Abstract
In response to escalating societal and environmental expectations, corporate social responsibility (CSR) has evolved into a strategic imperative rather than a voluntary or peripheral activity. This study investigates the effect of employees’ CSR perceptions on job performance, with corporate reputation (CR) examined as a mediating variable. Drawing on Social Identity and Social Exchange Theories, the research explores how CSR, as an element of business innovation and sustainable organizational practices, fosters internal stakeholder engagement and performance enhancement. Data were collected from five-star hotel employees in İstanbul/Türkiye, a service sector context where customer satisfaction is highly dependent on frontline employee behavior. Using PROCESS Macro for SPSS 27, the findings reveal that CSR perceptions significantly and positively influence employee performance both directly and indirectly through the enhancement of CR. This mediating effect underscores the role of CSR not only as an ethical framework but also as an internal mechanism that strengthens employee commitment and output. The study contributes to CSR and the organizational behavior literature by empirically validating that internal CSR perceptions shape strategic outcomes such as employee performance, especially within high-contact service environments. Theoretical implications emphasize CSR’s integrative function in reputation-building and performance systems, while practical insights recommend embedding socially responsible practices into HR and internal communication strategies to achieve sustainable outcomes and societal well-being. These findings offer meaningful contributions to the scope of business innovation by linking CSR with strategic performance indicators in labor-intensive industries.
1. Introduction
The increasing complexity of the global economic system has brought expectations such as sustainable growth, social responsibility, and environmental sensitivity to the center of strategic decision-making processes. In this context, it is not enough for businesses to focus only on financial outputs; they are expected to develop innovative business models that holistically address social and environmental impacts [1,2]. This transformation requires that the concept of business innovation be addressed not only through technology-based developments but also through the integration of organizational processes, social responsibility principles, and sustainable management systems [3,4]. In fact, corporate social responsibility (CSR)-based strategies are playing an increasingly important role in gaining competitive advantage, serving as a key indicator of both organizational innovation capacity and social value creation [5,6]. In this context, CSR is not only an ethical principle, but it is also considered a strategic tool through which businesses transform their ways of doing business by being sensitive to social expectations [7,8]. CSR is a multi-dimensional application area that triggers sustainability-oriented organizational transformation, strengthens employee commitment, and increases efficiency in internal processes [9,10]. How CSR practices are perceived within the organization and how these perceptions are reflected in employee performance is an issue of growing scholarly interest. It is stated that CSR is associated with performance through psychological factors, such as trust, commitment, and the creation of meaning, especially among employees [11,12].
In recent years, there has been a growing number of studies examining the impact of CSR practices on consumer behavior. However, the effects of these practices on employee perceptions and behaviors remain less well understood [13,14,15,16]. In particular, the perceptual or psychological mechanisms through which CSR affects employee performance remain an essential research area that has not been fully clarified in the literature. This gap raises the question of how employees evaluate CSR activities and how these evaluations interact with organizational factors, such as commitment to the organization, trust, or self-esteem, and are reflected in their performance. In addition, the accumulated literature states that the effects of CSR are mainly examined in relation to customers and other external stakeholders, while employees are often overlooked as internal stakeholders. As such, there is an increasing call for research that addresses this gap and contributes to a more holistic understanding of CSR’s internal effects [13,17]. Consequently, further empirical studies are needed to examine the link between CSR and employee performance, with particular attention to the mediating and moderating mechanisms involved.
Corporate reputation stands out as a crucial mediating factor that clarifies how CSR initiatives influence employee attitudes, behaviors, and overall performance. CR is a multidimensional perception that determines the extent to which an organization is perceived as reliable, ethical, and sustainable in the eyes of its stakeholders [18,19]. Since employees, especially in the service sector, are often seen as the carriers of the institution’s external image, the extent to which CSR practices are internalized directly affects the CR [20,21,22]. It is suggested that employees in businesses with a high reputation perception have higher motivation levels and task performance. Therefore, CR plays a mediating role, strengthening the relationship between CSR and performance [23,24,25]. The extant literature highlights limited studies on the relationship between CSR and CR. It emphasizes the importance of analyzing these relationships, not just at the corporate or customer level but also at the individual employee level. There is a call for further research in this area [16,22].
To strengthen the conceptual clarity, this study adopts an integrated framework in which Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is positioned as a strategic initiative that influences internal stakeholder perceptions. Corporate Reputation (CR) is conceptualized as a mediating variable that reflects how employees interpret and internalize CSR activities. These perceptions, in turn, are expected to shape job performance. While the notion of business innovation serves as a broader contextual foundation, the primary theoretical focus of the study lies in understanding the internal mechanisms through which CSR exerts its influence on employee behavior via CR. This approach provides a more structured perspective and aligns with current theoretical discussions on strategic responsibility and internal performance outcomes.
To address these research gaps systematically, this study is structured into five main sections. First, a comprehensive theoretical framework is presented, focusing on CSR, corporate reputation (CR), and employee performance. Second, the proposed research model and hypotheses are developed based on relevant literature. Third, the methodology section outlines the sampling strategy, data collection process, and analytical techniques employed. Fourth, the empirical results are reported and interpreted. Finally, the study concludes with a discussion of key findings, theoretical and practical implications, limitations, and directions for future research. This structure enables a coherent and in-depth investigation into how CSR initiatives affect employee performance through the mediating role of CR.
Aligned with the recent literature recommendations, this study investigates how CSR initiatives influence employee job performance, specifically by exploring the mediating role of CR. The analysis is based on data collected from employees employed at five-star hotels in İstanbul/Turkey. The aim was to shed light on the internal output of CSR practices in the service sector. While much of the existing literature focuses on the external outcomes of CSR (e.g., customer satisfaction, brand image, market share), its internal effects—particularly on employees—remain underexplored [26,27]. Therefore, the research aims to fill a significant gap by focusing on the effects of CSR as an internal social innovation and its indirect consequences on workforce performance.
The study considers CSR not as a side activity but as a strategic management style integrated into the value chain of the business. Analyzing the impact of CSR practices on employee performance through CR combines business innovation literature and organizational behavior research in a holistic framework; thus, it reveals the importance of ethical responsibility and innovative management approach to achieve sustainable performance.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and Employee Job Performance
Nowadays, financial performance alone is not enough to provide businesses with a sustainable competitive advantage; social and environmental responsibilities are also expected to be integrated into corporate strategies [7,28]. CSR has become one of the main tools of this integration, and it has been shown that businesses can have positive impacts on both external and internal stakeholders [29].
CSR has evolved into a fundamental principle of contemporary business strategy, especially as public expectations shift toward greater corporate accountability. CSR refers to an organization’s accountability for the social and environmental consequences of its actions, emphasizing the voluntary integration of societal and ecological considerations into both strategic operations and stakeholder relations [30]. While compliance with legal standards remains a fundamental expectation, organizations are increasingly required to proactively manage their broader societal and environmental impacts, positioning CSR as an essential element of sustainable business innovation [31,32,33].
Key conceptual models, including Carroll’s CSR pyramid—which outlines economic, legal, ethical, and philanthropic obligations—and Elkington’s triple bottom line approach, which focuses on financial performance, social justice, and environmental sustainability, have played a pivotal role in shaping the modern understanding and development of CSR [34,35,36]. Unlike mandatory legal compliance or profit-driven strategic actions, CSR initiatives are inherently geared toward addressing societal needs and expectations in the spirit of corporate citizenship [37,38,39].
