Conceptualizing Shadow IT Integration Drawbacks from a Systemic Viewpoint
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Shadow IT in the Enterprise Architecture
3. Research Approach
3.1. A Systemic Viewpoint on Shadow IT Integration: Path-Dependency and Switching Costs
3.2. Research Method
4. Results
4.1. Findings from Literature Search
4.2. Shadow IT Integration Drawbacks
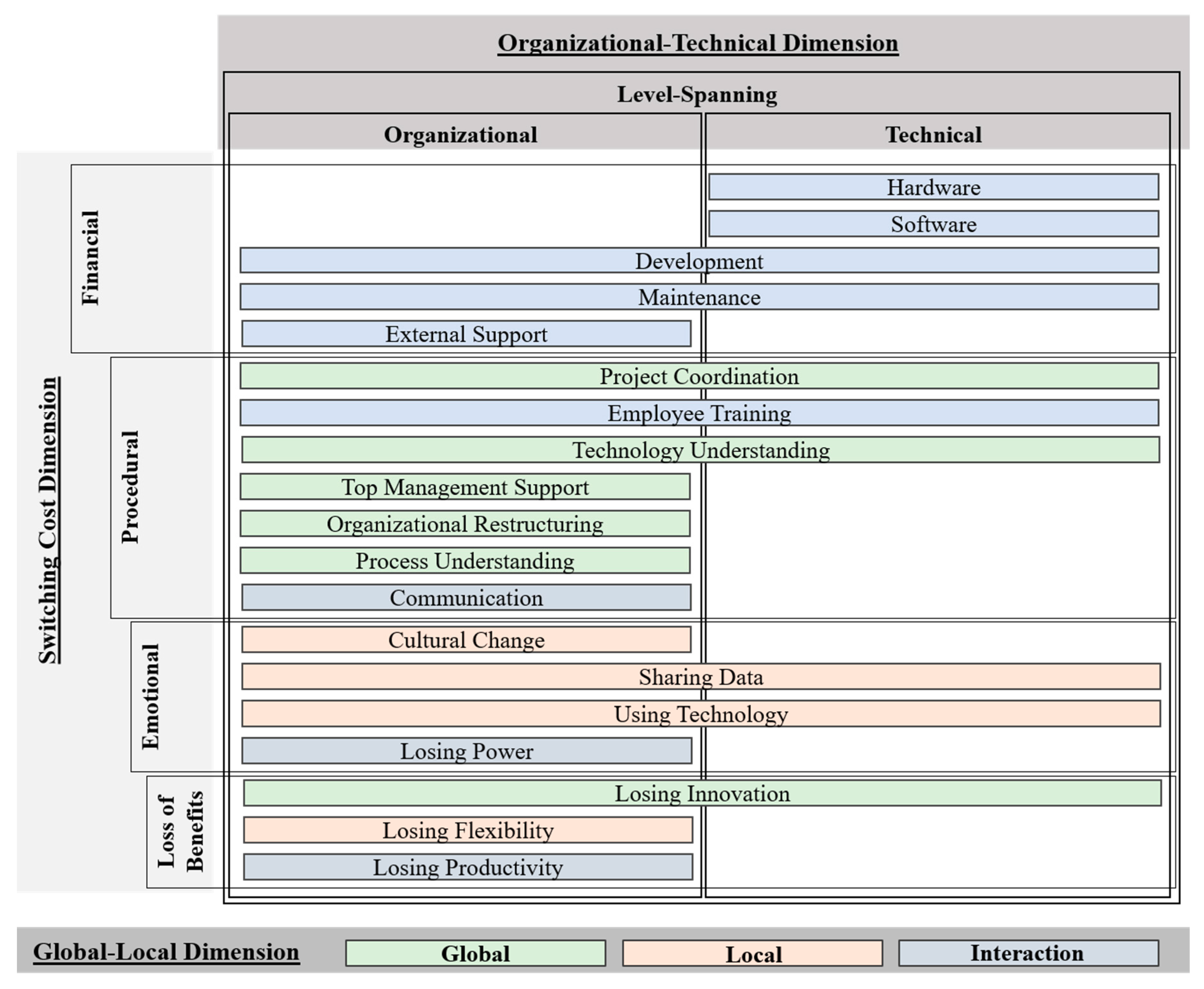
4.2.1. Analysis from a Switching Cost Dimension
4.2.2. Analysis from an Organizational-Technical Dimension
4.2.3. Analysis from Global-Local Dimension
4.3. Conceptual Framework for Shadow IT Integration and Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Legner, C.; Eymann, T.; Hess, T.; Matt, C.; Böhmann, T.; Drews, P.; Mädche, A.; Urbach, N.; Ahlemann, F. Digitalization: Opportunity and challenge for the business and information systems engineering community. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2017, 59, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey Nash/KPMG. CIO Survey. 2018. Available online: https://bit.ly/2KJ56Rl (accessed on 23 November 2018).
