Abstract
In view of the increasing depletion of fossil fuel resources, the concept “bioeconomy” aims at the gradual replacement of fossil fuels by renewable feedstock. Seen as a comprehensive societal transition, the bioeconomy is a complex field that includes a variety of sectors, actors, and interests and is related to far-reaching changes in today’s production systems. While the objectives pursued—such as reducing dependence on fossil fuels, mitigating climate change, ensuring global food security, and increasing the industrial use of biogenic resources—are not generally contentious, there is fierce controversy over the possible pathways for achieving these objectives. Based on a thorough literature review, the article identifies major lines of conflict in the current discourse. Criticism of the prevalent concept refers mainly to the strong focus on technology, the lack of consideration given to alternative implementation pathways, the insufficient differentiation of underlying sustainability requirements, and the inadequate participation of societal stakeholders. Since today it cannot be predicted which pathway will be the most expedient—the one already being taken or one of the others proposed—this paper suggests pursuing a strategy of diversity concerning the approaches to shape the bioeconomy, the funding of research topics, and the involvement of stakeholders.
1. Introduction
The core idea of the bioeconomy, also referred to as the bio-based economy or the knowledge-based bioeconomy, is the replacement of non-renewable fossil fuel resources used in industrial production and for energy supply by renewable biogenic feedstock. This replacement should pave the way for a more sustainable, eco-efficient economy and help tackle global challenges such as food security, climate change, resource scarcity, and environmental pressure [1]. The Baltic Sea Region, the European Union (EU), the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the West Nordic Countries (Iceland, Greenland and Faroe Islands), Australia, Finland, France, Germany, Japan, Malaysia, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, and the United States already have dedicated bioeconomy strategies (see selection in Table 1). There are also regional strategies for the Canadian provinces of British Columbia, Alberta, and Ontario, Flanders, the German states of North Rhine-Westphalia and Baden-Württemberg, Scotland, and South Australia. For Turkey, Austria, Ireland, and Norway, bioeconomy strategies are currently under development. A study of the German Bioeconomy Council (BÖR) identified 37 further countries that have strategies devoted to certain facets of the bioeconomy, such as bioenergy, biotechnology, or a green or blue economy [2].

Table 1.
Selected bioeconomy strategies in chronological order by date of appearance.
All the bioeconomy strategies use their own definitions. A narrow interpretation is the definition of the OECD, which treats the bioeconomy as equivalent to biotechnology: “bioeconomy can be understood as a world in which biotechnology contributes to a considerable extent to the economic output” [3] (p. 8). In contrast, more holistic approaches such as the German policy strategy [4] understand the bioeconomy to be a comprehensive societal transition that involves a variety of industries such as agriculture, forestry, horticulture, fisheries, plant and animal breeding, food processing, the wood, paper, leather, textile, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries, as well as parts of the energy sector. With the help of new technologies (e.g., biorefineries) and advanced biotechnological conversion processes, plants, animals, microorganisms, and biogenic residues should be used to produce food, feed, materials, chemicals, and energy. The economic use of the human body in terms of organs, blood, stem cells, oocytes, and fetal tissues represents another understanding of bioeconomy, which is mainly the subject of philosophical discourse [5,6,7,8,9] and is of no significance for the political bioeconomy strategies. Biomass from agriculture and forestry is seen as the most essential resource for the bioeconomy. The use of animals, in contrast, is given only marginal mention, mostly with regard to the negative ecological effects of meat-dominated nutrition or the exploration of possible alternatives to animal protein.
There are several motivations stimulating countries to promote the development of the bioeconomy. The main drivers are the finiteness of fossil fuels and the expectation that crude oil will become more expensive in the future [10]. While there are different renewable alternatives for meeting the future energy demand, such as wind, solar energy, or water power, biomass is the unique carbon source for serving as a substitute for fossil fuels in chemical or material applications [11]. The replacement of fossil fuels by biogenic alternatives would mitigate global warming and help countries to meet their CO2 reduction targets. The use of clean, resource-efficient biotechnological conversion procedures would avoid the damage caused by classic petrochemistry and relieve the environment. A shift towards a bio-based economy is also expected to enhance the international competitiveness of domestic industries, create new jobs, and contribute to a revitalization of rural areas (e.g., [12,13]). In order to gain technological leadership, it is considered crucial to build networks between science, industry, and politics as well as interdisciplinary collaboration within science [14,15]. Although the bioeconomy implies a major transition that will revise today’s production patterns and product lines, a fundamental change to the prevailing economic system, or even a turn away from the growth paradigm, as is intended by concepts such as “degrowth” or the solidarity-based economy, is not a subject of bioeconomy strategies.
Besides the abovementioned motivations promoting the bioeconomy, which are more or less relevant in all political strategies, different countries have set varying priorities due to country-specific characteristics or strengths. The position paper for a bioeconomy in North Rhine-Westphalia, for example, emphasizes the importance of the health sector as a key field of action in view of the long tradition and spatial concentration of pharmaceutical companies in this region [16]. The Canadian regions focus on the forestry sector due to the high potential of their forest resources [17,18], and the West Nordic Countries push the use of oceans and marine ecosystems [19].
While there is a broad consensus about the objectives pursued by the bioeconomy, such as reducing the dependence on fossil fuels, increasing the industrial use of biogenic resources, mitigating climate change, and ensuring food security, there is fierce controversy over the different pathways for achieving these objectives. The aim of the present article is a survey of the available literature according to three research questions: Which are the key issues of the current debate on shaping the bioeconomy? Are there different views regarding these issues? If yes, which are consensus points and where are the major points of conflict? The paper mainly represents the European debate. Due to the fact that Europe is highly dependent on imported fossil fuels but can make use of a wide range of technological approaches and know-how on biomass utilization, the concept of the bioeconomy seems very promising in order to reach autonomy in raw material supply. However, domestic biomass potentials are quite limited, which raises various questions about how to shape the bioeconomy.
2. Methodological Approach
To analyze the current bioeconomy discourse, a thorough literature review was carried out, which was primarily based on a survey of scientific articles but supplemented by the inclusion of political strategies and opinion papers of civil society organizations. Relevant articles to be incorporated in the analysis of the scientific discourse were identified by scanning the databases Scopus and Web of Science for peer-reviewed literature. The search was based on different uses of the term bioeconomy (e.g., bio-based economy, knowledge-based bioeconomy), and different spellings created by hyphens and disjunction (e.g., bio-economy, bioeconomy) in English and German, and was related to the occurrence of the terms in the title, abstract, and keywords of articles. If the number of results was too large to permit screening of the abstracts, catchword combinations were used in order to narrow down the results. The selection of catchwords was based on a collection of terms that were identified during an initial review of relevant literature. Examples are: biomass, bioenergy, biotechnolog*, life science, agricultur*, agro, innovation, technolog*, governance, policy, and sustainab*. In order to not prematurely rule out articles, no limitations were set on the timespan or research domain. Papers of a purely technical nature were subsequently excluded by hand. Based on the abstracts, 220 articles were identified that appeared to be potentially of interest, including editorials and conference proceedings. Starting from this basic stock, 65 contributions were selected for further analysis in the course of the study. The majority of these papers were published between 2011 and 2015.
In addition to the scientific literature, political strategies at an international level and reports from civil society organizations were gathered in order to gain insight into the societal discourse. For this purpose, a web search was carried out and the references to the literature contained in overview articles and relevant reports were used. During the inquiry, it soon became clear that alongside the immediate debate on the bioeconomy there are numerous other related discourses that are likewise relevant in the context of the bio-based economy, such as sustainable land use, technological development in agriculture, dietary trends, sustainable consumption, and a circular economy. Therefore, literature on these topics was included. This did not follow a bibliometric approach, but was mainly based upon the authors’ previous research. According to the major lines of discussion, thematic clusters were built (e.g., pathways of biomass supply, perspectives on nature, sustainable consumption, participation). The relevant literature was analyzed pursuant to these categories by identifying diverging positions and assigning statements of the articles to certain lines of argumentation. Points of consensus and opposing views were clustered for each topic. Figure 1 illustrates the single steps of the research framework, which also defines the structure of the paper.
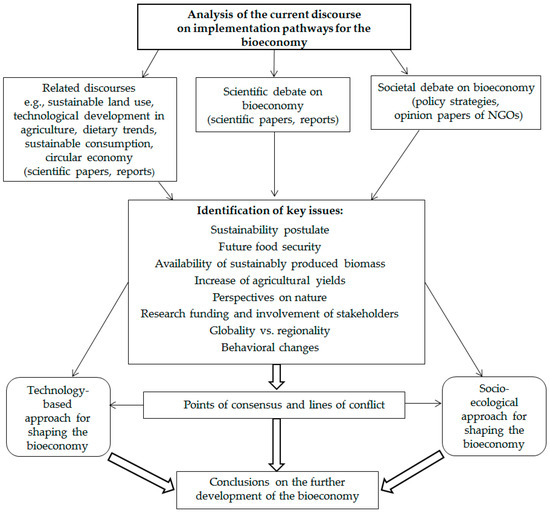
Figure 1.
Research framework.
3. Main Controversies Concerning the Design of the Bioeconomy
There has been considerable criticism of the conceptualization of the bioeconomy, at least of the dominant political agenda, which can be attributed to different topics. In the following sections, the key issues of the current discourse are presented.