CSR is critical in some sectors regarding environmental impacts and natural resource use. In particular, the energy, mining, and manufacturing sectors, as well as the tourism and hospitality sectors, are among the areas with high impact potential in terms of environmental sustainability [40,41]. Activities in these sectors are based on intensive resource use due to environmental factors such as water and energy consumption, waste production, and carbon emissions, increasing the strategic importance of CSR practices. In the hospitality sector, studies have shown that CSR efforts focused on environmental sustainability improve not only ecological outcomes but also employee behavior and organizational performance [42]. As such, adopting CSR initiatives is not merely advisable but essential for mitigating negative externalities and promoting sustainable development. Modern hospitality firms increasingly invest in green technologies, waste reduction, and community outreach as standard CSR practices [43,44].
Recent research suggests that CSR in hospitality not only enhances public image but also ensures organizational competitiveness by meeting institutional and competitive demands [45,46,47]. CSR initiatives have been found to positively affect financial performance [45,46,47,48,49,50], employee job satisfaction [51,52], organizational identification, and organizational citizenship behaviors [53,54].
Given the hospitality sector’s competitive intensity and service-centric nature, optimal functioning across the value chain is critical. Interactions between employees and customers are crucial moments where service quality and satisfaction are shaped. In this context, employee performance is assessed through both operational metrics and subjective indicators such as customer feedback [55,56]. Thus, superior performance is a key marker of strategic maturity and organizational success [57].
Employee performance is directly linked to customer experience, service delivery, and business reputation. Poor performance can lead to dissatisfied guests and service failures, while high performance is tied to productivity, service quality, and competitive advantage [58,59].
CSR activities enhance employee performance by fostering emotional attachment, a sense of purpose, and an alignment with organizational values [60,61,62,63]. Research in hospitality confirms a strong positive link between employees’ CSR perceptions and their performance [64,65]. Additional studies show that CSR perceptions boost employee engagement, job satisfaction, and service quality [43,51].
These relationships can be understood through Social Identity Theory (SIT) [66,67,68], which posits that individuals form part of their self-concept through organizational affiliation. Employees who view their employer as socially responsible experience greater identification and pride, leading to increased motivation and stronger performance [69]. In hospitality, CSR efforts such as environmental initiatives or community involvement reinforce employee identification with their organization’s values.
Furthermore, Social Exchange Theory (SET) further explains these dynamics. It argues that employees perceive CSR as a form of organizational goodwill, triggering a sense of reciprocity and moral obligation to contribute positively [70]. This reciprocal dynamic motivates employees to reciprocate through increased engagement and higher performance [61,71].
In sum, drawing upon SIT and SET, it is proposed that CSR initiatives foster a deeper sense of identification and reciprocal commitment among hotel employees, thereby enhancing their job performance and contributing to the organization’s broader sustainability and innovation strategies. In line with the above reasoning, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H1:
Hotel employees’ perceptions of CSR positively influence their job performance.
To further strengthen the theoretical foundation of the proposed model, this study explicitly integrates Social Identity Theory and Social Exchange Theory to explain the CSR–CR–performance pathway. From the SIT perspective, CSR enhances corporate reputation by reinforcing employees’ identification with the organization; those who perceive their employer as socially responsible are more likely to associate its reputation with their personal and professional identity. Similarly, SET explains how CSR signals organizational goodwill, which in turn builds trust and psychological obligation. Employees who perceive such fairness and commitment are more inclined to reciprocate with greater performance. In this integrated model, corporate reputation functions as both a psychological outcome and a perceptual signal, mediating the influence of CSR on employee behavior.
While corporate reputation is the primary mediating variable examined in this study, we acknowledge that other psychological mechanisms—such as organizational identification, sense of meaningfulness, or empowerment—may also play significant roles in this relationship. Given the context of the luxury hospitality sector, where external prestige and brand perception are especially influential, CR was selected as the most relevant and observable mediator. Future studies could expand this framework by incorporating alternative or complementary mediators to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the CSR–performance link.
2.2. CSR, Corporate Reputation, and Employee Job Performance
In an increasingly dynamic and complex business environment, organizations are compelled to shift their strategic focus from mere internal process optimization towards broader stakeholder engagement and environmental stewardship [72,73]. Growing competitive pressures, market uncertainties, and the diversification of customer expectations necessitate a more transparent, accountable, and socially responsible management approach. In this context, corporate reputation (CR) has become a critical intangible asset that influences organizational competitiveness, particularly in the service-intensive hospitality sector [74,75].
CR reflects the collective evaluation of an organization’s actions and overall standing among its stakeholders, significantly shaping customer behavior, talent acquisition, and supplier relationships, ultimately impacting financial and operational outcomes [76]. In the hospitality industry, the role of CR is even more pronounced. Hotels with a weak reputation often suffer from reduced occupancy and customer retention, whereas a strong corporate reputation fosters brand trust, improves perceived service quality, and enhances market positioning [77,78].
According to signaling theory, in highly competitive markets such as hospitality, CR serves as an essential signal that conveys organizational quality and integrity to both internal and external audiences [79,80,81]. Moreover, positive CR not only strengthens customer loyalty [82,83] but also fosters customer citizenship behaviors, wherein customers voluntarily advocate for and defend the organization based on their service experiences [84,85,86].
Beyond external outcomes, CR significantly influences internal dynamics, particularly employee behavior and job performance. Employees who perceive their organization as reputable are more likely to exhibit higher organizational commitment, creativity, and discretionary work behaviors [87,88]. In hospitality settings, where frontline employees are the primary interface between the brand and the customer, strong CR enhances employee engagement and service quality, ultimately contributing to organizational success and performance. In a study conducted on hotel staff, it was observed that CR generally enhances performance [89]. An empirical study conducted with a sample of 473 employees revealed a positive relationship between CSR practices and employee performance [88].
Recent literature increasingly recognizes CSR as a key antecedent in building and sustaining CR [90,91,92]. By engaging in socially and environmentally responsible activities, organizations build credibility and align their operations with stakeholder expectations. In the hospitality industry, empirical findings confirm that employee and customer perceptions of CSR enhance CR, customer satisfaction, and loyalty [93,94]. A study conducted in China involving 451 hotel customers revealed that CSR enhances CR, customer satisfaction, and customer loyalty [93]. Once more, A study conducted in different urban contexts also demonstrates a positive association between CSR efforts and CR [94].
Drawing from stakeholder theory and Social Identity Theory, employees internalize the socially responsible image of their organization, enhancing their organizational identification and motivating higher levels of performance [69,95]. When hospitality employees view their employer as socially responsible, they experience increased pride, trust, and emotional attachment, leading to enhanced job performance and service delivery. Furthermore, based on social exchange theory [70], CSR activities can create a reciprocal relationship wherein employees feel an obligation to reciprocate organizational investments in societal welfare through heightened engagement and job performance (11,61]. In the hospitality industry, this reciprocal exchange is critical, given the direct link between employee behaviors and customer satisfaction metrics.
While much of the existing research on CSR and organizational outcomes has focused on Western contexts, scholars have called for broader geographic and cultural diversity in this field [37], there is a growing call for more culturally diverse investigations, particularly in emerging markets such as Turkey, which bridges Western and Eastern business practices [96,97]. In addition, limited studies on CSR, CR, and performance include senior managers as samples, and the need for a study focusing on other stakeholders, such as hotel employees, is emphasized [96,97].
There is also a recognized need to further investigate the mechanisms underlying the CSR–performance link, particularly by examining mediating variables such as CR [56,98]. This study responds to these gaps by examining how employee perceptions of CSR influence job performance, with corporate reputation as a key mediating factor in the hospitality context.
