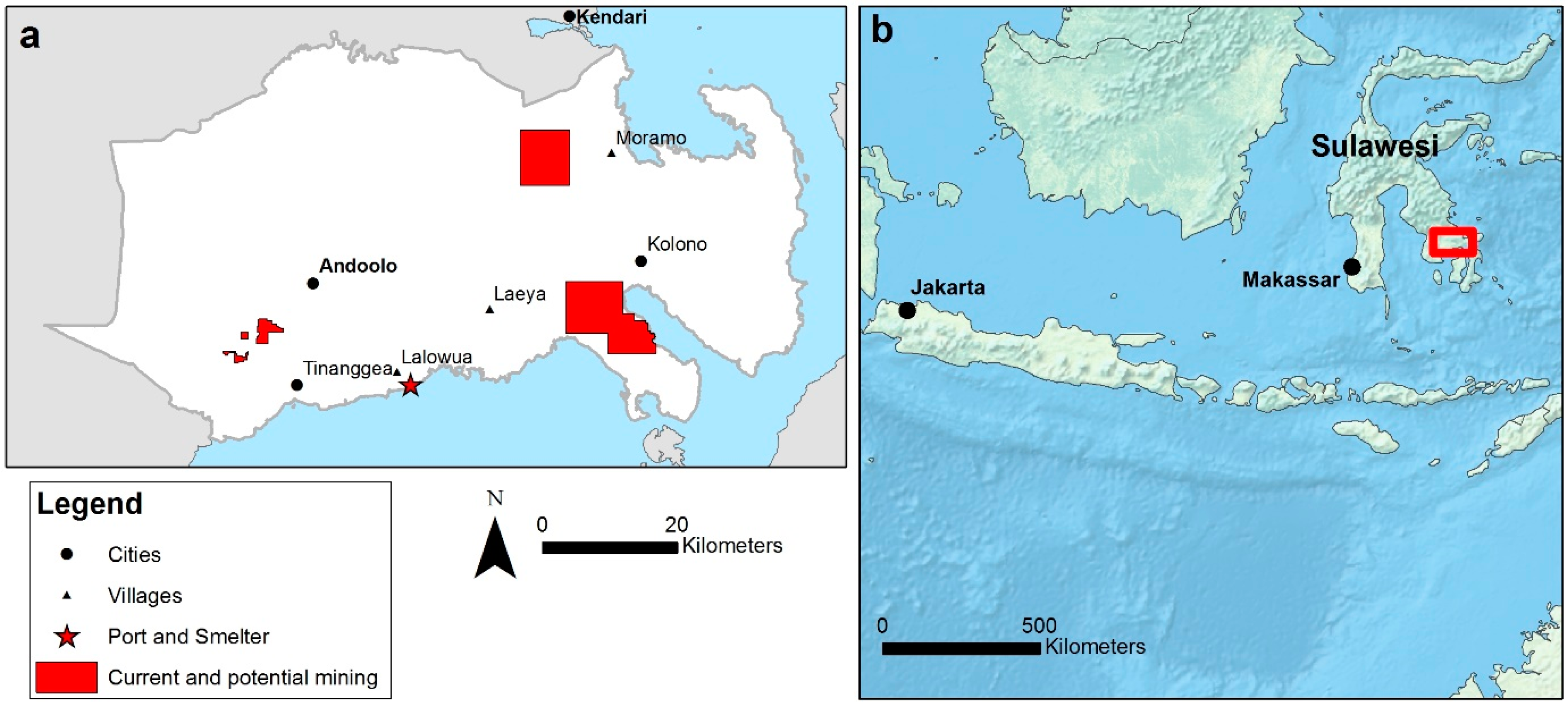
2.1. Study Area
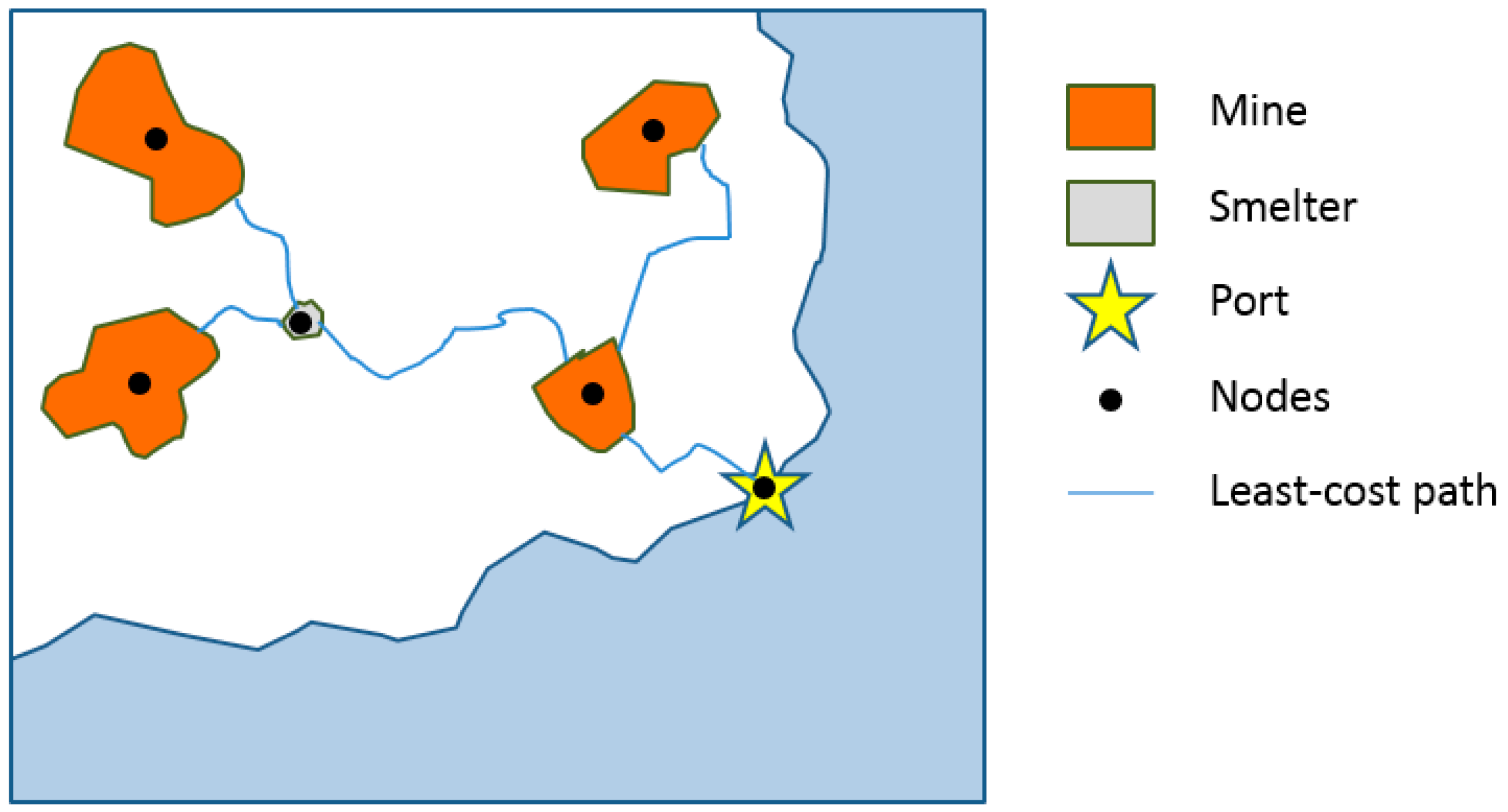
2.2. Least-Cost Paths Modelling of Infrastructure Networks
| <3° Suitable | no cost |
| 3°–25° No suitable | double cost |
| >25° Very unsuitable | five times the cost |
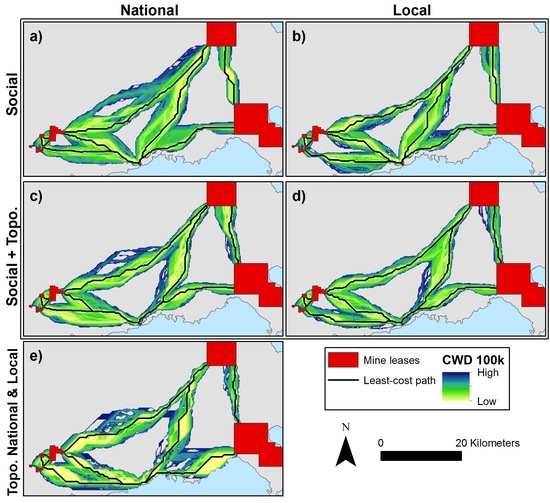
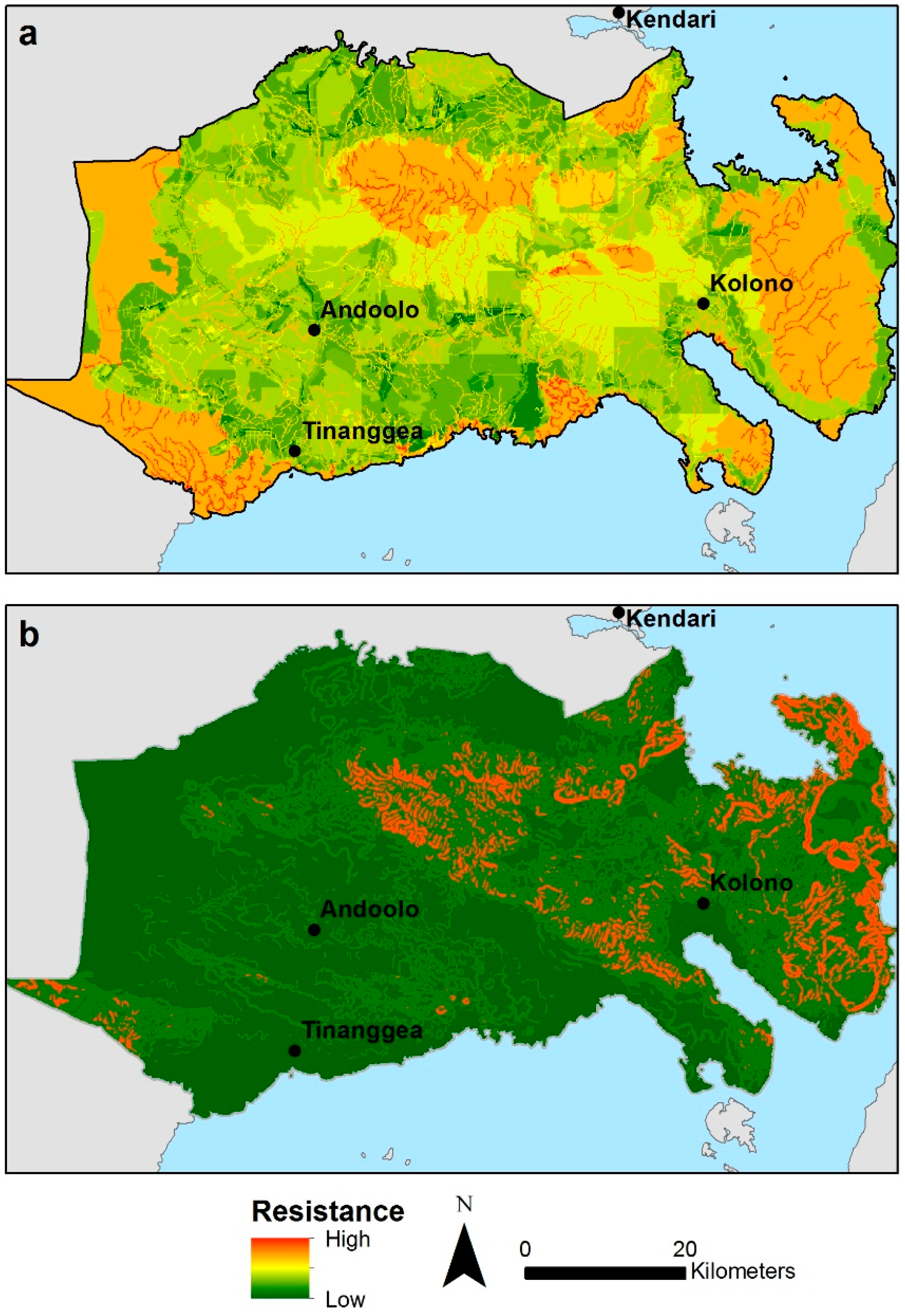
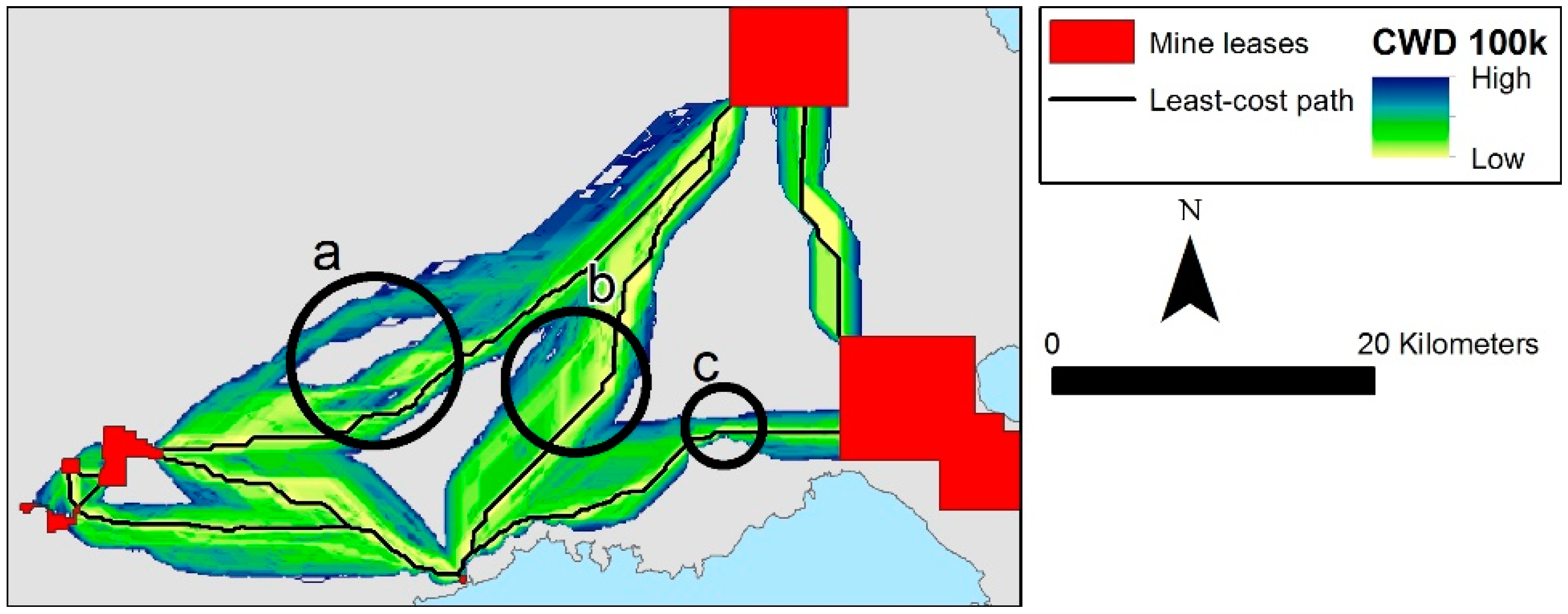
3. Results
4. Discussions
4.1. Contrasting Local Versus National-Scale Planning
4.2. Social-Ecological Analysis in the Context of Mine Planning
4.3. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ives, C.D.; Biggs, D.; Hardy, M.J.; Lechner, A.M.; Wolnicki, M.; Raymond, C.M. Using social data in strategic environmental assessment to conserve biodiversity. Land Use Policy 2015, 47, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, B.A.; Crossman, N.D.; King, D.; Meyer, W.S. Landscape futures analysis: Assessing the impacts of environmental targets under alternative spatial policy options and future scenarios. Environ. Model. Softw. 2011, 26, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.; Raymond, C.M. Methods for identifying land use conflict potential using participatory mapping. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 122, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, A.M.; Mcintyre, N.; Bulovic, N.; Kujala, H.; Whitehead, A.; Webster, A.; Wintle, B.; Rifkin, W.; Scott, M.H.; Kujala, A.; et al. A GIS Tool for Land and Water Use Planning in Mining Regions. In Proceedings of the 21st International Congress on Modelling and Simulation (MODSIM2015), Broadbeach, Queensland, Australia, 29 November–4 December 2015; pp. 1359–1365.
