Fruit and Vegetable Loss in Markets in the North of Lebanon: Drivers, Challenges, and Prevention
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
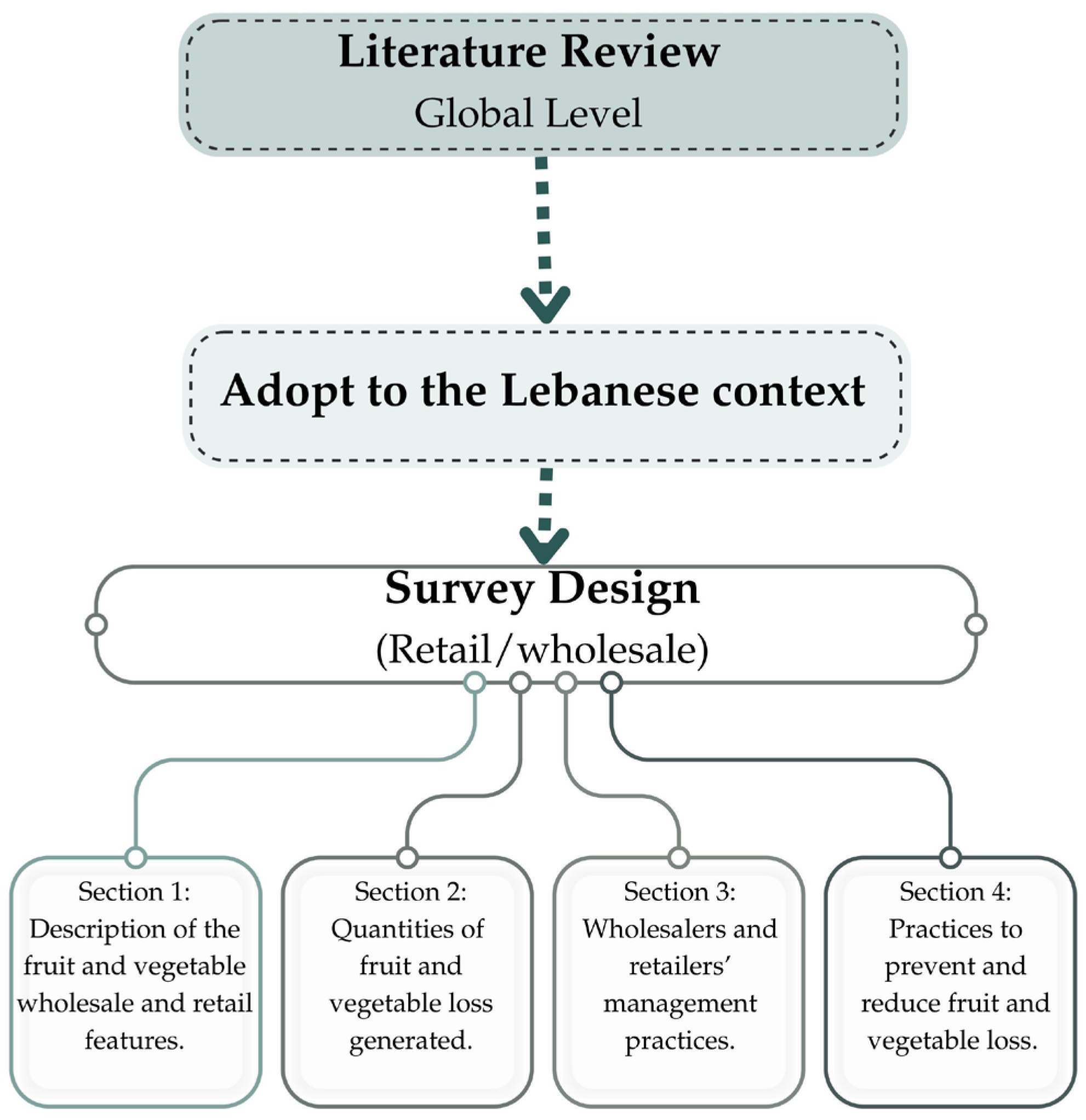
2.1. Overview of the Methodology
2.2. Sampling Methods and Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Study Area: Akkar and North Governorates
3. Results
3.1. Significance of Factors on the Loss Generated
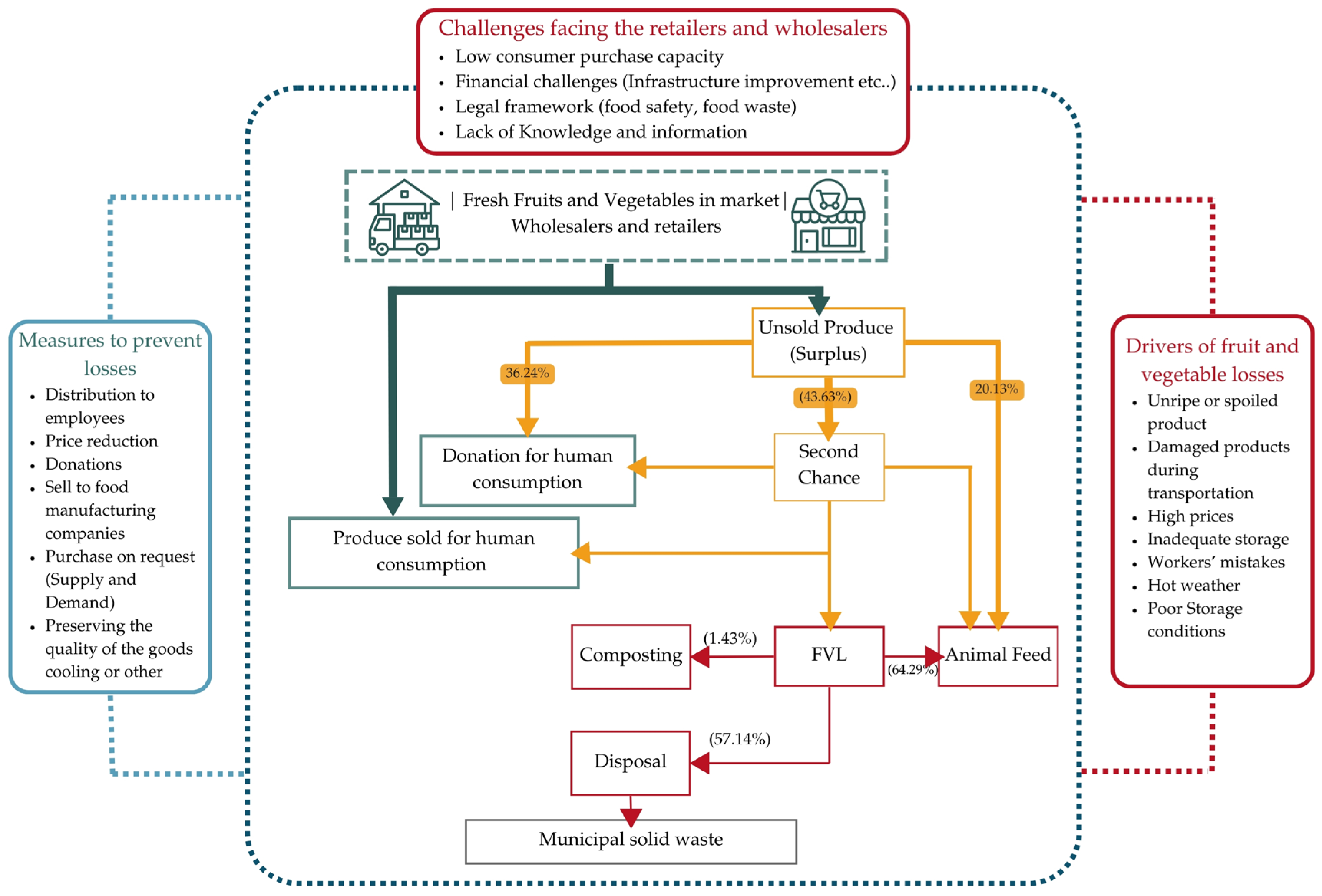
3.2. Management of Surplus Fruits and Vegetables to Reduce FVL
3.3. Key Drivers Contributing to Fruit and Vegetable Loss
3.4. FVL Prevention Measures and Their Efficiencies
3.5. Challenges to Preventing Fruit and Vegetable Losses
3.6. Clearance/Disposal of Fruits and Vegetables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FLW | Food Loss and Waste |
| FVL | Fruit and Vegetable Loss |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization |
| USAID | United States Agency for International Development |
| UNDP | United Nations Development Programme |
| DGCS | Directorate General of Civil Status—Lebanon |
| OCHA | United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs |
| WWO | World Weather Online |
| R | A programming language used for statistical computing and graphics |
References
- HLPE. Food Losses and Waste in the Context of Sustainable Food Systems; A report by the High-Level Panel of Experts on Food Security and Nutrition of the Committee on World Food Security; HLPE: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gustavsson, J.; Cederberg, C.; Sonesson, U.; Van Otterdijk, R.; Meybeck, A. Global Food Losses and Food Waste: Extent, Causes and Prevention; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2019—Building Resilience for Peace and Food Security; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Food Waste Index Report 2024—Think Eat Save: Tracking Progress to Halve Global Food Waste; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2024; Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/20.500.11822/45230 (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Mokrane, S.; Buonocore, E.; Capone, R.; Franzese, P.P. Exploring the Global Scientific Literature on Food Waste and Loss. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaf, L.; Franzese, P.P.; Capone, R.; Buonocore, E. Unfolding Hidden Environmental Impacts of Food Waste: An Assessment for Fifteen Countries of the World. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 310, 127523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibler, K.M.; Reinhart, D.; Hawkins, C.; Motlagh, A.M.; Wright, J. Food Waste and the Food-Energy-Water Nexus: A Review of Food Waste Management Alternatives. Waste Manag. 2018, 74, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbade, E.B. Estimating the Nutritional Loss and the Feeding Potential Derived from Food Losses Worldwide. World Dev. 2020, 134, 105038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Economist Impact. Global Food Security Index 2022. Available online: https://impact.economist.com/sustainability/project/food-security-index/explore-countries (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Keating, B.A.; Herrero, M.; Carberry, P.S.; Gardner, J.; Cole, M.B. Food Wedges: Framing the Global Food Demand and Supply Challenge Towards 2050. Glob. Food Secur. 