Techno-Economic Models for Optimised Utilisation of Jatropha curcas Linnaeus under an Out-Grower Farming Scheme in Ghana
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Models Description
2.1.1. Description of Model 1
2.1.2. Description of Model 2
2.2. Financial Appraisal Methodology
2.2.1. Financial Return on Investment
2.2.2. Estimation of Costs and Revenue
- (1)
- The direct production costs (consumption of materials and services, personnel, maintenance, general production costs).
- (2)
- Administrative and general expenditures.
- (3)
- Sales and distribution expenditures.
2.2.3. Criteria for Assessing the Projects Viability
2.2.4. Sensitivity Analysis
- (1)
- Variation in seed yield: 0.55, 4 and 7.5 tonnes/ha.
- (2)
- Variation in jatropha oil prices: 473, 600 and 1000 USD per tonne.
- (3)
- Variation in the purchase price of jatropha seeds: 0.05, 0.07 and 0.16 USD per kg.
- (4)
- Thirty per cent increase and decrease in the selling price of briquette, biogas, soap, compost and electricity.
- (5)
- Changes in the discount rate: discount rates from 0% to 30% were considered.
2.3. Methodology for Optimising Jatropha Oil and By-Products Utilisation
3. Results and Discussion
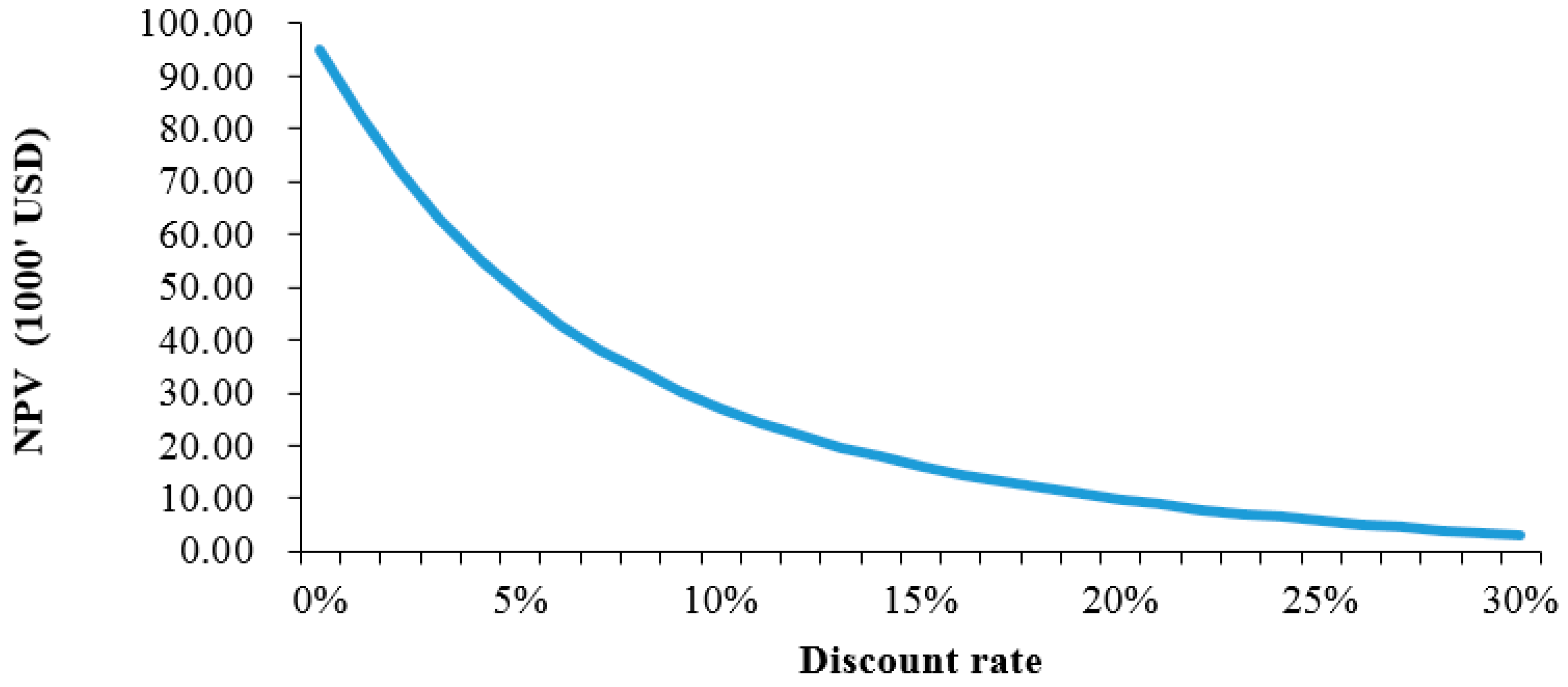
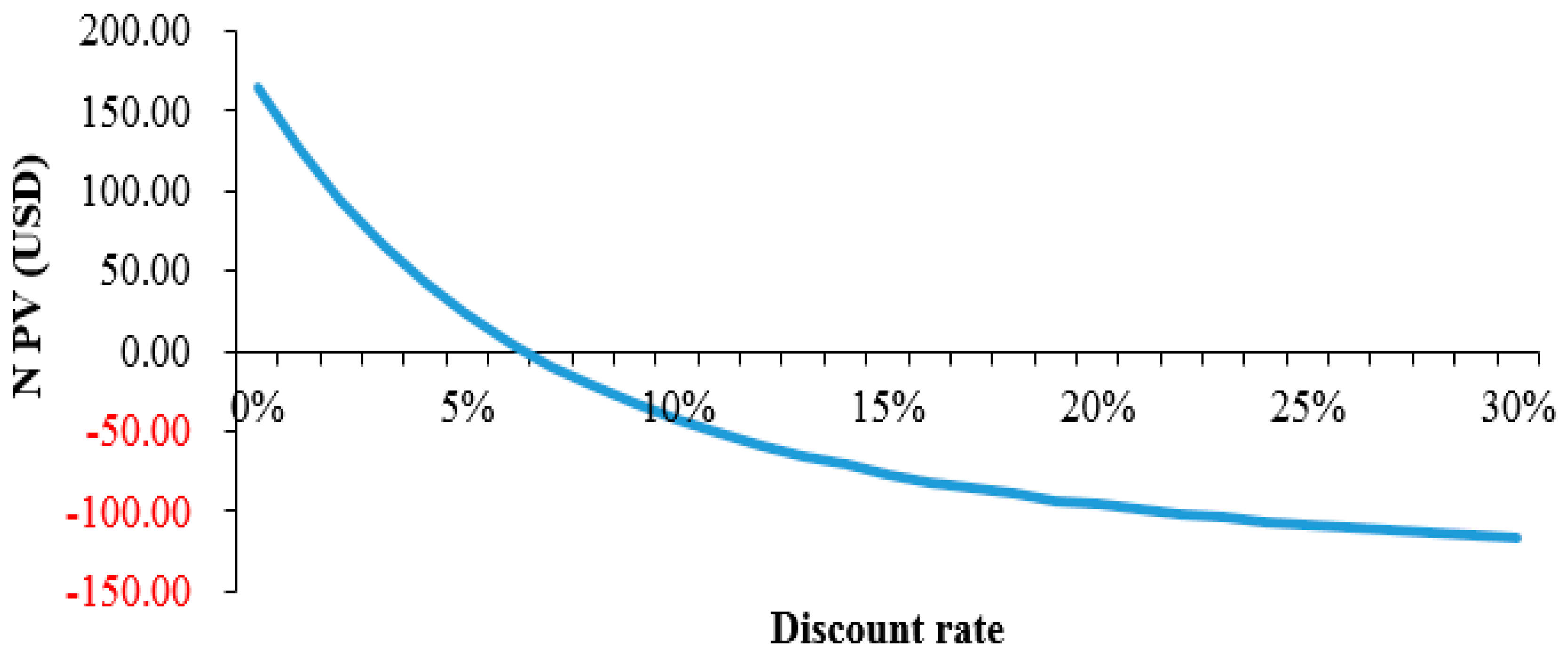
3.1. Technical and Cost Benefit Analysis of Model 1
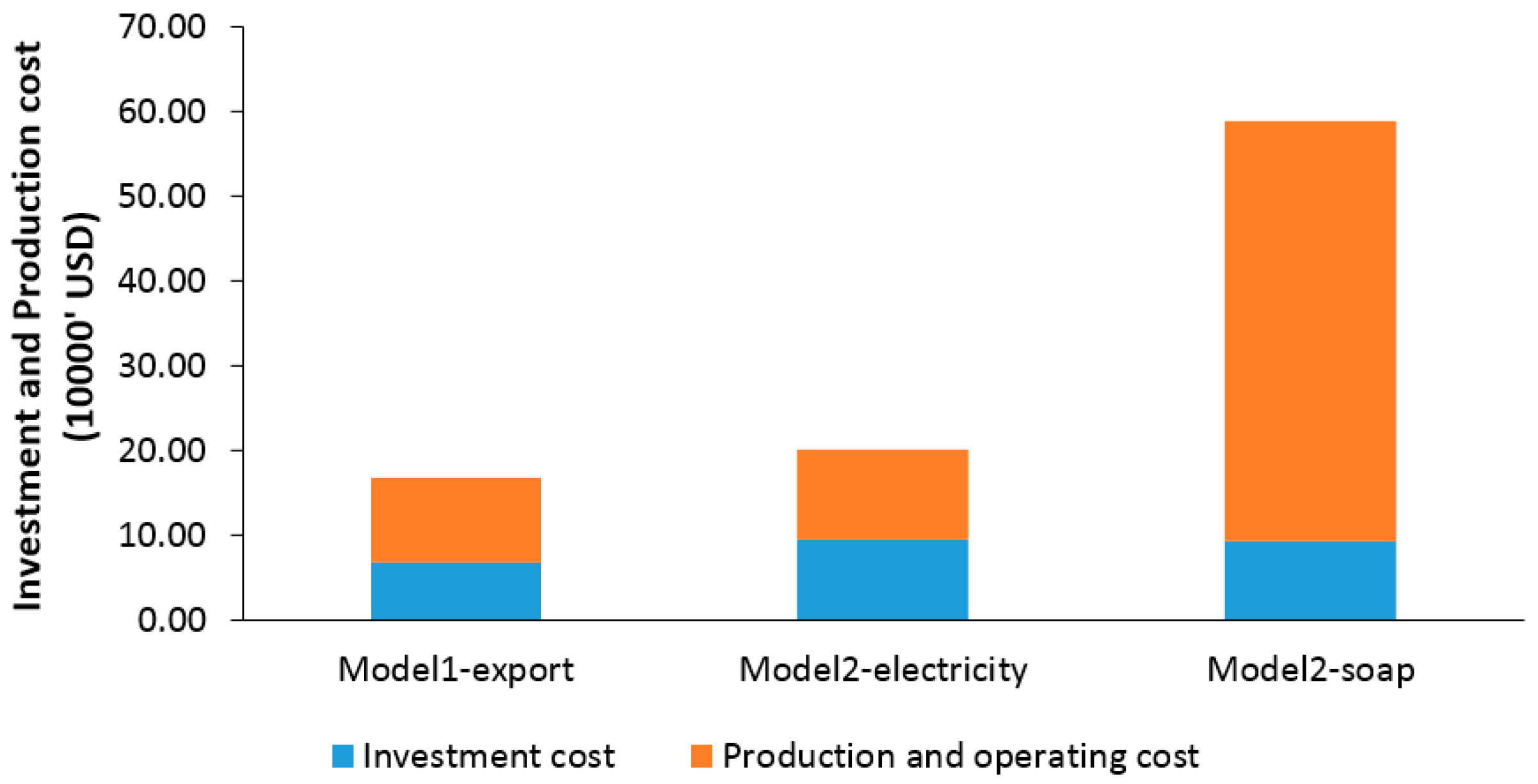
3.2. Technical and Cost Benefit Analysis of Model 2
3.3. Cost Benefit Analysis for Utilisation of Jatropha Oil
3.4. Optimisation of Jatropha Oil and By-Products Utilisation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. References for Technical Parameters, Assumptions and Cost Components Used in the Models
| Parameter | Value | References |
|---|---|---|
| Plantation establishment | ||
| Planting spacing | 2 m by 2 m for jatropha plantation and 1.5 m within rows for jatropha hedges | [11,30] |
| Lifespan of jatropha plantation | 30–50 years | [31] |
| Production start time (economic yield) | 3 years | [4] |
| Plant yield per ha | minimum 0.55, average 3 and maximum 7.5 tonnes per ha | [4,5,32,33,34,35,36,37] |
| Small-holder farmers (seed production) | ||
| Labour requirement for land preparation, planting weeding and pruning, harvesting and dehulling | - | [29,37] |
| Labour requirement for harvesting | 40 kg of seeds per person per day | [4] |
| Cost for dehulling | 10% of harvesting cost | [4] |
| Cost of labour per day | USD 7.2 | [38] |
| Purchase price of seeds per kg | Minimum USD 0.05, average USD 0.07 and maximum of USD 0.16 | [19] |
| General information | ||
| Fuel cost per litre | USD 0.99 | [39] |
| Electricity cost per kWh | USD 0.15 | [26] |
| Cost of building per square meter | USD 90 | [40] |
| Wages of workers | Calculated from daily minimum wage in Ghana-USD 2 | [41] |
| Oil extraction | ||
| Percentage composition of jatropha seeds, hulls, oil, press cake and residual oil | 66%, 34%, 30.89%, 65.1% and 3.60% respectively | [38] |
