Advancing Circularity in Small-Scale Rural Aquaponics: Potential Routes and Research Needs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
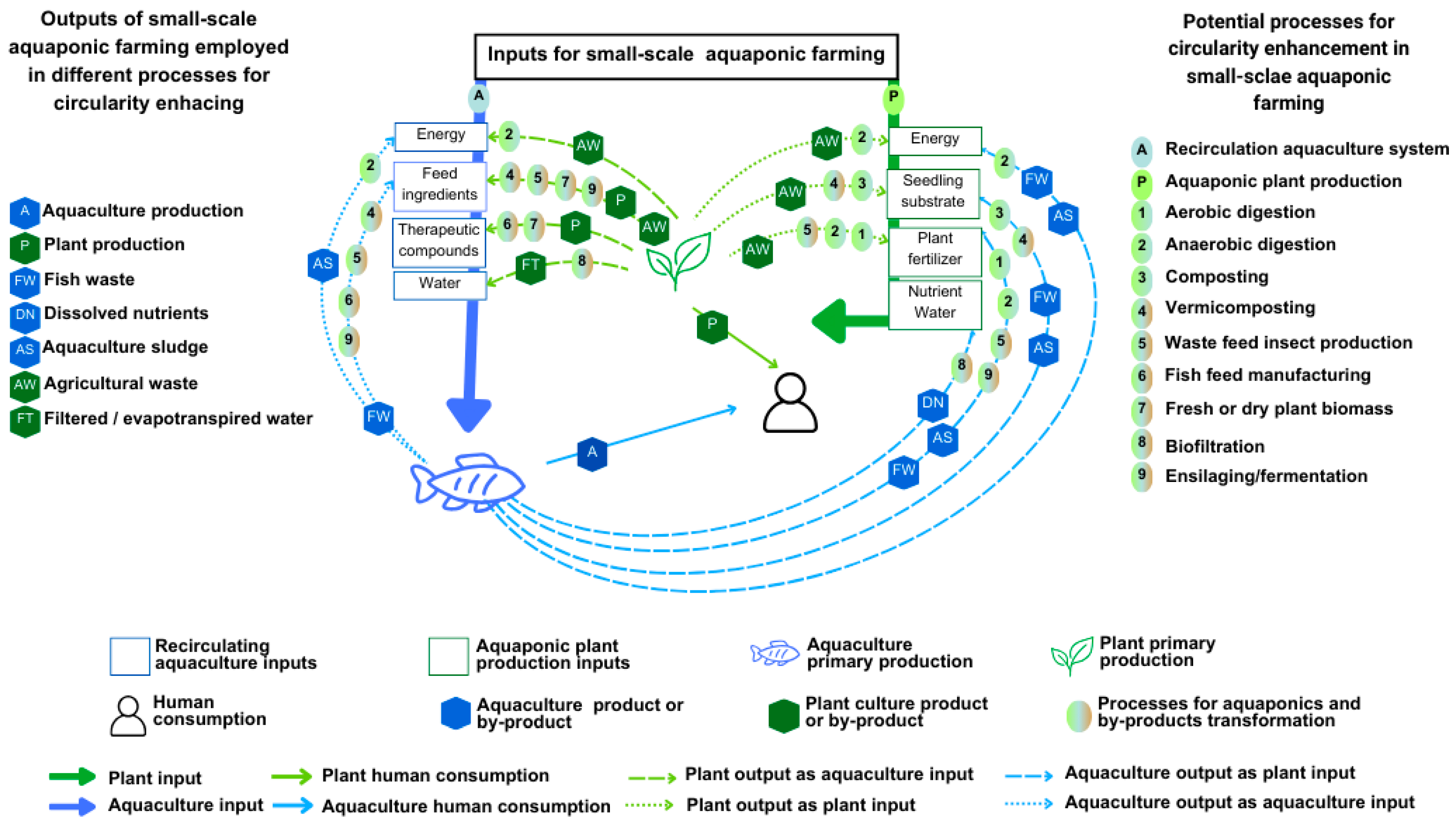
3. Results
3.1. Dissolved Nutrients
3.2. Aquaponics Solid Waste: Aquaculture Sludge, Fish Waste, Agricultural Waste
3.2.1. Composting, Ensilaging, and Organic Fertilizer
3.2.2. Aerobic and Anaerobic Digestion Inputs and Outputs for Aquaponic Circular Farming
3.2.3. Aquaponics and Waste-to-Energy Technologies
3.3. Production of Aquaculture Feed Ingredients for Small-Scale Aquaculture
| Process | Plant Specie | Animal Species | Key Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Production of insect meal with fish and agricultural waste | Hermetia illucens | H. illucens larvae (BSF) can be reared on agricultural and fish waste and when produced on by-products or waste rich in provitamin A carotenoids could be a sustainable strategy to recycle a fraction of vitamin A back into the food chain; the combination of fish and plant waste (fruit, vegetable, and rice) can be utilized for better mass production of BSF. | [116,118,140,141] | |
| Use of macrophytes as feed ingredients | Lemna spp., Spirodela polyrhiza | Oncorhynchus mykiss, Cyprinus carpio, Oreochromis niloticus | For O. mykiss culture 20% fed protein regular sources (fishmeal and soybean meal) can be substituted with Lemna minor without negative effects on the growth performance; C. carpio performs better when feeding with diets with partial replacement of soybean meal with Lemna minor and S. polyrhiza; the inclusion of 15% of L. minor as protein source for O. niloticus feed provides a similar performance when compared with an isonitrogenous control diet. | [142,143,144,145] |
| Ipomoea aquatica | Heteropneustes fossilis,
Oreochromis niloticus | I. aquatica can replace up to 25% of fishmeal without affecting O. niloticus performance; 20% dietary inclusion of I. aquatica can be used to increase fatty acids in O. niloticus. Fermented I. aquatica at 50% inclusion is an adequate protein supplement for H. fossilis feed. | [146,147,148] | |
| Eichhornia crassipes | Sander lucioperca | Diets containing 1.5% of Eichhornia crassipes leaves powder (WLP) increased the growth performance of S. lucioperca when compared with diets without WLP. | [149] | |
| Ensilage/fermentation | Cassava waste, peel of Annanas comosus, molasses, and corn stubble | Colossoma macropomum, mix of several species of fish waste, Oreochromis niloticus | C. macropomum viscera and cassava waste silage are well digested by C. macropomum; silage of fish, molasses, fruit, and agricultural waste with Lactobacillus B2 reaches stabilization within 14 days and presents high nutrient content; trials on animal feed are still needed. Production of Nile tilapia processing waste silages with 192 h of hydrolysis proved to be viable. Fermented silage processing revealed a better apparent digestibility coefficient than acid silage. | [77,137,150] |
3.4. Fish Welfare and Plant Production for Phytotherapy
3.5. General Considerations for ICAq Research and Implementation
4. Conclusions
Study Limitations and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SSA | rural small-scale aquaculture |
| ICAq | small-scale integrated circular aquaponics |
| SSFs | small-scale fisheries |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization |
| EE | ecological engineering |
| CE | circular economy |
| RAS | recirculating aquaculture system |
| NUE | nitrogen use efficiency |
| AWs | agricultural wastes |
| APW | aquaculture processing waste |
| AS | aquaculture sludge |
| TSs | total solids |
| VS | volatile solid content |
| FPW | fish processing waste |
| AnD | anaerobic digestion |
| AD | aerobic digestion |
| TAN | total ammonia nitrogen |
| ADBR | aerobic digestion bioreactor |
| SDGs | sustainable development goals |
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024. Blue Transformation in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024; ISBN 978-92-5-138763-4. [Google Scholar]
- Garlock, T.; Asche, F.; Anderson, J.; Bjørndal, T.; Kumar, G.; Lorenzen, K.; Ropicki, A.; Smith, M.D.; Tveterås, R. A Global Blue Revolution: Aquaculture Growth Across Regions, Species, and Countries. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 28, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Guidelines for Sustainable Aquaculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2025; ISBN 978-92-5-139497-7. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. International Year of Artisanal Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022; Final Report; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The International Year of Artisanal Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, P. Review of Small-Scale Aquaculture: Definitions, Characterization, Numbers. In Enhancing the Contribution of Smallscale Aquaculture to Food Security, Poverty Alleviation and Socio-Economic Development; Bondad-Reantaso, M.G., Subasinghe, R., Eds.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; pp. 37–61. [Google Scholar]
- Short, R.E.; Gelcich, S.; Little, D.C.; Micheli, F.; Allison, E.H.; Basurto, X.; Belton, B.; Brugere, C.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; et al. Harnessing the Diversity of Small-Scale Actors Is Key to the Future of Aquatic Food Systems. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; Prein, M. Measuring the Contribution of Small-Scale Aquaculture an Assessment; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Nava, A. Diagnóstico de La Acuicultura de Recursos Limitados (AREL) y de La Acuicultura de La Micro y Pequeña Empresa (AMYPE) En América Latina; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; ISBN 978-92-5-307462-4. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Cordero, F.J.; Delgadillo Tiburcio, S.; Sánchez-Zazueta, E.; Cai, J. Tilapia Aquaculture in Mexico: Assessment with a Focus on Social and Economic Performance; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Circular No. 1219; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.K.; Mandal, A. Diversification in Aquaculture Resources and Practices for Smallholder Farmers. In Agriculture, Livestock Production and Aquaculture: Advances for Smallholder Farming Systems: Volume 1; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 1, pp. 263–286. ISBN 978-3-030-93258-9. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, A.H.M.S. Dynamics and Determinants of Participation in Integrated Aquaculture–Agriculture Value Chain: Evidence from a Panel Data Analysis of Indigenous Smallholders in Bangladesh. J. Dev. Stud. 2021, 57, 1871–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baganz, G.; Junge, R.; Portella, M.C.; Goddek, S.; Keesman, K.J.; Baganz, D.; Staaks, G.; Shaw, C.; Lohrberg, F.; Kloas, W. The Aquaponic Principle—It Is All about Coupling. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Cabanás, V.M.; Suárez-Cáceres, G.P.; Pérez-Urrestarazu, L.; Lobillo-Eguíbar, J.; Gross, J.A. Contribution of Household Aquaponic Production to a Low Price Healthy Mediterranean Diet in an Economically Depressed Community. Agronomy 2023, 13, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obirikorang, K.A.; Sekey, W.; Gyampoh, B.A.; Ashiagbor, G.; Asante, W. Aquaponics for Improved Food Security in Africa: A Review. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 705549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baganz, G.F.M.; Timpe, A.; Baganz, D.; Staaks, G.; Hunger, B.; Kloas, W.; Lohrberg, F. City or Hinterland—Site Potentials for Upscaled Aquaponics in a Berlin Case Study. npj Urban Sustain. 2022, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Korte, M.; Bergman, J.; van Willigenburg, L.G.; Keesman, K.J. Towards a Zero-Waste Aquaponics-Centered Eco-Industrial Food Park. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 454, 142109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haswell, F.; Edelenbosch, O.Y.; Piscicelli, L.; van Vuuren, D.P. The Geography of Circularity Missions: A Cross-Country Comparison of Circular Economy Policy Approaches in the Global North and Global South. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2024, 52, 100883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babatunde, A.; Deborah, R.A.; Gan, M.; Simon, T. Economic Viability of a Small Scale Low-Cost Aquaponic System in South Africa. J. Appl. Aquac. 2023, 35, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bich, T.T.N.; Tri, D.Q.; Yi-Ching, C.; Khoa, H.D. Productivity and Economic Viability of Snakehead Channa Striata Culture Using an Aquaponics Approach. Aquac. Eng. 2020, 89, 102057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, F.; El Samrani, A.; Khalil, M.; Abdin, A.E.-D.; El-Kholy, R.; Embaby, M.; Negm, M.; De Ketelaere, D.; Spiteri, A.; Pana, E.; et al. Decentralized Wetland-Aquaponics Addressing Environmental Degradation and Food Security Challenges in Disadvantaged Rural Areas: A Nature-Based Solution Driven by Mediterranean Living Labs. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, B.; Cassim, S.; Taylor, S. Pathways to Low-Cost Aquaponic Systems for Sustainable Livelihoods and Economic Development in Poor Communities: Defining Critical Success Factors. Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 1575–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvarova, I.; Atstaja, D.; Volkova, T.; Grasis, J.; Ozolina-Ozola, I. The Typology of 60R Circular Economy Principles and Strategic Orientation of Their Application in Business. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 409, 137189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNIDO Circular Economy and Agribusiness Development. Available online: https://www.unido.org/sites/default/files/files/2022-03/Circular%20economy%20and%20agribusiness%20development.pdf (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Schönborn, A.; Junge, R. Redefining Ecological Engineering in the Context of Circular Economy and Sustainable Development. Circ. Econ. Sustain. 2021, 1, 375–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsch, W.J.; Jørgensen, S.E. Ecological Engineering: A Field Whose Time Has Come. Ecol. Eng. 2003, 20, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangas, P.C. Ecological Engineering: Principles and Practice; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-1-56670-599-8. [Google Scholar]
- Costa-Pierce, B. The Principles and Practices of Ecological Aquaculture and the Ecosystem Approach to Aquaculture. World Aquac. 2021, 52, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission: Directorate-General for Research and Innovation. Towards an EU Research and Innovation Policy Agenda for Nature-Based Solutions & Re-Naturing Cities: Final Report of the Horizon 2020 Expert Group on ‘Nature-Based Solutions and Re-Naturing Cities’: (Full Version); European Commission: Luxembourg, 2015; ISBN 978-92-79-46050-0. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.K.; Mondal, B.; Sarkar, U.K.; Das, B.K.; Borah, S. Understanding and Approaches towards Circular Bio-Economy of Wastewater Reuse in Fisheries and Aquaculture in India: An Overview. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 1100–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, B.; Yakoob, M.; Shah, M.P. Agricultural Waste Management Strategies for Environmental Sustainability. Environ. Res. 2022, 206, 112285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, S.; Ott, D.; Liebscher, J.; Höfling, D.; Müller, A.; Dautz, J.; Gutzeit, H.O.; Schmidt, D.; Reuss, R. Sustainability Analysis of Fish Feed Derived from Aquatic Plant and Insect. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yogev, U.; Keesman, K.J.; Gross, A. Promoting Circular Economy: Comparison of Novel Coupled Aquaponics with Anaerobic Digestion and Conventional Aquaponic Systems on Nutrient Dynamics and Sustainability. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 208, 107716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, C.; Knopf, K.; Klatt, L.; Marin Arellano, G.; Kloas, W. Closing Nutrient Cycles through the Use of System-Internal Resource Streams: Implications for Circular Multitrophic Food Production Systems and Aquaponic Feed Development. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baganz, G.; Proksch, G.; Kloas, W.; Lorleberg, W.; Baganz, D.; Staaks, G.; Lohrberg, F. Site Resource Inventories-A Missing Link in the Circular City’s Information Flow. Adv. Geosci. 2020, 54, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; McNevin, A.A.; Tucker, C.S. Resource Use and the Environment. In Aquaculture Farming Aquatic Animals and Plants; Lucas, J.S., Southgate, P.C., Tucker, C.S., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 93–112. [Google Scholar]
- Fruscella, L.; Kotzen, B.; Paradelo Perez, M.; Milliken, S. Investigating the Effects of Fish Effluents as Organic Fertilisers on Basil (Ocimum basilicum). Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, S.B.; Ahmad, A.; Imron, M.F.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Othman, A.R.; Hasan, H.A. Achieving a Biocircular Economy in the Aquaculture Sector Through Waste Valorization. Toxics 2025, 13, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunda, R.; Roy, K.; Másílko, J.; Mráz, J. Understanding Nutrient Throughput of Operational RAS Farm Effluents to Support Semi-Commercial Aquaponics: Easy Upgrade Possible beyond Controversies. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 245, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naegel, L.C.A. Combined Production of Fish and Plants in Recirculating Water. Aquaculture 1977, 10, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón-Silvas, S.G.; León-Cañedo, J.A.; Fierro-Sañudo, J.F.; Ramírez-Rochín, J.; Fregoso-López, M.G.; Frías-Espericueta, M.G.; Osuna-Martínez, C.C.; Páez-Osuna, F. Water Quality, Water Usage, Nutrient Use Efficiency and Growth of Shrimp Litopenaeus Vannamei in an Integrated Aquaponic System with Basil Ocimum basilicum. Aquaculture 2021, 543, 737023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, O.; Bisbis, M.B.; Baganz, G.F.M.; Baganz, D.; Staaks, G.B.O.; Monsees, H.; Goddek, S.; Keesman, K.J. Environmental Impact Assessment of Local Decoupled Multi-Loop Aquaponics in an Urban Context. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 313, 127135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.; Hernandez, M.; Escalante, E.; Valdés, D.; Gasca, E. Evaluation of a Semi-Intensive Aquaponics System, with and without Bacterial Biofilter in a Tropical Location. Sustainability 2017, 9, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkiew, S.; Hu, Z.; Chandran, K.; Lee, J.W.; Khanal, S.K. Nitrogen Transformations in Aquaponic Systems: A Review. Aquac. Eng. 2017, 76, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocken, N.M.P.; de Pauw, I.; Bakker, C.; van der Grinten, B. Product Design and Business Model Strategies for a Circular Economy. J. Ind. Prod. Eng. 2016, 33, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xie, H.; Liang, S.; Wang, J.; Yan, R. Attempts to Improve Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency of Aquaponics through Nitrifies Addition and Filler Gradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 6671–6679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Kim, H.J. Nutrient Management Regime Affects Water Quality, Crop Growth, and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Aquaponic Systems. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 256, 108619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerozi, B.d.S.; Fitzsimmons, K. Use of Bacillus Spp. to Enhance Phosphorus Availability and Serve as a Plant Growth Promoter in Aquaponics Systems. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 211, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerozi, B.d.S.; Fitzsimmons, K. The Effect of pH on Phosphorus Availability and Speciation in an Aquaponics Nutrient Solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerozi, B.d.S.; Fitzsimmons, K. Effect of Dietary Phytase on Phosphorus Use Efficiency and Dynamics in Aquaponics. Aquac. Int. 2017, 25, 1227–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, C.; Knopf, K.; Roy, K.; Ulrichs, C.; Kloas, W. Animal versus Plant Protein Sources in Marine Ingredient-Free Aquaponic Diets: A Case Study on Nutrient Release, and Retention of African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus) Reared in RAS. Aquaculture 2024, 584, 740641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, C.; Knopf, K.; Kloas, W. Fish Feeds in Aquaponics and Beyond: A Novel Concept to Evaluate Protein Sources in Diets for Circular Multitrophic Food Production Systems. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, K.S.; Sridhar, A.; Vishali, S. Utilization of Fruit and Vegetable Waste to Produce Value-Added Products: Conventional Utilization and Emerging Opportunities—A Review. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, I.; Lansing, S.; Martí-Herrero, J. (Eds.) Biogas for Rural Areas; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Garfí, M.; Martí-Herrero, J.; Garwood, A.; Ferrer, I. Household Anaerobic Digesters for Biogas Production in Latin America: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohee Romeela Waste Management Opportunities for Rural Communities. Composting as an Effective Waste Management Strategy for Farm Households and Others; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Song, K. Source, Treatment, and Disposal of Aquaculture Solid Waste: A Review. J. Environ. Eng. 2021, 147, 03120012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, I.; Dauksas, E.; Remme, J.F.; Richardsen, R.; Løes, A.-K. Fish and Fish Waste-Based Fertilizers in Organic Farming—With Status in Norway: A Review. Waste Manag. 2020, 115, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, M.; Nagao, N.; Syukri, F.; Rahim, A.A.; Toda, T.; Tran, Q.N.M.; Nakasaki, K. Ammonia Recovery and Microbial Community Succession during Thermophilic Composting of Shrimp Pond Sludge at Different Sludge Properties. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tung, T.; Tran, Q.B.; Phuong Thao, N.T.; Vi, L.Q.; Hieu, T.T.; Le, S.; Tuan, N.Q.; Sonne, C.; Lam, S.S.; Hai, L.T.; et al. Recycling of Aquaculture Wastewater and Sediment for Sustainable Corn and Water Spinach Production. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 129329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebeling, J.M.; Timmons, M.B. Recirculating Aquaculture Systems. Aquaculture Production Systems; Cayuga Aqua Ventures: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Piedrahita, R.H. Reducing the Potential Environmental Impact of Tank Aquaculture Effluents through Intensification and Recirculation. Aquaculture 2003, 226, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, I.G.; Braos, L.B.; Cruz, M.C.P.; Vidotti, R.M. Valorization of Animal Waste from Aquaculture through Composting: Nutrient Recovery and Nitrogen Mineralization. Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, J.; Sica, P.; Costa, C.; Márquez, M.C. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Fish Waste as an Alternative to Produce High Value-Added Products. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.T.Q.; Van Hien, H.; Doan Khoi, L.N.; Yagi, N.; Lerøy Riple, A.K. Quality Management Practices of Intensive Whiteleg Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Farming: A Study of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasmin, M.Y.; Syukri, F.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Karim, M. Potential of Bioremediation in Treating Aquaculture Sludge: Review Article. Aquaculture 2020, 519, 734905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, G.L.; Loss, A.; Lourenzi, C.R.; de Alcantara Lopes, D.L.; de Matos Siebeneichler, L.; Brunetto, G. Common Chicory Production in Aquaponics and in Soil Fertilized with Aquaponic Sludge. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 281, 109946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakali, M.E.; Mustapha, A. Phosphorus Waste Production in Fish Farming a Potential for Reuse in Integrated Aquaculture Agriculture. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Res. 2021, 7, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonawala, S.S.; Jardosh, H. Organic Waste in Composting: A Brief Review. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 2018, 8, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaher, J.J.; Rakocy, J.E.; Shultz, R.C.; Bailey, D.S.; Pantanella, E. Dewatering and Composting Aquaculture Waste as a Growing Medium in the Nursery Production of Tomato Plants. Acta Hortic. 2011, 891, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, A.; Lunda, R.; Hlaváč, D.; Kuklina, I.; Hamáčková, J.; Randák, T.; Kozák, P.; Koubová, A.; Buřič, M. Vermicomposting of Sludge from Recirculating Aquaculture System Using Eisenia andrei: Technological Feasibility and Quality Assessment of End-Products. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, I.G.; Lalander, C.; Vidotti, R.M.; Vinnerås, B. Using Hermetia illucens Larvae to Process Biowaste from Aquaculture Production. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimenko, A.; Belyi, L.; Podvolotskaya, A.; Son, O.; Tekutyeva, L. Exploring Sustainable Aquafeed Alternatives with a Specific Focus on the Ensilaging Technology of Fish Waste. Fermentation 2024, 10, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toppe, J.; Olsen, R.L.; Peñarubia, O.R.; James, D.G. Production and Utilization of Fish Silage a Manual on How to Turn Fish Waste into Profit and a Valuable Feed Ingredient or Fertilizer; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, N.U.; Lee, M.A.M.F.; Arshad, A.M. The Effectiveness of Fish Silage as Organic Fertilizer on Post-Harvest Quality of Pak Choy (Brassica rapa L. Subsp. Chinensis). Eur. Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2015, 4, 163–174. [Google Scholar]
- Toppe, J.; Olsen, R.L. Fish Silage Production by Fermentation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024; ISBN 978-92-5-138787-0. [Google Scholar]
