Abstract
Grey target decision making is a useful tool to solve multiple-criteria decision-making problems. Decision makers’ expected information can reflect their preferences and play an important role in decision process. In this paper, a new grey target group decision-making method considering decision makers’ expected information is proposed. First, based on the decision makers’ expected information, a novel method to obtain synthetical criteria weights combining subjective weights and objective weights is presented. Furthermore, a new way to determine decision makers’ weights is put forward. Moreover, on the basis of the decision matrix, criteria weights, and decision makers’ weights, a ranking method for all alternatives is proposed. Finally, a case for maintaining a precise instrument in a nursing home is used to illustrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
1. Introduction
Multi-criteria group decision making (MCGDM) is based on the knowledge and experience of multiple decision makers, and selects the optimal alternative according to their opinions on alternatives with respect to different criteria [1,2,3,4]. In recent years, MCGDM methods have been widely used in various fields, such as supplier selection [5,6], service quality evaluation [7,8], and risk management [9,10]. However, in traditional decision-making methods, the way to obtain the criteria weights is usually by using either subjective methods or objective ones, which may lead to inaccurate decision results. Therefore, it is meaningful to study the methods to obtain synthetical criteria weights combining subjective and objective information for decision makers.
In the actual decision-making process, when the decision problem is complex and involves subjective criteria, it is usually difficult for decision makers to use crisp numbers to provide evaluation information on the performance of alternatives under the criteria. It may be necessary for decision makers to use linguistic terms such as “high” and “low” to describe subjective criteria [11]. Scholars have conducted many valuable studies on this issue. Zadeh [12] proposed the concept of linguistic term sets, which can reflect the fuzzy information of decision makers using different linguistic terms. Based on the concept of linguistic term set, Rodriguez et al. [13,14] proposed the definition of hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set (HFLTS) to express the hesitation of decision makers. However, the importance of each linguistic term is assumed to be the same in HFLTSs, which overlooks the possibility that decision makers may have different preferences for various linguistic terms during the evaluation process. To address this issue, Pang et al. [15] extended the concept of HFLTS and introduced the concept of probabilistic linguistic term set (PLTS). Compared with the HFLTS, the PLTS can better characterize the uncertainty and fuzziness of the decision maker’s opinions. Currently, research on the application of PLTS in MCGDM has become highly abundant. Guo et al. [16] proposed an improved TODIM method based on PLTSs and applied this method to evaluate emergency logistics suppliers. Wang et al. [17] proposed a decision-making method that can handle collaborative emergency problems based on multi-granular PLTSs. Cui et al. [18] proposed a non-personalized product recommendation method based on PLTSs.
Grey system theory is a mathematical tool to handle problems involving incomplete information, and it has been widely applied in many complex decision-making scenarios. As a novel decision-making tool, the idea of the grey target decision method is to transform the decision problem into a relative distance measurement between the ideal solution and the alternatives [19]. In recent years, there have been many studies on target decision-making methods. Liu [20] proposed a weighted grey target decision-making method that considers both on-target and off-target situations in the target effect of the traditional grey target decision method. Dang et al. [21] proposed a normalization method for interval numbers and proposed a grey target decision method based on interval numbers. Wang et al. [22] proposed an improved grey target decision method based on weighted Mahalanobis distance, which takes into account the correlation between criteria. Xiao et al. [23] proposed a spider-web–grey target method based on a subjective–objective weighting approach. Liu et al. [24] proposed a grey target decision-making method considering group consensus and risk preference. Liu et al. [25] designed a generalized grey target decision-making method and proposed a distance measurement method for generalized grey numbers. Li et al. [26] proposed a weighted grey target decision-making method and applied it to address the selection problem of semiconductor equipment maintenance plans. Huang et al. [27] proposed a grey target group decision-making method based on veto function and unified effect measurement, and applied the method to the supplier selection problem of official vehicles. Interval grey numbers can be used to represent the decision maker’s expectation information for criteria, which reflect their evaluation information and experience level. However, most of the existing grey theory studies do not consider the impact of the decision maker’s expectations.
Motivated by the PLTS and the grey target decision-making method, the research motivations of this paper are outlined as follows.
(1) In MCGDM problems, criteria weights are vitally important to the ranking results for alternatives. Traditional methods to determine the criteria weights are subjective, using some subjective methods such as analytic hierarchy process (AHP), or objective, utilizing the decision matrices provided by decision makers. Using these two methods alone will lead to low robustness.