3.1. Understanding of the Sustainability Postulate
It is uncontested that the bioeconomy should contribute to a more sustainable future, but the term sustainability is understood differently and the sustainability requirements are often not clearly specified. The positions taken can be roughly divided into three groups: (1) those that consider sustainability an implicit result of a bioeconomy; (2) those that argue that the bioeconomy will only contribute to sustainability if certain preconditions are met; and (3) those that reason that beneficial impacts might be possible, but adverse impacts are likely to prevail (based on Pfau et al., who defined four groups [20]).
Those who consider sustainability to be a quasi-automatic result of a transition to the bioeconomy base their conviction on the intended replacement of non-renewable resources by renewable ones. So, the bioeconomy follows one of the central principles that Daly had already established in 1990 as one of the five management rules for environmental sustainability [21]. The use of biogenic feedstock will mitigate climate change since only that amount of CO2 is emitted that plants have previously absorbed from the atmosphere during their growth; the bioeconomy is thus seen as being climate-neutral. It uses environmentally friendly biotechnological conversion procedures, offers greater energy security by reducing the dependence on fossil fuels, and contributes to job creation and economic development [22,23,24,25,26].
The second group of authors welcomes a structural remodeling of the production base in principle, but argues that this change will only lead to a more sustainable future if certain preconditions are met [27,28,29,30]. A multitude of criteria and indicators for a sustainable bioeconomy have been developed in recent years (inter alia, [28,31,32]). Most of these criteria relate to the stage of biomass production and supply and are based on the already long-standing discourse on criteria for a sustainable agriculture. Different sets of principles, criteria, and indicators for specific types of feedstock have been developed in multi-stakeholder initiatives, such as the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil, the Roundtable Responsible Soy, Bonsucre (for sugar cane) and the Roundtable Biomaterials, in order to provide the basis for certification schemes [11]. However, an internationally agreed set of criteria for a sustainable bioeconomy still does not exist.
The third group of authors has a rather negative attitude towards a bioeconomy. Although they do not deny that the intended transformation could also have positive effects for a sustainable development, they believe that the negative impacts on environment and society will prevail. One of the most serious objections results from the conviction that the available biomass will be insufficient to meet the demand if food security and the maintenance of environmental capital and ecosystem services are given priority. Therefore, they expect that land use competition between food production and energy cropping will become exacerbated, that the scarcity of resources such as water and phosphorus will be intensified, that the conversion of primary forests, species-rich grassland, or wetlands into agricultural land will continue, that monocultures and the loss of biodiversity will increase, and that this development will be detrimental to indigenous people and small farmers in the developing world [33,34,35,36,37].
Since 2009, both the EU Renewable Energy Directive (2009/28/EC) [38] and the EU Fuel Quality Directive (2009/30/EC) [39] include mandatory ecological sustainability criteria for biomass feedstock to be used for conversion into biofuels and other bioliquids. These provisions require that the greenhouse gas reduction resulting from the use of biofuels and bioliquids must be at least 35% compared to the fossil fuel reference; from 2017 onwards, this saving must be at least 50% and from 2018 onwards at least 60%. Furthermore, land with high carbon stock (e.g., wetlands, peatlands) or areas of high biodiversity (e.g., primary forests, nature reserves, and species-rich grasslands) may not be utilized for the cultivation of biomass feedstocks, regardless of whether it takes place inside or outside the European Community. With regard to solid and gaseous biomass feedstocks, there are only recommendations formulated by the European Commission, which are adopted by the EU member states on a voluntary basis [40].
It has to be emphasized that the selection of criteria and the determination of the limits to be observed have a significant impact on the biomass potential that can be produced sustainably. The EU criteria are related to the potential of biofuels to contribute to greenhouse gas reduction and the avoidance of direct land use changes (LUC). The further inclusion of even stricter criteria would significantly reduce the available biomass potential. Elbersen et al. illustrate this interrelationship with reference to two scenarios [29]. The reference scenario was based on the EU’s current legal framework (50% reduction of greenhouse gas emissions compared to the fossil fuel reference, no biomass cropping on soils with high biodiversity or high carbon stock). The sustainability scenario applied a significantly higher greenhouse gas mitigation rate of 70% and broadened this requirement to include emissions from indirect land use change (iLUC). Furthermore, stricter conditions for the use of land with high biodiversity or high carbon stock were applied, such as a ban of the cultivation of energy crops on fallow land and extensively managed farmland. In addition, sustainability criteria—up to now only applied to biofuels and bioliquids—were extended to solid and gaseous bioenergy, used for the generation of heat and electricity. On this basis, the study estimated the available biomass potential in Europe for each scenario. The results showed that the available biomass potential in the sustainability scenario is 32% lower than in the reference scenario.
3.2. The Role of Future Food Security
There is a broad—though not always explicitly expressed—consensus that global food security, specifically the supply of sufficient, nutritious, healthy, and safe food for a growing world population, must be given priority over all other pathways for utilizing biomass. Food security, measured by the criteria of availability, accessibility, and usability, must be guaranteed not only for all people of the present generation, but also for those in future generations. This means that the social, economic, and environmental preconditions for generating future food security should not be compromised by today’s economy [41]. According to the Sustainable Development Commission (SDC) of the United Kingdom, a sustainable food system should respect the limits of the planet’s resources and address the various types of environmental impact, like greenhouse gas emissions, climate change, biodiversity loss, water scarcity, land use competition, and waste, as well as other productive assets on which food depends. It should contribute to human health by preventing food-related diseases, and embody social values such as fairness and animal welfare [42]. The acceptance of the ‘food first’ principle limits the operating space of the bioeconomy and has far-reaching implications.
In the coming decades, the food supply will be exposed to increasing pressure, both on the demand side because of global population growth, rising prosperity, progressing urbanization, and changing dietary patterns (increased consumption of dairy and meat products) and on the supply side due to climate change and growing competition for scarce inputs [43,44,45]. Against this background, some authors conclude that the best and most productive soils must be reserved for food production. However, since energy plants, especially those for the production of first-generation biofuels (maize, canola, soybean, sugarcane, sunflower), develop only on good soil, land use conflicts, the risk of indirect land use change, and competition regarding freshwater resources cannot be excluded [46,47]. Second-generation feedstocks do not place such strict requirements on soil quality, but can significantly limit the availability of water for the production of food crops. Miscanthus giganteus, for example, has double the water footprint of maize or sugarcane, but a smaller one than soybeans [36,48]. There are also voices that doubt that the cultivation of non-food crops is an appropriate way to avoid land use conflicts. Carus and Dammer instead advocate the cultivation of additional food crops that are grown according to the criteria of sustainable agriculture, provide high yields per hectare, whose ingredients can be efficiently converted into biogenic products using the existing technologies, and that may—in case of food shortages—also be used for nutrition [49].
There have been proposals that land that is unsuitable for growing food, i.e., that is idle, fallow, marginal, degraded, or abandoned, should mainly be used for the production of energy crops [37,50]. Marginal soils are often characterized by a combination of geophysical constraints (insufficient soil quality, high risk of erosion, unreliable water supply) and socioeconomic deficits (scarcity of labor, uncertain land tenure, limited infrastructure, poor market accessibility). Despite its low value for food cropping, marginal land often exhibits high biodiversity and provides vital ecosystem services, particularly in intensively farmed areas. This includes soil formation, carbon sequestration, nutrient recycling, genetic diversity, pest and weed suppression, chemical detoxification, water storage, groundwater filtration and purification, flood control, regulation of microclimates, and refuges for wildlife [36,44,51,52]. A conversion of these habitats into monocultures to produce biomass would diminish their capacity to provide the services outlined above. If this capacity should be maintained, alternative environmentally sound methods of cultivation for biomass cropping, such as low-input, high-diversity polycultures, are needed for the production of biomass [36,47].
A further option for avoiding land use conflicts is the use of residual and waste materials such as the non-edible parts of food crops, timber and forest residues, agricultural byproducts, and biogenic municipal or industrial waste [20,53]. However, it should be noted that most of the current biogenic residues and waste streams are already being used and that the volume of those not yet used is likely to be far more limited than commonly believed [27,54]. This means that the “food first” principle will not be easy to realize without provoking other conflicts. This fact is not being sufficiently taken into account in the current debate. Instead, the prevailing agenda of the bioeconomy suggests that all targets can be met simultaneously.
3.3. Availability of Sustainably Produced Biomass
Another important and contested issue is the question of if or to what extent the attainable potential of sustainably produced biomass will be sufficient to substitute the global demand for fossil fuels. Reliable information about the quantities of biogenic feedstock currently available, their spatial distribution, and their availability over time is still lacking. In recent years numerous studies that estimate the possible global supply of biomass for energetic and material use have been carried out (e.g., [55,56,57]). However, due to the use of different methods of calculation and a broad variety of underlying assumptions, they come to quite divergent results, ranging from less than 50 to several hundred exajoules (EJ) per year on a global level [58].
Various authors have reviewed the analytical steps and assumptions made in the available studies on biomass potentials (e.g., [54,59,60,61]). They identified several key factors that have a significant impact on the results, such as future productivity in agricultural production, water limitations, amount of degraded and marginal land incorporated in the calculations, nature conservation and biodiversity requirements, population growth and food demand, expectations about dietary trends, and the development of alternative sources of protein that shift consumption away from animal products. The key factors also include agricultural commodity prices and the cost of biomass production, political instabilities in producer countries, the availability of biogenic residues and wastes, and competing uses [54,59,61]. The effects of different assumptions about these factors are well illustrated by Dornburg et al. [54].
