A Low-Power, 65 nm 24.6-to-30.1 GHz Trusted LC Voltage-Controlled Oscillator Achieving 191.7 dBc/Hz FoM at 1 MHz
Abstract
1. Introduction
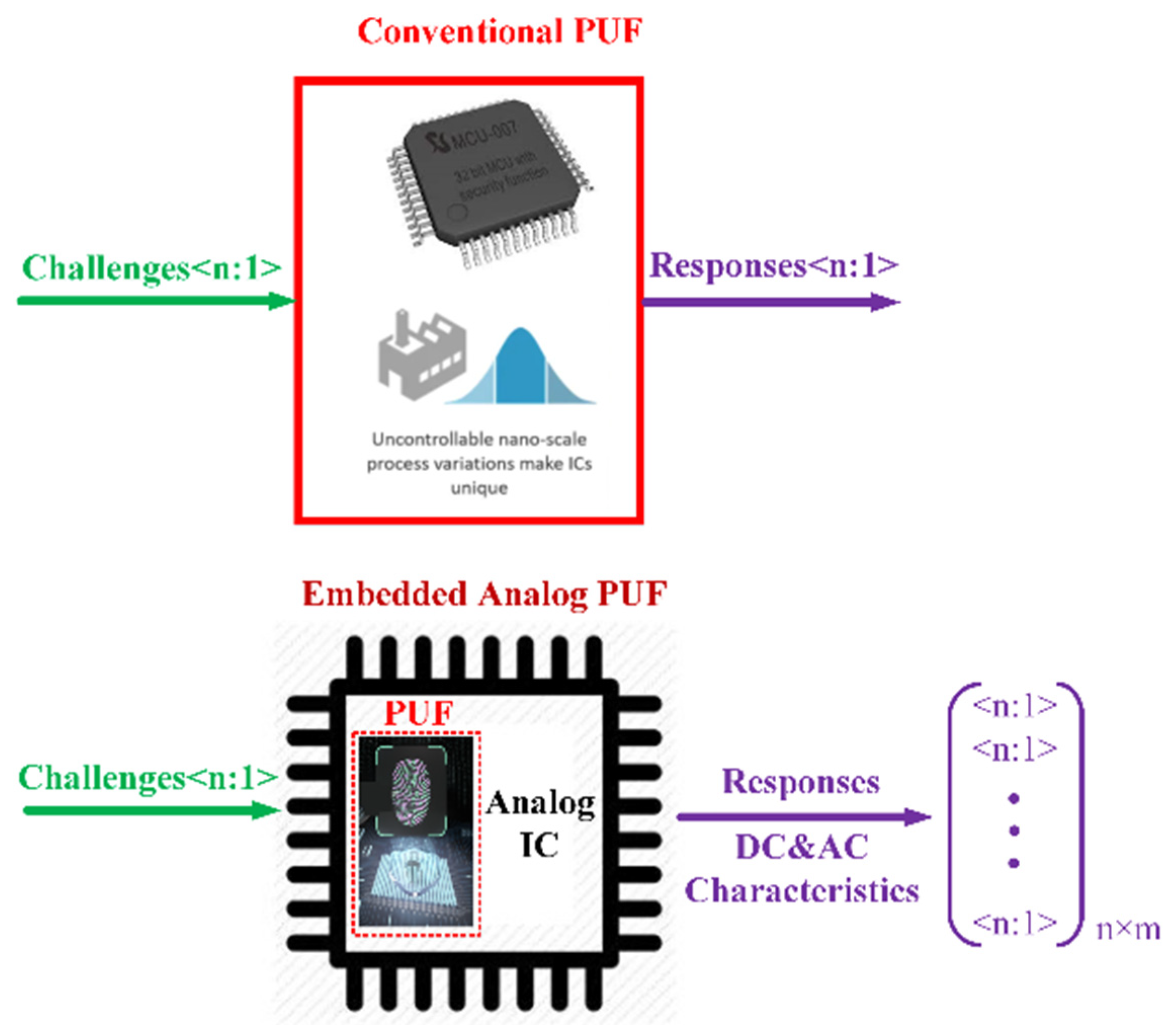
2. RFFE Threats and Embedded Analog PUF Design
2.1. Security Threats in RFFEs
2.2. Embedded Analog PUFs for RFFEs
3. Design of the Trusted CMOS LC VCO
4. Measurement Results
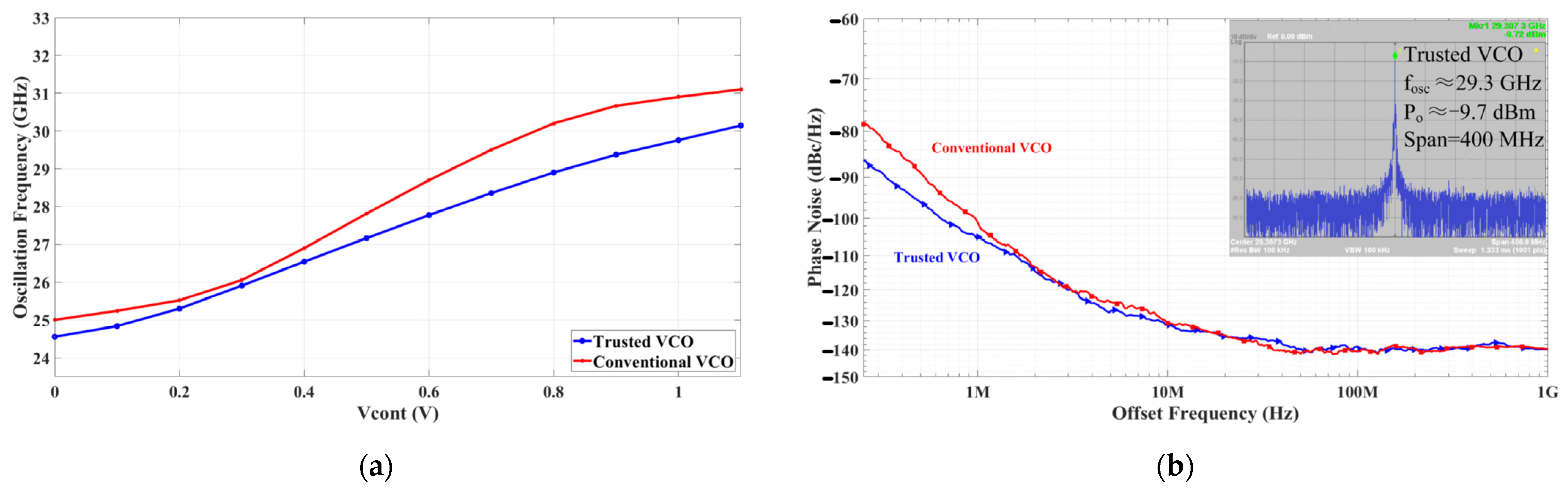
4.1. VCO Performance Measurement and Comparison
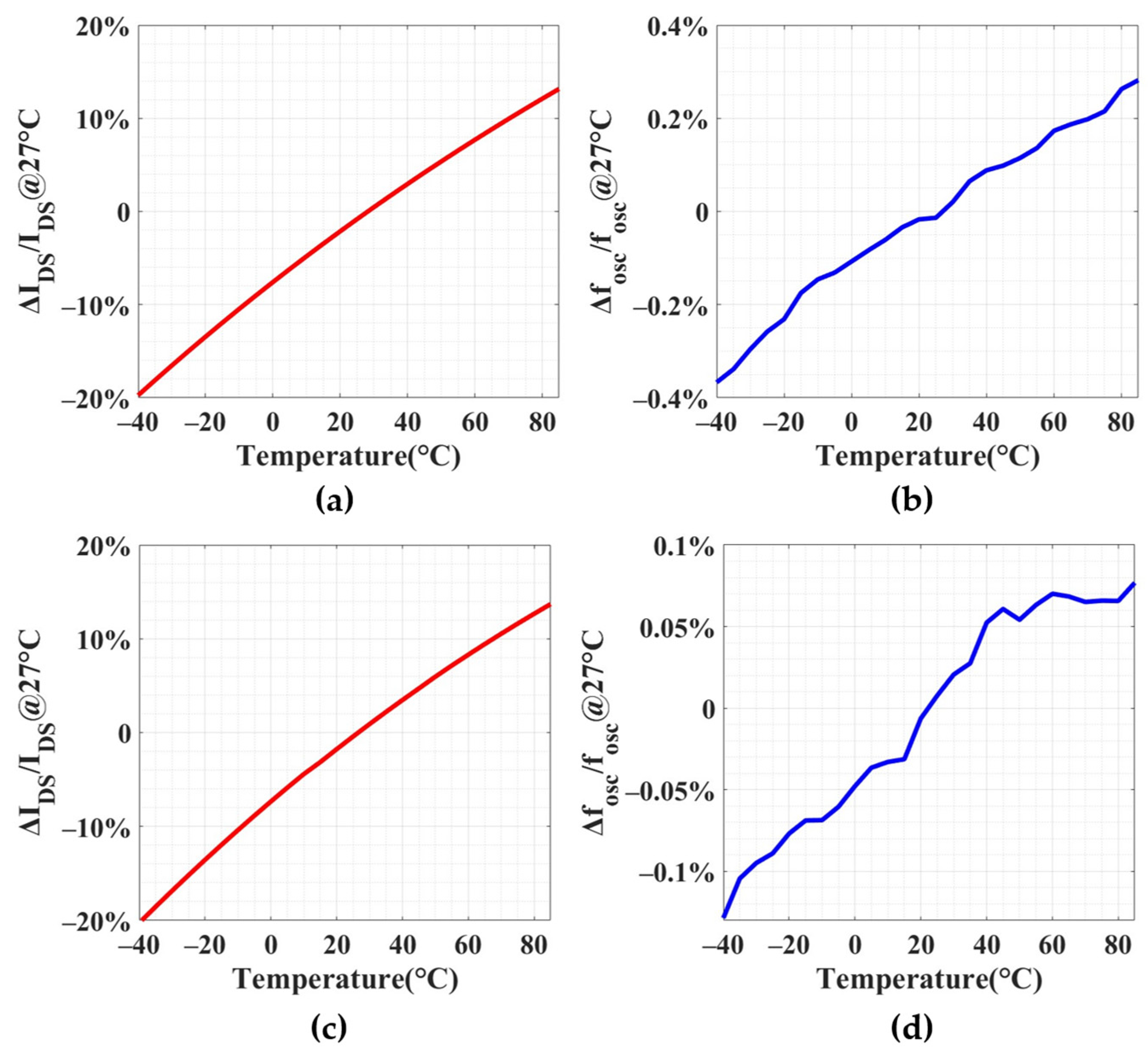
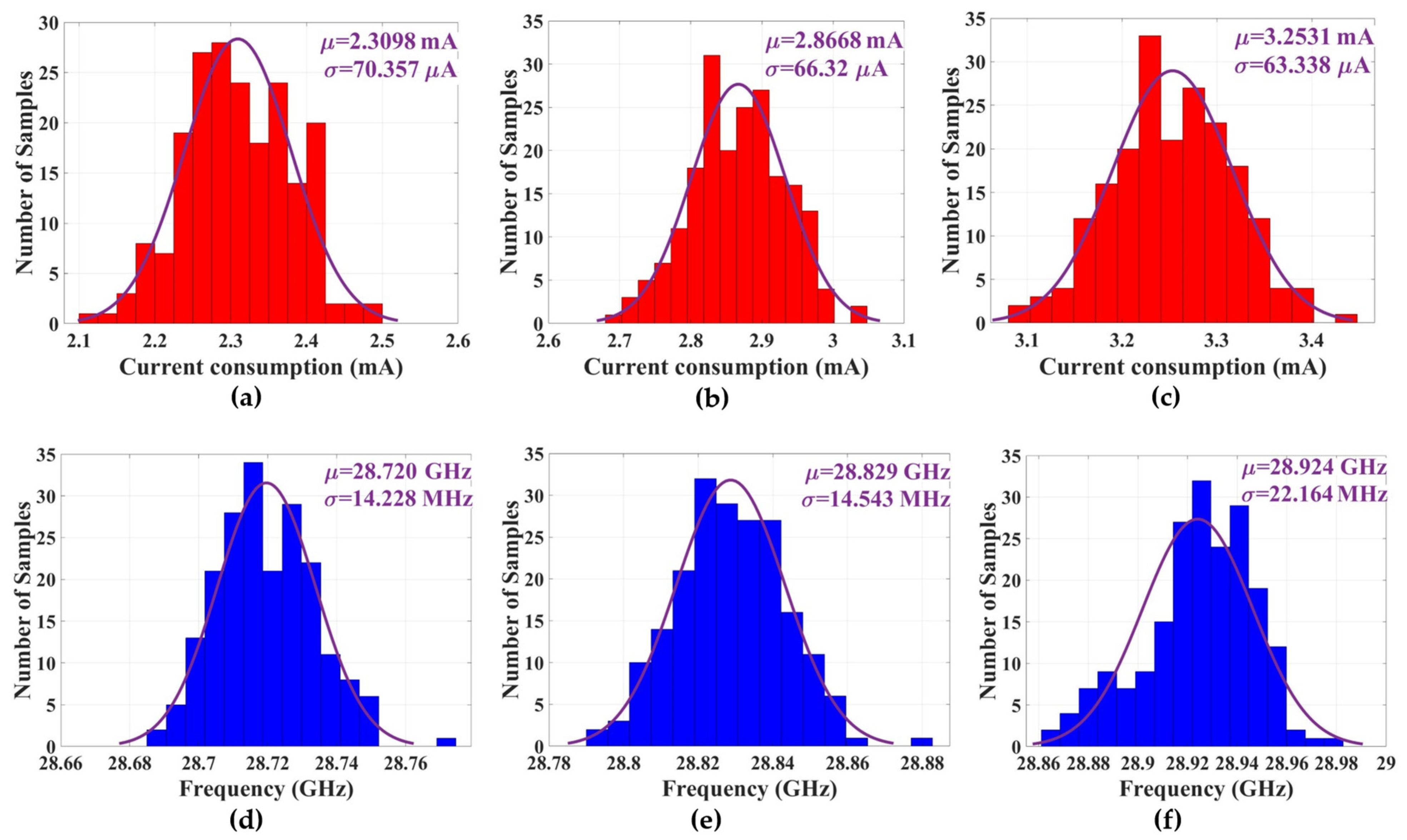
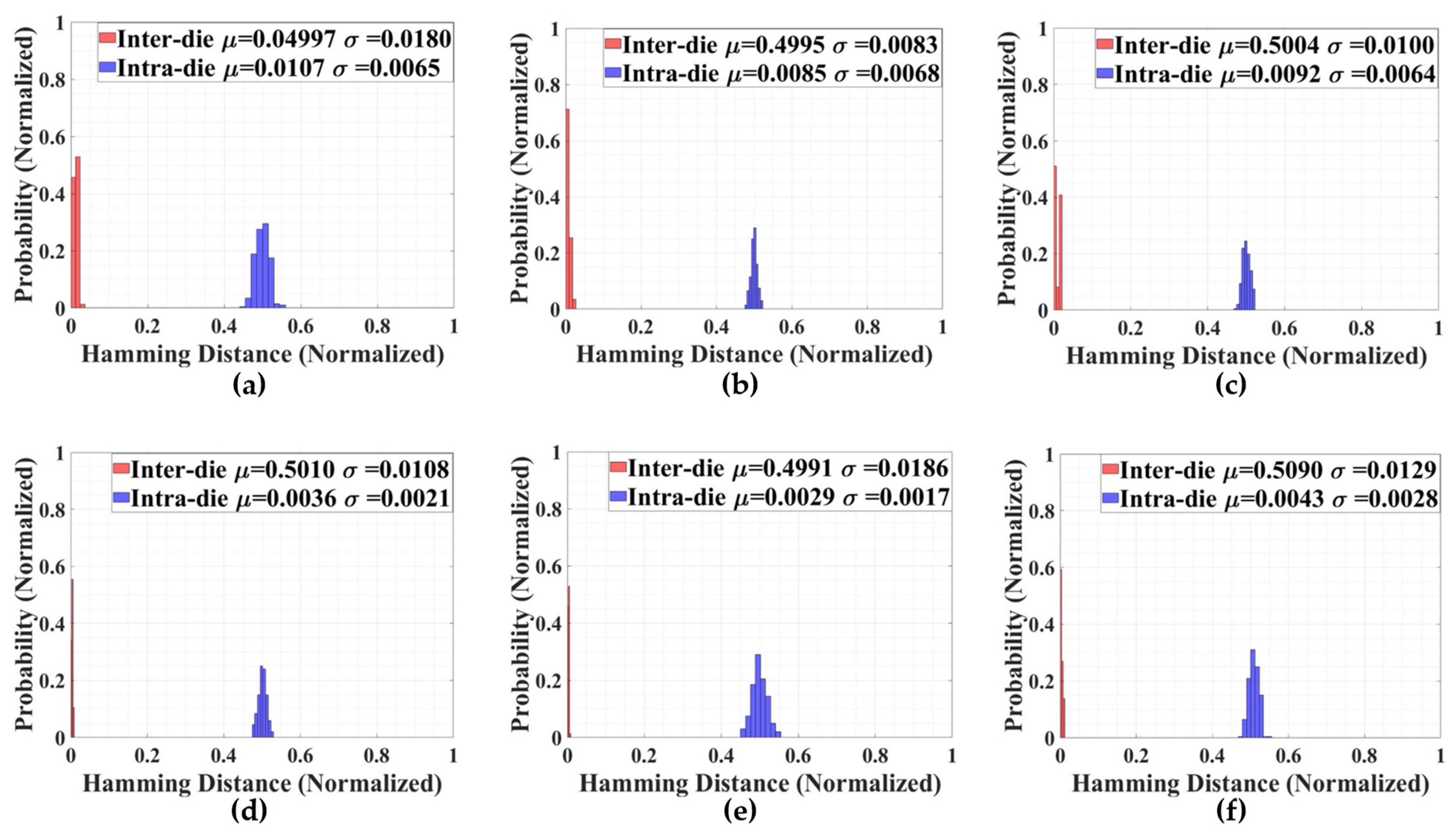
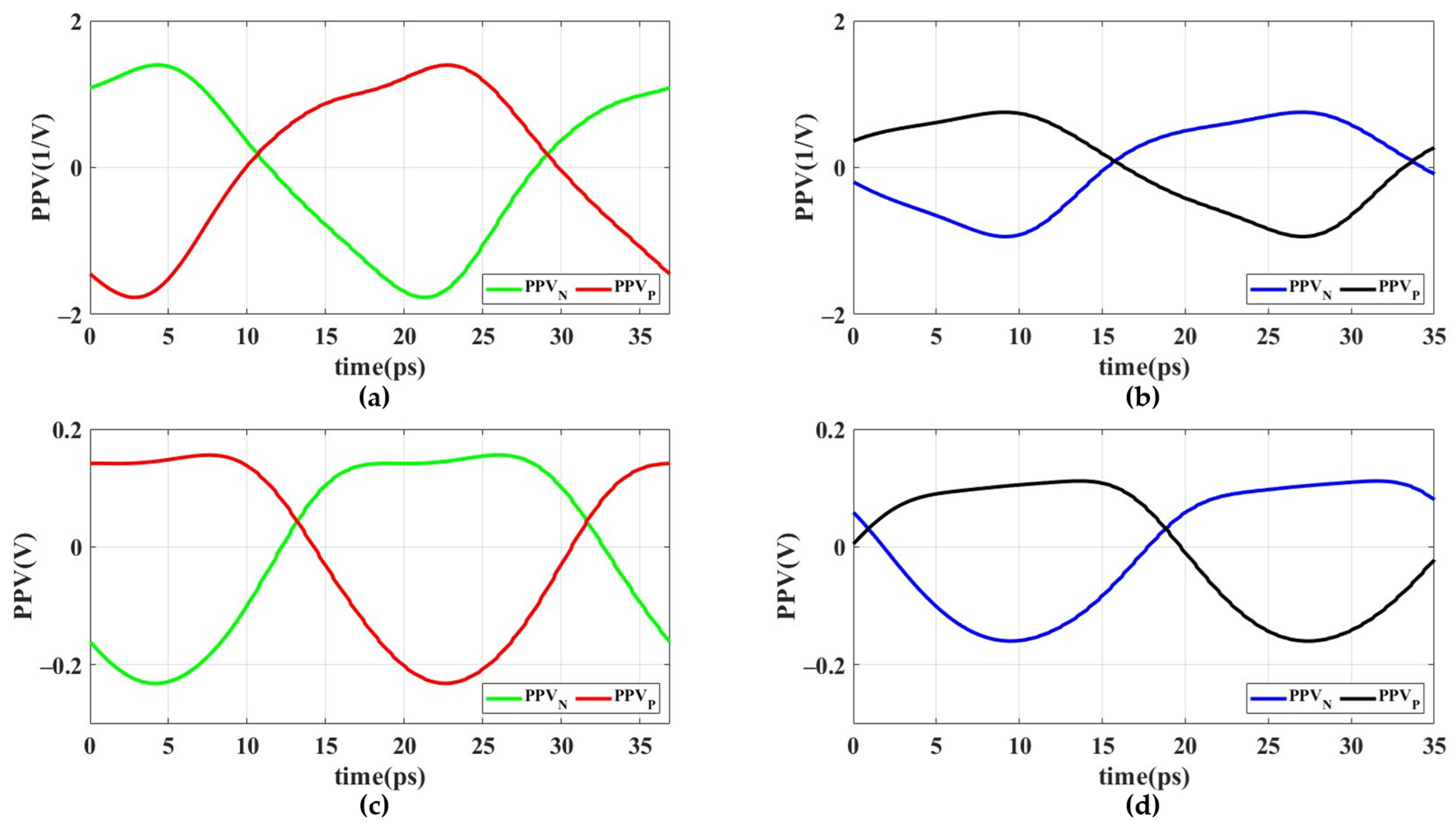
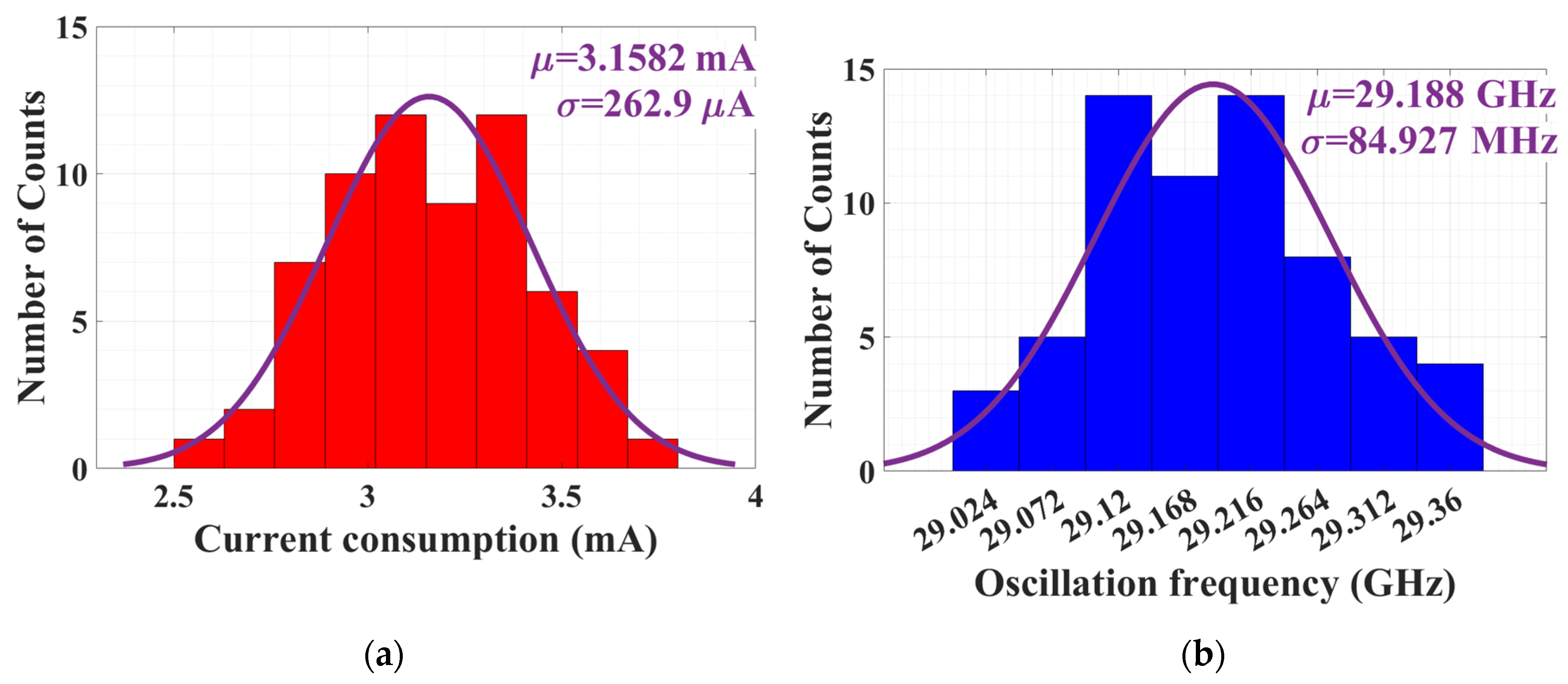
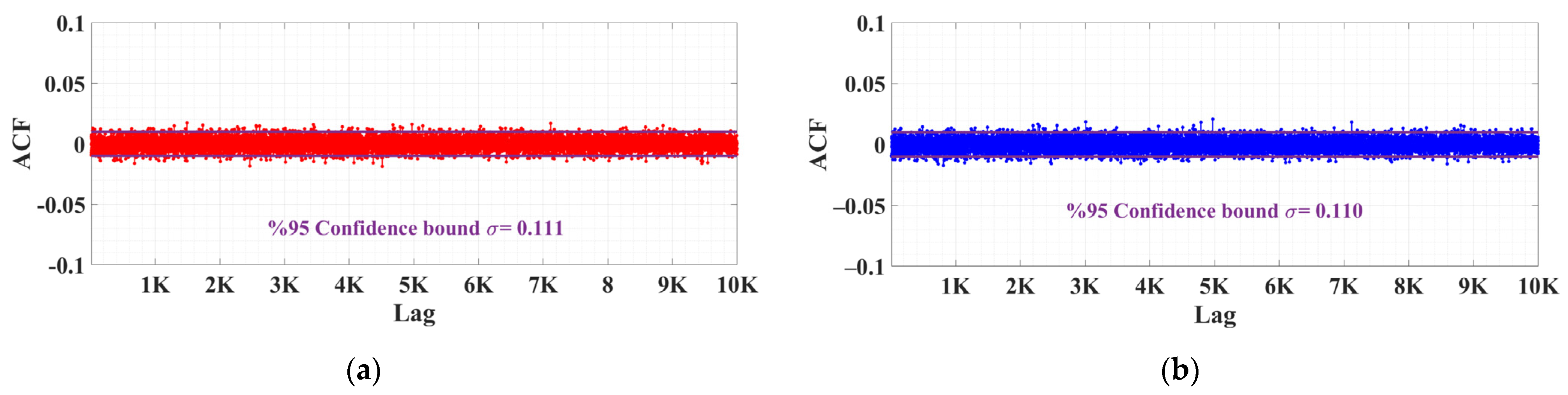
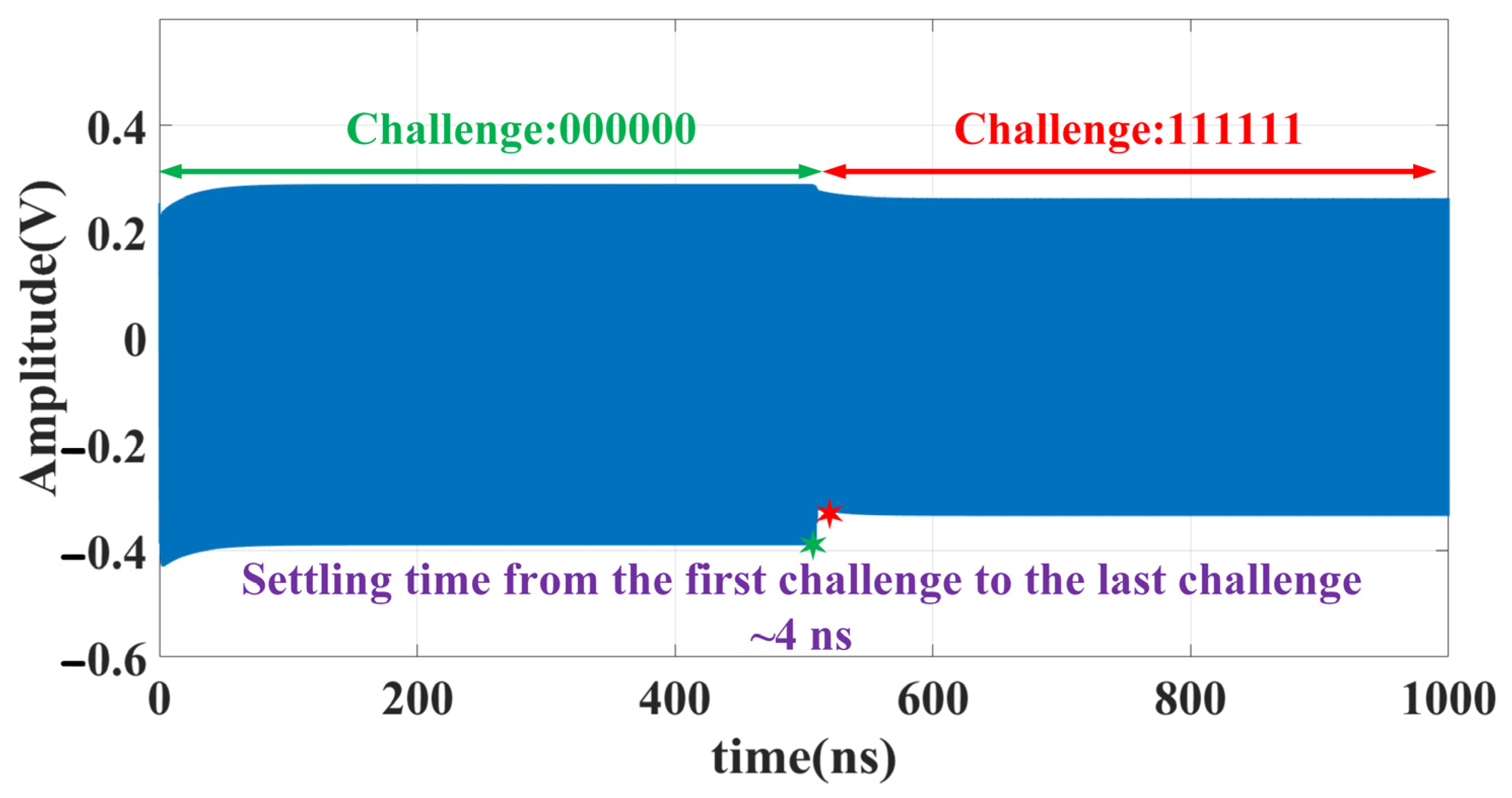
4.2. PUF Characterization and Randomness Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agiwal, M.; Roy, A.; Saxena, N. Next Generation 5G Wireless Networks: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 1617–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanabria-Borbón, A.C.; Jayasankaran, N.G.; Hu, J.; Rajendran, J.; Sánchez-Sinencio, E. Analog/RF IP Protection: Attack Models, Defense Techniques, and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs 2021, 68, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizo, A.R.D.; Leonhard, J.; Aboushady, H.; Stratigopoulos, H.