- Neira, L.M.; Gonçalves, A.M.; Buzollo, H.; de Sandre, L.C.G.; do Nascimento, T.M.T.; Coutinho, J.J.O.; Pizauro Junior, J.M.; Carneiro, D.J. Effect of Acid and Fermented Silage Hydrolysis Time on Protein Fractionation and Digestibility for Nile Tilapia. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2024, 318, 116126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Amaral, M.d.M.; Gómez-Serrano, C.; Acién, F.G.; Fernández-Sevilla, J.M.; Molina-Grima, E. Production of Microalgae Using Centrate from Anaerobic Digestion as the Nutrient Source. Algal Res. 2015, 9, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Lepine, C.; Witarsa, F.; Good, C. Anaerobic Digestion Challenges and Resource Recovery Opportunities from Land-Based Aquaculture Waste and Seafood Processing Byproducts: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 354, 127144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Song, K. Process Performance of Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Waste Activated Sludge and Aquaculture Sludge. Aquac. Eng. 2020, 90, 102090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, J.; Spanjers, H.; Van Lier, J.B. Performance of Inorganic Coagulants in Treatment of Backwash Waters from a Brackish Aquaculture Recirculation System and Digestibility of Salty Sludge. Aquac. Eng. 2014, 61, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Lepine, C.; Good, C. Methane and Hydrogen Sulfide Production from the Anaerobic Digestion of Fish Sludge from Recirculating Aquaculture Systems: Effect of Varying Initial Solid Concentrations. Fermentation 2023, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddek, S.; Delaide, B.P.L.; Joyce, A.; Wuertz, S.; Jijakli, M.H.; Gross, A.; Eding, E.H.; Bläser, I.; Reuter, M.; Keizer, L.C.P.; et al. Nutrient Mineralization and Organic Matter Reduction Performance of RAS-Based Sludge in Sequential UASB-EGSB Reactors. Aquac. Eng. 2018, 83, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddek, S.; Schmautz, Z.; Scott, B.; Delaide, B.; Keesman, K.; Wuertz, S.; Junge, R. The Effect of Anaerobic and Aerobic Fish Sludge Supernatant on Hydroponic Lettuce. Agronomy 2016, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Shi, H.; Lee, C.T.; Hashim, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, W.-M.; Li, C. Recovery of Nutrients from Fish Sludge in an Aquaponic System Using Biological Aerated Filters with Ceramsite plus Lignocellulosic Material Media. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsees, H.; Keitel, J.; Paul, M.; Kloas, W.; Wuertz, S. Potential of Aquacultural Sludge Treatment for Aquaponics: Evaluation of Nutrient Mobilization under Aerobic and Anaerobic Conditions. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2017, 9, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobanov, V.P.; Combot, D.; Pelissier, P.; Labbé, L.; Joyce, A. Improving Plant Health Through Nutrient Remineralization in Aquaponic Systems. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 683690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaide, B.; Panana, E.; Teerlinck, S.; Bleyaert, P. Suitability of Supernatant of Aerobic and Anaerobic Pikeperch (Sander lucioperca L.) Sludge Treatments as a Water Source for Hydroponic Production of Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. Var. Capitata). Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 1721–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, R.; Mousavi, S.E.; Goyette, B.; Adhikary, S. Coupling of Microalgae Cultivation with Anaerobic Digestion of Poultry Wastes: Toward Sustainable Value Added Bioproducts. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rude, K.; Yothers, C.; Barzee, T.J.; Kutney, S.; Zhang, R.; Franz, A. Growth Potential of Microalgae on Ammonia-Rich Anaerobic Digester Effluent for Wastewater Remediation. Algal Res. 2022, 62, 102613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaide, B.; Goddek, S.; Keesman, K.J.; Jijakli, M.H.M. A Methodology to Quantify the Aerobic and Anaerobic Sludge Digestion Performance for Nutrient Recycling in Aquaponics. Biotechnol. Agron. Soc. Environ. 2018, 22, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiari, Z.; Kaluthota, S.; Savidov, N. Aerobic Bioconversion of Aquaculture Solid Waste into Liquid Fertilizer: Effects of Bioprocess Parameters on Kinetics of Nitrogen Mineralization. Aquaculture 2019, 500, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madady, M.H.; Sarkheil, M.; Zahedi, S.; Arouei, H. Application of Liquid Organic Fertilizer Produced from Fish Sludge in an Aquaponics System: Influences on Growth of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and Peppermint (Mentha × piperita L.). Aquac. Eng. 2025, 110, 102541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillani, S.A.; Abbasi, R.; Martinez, P.; Ahmad, R. Review on Energy Efficient Artificial Illumination in Aquaponics. Clean. Circ. Bioeconomy 2022, 2, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddek, S.; Körner, O. A Fully Integrated Simulation Model of Multi-Loop Aquaponics: A Case Study for System Sizing in Different Environments. Agric. Syst. 2019, 171, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maucieri, C.; Forchino, A.A.; Nicoletto, C.; Junge, R.; Pastres, R.; Sambo, P.; Borin, M. Life Cycle Assessment of a Micro Aquaponic System for Educational Purposes Built Using Recovered Material. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 3119–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.; Valdés-Lozano, D.; Escalante, E.; Gasca-Leyva, E. Dynamic Root Floating Technique: An Option to Reduce Electric Power Consumption in Aquaponic Systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, K.; Tamaru, C.; Ako, H.; Leung, P. Economics of Small-Scale Commercial Aquaponics in Hawai’i. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2015, 46, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaoula, T.; Abdelouahid, R.A.; Ezzahoui, I.; Marzak, A. Architecture Design of Monitoring and Controlling of IoT-Based Aquaponics System Powered by Solar Energy. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 191, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorarinsdottir, R.; Unnthorsson, R. Direct Use of Geothermal Resources for Circular Food Production. Proceedings 2018, 2, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Kabir, Z. Waste-to-Energy Generation Technologies and the Developing Economies: A Multi-Criteria Analysis for Sustainability Assessment. Renew. Energy 2020, 150, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Bioenergy and Food Security (BEFS) Assessment—Seychelles; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, N. Biomass to Energy—An Analysis of Current Technologies, Prospects, and Challenges. Bioenergy Res. 2023, 16, 683–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Karishma, S.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Rangasamy, G. A Review on Regeneration of Biowaste into Bio-Products and Bioenergy: Life Cycle Assessment and Circular Economy. Fuel 2023, 338, 127221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzoyan, N.; Tal, Y.; Gross, A. Anaerobic Digestion of Sludge from Intensive Recirculating Aquaculture Systems: Review. Aquaculture 2010, 306, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yogev, U.; Keesman, K.J.; Gross, A. Onsite Anaerobic Treatment of Aquaponics Lettuce Waste: Digestion Efficiency and Nutrient Recovery. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainthola, J.; Kalamdhad, A.S.; Goud, V.V. A Review on Enhanced Biogas Production from Anaerobic Digestion of Lignocellulosic Biomass by Different Enhancement Techniques. Process Biochem. 2019, 84, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, A.; Siles, J.A.; Chica, A.F.; Martín, M.Á. Agri-Food Waste Valorization through Anaerobic Co-Digestion: Fish and Strawberry Residues. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 54, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogev, U.; Barnes, A.; Gross, A. Nutrients and Energy Balance Analysis for a Conceptual Model of a Three Loops off Grid, Aquaponics. Water 2016, 8, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ximenes, J.; Siqueira, A.; Kochańska, E.; Łukasik, R.M. Valorisation of Agri-and Aquaculture Residues via Biogas Production for Enhanced Industrial Application. Energies 2021, 14, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patinvoh, R.J.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Challenges of Biogas Implementation in Developing Countries. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2019, 12, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Supporting Local Feed Self-Sufficiency for Inland Aquaculture in Indonesia; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Prabakusuma, A.S.; Wardono, B.; Fahlevi, M.; Zulham, A.; Djoko Sunarno, M.T.; Syukur, M.; Aljuaid, M.; Saniuk, S.; Apriliani, T.; Pramoda, R. A Bibliometric Approach to Understanding the Recent Development of Self-Sufficient Fish Feed Production Utilizing Agri-Food Wastes and by-Products towards Sustainable Aquaculture. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemello, G.; Biasato, I.; Gai, F.; Capucchio, M.T.; Colombino, E.; Schiavone, A.; Gasco, L.; Pauciullo, A. Effects of Tenebrio molitor Larvae Meal Inclusion in Rainbow Trout Feed: Myogenesis-Related Gene Expression and Histomorphological Features. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 20, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangindaan, D.; Kaburuan, E.R.; Meindrawan, B. Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) for Biodiesel and/or Animal Feed as a Solution for Waste-Food-Energy Nexus: Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarantoniello, M.; Zimbelli, A.; Randazzo, B.; Compagni, M.D.; Truzzi, C.; Antonucci, M.; Riolo, P.; Loreto, N.; Osimani, A.; Milanović, V.; et al. Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Reared on Roasted Coffee by-Product and Schizochytrium sp. as a Sustainable Terrestrial Ingredient for Aquafeeds Production. Aquaculture 2020, 518, 734659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, P.K.; Awal, M.R.; Choudhury, M.A.R.; Hasan, M.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Ahmed, T.; Rahman, M.M.; Mondal, M.F. Evaluation of Different Food Waste for Sustainable Mass Rearing of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L) in Bangladesh. J. Insects Food Feed 2023, 9, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.Q.; Nguyen, T.T.; Prokešová, M.; Gebauer, T.; Doan, H.V.; Stejskal, V. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Production Performance of Aquaculture Species Fed Dietary Insect Meals. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 1637–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulu, S.; Langi, S.; Hasimuna, O.J.; Missinhoun, D.; Munganga, B.P.; Hampuwo, B.M.; Gabriel, N.N.; Elsabagh, M.; Van Doan, H.; Abdul Kari, Z.; et al. Recent Advances in the Utilization of Insects as an Ingredient in Aquafeeds: A Review. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 11, 334–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafique, L.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Hassan, F.U.; Alagawany, M.; Naiel, M.A.E.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Yilmaz, S.; Liu, Q. The Feasibility of Using Yellow Mealworms (Tenebrio molitor): Towards a Sustainable Aquafeed Industry. Animals 2021, 11, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, K.; Rajan, D.K.; Muralisankar, T.; Ganesan, A.R.; Sathishkumar, P.; Revathi, N. Use of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.) Larvae Meal in Aquafeeds for a Sustainable Aquaculture Industry: A Review of Past and Future Needs. Aquaculture 2022, 553, 738095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranga, B.; Kagali, R.; Mbogo, K.; Orina, P.; Munguti, J.; Ogello, E. Growth Performance of African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus) Fed on Diets Containing Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Under Aquaponic System. Aquac. Stud. 2023, 23, AQUAST910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.J.; Shaw, C.; Chen, T.W.; Staß, C.M.; Ulrichs, C.; Riewe, D.; Kloas, W.; Geilfus, C.M. Plant Nutritional Value of Aquaculture Water Produced by Feeding Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Alternative Protein Diets: A Lettuce and Basil Case Study. Plants People Planet 2024, 6, 362–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, S.; Leal, M.M.; Shaw, C.; Baganz, D.; Baganz, G.; Staaks, G.; Kloas, W.; Körner, O.; Monsees, H. Insect-Based Fish Feed in Decoupled Aquaponic Systems: Effect on Lettuce Production and Resource Use. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0295811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo-Castellanos, J.C.; Flores-García, L.; Herrera-Díaz, I.E.; Álvarez-González, C.A.; Albertos-Alpuche, P.J.; Martínez-Yáñez, R. System Management of Lemna minor in Aquaponics. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 974–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, S.; Bhat, S.U.; Gani, A.; Bhat, F.A. Perspectives on Utilization of Macrophytes as Feed Ingredient for Fish in Future Aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 282–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.; Ma, O.; Sp, A. Preliminary Assessment of Water Spinach (Ipomoea aquatica) and Morning Glory (Ipomoea asarifolia) Leaves Meals as Non-Conventional Fish Feed Stuffs. Int. J. Zool. Anim. Biol. 2019, 7, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Rahman, M.H.; Tina, F.W.; Shahjahan, M. Present Scenario and Prospects of the Use of Aquatic Plants in Aquaculture: A Review. Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 6791–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddik, M.A.B.; Julien, B.B.; Islam, S.M.M.; Francis, D.S. Fermentation in Aquafeed Processing: Achieving Sustainability in Feeds for Global Aquaculture Production. Rev. Aquac. 2024, 16, 1244–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, J.; Gong, Y.; Cui, K.; Mai, K.; Ai, Q. Effects of Fishmeal Substitution by Four Fermented Soybean Meals on Growth, Antioxidant Capacity and Inflammation Responses of Turbot Juveniles (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Aquaculture 2022, 560, 738414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, T.; Hegazi, E.; Nassef, E.; Habotta, O.A.; Gewaily, M.S. The Optimized Inclusion Level of Bacillus Subtilis Fermented Azolla Pinnata in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Diets: Immunity, Antioxidative Status, Intestinal Digestive Enzymes and Histomorphometry, and Disease Resistance. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 48, 767–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugwanya, M.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Kimera, F.; Sewilam, H. Replacement of Fish Meal with Fermented Plant Proteins in the Aquafeed Industry: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 62–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, R.; de Sousa, D.B.; Fernández-Ríos, A.; Mellett, S.; Rowan, N.; Morse, A.P.; Hayes, M.; Laso, J.; Regueiro, L.; Wan, A.H.; et al. A Circular Economy Framework for Seafood Waste Valorisation to Meet Challenges and Opportunities for Intensive Production and Sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 392, 136283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniasamy, S.; Rajasekaran, B.; Subramaniam, B.; Muniasamy, S.; Pailan, G.H. Utilization of Fish Waste and By-Products for Fish Meal Production as a Potential Feed Ingredient, Fish Waste to Valuable Products: Recent Applications and Research Update. In Fish Waste to Valuable Products; Maqsood, S., Naseer, M.N., Benjakul, S., Zaidi, A.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 301–316. [Google Scholar]
- Madage, S.S.K.; Medis, W.U.D.; Sultanbawa, Y. Fish Silage as Replacement of Fishmeal in Red Tilapia Feeds. J. Appl. Aquac. 2015, 27, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, T.M.; Dantas, F.d.M.; Monteiro Dos Santos, D.K.; Kojima, J.T.; Pastrana, Y.M.; De Jesus, R.S.; Gonçalves, L.U. Fish Viscera Silage: Production, Characterization, and Digestibility of Nutrients and Energy for Tambaqui Juveniles. Fishes 2023, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidotti, R.M.; Viegas, E.M.M.; Carneiro, D.J. Amino Acid Composition of Processed Fish Silage Using Different Raw Materials. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2003, 105, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodgate, S.L.; Wan, A.H.L.; Hartnett, F.; Wilkinson, R.G.; Davies, S.J. The Utilisation of European Processed Animal Proteins as Safe, Sustainable and Circular Ingredients for Global Aquafeeds. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 1572–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzepe, D.; Kuietche, H.M.; Magatsing, O.; Meutchieye, F.; Nana, P.; Tchuinkam, T.; Djouaka, R. From Agricultural Waste to Chicken Feed Using Insect-Based Technology. J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2023, 84, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrikov, D.; Morote, E.; Montes, J.; Sánchez-Muros, M.J.; Barroso, F.G.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, M.; González-Fernández, M.J.; Guil-Guerrero, J.L. Facing the Challenge of Discarded Fish: Improving Nutritional Quality of Two Insect Species Larvae for Use as Feed and Food. J. Insects Food Feed 2021, 7, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiordelmondo, E.; Ceschin, S.; Magi, G.E.; Mariotti, F.; Iaffaldano, N.; Galosi, L.; Roncarati, A. Effects of Partial Substitution of Conventional Protein Sources with Duckweed (Lemna minor) Meal in the Feeding of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) on Growth Performances and the Quality Product. Plants 2022, 11, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, R.K.; Sharma, J.G.; Shrivastav, A.K.; Kumar, G.; Glencross, B.D.; Tocher, D.R.; Chakrabarti, R. Effect of Lemna minor Supplemented Diets on Growth, Digestive Physiology and Expression of Fatty Acids Biosynthesis Genes of Cyprinus carpio. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opiyo, M.A.; Muendo, P.; Mbogo, K.; Ngugi, C.C.; Charo-Karisa, H.; Orina, P.; Leschen, W.; Glencross, B.D.; Tocher, D.R. Inclusion of Duckweed (Lemna minor) in the Diet Improves Flesh Omega-3 Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Profiles but Not the Growth of Farmed Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2022, 292, 115442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastav, A.K.; Kumar, G.; Mittal, P.; Tocher, D.R.; Glencross, B.D.; Chakrabarti, R.; Sharma, J.G. Effect of Greater Duckweed Spirodela polyrhiza Supplemented Feed on Growth Performance, Digestive Enzymes, Amino and Fatty Acid Profiles, and Expression of Genes Involved in Fatty Acid Biosynthesis of Juvenile Common Carp Cyprinus carpio. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 788455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, R.A.; Abdullah, O.J.; Ahmed, A.M.; Adam, M.I.; Mohamed Ahmed, F.A.; Idam, O.A. Effect of Replacing Fishmeal with Water Spinach (Ipomoea aquatica) on Growth, Feed Conversion and Carcass Composition for Nile Tilapia Fry (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Aquat. Sci. Mar. Biol. 2019, 2, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepkirui, M.; Orina, P.S.; Opiyo, M.; Muendo, P.; Mbogo, K.; Omondi, R. Fatty Acids Composition of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Fingerlings Fed Diets Containing Different Levels of Water Spinach (Ipomoea aquatica). J. Agric. Food Res. 2021, 5, 100156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.K.; Suma, A.Y.; Rashid, A.; Kabir, M.A.; Goh, K.W.; Abdul Kari, Z.; Van Doan, H.; Zakaria, N.N.A.; Khoo, M.I.; Seong Wei, L. The Potential of Fermented Water Spinach Meal as a Fish Meal Replacement and the Impacts on Growth Performance, Reproduction, Blood Biochemistry and Gut Morphology of Female Stinging Catfish (Heteropneustes fossilis). Life 2023, 13, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rufchaei, R.; Nedaei, S.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Hassanpour, S.; Golshan, M.; Sayad Bourani, M. Improved Growth Performance, Serum and Mucosal Immunity, Haematology and Antioxidant Capacity in Pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) Using Dietary Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) Leaf Powder. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 2194–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Ramírez, J.; Loya-Olguín, J.; Ulloa, J.; Rosas-Ulloa, P.; Gutiérrez-Leyva, R.; Silva-Carrillo, Y. Aprovechamiento de Desechos de Pescado y Cáscara de Piña Para Producir Ensilado Biológico. Abanico Vet. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, N.; Powell, A.; Islam, S.; Fischer, H.; Renukdas, N.; Sinha, A.K.; Francis, S. Supplementing Aquaponics with Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Frass Tea: Effects on the Production and Composition of Sweetpotato Slips and Sweet Banana Peppers. Aquaculture 2022, 555, 738160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, N.; Datta, S.N.; Pande, G.S.J.; Sinha, A.K.; Yamamoto, F.Y.; Beck, B.H.; Webster, C.D. Dietary Inclusions of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Frass Enhanced Production of Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) Juveniles, Stevia (Stevia rebaudiana), and Lavender (Lavaridula angustifolia) in an Aquaponic System. Aquaculture 2023, 575, 739742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschenbruck, T.; Esterhuizen, W.; Padmanabha, M.; Streif, S. Sustainability Analysis of Interconnected Food Production Systems via Theory of Barriers. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 15765–15770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirakov, I.; Velichkova, K.; Stoyanova, S.; Kaymakanova, M.; Slavcheva-Sirakova, D.; Atanasova, R.; Staykov, Y. Effect of Synbiotic Dietary Supplementation on Growth, Physiological and Immunological Parameters in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) Fingerlings and on Yield and Physiological Parameters in Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.), Cultivated in Mesocosmos Aquaponic System. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 24, 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Maucieri, C.; Nicoletto, C.; Zanin, G.; Birolo, M.; Trocino, A.; Sambo, P.; Borin, M.; Xiccato, G. Effect of Stocking Density of Fish on Water Quality and Growth Performance of European Carp and Leafy Vegetables in a Low-Tech Aquaponic System. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozzi, V.; Strofaldi, S.; Piquer, I.F.; Di Crescenzo, D.; Olivotto, I.; Carnevali, O. Amyloodinum Ocellatum in Dicentrarchus Labrax: Study of Infection in Salt Water and Freshwater Aquaponics. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 57, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baßmann, B.; Brenner, M.; Palm, H.W. Stress and Welfare of African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus Burchell, 1822) in a Coupled Aquaponic System. Water 2017, 9, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauch, S.M.; Bahr, J.; Baßmann, B.; Bischoff, A.A.; Oster, M.; Wasenitz, B.; Palm, H.W. Effects of Ortho-Phosphate on Growth Performance, Welfare and Product Quality of Juvenile African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Fishes 2019, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhu, G.; Tian, Y.; Li, K.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, J.; Gu, Q.; Li, X. Blood Biochemistry Profile of Qihe Crucian Carp Carassius auratus in Different Aquaponic Systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 42898–42907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Yuan, J.; Ni, M.; Gu, Z. Effect of Water Spinach Floating Bed and Chlorella pyrenoidosa on Water Quality and Shrimp Growth in an Aquaponics System. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroel, M.; la Lama, G.C.M.D.; Escobar-álvarez, R.; Moratiel, R. Fish Welfare in Urban Aquaponics: Effects of Fertilizer for Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) on Some Physiological Stress Indicators in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.). Water 2022, 14, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Wang, B.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Du, X.; Shi, Q. Influences of Aquaponics System on Growth Performance, Antioxidant Parameters, Stress Parameters and Gene Expression of Carassius Auratus. Fishes 2023, 8, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.J.Y.; Yusoff, N.A.H.; Elias, N.A.; Norhan, N.A.S.; Harun, N.A.; Abdullah, F.; Ishak, A.N.; Hassan, M. Phytotherapy Use for Disease Control in Aquaculture: A Review of the Last 5 Years. Aquac. Int. 2023, 32, 2687–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariappan, B.; Kaliyamurthi, V.; Binesh, A. Medicinal Plants or Plant Derived Compounds Used in Aquaculture. In Recent Advances in Aquaculture Microbial Technology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 153–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverter, M.; Bontemps, N.; Lecchini, D.; Banaigs, B.; Sasal, P. Use of Plant Extracts in Fish Aquaculture as an Alternative to Chemotherapy: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Aquaculture 2014, 433, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakroborty, K.; Lima, R.A.; Hossain, M.F.; Rafiquzzaman, S.M. Biobased Functional Feed Additives in Asian Aquaculture: Trends, Impacts, and Future Directions. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2025, 320, 116222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumana, S.L.; Xue, T.; Hu, H.; Abdullateef, M.M.; Shui, Y.; Ayana, G.U.; Kayiira, J.C.; Zhang, C.; Samwel, B.J.; Zhu, J.; et al. Medicinal Plants as Ecological Solutions for Fish Growth and Immunostimulatory Effects in Aquaculture. Aquac. Res. 2025, 2025, 9778623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, S.; Sirakov, I.; Velichkova, K. Sustainable Production: Integrating Medicinal Plants with Fish Farming in Aquaponics—A Mini Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albadwawi, M.A.O.K.; Ahmed, Z.F.R.; Kurup, S.S.; Alyafei, M.A.; Jaleel, A. A Comparative Evaluation of Aquaponic and Soil Systems on Yield and Antioxidant Levels in Basil, an Important Food Plant in Lamiaceae. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braglia, R.; Costa, P.; Di Marco, G.; D’Agostino, A.; Redi, E.L.; Scuderi, F.; Gismondi, A.; Canini, A. Phytochemicals and Quality Level of Food Plants Grown in an Aquaponics System. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Aguilar, P.S.; Rico-Chávez, A.K.; Rodriguez-deLeón, E.; Aguirre-Becerra, H.; Zamora-Castro, S.A.; Soto-Zarazúa, G.M. Bioactive Compounds of Endemic Medicinal Plants (Cuphea spp.) Cultured in Aquaponic Systems: A Short Study. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zantanta, N.; Kambizi, L.; Etsassala, N.G.E.R.; Nchu, F. Comparing Crop Yield, Secondary Metabolite Contents, and Antifungal Activity of Extracts of Helichrysum odoratissimum Cultivated in Aquaponic, Hydroponic, and Field Systems. Plants 2022, 11, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgadillo-Díaz, M.; Gullian-Klanian, M.; Sosa-Moguel, O.; Sauri-Duch, E.; Cuevas-Glory, L.F. Evaluation of Physico-Chemical Characteristics, Antioxidant Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity in Creole Tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum L. and S. pimpinellifolium L.) in an Aquaponic System or Organic Soil. Int. J. Veg. Sci. 2019, 25, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashry, A.M.; Habiba, M.M.; El-Zayat, A.M.; Badreldeen, A.H.; Younis, N.A.; Ahmed, H.A.; El-Dakroury, M.F.; Ali, M.A.M.; Dawood, M.A.O. Effects of Ginger (Zingiber officinale) on the Growth Performance, Digestive Enzyme Activity, Antioxidative Response, and Antibacterial Capacity of Striped Catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) Reared in Outdoor Conditions. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 33, 101760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, S.; Krishnani, K.K.; Sharma, A.; Sahoo, U.; Majeedkutty, B.R.A. Curcuma longa and Allium Sativum as Health Promoters in Genetically Improved Farmed Tilapia (GIFT)—A Green Drug Approach in Hi-Tech Aquaculture Using Biofloc. Aquaculture 2024, 582, 740516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverter, M.; Tapissier-Bontemps, N.; Sarter, S.; Sasal, P.; Caruso, D. Moving towards More Sustainable Aquaculture Practices: A Meta-Analysis on the Potential of Plant-Enriched Diets to Improve Fish Growth, Immunity and Disease Resistance. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 537–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, K.K.; Valencia, V.; Baraldo, J.; Schulte, R.P.O.; van Zanten, H.H.E. On-Farm Circular Technologies for Enhanced Sustainability: The Case of Uruguay. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 372, 133470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Rossignoli, C.M.; Dompreh, E.B.; Su, J.; Griffiths, D.; Htoo, K.K.; Nway, H.M.; Akester, M.; Gasparatos, A. Diversification Strategies Have a Stabilizing Effect for Income and Food Availability during Livelihood Shocks: Evidence from Small-Scale Aquaculture-Agriculture Systems in Myanmar during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Agric. Syst. 2024, 217, 103935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baganz, G.; Schrenk, M.; Körner, O.; Baganz, D.; Keesman, K.J.; Goddek, S.; Siscan, Z.; Baganz, E.; Doernberg, A.; Monsees, H.; et al. Causal Relations of Upscaled Urban Aquaponics and the Food-Water-Energy Nexus—A Berlin Case Study. Water 2021, 13, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Kajgrova, L.; Mraz, J. TILAFeed: A Bio-Based Inventory for Circular Nutrients Management and Achieving Bioeconomy in Future Aquaponics. New Biotechnol. 2022, 70, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langergraber, G.; Castellar, J.A.C.; Pucher, B.; Baganz, G.F.M.; Milosevic, D.; Andreucci, M.B.; Kearney, K.; Pineda-Martos, R.; Atanasova, N. A Framework for Addressing Circularity Challenges in Cities with Nature-Based Solutions. Water 2021, 13, 2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Young, R.F. (Eds.) Ecological Wisdom: Theory and Practice; EcoWISE; Springer: Singapore, 2019; ISBN 978-981-13-0570-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chary, K.; Jaeger, C.; Jansen, H.M.; Harchaoui, S.; Aubin, J. Evaluating Nutrient Circularity in Integrated Aquaculture Systems: Criteria and Indicators. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 504, 145414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Species (Animal and Plant)/Reference | Treatments | Analysis (Aquatic Organism) | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dicentrarchus labrax, Beta vulgaris [156] | Control, reared at 20 ppt salinity; aquaponics AFI, reared in freshwater (0 ppt), infected with Amyloodinium ocellatum; aquaponics, ASI, reared at 20 ppt salinity and infected with A. ocellatum | Growth: final body weight (g), survival rate (SR, %), hepatosomatic index (HSI, %), specific growth rate (SGR, %); histology: gills, liver, intestine; cortisol assay; molecular analysis (RNA): 18 s, IGF I, NPY, PPARa, IL-1, TNFa, GR | AFI is more similar to control. For Dicentrarchus labrax, an aquaponics system may be used as a solution against A. ocellatum infection. |
| Clarias gariepinus, Cucumis sativus [157] | Aquaponics, control | Growth: final length, final weight, FCR, SGR, daily growth rate (DGR, g/fish/day); | Co-cultivation of fish and plants might offer benefits to the welfare of the fish by reducing skin injuries. |
| stress responses: cortisol, blood glucose, and external injuries | |||
| Cyprinus carpio L. [154] | Aquaponics without symbiotic, S0; aquaponics with commercial symbiotic (Bio Balance®), S1 | Growth: SGR, FCR; | Positive effect of symbiotic on growth and feed utilization in carp fingerlings. |
| physiological: HIS, viscerosomatic index (VSI, %); | |||
| immunological: phagocytosis activity, bactericide activity, and content of hemoglobin | |||
| Clarias gariepinus [158] | PO43−-P different concentrations in mg/l: P0 (control), P40, P80, P120 | Growth and feed efficiency: final weight, total length, standard length, growth, fillet ratio, SGR, FCR, total feed intake (TFI); | Concentrations ranging from 40 to 80 mg/L of PO43−-P fall within safe levels for African catfish aquaculture. Elevated values (120 mg/L) affect fish welfare. |
| body and fillet composition: dry matter, ash, protein, fat, calcium, phosphorus, sodium, magnesium, potassium | |||
| Apparent net nutrient utilization (ANNU); | |||
| histology: gills; | |||
| plasma metabolites: calcium, ammonia, blood glucose, plasma cortisol; | |||
| behavior: agonistic behavior, group and individual air-breathing and swimming, and biting wounds | |||
| Carassius auratus, Ipomoea aquatica, Lactuca sativa, Lemna minor, Amaranthus tricolor, Ceratophyllum demersum, Vallisneria spiralis, and C. demersum [159] | Control, only fish (CK); aquaponics with Ipomoea aquatica (Ia), Lactuca sativa (Ls), Lemna minor (Lm), Amaranthus tricolor (At), Ceratophyllum demersum (Cd), Vallisneria spiralis (Vn), and C. demersum-net (Cd-ns) | Growth: weight gain rate (WGR, %), SGR (%), feeding ratio (FR, %), food conversion rate (FCR, %); | Hydroponic plants were more advantageous for C. auratus under intensive conditions by providing more energy to resist environmental stress than the aquatic plants. |
| blood chemistry: glucose (GLU), triglyceride (TG), cholesterol (CHOL), creatinine (CREA), urinary nitrogen (BUN), total proteins (TP), albumin (ALB), globulin (GLO) and A/G (calculated by dividing the ALB by the GLO), the activity of alkaline phosphatase (ALP), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) | |||
| Penaeus vannamei, Ipomoea aquatica, Chlorella pyrenoidosa [160] | S0, aquaculture water without vegetation and chlorella; S1, aquaculture water with water spinach; S2, aquaculture water with chlorella; S3, aquaculture water with vegetation and chlorella | Growth: SR, SGR, weight gain rate (%); | Aquaponic shrimp cultivation with water spinach and Chlorella pyrenoidosa maintains good water quality, which improves the immunity of Penaeus vannamei. |
| activities of the immune enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione reductase (GR), glutathione (GSH), glutathione S-transferase (GST), and peroxidase (POD) in the hepatopancreas | |||
| Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) [161] | With and without fertilizer; fertilizer: 580 ppm CaNO3, 280 mg/L KNO3, 490 mg/L MgSO4, 270 mg/L K2PO4, and 48 mg/LNutrel C YaraVita™ | Growth: gain weight and length; | Fish production parameters were not significantly different between treatments, nor were physiological indicators of fish stress (plasma cortisol, glucose, and triglycerides). |
| blood plasma stress indicators: cortisol, glucose, and triglycerides | |||
| Carassius auratus, Lactuca sativa [162] | NC, control, no hypoxia, hypoxia; T0, plant water; T1, fish water; T2, fish and plant water | Growth: FW, SGR, relative growth rate (WGR, %); stress parameters: cortisol, serum glucose; antioxidant parameters: catalase and superoxide dismutase; gene expression profiles: HSP70, Prdx3 | There is evidence that the hypoxia stress of crucian carp is reduced in aquaponics. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, L.; Martinez-Cordero, F.J.; Baganz, G.; Baganz, D.; Hernández-Pérez, A.; Coronado, E.; Portella, M.C. Advancing Circularity in Small-Scale Rural Aquaponics: Potential Routes and Research Needs. Resources 2025, 14, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14080119
Silva L, Martinez-Cordero FJ, Baganz G, Baganz D, Hernández-Pérez A, Coronado E, Portella MC. Advancing Circularity in Small-Scale Rural Aquaponics: Potential Routes and Research Needs. Resources. 2025; 14(8):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14080119
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Laura, Francisco Javier Martinez-Cordero, Gösta Baganz, Daniela Baganz, Ariadne Hernández-Pérez, Eva Coronado, and Maria Celia Portella. 2025. "Advancing Circularity in Small-Scale Rural Aquaponics: Potential Routes and Research Needs" Resources 14, no. 8: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14080119
APA StyleSilva, L., Martinez-Cordero, F. J., Baganz, G., Baganz, D., Hernández-Pérez, A., Coronado, E., & Portella, M. C. (2025). Advancing Circularity in Small-Scale Rural Aquaponics: Potential Routes and Research Needs. Resources, 14(8), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14080119