| Price and technical parameters of jatropha de-huller | - | [42] |
| Price and technical parameters of oil screw press | - | [43] |
| Price and technical parameters of filtering unit | - | |
| Selling price of crude jatropha oil per tonne | Minimum 473 average 600 Maximum 1000 | [11,44] |
| Biogas production | ||
| Density of jatropha press cake | 1200 kg/m3 | [45] |
| Sizing of biogas digester | [46] | |
| Unit cost of digester per cubic meter | 300 | [38] |
| Quantity of gas generated from press cake | Press cake consist of 92% oTS and biogas generated is 350 L/KgoTS with 65% methane | [47] |
| Quantity of digestate generated | 30% of feedstock | [48] |
| Price of bio-methane per cubic meter | Calculated from the relation that 1 m3 of biogas is proportional to 0.6 m3 of LPG gas, current price of LPG gas per kg USD 0.86 price of biogas is USD 0.39 per m3 | [38,46] |
| Price of bio-fertilizer kg | Price of bio-fertilizer is assumed to be 1/3 price of chemical fertilizer which is 100 Cedis per 50 kg bag | [38] |
| Briquette production | ||
| Price and technical parameters of briquette machine | [49] | |
| Price and technical parameters of carbonizing machine | [50] | |
| Fraction of cake that remains after compression | 0.6 | [51] |
| Unit price per kg of briquette | USD 0.12 (calculated from average price of wood charcoal in Ghana) | [52] |
| Electricity generation | ||
| Price and technical parameters of jatropha oil generator | [53] | |
| Price and technical parameters of biogas generator | [54] | |
| Feed in tariff rate | USD 0.18 | [55] |
| Soap production | ||
| Quantity of oil, caustic soda and water required to produce 1 kg of soap | 2.77 L, 0.41 kg and 2.07 litters respectively | [30,56] |
| Price and technical parameters of soap mixing tanks | [57] | |
| Price of caustic soda per 25 kg | USD 300 | [58] |
| Price of manual cutting moulds (32 kg capacity) | USD 375 | [59] |
| Price of soap manual cutter | USD 1895 | [60] |
| Price of bath bomb press and moulds | USD 275 and 285 respectively | [61] |
| Unit price of drying trays (12 kg capacity) | USD 25 | [62] |
| Period for curing | two weeks | [30] |
| Unit price of soap per 180 g | 1.5 USD | [38] |
| Compost production | ||
| Percentage volume of input materials that remains after composting | 50% | [63] |
| Ratio of press cake to bulking agent | 2:1 | [64] |
| Conditions for optimal compost production: temperature, moisture content, C:N ratio, PH and oxygen concentration | 48–65 °C, 50%–60%, 25–35:1, 6.5–8 and 10% respectively | [63,65] |
| Price and technical parameters of compost screen sieves | USD 1000 | [66] |
| Price of monitoring devices (compost thermometer, ph meters and moisture meter) | USD 125 | [67] |
References
- Energy Commission. Draft Bioenergy Policy of Ghana. 2010. Available online: http://cleancookstoves.org/resources_files/draft-bioenergy-policy-for.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2015).