- Haag, S.; Eckhardt, A. Shadow IT. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2017, 59, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstenau, D.; Rothe, H.; Sandner, M. Shadow Systems, Risk, and Shifting Power Relations in Organizations. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2017, 3, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Rentrop, C.; Felden, C. A Multiple Case Study on the Nature and Management of Shadow Information Technology. J. Inf. Syst. 2017, 31, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, S. Shadow systems: The good, the bad and the ugly. Commun. ACM 2009, 52, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.; Zimmermann, S.; Rentrop, C.; Felden, C. The Influence of Shadow IT Systems on Enterprise Architecture Management Concerns. In Proceedings of the 14th European, Mediterranean, and Middle Eastern Conference on Information Systems, Coimbra, Portugal, 7–8 September 2017; pp. 461–477. [Google Scholar]
- Mertens, P. Integrierte Informationsverarbeitung 1-Operative Systeme in der Industrie 18, Überarbeitete Auflage; Gabler: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, V.; Torres, R.; Nguyen, Q.; Snyder, M.; Kapelman, L. SIM IT Trends Study: Taking the Pulse of IT. Available online: https://bit.ly/2DREPN9 (accessed on 23 November 2018).
- Fürstenau, D.; Glaschke, C. Weighting of Integration Qualities in IS Architectures: A Production Case. In Proceedings of the 23th European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS), Münster, Germany, 26–29 May 2015; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, M.; Zimmermann, S.; Rentrop, C.; Felden, C. Integration of Shadow IT Systems with Enterprise Systems—A Literature Review. In Proceedings of the Twenty First Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems, Palau Langkawi, Malaysia, 16–20 July 2017; p. 134. [Google Scholar]
- Khoumbati, K.; Themistocleous, M.; Irani, Z. Evaluating the Adoption of Enterprise Application Integration in Health-Care Organizations. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2006, 22, 69–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Themistocleous, M.; Irani, Z. Benchmarking the benefits and barriers of application integration. Benchmark. Int. J. 2001, 8, 317–331. [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn, A.; Winter, R. Success Factors and Performance Indicators for Enterprise Application Integration. In Proceedings of the Eleventh Americas Conference on Information Systems, Omaha, NE, USA, 11–14 August 2005; p. 154. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, M.M.; Weerakkody, V.; Jones, S. The case of EAI in facilitating e-Government services in a Welsh authority. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2009, 29, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.-H.; Chang, I.-C.; Yen, D.; Lee, C.-M. Critical Factors of Adopting Enterprise Application Integration Technology: An Empirical Study on Larger Hospitals. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2015, 36, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.M.; Hackney, R.; Ali, M. Facilitating enterprise application integration adoption: An empirical analysis of UK local government authorities. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2013, 33, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzana, V.; Themistocleous, M. Benefits and barriers related to eai adoption: The case of a healthcare organisation. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS), Gothenburg, Sweden, 12–14 June 2006; p. 183. [Google Scholar]
- Chowanetz, M.; Legner, C.; Thiesse, F. Integration: An Omitted Variable in Information Systems Research. In Proceedings of the 20th European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS), Barcelona, Spain, 10–13 June 2012; p. 227. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, S.; Rentrop, C. On the Emergence of Shadow IT—A Transaction Cost-Based Approach. In Proceedings of the Twenty Second European Conference on Information Systems, Tel Aviv, Israel, 12–15 June 2014; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Haag, S.; Eckhardt, A. Normalizing the Shadows—The Role of Symbolic Models for Individuals’ Shadow IT Usage. In Proceedings of the Thirty Fifth International Conference on Information Systems, Auckland, New Zealand, 14–17 December 2014; p. 69. [Google Scholar]