According to some studies, the available biomass potential would be sufficient to satisfy the total global energy demand or at least a significant share of it, even if only land not required for food production is used to grow biomass (see [54]). Other, more recent, studies arrive at much lower figures (e.g., [62]). Based on this fact, Lewandowski supposes that the available biomass potential has often been overestimated because social, technical, and economic constraints, such as post-harvest losses, deficits in the supply chain, lacking infrastructure or poor market access, were ignored [11]. Many authors would apply a top-down-approach, starting from the largest—the theoretical biomass potential—and assuming ideal production conditions, like intensive crop management and high biomass yields. To get a more realistic picture of the available resources, Lewandowski advocates a bottom-up-approach that takes all the limiting factors into account. There is broad consensus that sound information on the attainable biomass potential is an essential prerequisite to shape the bioeconomy. Thus, different authors call for a binding international agreement on methodological standardization covering at least some minimum requirements, such as transparency of the assumptions, specifications on data collection, and regular updating of the existing data [54,56,58,60,63].
Total global energy demand currently amounts to approximately 550 EJ/yr [58] and is expected to rise by nearly one-third between 2013 and 2040 due to economic growth in non-OECD countries [64]. The global energy supply is still based on fossil fuels, which account for approximately 500 EJ per year, while biomass contributes approximately 50 EJ [65]. Against this background, it seems doubtful that a complete substitution of fossil fuels by biogenic alternatives will be possible, especially if food security is given priority and strict sustainability criteria have to be met. Even if there are some untapped potentials, mainly in Africa, Asia, and South America [61,62], biomass remains a scarce resource and different options for utilization should be balanced carefully. It should be in the public interest to direct biogenic raw materials to the uses most preferable for society in order to avoid misallocations [28].
Both exponents of a technology-based approach for shaping the bioeconomy and supporters of alternative routes call for the reuse and recycling of materials and the use of waste-streams. However, the views differ significantly. Proponents of a technology-based approach believe that technological progress and increased efficiency in the use of biomass will solve the problem of resource scarcity in the long run, without any need to change the prevailing production patterns. In contrast, supporters of alternative routes argue in favor of a circular economy that embodies the cascading approach. This approach would significantly reduce the demand for new resources but require fundamental changes in product design, including the entire life cycle of a product from cradle to cradle. Cascading means to feed biomass first into the production with the highest societal value, which likely coincides with the highest economic value, then in descending order into the second-best option and so on, until it is “lost by burning” at the very end of its life cycle [23,28,58,66,67]. In addition to the positive climate effects, the implementation of this principle would increase the total availability of biogenic resources as each unit of raw material might be used several times. This concept is linked to the demand for durable material goods, which in turn requires a product design that allows for the possibility of the repair, replacement of components, and the reuse of raw materials. The higher the number of cycles of repair, upgrading, reuse, and remanufacturing, the lower the ecological footprint of a product. At the same time, the longer the period of each cycle, the fewer resources are needed to create new products [28].
Given the scarcity of biogenic feedstock, the current practice in the EU of using a significant share of biomass for energy, which is mainly driven by the Renewable Energy Directive’s targets for bioenergy 2020 and the national targets based on them, is viewed rather critically today. Many experts agree that decision makers should give priority to the material use of biomass, rather than creating framework conditions that increase the overall demand for biomass and encourage competition for feedstock between material and energetic use [14,27,58,67]. The German Bioeconomy Council also advocates a revision of the funding schemes for bioenergy at the EU and national levels, especially because other renewable energy sources (wind, solar, water power) are available that have a higher long-term potential and lower risk. In the Council’s view, financial incentives for bioenergy hinder the most efficient use of biomass and undermine the competitiveness of food and biogenic industrial commodities [68].
Some experts argue that the EU’s waste hierarchy, with prevention of waste at the top and incineration as the last option, already guarantees the implementation of the cascade principle. However, this reading ignores the fact that the waste hierarchy only enters into play when a product has become waste, not before. This creates the paradoxical situation that, instead of making bio-based products, current incentives direct biomass to energetic use. Only when biomass is turned into a biogenic product that reaches the end of its life cycle does combustion become the least preferred option [28,66]. Besides the current European framework conditions, there are a number of other barriers that hinder the implementation of the cascading approach. This includes logistic and financial restrictions, the lower technical quality of recycled products, the lack of economic incentives for the use of secondary materials, an inadequate infrastructure for repairing products and for their second-hand use, and a lack of information and awareness about resource scarcity among consumers [28,66,67].
3.4. Routes to Increase Agricultural Yields
Given a projected global population growth to 9.3 billion in 2050, changing consumption patterns towards calorie-rich diets, and an increased demand for biogenic raw materials, agricultural productivity needs to increase. Since the early 1960s, advances in agricultural science, success in breeding, the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, irrigation, and the use of new technologies have made possible a significant gain in productivity all over the world. However, this boom has been accompanied by a high consumption of resources and serious environmental impacts in terms of greenhouse gas emissions, soil and groundwater pollution, scarcity of freshwater, and a loss of biodiversity. Considering its adverse impacts, it becomes more and more doubtful whether the continuation of the prevailing model of industrial intensive agriculture is still acceptable and useful [69]. However, the question of how much and what kind of growth is needed to cover the rising demand and to ensure food security remains controversial.
An increase in agricultural production by expanding the cultivated area is generally seen as impossible without jeopardizing the last remaining natural habitats and the ecosystem services they provide [43,70,71]. It is, on the contrary, expected that the existing amount of fertile soil will shrink in the course of coming decades due to global environmental changes, including climate change, progressive desertification, land degradation, water scarcity, declining biodiversity, and the extended use of land for settlement and transportation [43,72]. In order to achieve the indispensable increase in agricultural yield, many experts advocate a new and different management of agricultural ecosystems. This includes reducing harmful external inputs, promoting nutrient recycling, optimizing energy flows, using natural mechanisms of pest control, and thus creating structures that improve the resilience of the system and maintain its long-term productivity [44,51,69,73].
One important instrument of this new management is the concept of sustainable intensification, which means gaining more yield per hectare while minimizing environmental damage and maintaining soil fertility [71,74]. According to the relevant literature, sustainable intensification does not mean that production will be increased unrestrictedly in all agricultural regions. In certain regions, it may be desirable to dispense with yield increases and remove valuable habitats or unproductive agricultural land completely from cultivation in order to maintain their ability to provide ecosystem services [43]. If yields are already well above their sustainability thresholds, which is the case in many European growing areas, some experts even suggest a strategy of sustainable extensification, which may imply a reduction of yield until the balance with the agro-ecosystem carrying capacity is restored [28,70,75].
In the view of the Royal Society, the concept of sustainable intensification includes all farming and agricultural techniques that serve the twin aims of increasing yields and improving environmental performance; no techniques or technologies should be ruled out for ideological reasons [71]. Meanwhile, two opposing pathways of sustainable intensification have emerged: a high-tech strategy and an agro-ecological strategy [76]. The high-tech strategy focuses on improving the efficiency of external inputs, scientific progress in the field of plant breeding and genetic engineering, faster adoption of new agricultural techniques by farmers, and removal of trade barriers. One prominent approach to increase the efficiency of external inputs is precision farming. This is a new management system in crop production, striving for a site- and fruit-specific application of irrigation, seed, fertilizers, herbicides, and pesticides. The aim is to apply the right treatment in the right place at the right time, taking into account the local variations of soil and crop [77]. Precision farming is partly supported by digital techniques, such as satellite-based application systems, geographic information systems, yield mapping, sensor technologies, GPS navigation, remote sensing, and computer-assisted decision-support systems for farmers.
Also, genetic engineering plays a significant role in the high-tech strategy for sustainable intensification. The genetic code of plants should be modified in order to enhance their productivity in adverse conditions, e.g., those caused by diseases, pests, drought, and saline or infertile soils, or to meet new requirements such as for optimized nutritional contents. The protagonists of this strategy argue that the cultivation of GM crops protects the environment by reducing the need for mechanical tillage and pesticide use, increases yield, and permits an eco-efficient agriculture, which is able to ensure global food security [46,73]. Critics of genetic engineering fear environmental risks due to certain features of genetically optimized plants (novel crops) like reduced habitat preferences and pest resistance [37,78,79,80,81]. The main risks are seen in the possible invasion and introgression of GM-plants into natural ecosystems, the ingestion of toxic substances by humans and animals, allergic reactions to ingredients, or the introduction of new pests.
In contrast, the agro-ecological road to sustainable intensification strives to overcome industrial intensive agriculture, which makes farmers dependent on external inputs, ignores their tacit knowledge, and dissociates consumers from production. In focus are closed cycles, the use of farmers’ knowledge about plant species and their management, shorter supply chains, a relocation of production and consumption, and the creation of product identities by certification. External inputs like energy, inorganic fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation should be replaced by including supportive ecosystem services in agricultural practices. This encompasses regulating processes such as nutrient cycling, water retention, nitrogen fixation (for example, via the cultivation of legumes), soil regeneration, crop pollination, ecological pests, weeds, and disease regulation [51,76]. These natural processes are supported by agricultural techniques like reduced tillage, use of green manure, cover-cropping, diversified crop rotation including perennial grasses and legumes, intercropping, polyculture cropping, and agro-forest systems [44,51,82,83,84]. Hedgerows and riparian buffer strips should prevent rapid rainwater runoff and soil erosion. Biological pest control avoids the application of synthetic pesticides by using the landscape-specific variety of natural enemies, whose presence is favored by certain agricultural techniques such as diversified crop rotation and intercropping [51]. Biological weed control will replace the application of chemical herbicides by natural plant ingredients (allelochemicals), which suppress the germination and growth of weeds [84]. Genetic engineering is rejected completely.
