Dynamic Evolution and Resilience Enhancement of the Urban Tourism Ecological Health Network: A Case Study in Shanghai, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Construction of Tourism Flow Networks Under Ecological Constraints
2.2. Integrating the Ecosystem Health Index into Tourism Systems
2.3. Resilience Assessment Methods in Tourism Ecological Networks
2.4. Shortcomings in the Existing Research and Innovations
3. Study Area and Data
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data Source
4. Methodology
4.1. Assessment Framework for Ecosystem Health
4.1.1. Vigor
4.1.2. Organization
4.1.3. Resilience
4.1.4. Ecosystem Services
4.2. Construction of Tourism Ecological Health Network
4.3. Evaluation Method for the Resilience of the Tourism Ecological Health Network
4.3.1. Gravity Model
4.3.2. Assessment Framework for the Resilience of the Tourism Ecological Health Network
- Node robustness
- Network robustness
- Node tourism effect
- Node ecological effect
- Network integration
- Network choice.
5. Results
5.1. Dynamic Evolution of the Tourism Ecological Health Network
5.1.1. Evolution Characteristics of Ecosystem Health
5.1.2. Evolution Characteristics of the Tourism Ecological Health Network
5.2. Resilience Evaluation of the Tourism Ecological Health Network
5.3. Resilience Enhancement of Tourism Ecological Health Network
6. Discussion
6.1. Construction of Tourism Ecological Health Network
6.2. Resilience Analysis of the Tourism Ecological Health Network
6.3. Practical Implications
6.4. Limitations and Further Work
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TEHN | Tourism ecological health network |
| EHI | Ecosystem health index |
| VORS | Vigor–organization–resilience–services |
| MCR | Minimum cumulative resistance |
| AHP | Analytic hierarchy process |
| LULC | Land use and land cover |
| NDVI | Normalized difference vegetation index |
References
- Li, Y.; Qin, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Hao, H. Ecosystem health assessment of the largest lake wetland in the Yellow River basin using an improved vigor-organization-resilience-services model. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, P.; Frazier, A.E.; Xia, C.; Tiando, D.S.; Feng, Y. How does urban landscape pattern affect ecosystem health? Insights from a spatiotemporal analysis of 212 major cities in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 99, 104963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbage, K.G.; Debbage, N. Aviation carbon emissions, route choice and tourist destinations: Are non-stop routes a remedy? Ann. Tour. Res. 2019, 79, 102765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Uribe, D.A.; Daniels, D.; González- Álvarez, Á.; Vélez-Pereira, A.M. Influence of vehicular traffic on environmental noise spectrum in the tourist route of Santa Marta City. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, R.; Cheng, X.; Christos, V.; Philbin, S.P.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, X. Assessing the landscape ecological risk of road construction: The case of the Phnom Penh-Sihanoukville Expressway in Cambodia. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Li, J. Analysis and treatment of the conflict between sustainable development and environmental protection based on the ecotourism concept. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1056643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.; Laso, J.; Cristóbal, J.; Albertí, J.; Bala, A.; Fullana, M.; Fullana-i-Palmer, P.; Margallo, M.; Aldaco, R. Towards more sustainable tourism under a carbon footprint approach: The Camino Lebaniego case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 369, 133222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouridaki, M.; Apostolakis, A.; Kourgiantakis, M. Cultural routes through the perspective of sustainable mobility: A critical literature review. J. Tour. Res. 2024, 26, e2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shen, W. Spatial heterogeneity of the effects of human activities on ecosystem health of a coastal tourism city: A case study of Rizhao, China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2021, 19, 3029–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Xu, D.; Chen, D.; Tao, J.; Wang, J.; Ma, X. Study on driving factors of island ecosystem health and multi-scenario ecology simulation using ecological conservation and eco-friendly tourism for achieving sustainability. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Ju, H. Assessment of coastal zone ecosystem health in the context of tourism development: A case study of Jiaozhou Bay. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 169, 112874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Resilience and stability of ecological systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1973, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhurtyal, S.; Hernandez, S.; Amankwah-Nkyi, K. Data-driven methods to assess transportation system resilience: Case study of the Arkansas roadway network. J. Transp. Eng. Part A Syst. 2025, 151, 05024005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J. Tourism supply chain resilience assessment and optimization based on complex networks and genetic algorithms. Syst. Soft Comput. 2025, 7, 200214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Q.; Jin, P. Research on the spatial network structure of tourist flows in Hangzhou based on BERT-BiLSTM-CRF. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Luo, M. Evolution of international tourist flows from 1995 to 2018: A network analysis perspective. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2020, 36, 100752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vada, S.; Dupre, K.; Zhang, Y. Route tourism: A narrative literature review. Curr. Issues Tour. 2023, 26, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y. Spatial pattern evolution and influencing factors of tourism flow in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle in China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zeng, G.; Li, X.; Zhong, Z. Optimum spatial scale of regional tourism cooperation based on spillover effects in tourism flows. Tour. Econ. 2023, 29, 409–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zang, X.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Chen, S. Modelling the coupling relationship between urban road spatial structure and traffic fow. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S. An optimal round-trip route planning method for tourism based on improved genetic algorithm. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 7665874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Q.; Wang, L.; Du, P.; Wang, Z. Optimization of tourism routes in Lushunkou District based on ArcGIS. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Gan, X.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Niu, S.; Zhou, B. A new framework for assessing ecosystem health with consideration of the sustainable supply of ecosystem services. Landsc. Ecol. 2024, 39, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xia, G.; Lin, T.