2014, 3, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee-Jood, M.; Cai, X. Reducing Food Loss and Waste to Enhance Food Security and Environmental Sustainability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8432–8443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechagias, E.P.; Gayialis, S.P.; Panayiotou, N.; Papadopoulos, G.A. A Holistic Framework for Evaluating Food Loss and Waste Due to Marketing Standards Across the Entire Food Supply Chain. Foods 2024, 13, 3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santeramo, F.G.; Lamonaca, E. Food Loss–Food Waste–Food Security: A New Research Agenda. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalvedi, M.L.; Rossi, L. Comprehensive Measurement of Italian Domestic Food Waste in a European Framework. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancoli, P.; Rousta, K.; Bolton, K. Life Cycle Assessment of Supermarket Food Waste. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 118, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeze, J.; Axmann, H.; Castelein, B.; Guo, X.; Sander, B.O.; Nelson, K.M.; Wassmann, R.; Van Hung, N. Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Reducing Food Loss and Waste: Value Chain Interventions from Farmer to Fork. In Transforming Food Systems Under Climate Change Through Innovation; Campbell, B., Thornton, P., Loboguerrero, A.M., Dinesh, D., Nowak, A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 104–118. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, C.; Dhir, A.; Ul Akram, M.; Salo, J. Food Loss and Waste in Food Supply Chains: A Systematic Literature Review and Framework Development Approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, Y.; Berrens, P.; Custers, K.; Van Hemelryck, S.; Kellens, K.; Geeraerd, A. Correction to: How Origin, Packaging and Seasonality Determine the Environmental Impact of Apples, Magnified by Food Waste and Losses. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2019, 24, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, S.D.; Reay, D.S.; Higgins, P.; Bomberg, E. A Half-Century of Production-Phase Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Food Loss & Waste in the Global Food Supply Chain. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakar, B.; Aydin, S.; Varank, G.; Ozcan, H.K. Assessment of Environmental Impact of Food Waste in Turkey. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, S.; Saikumar, A.; Badwaik, L.S. Food Losses and Wastage within Food Supply Chain: A Critical Review of Its Generation, Impact, and Conversion Techniques. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2024, 6, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, T. Where Are the Best Opportunities for Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions in the Food System (Including the Food Chain)? Food Policy 2011, 36 (Suppl. 1), S23–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfitt, J.; Barthel, M.; Macnaughton, S. Food Waste within Food Supply Chains: Quantification and Potential for Change to 2050. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 3065–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, M.; Solazzo, E.; Guizzardi, D.; Monforti-Ferrario, F.; Tubiello, F.N.; Leip, A. Food Systems Are Responsible for a Third of Global Anthropogenic GHG Emissions. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Luo, Z.; Sun, T.; Li, W.; Zhou, W.; Wang, X.; Fei, X.; Tong, H.; Yin, K. Cradle-to-Grave Emissions from Food Loss and Waste Represent Half of Total Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Food Systems. Nat. Food 2023, 4, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancal, V.; Ray, R.C. Overview of Food Loss and Waste in Fruits and Vegetables: From Issue to Resources. In Fruits and Vegetable Wastes; Ray, R.C., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sial, T.A.; Rajpar, I.; Khan, M.N.; Ali, A.; Shan, M.; Rajput, A.B.; Shah, P.A.N. Impact of Fruit and Vegetable Wastes on the Environment and Possible Management Strategies. In Planet Earth: Scientific Proposals to Solve Urgent Issues; Núñez-Delgado, A., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of Food and Agriculture 2019—Moving Forward on Food Loss and Waste Reduction; Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2019; Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/ca6030en/ca6030en.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Garavito Realpe, N. Risk Factors of Food Loss and Waste, and Life Cycle Assessment of Waste Management Strategies in the Brazilian Leafy Vegetable Supply Chain. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Borås, Borås, Sweden, 2023. Available online: https://hb.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1800691/FULLTEXT01.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Abadi, B.; Mahdavian, S.; Fattahi, F. The Waste Management of Fruit and Vegetable in Wholesale Markets: Intention and Behavior Analysis Using Path Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehr, M.; Romão, D.C. Measurement of Fruit and Vegetable Losses in Brazil: A Case Study. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2001, 3, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismael, R.K. Quantification of Food Waste in Retail Operations: A Fruit and Vegetable Wastage Case in Paraguay. Environ. Chall. 2023, 10, 100665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnieri, P.; de Aguiar, R.C.C.; Thomé, K.M.; Watanabe, E.A.M. The Role of Logistics in Food Waste Reduction in Wholesalers and Small Retailers of Fruits and Vegetables: A Multiple Case Study. Logistics 2021, 5, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porat, R.; Lichter, A.; Terry, L.A.; Harker, R.; Buzby, J. Postharvest Losses of Fruit and Vegetables During Retail and in Consumers’ Homes: Quantifications, Causes, and Means of Prevention. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 139, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, S.F.; Eini-Zinab, H.; Anari, F.M.; Amirolad, M.; Babaei, Z.; Sobhani, S.R. Food Waste Reduction and Its Environmental Consequences: A Quasi-Experimental Study in a Campus Canteen. Agric. Food Secur. 2024, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiad, M.; Meho, L.I. Food Loss and Food Waste Research in the Arab World: A Systematic Review. Food Secur. 