-G. RF Transceiver Security against Piracy Attacks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs 2022, 69, 3169–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorobogatov, S. Semi-Invasive Attacks—A New Approach to Hardware Security Analysis; Technical Report; University of Cambridge, Computer Laboratory: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tehranipoor, M.; Wang, C. Introduction to Hardware Security and Trust; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshamy, M.; Di Natale, G.; Sayed, A.; Pavlidis, A.; Louërat, M.-M.; Aboushady, H.; Stratigopoulos, H.-G. Digital-to-Analog Hardware Trojan Attacks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I-Regul. Pap. 2022, 69, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorobogatov, S. Side-Channel Attacks: New Directions and Horizons; ECRYPT2 School on Design and Security of Cryptograph-ic Algorithms and Devices: Albena, Bulgaria, 2011; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Zoni, D. Analysis and Countermeasures to Side-Channel Attacks: A Hardware Design Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th International Symposium on Reconfigurable Communication-Centric Systems-on-Chip (ReCoSoC), New York, NY, USA, 1–3 July 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Leonhard, J.; Sayed, A.; Louërat, M.-M.; Aboushady, H.; Stratigopoulos, H.-G. Analog and Mixed-Signal IC Security via Sizing Camouflaging. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2021, 40, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, A.; Zimmermann, L.; Sikora, A.; Tahoori, M.B.; Aghassi-Hagmann, J. Embedded Analog Physical Unclonable Function System to Extract Reliable and Unique Security Keys. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, L.; Scholz, A.; Tahoori, M.B.; Aghassi-Hagmann, J.; Sikora, A. Design and Evaluation of a Printed Analog-Based Differential Physical Unclonable Function. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2019, 27, 2498–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Choi, W.H.; Everson, L.; Parhi, K.K.; Kim, C.H. A Physical Unclonable Function Based on Capacitor Mismatch in a Charge-Redistribution SAR-ADC. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (IS-CAS), Florence, Italy, 27–30 May 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Danesh, M.; Venkatasubramaniyan, A.B.; Kapoor, G.; Sanyal, A. A 0.36pJ/Bit Analog PUF Based on Current Steering DAC and VCO. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 62nd International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Dallas, TX, USA, 4–7 August 2019; pp. 578–581. [Google Scholar]
- Asghari, M.; Guzman, M.; Maghari, N. Cross-Coupled Impedance-Based Physically Unclonable Function (PUF) with 1.06% Native Instability. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Lett. 2020, 3, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, W.; Qu, G. DA PUF. In Proceedings of the 59th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference, New York, NY, USA, 