- Longley, P.A.; Goodchild, M.; Maguire, D.J.; Rhind, D.W. Geographic Information Systems and Science, 3rd ed.; Wiley & Sons: Hobeken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Goodchild, M.F.; Anselin, L.; Appelbaum, R.P.; Harthorn, B.H. Toward Spatially Integrated Social Science. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2000, 23, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G. Public participation GIS (PPGIS) for regional and environmental planning: Reflections on a decade of empirical research. URISA J. 2012, 24, 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lechner, A.M.; Raymond, C.M.; Adams, V.M.; Polyakov, M.; Gordon, A.; Rhodes, J.R.; Mills, M.; Stein, A.; Ives, C.D.; Lefroy, E.C. Characterizing spatial uncertainty when integrating social data in conservation planning. Conserv. Biol. 2014, 28, 1497–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, A.M.; Brown, G.; Raymond, C.M. Modeling the impact of future development and public conservation orientation on landscape connectivity for conservation planning. Landsc. Ecol. 2015, 30, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtegha, H.; Leeuw, P.; Naicker, S.; Molepo, M. Resources Corridors: Experiences, Economics and Engagement; A Typology of Sub-Saharan; Extractive Industries SourceBook: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, L.; Boedhihartono, A.K.; Dirks, P.H.G.M.; Dixon, J.; Lubis, M.I.; Sayer, J.A. Mineral industries, growth corridors and agricultural development in Africa. Glob. Food Secur. 2013, 2, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagli, S.; Geneletti, D.; Orsi, F. Routeing of power lines through least-cost path analysis and multicriteria evaluation to minimise environmental impacts. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2011, 31, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, S.; Friedli, R.; Grangier, M.; Raubal, M. A GIS-Based Process for Calculating Visibility Impact from Buildings During Transmission Line Routing. In Connecting a Digital Europe Through Location and Place, 383 Lecture Notes in Geoinformation and Cartography; Huerta, J., Schade, S., Granell, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 383–402. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, S.C.; Pelletier, R.E.; Walser, E.; Smoot, J.C.; Ahl, D. A Prototype for Pipeline Routing Using Remotely-Sensed Data and Geographic Information-System Analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 53, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlot, V.; Swami, B.L.; Parida, M.; Kalla, P. User oriented planning of bus rapid transit corridor in GIS environment. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2012, 1, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, D.M.; Deadman, P.; Dudycha, D.; Traynor, S. Multi-criteria evaluation and least cost path analysis for an arctic all-weather road. Appl. Geogr. 2005, 25, 287–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Park, H.-D.; Sunwoo, C.; Clarke, K.C. Multi-criteria evaluation and least-cost path analysis for optimal haulage routing of dump trucks in large scale open-pit mines. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2009, 23, 1541–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Nieto, A. Optimal haulage routing of off-road dump trucks in construction and mining sites using Google Earth and a modified least-cost path algorithm. Autom. Constr. 2011, 20, 982–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitzia, T.; Rizzi, A.; Cattaneo, D.; Semenzato, P. Designing recreational trails in a forest dune habitat using least-cost path analysis at the resolution of visitor sight distance. Urban For. Urban Green. 2014, 13, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, B.H.; Kavanagh, D.M. Linkage Mapper Connectivity Analysis Software, Linkage Mapper: Seattle, WA, USA, 2011.