- Kemausuor, F.; Nygaard, I.; Mackenzie, G. Prospects for bioenergy use in Ghana using Long Range Energy Alternative Planning model. Energy 2015, 93, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, S. An evaluation of multipurpose oil seed crop for industrial uses (Jatropha curcas L.): A review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2008, 28, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dorp, M. Economic Feasibility of Jatropha Production and Processing: A calculation Model for Business Case Development by Small Producer Organizations (SPO). 2013. Available online: http://www.jatropha.pro/PDF%20bestanden/5.%20Annex%20-%20Economic%20feasibility%20of%20Jatropha.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- Openshaw, K. A review of Jatropha curcas: An oil plant of unfulfilled promise. Biomass Bioenergy 2000, 19, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kywe, T.T.; Oo, M.M. Production of biodiesel from Jatropha oil (Jatropha curcas) in pilot plant. Proc. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2009, 38, 481–487. [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan, J.; Camobreco, V.; Duffield, J.; Graboski, M.; Shapouri, H. Life Cycle Inventory of Biodiesel and Petroleum Diesel for Use in an Urban Bus. Available online: http://www.nrel.gov/docs/legosti/fy98/24089.pdf (accessed on 2 August 2015).
- Vollner, T. Safety Evaluation of the Cosmetic Product “Pure Jatropha Soap” and Its Effects on Human Health. 2011. Available online: http://www.jatropha.pro/PDF%20bestanden/sb_pure_jatropha_soap_engl.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2015).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Jatropha: A Smallholder Bioenergy Crop: The Potential for Pro-Poor Development. 2010. Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/012/i1219e/i1219e.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- Achten, W.; Maes, W.; Aerts, R.; Verchot, L.; Trabucco, A.; Mathijs, E.; Singh, V.; Muys, B. Jatropha: From global hype to local opportunity. J. Arid Environ. 2009, 74, 164–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, L.T.; Hildebrandt, C.; Moser, F.; Lüdeke-Freund, K.; Averdunk, R.; Bailis, K.K. Insights into Jatropha Projects Worldwide: Key Facts & Figures from a Global Survey; Leuphana Universität: Lüneburg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sawe, E.; Shuma, J. Socio-economic experiences of Different Jatropha Business Model in Africa. In Socio-Economic Impacts of Bioenergy Production, 2nd ed.; Rutz, D., Janssen, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA; Doredrecht, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 67–90. [Google Scholar]
- Ofori-Boateng, C.; Lee, K.T. Feasibility of Jatropha oil for biodiesel: Economic Analysis. In Proceedings of the World Renewable Energy Congress, Linkoping, Sweden, 18–13 May 2011.
- Romijn, H.; Heijnen, S.; Colthoff, J.M.; Jong, B.D.; Eijck, J.V. Economic and Social Sustainability Performance of Jatropha Projects: Results from Field Surveys in Mozambique, Tanzania and Mali. Sustainability 2014, 6, 6203–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüntrup, M.; Swetman, T.; Michalscheck, M.; Asante, F. Factors of Success and Failure of Large Agro-Enterprises (Production, Processing and Marketing), A Pilot Study in Ghana Results of Case Studies in the Fruit, Maize, and Palm Oil Sub-Sectors. 2013. Available online: http://www.diegdi.de/uploads/media/Reprint-Factors_of_Success_and_Failure.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2014).
- Boamah, F. Imageries of the contested concepts “land grabbing” and “land transactions”: Implications for biofuels investments in Ghana. Geoforum 2014, 54, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eijck, J.; Rom Colthoff, J.; Romijn, H.; Heijnen, S.; de Ruijter, F.; Jongschaap, R. Jatropha Sustainability Assessment, Data from Tanzania, Mali & Mozambique; NL Agency: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; p. 101. [Google Scholar]
- FACT Foundation. Jatropha, retrospective and future development. In Proceedings of the Jatropha Conference, Groningen, The Netherlands, 1–2 November 2010.
- Van Eijck, J.V.; Smeets, E.; Romijn, H.; Balkema, A.; Jongschaap, R. Jatropha Assessment—Agronomy, Socio-Economic Issues, and Ecology. Available online: http://english.rvo.nl/sites/default/files/2013/12/Report%20Jatropha%20assessment%20-%20Copernicus%20-%20NPSB.pdf (accessed on 5 August 2014).
- Ghana Statistical Service (GSS). Ghana’s Inflation Rate. Available online: http://www.statsghana.gov.gh/ (accessed on 26 June 2015).
- Bank of Ghana (BoG). Daily Interest Rate. Available online: http://www.bog.gov.gh/index.php?option=comwrapper&view=wrapper&Itemid=255 (accessed on 26 June 2015).
- Sidho, H.S.; Singh, S.; Ahuja, S. Optimisation of energy use in different crop production systems. J. Agric. 2004, 85, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Barbee, M.J. Preliminary Investigation of the Risks Associated with Applying Non-composted Jatropha Curcas Seed Cake as a Fertilizer; Masters Project Report Environmental Engineering; University of Colorado Boulder: Boulder, CO, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Kumar, A. Bio-diesel waste as tailored organic fertilizer for improving yields and nutritive values of Lycopercicum esculatum (tomato) crop. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2012, 12, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimpl, E.; Blunck, M. Small-Scale Electricity Generation from Biomass Part III: Vegetable Oil, GIZ-HERA—Poverty-oriented Basic Energy Services, 1st ed.; GIZ-HERA: Eschborn, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Public Utility Regulatory Commission (PURC). Approved Electricity Tariffs in Ghana. 2014. Available online: http://gbcghana.com/kitnes/data/2013/12/23/1.1644223.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2015).
- Holl, M.A.; Gush, M.B.; Hallowes, J.; Versfeld, D.B. Jatropha curcas in South Africa: An Assessment of its Water Use and Bio-Physical Potential. WRC Report No 1497/1/07. Available online: http://jatropha.pro/PDF%20bestanden/JatrophaWater%20South%20Africa.pdf (assessed on 2 July 2015).
- Soto, I.; Feto, A.; Keane, J. Are Jatropha and Other Biofuels Profitable in Africa? Available online: http://www.cde.unibe.ch/unibe/portal/fak_naturwis/g_dept_kzen/b_cde/content/e65013/e85096/e100920/e133161/e187335/pane187341/e187345/files187349/BIA_policy_brief_profitability_eng.pdf (accessed on 27 January 2015).
- Van Eijck, J.V.; Smeete, E.; Faaij, A. Jatropha, A promising crop for Africa’s Biofuel Production? In Socio-Economic Impacts of Bioenergy Production, 2nd ed.; Rutz, D., Janssen, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA; Doredrecht, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Mawire, B. Biofuels and Economic Welfare a Cost-Benefit Analysis of Jatropha Schemes in Zimbabwe; Institute of Development Research and Development Policy: Bochum, Germany, 2008; Volume 186. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.N.; Vyas, D.K.; Srivastava, N.S.L.; Narra, M. SPERI experience on holistic approach to utilise all parts of Jatropha curcas fruit for energy. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 1868–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, G.; Edinger, R.; Becker, K. A concept for simultaneous wasteland reclamation, fuel production, and socio-economic development in degraded areas in India: Need, potential and perspectives of Jatropha plantations. Nat. Resour. Forum 2005, 29, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, J. Physic nut, Jatropha curcas L. In Promoting the Conservation and Use of Underutilised and Neglected Crops; Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research: Gatersleben, Germany; International Plant Genetic Resources Institute: Rome, Italy, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Achten, W.M.J.; Verchot, L.; Franken, Y.J.; Mathijs, E.; Singh, V.P.; Aerts, R.; Muys, B. Jatropha biodiesel production and use. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 1063–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Patolia, J.S.; Chaudhary, D.R.; Chikara, J.; Rao, S.N.; Kumar, D. Response of Jatropha curcas under Different Spacing to Jatropha De-Oiled Cake, in FACT Seminar on Jatropha curcas L. Agronomy and Genetics; Article No. 8; Wageningen FACT Foundation: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jongschaap, R.; Corré, W.; Bindraban, P.; Brandenburg, W. Claims and Facts on Jatropha curcas L. Global Jatropha curcas Evaluation, Breeding and Propagation Programme; Plant Research International BV: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ). Jatropha Reality Check: A Field Assessment of the Agronomic and Economic Viability of Jatropha and Other Oilseed Crops in Kenya. 2009. Available online: http://www.worldagroforestry.org/downloads/Publications/PDFS/B16599.pdf (accessed on 3 June 2015).