Based on the prior discussion and observed gaps in existing studies, the hypotheses below are formulated, and the research model is illustrated in Figure 1:
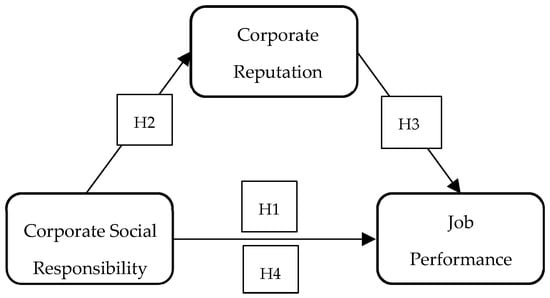
Figure 1.
Research model. Source: Author’s own elaboration.
H2:
Hotel employees’ perceptions of CSR positively influence their perceptions of CR.
H3:
Hotel employees’ perceptions of CR positively influence their job performance.
H4:
CR mediates the relationship between hotel employees’ perceptions of CSR and their job performance.
3. Methods
3.1. Sample and Procedure
The population of the research consists of employees of 5-star hotels in Istanbul. The reason why 5-star hotels were chosen as the population of the study is that these hotels are more corporate and more likely to engage in CSR and CR initiatives. To determine the sample, 5-star hotels in Istanbul were identified through the international reservation platform (www.hotels.com, accessed on 10 April 2025), and the contact information of 149 hotels was collected. Emails explaining the purpose of the study were sent to hotel management, requesting permission to conduct the survey. After receiving approval from 9 hotels, face-to-face meetings were conducted with the relevant personnel, and printed questionnaires were delivered in sealed envelopes (100 surveys for each hotel) to ensure confidentiality and encourage participation.
The data collection process was conducted over a three-month period, from December 2023 to February 2024. This extended timeframe allowed for coordination with hotel management, distribution across different employee shifts, and the collection of responses during varying work schedules. The final version of the survey included no items requesting personal or identifying information, thereby preserving participant anonymity and ensuring ethical compliance. To allow employees adequate time to complete the surveys, each hotel was given approximately two weeks before sealed envelopes containing the completed questionnaires were retrieved by the researchers.
At the end of the research, 399 surveys were collected, and the researchers analyzed them. As a result of the examination, 16 surveys with a high percentage of incorrect and missing data (more than 50%) were excluded from the research. The return rate was 38%. As a result, 383 of the questionnaires were found to be usable.
3.2. Measurement Tools
This study employed measurement tools previously validated in research involving hotel and hospitality employees. All items were rated on a 5-point Likert scale, with 1 representing ‘Strongly Disagree’ and 5 representing ‘Strongly Agree’. The following section outlines the measurement instruments used:
Corporate Social Responsibility: The CSR perception scale was based on prior works by Panagopoulos, Rapp, and Vlachos, as well as Boğan [99,100]. The scale is one-dimensional and consists of four statements. The full scale includes “This hotel is a socially responsible hotel”, “This hotel adheres to ethical standards”, “This hotel generally strives to improve the welfare of its stakeholders”, and “This hotel exhibits environmentally responsible behaviors”. These items reflect both the social and ecological dimensions of CSR as perceived by employees in the hospitality sector.
Corporate Reputation: A corporate reputation scale established by Bartels et al. and applied in Boğan’s study on hotel staff was used to evaluate employees’ perceptions [100,101]. The scale is one-dimensional and consists of three statements. The full scale includes “This hotel has a generally good reputation”, “This hotel is regarded as a role model”, and “This hotel is an appreciated hotel”, highlighting the overall perception of the organization’s prestige and recognition.
Job Performance: Employee job performance was measured using a scale developed by Kirkman and Rosen, Sigler, and Pearson, with a Turkish adaptation by Çöl [102,103,104]. This scale was also utilized by Yabacı in his study on hotel employees [105]. The scale is one-dimensional and consists of four statements. The full scale includes: “I complete my tasks on time”, “I exceed my job objectives”, “I ensure that I meet service and quality standards to a great extent”, and “I respond quickly when problems arise”. These statements emphasize proactive behavior, quality assurance, and goal achievement as key indicators of individual performance.
3.3. Common Method Variance
In research conducted in the fields of social sciences, collecting data in a single time period may cause linear relationships that do not actually exist between variables to emerge artificially. This situation, called common method variance, causes misleading findings in the analysis results and misinterpretation of the data. For this reason, it is recommended to perform factor analysis to check whether there is a common method variance problem in the analyses [106,107]. To discuss the common method variance assumption, the first factor must independently explain a significant part of the variance (more than 50%) [106]. In line with this recommendation in the literature, Harman’s Single Factor Test was performed to check whether there was a common method variance problem. As a result of the analysis, no factor explaining more than 55% (max 33%) was found. This result shows no common method variance problem in the study.
4. Results
4.1. Demographic Profile and Descriptive Findings
Table 1 includes data on gender, marital status, age, and industry experience for 383 employees who participated in the survey.

Table 1.
Demographic characteristics.
Most participants are male (65.27%) and single (51.96%). A large proportion of the respondents are between 25 and 34 years old. In terms of industry experience, a notable share (39.95%) has been employed in the sector for a period ranging from 6 to 10 years. These findings reveal that the participant group is largely composed of individuals aged between 25 and 34, with a considerable portion having 6 to 10 years of industry experience. This suggests a relatively young and professionally active employee profile. The gender distribution, with 65.27% female respondents, reflects the structure of employment in the service sector. Marital status appears nearly evenly split, which allows for a diverse range of perspectives to be captured. These demographic characteristics offer important context for understanding the descriptive and inferential results presented in the following sections.
4.2. Validity and Reliability Analyses
To ensure the reliability and validity of the measurement instruments, confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was employed in the study. Reliability was assessed using both Cronbach’s Alpha and Composite Reliability (CR) values. Cronbach’s Alpha indicates the internal consistency of each construct, whereas CR reflects the extent to which the observed items are more strongly associated with their intended latent variable than with other unrelated factors [107].
The scales’ validity was measured using convergent and discriminant validity methods. Table 2 offers a summary of the key analytical results.

Table 2.
Findings on the validity of the scales.
When the findings in Table 2 are examined, it is seen that the Cronbach’s Alpha value of the CSR scale is 0.840, the perceived CR scale is 0.850, the Cronbach’s Alpha value of the business performance scale is 0.841, and the CR values are 0.844, 0.852, and 0.846, respectively. All of these values are 0.7 and above. Based on these findings, it can be concluded that the scales demonstrate a high level of reliability [107,108].
To confirm convergent validity, the Composite Reliability for each scale should surpass its AVE, with the AVE value being greater than 0.50. Table 2 shows that AVE values are greater than 0.50 and CR values are greater than 0.70 for all variables. According to these results, the scales used in the study are convergent. The fact that the √AVE value is greater than the correlation values between the structures and does not exceed 0.85 indicates that the scales have discriminant validity. The findings in Table 3 confirm that this condition is also met and that the scales used in the study have discriminant validity [107,109].

Table 3.
Correlations between key variables.
4.3. Descriptive Statistics on Variables
Table 3 shows the descriptive statistical results of the variables and the findings obtained from the correlation analysis to determine the relationship between them.
The results of the correlation analysis indicate a positive relationship between CSR and both CR (r = 0.588, p < 0.05) and job performance (r = 0.610, p < 0.05). Furthermore, there is also a positive relationship between CR and job performance (r = 0.453, p < 0.05).