10–14 July 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraja, S.A.; Khandelwal, V.; Tang, X.; Li, X. Wide Bandgap Semiconductor-Based Integrated Circuits. Chip 2023, 2, 100072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, D.A.; Hajimiri, A. Concepts and Methods in Optimization of Integrated LC VCOs. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2001, 36, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiebout, M. Low Power VCO Design in CMOS; Springer Science and Business Media: Boston, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.Y.D. Design Considerations, of Differential Inductors in CMOS Technology for RFIC. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Systems. Digest of Papers, Forth Worth, TX, USA, 6–8 June 2004; pp. 449–452. [Google Scholar]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajimiri, A.; Lee, T.H. A General Theory of Phase Noise in Electrical Oscillators. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1998, 33, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, J.; Roblin, P.; Akhtar, S. An Analytic Circuit-Based Model for White and Flicker Phase Noise in LC Oscillators. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 2007, 54, 1584–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, A.; Roychowdhury, J. A Reliable and Efficient Procedure for Oscillator PPV Computation, with Phase Noise Macromodeling Applications. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2003, 22, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xu, T.; Meng, J.; Chen, J. Analysis of Phase Noise Model in Cross-Coupled LC VCO. Chin. J. Electron. 2012, 21, 379–383. [Google Scholar]
- Andreani, P.; Wang, X.; Vandi, L.; Fard, A. A Study of Phase Noise in Colpitts and LC-Tank CMOS Oscillators. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2005, 40, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masnadi, A.; Mahani, M.; Lavasani, H.M.; Mirabbasi, S.; Shekhar, S.; Zavari, R.; Djahanshahi, H. A Compact Dual-Core 26.1-to-29.9GHz Coupled-CMOS LC-VCO with Implicit Common-Mode Resonance and FoM of-191 dBc/Hz at 10MHz. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), Boston, MA, USA, 22–25 March 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Chen, Y.; Mak, P.-I.; Martins, R.P. 26.2 A 0.08mm2 25.5-to-29.9GHz Multi-Resonant-RLCM-Tank VCO Using a Sin-gle-Turn Multi-Tap Inductor and CM-Only Capacitors Achieving 191.6dBc/Hz FoM and 130kHz 1/F3 PN Corner. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference—(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 17–21 February 2019; pp. 410–412. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, A.; Lee, S.B.; Byeon, C.W. 30-GHz Low-Phase-Noise VCO With Negative Transconductance Optimization in 65-Nm CMOS. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Technol. Lett. 2023, 33, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Nam, J.