- Osei, I. Development of Techno-Economic Models for Optimized Utilization of Jatropha Curcas Linnaeus. Master’s Thesis, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi, Ghana, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- National Petroleum Authority (NPA). Fuel Prices in Ghana. Available online: http://npa.gov.gh/npa_new/index.php (accessed on 1 September 2015).
- Ghana Statistical Service (GSS). Prime Building Cost Index (CPI). 2011. Available online: http://www.statsghana.gov.gh/docfiles/news/prime_building_costs_index(pbci)_jan2000sept2011_P3_2011nov30.pdf (accessed on 13 September 2015). [Google Scholar]
- Daily Minimum Wage in Ghana. Available online: http://www.myjoyonline.com/business/2015/January-20th/minimum-wage-increased-by-ghc1.php (accessed on 12 August 2015).
- Prices of Dehuller. Available online: http://www.alibaba.com/product-detail/Dehuller_552004548.html (accessed on 15 August 2015).
- Jatropha Oil Crushers, including FACT Information. Available online: http://www.jatropha.pro/jatropha_oil_expellers.htm (accessed on 25 August 2015).
- Jatropha World. Economics of Jatropha Oil Production. 2013. Available online: http://www.jatrophabiodiesel.org/extraction.php (accessed on 25 August 2015).
- Lestari, D.; Mulder, W.; Weusthuis, R.; Sanders, J. Jatropha Protein Products for Technical Applications. 2008. Available online: http://jatropha.pro/PDF%20bestanden/Wageningen%20U.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2015).
- Ananthakrishnan, R.; Sudhakar, K.; Abhishek, G.; Sravan, S.S. Economic Feasibility of Substituting LPG with Biogas for MANIT Hostels. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2013, 5, 891–893. [Google Scholar]
- Stelyus, L.; Mkoma, F.; Mabiki, P. Jatropha as energy potential biofuel in Tanzania. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 2, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staubmann, R.; Foidl, G.; Foidl, N.; Gubitz, G.M.; Lafferty, R.M.; Arbizu, V.M.; Steiner, W. Biogas production from jatropha press cake. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1997, 63–65, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biomass charcoal briquettes. Available online: http://www.alibaba.com/product-detail/barbecue-charcoal-machine-biomass-charcoal-briquette_1342594014.html?spm=a2700.7724857.35.1.I3lhLC (accessed on 11 July 2015).
- High Guality Factory Manufacture Biomass Briquette Carbonization Furnace. Available online: http://www.alibaba.com/product-detail/High-quality-factory-manufacture-biomass-briquette_1896817002.html (accessed on 4 April 2015).
- Fact Foundation. The Jatropha Handbook from Cultivation to Application. 2010. Available online: http://www.snvworld.org/files//fact_foundation_jatropha_handbook_2010.pdf (accessed on 29 March 2015).
- Energy Commission. Charcoal Price Tracking in Major Urban Centres of Ghana. 2014. Available online: http://energycom.gov.gh/files/Charcoal%20Price%20Tracking%20_January%20to%20_December%202013.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2015). [Google Scholar]
- 20KVA Soundproof Diesel Generator Powered by Perkins. Available online: http://www.alibaba.com/product-detail/20KVA-Soundproof-Diesel-Generator-Powered-by_60265698698.html?spm=a2700.7724857.35.1.iF073v (accessed on 2 May 2016).
- CE ISO 10KVA-1250KVA biogas generator price. Available online: http://www.alibaba.com/product-detail/CE-ISO-10KVA-1250KVA-biogas-generator_60088055040.html?spm=a2700.7724857.35.1.4nDNvS (accessed on 3 August 2015).
- Public Utility Regulatory Commission. Approved Feed in Tariff Rate in Ghana. 2014. Available online: http://www.purc.com.gh/purc/sites/default/files/fit_2014.pdf (accessed on 21 August 2015).
- Henning, R. Identification, Selection and Multiplication of High Yielding Jatropha curcas L. Plants and Economic Key Points for Viable Jatropha Oil Production Costs. In Presented at the International Consultation on Pro-Poor Jatropha Development, Rome, Italy, 10–11 April 2008; Available online: https://www.ifad.org/documents/10180/0574242c-a63b-43d8–986c-fdd906f8128b (accessed on 11 October 2015).
- Pot Tipper Kettle Tank Complete Soap Maker. Available online: http://www.soapmelters.com/Pot-Tipper-Complete-Soap-Equipment-With-Heat-Mix-p/pot%20tipper%20c.htm (accessed on 13 August 2015).
- Caustic Soda prices. Available online: http://www.alibaba.com/product-detail/Caustic-Soda_1948037717.html?spm=a2700.7724857.35.1.pedyJi&s=p (accessed on 10 August 2015).
- Professional Large Production Soap Molds. Available online: http://soapequipment.com/lpmolds/#Manual_Cutter_Soap_Mold_-_Model_MCM2C (accessed on 2 August 2015).
- Manual Cutter. Available online: http://soapequipment.com/mcutter/ (accessed on 2 September 2015).
- Pneumatic Bath Bomb Press. Available online: http://soapequipment.com/bathbomb/ (accessed on 16 July 2015).
- Soap Drying Trays and Racks. Available online: http://soapequipment.com/trays/ (accessed on 20 September 2015).
- Van de Kamp, R.M.; Willson, B.G.; Mark, E.; Singley, M.E.; Tom, L.; Richard, L.T.; Kolega, J.J.; Gouin, R.F.; Lalibery, L.; Kay, D.; et al. On-Farm Composting Hand Book; NRAES-54; Natural Resource, Agriculture, and Engineering Service, Cooperative Extension: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Sarpong, S.Y. Co-Composting Organic Solid Waste with Moringa Oleifera Leaves, Sawdust and Grass Clippings. Master’s Thesis, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi, Ghana, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; de Haro, M.M.; Moore, A.; Falen, C. The Composting Process. Available online: http://www.cals.uidaho.edu/edcomm/pdf/CIS/CIS1179.pdf (accessed on 17 August 2015).
- Compost screen sieve. Available online: http://www.alibaba.com/product-detail/Greatly-welcomed-Compost-trommel-screen-sieve_1749472131.html?spm=a2700.7724857.35.14.p712Ev (accessed on 13 June 2015).
- Stainless Steel Compost Thermometer. Available online: http://www.alibaba.com/product-detail/Stainless-Steel-Compost-Thermometer_675547220.html?spm=a2700.7724838.35.1.935CLd&s=p (accessed on 11 September 2015).