4.4. Hypothesis Testing Results
The SPSS-27 statistical package was preferred for testing the study’s hypotheses. Although many methods are suggested in the literature for testing mediation effects, Process Macro, developed as an add-on to SPSS in recent studies and considered to provide more reliable results than traditional methods, was used [107,110]. In the analyses conducted using Model 4, 2000 bootstrap samples were taken to calculate the regression coefficients and significance levels statistically, and coefficients were preferred at a 95 percent confidence interval. Table 4 presents the outcomes obtained through the analytical procedures.

Table 4.
Process macro analysis results.
Table 4 illustrates the outcomes derived from the PROCESS Macro analysis, indicating that CSR positively impacts CR (β = 0.569, p < 0.05, CI [0.625; 0.986]) and job performance (β = 0.419, p < 0.05, CI [0.196; 0.364]). Additionally, CR significantly and positively influences job performance (β = 0.328, p < 0.05, CI [0.510; 0.809]). The significance of the indirect effect was examined to ascertain the mediating role of CR in the relationship between CSR and job performance. Through controls, the mediating effect of CR on the influence of CSR on job performance was validated (β = 0.258, p < 0.05, CI [0.418; 0.752]). Consequently, all hypotheses proposed in the research were supported.
5. Discussion
In this study, the impact of CSR practices on employee job performance was analyzed in the context of the mediating role of CR. The hypothesis tests indicated that CSR affects employee performance both directly and indirectly, with CR serving as a significant mediating mechanism in this effect. These results are consistent with prior research and contribute to discussions on organizational innovation and sustainability, particularly in service industries.
One of the main findings of the study is that the perception of CSR among employees in the hotel sector has a direct and significant impact on their job performance. This demonstrates that CSR practices provide tangible benefits not only to external stakeholders (e.g., customers, investors) but also to internal stakeholders, namely employees [111]. Since employee performance plays a crucial role in customer experience and business success in service-oriented sectors, employees’ perceptions of CSR are closely linked to job satisfaction, belonging, and performance [52]. Studies conducted especially in the hotel sector show that service quality and customer satisfaction are directly achieved through employee performance, and that CSR perceptions play a motivational role in this performance [56].
Moreover, employees with strong CSR perceptions are more likely to demonstrate organizational citizenship behaviors (OCBs), take initiative, and perform effectively in their roles [112,113]. A study conducted within the hospitality sector emphasizes that hotel employees’ perceptions of CSR have a notable positive impact on their job performance, primarily through the increased job satisfaction derived from organizational CSR efforts [64]. These findings, along with the current study, reveal that CSR serves as a strategic tool for enhancing internal performance outcomes in sectors with intensive customer interaction, such as hotel management, and underscore its importance in a sector where performance directly influences customer satisfaction and organizational performance.
Social Identity Theory offers a strong explanation for this relationship. Employees who view their organization as socially responsible tend to identify more strongly with it, aligning their values and self-concept with the organization’s image. In the hospitality sector, where employees serve as the public face of the company, this identification enhances engagement and a sense of meaningful contribution. From the Social Exchange Theory perspective, CSR is seen as an organizational investment in employee well-being. In response, employees reciprocate with greater commitment and performance. This mutual exchange is especially relevant in service contexts, where fairness, trust, and shared values directly influence customer-facing behavior
The second important finding is that employees’ CSR perceptions positively influence their views on CR. When hotel employees embrace their organization’s social responsibility activities, a more favorable perception of the organization’s reputation emerges. The existing literature indicates that both employees’ and customers’ perceptions of the company’s CSR performance enhance its CR. Particularly, hotel employees’ active engagement in their organization’s social responsibility projects bolsters the reputation of their business, which in turn improves service quality and fosters trust in their organization [22,91,114].
Social Identity Theory helps explain why employees’ CSR perceptions enhance their views of corporate reputation. When employees recognize that their organization contributes positively to society, they are more likely to associate their self-worth with the organization’s external image. This identification strengthens the belief that the organization is reputable. Additionally, Social Exchange Theory suggests that CSR activities improve perceptions of organizational credibility, as employees see these efforts as signs of integrity and ethical leadership—factors that shape how reputation is constructed internally and externally. An empirical investigation involving 221 employees in the hospitality sector revealed that perceptions of organizational CSR initiatives positively influenced employee work engagement, which subsequently contributed to an increase in CR [115].
The results of this study support these previous findings. Positive CSR perceptions enhance not only the external image of the organization but also strengthen internal loyalty and employee morale. In service-intensive sectors, CR becomes a core factor influencing motivation and service quality.
The third finding highlights the positive effect of CR on employee job performance. This finding confirms that CR is not only a brand element in external markets but also has a significant internal impact on employee motivation and performance [88,116]. Especially in the service sector, an employee’s sense of trust in the institution and their level of identification with the organization are factors that directly affect the quality of service provided. In the study conducted by Almeida and Coelho, it was found that employee performance indicators were significantly higher in hotel businesses with a high CR [88].
Social Identity Theory explains this by emphasizing how reputation fosters psychological attachment, encouraging deeper work engagement. Social Exchange Theory adds that employees interpret a good reputation as a sign of a trustworthy and fair workplace. This fosters reciprocal commitment, leading to greater effort and higher service standards. The current study confirms that companies must not only manage their external reputation but also consider how employees perceive it.
Perhaps the most important finding is that CR mediates the relationship between CSR and employee job performance. This indicates that the effect of CSR on performance occurs largely through employees’ internalization of the organization’s reputation, rather than through CSR itself [117,118].
Social Identity Theory again provides insight, as employees adopt the values and image of organizations they identify with. CSR strengthens reputation, which reinforces self-concept and engagement—both of which lead to improved performance. In terms of Social Exchange Theory, employees perceive reputation as the product of consistent ethical conduct. Feeling aligned with a reputable company encourages mutual trust and motivates higher performance. This dynamic is particularly evident in hotel staff, where service quality hinges on employee attitudes.
Singh and Misra demonstrated the importance of CR in mediating CSR’s impact on organizational performance using a sample of European managers [23]. Particularly in highly competitive service sectors such as five-star hotels, employees’ positive perceptions of their organizations are crucial for service quality and customer experience. González-Rodríguez and colleagues demonstrated that CSR practices are significant for both internal and external stakeholders, as this positive impression fosters a sense of belonging and loyalty to the company, enhancing the company’s CR, which in turn positively affects the overall performance of the company [89].
The results of the current study align with the limited previous research in the hotel sector and demonstrate that CSR practices significantly influence employee performance through CR. These findings empirically confirm that CSR is not only a strategic communication tool for external stakeholders but also an essential institutional element that enhances business performance by strengthening psychological security and fostering a sense of belonging for internal stakeholders, specifically employees.
While interpreting these findings, it is also important to consider the specific characteristics of the five-star hotel context in which the study was conducted. Luxury hotel environments are inherently focused on service quality, brand prestige, and external image. In such settings, employees may be more attuned to their organization’s social reputation and the perceived value of CSR practices. This heightened sensitivity could strengthen the observed effects of CSR and CR on performance. Therefore, while the results offer valuable theoretical and practical insights, their strength and generalizability may be influenced by the prestige-driven nature of the sector. Further studies conducted in other service settings may help verify whether these relationships hold across less reputation-focused industries.
When evaluated from a business innovation perspective, the findings are especially meaningful. Integrating CSR into corporate strategy represents not just a branding effort, but an internal innovation approach that improves processes and strengthens employee performance [119,120]. Especially in the service sector, integrating CSR into the organizational structure fosters a sustainable competitive advantage by enhancing employee commitment, motivation, and service quality.
