Impact Assessment of Mining Dewatering on Vegetation Based on Satellite Image Analysis and the NDVI Index—A Case Study of a Chalk Mine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
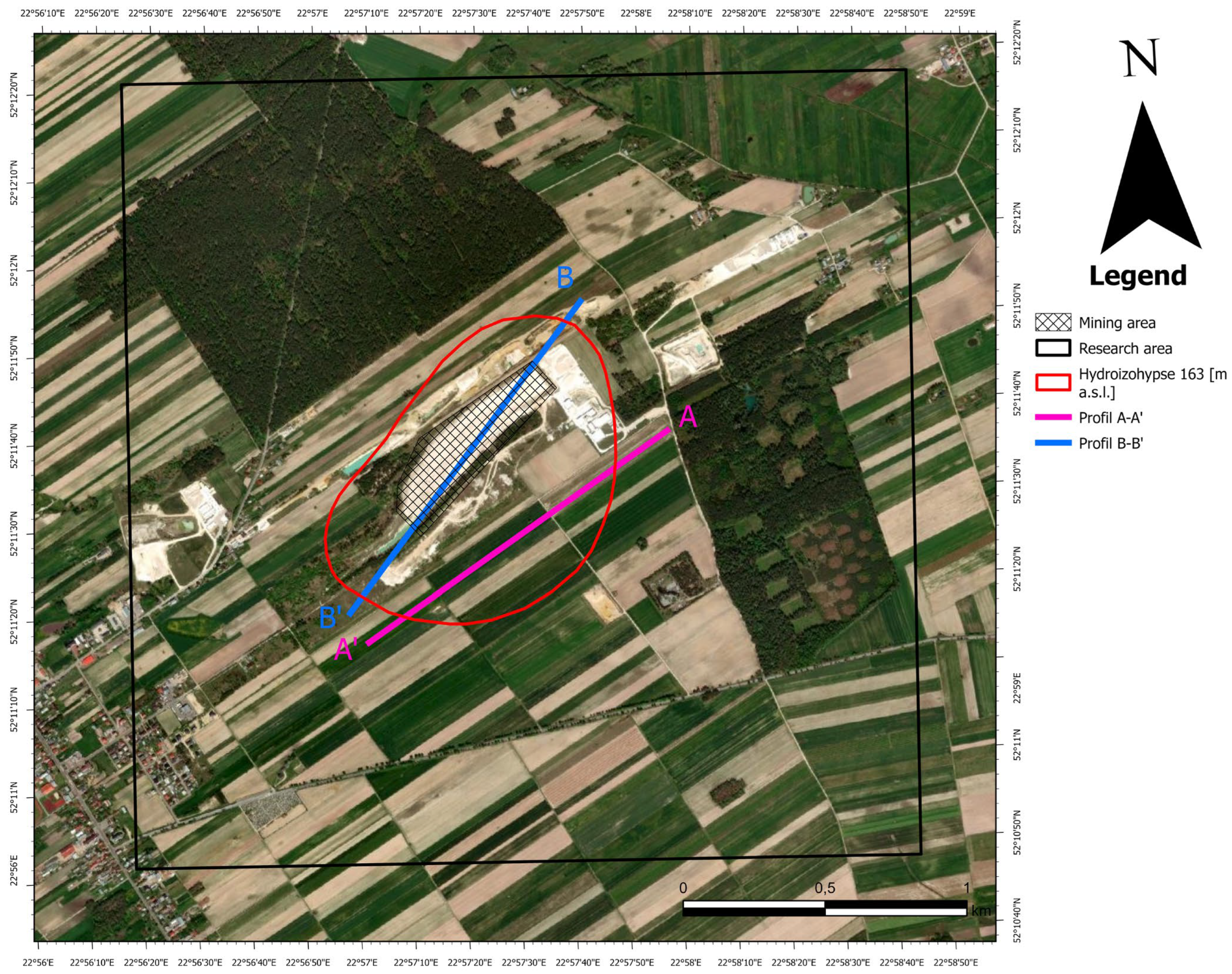
2.1. Study Area
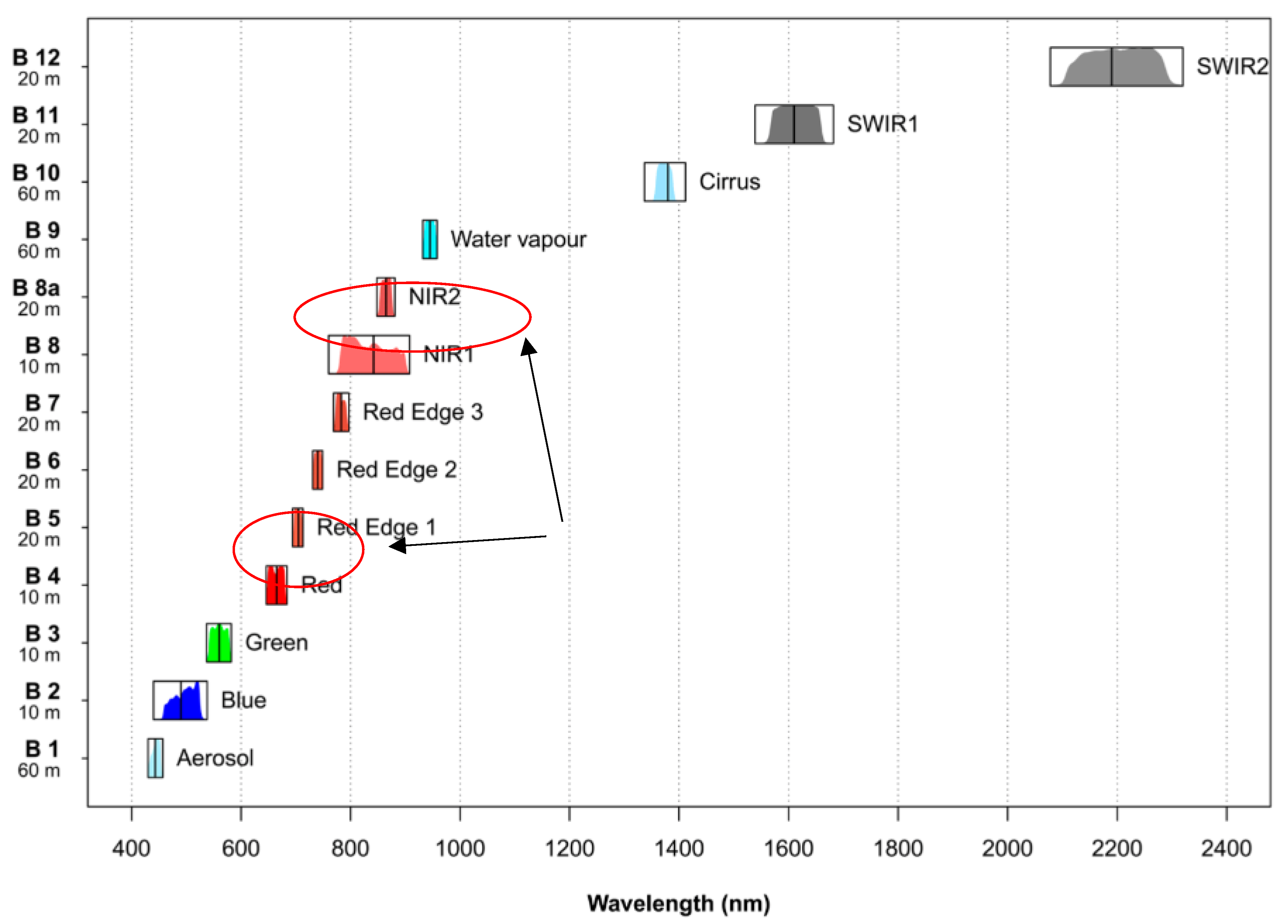
2.2. Application of Satellite Data
2.3. Spatial Analysis
2.4. Technological Limitations and Minimization of Measurement Errors