2018, 10, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of Food and Agriculture: Innovation in Family Farming; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- USAID. Lebanon Food Security Assessment 2024; United States Agency for International Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sawaya, R. Effect of Naameh Landfill on the Environment of the Surrounding Area in South Lebanon. Ph.D. Thesis, Lebanese University, Beirut, Lebanon, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- UNDP. Poverty in Lebanon: The Socio-Economic Challenges and Implications; United Nations Development Programme: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Statistics Division. Available online: https://unstats.un.org (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- World Bank. Country Classifications by Income Level for Year 2022. Available online: https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519 (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Hassan, H.; Mattar, L.; Rizk, Y.; Abiad, M.; Chalak, A. Household Food Waste Generation During COVID-19 Pandemic and Unprecedented Economic Crisis: The Case of Lebanon. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalak, A.; Abiad, M.; Diab, M.; Nasreddine, L. The Determinants of Household Food Waste Generation and Its Associated Caloric and Nutrient Losses: The Case of Lebanon. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Ghandour, L.; Chalak, A.; Aoun, P.; Reynolds, C.; Abiad, M. The Influence of Religion and Religiosity on Food Waste Generation Among Restaurant Clienteles. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 1010262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeineddine, M.; Kharroubi, S.; Chalak, A.; Hassan, H.; Abiad, M. Post-Consumer Food Waste Generation While Dining Out: A Close-Up View. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoteit, M.; Badreddine, N.; Mohamad, J.; Khattar, M.; Fattouh, F.; Malli, D.; Antar, E.; El Khatib, S.; Abiad, M.; Hassan, H. Quantifying Hospital Plate Waste and Identifying Its Correlates from Patients’ Perspectives in Lebanon. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Khattar, M.; Fattouh, F.; Malli, D.; Antar, E.; Mohamad, J.; Badreddine, N.; El Khatib, S.; Abiad, M.; Hoteit, M. Food Waste Management in Lebanese Hospital Food Services: Findings from a First-of-Its-Kind Cross-Sectional Study in the Arab Region. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 16, 101127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pano, N.; Nehme, N.; Halwani, J.; Karantininis, K.; Karameh, J.; Taleb, N. Food Loss at Retail Stores in Lebanon: A Pilot Assessment Study. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 14, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göbel, C.; Langen, N.; Blumenthal, A.; Teitscheid, P.; Ritter, G. Cutting Food Waste Through Cooperation Along the Food Supply Chain. Sustainability 2015, 7, 1429–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellemare, M.F.; Çakir, M.; Peterson, H.H.; Novak, L.; Rudi, J. On the Measurement of Food Waste. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2017, 99, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Food Waste Index Report 2021; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2021; Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/report/unep-food-waste-index-report-2021 (accessed on 14 August 2022).