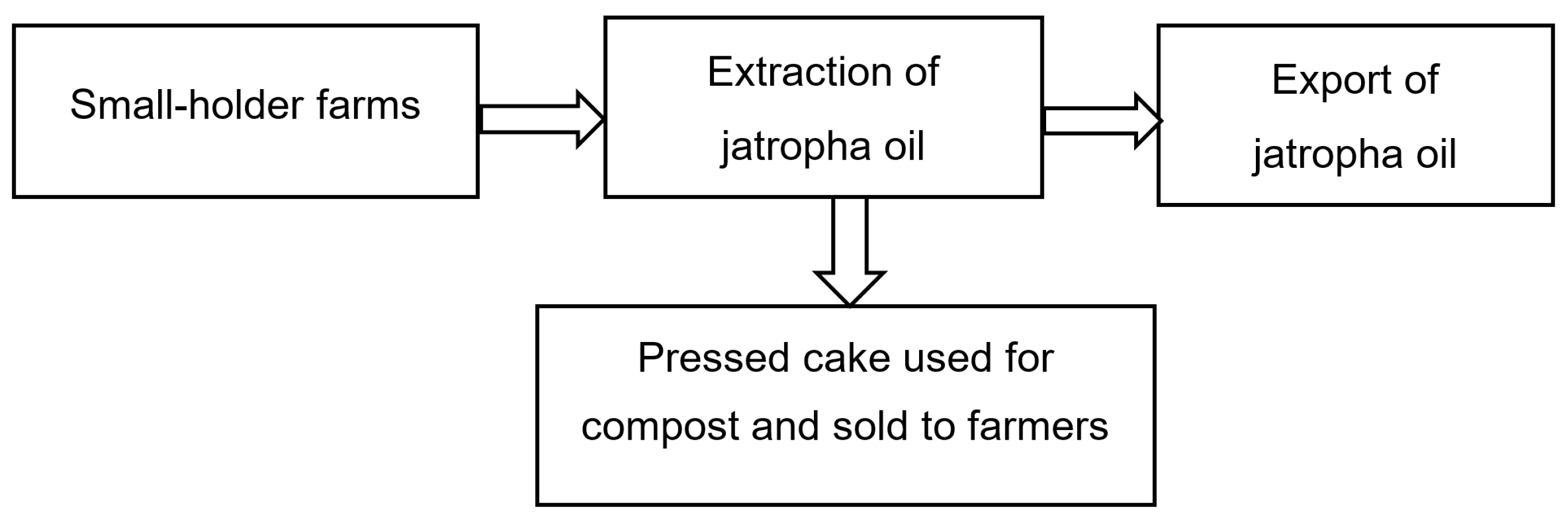
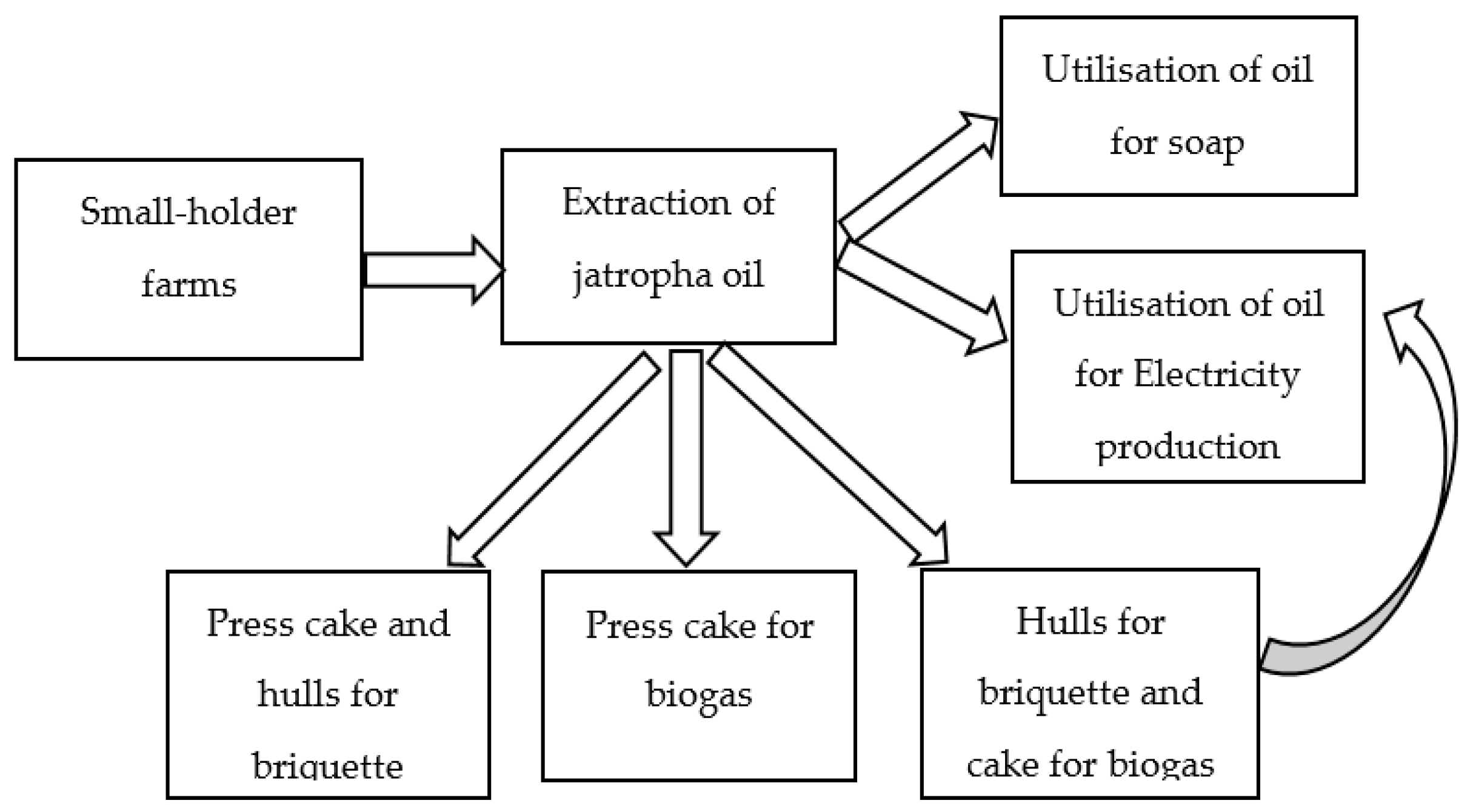
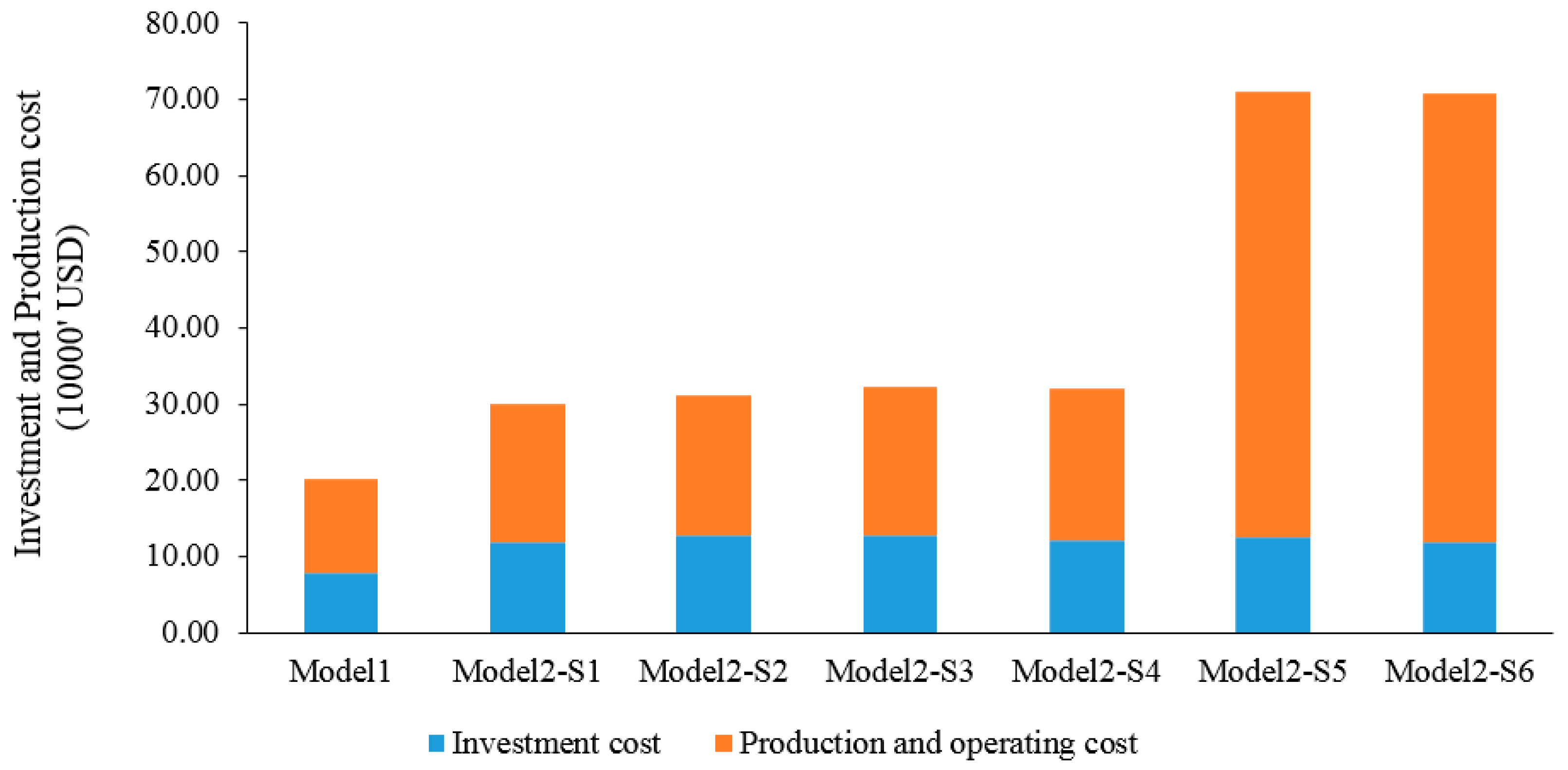
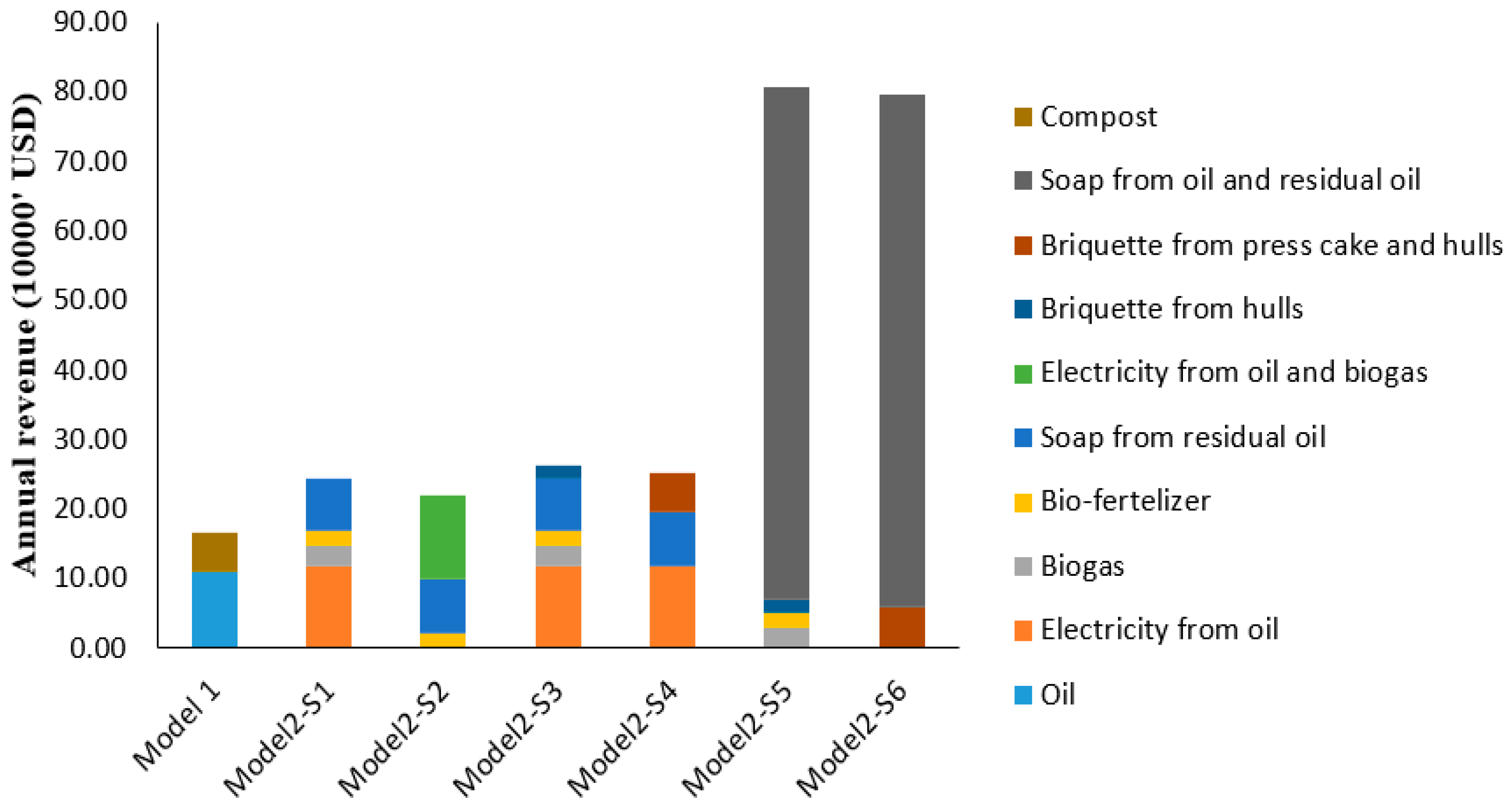
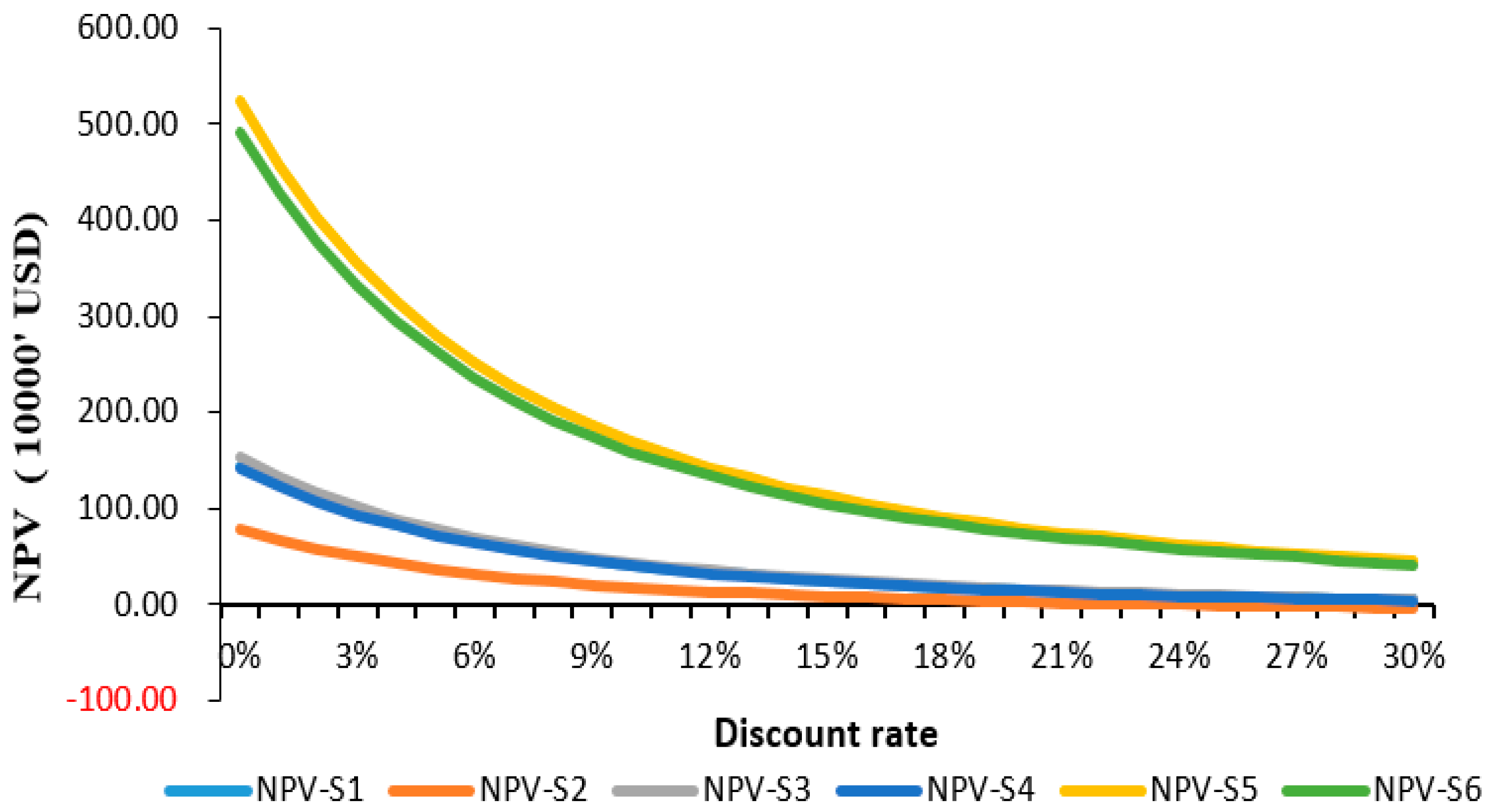
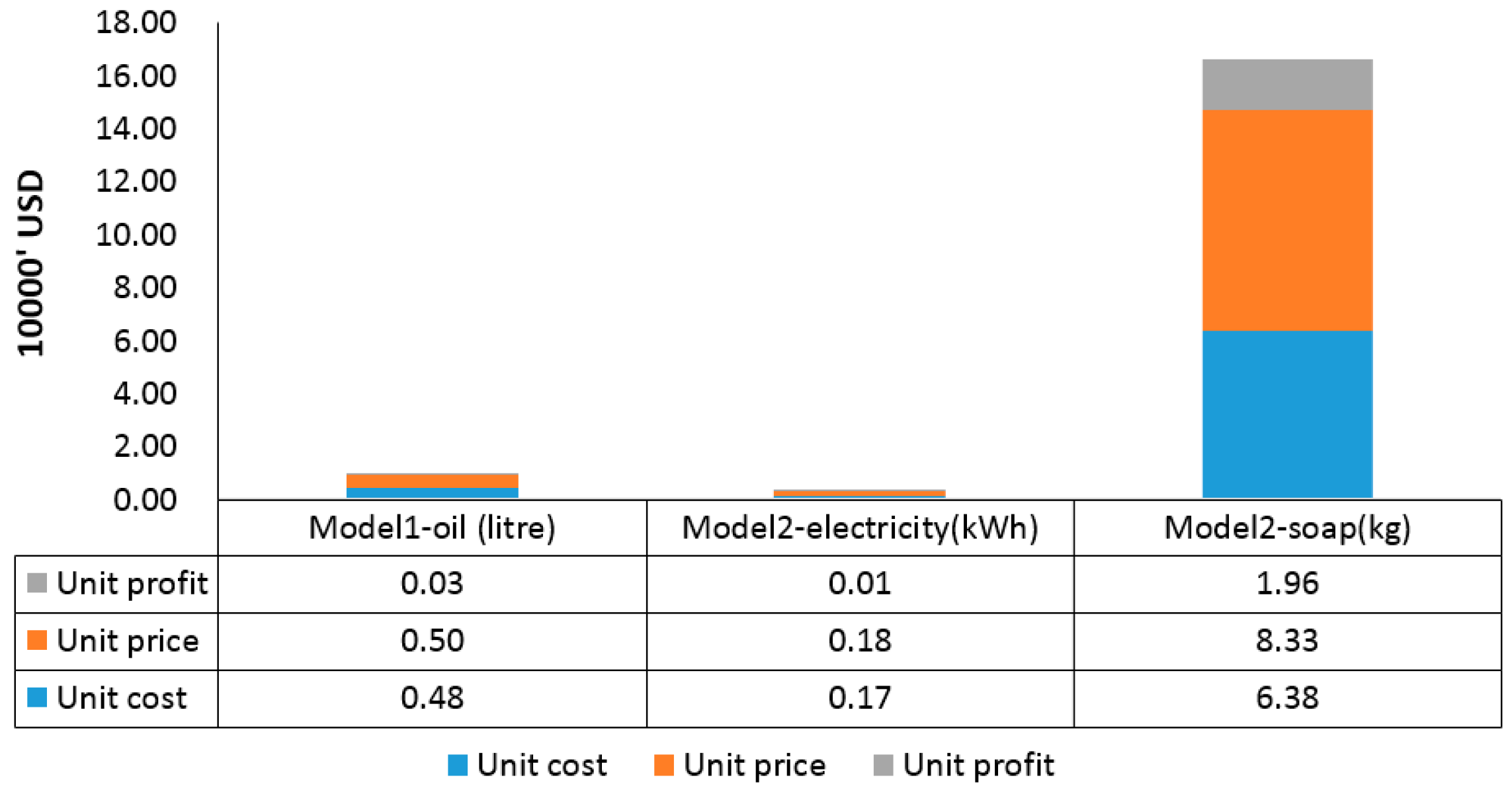
| Scenario | Description |
|---|---|
| Scenario 1 (S1) | Utilisation of oil for electricity generation, residual oil for soap and press cake for biogas production. |
| Scenario 2 (S2) | Utilisation of oil and biogas for electricity generation and residual oil for soap production. |
| Scenario 3 (S3) | Utilisation of oil for electricity, press cake for biogas, fruit hulls for briquette and residual oil for soap production. |
| Scenario 4 (S4) | Utilisation of oil for electricity generation, residual oil for soap production, press cake and fruit hulls for briquette production. |
| Scenario 5 (S5) | Utilisation of filtered and residual oil for soap production, press cake for biogas and fruit hulls for briquette production. |
| Scenario 6 (S6) | Utilisation of filtered and residual oil for soap production, press cake and hulls for briquette production. |
| Objective Function | Constraints |
|---|---|
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Cropping model | Intercropping/hedges |
| Planting spacing for intercropping (m) | 3 by 2 |
| Area covered per plant (m2) | 6 |
| Plant population per hectare | 1667 |
| Total plant population | 333,333 |
| Size of farm for each farmer (ha) | 0.5 |
| Number of plants per farmer | 833 |
| Total number of farmers required | 400 |
| Planting distance for hedges (m) | 1.5 |
| Total planting distance required by each farmer to achieve the required plant population (m) | 555.6 |
| Purchase price of jatropha seeds (kg) (USD) | 0.07 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Composting method | Windrow system |
| Quantity of press cake available for composting (tonnes) | 387 |
| Volume of press cake available (m3) | 1734 |
| Mixing ratio of press cake to bulking agents (grass clippings) | 2:1 |
| Volume of bulking agent required (m3) | 867 |
| Total volume of input material (m3) | 2601 |
| Quantity of compost generated annually (50% volume of input materials) (m3) | 1301 |
| Quantity of compost generated (kg) | 290,021 |
| Capacity of sieves (t/h) | 1 |
| Power of motor of sieves (kW) | 3 |
| Operational hours | 290 |
| Electricity consumption (kWh) | 870 |
| Unit price of sieves (USD) | 1000 |
| Unit price of compost thermometer (USD) | 10 |
| Unit price of moisture meter (USD) | 90 |
| Unit price of PH meter (USD) | 25 |
| Number of days for compost to reach maturity | 40 |
| Required temperature (°C) | 48–65 |
| Moisture content (% by weight) | 50–60 |
| C:N ratio | 25–35:1 |
| PH | 6.5–8 |
| Oxygen concentration (%) | 10 |
| Size of building required for sieving and storage (m2) | 90 |
| Unit price of compost/kg (USD) | 0.17 |
| Unit price of compost (50 kg bag) (USD) | 8.5 |