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y. Construction of urban green space network in Kashgar City, China. Land 2022, 11, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, X.; He, Y. Nanjing’s intracity tourism flow network using cellular signaling data: A comparative analysis of residents and non-local tourists. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Luo, Y.; Xu, L.; Xi, Y.; Zhou, Y. Construction of ecological security pattern based on InVEST-Conefor-MCRM: A case study of Xinjiang, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Lei, S.; Yan, Q.; Bian, Z.; Lu, Q. Landscape ecological network construction controlling surface coal mining effect on landscape ecology: A case study of a mining city in semi-arid steppe. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tao, S.; Kong, Y.; Chen, J. A wildlife corridor site selection method based on the habitat suitability assessment of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2025, 58, e03452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R. Ecosystem health and ecological engineering. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 45, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Pan, Z.; Liu, D.; Guo, X. Exploring the regional differences of ecosystem health and its driving factors in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Wu, J. Regional ecosystem health response to rural land use change: A case study in Lijiang City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Huang, X. The impact of land urbanization on ecosystem health in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomerations, China. Cities 2022, 130, 103981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Wen, Q.; Lev, B.; Jiang, W. Tourism ecological security evaluation based on dynamic super-efficiency network SBM from the perspective of all-for-one tourism. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 429, 139333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergantino, A.S.; Gardelli, A.; Rotaris, L. Assessing transport network resilience: Empirical insights from real-world data studies. Transp. Rev. 2024, 44, 834–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z. Assessment of Temporal and Spatial. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 66, 102578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Sun, C.; Zou, W.; Hao, S. Spatiotemporal characteristic and evolution of China’s marine economic resilience. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 238, 106562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ginkel, K.C.H.; Dottori, F.; Alfieri, L.; Feyen, L.; Koks, E.E. Flood risk assessment of the European road network. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 21, 1011–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Tang, H.; Wang, D. Spatio-temporal evolution of population mobility differentiation patterns in a pandemic context: Based on a network perspective. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2023, 14, 2240945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ge, Q. Spatial association network of economic resilience and its influencing factors: Evidence from 31 Chinese provinces. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, D. Analysis of regional resilience network from the perspective of relational and dynamic equilibrium. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 138859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ma, S.; Chen, L.; Yang, L. Resilience measurement and analysis of intercity public transportation network. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2024, 131, 104202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Nie, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Dong, H.; Xu, B. Assessment and optimization of urban ecological network resilience based on disturbance scenario simulations: A case study of Nanjing city. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 438, 140812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Cui, L. Characteristics of high impact weather and meteorological disaster in Shanghai, China. Nat. Hazards 2012, 60, 951–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Mu, X.; Jiao, J.; Li, D.; Li, J. How to enhancing urban space renewal through visual landscape perception? An approach from street view image recognition. Soc. Indic. Res. 2024, 175, 659–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Tian, Y.; Guo, M.; Tran, D.; Alwah, A.A.Q.; Xu, D. Evaluating the disparity between supply and demand of park green space sing a multi-dimensional spatial equity evaluation framework. Cities 2022, 121, 103484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Qin, F.; Li, L.; Dong, X. Construction and optimisation of watershed scale ecological network: A case study of Kuye River Basin. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1364568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; You, X. Landscape pattern analysis and ecological network planning of Tianjin City. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 46, 126479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Inverno, G.; Carosi, L.; Romano, G. Meeting the challenges of the waste hierarchy: A performance evaluation of EU countries. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Ji, R.; Shi, H. Food supply networks in the Pearl River Delta mega-city region: Characteristics, resilience and security strategies. J. Nat. Resour. 2024, 39, 564–581. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikirya, B.; Xing, Y.; Zhou, C. The matching relationship between the distribution characteristics of high-grade tourist attractions and spatial vitality in Xinjiang. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, P. Characteristics of the urban environmental regulation network and its impact on carbon emission efficiency in China. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lv, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Zhong, C.; Hijazi, I.H.; Cheng, S. Assessment of Lively Street Network Based on Geographic. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 17801–17819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, D.; Meng, Y.; Guo, C. The relationship between emotional perception and high-density built environment based on social media data: Evidence from spatial analyses in Wuhan. Land 2024, 13, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Jiang, Y. Exploring behavioral determinants of residents’ ecological conservation in rural tourism development. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ran, H. Research on the driving mechanism of tourists’ ecological protection behavior in intangible cultural heritage sites. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1514482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Barzel, B.; Barabási, A. Universal resilience patterns in complex networks. Nature 2016, 530, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Liu, Z.; Shi, L.; Huang, X. Geospatial analysis of sports tourism resources in China’s urban clusters: A case study of the Sichuan-Chongqing region utilizing GIS and the geographic detector. Front. Sports Act. Living 2024, 6, 1496469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, D. The dynamic analysis and evaluation on tourist ecological footprint of city: Take Shanghai as an instance. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 37, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Thompson, P.; Loreau, M. Spatial ecological networks: Planning for sustainability in the long-term. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2017, 29, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.; Albert, B. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 1999, 286, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.; Holling, C.S.; Carpenter, S.R.; Kinzig, A.P. Resilience, adaptability and transformability in social–ecological systems. Ecol. Soc. 2004, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, M. Accessibility: In search of a unified theory. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2009, 36, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medaglia, J.D.; Huang, W.; Karuza, E.A.; Thompson-Schill, S.L.; Ribeiro, A.; Bassett, D.S. Functional alignment with anatomical networks is associated with cognitive flexibility. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2018, 2, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-J.; Friston, K. Structural and functional brain networks: From connections to cognition. Science 2013, 342, 1238411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Li, H.; Huang, Y. The complex ecological network’s resilience of the Wuhan metropolitan area. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



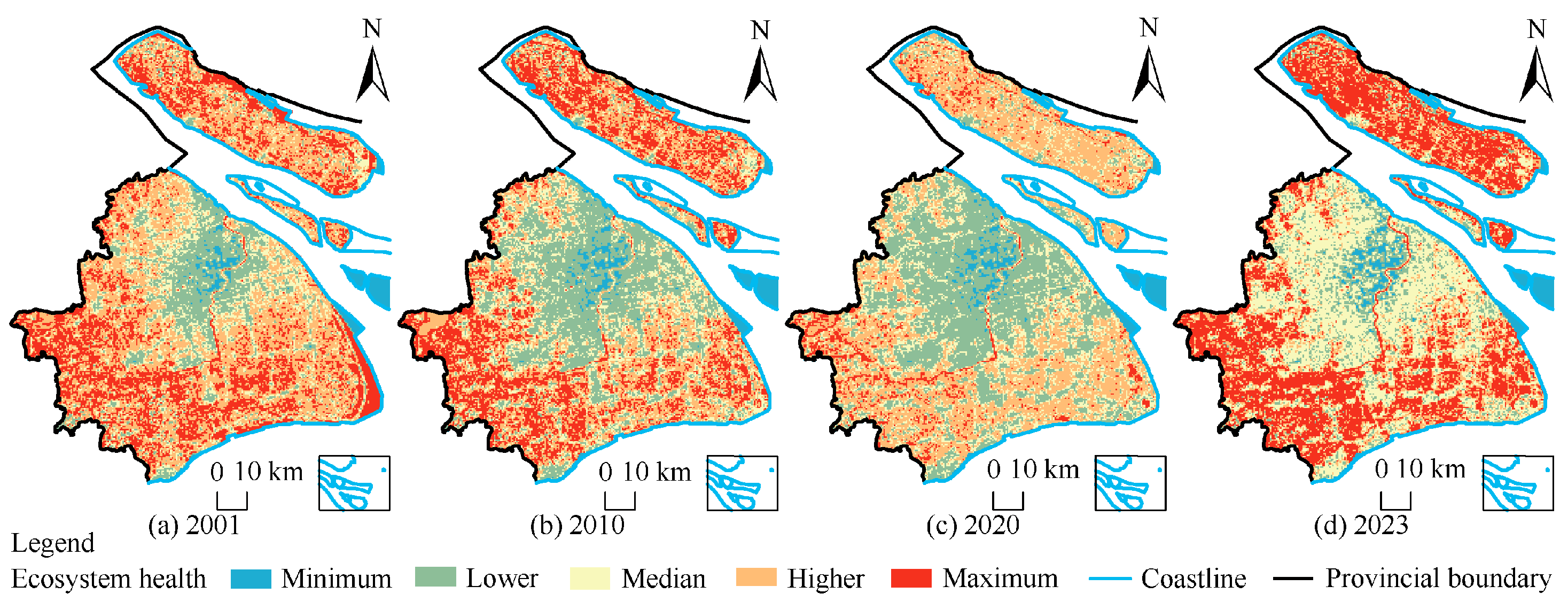


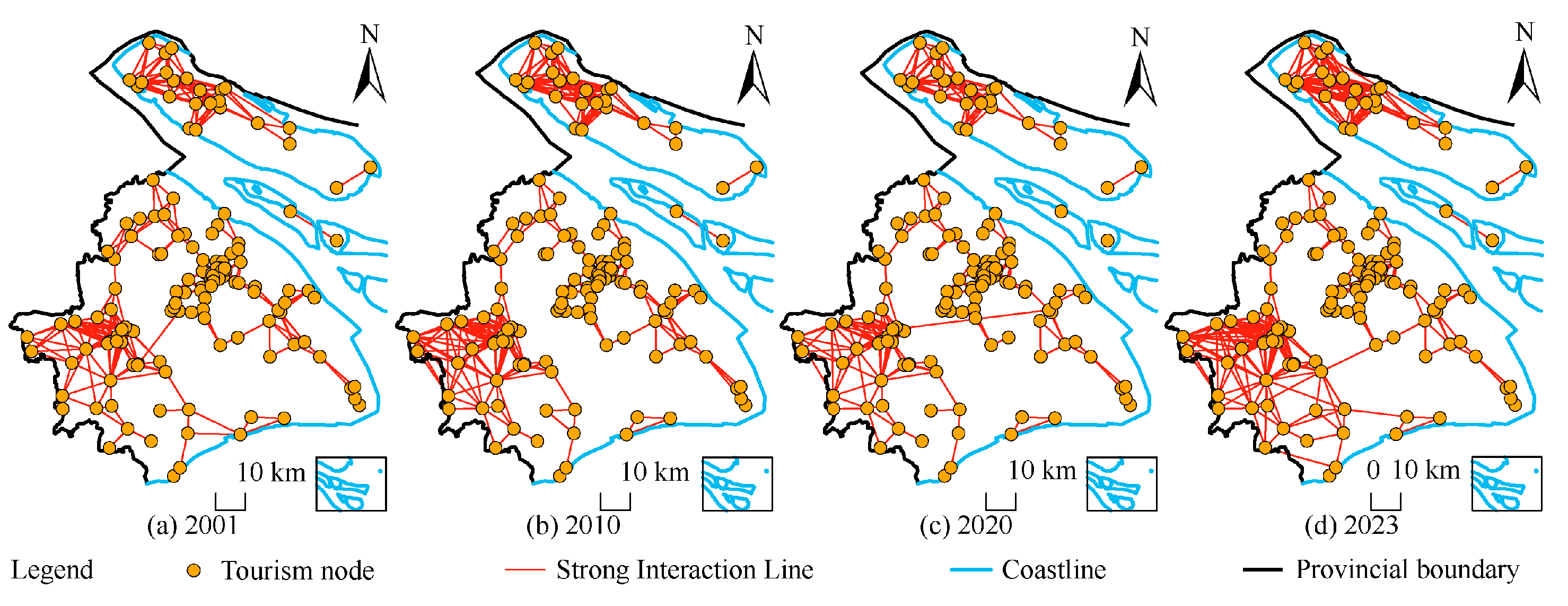

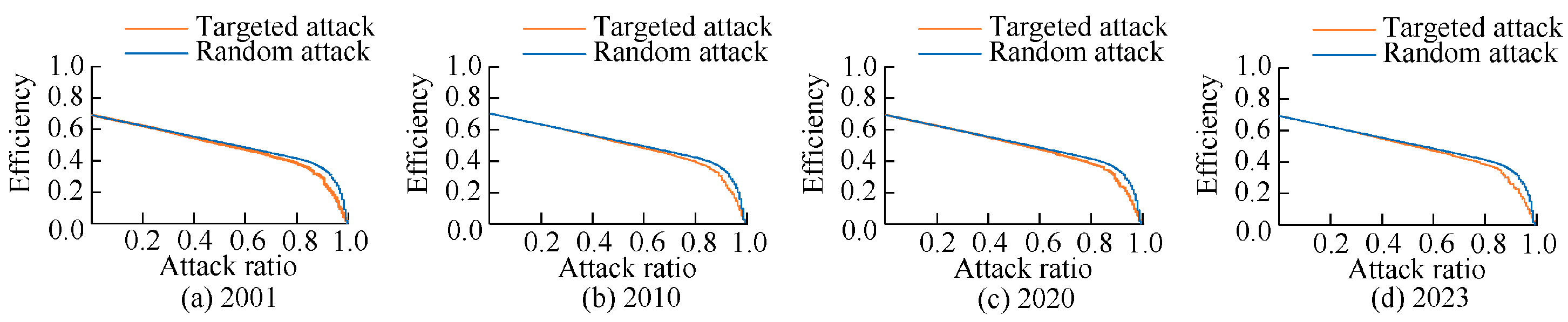



| Ecosystem Type | Cropland | Forestland | Grassland | Waterbody | Built-Up Land | Barren Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERC | 0.500 | 0.900 | 0.700 | 0.800 | 0.200 | 0.100 |
| ESC | 0.500 | 1.000 | 0.800 | 0.850 | 0.330 | 0.013 |
| Dimension | Indicator | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Structural resilience | Node robustness | 0.088 |
| Network robustness | 0.140 | |
| Functional resilience | Node tourism effect | 0.394 |
| Node ecological effect | 0.283 | |
| Network integration | 0.059 | |
| Network choice | 0.036 |
| Resilience Indicator | 2001 | 2010 | 2020 | 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Node robustness | 0.793 | 0.795 | 0.794 | 0.793 |
| Network robustness | 0.494 | 0.496 | 0.496 | 0.495 |
| Node tourism effect | 0.005 | 0.065 | 0.151 | 0.203 |
| Node ecological effect | 0.115 | 0.131 | 0.112 | 0.143 |
| Network integration | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.036 | 0.056 |
| Network choice | 0.015 | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.013 |
| Resilience | 0.175 | 0.203 | 0.233 | 0.263 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, M.; Huang, T. Dynamic Evolution and Resilience Enhancement of the Urban Tourism Ecological Health Network: A Case Study in Shanghai, China. Systems 2025, 13, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13080654
Wei M, Huang T. Dynamic Evolution and Resilience Enhancement of the Urban Tourism Ecological Health Network: A Case Study in Shanghai, China. Systems. 2025; 13(8):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13080654
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Man, and Tai Huang. 2025. "Dynamic Evolution and Resilience Enhancement of the Urban Tourism Ecological Health Network: A Case Study in Shanghai, China" Systems 13, no. 8: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13080654
APA StyleWei, M., & Huang, T. (2025). Dynamic Evolution and Resilience Enhancement of the Urban Tourism Ecological Health Network: A Case Study in Shanghai, China. Systems, 13(8), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13080654





