The Influence of the Rainfall Extremes and Land Cover Changes on the Major Flood Events at Bekasi, West Jawa, and Its Surrounding Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
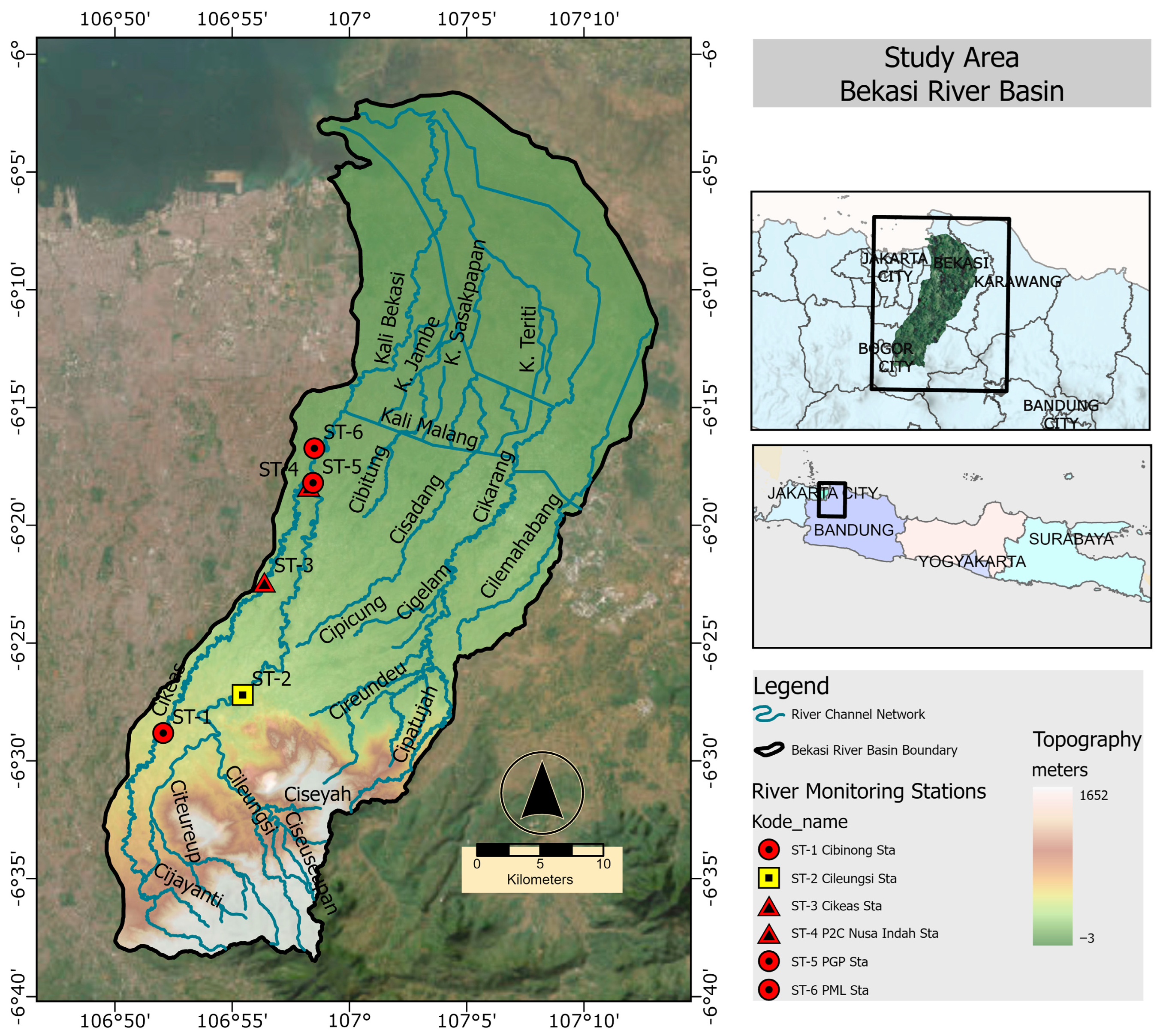
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Materials
2.2.1. Rainfall
2.2.2. Land Cover (LC)
2.2.3. Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
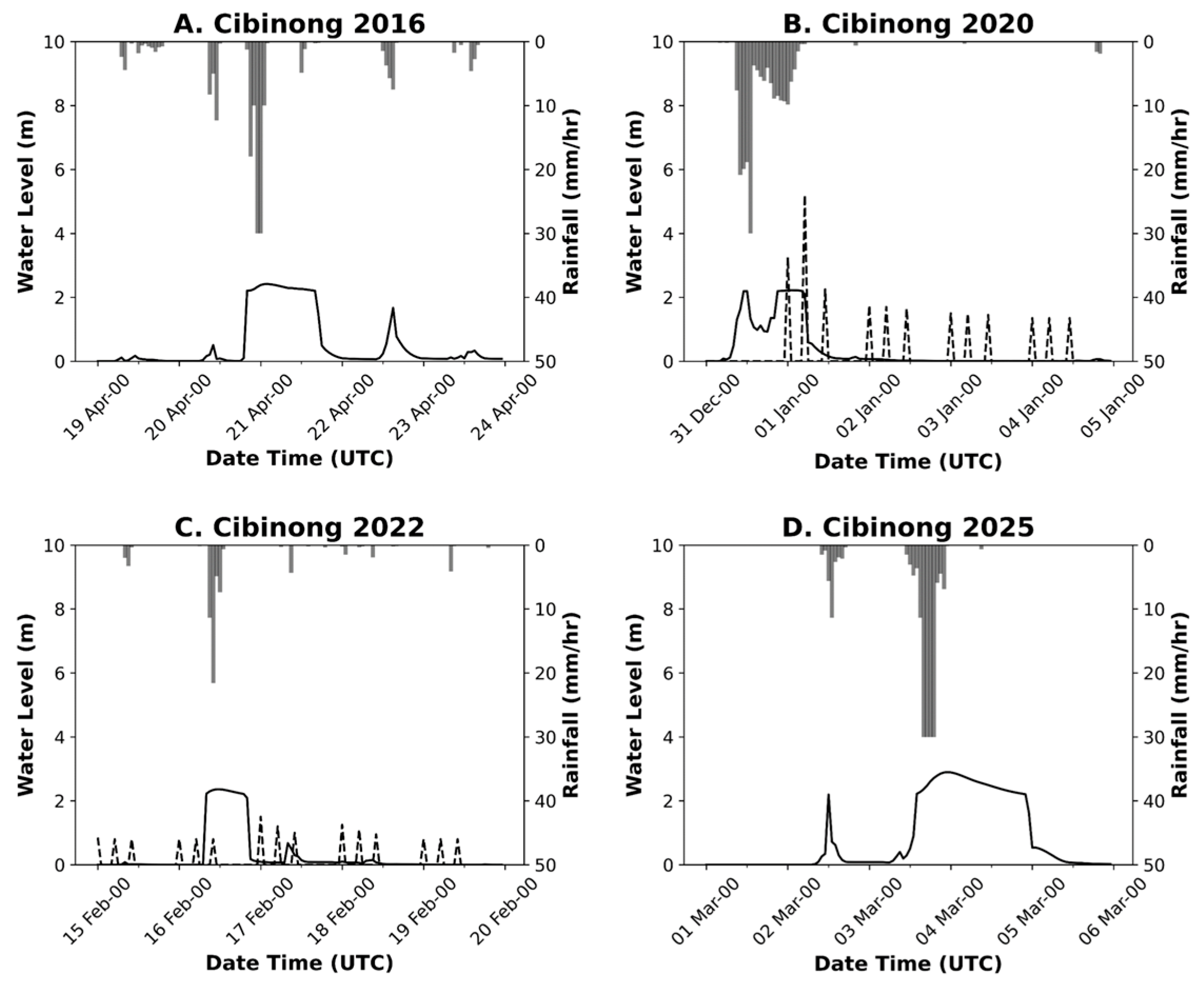
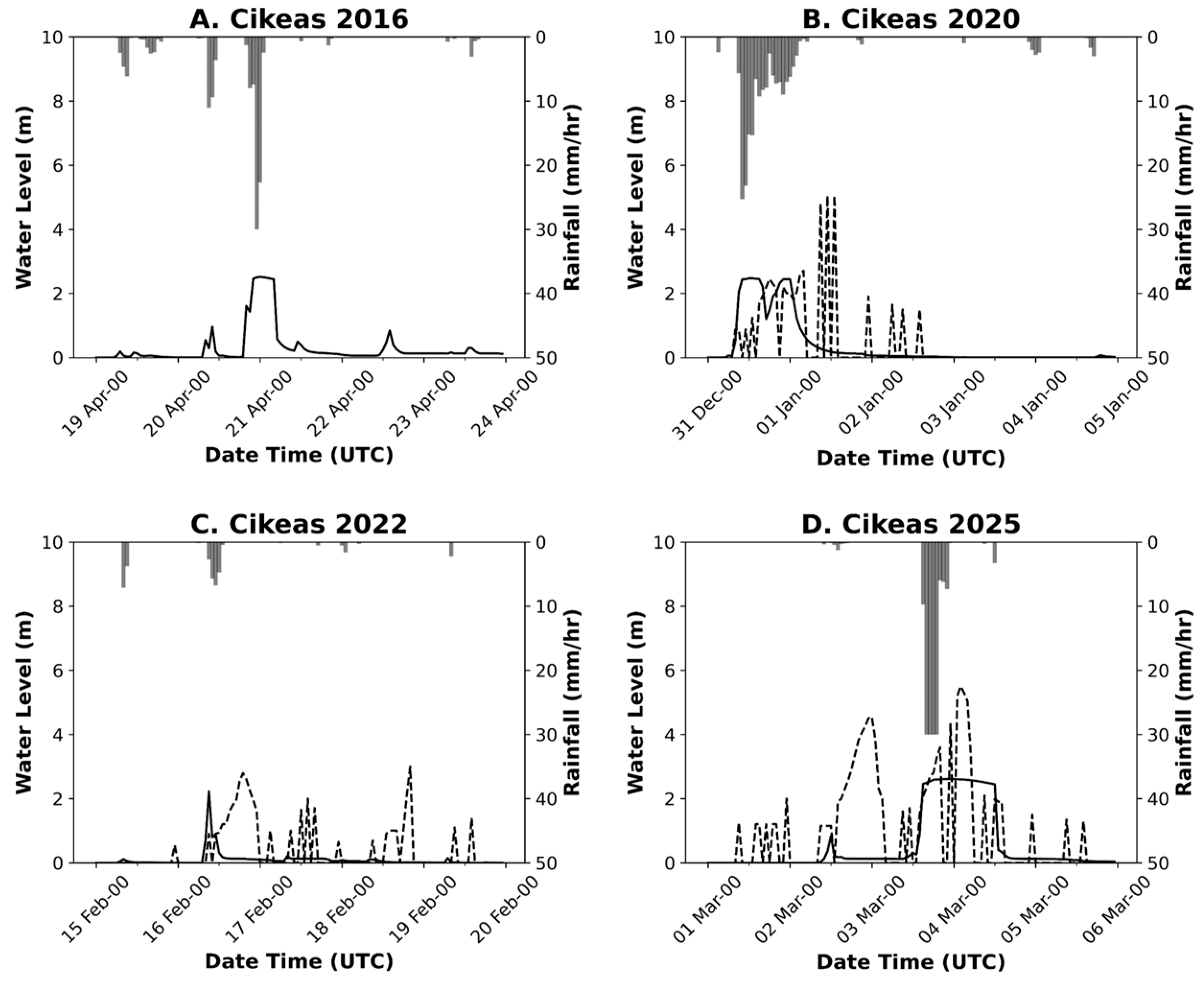
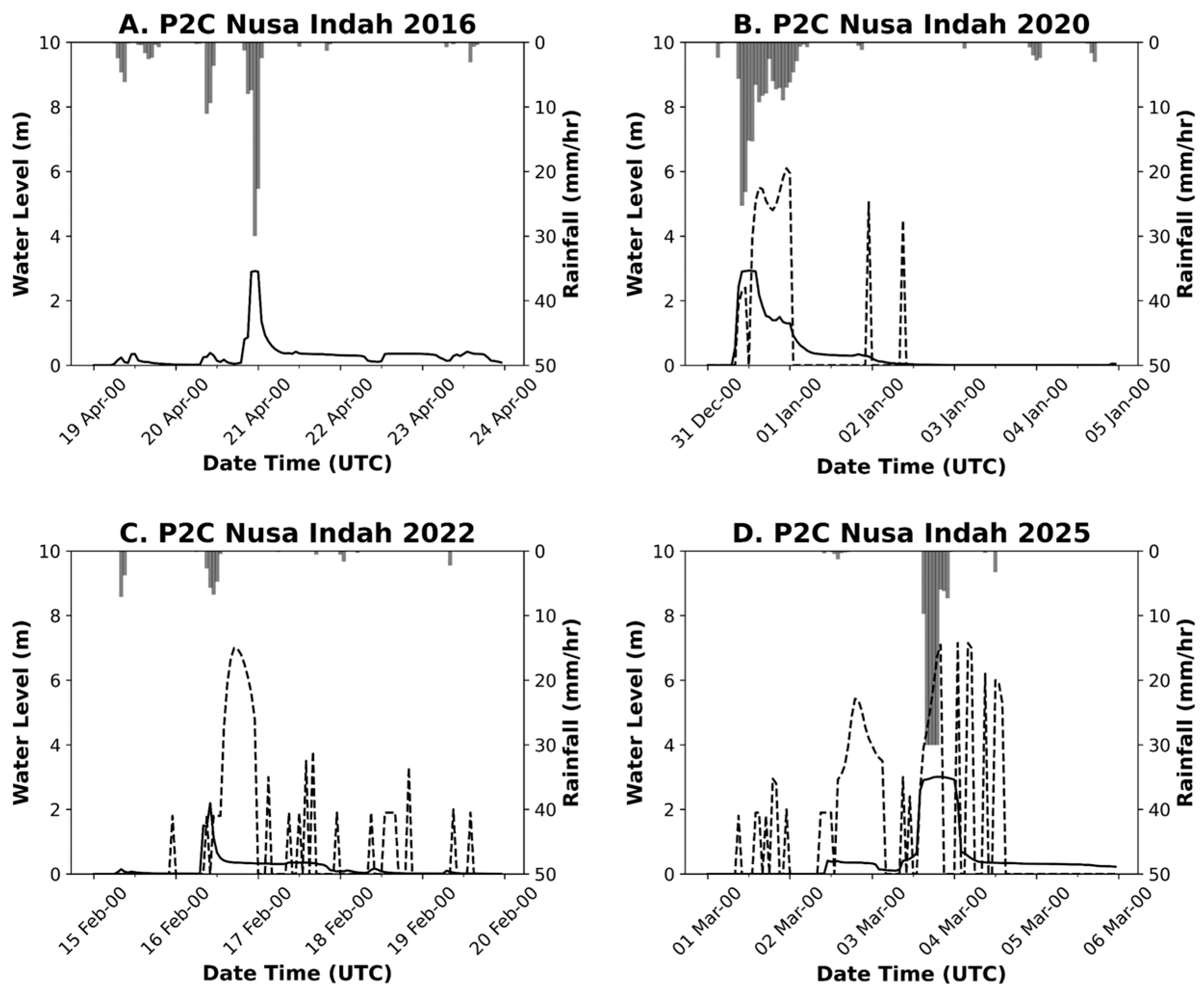
2.2.4. River Water Level (WL)
2.2.5. Sentinel-1 Inundation
2.3. Methods
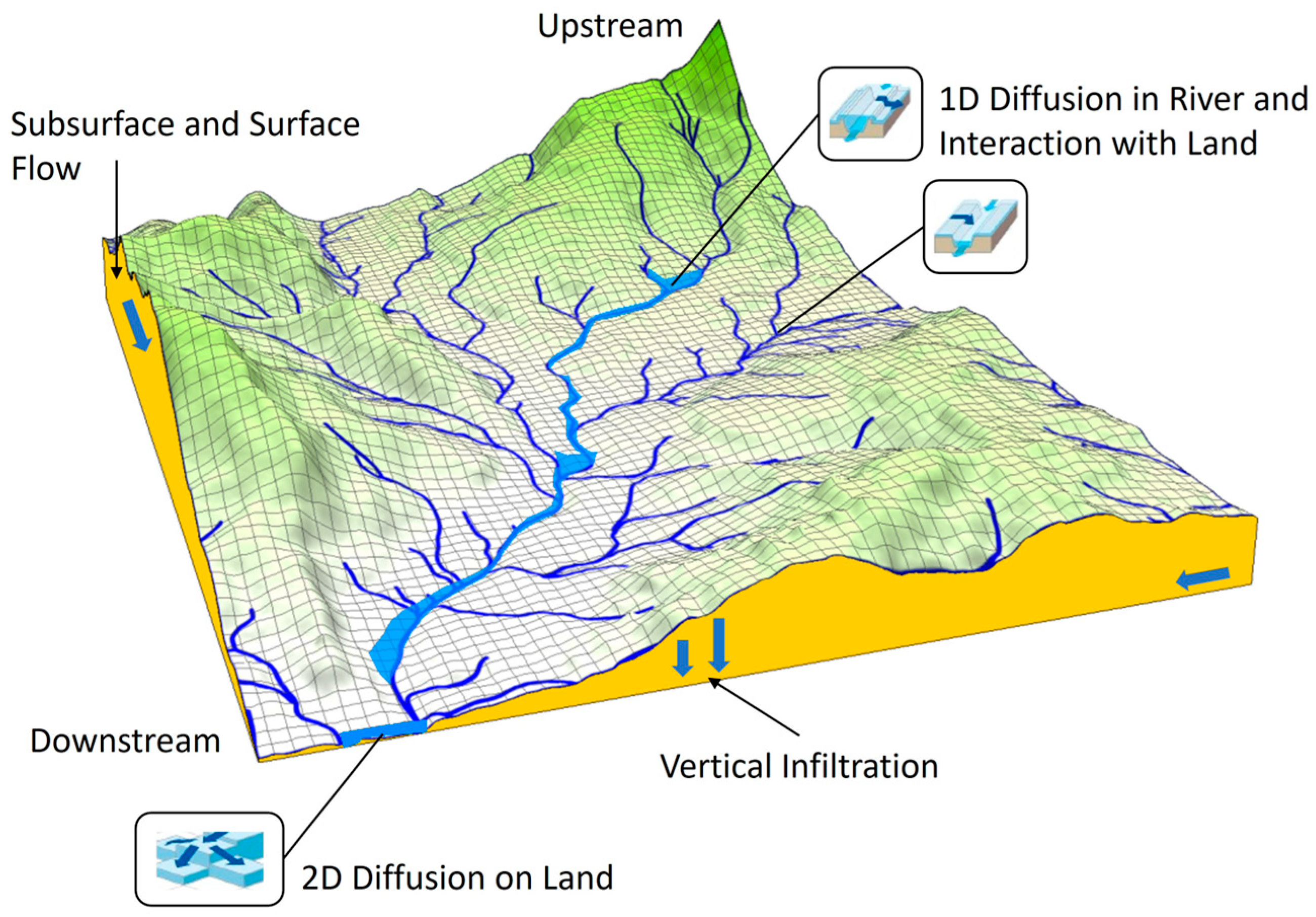
2.3.1. Inundation Model
2.3.2. Statistical Method
3. Results
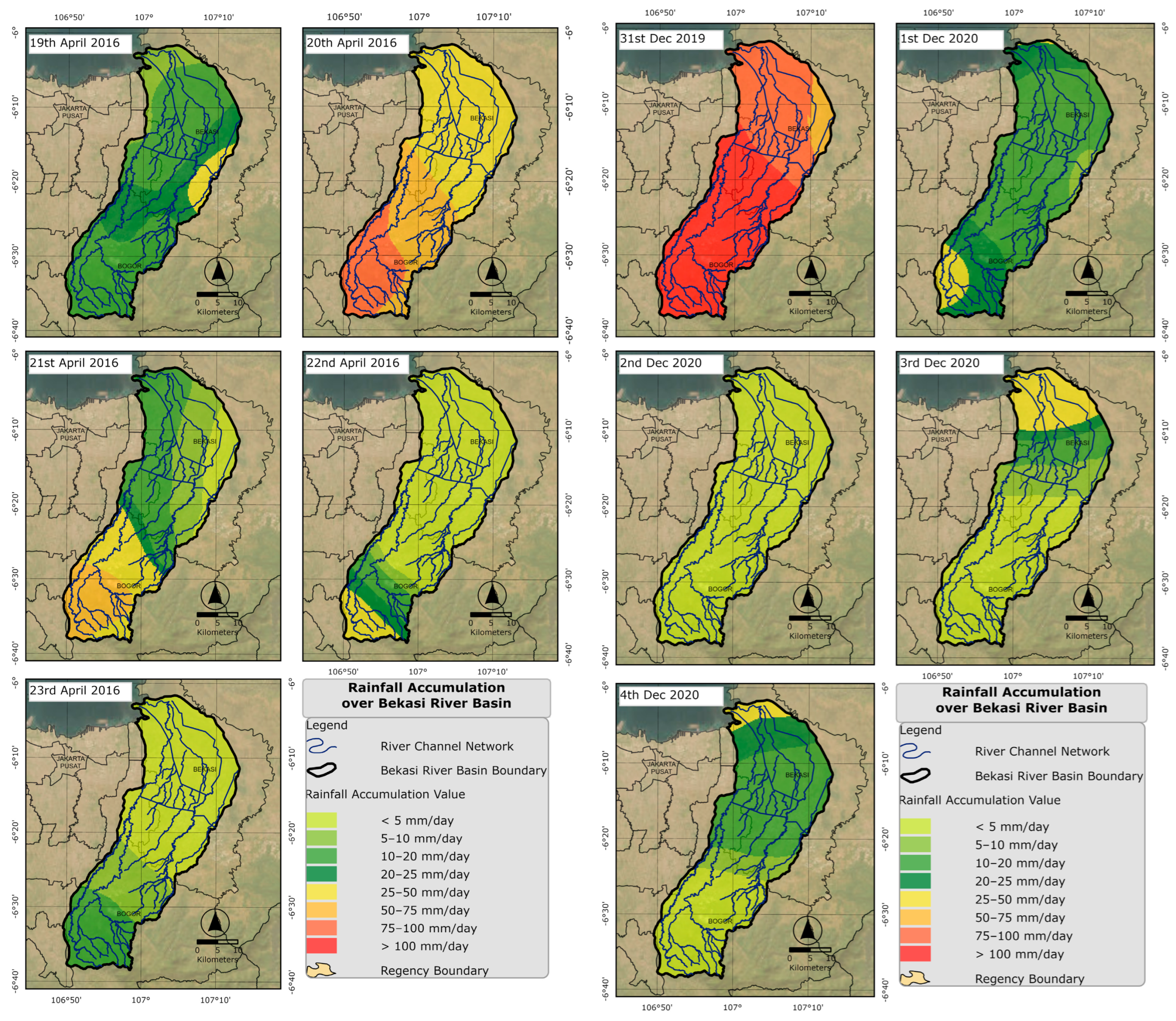
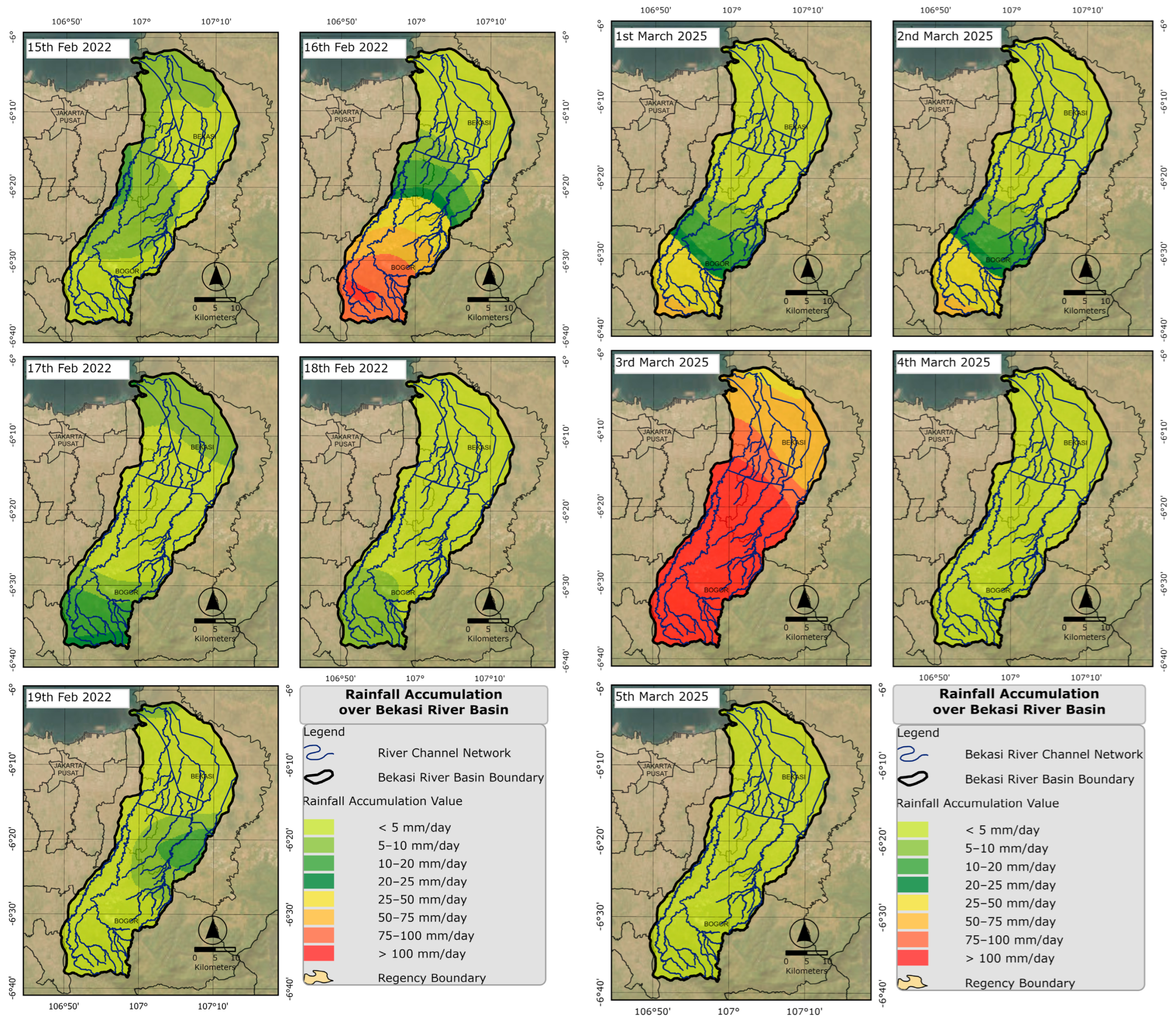
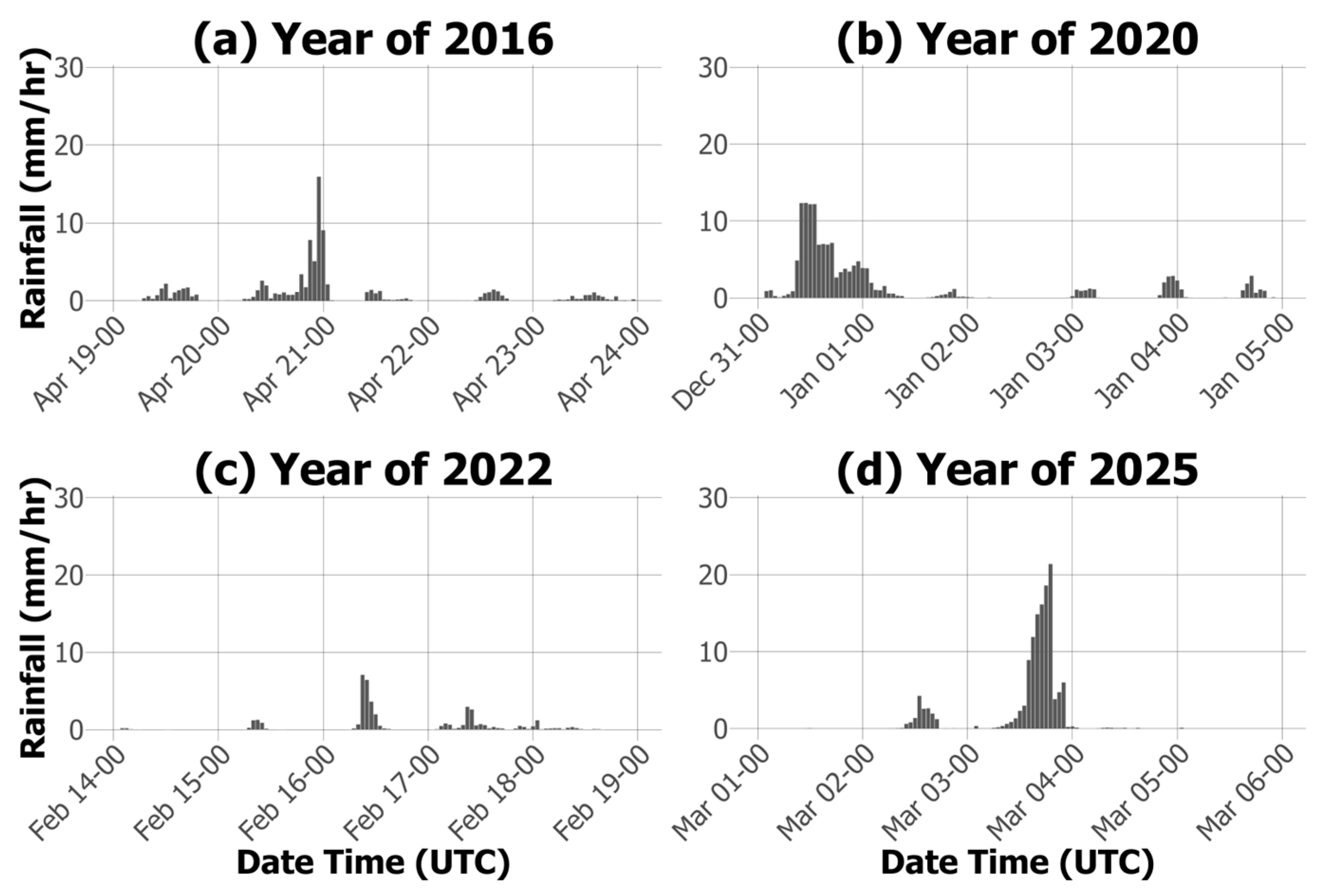
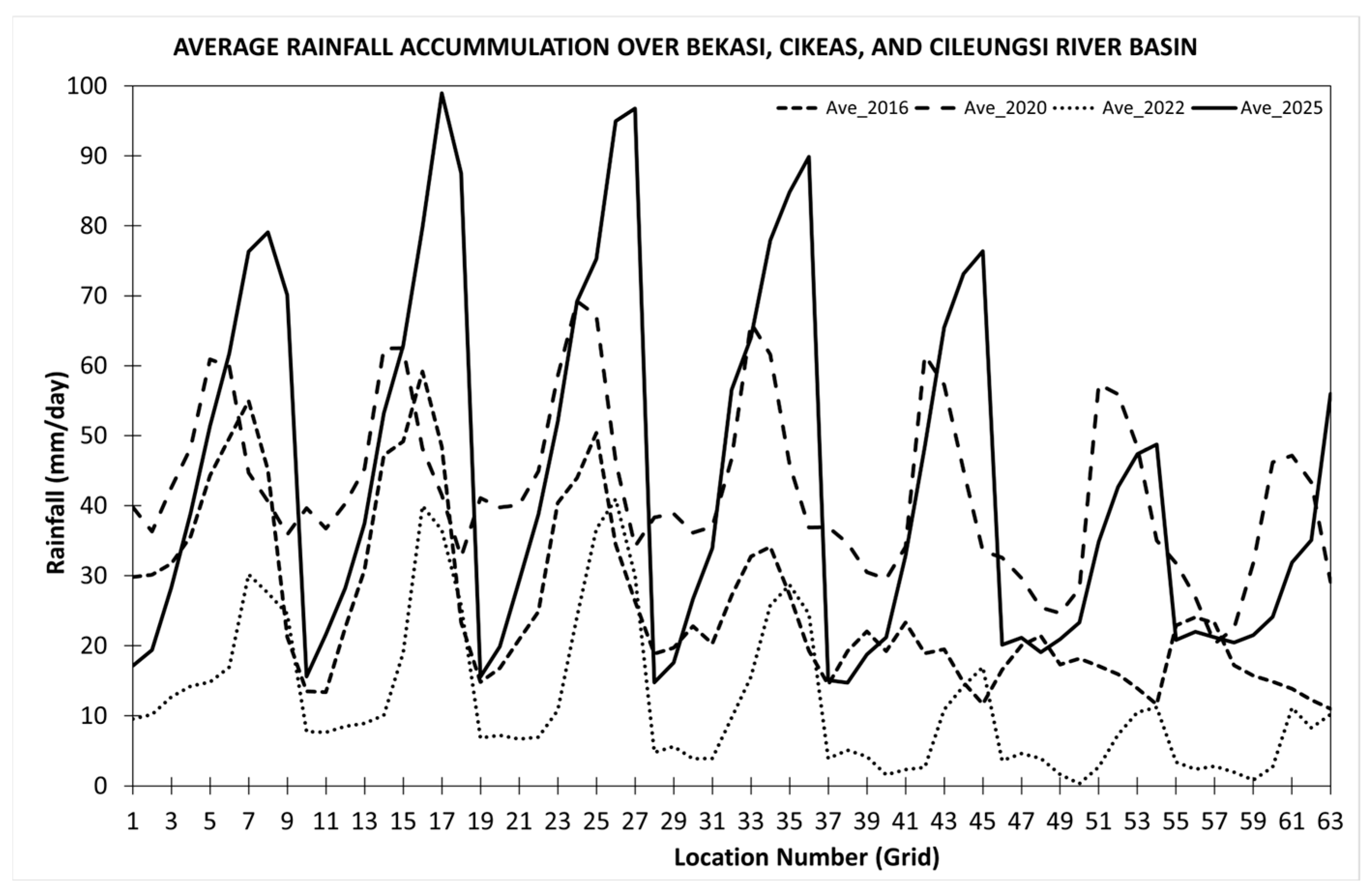
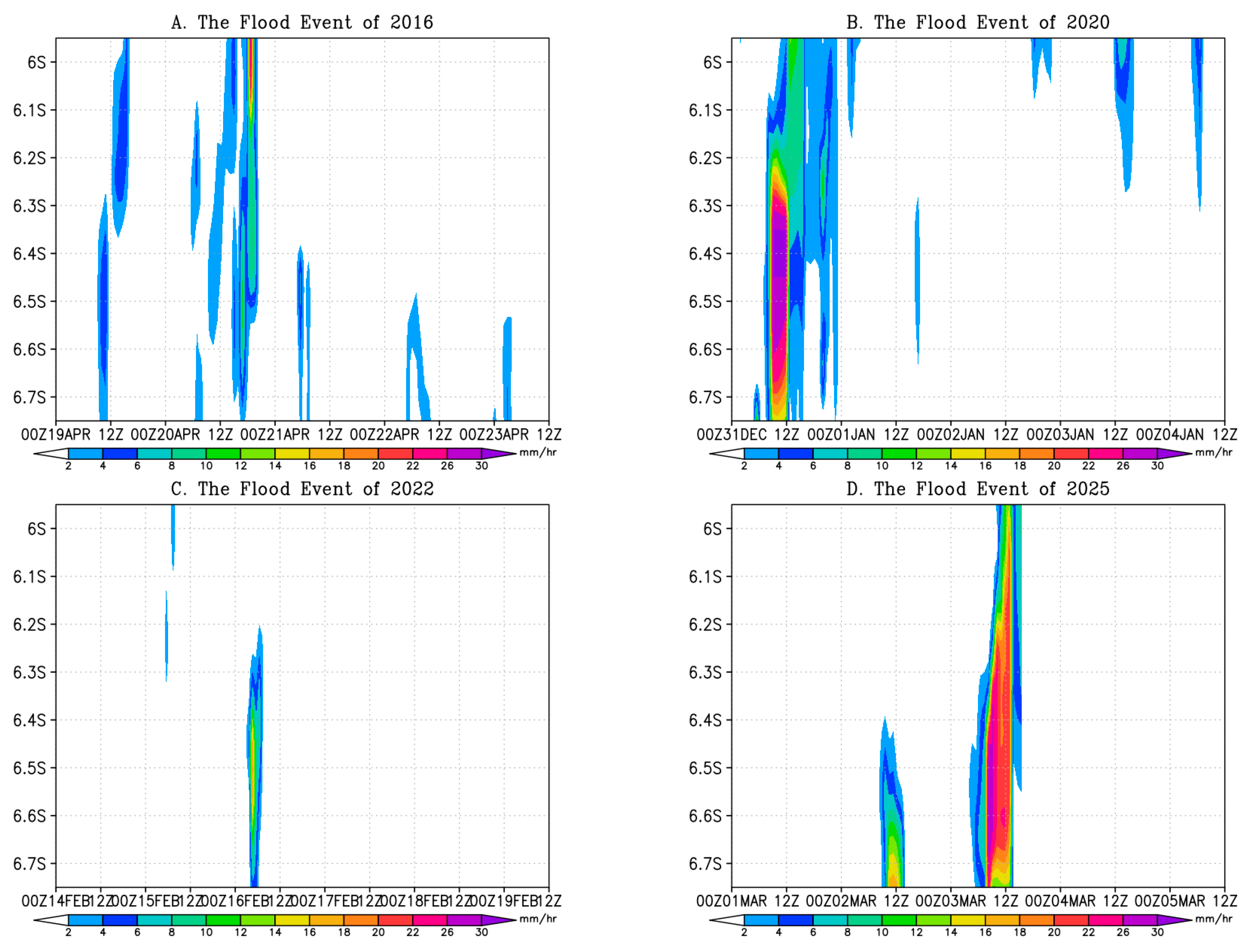
3.1. Rainfall Conditions
3.2. Model Validation
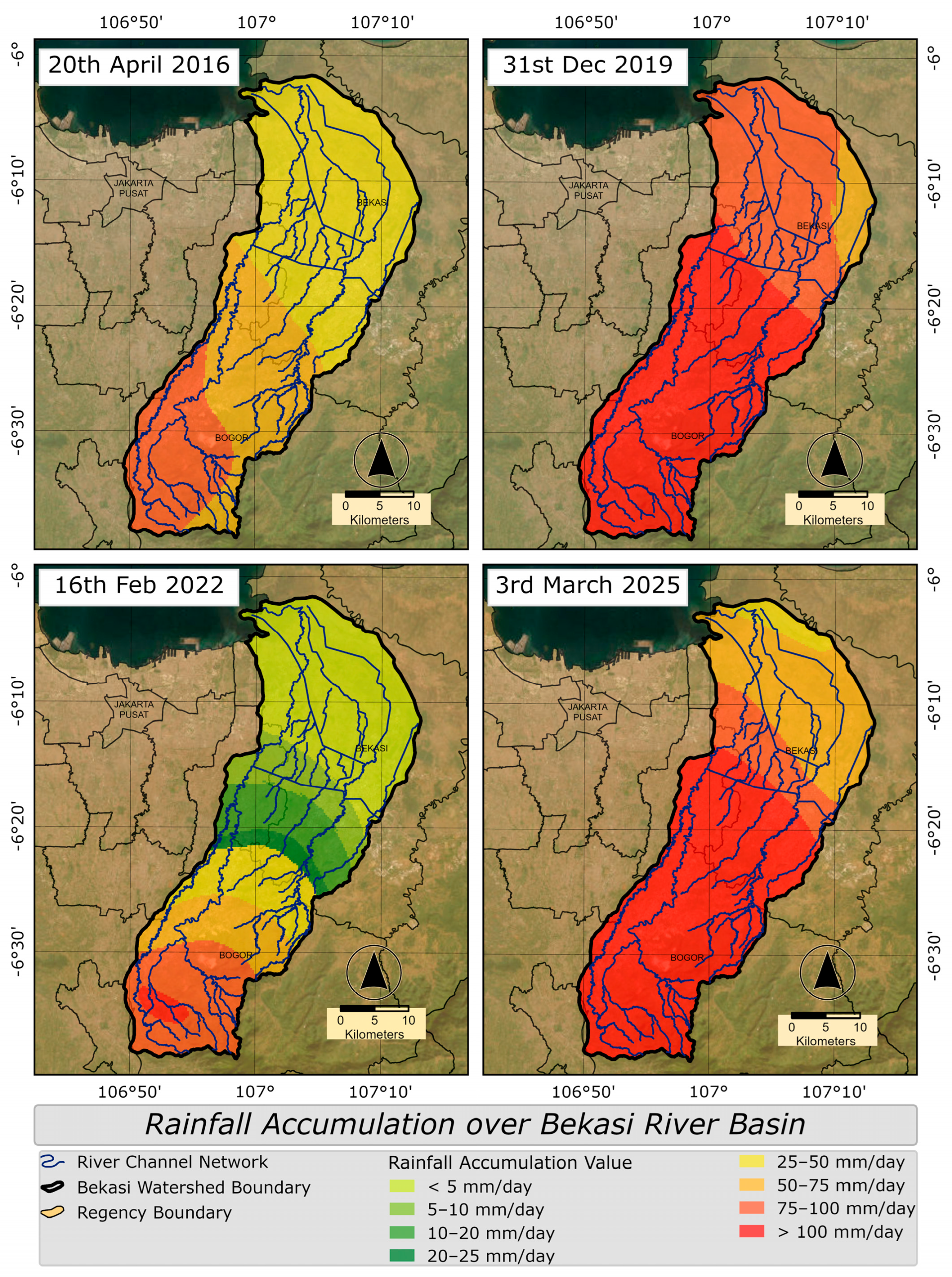
3.3. Rainfall Impact on Flood Events
3.4. The Influence of Land Cover Changes on the Intensification of Inundation Area
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RRI | Rainfall-Runoff Inundation |
| IMC | Indonesian Maritime Continent |
| SST | Sea Surface Temperature |
| ENSO | El-Niño Southern Oscillation |
| IOD | Indian Ocean Dipole |
| NSE | Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency |
| LC | Land Cover |
| GSMaP | Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation |
| HEC-RAS | Hydrologic Engineering Center-River Analysis System |
| IKN | Ibu Kota Nusantara |
| MoEF | Indonesian Ministry of Environment and Forestry |
| JAXA | Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency |
| ESA | European Space Agency |
| GPM | Global Precipitation Measurement |
| BMKG | Badan Meteorologi, Klimatologi dan Geofisika (Indonesian Agency for Meteorological, Climatological and Geophysics) |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| HydroSHEDS | Hydrological data and maps based on SHuttle Elevation Derivatives at multiple Scales |
| SRTM | Shuttle Radar Topography Mission |
| WL | Water Level |
| AWLR | Automatic Water Level Recorder |
| BBWSCC | Balai Besar Wilayah Sungai Ciliwung Cisadane (Ciliwung Cisadane River Basin Authority—Ministry of Public Works) |
| KP2C | Komunitas Peduli Sungai Cileungsi Cikeas (Cileungsi Cikeas River Care Community) |
| P2C | Pertemuan Cileungsi Cikeas (Cileungsi Cikeas Meeting Point) |
| PGP | Pondok Gede Permai |
| PML | Pondok Mitra Lestari |
| GEE | Google Earth Engine |
| IW | Interferometric Wide Swath |
| TOPSAR | Terrain Observation with Progressive Scanning SAR |
| VV | Vertical transmit—Vertical receive |
| VH | Vertical transmit—Horizontal receive |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| R2 | Coefficient of Determination |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| BPBD | Badan Penanggulangan Bencana Daerah (Regional Disaster Management Agency) |
Appendix A
| Year | Month | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 | April May | 4, 7, 12, 28 13, 22, 25, 30 |
| 2020 | December 2019 January | 29 2 |
| 2022 | February | 4, 8, 11, 16 |
| 2025 | February March | 19, 28 3, 12 |
| Period | Location (District) | Source |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 | Muara Gembong, East Bekasi, North Bekasi, Jatiasih, Pondok Melati, Babelan, Kedung Waringin, Gunung Putri, Cibarusah, Tambun Utara, Citeureup, Cileungsi, Babakan Madang | https://pusatkrisis.kemkes.go.id/banjir-di-bekasi-jawa-barat-27-05-2016 (accessed on 8 April 2025) https://www.tribunnews.com/metropolitan/2016/04/22/600-kk-terdampak-banjir-bekasi (accessed on 8 April 2025) https://jakarta.bisnis.com/read/20160421/383/540338/bekasi-banjir-kata-warga-terbesar-sepanjang-2016 (accessed on 8 April 2025) |
| 2020 | Jatiasih, West Bekasi, Rawa Lumbu, East Bekasi, North Bekasi, Medan Satria, South Bekasi, Pondok Gede, Mustika Jaya, Bantar Gebang, Babelan, Muara Gembong, Gunung Putri | https://www.tempo.co/arsip/ini-puluhan-titik-banjir-di-kota-bekasi-ribuan-rumah-terendam--669056 (accessed on 10 April 2025) https://pusatkrisis.kemkes.go.id/Banjir-di-BEKASI-JAWA-BARAT-01-01-2020-48 (accessed on 10 April 2025) https://megapolitan.antaranews.com/berita/366793/banjir-bekasi-tersebar-di-20-titik-dan-tujuh-wilayah-kecamatan (accessed on 10 April 2025) |