| Parameter | Model 1-Processor | Model 1-Farmer | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRR 25 Years (%) | NPV ($) | IRR 30 Years | NPV ($) | |
| Base scenario | 39.16 | 119,504 | 7.05 | −88.65 |
| Inclusion of carbon credit | NA | NA | 11.33 | −57.52 |
| Parameter | Model 1-Processor | Model 1-Farmer | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRR 25 Years (%) | NPV ($) | IRR 30 Years (%) | NPV ($) | |
| Selling/purchase price of seeds | ||||
| USD 0.05 | 47.26 | 174,383 | Negative value * | −227.33 |
| USD 0.16 | Negative value * | −127,452 | 60.84 | 535.41 |
| Price of crude oil | ||||
| USD 473/tonne | 20.44 | 11,858 | NA | NA |
| USD 1000/tonne | 81.44 | 458,547 | NA | NA |
| Seed yield | ||||
| 0.55 tonnes/ha/year | NA | NA | Negative value * | −274.69 |
| 7.5 tonnes/ha/year | NA | NA | 41.49 | 261.13 |
| Price of compost | ||||
| USD 0.13 | 25.68 | 39,120 | NA | NA |
| USD 0.25 | 50.81 | 199,889 | NA | NA |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Electricity generation from jatropha oil | |
| Capacity of generator set @ 50 HZ, 1500 rev/min (kW) | 16 |
| Fuel consumption at 100% power ratings (litres/h) | 5.4 |
| Quantity of oil available (L) | 219,744 |
| Number of hours generator must operates based on fuel consumption rate | 40,693.41 |
| Number of generators required assuming operational hours of 8700 annually | 5 |
| Electricity generated (kWh) | 651,095 |
| Unit price of generator (USD) | 4269 |
| Lifespan of generator (years) | 25 |
| Feed in tariff rate (USD/kWh) | 0.18 |
| Electricity generation from biogas | |
| Generator rated power @ 50 HZ, 1500 rev/min (kW) | 8 |
| Fuel consumption @ 100% power ratings (m3/kWh) | 0.38 |
| Quantity of methane available (m3) | 76,888 |
| Electricity generated (kWh) | 29,218 |
| Number of hours generator must operate | 3652.19 |
| Number of generators required | 1 |
| Oil consumption (g/kWh) | 2 |
| Unit price of generator (USD) | 7000 |
| Lifespan of generator (years) | 20 |
| Feed in tariff rate (USD/kWh) | 0.18 |
| Size of building for housing biogas generator (m2) | 10 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantity of oil required to produce 1 kg of soap (litres) | 2.77 |
| Quantity of water required to produce 1 kg of soap (litres) | 2.07 |
| Quantity of caustic soda required to produce 1 kg of soap (kg) | 0.41 |
| Quantity of oil available (tonnes) | 205 |
| Quantity of oil available (litres) | 245,496 |
| Quantity of soap produced from the available oil (kg) | 88,756 |
| Quantity of caustic soda required (kg) | 36,824.44 |
| Quantity of water required (litres) | 184,122 |
| Unit price of caustic soda per 25 kg (USD) | 300 |
| Capacity of soap mixing tanks (litres) | 98 |
| Number of soap mixing tanks required | 3 |
| Unit price of soap mixing tanks (USD) | 2800 |
| Capacity of manual cutting molds (kg) | 32 |
| Number of hours it takes for soap to harden in molds before removal | 24 |
| Number of manual soap cutting molds required | 12 |