- Goldberg, C.S.; Pocewicz, A.; Nielsen-Pincus, M.; Waits, L.P.; Morgan, P.; Force, J.E.; Vierling, L.A. Predictions of ecological and social impacts of alternative residential development policies to inform decision making in a rural landscape. Conserv. Lett. 2011, 4, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, M.; Pannell, D.J.; Pandit, R.; Tapsuwan, S.; Park, G. Valuing Environmental Assets on Rural Lifestyle Properties. Agric. Resour. Econ. Rev. 2013, 42, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesslie, R. Mapping Our Priorities—Innovation in Spatial Decision Support. In Innovation for 21st Century Conservation; Figgis, P., Fitzsimon, J., Irving, J., Eds.; Australian Committee for IUCN Inc.: Sydney, Australia, 2012; pp. 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- Bkpm Statistik Penduduk Menurut Jenis Kelamin. Available online: http://regionalinvestment.bkpm.go.id/newsipid/demografipendudukjkel.php?ia=7408&is=37 (accessed on 20 April 2015).
- BPK RI Profil Kabupaten Konawe Selatan. Available online: http://kendari.bpk.go.id/?page_id=391 (accessed on 20 April 2015).
- Morrison, J. Indonesia: Island of Sulawesi. Available online: www.worldwildlife.org/ecoregions/aa0123 (accessed on 29 November 2016).
- Environmental Systems Research Institute. ArcGIS Desktop: Release 10.2; Environmental Systems Research Institute: Redlands, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Heri, S. Spatial Planning Support System for an Integrated Approach to Disaster Risk Reduction. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- USAID. The Role of Local Governments in Promoting Decentralized Economic Governance in Indonesia; Local Governance Support Program; USAID: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Devi, B.; Schleger, A.; Lechner, A.; Rogers, P.; Ali, S.; Rachmat, S. Socio-Ecological Tools in the Development of Mineral Infrastructure in Indonesia; The University of Queensland: Brisbane, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dukes, E.F.; Firehock, K.E.; Birkhoff, J.E. Community-Based Collaboration: Bridging Socio-Ecological Research and Practice; University of Virginia Press: Charlottesville, VA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cane, I.; Schleger, A.; Ali, S.; Kemp, D.; McIntyre, N.; McKenna, P.; Lechner, A.; Dalaibuyan, B.; Lahiri-Dutt, K.; Bulovic, N. Responsible Mining in Mongolia: Enhancing Positive Engagement; Sustainable Minerals Institute: Brisbane, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, G.; Fagerholm, N. Empirical PPGIS/PGIS mapping of ecosystem services: A review and evaluation. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 13, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, A.M.; Langford, W.T.; Bekessy, S.A.; Jones, S.D. Are landscape ecologists addressing uncertainty in their remote sensing data? Landsc. Ecol. 2012, 27, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotway, C.A.; Young, L.J. Combining Incompatible Spatial Data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2002, 97, 632–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comber, A.; Fisher, P.; Wadsworth, R. You know what land cover is but does anyone else? An investigation into semantic and ontological confusion. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
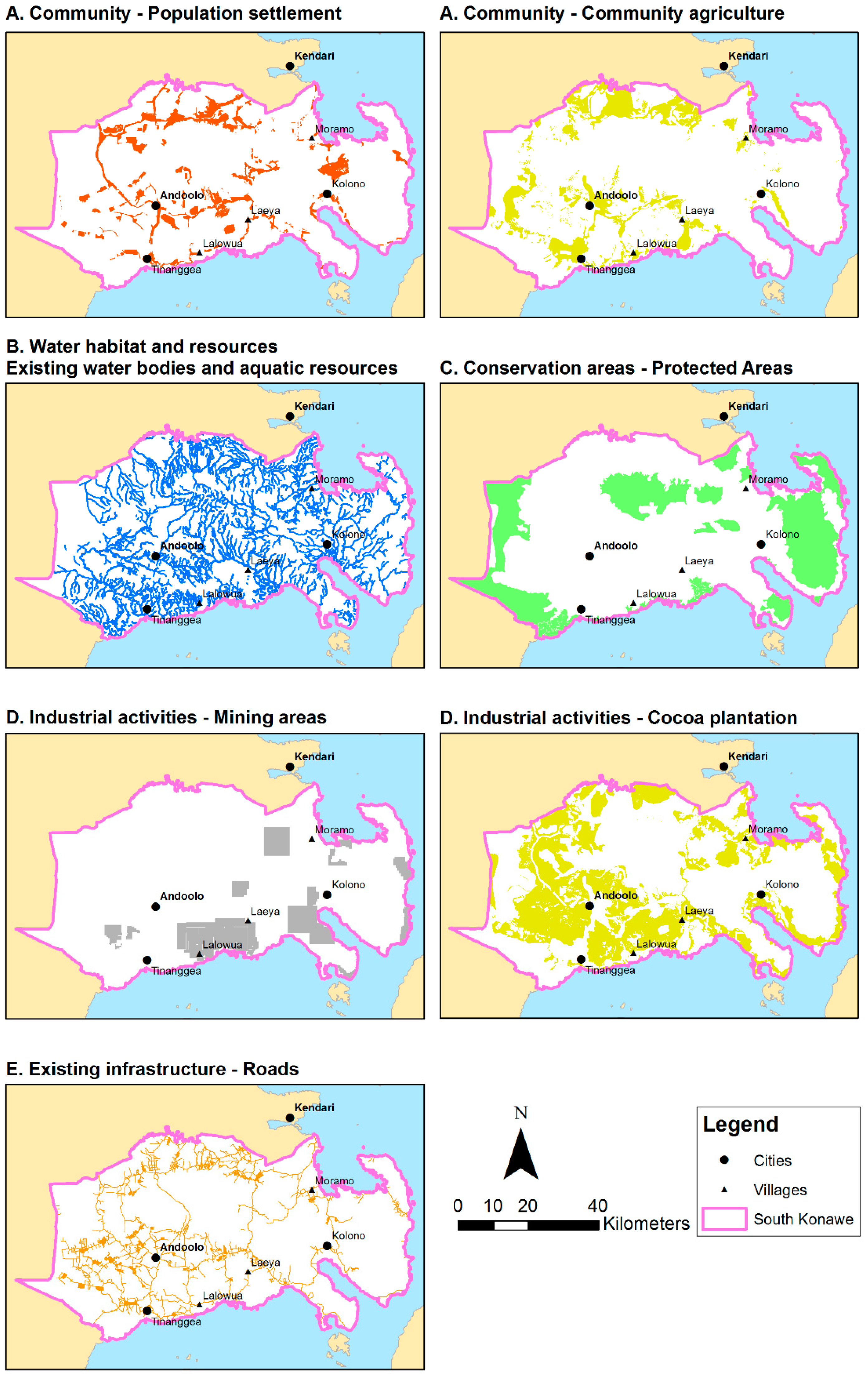

| Factor | Subfactor | Spatial Data Present | Orientation | Questionnaire Response | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| National | Local | ||||
| A. Community factors | Population settlements | Y | Positive | 4.3 | 4.8 |
| Community agriculture | Y | Positive | 3.5 | 4.4 | |
| Community forestry | N | Positive | 3.7 | 4.2 | |
| Community fishing areas | N | Positive | 3.2 | 4.0 | |
| Artisanal mining | N | Negative | 3.3 | 3.7 | |
| Social infrastructure | N | Positive | 4.0 | 4.7 | |
| Indigenous peoples | N | Negative | 4.3 | 4.0 | |
| Cultural heritage | N | Negative | 4.3 | 4.0 | |
| B. Water habitat and resources | Existing water bodies | Y | Negative | 4.3 | 4.7 |
| Aquatic resources | Y | Negative | 3.7 | 4.7 | |
| Community wells | N | Negative | 4.0 | 4.9 | |
| C. Conservation area | Protected areas | Y | Negative | 4.7 | 4.5 |
| Ecological zones | Y | Negative | 4.2 | 4.2 | |
| High biological diversity | Y | Negative | 4.5 | 4.4 | |
| Listed species | Y | Negative | 4.5 | 4.4 | |
| Wildlife corridors | N | Negative | 4.0 | 4.0 | |
| D. Industrial activities | Mining areas | Y | Positive | 4.2 | 4.3 |
| Palm oil | Y | Positive | 3.0 | 3.8 | |
| Cocoa plantation | Y | Positive | 2.7 | 4.1 | |
| Fishing zones | N | Positive | 3.2 | 4.1 | |
| Industrial estate | N | Positive | 3.5 | 4.3 | |
| E. Existing infrastructure | Sea-Ports | Y | Positive | 4.0 | 4.5 |