2.5. Image Processing and Quality Control
3. Results
3.1. Satellite Image Dataset and Temporal Coverage
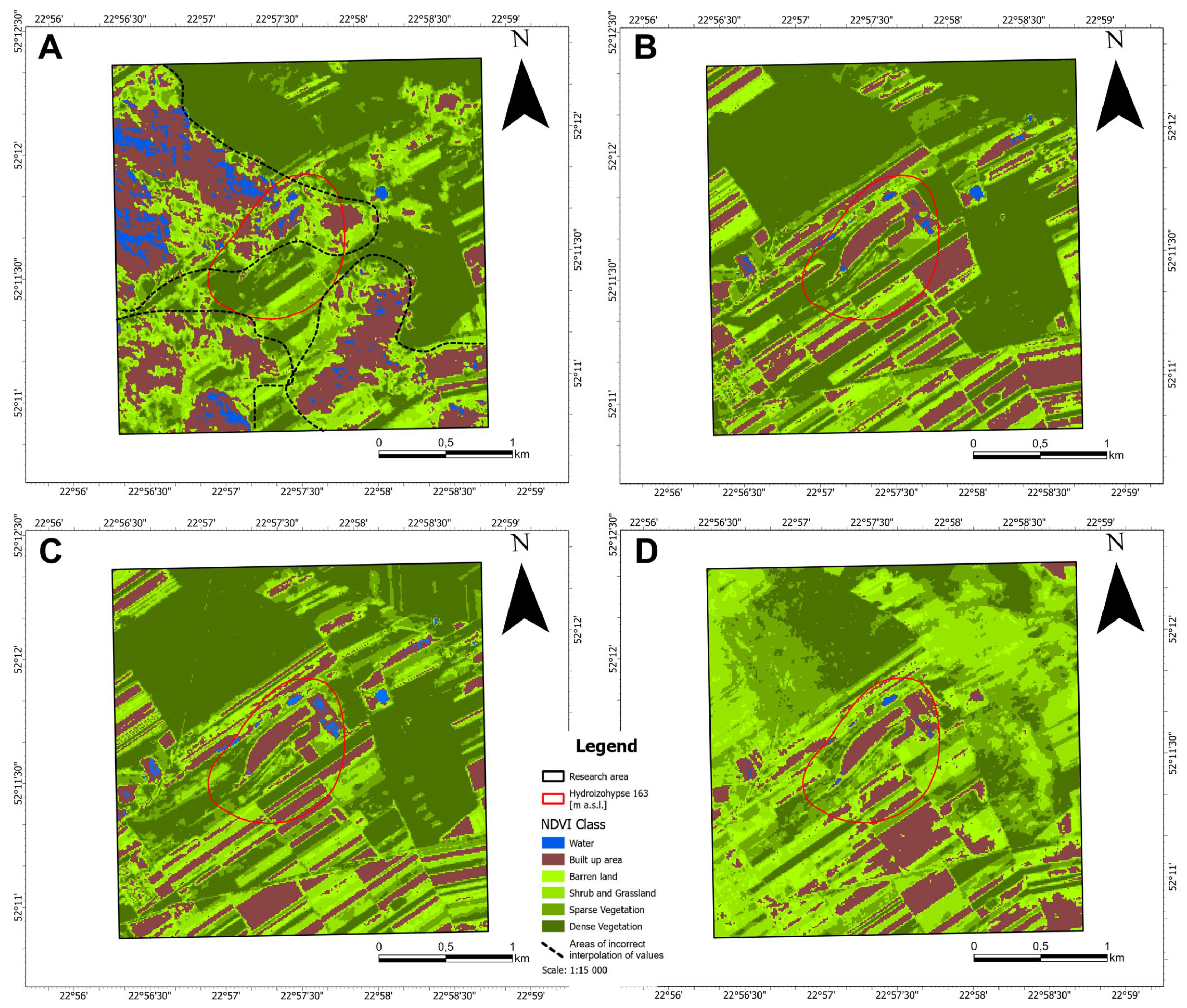
3.2. Spatial Distribution of NDVI Values
3.3. Temporal Variability of NDVI
3.4. Comparison of NDVI Inside and Outside Depression Cone
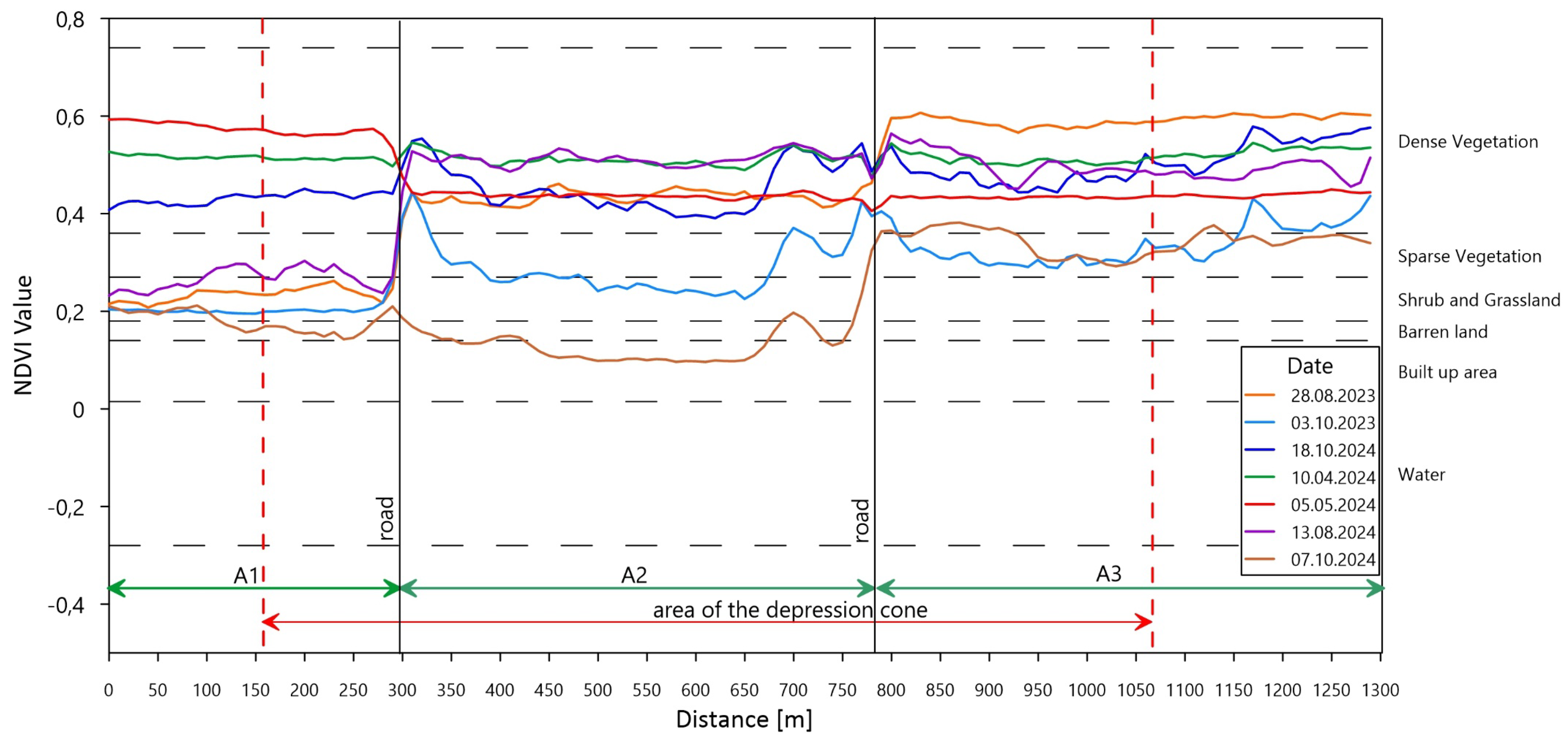
3.5. Spectral Profile Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Vegetation health, as indicated by NDVI index, is driven mainly by phenological cycles and agronomic practices rather than by modest changes in the groundwater table. Seasonal NDVI index changes—from spring green-up through summer peak to autumn decline—mirror crop development and mask any hydrological signal.
- Spatial profiles crossing the depression cone (Figure 7 and Figure 8) revealed uniform NDVI signatures for meadows (0.20–0.40), forests (up to 0.60), and arable fields (peak 0.60), with no consistent depression near the dewatering boundary. This implies effective root-zone moisture buffering by local fine sands and chalk.
- The absence of significant differences in NDVI index inside versus outside the cone confirms that groundwater drawdown did not have a negative impact on the vitality of vegetation.