-W.; Lee, S. A Low-Power Class-C Voltage-Controlled Oscillator with Robust Start-Up and Compact High-Q Capacitor Array. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs 2022, 69, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.A.; Siriburanon, T.; Staszewski, R.B. Oscillator Flicker Phase Noise: A Tutorial. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs 2021, 68, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Hajimiri, A. Oscillator Phase Noise: A Tutorial. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2000, 35, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, B. The Design of a Millimeter-Wave VCO [The Analog Mind]. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Mag. 2022, 14, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hajimiri, A.; Lee, T.H. Comments on “Design Issues in CMOS Differential LC Oscillators” [and Reply]. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2000, 35, 286–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.A.; Wang, P.; Ma, X.; Shi, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Y. A Multimode Configurable Physically Unclonable Function with Bit-Instability-Screening and Power-Gating Strategies. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2021, 29, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proakis, J.G. Digital Communications. In Routledge eBooks; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| This Work (CVCO/Trusted VCO) | [26] | [27] | [28] | [29] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDC (mW) | 1.5/1.75 | 3.4 | 3.8 | 7.2 | 3.8 |
| fosc (GHz) | 29.6/29.3 | 27.45 | 25.48 | 28.11 | 19.7 |
| Tuning Range (GHz) | 25–31.2/24.6–30.1 | 26.1–29.9 | 25.48–29.92 | 28.11–31.46 | 19.3–22.0 |
| PN@1MHz (dBc/Hz) | −101/−104.8 | −105.7 | −109.3 * | −107.2 | −106.33 |
| PN@10MHz (dBc/Hz) | −130.4/−132.2 | −127.5 | −128 * | −123 # | −127.82 |
| FoM@1MHz (dBc/Hz) | 188.7/191.7 | 189.1 | 191.6 | 187.6 | 186.4 |
| FoMT@1Mz (dBc/Hz) | 194.7/197.6 | 191.7 | 195.7 | 189.13 | 188.8 |
| FoM@10MHz (dBc/Hz) | 198/199.1 | 191 | 190.3 | N/A | N/A |
| FoMT@10Mz (dBc/Hz) | 204/205 | 193.4 | 194.4 | N/A | N/A |
| Core Area (mm2) | 0.018/0.018 | 0.038 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.064 |
| Technology | 65 nm/65 nm | 65 nm | 65 nm | 65 nm | 65 nm |
| This Work | [12] | [14] | [15] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | 65 nm | 65 nm | 65 nm | 55 nm |
| PUF type | Weak | Weak | Weak | Weak |
| Chip area | 594 um2 | 40,000 um2 | 37,511 um2 | 997 um2 |
| CRP space | (64,2) | (16,8) | (16,20) | (128,1) |
| Entropy Source | Capacitance and Impedance mismatch | Process variation | Impedance mismatch | Process variation |
| Bit rate | 1.5 Gbps | 100 Mbps | 320 Kbps | 40 Kbps |
| ACF | 0.0111/0.0110 | 0.0108 | 0.0123 | 0.0142 |
| Energy/bit | 0.83 pJ | 0.36 pJ | 6 pJ | 0.91 pJ |
| Intra-HD | 0.0055/0.0054 | 0.0906 | 0.0031 | N/A |