| Unit price of manual soap cutting molds (USD) | 375 |
| Capacity of manual soap cutter per minute (kg) | 1 |
| Number of soap cutters required | 1 |
| Unit price of soap cutter (USD) | 1895 |
| Unit price of bath bomb press (USD) | 275 |
| Unit price of bath bomb molds (USD) | 285 |
| Capacity of drying tray (kg) | 12 |
| Number of hours it takes for soap to cure before packaging (hours) | 336 |
| Number of drying trays required | 270 |
| Unit cost per tray (USD) | 25 |
| Size of building required for soap production (m2) | 100 |
| Unit price of soap bar (180 g in weight) (USD) | 1.5 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Digester type | Fixed dome system |
| Density of jatropha press cake (kg/m3) | 1200 |
| Volume of press cake (m3/day) | 0.88 |
| Mixing ratio of press cake and water | 1:1 |
| Daily substrate input (m3/day) | 1.77 |
| Retention time (days) | 25 |
| Digester volume (m3) | 44.14 |
| Required digester volume for optimal gas production (m3) | 25 |
| Number of biogas plant required | 2 |
| Operating temperature (°C) | 30 |
| Quantity of total solids available (Degradable material) (tonnes) | 355.76 |
| Quantity of gas generated (L) (350 L/kgTS) | 124,515,468 |
| Quantity of methane available (L) (65% of biogas) | 80,935,054 |
| Quantity of methane available assuming 5% losses (L) | 76,888,301 |
| Quantity of methane available (m3) | 76,888 |
| Quantity of digestate generated (kg) (30% of feedstock) | 106,728 |
| Cost of Biogas plant per cubic meter (USD) | 300 |
| Lifespan of digester (years) | 25 |
| Unit price of bio methane per cubic meter | 0.39 |
| Unit price of bio fertilizer generated/kg | 0.19 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantity of press cake and hulls available (tonnes) | 693 |
| Capacity of briquette machine (t/h) | 0.18 |
| Operational hours (h) | 1750 |
| Number of briquette machines required | 2 |
| Fraction in weight of cake that remains after compression | 0.6 |
| Quantity of briquettes produced per year (tonnes) | 416 |
| Quantity of briquette assuming 1% losses (tonnes) | 411 |
| Unit cost of briquette machine (USD) | 1000 |
| Power of motor of briquette machine (kW) | 15 |
| Capacity of carbonizer machine (t/h) | 0.70 |
| Unit price of Carbonizer machine (USD) | 3000 |
| Number of carbonizer machine required | 1 |
| Power of motor of carbonizer (kW) | 1.5 |
| Annual electricity consumption of briquette and carbonizer (kWh) | 60,841.62 |
| Lifespan of briquette and carbonizer (years) | 20 |
| Oil and lubrication charges (% of fuel cost) | 2 |
| Size of building required for briquetting (m2) | 100 |
| unit price per kg of briquette (USD) | 0.12 |
| Unit price per bag of briquette (32 kg) (USD) | 3.84 |
| Parameter | Scenario 1 | Scenario 2 | Scenario 3 | Scenario 4 | Scenario 5 | Scenario 6 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRR 25 Years (%) | NPV ($) | IRR 25 Years (%) | NPV ($) | IRR 25 Years (%) | NPV ($) | IRR 25 Years (%) | NPV ($) | IRR 25 Years (%) | NPV ($) | IRR 25 Years (%) | NPV ($) | |