- Silic, M. Critical impact of organizational and individual inertia in explaining non-compliant security behavior in the Shadow IT context. Comput. Secur. 2019, 80, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallmann, G.L.; Maçada, A.C.G.; Eckhardt, A. We are Social—A Social Influence Perspective to Investigate Shadow IT Usage. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS2018), Portsmouth, UK, 23–28 June 2018; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Fürstenau, D.; Rothe, H. Shadow IT systems: Discerning the good and the evil. In Proceedings of the 22nd European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS), Tel Aviv, Israel, 9–11 June 2014; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Tambo, T.; Baekgaard, L. Dilemmas in enterprise architecture research and practice from a perspective of feral information systems. In Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Enterprise Distributed Object Computing Conference Workshops, Vancouver, ON, Canada, 9–13 September 2013; pp. 289–295. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, M.; Zimmermann, S.; Rentrop, C.; Felden, C. The Relation of Shadow Systems and ERP Systems—Insights from a Multiple-Case Study. Syst. Spec. Issue ERP Syst. 2016, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.; Zimmermann, S.; Rentrop, C.; Felden, C. Toward a Conceptual Decision Framework for Shadow IT Integration. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fourth Americas Conference on Information Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 16–18 August 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kopper, A.; Fuerstenau, D.; Rothe, H.; Strahringer, S.; Westner, M. Business-Managed IT: A Conceptual Framework and Empirical Illustration. In Proceedings of the 26th European Conference on Information Systems, Portsmouth, UK, 23–28 June 2018; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, R. An architecture model for supporting application integration decisions. In Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Information Systems, Naples, Italy, 16–21 June 2003; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Themistocleous, M. Justifying the decisions for EAI implementations: A validated proposition of influential factors. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2004, 17, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W. Investigating success factors in enterprise application integration: A case-driven analysis. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2005, 14, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, P. Research of Strategic Route in Heterogeneous System Integration Based on ESB-SOA. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Software Engineering, Wuhan, China, 11–13 December 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Arthur, W.B. Competing technologies, increasing returns, and lock-in by historical events. Econ. J. 1989, 99, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydow, J.; Schreyögg, G.; Koch, J. Organizational path dependence: Opening the black box. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2009, 34, 689–709. [Google Scholar]
- Rolland, K.H.; Ghinea, G.; Gronli, T.-M. Ambidextrous Enterprise Architecting: Betting on the Future and Hacking Path-dependencies. In Proceedings of the 23th European Conference on Information Systems, Münster, Germany, 26–29 May 2015; p. 150. [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, T.A.; Frels, J.K.; Mahajan, V. Consumer switching costs: A typology, antecedents, and consequences. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2003, 31, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C. A national customer satisfaction barometer: The Swedish experience. J. Mark. 1992, 56, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciborra, C.; Braa, K.; Cordella, A.; Hepsø, V.; Dahlbom, B.; Failla, A.; Hanseth, O. From Control to Drift. In The Dynamics of Corporate Information Infastructures; Oxford University Press on Demand: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, J.; Watson, R.T. Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: Writing a literature review. Manag. Inf. Syst. Q. 2002, 26, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel, M.; Schmidt, T.; Fuerstenau, D. The Path Biography Methodology: Analyzing Self-Reinforcing Mechanisms on Technical and Organizational Levels. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Systems—Exploring the Information Frontier, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 13–16 December 2015; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Henfridsson, O.; Bygstad, B. The generative mechanisms of digital infrastructure evolution. MIS Q. 2013, 37, 907–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drnevich, P.L.; Croson, D.C. Information Technology and Business-Level Strategy: Toward an Integrated Theoretical Perspective. MIS Q. 2013, 37, 483–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynne, P.; Henningsson, S. The Paradox of Post-Acquisition IS Integration Preparation: Preparing Under Incomplete Information. In Proceedings of the IEEE 20th Conference on Business Informatics, Vienna, Austria, 11–14 July 2018; pp. 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- Corbin, J.; Strauss, A. Basics of Qualitative Research: Techniques and Procedures for Developing Grounded Theory; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, J.; Xue, Y.; Liang, H. Organization Structural and Cultural Influences in Hospital Information Systems Integration. In Proceedings of the 11th Americas Conference on Information Systems, Omaha, NE, USA, 11–14 August 2005; p. 289. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, A.A.; Saif, S.; Khan, M.; Iqbal, J.; Akhunzada, A.; Wadood, A.; Al-Mogren, A.; Alamri, A. Taxonomy of Factors Causing Integration Failure during Global Software Development. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 22228–22239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achkoski, J.; Trajkovik, V. Intelligence information system (IIS) with SOA-based information systems. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Information Technology Interfaces, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 27–30 June 2011; pp. 353–358. [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari, P. Enterprise application integration using a component-based architecture. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual International Computer Software and Applications Conference, Dallas, TX, USA, 3–6 November 2003; pp. 557–562. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, P.; Feng, D.; Lim, Y.S. An Intelligent Middleware for Dynamic Integration of Heterogeneous Health Care Applications. In Proceedings of the 11th Joint Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, Melbourne, Australia, 18–22 January 2005; pp. 198–205. [Google Scholar]
- Themistocleous, M.; Irani, Z. Taxonomy of Factors for Information System Application Integration. In Proceedings of the 6th Americas Conference on Information Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 6–9 August 2000; p. 339. [Google Scholar]
- Mocker, M.; Fonstad, N. Driving Digitization at Audi. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Information Systems, Seoul, Korea, 10–13 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Silic, M.; Silic, D.; Oblakovic, G. Influence of Shadow IT on Innovation in Organizations. Complex Syst. Inform. Model. Q. 2016, 8, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Györy, A.; Cleven, A.; Uebernickel, F.; Brenner, W. Exploring the shadows: IT governance approaches to user-driven Innovation. In Proceedings of the 20th Educational Collaborative for International Schools (ECIS), Barcelona, Spain, 1–2 February 2012; p. 222. [Google Scholar]
- Köffer, S.; Ortbach, K.; Junglas, I.; Niehaves, B.; Harris, J. Innovation Through BYOD?—The Influence of IT Consumerization on Individual IT Innovation Behavior. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2015, 57, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H. Emergence and Consequences of Drift in Organizational Information Systems. In Proceedings of the 19th Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems, Singapore, 5–9 July 2015; p. 202. [Google Scholar]
- Steinhueser, M.; Waizenegger, L.; Vodanovich, S.; Richter, A. Knowledge Management without Management—Shadow IT in Knowledge-Intensive Manufacturing Practices. In Proceedings of the 25th European Conference on Information Systems, Guimarães, Portugal, 5–10 June 2017; p. 106. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, S.; Winkler, T.; Xiao, X. Two Tales of Technology: Business and IT Managers’ Technological Frames Related to Cloud Computing. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Information Systems, Seoul, Korea, 10–13 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