A common objection to agro-ecological farming is that yields per hectare are often lower than in conventional farming. More arable land would be needed in order to ensure food security, which in turn would lead to a loss of natural habitats. Various comparative studies show that yield differences do exist, but that they are highly contextual and hard to generalize. As a rule of thumb, one can assume that the yields of agro-ecological cultivation may be 15% to 20% lower than yields of high-performance agriculture in industrial countries, while they can be 10% to 80% higher compared to the yields of locally prevalent low-input systems in developing countries [44,69,77,85]. There is abundant evidence that food security and living conditions of smallholders in resource-poor rural environments in developing countries can be significantly improved by applying agro-ecological approaches in participatory processes of co-development and learning to build natural, human, and social capital simultaneously [69]. However, regarding the three major global staple foods (rice, wheat, and maize) a drop in yields cannot be completely excluded. That is why most proponents of an agro-ecological strategy advocate accompanying political measures, such as a reduction in food waste and a change in nutrition patterns towards the consumption of fewer animal products [43,51,69].
It should be noted that the degree of intervention in each of the two roads to sustainable intensification is rather different. While the high-tech strategy can be seen more or less as a correction and completion of conventional intensive farming, the agro-ecological strategy implies a radical shift away from the prevailing model and a transition to a knowledge-based, site-sensitive agriculture, in which insights from scientific research and the tacit knowledge of local farmers play an equally important role. Given the great diversity of existing European farming systems, the Strategic Implementation Plan of the European Partnership for Agricultural Productivity and Sustainability (EIP) pleads for a combination of both pathways, depending on the conditions of the respective site [86].
3.5. Perspectives on Nature
Compared to its original meaning, the currently prevailing understanding of bioeconomy has undergone major changes. Nicholas Georgescu-Roegen, considered a pioneer of bioeconomy, called in his 1971 book The Entropy Law and the Economic Process [87] for a new economic model that will be compatible with the biophysical limits of the planet. In his concept nature is seen as the limiting factor for economic activities on the one hand, and on the other hand as a paragon for improving the functionality of economic systems [87]. This early understanding of an “ecologization of the economy” has been reversed by present bioeconomists [88]. Instead of adapting industrial material flows to natural metabolic cycles, nature should be manipulated and optimized to fit economic purposes. Critics regard today’s bioeconomy as “economization of ecology”, “neo-liberalisation of nature”, or “biocapitalism” (see [5,35,76,89,90,91]).
The technical view of nature implies the presumption that natural ecosystems can be partially or even entirely replaced by human artifacts. Proponents of this position argue in favor of methods to produce biomass under controlled technological conditions. This includes approaches like indoor crop production in high-rise buildings (vertical farming) or site-independent breeding of algae in bio-reactors. Other important technologies are synthetic biology, which pursues the development of biological systems with new properties in the laboratory [92], and metabolic engineering, which refers to the production of desired chemical compounds by intervention in the metabolism of organisms (e.g., [93,94]). For these approaches the metaphor of a cell factory or micro-biological factory has become established (among others, [95]). Some of these technologies are still dependent on naturally grown raw materials, such as lignocellulose and sugary plants, while others are aligned to a complete replacement of the natural precursors. In this philosophy resource scarcity is seen as a result of deficiencies in resource productivity, rather than as a result of the inherent limits of the biosphere. Correspondingly, the productivity of ecosystems should be improved by biotechnological manipulations. Supporters of this approach stress that the technological options will increase the availability of biogenic feedstock, reduce the need for external inputs, and lower environmental burdens. Possible fields of application are genetically modified cows, which produce milk with increased protein content, plants with higher tolerance to water stress and soil contamination, or fish with resistance to diseases in fish farms [95].
In contrast, supporters of an ecologization of economy favor a cyclical use of resources that follows the metabolic cycles of nature (the cradle-to-cradle principle). Human economy should be integrated in the systemic interrelationships of nature. A sparing and responsible use of scarce biogenic feedstock, the prevention of waste, and the reuse of raw materials in succeeding cascades (see Section 3.3) are the guiding principles in this concept. According to Gottwald, the preservation of the natural living conditions of as many animal and plant species as possible will meet basic human needs as well as economic interests [37]. The variety of living forms concerning both biodiversity as well as cultural diversity is considered a key element for the viability of modern societies and the guarantee of livelihood for future generations. Defenders of traditional cultivation methods of biomass further emphasize the social value and the multiple environmental and sociocultural services provided by agriculture, which cannot be furnished by new biotechnological approaches that are carried out in isolatation from nature [37].
3.6. Priority Setting in Research Funding and Involvement of Stakeholders
There is a broad consensus that research funding is an important tool for stimulating the bioeconomy, but the discussion of which research areas and what type of knowledge should be promoted is highly controversial. The dominant political agenda builds on progress in the life sciences to ensure an efficient use of biomass and to produce high value added bio-based products [96]. The main objectives are a close alignment of policy, science, and industry, global value chains, improved competitiveness, and the granting of international patents (see e.g., [97]). Public–private partnerships and the creation of technological clusters are given high priority. Critics complain that the original variety of possible implementation pathways for the bioeconomy has been limited to technical solutions from the very beginning, including socially strongly contested technologies such as genetic engineering and synthetic biology (e.g., [98]). According to the critics, the prevailing vision represents only certain interests and not society as a whole, and excludes alternative pathways right from the start [76,99,100]. While funding is strongly focused on the life sciences, little attention is paid to other areas of research, such as agro-ecological farming, breeding of alternative crops for marginal sites, or social innovations [14,35]. Referring to various examples of smallholder agriculture in developing countries, Grefe calls for a broad understanding of innovation. In her view, even in a peasant rural environment, innovations are taking place (e.g., mutual learning, joint marketing activities) that focus on the conservation of native plant species and traditional cultivation methods [88] (p. 237). This includes a wide variety of locally adapted solutions, whose development and dissemination depend strongly on social interactions. Social innovations are also attributed a key role with regard to the promotion of sustainable consumption patterns [101,102]. The social sciences are generally perceived as under-represented in bioeconomy research, and more interdisciplinary research is claimed [103,104,105].
The setting of priorities in research funding is closely linked to the question of what kind of stakeholders should be involved in shaping the bioeconomy. The dominant political agenda highlights the importance of enhanced cooperation between policy, science, and industry. Critics assume that these three players have negotiated much behind closed doors, while the participation of societal groups and the general public has been insufficient and unsystematic [1,34]. Although the German research strategy states that a “dialog with the public” is important [97], the issue of how and for what purpose this should take place is still unresolved. It is supposed that this dialogue will serve to create acceptance for priorities that have already been set rather than to reach real democratic participation and active involvement in shaping the bioeconomy [106,107]. Since the German strategy, like many others, is purely a governmental initiative, the possibility of control and intervention by Parliament is deemed to be insufficient as well [108].
The equal distribution of powers and the establishment of a “bioeconomy democracy” are seen as crucial success factors for a comprehensive societal transition to the bioeconomy [88]. It is important to clarify which implementation pathway society wants to promote, whether the effort should be focused on a particular research area or whether different research subjects should be encouraged, and which stakeholders should be involved in the decision-making process and with regard to which issues. According to McCormick, a combination of consumer information that informs on the advantages of bio-based products and possibilities for participation by citizens and civil society organizations in the implementation process should be provided [109]. There are different proposals for achieving successful participation, such as the creation of transparency and equal levels of knowledge, building trust between stakeholders, a willingness to critically reflect opposing positions, and early conflict management (e.g., [34,110]). However, these approaches have not been implemented in the context of the bioeconomy up to now.
3.7. Globality versus Regionality
Another controversy concerns the question of whether the spatial perspective of the bioeconomy should be regional or global. In a global perspective, which is currently the main orientation within most political bioeconomy strategies, industrialized countries claim the technology leadership and see other countries as feedstock suppliers on the one hand and markets for the produced bio-based products and the developed technologies on the other hand [3,22,97]. Due to the fact that the domestic biomass potential that can be mobilized in Germany and Europe will not be sufficient to meet demand, industrial players have built on the import of cheap biomass from abroad (e.g., [111,112]). Sixty-five percent of the cropland satisfying EU consumption is located in other world regions, primarily in Asia, including China, Indonesia, and Thailand [113]. One can anticipate that the increased demand for biomass in industrialized countries will continue the process of land acquisition by foreign companies in developing countries (so-called land grabbing). Experiences from the past have shown that this practice can have negative environmental and social consequences, mainly on subsistence farmers with uncertain rights to land access. Studies have further revealed that the development of human capital and democratic institutions in the countries concerned is delayed compared to countries with established smallholder structures [114]. There is broad agreement that land investments, whether by private or public organizations, can also have positive effects on the economic and social situation of the local population if certain preconditions are met. Therefore, many authors call for a mandatory, globally valid sustainability certification procedure for biomass production that takes ecological, economic, and social aspects into account. Existing schemes should be continuously updated [14,32]. In addition, measures to improve the situation of smallholders, such as capacity building, the opening of markets for their products, and the establishment of formal land tenure systems, are considered necessary.