- Directorate General of Civil Status. Available online: https://www.dgcs.gov.lb/arabic/statistics-map (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs. Available online: https://www.unocha.org/lebanon (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Elbiyad, J.; Aboukhalaf, A.; Kalili, A.; Belaoufi, H.; Atouife, S.; Essaih, S.; El Amraoui, B.; Belahsen, R. Quantitative and Qualitative Assessment of Food Waste in Rural Markets in Morocco. N. Afr. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2024, 8, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, M.; Strid, I.; Hansson, P.-A. Food Losses in Six Swedish Retail Stores: Wastage of Fruit and Vegetables in Relation to Quantities Delivered. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 68, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Liu, G.; Parfitt, J.; Liu, X.; van Herpen, E.; Stenmarck, Å.; O’Connor, C.; Östergren, K.; Cheng, S. Missing Food, Missing Data? A Critical Review of Global Food Losses and Food Waste Data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6618–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaipia, R.; Dukovska-Popovska, I.; Loikkanen, L. Creating Sustainable Fresh Food Supply Chains Through Waste Reduction. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2013, 43, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, M.; Ghosh, R.; Mattsson, L.; Ismatov, A. Take-back agreements in the perspective of food waste generation at the supplier-retailer interface. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 122, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yao, X.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Q. Impact of Pricing and Product Information on Consumer Buying Behavior With Customer Satisfaction in a Mediating Role. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 720151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schudel, S.; Shoji, K.; Shrivastava, C.; Onwude, D.; Defraeye, T. Solution Roadmap to Reduce Food Loss Along Your Postharvest Supply Chain from Farm to Retail. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 36, 101057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, G.T.; Meinert, C.; Ormelez, F.; Campani, M.; Bertoli, S.L.; Ender, L.; Souza, C.K. Fresh food shelf-life improvement by humidity regulation in domestic refrigeration. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 217, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, M.; Strid, I.; Hansson, P.-A. Food waste reduction in supermarkets—Net costs and benefits of reduced storage temperature. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 107, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Weather Online. Available online: https://www.worldweatheronline.com (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Teigiserova, D.A.; Hamelin, L.; Thomsen, M. Towards Transparent Valorization of Food Surplus, Waste and Loss: Clarifying Definitions, Food Waste Hierarchy, and Role in the Circular Economy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 136033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabella, N.; Castellani, V.; Sala, S. Current Options for the Valorization of Food Manufacturing Waste: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukahhal, W.; Abebe, G.K.; Bahn, R.A. Opportunities and Challenges for Lebanese Horticultural Producers Linked to Corporate Buyers. Agriculture 2022, 12, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A. In Lebanon, Small-Scale Farmers Are Struggling to Survive. The New Arab. 22 September 2022. Available online: https://www.newarab.com/features/lebanon-small-scale-farmers-are-struggling-survive#:~:text=Lebanese%20farmers%20are%20feeling%20the,many%20will%20turn%20to%20bankruptcy (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Hamadi, G. Akkar Farmers Announce Halt to Potato Harvest Due to Low Profit. L’Orient Today. 