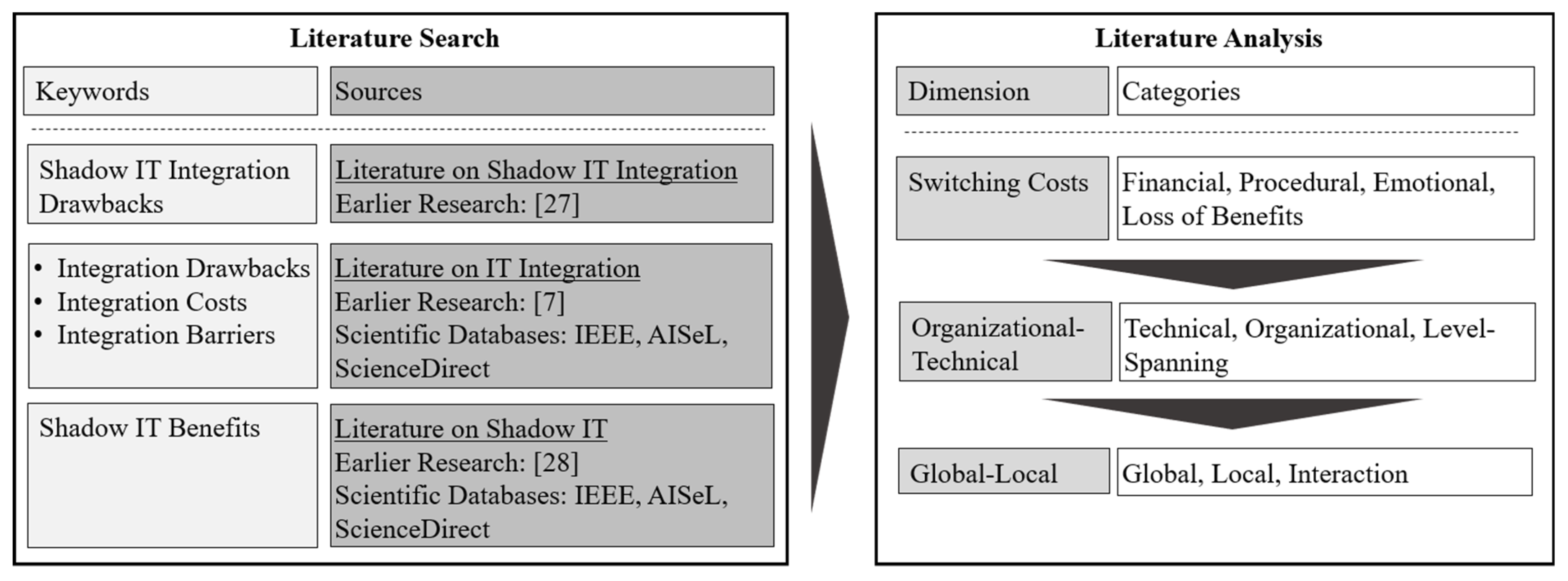
| Literature on Shadow IT Integration | Literature on IT Integration | Literature on Shadow IT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sources | [27] | [7] | IEEE; AISeL, ScienceDirect | [28] | IEEE, AISeL, ScienceDirect | |
| IT Integration Costs | Found Studies | 1 | 13 | 38 | 0 | 0 |
| Relevant | 1 | 13 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| IT Integration Barriers | Found Studies | 1 | 17 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Relevant | 1 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| IT Integration Drawbacks | Found Studies | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Relevant | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Shadow IT Benefits | Found Studies | 1 | 0 | 0 | 44 | 15 |
| Relevant | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 2 | |
| Sum (unique, relevant) | 1 | 14 | 1 | 7 | 2 | |
| Total | 25 | |||||
| Pre-Set Codes: Costs Dimension | Properties: Integration Drawbacks | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Financial: Financially quantifiable resources for | hardware | [12,13,18] |
| software | [12,13,18] | |
| development/adaption | [12,13,17,18,30,32,45] | |
| maintenance | [13,15] | |
| external support | [12,13,18] | |
| Procedural: Expenditure of time and effort for | project coordination | [12,15,45,46] |
| employee training | [12,13,15,18,30,45,46] | |
| technology understanding | [12,16,47,48,49] | |
| top management support | [12,13,18,45] | |
| organizational restructuring | [13,18,30] | |
| process understanding | [12,13,15,18,30,45,46] | |
| communication | [12,13,18,45,46] | |
| changing culture | [12,13,15,18,30,45,50] | |
| Relational: Psychological or emotional discomfort due to | sharing data | [18] |
| using technology | [12,13,30] | |
| losing power | [13,18,30,45,49] | |
| Loss of shadow IT benefits: Losing former | innovation | [5,6,51,52,53,54] |
| flexibility | [5,27,55] | |
| productivity | [5,22,27,56] |
| Pre-Set Codes: Organizational-Technical Dimension | Properties: Integration Drawbacks |
|---|---|
| Drawbacks from Organizational Change | External Support |
| Top Management Support | |
| Organizational Restructuring | |
| Process Understanding | |
| Communication | |
| Cultural Change | |
| Losing Power | |
| Losing Flexibility | |
| Losing Productivity | |
| Drawbacks from Technological Change | Hardware |
| Software | |
| Drawbacks from Level-Spanning Activities | Development |
| Maintenance | |
| Project Coordination | |
| Employee Training | |
| Technology Understanding | |
| Sharing Data | |
| Using Technology | |
| Losing Innovation |
| Pre-Set Codes: Global-Local Dimension | Properties: Integration Drawbacks |
|---|---|
| Drawbacks in the IT Department/Organization | Project Coordination |
| Technology Understanding | |
| Top Management Support | |
| Organizational Restructuring | |
| Drawbacks in the Business Units | Sharing Data |
| Using Technology | |
| Losing Flexibility | |
| Process Understanding | |
| Losing Innovation | |
| Drawbacks for the Interaction of Both Levels | Hardware |
| Software | |
| Development | |
| Maintenance | |
| Employee Training | |
| External Support | |
| Communication | |
| Cultural Change | |
| Losing Power | |
| Losing Productivity |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huber, M.; Zimmermann, S.; Rentrop, C.; Felden, C. Conceptualizing Shadow IT Integration Drawbacks from a Systemic Viewpoint. Systems 2018, 6, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems6040042
Huber M, Zimmermann S, Rentrop C, Felden C. Conceptualizing Shadow IT Integration Drawbacks from a Systemic Viewpoint. Systems. 2018; 6(4):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems6040042
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuber, Melanie, Stephan Zimmermann, Christopher Rentrop, and Carsten Felden. 2018. "Conceptualizing Shadow IT Integration Drawbacks from a Systemic Viewpoint" Systems 6, no. 4: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems6040042
APA StyleHuber, M., Zimmermann, S., Rentrop, C., & Felden, C. (2018). Conceptualizing Shadow IT Integration Drawbacks from a Systemic Viewpoint. Systems, 6(4), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems6040042