In contrast, the regional perspective relies on site-specific solutions, based on flexible, regional networks with largely closed cycles, a regional supply of food and renewable energy, and an orientation towards autarchy [35]. This philosophy is based on the thesis that innovation always includes a social and a cultural component that evolves primarily at the regional level. Regions accommodate a critical mass of scientists, companies, and sponsors, and short distances facilitate the establishment of communication structures [14,115]. Each region has specific strengths that can mobilize particular innovation potential. Examples are Silicon Valley and also trans-regional arrangements, like the so-called bio-based Delta in South Holland, where the regions of Zeeland, Zuid-Holland, and Brabant jointly foster a bio-based economy [109,115]. In addition to the favorable conditions of cooperation, the entire use of biomass, structures for recycling, and the recovery of waste can be optimized more easily in a regional context. This in turn would reduce the demand for raw materials. Furthermore, the objectives of the bioeconomy can be specified and monitored better at the regional than at the global level [109].
The Finnish strategy strives for a middle way and introduces the term “glocal solutions”, which means that the local and global levels need to be interlinked [116]. Kircher highlights that the regional level has limitations too and that the global level is important to facilitate exchange between innovation clusters specialized in certain areas, such as industrial biotechnology in Germany or the palm oil industry in Malaysia [115]. In his opinion, progress towards a bioeconomy could only be accelerated by sharing knowledge with clusters from other countries.
The tension between globality and regionality is also reflected in the question of whether large- or small-scale facilities, and centralized or decentralized solutions, should be pursued. According to the prevailing opinion, bio-refineries, as a prime example of the bioeconomy, should be planned as large-scale facilities with a throughput of several million tons of biomass per year in order to benefit from economies of scale (e.g., [58]). Plants of this size could only be economically operated at a couple of sites in order to keep the transportation costs of biomass (a feedstock with rather low energy content compared to the fossil fuel reference) within reasonable limits. This includes large ports (e.g., Hamburg, Rotterdam, and Antwerp) where an import of cheap biomass from abroad is possible or regions with huge untapped biomass potentials like Russia, Finland, or Sweden. Instead of large-scale technologies, some authors advocate decentralized, smaller, and specialized bio-refineries that are tailored to the respective regional biomass supply and produce high-value products, such as fine chemicals [24,27,58]. If raw materials are processed locally, the added value remains in the region, transport costs are minimized, and new jobs are created in the rural area.
3.8. The Role of Behavioral Changes
Current attempts to advance the bioeconomy are focused on increasing the efficiency of biomass production and use, while changes in consumer behavior hardly matter. Only a few policy strategies (e.g., Germany [4], and Sweden [117]) include sustainable consumption as a relevant part of the transition process. Critics suppose that the bioeconomy in its prevailing technology-based understanding will reinforce the excessive consumption of resources and represents the exact opposite of alternative growth paradigms [90,118]. In their view, a societal transition towards a bioeconomy can only provide sustainable solutions to global challenges if it also includes changes in consumer behavior (e.g., [90,100]).
The importance of behavioral changes towards sparing and responsible handling of goods and the prevention of waste can be illustrated by the example of nutrition. It is estimated that roughly one-third of the food produced for human nutrition gets lost globally, which amounts to approximately 1.3 billion tons per year [119]. Thus, a reduction in food waste would be equally important for meeting the future food demand as an increase in agricultural yields [43,51,69,120]. In low-income countries, food is mainly lost during the early stages of the supply chain as a result of limited harvesting and storing techniques, while in industrialized countries food is mainly lost at the consumption stage due to consumer behavior. On a per capita basis, much more food is wasted in industrialized than in developing countries. The avoidance of food waste would result in considerable savings of resources in terms of land, water, energy, and labor. According to calculations by Noleppa and von Witzke, 1.2 million hectares of arable land could be saved by halving the avoidable food waste in Germany [121]. The freed-up farmland could be made available for other uses, such as cropping of biomass for material or energetic purposes. Complementary to the saving of resources, an efficient handling of food would reduce agricultural emissions.
A further example of the importance of consumer behavior to the availability of biomass is a change in dietary patterns. Due to increasing prosperity in developing countries, the per capita caloric intake from animal-based products is set to rise by 40% by midcentury [122]. The production of meat and dairy products requires significantly more resources than the production of grain-based food [123,124]. Livestock farming occupies 70% of global farmland and 30% of global land. It is responsible for 18% of worldwide greenhouse gas emissions (measured in CO2 equivalents), and for 37% of anthropogenic methane and 65% of nitrous oxide emissions. The ongoing expansion of farmland and pastures in protected habitats, such as rainforests or wetlands, is an important factor in the loss of biodiversity [125]. The largest demand for resources and the highest greenhouse gas emissions per kg are caused by meat products, of which beef products are the most serious [119,126,127]. In view of rapid population growth, consumer education towards the development of sustainable dietary patterns with reduced meat intake and the avoidance of food waste is considered crucial for future food security [128] and the preservation of the resource base of the bioeconomy.
Because of its high demand for resources, the nutrition sector is particularly important. However, in the face of a limited availability of biogenic as well as fossil resources, the call for sustainable consumption habits applies to all material goods. In recent years, a number of alternative consumption and ownership models have been developed in the field of mobility, clothing, housing, and leisure, which replace ownership of products with utilization of products [129]. These approaches encompass: extension of a product’s life cycle (e.g., by repairing, upgrading, or re-use as second-hand goods), time-limited periods of use (e.g., rental or lease), and collaborative use (e.g., networks for sharing and exchanging) [130]. The dissemination of these developments ranges from niche applications (e.g., food sharing networks) to concepts like car sharing, which have already reached a mass market. Although the market potential and acceptance of these options have not been sufficiently investigated and possible rebound effects have not been fully clarified, a relevant contribution to reducing the demand for resources is expected.
3.9. Facet
Assessing the contrasting positions taken on the key issues discussed in the previous paragraphs, two different pathways for shaping the bioeconomy emerge: a technology-based approach, which is the currently prevailing one, and a socio-ecological approach (Table 2; see similar distinctions in [96,105]).

Table 2.
Overview of contrasting implementation pathways for the bioeconomy.
The technology-based approach is built on advances in the life sciences and the support of biotechnology as an enabling technology in various sectors. A strong partnership between policy, science, and industry, the promotion of international cooperation, the establishment of global value chains, and the granting of patents should improve international competitiveness and contribute to economic growth and employment. Since technological progress and an increased efficiency of biomass use are expected to solve resource shortages, changes in the ruling consumption patterns are not seen as necessary. Due to the fact that renewable biogenic feedstock and environmentally friendly biotechnological conversion processes are used, the bioeconomy is considered to be inherently sustainable. Thus, there would be no need for further sustainability requirements. To meet the demand for biomass, the yields of intensive agriculture must be enhanced by improving the efficiency of external inputs, speeding up scientific progress in the field of plant breeding and genetic engineering, faster adoption of new agricultural techniques by farmers, and removal of trade barriers. In addition to raising yields in conventional agriculture, the development of anthropogenically created biological systems with new properties in the laboratory is envisaged. Nature should be manipulated to fit economic purposes. Biomass conversion should happen in large-scale facilities with a throughput of several million tons per year in order to profit from economies of scale. These plants should be situated in regions with high untapped biomass potentials (e.g., Russia, Finland, and Sweden) or close to big harbors using imports of cheap biomass from abroad in order to minimize the transportation costs. While a close cooperation between policy, science, and industry is paramount, the participation of societal stakeholders and the general public is not considered a major factor. Dialogue with the public is thought to create acceptance for already fixed priorities and to promote openness to technology by providing information about the advantages of new technologies.
In the socio-ecological approach to shaping bioeconomy, sustainability concerns are given high priority. This implies a radical shift away from the conventional intensive agriculture and a transition to a site-specific agriculture, in which insights from scientific research and the tacit knowledge of local farmers play an equally important role. External inputs like energy, inorganic fertilizers, agrochemicals, and irrigation are replaced by the integration of natural regulation processes such as nutrient cycling, water retention, nitrogen fixation, soil regeneration, and ecological pest, weed, and disease regulation. Genetic engineering is ruled out completely. Regarding production, a cyclical use of resources that follows the metabolic cycles of nature, is favored. Sparing and responsible handling of scarce biogenic feedstock, the prevention of waste, and the reuse of raw materials in succeeding cascades are the guiding principles, which also apply to consumer behavior. The spatial orientation of the socio-ecological approach is regional in nature rather than global. It relies on site-specific solutions, based on flexible, regional networks with largely closed cycles and regional autonomy concerning food and renewable energy. Correspondingly decentralized, smaller conversion facilities are preferred, which are tailored to the specific regional biomass supply. Research funding will be focused on a variety of topics, such as agro-ecological farming, breeding of alternative crops for marginal sites, and social innovation. The involvement of civil society organizations and the general public in the process of shaping the bioeconomy are seen as crucial factors for a successful transition.
These two pathways are characterized by the linking of extreme positions. However, the individual features listed in Table 2 are not always mutually exclusive. Some of them can be linked; for others compatibility is at least theoretically conceivable. So, further efforts to shape the bioeconomy may originate from other combinations. Since it is impossible today to predict which pathway will be the most expedient—the one already taken or others proposed in the debate—it would contradict the precautionary principle to exclude certain roads from the outset and to dispense with their possible benefits to society.