| Inter-HD | 0.5113/0.4892 | 0.4859 | 0.4986 | 0.4681 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kurtoglu, A.; Shirazi, A.H.M.; Mirabbasi, S.; Miri Lavasani, H. A Low-Power, 65 nm 24.6-to-30.1 GHz Trusted LC Voltage-Controlled Oscillator Achieving 191.7 dBc/Hz FoM at 1 MHz. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2024, 14, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea14010010
Kurtoglu A, Shirazi AHM, Mirabbasi S, Miri Lavasani H. A Low-Power, 65 nm 24.6-to-30.1 GHz Trusted LC Voltage-Controlled Oscillator Achieving 191.7 dBc/Hz FoM at 1 MHz. Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications. 2024; 14(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea14010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleKurtoglu, Abdullah, Amir H. M. Shirazi, Shahriar Mirabbasi, and Hossein Miri Lavasani. 2024. "A Low-Power, 65 nm 24.6-to-30.1 GHz Trusted LC Voltage-Controlled Oscillator Achieving 191.7 dBc/Hz FoM at 1 MHz" Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications 14, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea14010010
APA StyleKurtoglu, A., Shirazi, A. H. M., Mirabbasi, S., & Miri Lavasani, H. (2024). A Low-Power, 65 nm 24.6-to-30.1 GHz Trusted LC Voltage-Controlled Oscillator Achieving 191.7 dBc/Hz FoM at 1 MHz. Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications, 14(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea14010010