| Roads and bridges | Y | Negative | 4.2 | 4.8 | |
| Airports | Y | Positive | 4.0 | 4.0 | |
| Railways | N | Positive | 4.0 | 3.6 | |
| CWD Threshold | Resistance | Nat. Social | Topo. | Loc. Social | Loc. Topo. + Social | Nat. Topo. + Social |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50,000 m | Nat. Social | 100% | 47% | 70% | 61% | 68% |
| Topo. | 51% | 100% | 44% | 62% | 70% | |
| Loc.Social | 86% | 50% | 100% | 70% | 68% | |
| Loc. Topo. + Social | 75% | 71% | 71% | 100% | 91% | |
| Nat. Topo. + Social | 75% | 71% | 61% | 81% | 100% | |
| 100,000 m | Nat. Social | 100% | 67% | 73% | 69% | 79% |
| Topo. | 70% | 100% | 61% | 70% | 77% | |
| Loc. Social | 91% | 73% | 100% | 82% | 84% | |
| Loc. Topo. + Social | 89% | 87% | 84% | 100% | 97% | |
| Nat. Topo. + Social | 89% | 84% | 76% | 85% | 100% |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lechner, A.M.; Devi, B.; Schleger, A.; Brown, G.; McKenna, P.; Ali, S.H.; Rachmat, S.; Syukril, M.; Rogers, P. A Socio-Ecological Approach to GIS Least-Cost Modelling for Regional Mining Infrastructure Planning: A Case Study from South-East Sulawesi, Indonesia. Resources 2017, 6, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources6010007
Lechner AM, Devi B, Schleger A, Brown G, McKenna P, Ali SH, Rachmat S, Syukril M, Rogers P. A Socio-Ecological Approach to GIS Least-Cost Modelling for Regional Mining Infrastructure Planning: A Case Study from South-East Sulawesi, Indonesia. Resources. 2017; 6(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources6010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleLechner, Alex M., Bernadetta Devi, Ashlee Schleger, Greg Brown, Phill McKenna, Saleem H. Ali, Shanty Rachmat, Muhammad Syukril, and Paul Rogers. 2017. "A Socio-Ecological Approach to GIS Least-Cost Modelling for Regional Mining Infrastructure Planning: A Case Study from South-East Sulawesi, Indonesia" Resources 6, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources6010007
APA StyleLechner, A. M., Devi, B., Schleger, A., Brown, G., McKenna, P., Ali, S. H., Rachmat, S., Syukril, M., & Rogers, P. (2017). A Socio-Ecological Approach to GIS Least-Cost Modelling for Regional Mining Infrastructure Planning: A Case Study from South-East Sulawesi, Indonesia. Resources, 6(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources6010007