4. Conclusions
The orientation towards sustainability is a major challenge, but also an important prerequisite for a successful transition to the bioeconomy. As the analysis of the current discourse has shown, there are different understandings of the relationship between sustainability and the bioeconomy. To follow the opinion that sustainability will be an implicit result of the bioeconomy would reinforce the excessive consumption of resources and restrain development. According to the majority of experts, the bioeconomy will only contribute to a more sustainable future if certain requirements are met. The development of a framework of principles and criteria for a sustainable bioeconomy, involving ecological, social, and economic aspects, is a key task for policy, science, and society [1]. This is actually addressed by the program on sustainable bioeconomy guidelines being developed under the FAO’s coordination. The debate on this topic is still in its infancy and needs to be strengthened in order to reach an internationally agreed set of criteria, including appropriate indicators for measuring progress towards sustainability. It has to be noted that the selection of criteria and the determination of limits to be observed have a significant impact on the biomass potential that can be produced sustainably. Another factor that limits operating space for the bioeconomy is the commonly accepted principle of ‘food first’, which requires giving global food security and the supply with sufficient, nutritious, healthy, and safe food for a growing world population priority over all other pathways for utilizing biomass.
There is a broad consensus that sound information on the attainable potential of sustainably produced biomass is essential to shaping the bioeconomy. However, reliable knowledge about the biogenic feedstock quantities currently available, their spatial distribution, and their availability over time is still lacking. Without that knowledge, neither an estimate of the extent to which fossil fuels can be replaced by biogenic feedstock, nor an assessment of the extent to which society can rely on bio-based products in the long run, is possible [58]. Against this background, there is an urgent need for a binding international agreement on methodological standardization covering at least some of the minimum requirements, such as the transparency of the assumptions, specifications on data collection, and regular updating of the existing database.
Global population growth, changing consumption patterns towards calorie-rich diets, and rising demand for biogenic raw materials necessitate an increase in agricultural productivity. The option of expanding the cultivated area is generally seen as hardly feasible without endangering the remaining natural habitats and the ecosystem services they provide. It is rather expected that the availability of fertile soil will shrink due to global environmental changes. To increase yields and simultaneously improve the environmental performance, there are two different roads to sustainable intensification. The high-tech strategy can be seen more or less as a correction and completion of conventional intensive farming, while the agro-ecological strategy implies a radical shift away from the prevailing model and a transition to a knowledge-based, site-sensitive agriculture, in which insights from scientific research and the tacit knowledge of local farmers play an equally important role. Given the great diversity of existing European farming systems, a combination of both pathways might be prudent, depending on the conditions of the respective site.
Even if there are certain untapped potentials, biomass remains a scarce resource, especially if food security is given priority and ambitious sustainability criteria have to be met. Thus, the different options for use should be balanced carefully and biogenic raw materials should be directed to the uses most preferable for society, e.g., those with the highest added value or the highest CO2 mitigation potential. It has been increasingly recognized that the use of biomass for the provision of heat and electricity in a so-called single-stage cascade, which has been considerably pushed by the current incentive structure, is no longer acceptable. This is above all because biomass is the only available carbon source that can replace the fossil fuels utilized for chemical or material purposes, while there are different renewable alternatives to cover future energy demand, such as wind, solar energy, or water power. Against this backdrop, the energetic use of biomass should be limited to exceptions, such as the decentralized supply of heat and power in sparsely populated rural areas or in the form of biofuels for certain uses (e.g., shipping, air transport) where sun and wind energy do not offer viable alternatives [131]. According to the European waste hierarchy, combustion should only be considered an option for the final stage of a cascade, i.e., at the very end of the life cycle of biogenic products. Up to now, other renewable energy sources have not played an adequate role within political bioeconomy strategies.
The implementation of a sustainable bioeconomy depends not least on the extent to which the behavior of consumers is included in the concept. Many experts agree that solutions that solely address increases in resource efficiency and improvements in conversion procedures are not sufficient to meet the needs of a growing world population [14,82,96,132]. Environmentally conscious consumption patterns (e.g., avoidance of food waste) and sufficiency approaches (e.g., reduced meat consumption) are important levers for reducing the demand for biomass and lessening the pressure on land as the limiting factor. The realization of sustainable consumption patterns requires not only greater consciousness on the part of consumers, but also responsible behavior from producers. The call for longer durability of material goods necessitates a product design that opens up the possibility of repair, upgrading, replacement of components, and reuse of raw materials. The higher the number of cycles of repair, upgrading, reuse, and remanufacturing, the lower the ecological footprint of a product and the need for raw materials to produce new products [28].
At the core of the critical dispute on the bio-economy is the finding that the pathway currently being pursued is too reliant on technology, both in terms of the research focused on the area of the life sciences and related technologies and the stakeholders involved. According to critics, two shortcomings result from this narrow understanding of the concept: on the one hand, an underrepresentation of certain disciplines and research topics, mainly in the social sciences; and, on the other hand, insufficient involvement of different societal stakeholders. The more far-reaching the consequences of a switch-over to another resource base, the more important a holistic view that encompasses different aspects of societal life, a variety of alternative implementation pathways, and a broad spectrum of research topics becomes (inter alia, [35,103,106]). Since this transition is a highly complex process that leads to fundamental changes in society, a strategy of diversity is needed that broadens the prevailing technology-based road by integrating socio-ecological approaches and opening up to new ideas that may arise from future challenges.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research Program “Technology, Innovation and Society” of the Helmholtz Association and the Ministry of Science, Research and the Arts of Baden-Württemberg within the framework of the Bioeconomy Research Program Baden-Württemberg.
Author Contributions
Carmen Priefer designed the research, performed the literature review, and wrote the first draft of the paper; Juliane Jörissen searched for additional literature in related topics and contributed particularly to the linkages between bioeconomy and sustainability; Juliane Jörissen and Carmen Priefer revised the manuscript; and Oliver Frör added useful comments and some supplements to the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. How Sustainability Is Addressed in Official Bioeconomy Strategies at International, National and Regional Levels; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bioökonomierat—German Bioeconomy Council. Bioeconomy Policy (Part II). Synopsis of National Strategies around the World; Bioökonomierat: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development. The Bioeconomy to 2030: Designing a Policy Agenda. Main Findings and Policy Conclusions; Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD): Paris, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bundesministerium für Landwirtschaft und Ernährung—Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture (Germany). Nationale Politikstrategie Bioökonomie; Nachwachsende Ressourcen und biotechnologische Verfahren als Basis für Ernährung, Industrie und Energie; Bundesministerium für Landwirtschaft und Ernährung: Berlin, Germany, 2014.
- Lettow, S. Biokapitalismus und inwertsetzung der körper—Perspektiven der kritik. PROKLA 2015, 1, 33–49. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, B. Law and ethics for the bioeconomy and beyond. J. Law Med. 2007, 15, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kent, J. The fetal tissue economy: From the abortion clinic to the stem cell laboratory. Soc. Sci. Med. 2008, 67, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fannin, M. The hoarding economy of endometrial stem cell storage. Body Soc. 2013, 19, 32–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, G.; Morrison, M. Patenting human pluripotent cells: Balancing commercial, academic and ethical interests. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehlje, M.; Bröring, S. The increasing multifunctionality of agricultural raw materials: Three dilemmas for innovation and adoption. Int. Food Agribus. Man. 2011, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowski, I. Securing a sustainable biomass supply in a growing bioeconomy. Glob. Food Secur. 2015, 6, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staffas, L.; Gustavsson, M.; McCormick, K. Strategies and Policies for the Bioeconomy and Bio-Based Economy: An Analysis of Official National Approaches. Sustainability 2013, 5, 2751–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermeulen, V.; Van der Stee, M.; Stevens, C.V.; Van Huylenbroeck, G. Industry expectations regarding the transition toward a biobased economy. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2012, 6, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Besi, M.; McCormick, K. Towards a bioeconomy in Europe. National, regional and industrial strategies. Sustainability 2015, 7, 10461–10478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golembiewski, B.; Sick, N.; Bröring, S. The emerging research landscape on bioeconomy: What has been done so far and what is essential from a technology and innovation management perspective? Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 29, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerium für Innovation, Wissenschaft und Forschung des Landes Nordrhein-Westfalen—Ministry of Innovation, Science and Research of North Rhine-Westphalia. Eckpunkte einer Bioökonomiestrategie für Nordrhein-Westfalen; Ministerium für Innovation, Wissenschaft und Forschung des Landes Nordrhein-Westfalen: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2013.
- British Columbia Committee on Bio-Economy. BC Bio-Economy; British Columbia Committee on Bio-Economy: Victoria, BC, Canada, 2011.