8 May 2023. Available online: https://today.lorientlejour.com/article/1336788/akkar-farmers-announce-halt-to-potato-harvest-due-to-low-profit.html (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Liakou, V.; Pateraki, C.; Palaiogeorgou, A.-M.; Kopsahelis, N.; de Castro, A.M.; Freire, D.M.G.; Nychas, G.-J.E.; Papanikolaou, S.; Koutinas, A. Valorisation of fruit and vegetable waste from open markets for the production of 2,3-butanediol. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 108, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plazzotta, S.; Cottes, M.; Simeoni, P.; Manzocco, L. Evaluating the environmental and economic impact of fruit and vegetable waste valorisation: The lettuce waste study-case. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Râpă, M.; Darie-Niță, R.N.; Coman, G. Valorization of Fruit and Vegetable Waste into Sustainable and Value-Added Materials. Waste 2024, 2, 258–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Report of the Expert Consultation Meeting on Food Losses and Waste Reduction in the Near East Region: Towards a Regional Comprehensive Strategy; FAO: Cairo, Egypt, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mattsson, L.; Williams, H. Avoidance of Supermarket Food Waste—Employees’ Perspective on Causes and Measures to Reduce Fruit and Vegetables Waste. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, E.C.D.; Faour-Klingbeil, D. Impact of Food Waste on Society, Specifically at Retail and Foodservice Levels in Developed and Developing Countries. Foods 2024, 13, 2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinie, C.; Biclesanu, I.; Bellini, F. The Impact of Awareness Campaigns on Combating the Food Wasting Behavior of Consumers. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.; Lucas, M.R.; Marta-Costa, A. Food Waste Reduction: A Systematic Literature Review on Integrating Policies, Consumer Behavior, and Innovation. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Voluntary Code of Conduct for Food Loss and Waste Reduction; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Journal Officiel Électronique Authentifié n° 0036 du 12/02/2016, Texte 2 sur 178: LOI No 2016-138 du 11 Février 2016 Relative à la Lutte Contre le Gaspillage Alimentaire (1). Available online: https://www.legifrance.gouv.fr/jorf/id/JORFTEXT000032036289 (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- Boletín Oficial del Estado 2-04-2025. Sec. I. Pág. 44747. Ley 1/2025, de 1 de abril, de prevención de las pérdidas y el desperdicio alimentario. Available online: https://www.boe.es/eli/es/l/2025/04/01/1/con (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- EU Food Loss and Waste Prevention Hub. Norway’s Food Waste Act Recently Adopted by the Parliament. 26 June 2025. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/safety/food_waste/eu-food-loss-waste-prevention-hub/resource/show/7840 (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- Law No. 183 of 16 June 2020—Incentivizing Food Donations (Lebanon). University of Lebanon—Legal Informatics Center, published in the Official Gazette No. 26. 18 June 2020, pp. 1403–1404. Available online: https://faolex.fao.org/docs/pdf/leb237087.pdf (accessed on 16 August 2025).