The results of the study also show that businesses should consider CSR practices not just as a marketing strategy to enhance CR, but also as an internal management tool that improves employee relations and boosts organizational efficiency. Such an approach enables a truly innovative and sustainable organizational transformation by integrating CSR into business processes.
6. Conclusions
This study examined the impact of CSR practices on the job performance of hotel employees, focusing on the mediating role of CR. The findings reveal that CSR perception significantly affects employee performance, both directly and indirectly through CR. This suggests that CSR should be seen as a multidimensional management strategy that enhances intrinsic performance motivation and fosters a positive corporate perception of the external environment.
Especially in the accommodation sector, which requires intensive customer interaction, employees’ positive perceptions of CSR activities increase trust in the institution, enhance organizational commitment, and foster devoted attitudes towards service quality, leading to tangible improvements in business performance. The findings show that CR is not only a reputation element for customers but also serves as an internal value area that strengthens employees’ perceptions of the institution, their motivation, and their commitment to their involvement within its duties. Moreover, the study confirmed that CR plays a mediating role in the relationship between CSR and business/employee performance. This finding shows that employees view the social responsibility activities of their institutions as meaningful not only for the outside world but also for creating internal value and fostering a sense of belonging. This internal psychological effect provided by CSR lays the foundation for an employee profile that demonstrates high performance, develops loyalty to the institution, and contributes in the long term.
As a result, this study shows that CSR is not only a responsibility area for businesses that addresses external stakeholders, but also a strategic internal management tool that affects employee performance through CR. In this respect, CSR practices offer an innovative opportunity for organizational transformation in hotel businesses that want to ensure the sustainability of their processes, enhance employee satisfaction, and gain a competitive advantage.
6.1. Theoretical and Practical Implications
This study offers a nuanced contribution to the organizational behavior domain by systematically analyzing the interconnections between CSR, CR, and employee job performance within service-based institutions, utilizing a comprehensive and multi-layered analytical lens. The current study demonstrates that CSR is not merely a communication tool aimed at external stakeholders; it also represents a sustainable business innovation component with psychological significance for internal stakeholders, such as employees, and is directly linked to their commitment and performance.
From the lens of Social Identity Theory [95] and Social Exchange Theory [70], the findings show that employees who embrace their organization’s CSR activities develop a stronger sense of belonging and motivation, which translates into improved job performance. The study provides empirical evidence supporting the claim that the internalization of CSR practices influences both individual behavior and perceptions of organizational reputation. Accordingly, this research enriches the theoretical application of both SIT and SET in the CSR context.
Incorporating CR as a mediating variable offers a more refined explanation of the CSR–performance link by addressing perceptual and organizational mechanisms, rather than assuming a direct linear connection. This approach sheds light on often overlooked psychological pathways and confirms that CSR influences internal operations as well as external stakeholder engagement.
The study responds to recent scholarly calls [13,16,17,22,96,97] by focusing on the hospitality sector—a high-contact service industry—and exploring the effects of CSR on employee outcomes. The selection of the sample from an area with high customer interaction, such as the hotel sector, enables specific contextual inferences related to the service sector to be drawn, fills the sectoral gaps in CSR research, and responds to the accumulated calls in the literature.
The research findings offer important practical implications, especially for human resources managers, hotel operators, and decision-makers. It has been revealed that employee performance is not only dependent on technical skills or wage policies; it is directly related to how the organization’s social responsibility strategies are perceived by employees and to what extent this perception fosters trust, motivation, and a sense of belonging. These findings show that CSR practices are not merely an external reputation tool but also an element that enhances the effectiveness of internal management systems.
Especially in service sectors such as hotel management, where competition is fierce and customer interaction is high, strengthening CR in the eyes of employees positively impacts outputs like business performance, service quality, and customer satisfaction. In this context, CSR practices should be regarded not only as a brand management tool for external stakeholders but also as a versatile resource to ensure employee loyalty, workforce efficiency, and strategic alignment. Companies should reassess their strategies in this area. They should develop not only visible projects for external stakeholders but also practices that directly affect internal stakeholders, encouraging participation and fostering social benefits.
Examples of such practices include employee volunteering programs, collaborations with local communities, promoting environmentally friendly practices through internal training, and including employees in CSR decision-making processes will be concrete steps that reinforce both motivation and trust in the institution [23,121]. In addition, strengthening internal communication strategies regarding CSR performance will enhance the internal perception dimension of CR by ensuring that employees take greater ownership of these activities. As a result, positioning CSR not only as an external promotional tool but also as a central part of an employee-focused sustainability strategy will increase both employee productivity and organizational reputation.
This study suggests an internal transformation-based strategy for businesses seeking to achieve long-term sustainable outcomes by revealing the indirect impact of CSR on employee performance through CR. It emphasizes that CR creates a unifying and transformative value in this context; it aligns employees with corporate goals and contributes to building organizational cultures that promote social well-being.
The findings of this study, which reveal the impact of CSR on employee performance through CR, demonstrate that businesses must move beyond traditional approaches that focus solely on generating external benefits. The results indicate that CR is not only an external image element but also one of the fundamental building blocks of internal organizational transformation and employee performance enhancement. In this context, it is crucial for businesses aiming for long-term sustainable outcomes to develop holistic approaches that will strengthen CR and strategically align employees with this process [23,39].
In this context, it is crucial to review or develop strategies within both the human resources department and top management regarding the administrative practices of enterprises. In these practices, CR should not be seen solely as a promotional tool for external stakeholders, but also as an “organizational capital” built internally to enhance emotional commitment, motivation, and contribution levels among employees. Therefore, the enterprise should establish transparent communication processes that particularly reinforce employees’ perceptions of CR, actively involve them in internal CSR activities, and make the significance of these activities visible to employees [121,122].
Ultimately, designing this process as an organizational culture transformation will ensure that employees contribute to the organization not only in terms of performance but also in terms of belonging and citizenship behavior. Consequently, internalizing CSR as a strategic management tool and integrating it into employee behavior through CR will enable businesses to achieve their social responsibility goals and build a high-performance culture.
6.2. Limitations and Future Research Directions
The results obtained in this study should be evaluated by considering certain contextual and methodological limitations. Firstly, the study sample is limited to employees working in five-star hotels in Turkey. This situation restricts the generalizability of the findings concerning sectoral, cultural, and geographical aspects; it necessitates comparative testing of the results with studies conducted in different service sectors or countries. Additionally, the collection of data cross-sectionally provided a limited interpretation of the causal relationships between the variables. Therefore, future studies can employ longitudinal data collection designs to clarify cause-and-effect relationships more effectively [123].
Another limitation of the study is that all variables were measured using self-report methods. This may increase the risk of common method bias. Although this effect was controlled for in the analyses, it is recommended that future studies use more objective measurements from multiple data sources (e.g., data from managers or customers) [124].
In addition, the model only examined the mediating role of CR, while other psychological or organizational mediator/moderator variables that could influence the CSR-performance relationship in the business environment were excluded. For example, variables such as organizational support perception, psychological ownership, or leadership styles (such as servant leadership) may be considered elements that can strengthen or weaken this relationship [125]. Accordingly, multivariate models (e.g., serial mediation or moderated mediation) can be utilized in the future to explain the impact of CSR on employee behavior.