- Alberta Innovates Bio Solutions. Recommendations to build Alberta’s Bioeconomy; Alberta Innovates Bio Solutions: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Matis. Future Opportunities for Bioeconomy in the West Nordic Countries; Matis Reports 37-14; Matis: Reykjavík, Iceland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pfau, S.F.; Hagens, J.E.; Dankbaar, B.; Smits, A.J.M. Visions of Sustainability in Bioeconomy Research. Sustainability 2014, 6, 1222–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, H. Towards some Operational Principles of Sustainable Development. Ecol. Econ. 1990, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The White House. National Bioeconomy Blueprint; The White House: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Scarlat, N.; Dallemand, J.F.; Monforti-Ferrario, F.; Nita, V. The role of biomass and bioenergy in a future bioeconomy: Policies and facts. Environ. Dev. 2015, 15, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruins, M.E.; Sanders, J.P.M. Small-scale processing of biomass for biorefinery. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2012, 6, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navia, R.; Mohanty, A.K. Resources and waste management in a bio-based economy. Waste Manag. Res. 2012, 30, 215–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S. Industrial biosystems engineering and biorefinery. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carus, M.; Raschka, A.; Iffland, K.; Dammer, L.; Essel, R.; Piotrowski, S. How to Shape the Next Level of the European Bio-Based Economy? The Reasons for the Delay and the Prospects of Recovery in Europe; Nova-Institute: Hürth, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Sustainable Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries in the Bioeocnomy—A challenge for Europe; 4th SCAR Foresight Exercise; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Elbersen, B.; Fritsche, U.; Petersen, J.E.; Lesschen, J.P.; Böttcher, H.; Overmars, K. Accessing the effect of stricter sustainability criteria on EU biomass crop potential. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2013, 7, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellisch, M.; Jungmeier, G.; Karbowski, A.; Patel, A.; Rogulska, M.K. Biorefinery systems—Potential contributors to sustainable innovation. Biofuel. Bioprod. Bior. 2010, 4, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsches Biomasseforschungszentrum—German Biomass Research Centre. Sachstandsbericht über Vorhandene Grundlagen für ein Monitoring der Bioökonomie: Nachhaltigkeit und Ressourcenbasis der Bioökonomie; Deutsches Biomasseforschungszentrum: Leipzig, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fritsche, U.R.; Iriarte, L. Sustainability criteria and indicators for the bio-based economy in Europe: State of discussion and way forward. Energies 2014, 7, 6825–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringezu, S.; O’Brien, M.; Schütz, H. Beyond biofuels: Assessing global land use for domestic consumption of biomass. A conceptual and empirical contribution to sustainable management of global resources. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, S.; Gottschick, M.; Schorling, M.; Stirn, S. Bio-Ökonomie: Gesellschaftliche Transformation ohne Verständigung über Ziele und Wege? BIOGUM-Forschungsbericht FG Landwirtschaft Nr. 27; Universität Hamburg: Hamburg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gottwald, F.-T. Irrweg Bioökonomie. Über die zunehmende Kommerzialisierung des Lebens. In Der Kritische Agrarbericht 2015—Schwerpunkt “Agrarindustrie und Bäuerlichkeit”; ABL-Verlag: München, Germany, 2015; pp. 259–264. [Google Scholar]
- Raghu, S.; Spencer, J.L.; Davis, A.S.; Wiedenmann, R.N. Ecological consideration in the sustainable development of terrestrial biofuel crops. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2011, 3, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, A.W.; Gillespie, I.; Hirsch, M.; Begley, C. Biosecurity and sustainability within the growing global bioeconomy. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2011, 3, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament. Directive 2009/28/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 April 2009 on the Promotion of the Use of Energy from Renewable Sources and Amending and Subsequently Repealing Directives 2001/77/EC and 2003/30/EC; European Parliament: Strasbourg, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament. Directive 2009/30/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 April 2009 amending Directive 98/70/EC as Regards the Specification of Petrol, Diesel and Gas-Oil and Introducing a Mechanism to Monitor and Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Amending Council Directive 1999/32/EC as Regards the Specification of Fuel Used by Inland Waterway Vessels and Repealing Directive 93/12/EEC; European Parliament: Strasbourg, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Commission Adopts Biomass Sustainability Report. European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2010. Available online: http://europa.eu/rapid/press-release_IP-10–192_en.htm (accessed on 15 December 2016).
- High Level Panel of Experts on Food Security and Nutrition. Investing in Smallholder Agriculture for Food Security; High Level Panel of Experts on Food Security and Nutrition of the Committee on World Food Security: Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sustainable Development Commission. Looking Back, Looking Forward—Sustainability and UK Food Policy 2000–2011; Sustainable Development Commission: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Godfray, J.; Garnett, T. Food security and sustainable intensification. Philos. Trans. Ro. Soc. 2014, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretty, J. Agricultural sustainability: Concepts, principles and evidence. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. 2008, 363, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. How to feed the world in 2050. In Proceedings of the High Level Expert Forum, Rome, Italy, 12–19 October 2009; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rosengrant, M.W.; Ringler, C.; Zhu, T.; Tokgoz, S.; Bhandary, P. Water and food in the bioeconomy: Challenges and opportunities for development. Agric. Econ. 2013, 44, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroli, B.; Elbersen, B.; Frederiksen, P.; Grandin, U.; Heikkilä, R.; Krogh, P.H.; Izakovicova, Z.; Johansen, A.; Meiresonne, L.; Spijker, J. Is energy cropping in Europe compatible with biodiversity? Opportunities and threats to biodiversity from land-based production of biomass for bioenergy purposes. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 55, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbens-Leenes, P.W.; Hoekstra, A.Y.; van der Meer, T. The water footprint of energy from biomass. A quantitative assessment and consequences of an increasing share of bio-energy in energy supply. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carus, M.; Dammer, L. Food or Non-Food: Which Agricultural Feedstocks Are Best for Industrial Uses? Nova-Paper #2 on Bio-Based Economy; Nova-Institute: Hürth, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zilberman, D.; Hochman, G.; Rajagopal, D.; Sexton, S.; Timilsina, G. The impact of biofuels on commodity food prices: Assessment of findings. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2012, 95, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommarco, R.; Kleijn, D.; Potts, S.G. Eocological intensification: Harnessing ecosystem services for food security. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ricketts, T.H.; Kremen, C.; Carney, K.; Swinton, S.M. Ecosystem services and dis-services to agriculture. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 64, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachagentur für Nachwachsende Rohstoffe e. V.—Agency of Renewable Resources. Biomassepotenziale von Rest- und Abfallstoffen; Fachagentur für Nachwachsende Rohstoffe e. V.: Gülzow, Germany, 2015.
- Dornburg, V.; van Vuuren, D.; van de Ven, G.; Langeveld, H.; Meeusen, M.; Banse, M.; van Oorschot, M.; Ros, J.; van den Born, G.J.; Aiking, H.; et al. Bioenergy revisited: Key factors in global potentials of bioenergy. Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, M.; Schütz, H.; Bringezu, S. The land footprint of the EU bioeconomy: Monitoring tools, gaps and needs. Land Use Policy 2015, 47, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, C.S.; Junginger, M.; Faaij, A. Monitoring sustainable biomass flows: General methodology development. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2014, 8, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.P.M.; Bos, H.L. Raw material demand and sourcing options for the development of a bio-based chemical industry in Europe: Part 2: Sourcing options. Biofuel. Bioprod. Biorefin. 2013, 7, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, C.; Brosowski, A.; Majer, S. Sustainable feedstock potential—A limitation for the bio-based economy? J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 123, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, S.; Malins, C. A reassessment of global bioenergy potential in 2050. GCB Bioenergy 2015, 7, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batidzirai, B.; Smeets, E.M.W.; Faaij, A.P.C. Harmonising bioenergy resource potentials—Methodological lessons from review of state of the art bioenergy potential assessments. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 6598–6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offermann, R.; Seidenberger, T.; Thrän, D.; Kaltschmitt, M.; Zinoviev, S.; Miertus, S. Assessment of global bioenergy potentials. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2011, 16, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauri, P.; Havlík, P.; Kindermann, G.; Forsell, N.; Böttcher, H.; Obersteiner, M. Woody biomass energy potential in 2050. Energy Policy 2014, 66, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentsen, N.S.; Felby, C. Biomass for energy in the European Union—A review of bioenergy resource assessments. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2012, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Energy Agency. World Energy Outlook 2015 Factsheet—Global Energy Trends to 2040; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- World Energy Council. World Energy Resources 2016; World Energy Council: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Essel, R.; Carus, M. Increasing resource efficiency by cascading use of biomass. Rural 2014, 21, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Keegan, D.; Kretschmer, B.; Elbersen, B.; Panoutsou, C. Cascading use: A systematic approach to biomass beyond the energy sector. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2013, 7, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioökonomierat. Landwirtschaft in Deutschland—Ihre Rolle für die Wettbewerbsfähigkeit der Bioökonomie; BÖRMEMO 01 vom 13.01.2015; Bioökonomierat: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Halberg, N.; Panneerselvam, P.; Treyer, S. Eco-functional Intensification and Food security. Synergy or Compromise? SAR 2015, 4, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckwell, A.; Heissenhuber, A.; Blum, W. The Sustainable Intensification of European Agriculture; The RISE Foundation: Brussels, Belgium, 2014; Available online: http://www.risefoundation.eu/images/files/2014/2014_%20SI_RISE_FULL_EN.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2016).