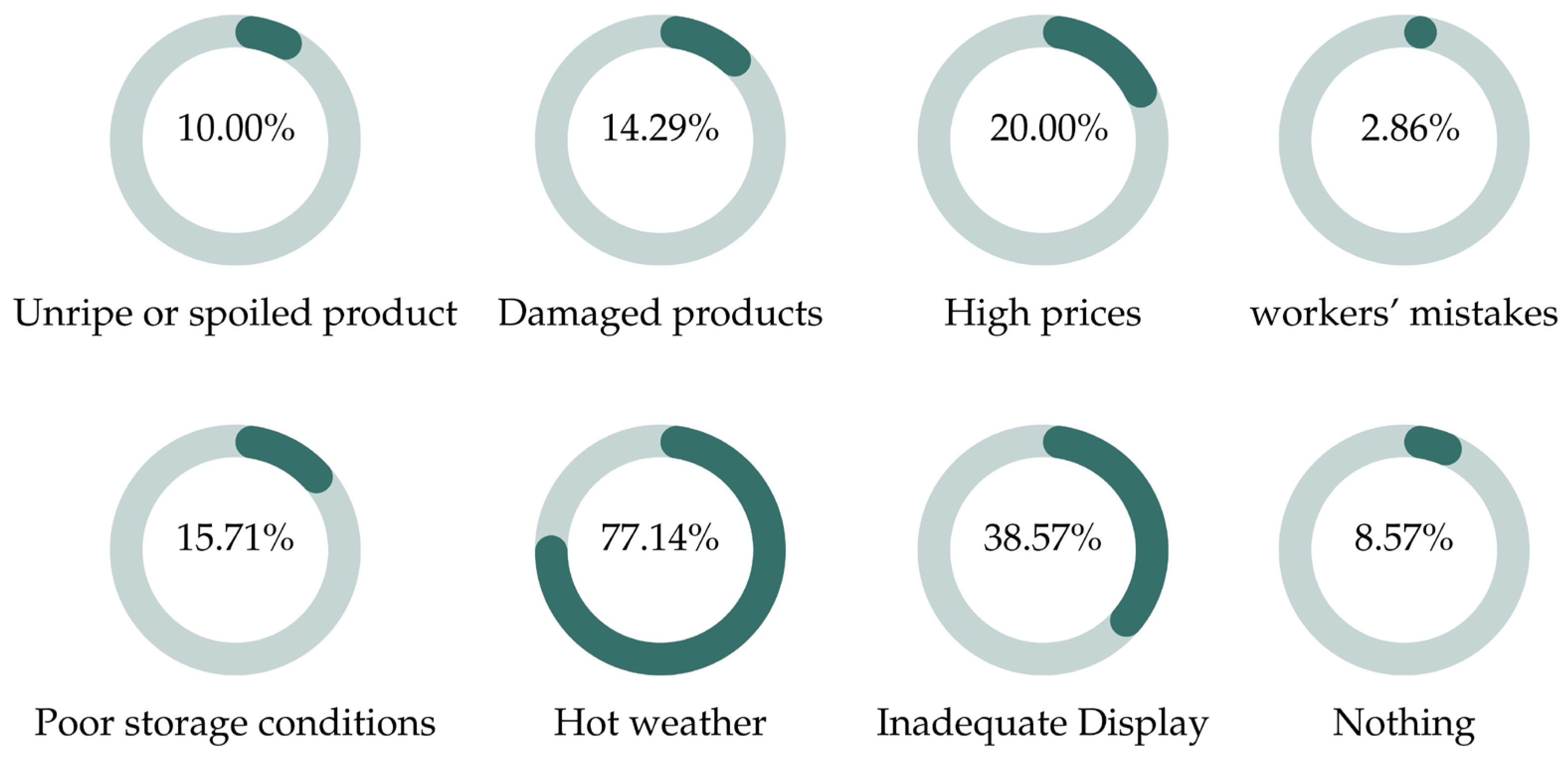


| Quantity of Fruits and Vegetables Loss Generated | Percentage Answers |
|---|---|
| Rare | 45.7% |
| A little | 40.0% |
| A lot | 14.3% |
| Variables | Factors (Level) | A Little Waste p-Value | A Lot of Waste p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Return to supply | Do return | 0.99 | 0 |
| Supply source | Local production and import | 0.99 | 0 |
| Purchase frequency | Daily and randomly | 0.99 | 0 |
| Daily and based on supply and demand | 0 | 0 | |
| Daily, Weekly, and based on Supply and demand | 0 | 0 | |
| Randomly | 0 | 0 | |
| Pricing and sales | Price increase | 0 | 0 |
| Transportation and Distributions | Refrigerated trucks and private cars | 0.99 | 0 |
| Refrigerated trucks | 0 | 0.99 | |
| Display | In the fridge, on shelves inside the store | 0.90 | 0 |
| In the fridge, on shelves inside the store, and on shelves outside | 0 | 0 | |
| On the ground and in the fridge | 0 | 0 | |
| On the ground and on shelves inside the store | 0 | 0 | |
| On the ground, on shelves inside the store, and on shelves outside | 0 | 0 | |
| On shelves inside the store and on shelves outside | 0 | 0 | |
| On shelves outside | 0 | 0 | |
| Storage conditions | Inside the store with air-conditioning | 0 | 0 |
| On the ground, in refrigerators, inside the store with air-conditioning, on shelves, and in a large storage room | 0 | 0 | |
| On the ground, and on the shelves | 0 | 0 | |
| In refrigerators | 0.95 | 0 | |
| In refrigerators and inside the store with air-conditioning | 0.99 | 0 | |
| In refrigerators, inside the store with air-conditioning, and in a large storage room | 0 | 0 | |
| In refrigerators and on the shelves | 0 | 0 | |
| Measures to reduce losses | Do nothing | 0.99 | 0 |
| Prevention measures | Prevention Methods (price reduction, donation) | 0.99 | 0 |