| 2022 | Jatiasih, Pondok Gede, East Bekasi, North Bekasi, South Bekasi, Medan Satria, Rawa Lumbu, Babelan, Tambun Utara, Gunung Putri, Muara Gembong | https://www.liputan6.com/news/read/4890876/bpbd-bekasi-ada-13-titik-banjir-4958-jiwa-terdampak (accessed on 14 April 2025) https://www.sonora.id/read/423147484/banjir-pertama-di-tahun-2022-kali-bekasi-meluap-sebabkan-8-kelurahan-tergenang-banjir-ada-yang-mencapai-2-m (accessed on 14 April 2025) |
| 2025 | Rawalumbu, Pondok Gede, West Bekasi, Bantar Gebang, North Bekasi, South Bekasi, Jatiasih, East Bekasi, Bogor City, Bogor Regency, Depok City and Jakarta | https://pusatkrisis.kemkes.go.id/situation-report-banjir-kota-bekasi-tanggal-05-maret-2025 (accessed on 15 April 2025) https://bekasikota.go.id/detail/rakor-evaluasi-banjir-kota-bekasi-bahas-pemulihan-pasca-banjir (accessed on 15 April 2025) BPBD Bogor Regency, Bekasi Regency, Bekasi City, Depok City, Jakarta |
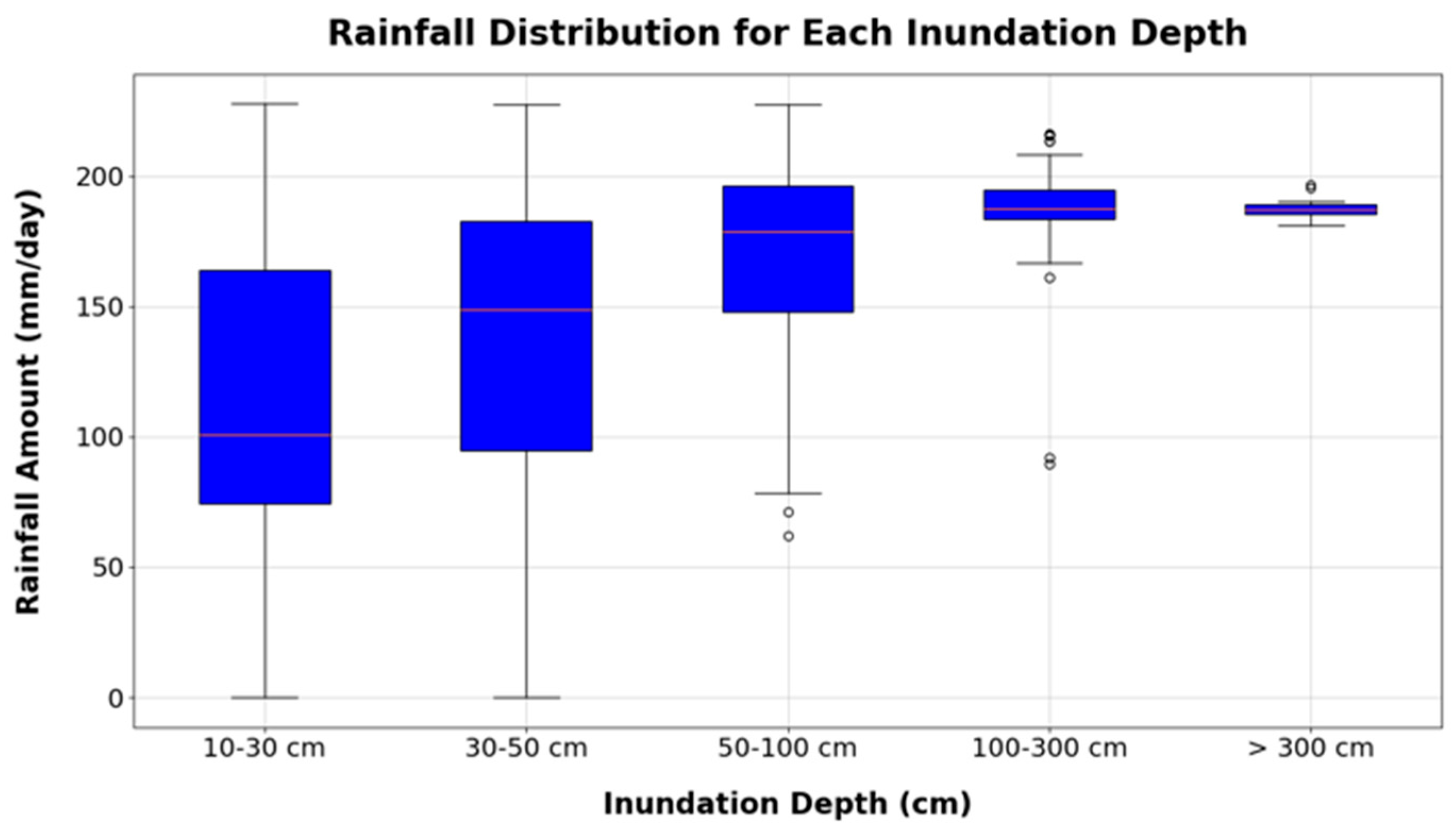
| Depth | Total Data | Mean | Median | Std | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10–30 cm | 3304 | 115.71 | 100.75 | 50.19 | 0 | 227.87 |
| 30–50 cm | 580 | 140.8 | 148.86 | 48.4 | 0 | 227.58 |
| 50–100 cm | 287 | 168.93 | 178.81 | 37.02 | 62.06 | 227.62 |
| 100–300 cm | 94 | 187.02 | 187.6 | 17.75 | 89.42 | 216.32 |
| >300 cm | 14 | 187.96 | 187.33 | 4.15 | 181.25 | 196.65 |
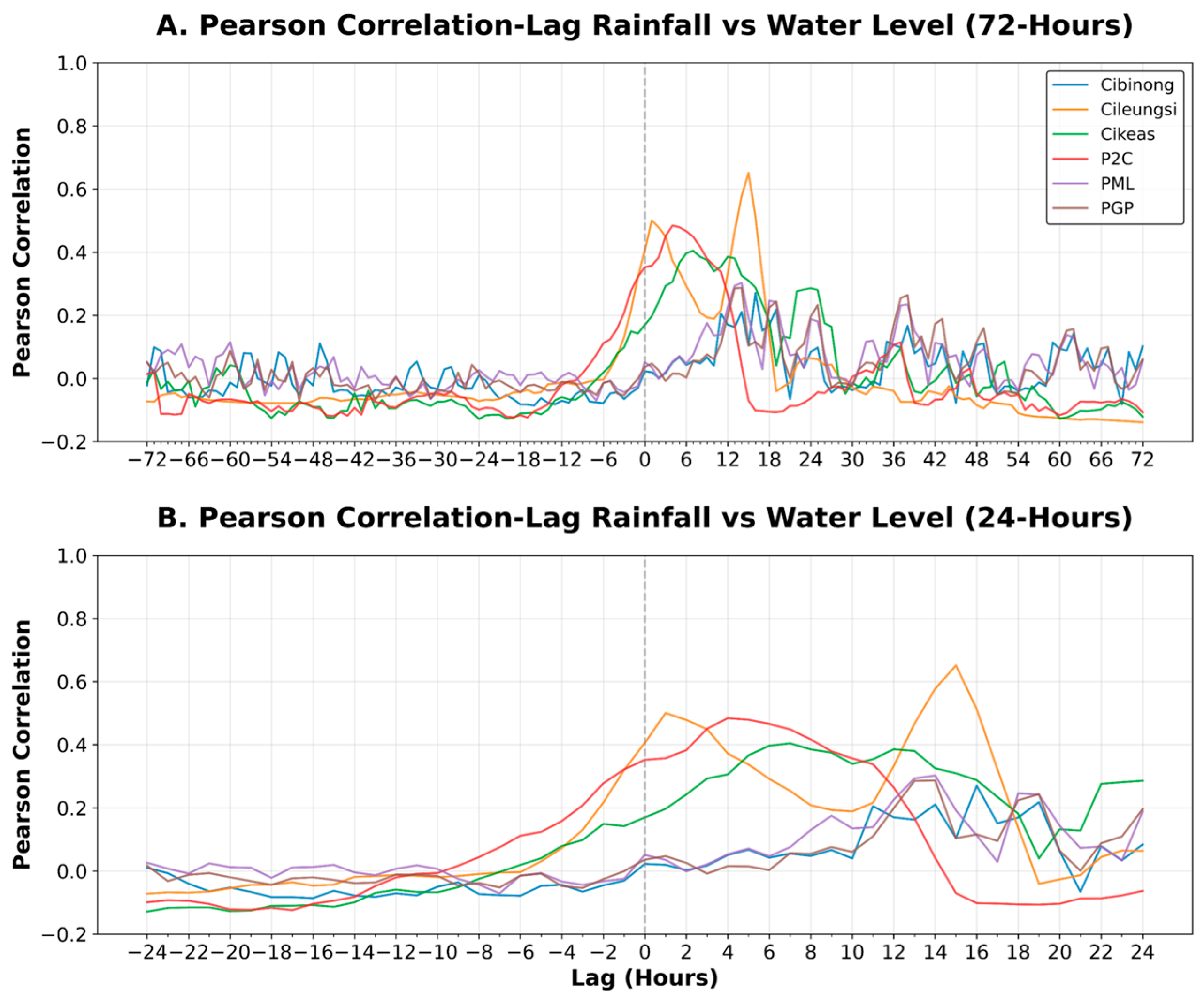
| Station | Total Event | Mean | Std Dev | Min | Q1 | Median | Q3 | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cibinong | 19 | 4.74 | 13.55 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.36 | 56.37 |
| Cileungsi | 24 | 48.75 | 40.25 | 0 | 23.61 | 39.6 | 63.55 | 136.47 |
| Cikeas | 24 | 24.83 | 31.08 | 0 | 0 | 3.46 | 47.12 | 103.14 |
| P2C | 24 | 36.67 | 36.58 | 0 | 0.34 | 32.76 | 58.22 | 103.14 |
| PGP | 24 | 6.17 | 13.99 | 0 | 0 | 0.49 | 3.26 | 54.1 |
| PML | 24 | 4.71 | 10.39 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.52 | 41.18 |

References
- Yuanita, C.N.; Sagala, S. Blue-Green Infrastructure in Jakarta’s Fringe: An Analysis of Accessibility to Blue-Green Spaces as a Flood Solution in Bekasi City. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2025, 121, 105425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cea, L.; Costabile, P. Flood Risk in Urban Areas: Modelling, Management and Adaptation to Climate Change. A Review. Hydrology 2022, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkhowa, S.; Sarma, J. Climate Change and Flood Risk, Global Climate Change. In Global Climate Change; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adikari, Y.; Osti, R.; Noro, T. Flood-related Disaster Vulnerability: An Impending Crisis of Megacities in Asia. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2010, 3, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaprasad Sharma, S.V.; Parth Sarathi, R.; Chakravarthi, V.; Srinivasa Rao, G. Flood Risk Assessment Using Multi-Criteria Analysis: A Case Study from Kopili River Basin, Assam, India. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2018, 9, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsono, A. Bekasi Floods Worst in City’s History. Available online: https://en.tempo.co/read/764994/bekasi-floods-worst-in-citys-history (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Sihombing, Y.I.; Rizaldi, A.; Farid, M.; Januriyadi, N.F.; Moe, I.R. Jakarta’s 2020 New Year Flood Assessment with a Rainfall–Runoff–Inundation (RRI) Model. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 25, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human Initiative. Current Condition of Floods Submerdging 8 Urban Villages in Bekasi. Available online: https://human-initiative.org/current-condition-of-floods-submerdging-8-urban-villages-in-bekasi/?lang=en#:~:text=Initiator (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Dhany, F.W.W. Bekasi River Overflow Paralyzes Bekasi City. Available online: https://www.kompas.id/artikel/en-luapan-kali-bekasi-lumpuhkan-kota-bekasi (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Warsono, A. Mall in Bekasi Paralyzed as Floods Reach 2 Meters High. Available online: https://en.tempo.co/read/1982429/mall-in-bekasi-paralyzed-as-floods-reach-2-meters-high (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Kurniawan, P. Widespread Flooding Paralyzes Public Activities: Bekasi Mayor. Available online: https://en.antaranews.com/news/347061/widespread-flooding-paralyzes-public-activities-bekasi-mayor (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Bekasi Regency Central Bureau of Statistics. Total Population by Age Group and Sex in Bekasi Regency. 2024. Available online: https://bekasikab.bps.go.id/id/statistics-table?subject=519 (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Rachmat, F.B.; Muhammad, H. Analysis of Land Use Changes to the Criticality Level of the Catchment Area in Eight Watersheds That Flow into Jakarta Bay, Indonesia. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 73, 03001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owuor, M.O.; Mwiturubani, D.A. Nexus between Flooding Impacts and Coping Strategies in Nairobi’s Settlements. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 64, 102480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agonafir, C.; Lakhankar, T.; Khanbilvardi, R.; Krakauer, N.; Radell, D.; Devineni, N. A Review of Recent Advances in Urban Flood Research. Water Secur. 2023, 19, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahayu, R.; Mathias, S.A.; Reaney, S.; Vesuviano, G.; Suwarman, R.; Ramdhan, A.M. Impact of Land Cover, Rainfall and Topography on Flood Risk in West Java. Nat. Hazards 2023, 116, 1735–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zope, P.E.; Eldho, T.I.; Jothiprakash, V. Impacts of Land Use–Land Cover Change and Urbanization on Flooding: A Case Study of Oshiwara River Basin in Mumbai, India. Catena 2016, 145, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhanu, B.; Seleshi, Y.; Demisse, S.; Melesse, A. Flow Regime Classification and Hydrological Characterization: A Case Study of Ethiopian Rivers. Water 2015, 7, 3149–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yu, D.; Yin, Z.; Liu, M.; He, Q. Evaluating the Impact and Risk of Pluvial Flash Flood on Intra-Urban Road Network: A Case Study in the City Center of Shanghai, China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 537, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertan, S.; Çelik, R.N. The Assessment of Urbanization Effect and Sustainable Drainage Solutions on Flood Hazard by GIS. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, S.; Sapan, E.G.A.; Sulistyowati, R.; Belgaman, H.A.; Meliani, F.; Winarno; Hapsari, R.I.; Cahyaningtiyas, I.F.; Pianto, T.A.; Akbar, H.I.; et al. Characteristic of Rain Rate Associated with Floods during the 2021 Rainy Season around Jakarta and Bekasi River. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1109, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M.; Pratama, M.I.; Kuntoro, A.A.; Adityawan, M.B.; Rohmat, F.I.W.; Moe, I.R. Flood Prediction Due to Land Cover Change in the Ciliwung River Basin. Int. J. Technol. 2022, 13, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardiansyah, M.; Nugraha, R.A.; Iman, L.O.S.; Djatmiko, S.D. Impact of Land Use and Climate Changes on Flood Inundation Areas in the Lower Cimanuk Watershed, West Java Province. J. Ilmu Tanah Dan Lingkung. 2021, 23, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Phakdimek, S.; Nagami, K.; Komori, D. Relationship Between Urbanization–Induced Land Use Changes and Flood Risk: Case Study in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Water 2025, 17, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handyastono, B.; Alghoul, M.A.; Rizki, A.; Djambek, N.P.; Kusuma, M.S.B.; Kuntoro, A.A.; Harlan, D.; Nugroho, E.O.; Munthe, H.M.; Hazmi, M.; et al. Flood Hazard Assessment in Pemaluan Village Due to Land Use Change in IKN (Ibu Kota Nusantara) as the New Capital City of Indonesia. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2025, 11, 101211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phyoe, P.P.; Uchida, T. Flood Simulation Studies with Rainfall-Runoff-Inundation (RRI) Model, Over Yangon City, Myanmar. Proc. IAHS 2024, 386, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhou, L.; Du, J.; Yue, J.; Ao, T. Accuracy Evaluation and Comparison of GSMaP Series for Retrieving Precipitation on the Eastern Edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 56, 102017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, K.V.; Mangukiya, N.K.; Tiwari, D.K.; Ramkar, P.V.; Rathnayake, U. Machine Learning Applications in Flood Forecasting and Predictions, Challenges, and Way-out in the Perspective of Changing Environment. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2025, 12, 72–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevo, S.; Elidan, G.; Hassidim, A.; Shalev, G.; Gilon, O.; Nearing, G.; Matias, Y. ML-Based Flood Forecasting: Advances in Scale, Accuracy and Reach. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Try, S.; Tanaka, S.; Tanaka, K.; Sayama, T.; Oeurng, C.; Uk, S.; Takara, K.; Hu, M.; Han, D. Comparison of Gridded Precipitation Datasets for Rainfall-Runoff and Inundation Modeling in the Mekong River Basin. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayama, T.; Ozawa, G.; Kawakami, T.; Nabesaka, S.; Fukami, K. Rainfall–Runoff–Inundation Analysis of the 2010 Pakistan Flood in the Kabul River Basin. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2012, 57, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastiti, K.D.; An, H.; Kim, Y.; Jung, K. Large-Scale Rainfall–Runoff–Inundation Modeling for Upper Citarum River Watershed, Indonesia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Sayama, T.; Apip. Impact of Climate Change on Flood Inundation in a Tropical River Basin in Indonesia. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2021, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitriyati, N.; Arifin, H.S.; Kaswanto; Marimin. Towards a Resilient and Sustainable City: New Paradigm of Flood Disaster Governance Study Case Bekasi City. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2024, 19, 3393–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.P.; Ramirez, J.A.; Srivastava, P.K.; Bray, M.; Han, D. Assessment of Flood Inundation Mapping of Surat City by Coupled 1D/2D Hydrodynamic Modeling: A Case Application of the New HEC-RAS 5. Nat. Hazards 2017, 89, 93–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, D.S.; Chatterjee, C.; Kalakoti, S.; Upadhyay, P.; Sahoo, M.; Panda, A. Modeling Urban Floods and Drainage Using SWMM and MIKE URBAN: A Case Study. Nat. Hazards 2016, 84, 749–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Amarnath, G. Applications of Satellite-Based Rainfall Estimates in Flood Inundation Modeling—A Case Study in Mundeni Aru River Basin, Sri Lanka. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojinovic, Z.; Hammond, M.; Golub, D.; Hirunsalee, S.; Weesakul, S.; Meesuk, V.; Medina, N.; Sanchez, A.; Kumara, S.; Abbott, M. Holistic Approach to Flood Risk Assessment in Areas with Cultural Heritage: A Practical Application in Ayutthaya, Thailand. Nat. Hazards 2016, 81, 589–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayama, T.; Tatebe, Y.; Iwami, Y.; Tanaka, S. Hydrologic Sensitivity of Flood Runoff and Inundation: 2011 Thailand Floods in the Chao Phraya River Basin. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 1617–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Kiyohara, K.; Tachikawa, Y. Comparison of Fluvial and Pluvial Flood Risk Curves in Urban Cities Derived from a Large Ensemble Climate Simulation Dataset: A Case Study in Nagoya, Japan. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San, Z.M.L.T.; Zin, W.W.; Kawasaki, A.; Acierto, R.A.; Oo, T.Z. Developing Flood Inundation Map Using RRI and SOBEK Models: A Case Study of the Bago River Basin, Myanmar. J. Disaster Res. 2020, 15, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmy, M.; Sayama, T.; Koike, T. Development of Water and Energy Budget-Based Rainfall-Runoff-Inundation Model (WEB-RRI) and Its Verification in the Kalu and Mundeni River Basins, Sri Lanka. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagabati, S.S.; Kawasaki, A. Consideration of the Rainfall-Runoff-Inundation (RRI) Model for Flood Mapping in a Deltaic Area of Myanmar. Hydrol. Res. Lett. 2017, 11, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyaningtiyas, I.F.; Djoharin, M.; Grace, T.; Eugenie, A.; Aviantie, E.; Amaliyah, R.; Sapan, E.G.A.; Meliani, F.; Sulistyowati, R.; Priyadi, H.; et al. Preliminary Study on the Rainfall-Runoff Inundation and Its Economic Lost at Bekasi River Basin, West Jawa. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Geoscience, Electronics and Remote Sensing Technology (AGERS), Surabaya, Indonesia, 21–22 December 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, T.; Kurniyaningrum, E. Impact of Land Use on Frequency of Floods in Upper Bekasi Watershed, Indonesia. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2019, 8, 3328–3334. [Google Scholar]
- Effendi, H.; Prayoga, G.; Azhar, A.R.; Permadi, T.; Santoso, E.N. Pollution Index of Cileungsi-Cikeas-Bekasi River. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 744, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prihartanto; Ganesha, D. Flood Time Arrival Estimation Based on Empirical Analysis of Recorded Data of Flood Early Warning System in Bekasi City. J. Sains Teknol. Mitigasi Bencana 2019, 14, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kadri, T.; Sinukaban, N.; Pawitan, H.; Darma Tarigan, S. Analysis of Bekasi City Flood Reduction Using Watershed Management. Forum Pascasarj. 2011, 34, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Yuwono, R.A. Aplikasi Fast Fourier Transform untuk Menentukan Periode Maksimum Curah Hujan: Studi Kasus di Stasiun Klimatologi BMKG Bogor. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitas Brawijaya, Malang, Indonesia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fatkhuroyan; TrinahWati. Accuracy Assessment of Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) Product Over Indonesian Maritime Continent. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 187, 012060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Ruan, R.; Liu, Y. Accuracy Assessment of Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) Product over Poyang Lake Basin, China. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 2265–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Yong, B. A Preliminary Assessment of the Gauge-Adjusted Near-Real-Time GSMaP Precipitation Estimate over Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawati, M.D.; Miura, F. Evaluation of GSMaP Daily Rainfall Satellite Data for Flood Monitoring: Case Study—Kyushu Japan. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2016, 4, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofiati, I.; Avia, L.Q. Analysis of Rainfall Data Based on GSMaP and TRMM towards Observations Data in Yogyakarta. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 166, 012031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulistyowati, R.; Meliani, F.; Sapan, E.G.A.; Winarno; Lestari, S.; Hapsari, R.I.; Cahyaningtiyas, I.F.; Avianti, E.; Eugenie, A.; Grace, T.; et al. Distributed Flood Simulation Based on Satellite Rainfall Data at the Ciliwung River Basin, Jawa, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1127, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helda, N.; Nashrullah, E.; Wijayanto, M.R.; Noralamsyah, M.; Jannah, N.; Erisa, E.; Saputri, D.S. Evaluation of GSMap (Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation) with the Reference to Rain Gauge Observations in Banjarbaru City, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1343, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BMKG. Press Release Kondisi Cuaca Ekstrem Dan Iklim Tahun 2010–2011; BMKG: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lehner, B.; Verdin, K.; Jarvis, A. New Global Hydrography Derived From Spaceborne Elevation Data. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2008, 89, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, M.; Kantoush, S.A.; Saber, M.; Sumi, T. Rainfall-Runoff Modeling for Extreme Flash Floods in Wadi Samail, Oman. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. (Hydraul. Eng.) 2018, 74, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulistyowati, R.; Meliani, F.; Winarno; Belgaman, H.A.; Syamsudin, F. Flood Early Warning System (FEWS) Based on Weather Radar Observation at Ciliwung River Basin: Preliminary Study. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Geoscience, Electronics and Remote Sensing Technology (AGERS), Jakarta, Indonesia, 7–8 December 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.; Snoeij, P.; Geudtner, D.; Bibby, D.; Davidson, M.; Attema, E.; Potin, P.; Rommen, B.; Floury, N.; Brown, M.; et al. GMES Sentinel-1 Mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarpanelli, A.; Mondini, A.C.; Camici, S. Effectiveness of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 for Flood Detection Assessment in Europe. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 2473–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twele, A.; Cao, W.; Plank, S.; Martinis, S. Sentinel-1-Based Flood Mapping: A Fully Automated Processing Chain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 2990–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayama, T.; Tatebe, Y.; Tanaka, S. An Emergency Response-type Rainfall-runoff-inundation Simulation for 2011 Thailand Floods. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2015, 10, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastiti, K.D.; Kim, Y.; Jung, K.; An, H. The Application of Rainfall-Runoff-Inundation (RRI) Model for Inundation Case in Upper Citarum Watershed, West Java-Indonesia. Procedia Eng. 2015, 125, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Try, S.; Lee, G.; Yu, W.; Oeurng, C.; Jang, C. Large-Scale Flood-Inundation Modeling in the Mekong River Basin. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2018, 23, 05018011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayama, T. Rainfall-Runoff-Inundation (RRI) Model (updated version); Kyoto University: Kyoto, Japan, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, V.T. Open Channel Hydraulics; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1959; ISBN 07-010776-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kouzehgar, K.; Eslamian, S. Application of Experimental Data and Soft Computing Techniques in Determining the Outflow and Breach Characteristics in Embankments and Landslide Dams. In Handbook of Hydroinformatics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Yu, D.; Gu, Y. Air Quality Index and Air Pollutant Concentration Prediction Based on Machine Learning Algorithms. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, K.M.; Tsokos, C.P. Mathematical Statistics with Applications; Elsevier Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Deng, Y. Dependent Evidence Combination Based on Shearman Coefficient and Pearson Coefficient. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 11634–11640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murodi, E.H. Banjir di BEKASI, JAWA BARAT, 27-05-2016. Available online: https://pusatkrisis.kemkes.go.id/banjir-di-bekasi-jawa-barat-27-05-2016 (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Warsono, A. Ini Puluhan Titik Banjir di Kota Bekasi, Ribuan Rumah Terendam. Available online: https://www.tempo.co/arsip/ini-puluhan-titik-banjir-di-kota-bekasi-ribuan-rumah-terendam--669056 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Tim Diskominfostandi. Rakor Evaluasi Banjir Kota Bekasi Bahas Pemulihan Pasca-Banjir. Available online: https://bekasikota.go.id/detail/rakor-evaluasi-banjir-kota-bekasi-bahas-pemulihan-pasca-banjir (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Abdelmoneim, H.; Eldardiry, H.; Saber, M.; Kantoush, S.A.; Moghazy, H.M.; Sumi, T. Integrating Multi-Sensor Observations and Rainfall-Runoff Inundation Modeling for Mapping Flood Extents over the Nile River Basin: Example from the 2020 Flooding in Sudan. Geocarto Int. 2023, 38, 2197504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakoksung, K.; Takagi, M. Effect of Satellite Based Rainfall Products on River Basin Responses of Runoff Simulation on Flood Event. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyambodoho, B.A.; Kure, S.; Yagi, R.; Januriyadi, N.F. Flood Inundation Simulations Based on GSMaP Satellite Rainfall Data in Jakarta, Indonesia. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2021, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlis, A.P.; Farid, M.; Wahid, A.N.; Suryadi, Y.; Kuntoro, A.A. Prediction of Flooding Area in Batang Sinamar River Basin Based on Design Return Period Simulation by Using Rainfall Runoff Inundation Model. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 25, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakoksung, K. Impact of Spatial Rainfall Scenarios on River Basin Runoff Simulation a Nan River Basin Study Using the Rainfall-Runoff-Inundation Model. Eng 2023, 5, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulistyowati, R.; Hapsari, R.I.; Syamsudin, F.; Mori, S.; Oishi, S.T.; Yamanaka, M.D. Rainfall-Driven Diurnal Variations of Water Level in the Ciliwung River, West Jawa, Indonesia. SOLA 2014, 10, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damayanti, A.; Dwiputra, N.A. Flood Exposure of Settlement Areas in Bekasi City. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 248, 012054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, I.R.; Kure, S.; Januriyadi, N.F.; Farid, M.; Udo, K.; Kazama, S.; Koshimura, S. Future Projection of Flood Inundation Considering Land-Use Changes and Land Subsidence in Jakarta, Indonesia. Hydrol. Res. Lett. 2017, 11, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kure, S.; Yamada, T.; Kure, S.; Watanabe, A.; Akabane, Y.; Yamada, T. Field Observations of Discharge and Runoff Characteristics in Urban Catchments Area. 2008. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/267948338 (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Moe, I.R.; Kure, S.; Farid, M.; Udo, K.; Kazama, S.; Koshimura, S. Evaluation of Flood Inundation in Jakarta Using Flood Inundation Model Calibrated by Radar Rainfall. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. 2016, 72, I_1243–I_1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradiko, H.; Arwin; Soewondo, P.; Suryadi, Y. The Change of Hydrological Regime in Upper Cikapundung Watershed, West Java Indonesia. Procedia Eng. 2015, 125, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sugianto, S.; Deli, A.; Miswar, E.; Rusdi, M.; Irham, M. The Effect of Land Use and Land Cover Changes on Flood Occurrence in Teunom Watershed, Aceh Jaya. Land 2022, 11, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Leng, G.; Su, J.; Ren, Y. Comparison of Urbanization and Climate Change Impacts on Urban Flood Volumes: Importance of Urban Planning and Drainage Adaptation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trihono, K. Analysis of Bekasi Watershed Erosion and Sedimentation Problem. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 620, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramesti Kameswara, A.S.; Suharjito. Analysis of Flood Disaster Risk Factors with Geographic Information System (GIS) and Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) Methods in Bekasi City, West Java, Indonesia. Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. 2023, 71, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



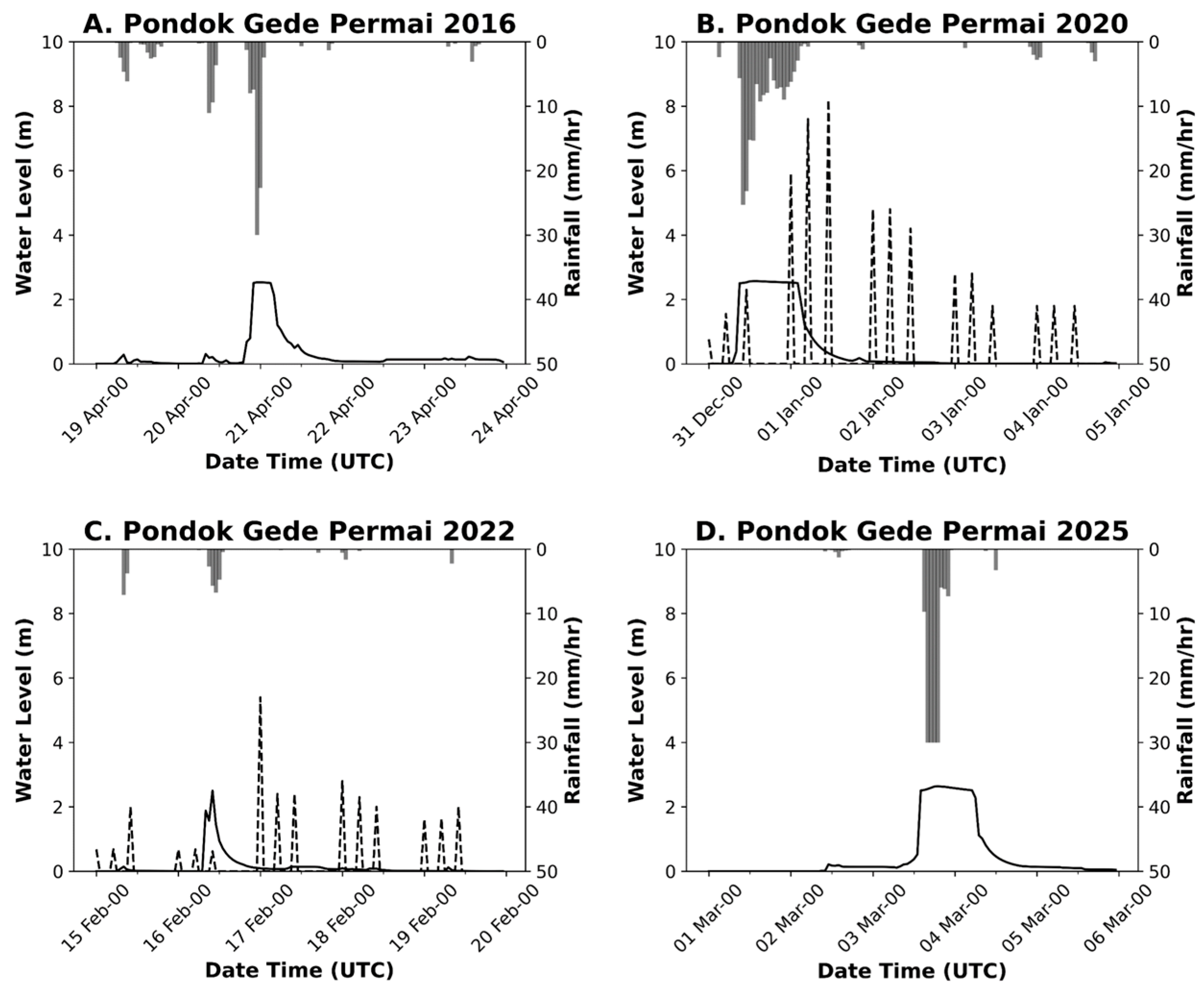
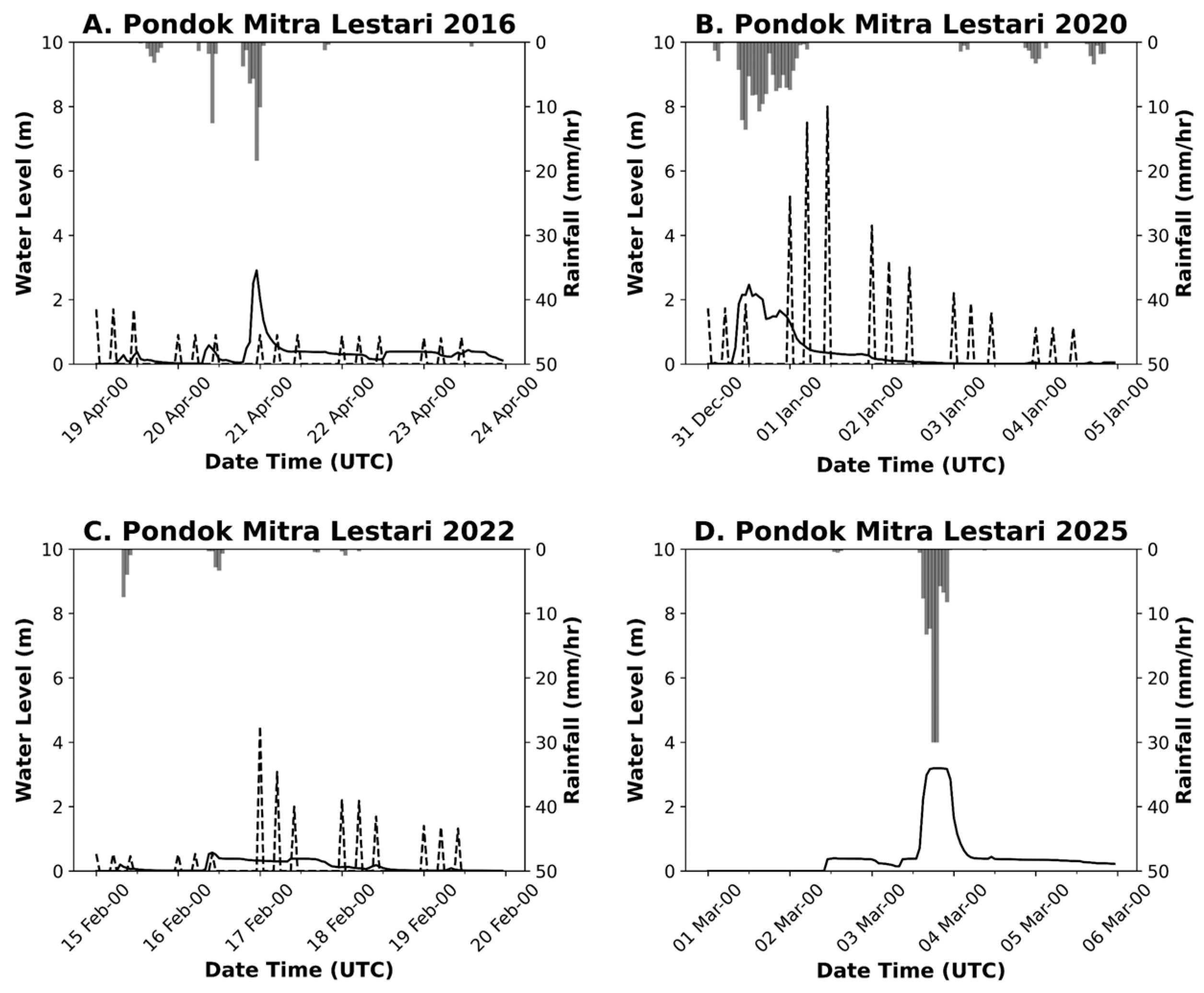
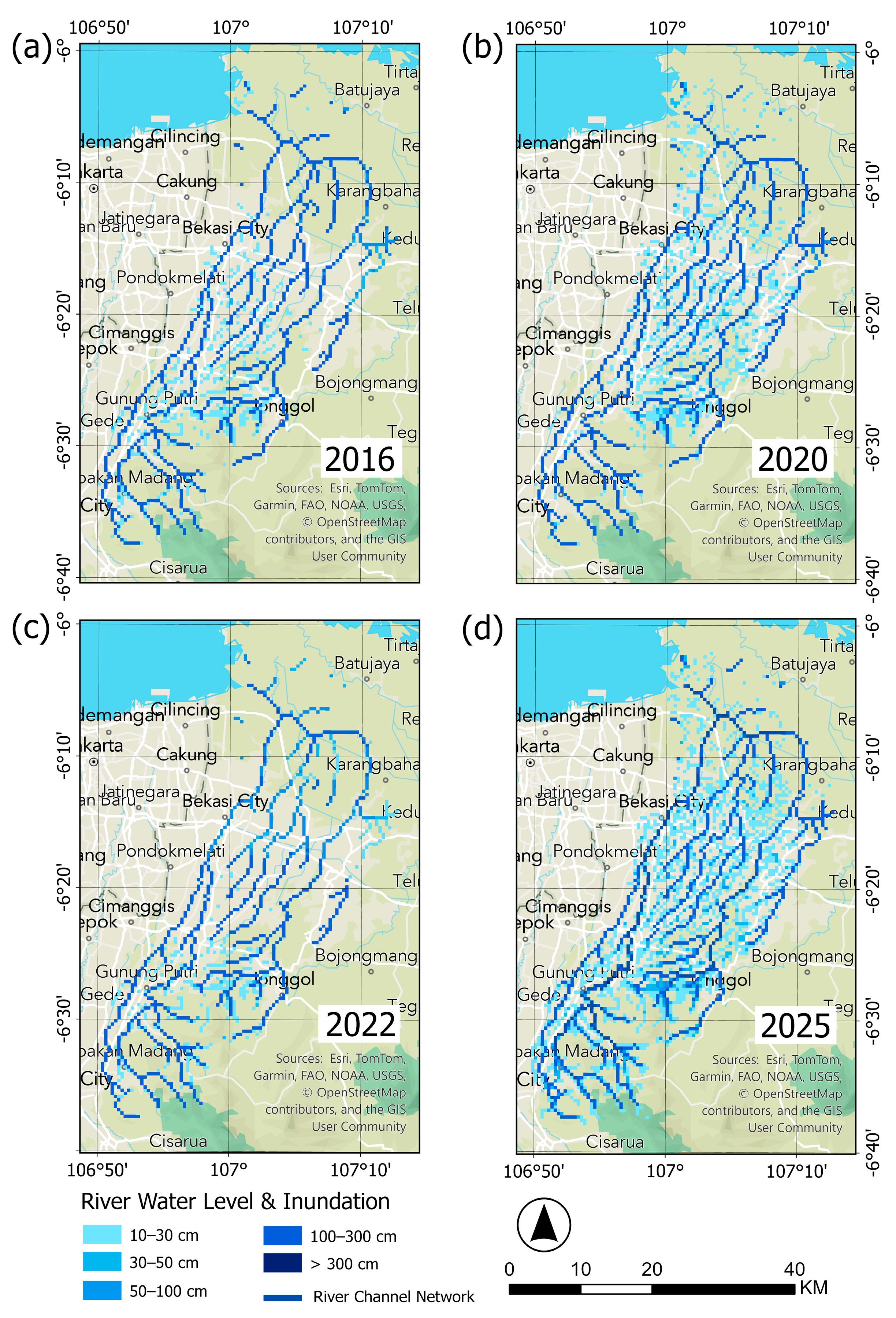
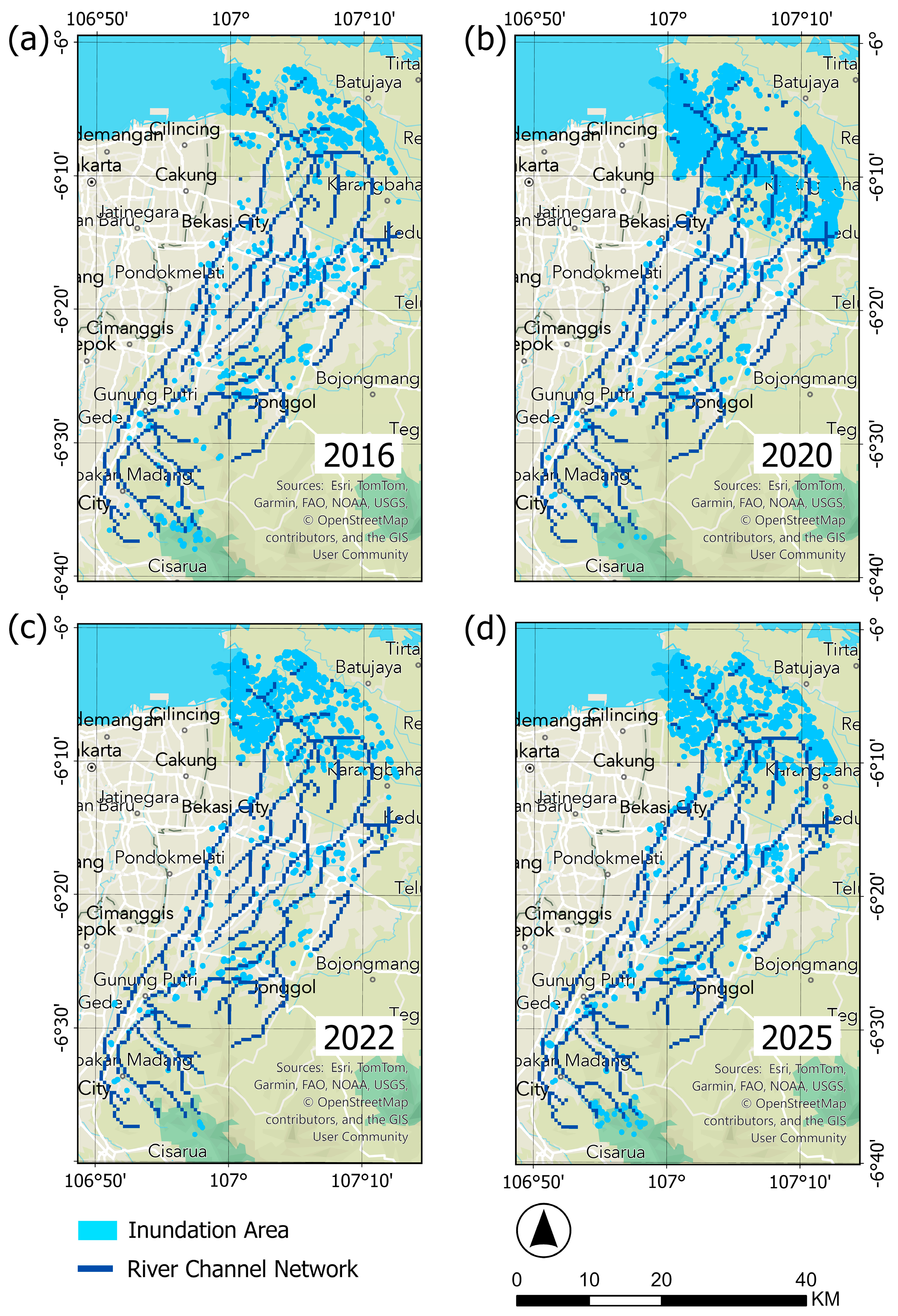


| Variable | Data | Source | Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfall | GSMaP (0.1°~10 km) | Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Global Rainfall Watch (https://sharaku.eorc.jaxa.jp/GSMaP/) (accessed on 24 January 2025) | 19–23 April 2016 31 December 2019–4 January 2020 15–19 February 2022 1–5 March 2025 |
| Land Cover | Indonesian Ministry of Environment and Forestry (MoEF) (~450 m) | 2015, 2019, 2021, 2024 | |
| Digital Elevation Model | Hydrological data and maps based on SHuttle Elevation Derivatives at multiple Scales (HydroSHEDS) (15 arc-seconds~450 m) | https://hydrosheds.org/hydrosheds-core-downloads (accessed on 30 January 2025) | |
| River Water Level | Automatic Water Level Recorder (AWLR) | Balai Besar Wilayah Sungai Ciliwung Cisadane (BBWSCC) | 2016, 2020, 2022 |