- The applied approach—combining Sentinel-2 surface reflectance NDVI with piezometric mapping—provides a solid basis for monitoring vegetation response to mine drainage.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Libicki, J. Changes in the Groundwater Due to Surface Mining. Górnictwo Geol. 1982, 25, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzki, J.; Przeżdziecki, K.; Miatkowski, Z. Determining the Area of Influence of Depression Cone in the Vicinity of Lignite Mine by Means of Triangle Method and LANDSAT TM/ETM+ Satellite Images. Geologia 2016, 166, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, A.; Witkowski, A.; Różkowski, A.; Szczepański, A.; Rogoż, M.; Przybyłek, J.; Staśko, S. What Polish Mining Owes to Polish Hydrogeology? Przegląd Geol. 2010, 58, 774–786. [Google Scholar]
- Kleczkowski, A.S.; Różkowski, A. Słownik Hydrogeologiczny; Wydawnictwo Trio: Warszawa, Poland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Paull, D.; Banks, G.; Ballard, C.; Gillieson, D. Monitoring the Environmental Impact of Mining in Remote Locations through Remotely Sensed Data. Resources 2006, 21, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajewski, P.; Kaczmarek, Z. Selected Properties of Soils Located within the Depression Cone of a Planned Excavation of the Drzewce Open Cast Pit (Central Poland). Soil Sci. Annu. 2021, 72, 143890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, K.; Kaznowska-Opala, K.; Różkowski, K.; Pawlecka, K. Cone of Depression and Range of Negative Impact of Dewatering. J. Environ. Eng. 2025, 71, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Kasperek, R.; Wiatkowski, M.; Rosik-Dulewska, C. Investigations of Hydrological Regime Changes in an Area Adjacent to a Mine of Rock Raw Materials. J. Water Land Dev. 2015, 17, 256–274. [Google Scholar]
- Hejmanowska, B.; Wezyk, P. Dane Satelitarne dla Administracji Publicznej. 2020. Available online: https://polsa.gov.pl/wp-content/themes/polsa/files/Podrecznik.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Cacciuttolo, C.; Guzmán, V.; Catriñir, P.; Atencio, E.; Komarizadehasl, S.; Lozano-Galant, J.A. Low-Cost Sensor Technologies for Monitoring Sustainability and Safety Issues in Mining Activities: Advances, Gaps, and Future Directions in the Digitalization for Smart Mining. Sensors 2023, 23, 6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adynkiewicz-Pirgas, M.; Lejcuś, I. Studies on Hydromorphological Attributes Variability and the Degree of Transformation of Combined Water Body of Chosen River Valleys in South-Western Poland; IMGW-PIB. 2016. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320444593_Studies_on_hydromorphological_attributes_variability_and_the_degree_of_transformation_of_combined_water_body_of_chosen_river_valleys_in_south-western_Poland (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- West, L.J.; Farrell, R.P.; Foley, A.E.; Howlett, P.R.; Massei, N. An introduction to the chalk aquifers of northern Europe. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2023, 517, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Downing, R.A.; Price, M.; Jones, G.P. The Hydrogeology of the Chalk of Nirth-West Europe, The Chalk as an Aquifer in the Netherlands; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Gould, S. A Guide to Soil Moisture. Available online: https://connectedcrops.ca/the-ultimate-guide-to-soil-moisture/ (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service. Soil Quality Indicators; USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2008.
- Państwowy Instytut Badawczy. Złoża Kopalin. Available online: https://geoportal.pgi.gov.pl/portal/page/portal/midas/zrodlo_danych (accessed on 22 January 2025).
- Copernicus. A European Wide-Swath, High-Resolution, Multi-Spectral Imaging Mission. Available online: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/explore-data/data-collections/sentinel-data/sentinel-2 (accessed on 22 January 2025).