| SD (supply and demand) | 0.99 | 0 | |
| PM and SD | 0.99 | 0 |
| Management of Surplus Fruits and Vegetables | % of Responses | Categories (Weight Percentage) |
|---|---|---|
| Price Reduction | 78.57% | Second chance (43.63%) |
| I do not get rid of it, but keep it for the next day | 14.29% | |
| Sold as animal feed | 42.86% | Animal feed (20.13%) |
| Sold for food manufacturing and juice stores | 15.71% | Sold or donated for human consumption (36.24%) |
| Donate to charities or persons in need | 41.43% | |
| Distribution to employees | 10.00% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pano, N.; Karantininis, K.; Nehme, N.; Halwani, J.; Karameh, J.; Abou Abbass, F.; Mikhael, A. Fruit and Vegetable Loss in Markets in the North of Lebanon: Drivers, Challenges, and Prevention. Resources 2025, 14, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14080132
Pano N, Karantininis K, Nehme N, Halwani J, Karameh J, Abou Abbass F, Mikhael A. Fruit and Vegetable Loss in Markets in the North of Lebanon: Drivers, Challenges, and Prevention. Resources. 2025; 14(8):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14080132
Chicago/Turabian StylePano, Nathalie, Kostas Karantininis, Nada Nehme, Jalal Halwani, Jihane Karameh, Fatima Abou Abbass, and Aziz Mikhael. 2025. "Fruit and Vegetable Loss in Markets in the North of Lebanon: Drivers, Challenges, and Prevention" Resources 14, no. 8: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14080132
APA StylePano, N., Karantininis, K., Nehme, N., Halwani, J., Karameh, J., Abou Abbass, F., & Mikhael, A. (2025). Fruit and Vegetable Loss in Markets in the North of Lebanon: Drivers, Challenges, and Prevention. Resources, 14(8), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14080132