- Royal Society. Reaping the Benefits: Science and the Sustainable Intensification of Global Agriculture; The Royal Society: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ericksen, P.J. Food security and global environmental change: Emerging challenges. Environ. Sci. Policy 2009, 12, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, H.; Ghanian, M.; Ghoochani, O.M.; Rafiaani, P.; Taning, C.N.; Hajivand, R.Y.; Dogot, T. Genetically modified crops: Towards agricultural growth, agricultural development, or agricultural sustainability? Food Rev. Int. 2015, 31, 195–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Save and Grow. A Policymaker’s Guide to the Sustainable Intensification of Smallholder Crop Production; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Van Grinsven, H.J.M.; Erisman, J.W.; de Vries, W.; Westhoek, H. Potential of extensification of European agriculture for a more sustainable food system, focusing on nitrogen. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levidow, L. European transitions towards a corporate-environmental food regime: Agroecological incorporation or contestation? J. Rural Stud. 2015, 40, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R. Diversity of European farming systems and pathways to sustainable intensification. TATuP 2014, 23, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ferdinands, K.; Virtue, J.; Johnson, S.B.; Setterfield, S.A. ‘Bio-insecurities’: Managing demand for potentially invasive plants in the bioeconomy. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2011, 3, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, J.-L. Requirements for the development of a bioeconomy for chemicals. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2011, 3, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, Y. Bioökonomie—Gefahr oder Chance? Eine kritische Anmerkung zu den Prioritäten der Bioökonomieforschung in Bezug auf den Erhalt der biologischen Vielfalt. In Treffpunkt Biologische Vielfalt XI; Feit, U., Korn, H., Eds.; Bundesamt für Naturschutz: Bonn, Germany, 2012; pp. 145–148. [Google Scholar]
- Levidow, J.; Boschert, K. Coexistence or contradiction? GM corps versus alternative agriculture in Europe. Geoforum 2008, 39, 174–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, O.; Padel, S.; Levidow, L. The Bio-Economy Concept and Knowledge Base in a Public Goods and Farmer Perspective. Biobased Appl. Econ. 2012, 1, 47–63. [Google Scholar]
- Doré, T.; Makowski, D.; Malézieux, E.; Munier-Jolain, N.; Tchamitchian, M.; Tittonell, P. Facing up the paradigm of ecological intensification in agronomy: Revisiting methods, concepts and knowledge. Eur. J. Agron. 2011, 34, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanh, T.D.; Chung, M.I.; Xuan, T.D.; Tawata, S. The exploitation of crop allelopathy in sustainable agricultural production. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2005, 191, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seufert, V.; Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J.A. Comparing the yields of organic and conventional agriculture. Nature 2012, 485, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Innovation Partnership. Strategic Implementation Plan European Innovation Partnership ‘Agricultural Productivity and Sustainability’; Adopted by the High Level Steering Board on 11 July 2013; European Innovation Partnership: Brussels, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Georgescu-Roegen, N. The Entropy Law and the Economic Process; Harvard University Press: Lincoln, NE, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Grefe, C. Global gardening. Bioökonomie—Neuer Raubbau oder Wirtschaftsform der Zukunft; Verlag Antje Kunstmann: München, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, C. Intellectual property rights, the bioeconomy and the challenges of biopiracy. Genome Soc. Policy 2008, 4, 26–45. [Google Scholar]
- Birch, K.; Levidow, L.; Papaioannou, T. Sustainable Capital? The Neoliberalization of Nature and Knowledge in the European “Knowledge-based Bio-economy”. Sustainability 2010, 2, 2898–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, L.; Marsden, T. Constructing sustainable communities: A theoretical exploration of the bio-economy and eco-economy paradigm. Local Environ. Int. J. Justice Sustain. 2011, 16, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philp, J.; Ritchie, R.J.; Allan, J.E.M. Synthetic biology, the bioeconomy, and a societal quandary. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Babtie, A.; Stephanopoulos, G. Metabolic engineering: Enabling technology of a bio-based economy. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2012, 1, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner Garcez Lopes, M. Engineering biological systems toward a sustainable bioeconomy. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 42, 813–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Sánchez, G.; Philp, J. Omics and the bioeconomy. Applications of genomics hold great potential for a future bio-based economy and sustainable development. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levidow, L.; Birch, K.; Papaioannou, T. EU agri-innovation policy: Two contending visions of the bio-economy. Crit. Policy Stud. 2012, 6, 40–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundesministerium für Forschung und Bildung—Federal Ministry of Education and Research (Germany). Nationale Forschungsstrategie Bioökonomie. Unser Weg zu einer bio-basierten Wirtschaft; Bundesministerium für Forschung und Bildung: Berlin, Germany, 2010.
- Schaper-Rinkel, P. Bio-Politische Ökonomie. Zur Zukunft des Regierens von Biotechnologien. In Bioökonomie: Die Lebenswissenschaften und die Bewirtschaftung der Körper; Lettow, S., Ed.; Transcript Verlag: Bielefeld, Germany, 2012; pp. 155–180. [Google Scholar]
- Birch, K.; Levidow, L.; Papaioannou, T. Self-fulfilling prophecies of the European knowledge-based bio-economy. The discursive shaping of institutional and policy frameworks in the biopharmaceuticals sector. J. Knowl. Econ. 2014, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwier, J.; Blok, V.; Lemmens, P.; Geerts, R.-J. The ideal of a zero-waste humanity: Philosophical reflections on the demand for a bio-based economy. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2015, 28, 353–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger-Erben, M.; Rückert-John, J.; Schäfer, M. Sustainable consumption through social innovation: A typology of innovations for sustainable consumption practices. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108 Pt A, 784–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umweltbundesamt. Soziale Innovationen im Aufwind. Ein Leitfaden zur Förderung Sozialer Innovationen für Nachhaltigen Konsum; Umweltbundesamt: Dessau-Roßlau, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmit, D.; Hauger Lindstad, B.; Jellesmark Thorsen, B.; Toppinen, A.; Roos, A.; Baardsen, S. Shades of green: A social scientific view on bioeconomy in the forest sector. Scand. J. For. Res. 2014, 29, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wield, D.; Hanlin, R.; Mittra, J.; Smith, J. Twenty-first century bioeconomy: Global challenges of biological knowledge for health and agriculture. Sci. Public Policy 2013, 40, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugge, M.M.; Hansen, T.; Klitkou, A. What is the bioeconomy? A review of the literature. Sustainability 2016, 8, 691–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, S. Bioökonomie am Scheideweg—Industrialisierung von Biomasse oder nachhaltige Produktion? GAIA 2012, 21, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Kircher, M. The transition to a bio-economy: National perspectives. Biofuel. Bioprod. Biorefin. 2012, 6, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naturschutzbund Deutschland e. V. Nachhaltigkeit in der Bioökonomie. Zusammenfassung und Thesen als Ergebnis eines Workshops auf VILM Dezember 2013; Naturschutzbund Deutschland e. V.: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- McCormick, K. The emerging bio-economy in Europe: Exploring the key governance challenges. In Proceedings of the World Renewable Energy Congress, Linköping, Sweden, 8–13 May 2011.
- Asveld, L.; Ganzevles, J.; Osseweijer, P. Trustworthiness and Responsible Research and Innovation: The Case of the Bio-Economy. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2015, 28, 571–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essent New Energy. Natural Power—Essent and the Bio-Based Economy; Essent New Energy, a RWE company: Hertogenbosch, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Confederation of European Paper Industries. The Forest Fibre Industry—2050 Roadmap to a Low-Carbon Bio-Economy; Confederation of European Paper Industries: Brussels, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Friends of the Earth. Land under pressure—Global impacts of the EU bioeconomy; Friends of the Earth: Brussels, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Deiniger, K. Global land investments in the bio-economy: Evidence and policy implications. Agric. Econ. 2013, 44, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircher, M. The transition to a bio-economy: Emerging from the oil age. Biofuel. Bioprod. Biorefin. 2012, 6, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Employment and the Economy. Sustainable Growth from Bioeconomy—The Finnish Bioeconomy Strategy; Ministry of Employment and the Economy; Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry; Ministry of the Environment: Helsinki, Finland, 2014.
- Formas. Swedish Research and Innovation Strategy for a Bio-based Economy; The Swedish Research Council for Environment, Agricultural Sciences and Spatial Planning (formas): Stockholm, Sweden, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Demaria, F.; Schneider, F.; Sekulova, F.; Martinez-Alier, J. What is degrowth? From an activist slogan to a social movement. Environ. Values 2013, 22, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Food Wastage Footprint: Impacts on Natural Resources; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- High Level Panel of Experts on Food Security and Nutrition. Food Losses and Waste in the Context of Sustainable Food Systems; High Level Panel of Experts on Food Security and Nutrition of the Committee on World Food Security: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Noleppa, S.; von Witzke, H. Tonnen für die Tonne; World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) Deutschland: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Institution of Mechanical Engineers. Global Food: Waste Not, Want Not; Institution of Mechanical Engineers: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kastner, T.; Ibarrola Rivas, M.J.; Koch, W.; Nonhebel, S. Global changes in diets and the consequences for land requirements for food. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6868–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerbens-Leenes, W.; Nonhebel, S. Food and land use. The influence of consumption patterns on the use of agricultural resources. Appetite 2005, 45, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Livestock’s Long Shadows. Environmental Issues and Options; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Waste and Resources Action Programme. Waste Arisings in the Supply of Food and Drink to Households in the UK; Waste and Resources Action Programme: Banbury, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, K.; Erikkson, M.; Strid, I. Carbon footprint of supermarket food waste. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 94, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, T. Where are the best opportunities for reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the food system (including the food chain)? Food Policy 2011, 36, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rückert-John, J.; Jaeger-Erben, M. Alternative Konsumformen als Herausforderungen für die Verbraucherpolitik. In Prosuming und Sharing—Neuer Sozialer Konsum: Aspekte kollaborativer Formen von Konsumtion und Produktion; Bala, C., Schuldzinski, W., Eds.; Verbraucherzentrale NRW: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2016; pp. 63–83. [Google Scholar]
- Gullstrand Edbring, E.; Lehner, M.; Mont, O. Exploring consumer attitudes to alternative models of consumption: Motivations and barriers. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 123, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioökonomierat. Bioenergiepolitik in Deutschland und gesellschaftliche Herausforderungen; BÖRMEMO 04 vom 1.11.2015; Bioökonomierat: Berlin, Germany, 2015.
- Birch, K.; Tyfield, D. Theorizing the Bioeconomy: Biovalue, Biocapital, Bioeconomics or What? Sci. Technol. Hum. Values 2012, 38, 299–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).