- Gascon, F.; Bouzinac, C.; Thépaut, O.; Jung, M.; Francesconi, B.; Louis, J.; Lonjou, V.; Lafrance, B.; Massera, S.; Gaudel-Vacaresse, A.; et al. Copernicus Sentinel-2A Calibration and Products Validation Status. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immitzer, M.; Vuolo, F.; Atzberger, C. First Experience with Sentinel-2 Data for Crop and Tree Species Classifications in Central Europe. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polska Agencja Kosmiczna. Wskaźniki Teledetekcyjne Jako Miara Stanu Środowiska, Scenariusz Warstwowy 2. Available online: https://sat4envi.imgw.pl/elearning/mod/resource/view.php?id=548 (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Rodríguez-Puerta, F.; Perroy, R.L.; Barrera, C.; Price, J.P.; García-Pascual, B. Five-Year Evaluation of Sentinel-2 Cloud-Free Mosaic Generation under Varied Cloud Cover Conditions in Hawai’i. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tao, P.; Cui, Y. Research on cloud removal based on fusing Multi-temporal Remote Sensing Images. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 10th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC), Chongqing, China, 17–19 June 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Pang, T.; Wang, B.; Chachan, R.; Tian, Y. A Comprehensive Study on Spectral Analysis and Anomaly Detection of River Water Quality Dynamics with High Time Resolution Measurements. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 589, 125175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraner, A.; Ebel, P.; Zhu, X.X.; Schmitt, M. Cloud Removal in Sentinel-2 Imagery Using a Deep Residual Neural Network. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 166, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- METEO IMGW-PIB. Najważniejsze Pojęcia i Zwroty w Hydrogeologii. Available online: https://imgw.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/slownik-dla-mediow_chok.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Maurice, L.; Farrant, A.R.; Mathewson, E.; Atkinson, T. Karst hydrogeology of the Chalk and implications for groundwater protection. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2021, 517, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, R.J.; Lawrence, A.R.; Whitehead, E.J.; Cobbing, J.E.; Darling, W.G.; Hughes, A.G. Groundwater Systems and Water Quality Programme, Internal Report IR/04/007, Recharge to the Chalk Aquifer; British Geological Survey: Nottingham, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ebel, P.; Garnot, V.S.F.; Schmitt, M.; Wegner, J.D.; Zhu, X.X. UnCRtainTS: Uncertainty Quantification for Cloud Removal in Optical Satellite Time Series. Remote Sens. 2023, 202, 2086–2096. [Google Scholar]
- El Mendili, L.; Puissant, A.; Chougrad, M.; Sebari, I. Towards a Multi-Temporal Deep Learning Approach for Mapping Urban Fabric Using Sentinel-2 Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebel, P.; Xu, Y.; Schmitt, M.; Zhu, X. SEN12MS-CR-TS: A Remote Sensing Data Set for Multi-Modal Multi-Temporal Cloud Removal. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, Q.-T.; Jamet, C.; Vantrepotte, V.; Mériaux, X.; Cauvin, A.; Mograne, M.A. Evaluation of Sentinel-2/MSI Atmospheric Correction Algorithms over Two Contrasted French Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravec, D.; Komárek, J.; López-Cuervo Medina, S.; Molina, I. Effect of Atmospheric Corrections on NDVI: Intercomparability of Landsat 8, Sentinel-2, and UAV Sensors. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khetkeeree, S.; Petchthaweetham, B.; Liangrocapart, S.; Srisuk, S. Sentinel-2 Image Dehazing using Correlation between Visible and Infrared Bands. In Proceedings of the 2020 8th International Electrical Engineering Congress (iEECON), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 4–6 March 2020. [Google Scholar]




| Class | NDVI Range |
|---|---|
| Water | −0.28 to 0.015 |
| Built up area | 0.015 to 0.14 |
| Barren land | 0.14 to 0.18 |
| Shrub and Grassland | 0.18 to 0.27 |
| Sparse Vegetation | 0.27 to 0.36 |
| Dense Vegetation | 0.36 to 0.74 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gromnicki, K.; Chudy, K. Impact Assessment of Mining Dewatering on Vegetation Based on Satellite Image Analysis and the NDVI Index—A Case Study of a Chalk Mine. Resources 2025, 14, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14090134
Gromnicki K, Chudy K. Impact Assessment of Mining Dewatering on Vegetation Based on Satellite Image Analysis and the NDVI Index—A Case Study of a Chalk Mine. Resources. 2025; 14(9):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14090134
Chicago/Turabian StyleGromnicki, Kamil, and Krzysztof Chudy. 2025. "Impact Assessment of Mining Dewatering on Vegetation Based on Satellite Image Analysis and the NDVI Index—A Case Study of a Chalk Mine" Resources 14, no. 9: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14090134
APA StyleGromnicki, K., & Chudy, K. (2025). Impact Assessment of Mining Dewatering on Vegetation Based on Satellite Image Analysis and the NDVI Index—A Case Study of a Chalk Mine. Resources, 14(9), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14090134