| Base Scenario | 39.40 | 184,768 | 23.90 | 48,281 | 39.10 | 193,654 | 37.34 | 172,668 | 92.75 | 907,230 | 91.62 | 847,265 |
| Sensitivity analysis | ||||||||||||
| Purchase price of seeds/kg | ||||||||||||
| USD 0.05 | 44.78 | 239,647 | 29.98 | 103,160 | 44.18 | 248,533 | 42.63 | 227,547 | 96.04 | 962,109 | 95.10 | 902,144 |
| USD 0.16 | 8.19 | −62,188 | Negative value * | −198,675 | 10.37 | −53,302 | 6.74 | −74,288 | 76.89 | 660,274 | 74.78 | 600,309 |
| Price of biogas/m3 | ||||||||||||
| USD 0.27 | 34.99 | 142,146 | NA | NA | 34.95 | 151,032 | NA | NA | 90.14 | 864,608 | NA | NA |
| USD 0.51 | 43.60 | 227,389 | NA | NA | 43.07 | 236,276 | NA | NA | 95.31 | 949,851 | NA | NA |
| Price of bio fertilizer/kg | ||||||||||||
| USD 0.13 | 36.29 | 154,482 | 20.28 | 17,995 | 36.17 | 163,368 | NA | NA | 90.90 | 876,944 | NA | NA |
| USD 0.25 | 42.27 | 213,645 | 27.17 | 77,158 | 41.81 | 222,531 | NA | NA | 94.49 | 936,1066 | NA | NA |
| Price of briquette/kg | ||||||||||||
| USD 0.08 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 36.40 | 165,666 | 28.05 | 83,967 | 91.04 | 879,241 | 85.81 | 758,564 |
| USD 0.16 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 41.73 | 221,642 | 45.75 | 261,368 | 94.44 | 935,218 | 97.20 | 935,965 |
| Feed-in-tariff rate(kWh) | ||||||||||||
| USD 0.23 | 53.25 | 332,669 | 39.91 | 202,819 | 52.19 | 341,555 | 50.99 | 320,569 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Price of soap/180 g | ||||||||||||
| USD 1.1 | 28.86 | 86,710 | 10.94 | −49,888 | 29.21 | 95,596 | 27.00 | 74,610 | 17.48 | −3,893 | 7.78 | −63,858 |
| USD 1.95 | 49.43 | 289,805 | 35.12 | 153,207 | 48.58 | 298,691 | 47.22 | 277,705 | 145.3 | 1,932,243 | 146.7 | 1,872,278 |
| Objective Function | Constraints |
|---|---|
| Utilisation of Oil | |
| where: | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osei, I.; Akowuah, J.O.; Kemausuor, F. Techno-Economic Models for Optimised Utilisation of Jatropha curcas Linnaeus under an Out-Grower Farming Scheme in Ghana. Resources 2016, 5, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources5040038
Osei I, Akowuah JO, Kemausuor F. Techno-Economic Models for Optimised Utilisation of Jatropha curcas Linnaeus under an Out-Grower Farming Scheme in Ghana. Resources. 2016; 5(4):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources5040038
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsei, Isaac, Joseph O. Akowuah, and Francis Kemausuor. 2016. "Techno-Economic Models for Optimised Utilisation of Jatropha curcas Linnaeus under an Out-Grower Farming Scheme in Ghana" Resources 5, no. 4: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources5040038
APA StyleOsei, I., Akowuah, J. O., & Kemausuor, F. (2016). Techno-Economic Models for Optimised Utilisation of Jatropha curcas Linnaeus under an Out-Grower Farming Scheme in Ghana. Resources, 5(4), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources5040038