| Komunitas Peduli Sungai Cileungsi Cikeas (KP2C) | 2020, 2022, 2025 | ||
| Inundation | Sentinel-1 (10 m) | European Space Agency (ESA) Copernicus Programme | 2016, 2020, 2022, 2025 |
| Category | Rainfall Intensity |
|---|---|
| Light | 1.0–5.0 mm/hour or 5–20 mm/day |
| Moderate | 5.0–10 mm/hour or 20–50 mm/day |
| Heavy | 10–20 mm/hour or 50–100 mm/day |
| Very heavy/Extreme | >20 mm/hour or >100 mm/day |
| No. | Stations | BBWSCC | KP2C | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2020 | 2022 | 2020 | 2022 | 2025 | ||
| 1 | Cibinong | √ | √ | ||||
| 2 | Cileungsi | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 3 | Cikeas | √ | √ | √ | |||
| 4 | P2C | √ | √ | √ | |||
| 5 | PGP | √ | √ | ||||
| 6 | PML | √ | √ | √ | |||
| No. | Stations | RMSE | R2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2020 | 2022 | 2025 | 2016 | 2020 | 2022 | 2025 | ||
| 1 | Cibinong | 1.71 | 0.98 | 0.60 * | 0.09 | ||||
| 2 | Cileungsi | 0.81 | 1.18 | 0.66 | 2.27 | 0.70 * | 0.75 * | 0.61 * | 0.39 |
| 3 | Cikeas | 1.98 | 1.56 | 2.09 | 0.38 * | 0.10 | 0.53 * | ||
| 4 | P2C | 3.45 | 3.88 | 3.65 | 0.65 * | 0.41 | 0.47 * | ||
| 5 | PGP | 3.74 | 2.21 | 0.28 | 0.02 | ||||
| 6 | PML | 0.94 | 3.45 | 1.74 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.48 | ||
| All Stations | 0.88 | 2.51 | 1.68 | 2.72 | 0.40 * | 0.40 * | 0.16 * | 0.28 | |
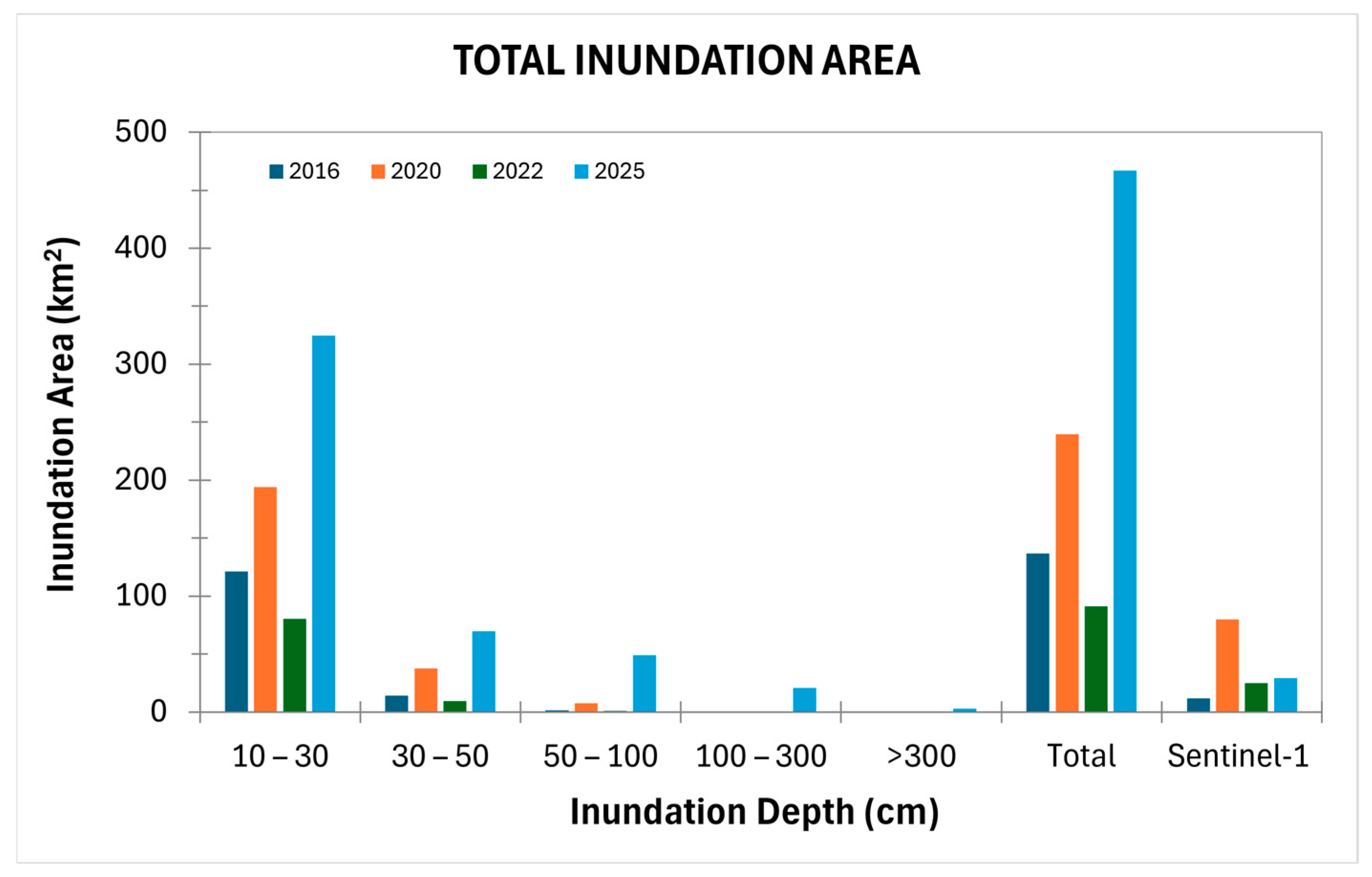
| No. | Depths | Inundation Area (km2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (cm) | 2016 | 2020 | 2022 | 2025 | |
| RRI results | |||||
| 1 | 10–30 | 121.10 | 194.25 | 80.30 | 324.51 |
| 2 | 30–50 | 14.02 | 37.83 | 9.35 | 69.69 |
| 3 | 50–100 | 1.48 | 7.65 | 1.06 | 48.87 |
| 4 | 100–300 | - | - | 0.42 | 20.82 |
| 5 | >300 | - | - | - | 2.97 |
| Total | 136.60 | 239.73 | 91.13 | 466.86 | |
| Sentinel-1 | |||||
| Total | 11.98 | 79.81 | 25.15 | 29.15 | |
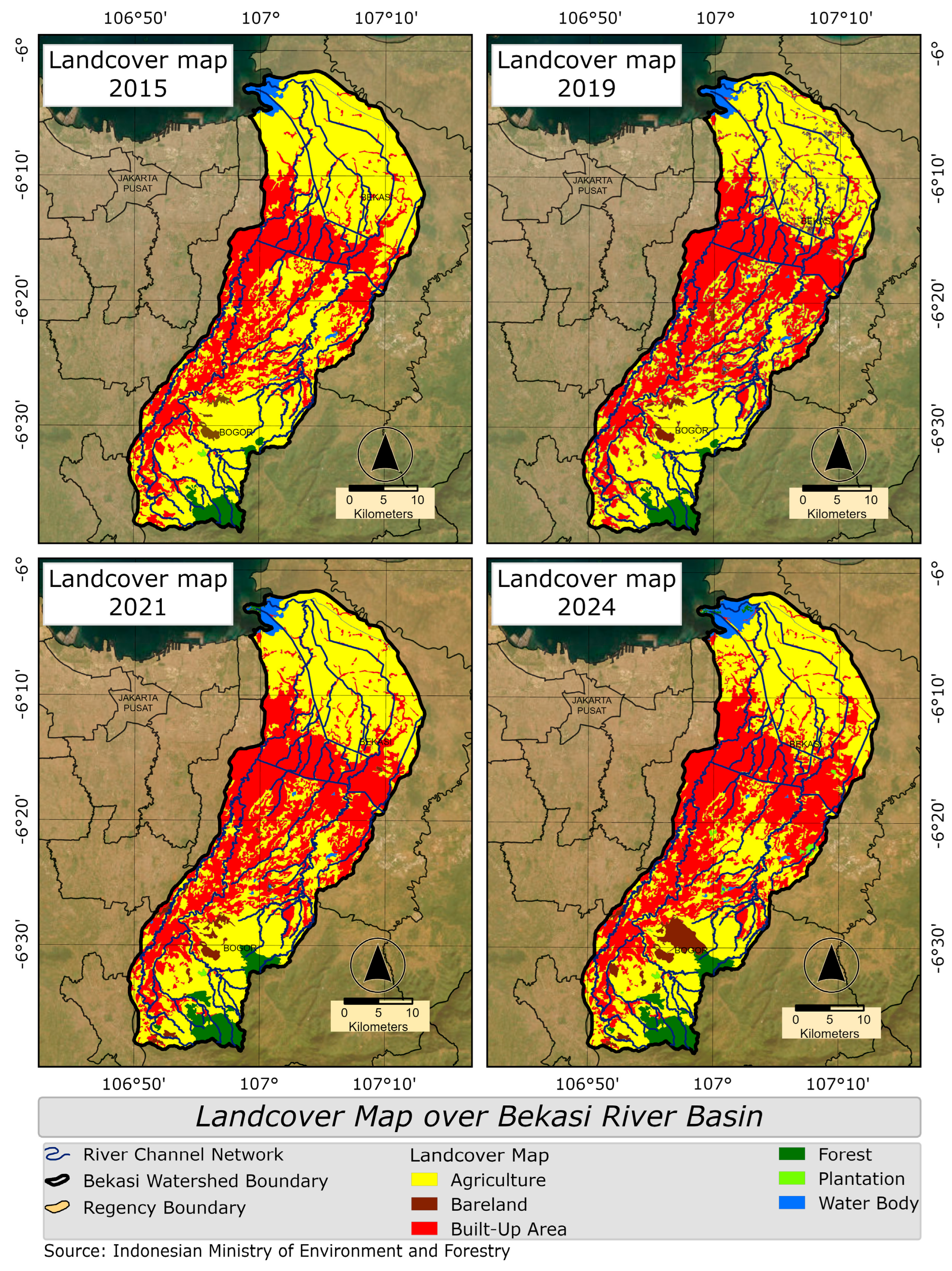
| No. | Land Cover | 2015 (km2) | 2019 (km2) | 2021 (km2) | 2024 (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Agriculture | 854.69 | 764.80 | 742.39 | 703.08 |
| 2 | Bare Land | 7.45 | 24.63 | 21.14 | 38.57 |
| 3 | Built-Up Area | 492.40 | 565.06 | 572.13 | 578.34 |
| 4 | Forest | 31.86 | 31.86 | 51.42 | 51.47 |
| 5 | Plantation | 0.89 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 6.21 |
| 6 | Water Body | 21.16 | 21.31 | 17.78 | 28.68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meliani, F.; Sulistyowati, R.; Sapan, E.G.A.; Sumargana, L.; Lestari, S.; Suryanta, J.; Rudiastuti, A.W.; Cahyaningtiyas, I.F.; Pianto, T.A.; Akbar, H.I.; et al. The Influence of the Rainfall Extremes and Land Cover Changes on the Major Flood Events at Bekasi, West Jawa, and Its Surrounding Regions. Resources 2025, 14, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14110169
Meliani F, Sulistyowati R, Sapan EGA, Sumargana L, Lestari S, Suryanta J, Rudiastuti AW, Cahyaningtiyas IF, Pianto TA, Akbar HI, et al. The Influence of the Rainfall Extremes and Land Cover Changes on the Major Flood Events at Bekasi, West Jawa, and Its Surrounding Regions. Resources. 2025; 14(11):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14110169
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeliani, Fanny, Reni Sulistyowati, Elenora Gita Alamanda Sapan, Lena Sumargana, Sopia Lestari, Jaka Suryanta, Aninda Wisaksanti Rudiastuti, Ilvi Fauziyah Cahyaningtiyas, Teguh Arif Pianto, Harun Idham Akbar, and et al. 2025. "The Influence of the Rainfall Extremes and Land Cover Changes on the Major Flood Events at Bekasi, West Jawa, and Its Surrounding Regions" Resources 14, no. 11: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14110169
APA StyleMeliani, F., Sulistyowati, R., Sapan, E. G. A., Sumargana, L., Lestari, S., Suryanta, J., Rudiastuti, A. W., Cahyaningtiyas, I. F., Pianto, T. A., Akbar, H. I., Yulianingsani, Winarno, Priyadi, H., Cahya, D. L., Winarno, B., & Sutejo, B. (2025). The Influence of the Rainfall Extremes and Land Cover Changes on the Major Flood Events at Bekasi, West Jawa, and Its Surrounding Regions. Resources, 14(11), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14110169