Another contextual limitation is directly related to the unique characteristics of the five-star hotel environment. These institutions operate in a prestige-driven and reputation-sensitive sector, where external image and brand value are closely tied to organizational success. In such settings, corporate reputation may play a disproportionately strong role in influencing employee perceptions and performance. As a result, the mediating effect of CR observed in this study could be amplified by the specific demands and values of the luxury hospitality industry. Future research should explore whether similar dynamics are observed in organizations where prestige and brand perception are less central to the business model.
Finally, this study utilized data solely from the employee perspective. However, the effects of CSR are multi-layered, and the perceptions of other stakeholder groups, such as customers, suppliers, and local communities, can also influence performance and CR [111]. Therefore, in future studies, more comprehensive analyses can be conducted by choosing mixed-method research designs that include a multi-stakeholder perspective.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.Y., A.M. and B.C.; methodology, L.S. and I.Y.; formal analysis, L.S. and A.M.; writing—original draft preparation, I.Y., A.M. and B.C.; writing—review and editing, I.Y., L.S. and A.M.; visualization, B.C.; supervision, I.Y. and L.S.; project administration, I.Y. and L.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the World Peace University Ethics Committee. (Decision number: WPU-ETK-2023/14, date of approval: 10 May 2023).
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting this study’s findings are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- George, G.; Merrill, R.K.; Schillebeeckx, S.J. Digital sustainability and entrepreneurship: How digital innovations are helping tackle climate change and sustainable development. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2021, 45, 999–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centobelli, P.; Cerchione, R.; Esposito, E. Pursuing supply chain sustainable development goals through the adoption of green practices and enabling technologies: A cross-country analysis of LSPs. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 153, 119920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Vivanco, A.; Bernardo, M.; Cruz-Cázares, C. Sustainable innovation through management systems integration. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 1176–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Yu, Q. Sustainability-oriented social responsibility and corporate innovation. China J. Account. Res. 2024, 17, 100359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.C.; Chou, L.C.; Chang, T.C.; Darcy, J. The impact of social responsibility on corporate performance: Evidence from Taiwan. Account. Financ. Res. 2017, 6, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garriga, E. Evolution of the business and society field: From a functionalist to a supra-functionalist orientation. In The Routledge Companion to Corporate Social Responsibility; Routledge: London, UK, 2021; pp. 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Aguinis, H.; Villamor, I.; Gabriel, K.P. Understanding employee responses to COVID-19: A behavioral corporate social responsibility perspective. Manag. Res. J. Iberoam. Acad. Manag. 2020, 18, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.S.T.; Tran, H.T. CSR disclosure and firm performance: The mediating role of corporate reputation and moderating role of CEO integrity. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 120, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavas, A. Corporate social responsibility and organizational psychology: An integrative review. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, W.M.; Moon, T.W.; Ko, S.H. How employees’ perceptions of CSR increase employee creativity: Mediating mechanisms of compassion at work and intrinsic motivation. J. Bus. Ethics 2018, 153, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Story, J.S.; Castanheira, F. Corporate social responsibility and employee performance: Mediation role of job satisfaction and affective commitment. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2019, 26, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Di Fan, D.; Zhu, C.J. High-performance work systems, corporate social performance and employee outcomes: Exploring the missing links. J. Bus. Ethics 2014, 120, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, P.A.; Theotokis, A.; Panagopoulos, N.G. Sales force reactions to corporate social responsibility: Attributions, outcomes, and the mediating role of organizational trust. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2010, 39, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Yin, J.; Manzoor, F.; An, M. The impact of corporate social responsibility on firm reputation and organizational citizenship behavior: The mediation of organic organizational cultures. Front. Psychol. 2023, 13, 1100448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, S.; Proença, T.; Ferreira, M.R. Employees perceptions about corporate social responsibility-Understanding CSR and job engagement through meaningfulness, bottom-up approach and calling orientation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A. The Impact of Perceived CSR on Employee Performance and Turnover Intention: An Examination of the Mediating Effects of Organizational Justice and Organization Based Self-Esteem. Master’s Thesis, Singapore Management University, Singapore, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, S.; Bhattacharya, C.B.; Korschun, D. The role of corporate social responsibility in strengthening multiple stakeholder relationships: A field experiment. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2006, 34, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T. Corporate social responsibility and SMEs’ performance: Mediating role of corporate image, corporate reputation and customer loyalty. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 2023, 18, 4565–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axjonow, A.; Ernstberger, J.; Pott, C. The impact of corporate social responsibility disclosure on corporate reputation: A non-professional stakeholder perspective. J. Bus. Ethics 2018, 151, 429–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Frynas, J.G.; Mahmood, Z. Determinants of corporate social responsibility (CSR) disclosure in developed and developing countries: A literature review. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2017, 24, 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. Toward a communality with employees: The role of CSR types and internal reputation. Corp. Reput. Rev. 2020, 23, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.S.; Dash, S.S.; Chakraborty, S.; Kumar, M. Perceived CSR and corporate reputation: The mediating role of employee trust. Vikalpa 2018, 43, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Misra, M. Linking corporate social responsibility (CSR) and organizational performance: The moderating effect of corporate reputation. Eur. Res. Manag. Bus. Econ. 2021, 27, 100139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghian, M.; D’Souza, C.; Polonsky, M. A stakeholder approach to corporate social responsibility, reputation and business performance. Soc. Responsib. J. 2015, 11, 340–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yu, T.R. The impact of corporate social responsibility on employee performance and cost. Rev. Account. Financ. 2015, 14, 262–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, D.E.; Shao, R.; Thornton, M.A.; Skarlicki, D.P. Applicants’ and employees’ reactions to corporate social responsibility: The moderating effects of first?party justice perceptions and moral identity. Pers. Psychol. 2013, 66, 895–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tong, L.; Takeuchi, R.; George, G. Corporate social responsibility: An overview and new research directions: Thematic issue on corporate social responsibility. Acad. Manag. J. 2016, 59, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Swanson, S.R.; Hsu, M.; Chen, X. How does perceived corporate social responsibility contribute to green consumer behavior of Chinese tourists: A hotel context. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2017, 29, 3157–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, K.R.; Zada, M.; Ghani, B.; Ullah, R.; Azim, M.T.; Mubarik, M.S.; Vega-Muñoz, A.; Castillo, D. Linking corporate social responsibility to workplace deviant behaviors: Mediating role of job satisfaction. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 803481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. A Renewed EU Strategy 2011-14 for Corporate Social Responsibility. 2011. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A52011DC0681 (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Coombs, W.T.; Holladay, S.J. Managing Corporate Social Responsibility: A Communication Approach; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Piantoni, G.; Arena, M.; Azzone, G. Innovation ecosystems and Corporate Social Responsibility: Which dynamic capabilities are needed? J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 486, 144594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, X.; Lynes, J. Corporate social responsibility in tourism and hospitality. J. Sustain. Tour. 2018, 26, 1027–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.B. A three-dimensional conceptual model of corporate performance. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1979, 4, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.B. The pyramid of corporate social responsibility: Toward the moral management of organizational stakeholders. Bus. Horiz. 1991, 34, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkington, J. Partnerships from cannibals with forks: The triple bottom line of 21st?century business. Environ. Qual. Manag. 1998, 8, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbreath, J.; Shum, P. Do customer satisfaction and reputation mediate the CSR-FP link? Evidence from Australia. Aust. J. Manag. 2012, 37, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shum, P.K.; Yam, S.L. Ethics and law: Guiding the invisible hand to correct corporate social responsibility externalities. J. Bus. Ethics 2011, 98, 549–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidi, S.P.; Sofian, S.; Saeidi, P.; Saeidi, S.P.; Saaeidi, S.A. How does corporate social responsibility contribute to firm financial performance? The mediating role of competitive advantage, reputation, and customer satisfaction. J. Bus. Res. 2015, 68, 341–350. [Google Scholar]
- Goffi, G.; Masiero, L.; Pencarelli, T. Corporate social responsibility and performances of firms operating in the tourism and hospitality industry. TQM J. 2022, 34, 1626–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, X.; Walmsley, A.; Cogotti, S.; McCombes, L.; Häusler, N. Corporate social responsibility: The disclosure-performance gap. Tour. Manag. 2012, 33, 1544–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Bhatti, S.M.; Naveed, R.T.; Kanwal, S.; Adnan, M. Green sustainability in the hotel sector: The role of CSR, intrinsic green motivation, and personal environmental norms. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0295850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Kim, Y. An investigation of green hotel customers’ decision formation: Developing an extended model of the theory of planned behavior. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2010, 29, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wut, T.M.; Xu, B.; Wong, H.S.M. A 15-year review of “corporate social responsibility practices” research in the hospitality and tourism industry. J. Qual. Assur. Hosp. Tour. 2022, 23, 240–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.L. Why would corporations behave in socially responsible ways? An institutional theory of corporate social responsibility. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2007, 32, 946–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, S.; Grappi, S.; Bagozzi, R.P. Corporate social responsibility and cause-related marketing: An overview. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2016, 18, 98–119. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, C.C.; Lu, C.S.; Chang, S.C. Evaluating corporate social responsibility programs in the hotel industry. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2015, 32, 616–633. [Google Scholar]
- Boluk, K. Using CSR as a tool for development: An investigation of the fair hotels scheme in Ireland. J. Qual. Assur. Hosp. Tour. 2013, 14, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Seo, K.; Sharma, A. Corporate social responsibility and firm performance in the airline industry: The moderating role of oil prices. Tour. Manag. 2013, 38, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Lee, S. Effects of different dimensions of corporate social responsibility on corporate financial performance in tourism-related industries. Tour. Manag. 2011, 32, 790–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmaki, A.; Pappas, N.; Kvasova, O.; Stergiou, D.P. Hotel CSR and job satisfaction: A chaordic perspective. Tour. Manag. 2022, 91, 104526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Rhou, Y.; Topcuoglu, E.; Kim, Y.G. Why hotel employees care about Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Using need satisfaction theory. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 87, 102505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozes, M.; Josman, Z.; Yaniv, E. Corporate social responsibility organizational identification and motivation. Soc. Responsib. J. 2011, 7, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, H.; Kim, J.H. Corporate social responsibility and hotel employees’ organizational citizenship behavior: The roles of organizational pride and meaningfulness of work. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milkovich, G.T.; Boudreau, J.W. Personnel/Human Resource Management; Irwin: Huntersville, NC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Lho, L.H.; Han, H. Corporate social responsibility (environment, product, diversity, employee, and community) and the hotel employees’ job performance: Exploring the role of the employment types. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2022, 29, 1825–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgunduz, Y. The influence of self-esteem and role stress on job performance in hotel businesses. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2015, 27, 1082–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Song, H.J.; Lee, H.M.; Lee, S.; Bernhard, B.J. The impact of CSR on casino employees’ organizational trust, job satisfaction, and customer orientation: An empirical examination of responsible gambling strategies. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2013, 33, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, J. Corporate social responsibility, employee engagement, well-being and the task performance of frontline employees. Manag. Decis. 2021, 59, 2040–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.M.; Park, S.; Lee, H.J. Employee perception of CSR activities: Its antecedents and consequences. J. Bus. Res. 2013, 66, 1716–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korschun, D.; Bhattacharya, C.B.; Swain, S.D. Corporate social responsibility, customer orientation, and the job performance of frontline employees. J. Mark. 2014, 78, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.; Kudert, S. Multi-foci CSR perceptions, procedural justice and in-role employee performance: The mediating role of commitment and pride. Hum. Resour. Manag. J. 2017, 27, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Majid, A.; Qudratullah, H.; Ullah, R.; Khattak, A. Participation of hotel managers in CSR activities in developing countries: A defining role of CSR orientation, CSR competencies, and CSR commitment. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2021, 28, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, I.; Hur, W.M.; Kang, S. Employees’ perceptions of corporate social responsibility and job performance: A sequential mediation model. Sustainability 2016, 8, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, W.M.; Moon, T.W.; Choi, W.H. The role of job crafting and perceived organizational support in the link between employees’ CSR perceptions and job performance: A moderated mediation model. Curr. Psychol. 2021, 40, 3151–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajfel, H.; Turner, J.C. An integrative theory of intergroup conflict. In The Social Psychology of Intergroup Relations; Austin, W.G., Worchel, S., Eds.; Brooks/Cole: Monterey, CA, USA, 1979; pp. 33–47. [Google Scholar]
- Hogg, M.A.; Terry, D.J.; White, K.M. A tale of two theories: A critical comparison of identity theory with social identity theory. Soc. Psychol. Q. 1995, 58, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornsey, M.J. Social identity theory and self-Categorization theory: A historical review. Soc. Personal. Psychol. Compass 2008, 2, 204–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, J.E.; Dukerich, J.M.; Harquail, C.V. Organizational images and member identification. Adm. Sci. Q. 1994, 39, 239–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, P.M. Exchange and Power in Social Life; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1964; pp. 1–352. [Google Scholar]
- Abdou, A.H.; Hassan, T.H.; Salem, A.E.; Albakhit, A.I.; Almakhayitah, M.Y.; Salama, W. The nexus between environmentally sustainable practices, green satisfaction, and customer citizenship behavior in eco-friendly hotels: Social exchange theory perspective. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral Luis, M.B. Living Up to Expectations: Corporate Reputation and Sustainable Competitive Advantage (November 2012). NYU Working Paper No. 2451/31643. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2172651 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Lai, C.S.; Chiu, C.J.; Yang, C.F.; Pai, D.C. The effects of corporate social responsibility on brand performance: The mediating effect of industrial brand equity and corporate reputation. J. Bus. Ethics 2010, 95, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, L. Corporate reputation: Our role in sustaining and building a valuable asset. J. Advert. Res. 2005, 45, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Iuklanov, D. Antecedents and consequences of corporate reputation: A dataset. Data Brief 2023, 48, 109079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raithel, S.; Schwaiger, M. The effects of corporate reputation perceptions of the general public on shareholder value. Strateg. Manag. J. 2015, 36, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Yong Park, J.; Kim, J. Cross-cultural examination of the relationships among firm reputation, e-satisfaction, e-trust, and e-loyalty. Int. Mark. Rev. 2008, 25, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.; Thomsen, S. The Impact of Corporate Reputation on Performance:: Some Danish Evidence. Eur. Manag. J. 2004, 22, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, M. Signaling in retrospect and the informational structure of markets. Am. Econ. Rev. 2002, 92, 434–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, K.F. Recipes for customer loyalty: A cross-country study of the hotel industry. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2021, 33, 1892–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.S.; Pal, S. Customers’ perception of service quality and its impact on reputation in the hospitality industry. Int. J. Manag. (IJM) 2020, 11, 2954–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Huang, S.; van der Veen, R.; Chen, X. Corporate social responsibility, corporate reputation, customer emotions and behavioral intentions: A structural equation modeling analysis. J. China Tour. Res. 2014, 10, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, P.; Assaker, G. Examining the antecedents and effects of hotel corporate reputation on customers’ loyalty and citizenship behavior: An integrated framework. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2022, 31, 640–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assiouras, I.; Skourtis, G.; Giannopoulos, A.; Buhalis, D.; Koniordos, M. Value co-creation and customer citizenship behavior. Ann. Tour. Res. 2019, 78, 102742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Lyu, S.O. Relationships among green image, consumer attitudes, desire, and customer citizenship behavior in the airline industry. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2020, 14, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Yin, X.; Lee, G. The effect of CSR on corporate image, customer citizenship behaviors, and customers’ long-term relationship orientation. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 88, 102520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauermann, H. Fire in the belly? Employee motives and innovative performance in start-ups versus established firms. Strateg. Entrep. J. 2018, 12, 423–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.D.G.M.C.; Coelho, A.F.M. The antecedents of corporate reputation and image and their impacts on employee commitment and performance: The moderating role of CSR. Corp. Reput. Rev. 2019, 22, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rodríguez, M.R.; Martín-Samper, R.C.; Köseoglu, M.A.; Okumus, F. Hotels’ corporate social responsibility practices, organizational culture, firm reputation, and performance. J. Sustain. Tour. 2019, 27, 398–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, P.; Pérez, A.; Del Bosque, I.R. CSR influence on hotel brand image and loyalty. Acad. Rev. Latinoam. De Adm. 2014, 27, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilvand, M.R.; Nasrolahi Vosta, L.; Kazemi Mahyari, H.; Khazaei Pool, J. Social responsibility influence on customer trust in hotels: Mediating effects of reputation and word-of-mouth. Tour. Rev. 2017, 72, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, E.; Bruno, J.M.; Sarabia-Sanchez, F.J. The impact of perceived CSR on corporate reputation and purchase intention. Eur. J. Manag. Bus. Econ. 2019, 28, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Pan, Y.; Chen, X. Corporate social responsibility: Findings from the Chinese hospitality industry. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2017, 34, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, C. Corporate social responsibilities, consumer trust and corporate reputation: South Korean consumers’ perspectives. J. Bus. Res. 2014, 67, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajfel, H.; Turner, J.C. The Social Identity Theory of Intergroup Behaviour. In Psychology of Intergroup Relations, 2nd ed.; Worchel, S., Austin, W., Eds.; Nelson-Hall: Chicago, IL, USA, 1985; pp. 7–24. [Google Scholar]
- González-Rodríguez, M.R.; Díaz-Fernández, M.C.; Shi, F.; Okumus, F. Exploring the links among corporate social responsibility, reputation, and performance from a multi-dimensional perspective. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2021, 99, 103079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, L.Y.; Leung, A.S. Corporate social responsibility, firm reputation, and firm performance: The role of ethical leadership. Asia Pac. J. Manag. 2014, 31, 925–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, M.; Koo, D. From teamwork to psychological well-being and job performance: The role of CSR in the workplace. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2022, 34, 3764–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, N.G.; Rapp, A.A.; Vlachos, P.A. I think they think we are good citizens: Meta-perceptions as antecedents of employees’ reactions to corporate social responsibility. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 2781–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boğan, E. Otel çalışanlarının kurumsal sosyal sorumluluk algısının işveren çekiciliği ve duygusal bağlılık üzerine etkisi: Kurumsal itibarın aracılık rolü. Alanya Akad. Bakış 2020, 4, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, J.; Pruyn, A.; de Jong, M. Employee identification before and after an internal merger: A longitudinal analysis. J. Occup. Organ. Psychol. 2009, 82, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkman, B.L.; Rosen, B. Beyond Self- Management: Antecedents and Consequences of Team Empowerment. Acad. Manag. J. 1999, 42, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigler, T.H.; Pearson, C.M. Creating an empowering eulture: Examining the relationship between organizational culture and perceptions of empowerment. J. Qual. Manag. 2000, 5, 27–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çöl, G. Algılanan Güçlendirmenin İşgören Performansı Üzerine Etkileri. Doğuş Üniversitesi Derg. 2008, 9, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabacı, N. Otel Işletmelerinde Çalışma Yaşam Kalitesinin iş Performansına Etkisinde Yönetici Desteğinin Rolü. Master’s Thesis, Nevşehir Hacı Bektaş Veli Üniversitesi, Nevşehir, Türkiye, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Podsakoff, N.P.V. Common Method Biases in Behavioral Research: A Critical Review of the Literature and Recommended Remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sürücü, L.; Şeşen, H.; Maslakçı, A. Regression, Mediation/Moderation, and Structural Equation Modeling with SPSS, AMOS, and PROCESS Macro; Livre de Lyon: Lyon, France, 2023; pp. 1–420. [Google Scholar]
- Sürücü, L.; Maslakçı, A.V. Validity and reliability in quantitative research. Bus. Manag. Stud. Int. J. 2020, 8, 2694–2726. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables And Measurement Error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–507. [Google Scholar]
- Aguinis, H.; Glavas, A. What we know and don’t know about corporate social responsibility: A review and research agenda. J. Manag. 2012, 38, 932–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.K.F.; Kim, S.; Hwang, Y. Effects of perceived corporate social responsibility (CSR) performance on hotel employees’ behavior. Int. J. Hosp. Tour. Adm. 2022, 23, 1145–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, H.; Morrison, A.M. The impacts of corporate social responsibility on organization citizenship behavior and task performance in hospitality: A sequential mediation model. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2019, 31, 2582–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Kim, D.Y. The impacts of corporate social responsibility, service quality, and transparency on relationship quality and customer loyalty in the hotel industry. Asian J. Sustain. Soc. Responsib. 2016, 1, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, J.; Putra, Z.D.P. Demographic factors, corporate social responsibility, employee engagement and corporate reputation: A perspective from hotel industries in Indonesia. Chin. Bus. Rev. 2014, 13, 509–520. [Google Scholar]
- Arikan, E.; Kantur, D.; Maden, C.; Telci, E.E. Investigating the mediating role of corporate reputation on the relationship between corporate social responsibility and multiple stakeholder outcomes. Qual. Quant. 2016, 50, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, B.N.; Tung, D.D.; Huan, D.D. The contribution of corporate social responsibility perception on job performance: Does corporate reputation matter? Bus. Theory Pract. 2022, 23, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fu, Y.; Qiu, H.; Moore, J.H.; Wang, Z. Corporate social responsibility and employee outcomes: A moderated mediation model of organizational identification and moral identity. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ramírez, R.; Gasco, J.; Llopis, J. Digitalisation and sustainability: Their role in corporate social responsibility through innovation. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2024. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, G.; Tsai, F.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, C.H. The effects of corporate social responsibility on service innovation performance: The role of dynamic capability for sustainability. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavas, A. Corporate social responsibility and employee engagement: Enabling employees to employ more of their whole selves at work. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Farooq, O.; Jasimuddin, S.M. Employees response to corporate social responsibility: Exploring the role of employees’ collectivist orientation. Eur. Manag. J. 2014, 32, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Podsakoff, N.P. Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2012, 63, 539–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.J.; van Witteloostuijn, A.; Eden, L. Common method variance in international business research. In Research Methods in International Business; Eden, L., Nielsen, B.B., Verbeke, A., Eds.; JIBS Special Collections; Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 385–398. [Google Scholar]
- Afsar, B.; Cheema, S.; Javed, F. Activating employee’s pro-environmental behaviors: The role of CSR, organizational identification, and environmentally specific servant leadership. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2018, 25, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).