(2) Decision makers’ expected information can reflect their preferences for the decision-making problems. Traditional MCGDM methods rarely take the expected information into account.
In this paper, a novel probabilistic linguistic grey target group decision-making method considering the decision makers’ expected information is proposed. The contributions of this paper can be summarized as follows:
(1) Establish a new frame for determining criteria weights considering the subjective weights and objective weights based on decision makers’ expected information.
(2) Propose a two-stage decision-making process including obtaining the criteria weights according to decision makers’ expected information and ranking method using PLTSs based on the new way to obtain the decision makers’ weights.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the basic concepts of interval grey number, PLTS, and grey target decision-making method. In Section 3, a novel grey target decision-making method considering the decision makers’ expected information is proposed. Section 4 demonstrates our proposed method through a case study for evaluating the maintenance strategies for precision instruments in nursing homes. Finally, conclusions and future research are presented in Section 5.
2. Preliminaries
In this section, we will review some basic definitions and operational rules for interval grey number, PLTS, and grey target decision-making method.
2.1. Interval Grey Number
Grey number, as a key factor of grey system, is usually defined as the number that we only know its value range lacking the information of exact value.
Definition 1
([28]). An interval grey number can be defined as .
Definition 2
([28]). Let be an interval grey number. If , then degenerates into a crisp number .
Definition 3
([28]). Let be an interval grey number; the core of can be defined as .
Definition 4
([29]). Let and be two interval grey numbers; the following operational rules hold
- (1)
- (2)
- (3)
- (4)
2.2. Probabilistic Linguistic Term Set
Linguistic terms, such as “good” and “poor”, are usually used to express the preference of the decision maker. To address the issue of the hesitance of the decision maker, the definition of PLTS was proposed by Pang in 2016. Probabilistic information and linguistic terms are both considered in probabilistic linguistic term set, which can be more flexible to cope with uncertain information than traditional linguistic terms.
Definition 5
([15]). Let be a linguistic term set, where is a positive number; then, a probabilistic linguistic term set on can be defined as
where is the linguistic term with the probability , and is the number of all elements in .
Definition 6
([15,30]). Let be a probabilistic linguistic term set; then, the score function, deviation degree, and hesitancy degree of are, respectively, defined as follows
where is the subscript of , and .
Based on Definition 6, we can compare arbitrary two PLTSs as follows.
Let and be two arbitrary PLTSs; then
- (1)
- If , then
- (2)
- If , then
- (i)
- If , then
- (ii)
- If , then
- (a)
- If , then
- (b)
- If , then .
2.3. Grey Target Decision-Making Method
The grey target decision-making method is a useful tool to select or rank the alternatives. The bullseye is the key part in grey target decision-making method.
Let the alternative set be , the criterion set be , and the evaluation matrix be , where (;) indicates the evaluation value for alternative with respect to criterion .
To obtain the bullseye of the grey target decision-making problem, three types of criteria should be considered: benefit type, cost type, and fixed type.
If the criterion is benefit type, then set ;
If the criterion is cost type, then set ;
If the criterion is fixed type, then set .
Therefore, the bullseye can be defined as .
3. A Novel Grey Target Decision-Making Method Considering the Decision Makers’ Expected Information
3.1. Decision-Making Problem Description
Considering a group decision-making problem, the alternative set is and the criterion set is . The criteria weights are satisfying and (). The decision-maker (expert) set is and the weights of the decision makers are being subjected to and ().
For decision maker (), two types of information should be considered. The first type of information is the expected information, which can embody his/her expected value for the decision-making problem for each criterion. This information can use an expected-value vector to describe the criterion, where is an interval grey number and indicates the expected value of criterion for decision maker . The second type of information is the evaluation information for all the alternatives, using a probabilistic linguistic information decision matrix for expression, where is a PLTS and indicates the evaluation for alternative under the criterion .
3.2. Grey Target Decision-Making Method Considering the Decision Makers’ Expected Information
- (1)
- Obtaining the criteria weights
For a multiple criteria decision-making problem, criteria weights reflect the preferences of decision makers. Subjective weights, objective weights, and synthetical weights are three types of common weights [31]. To embody the experiences of decision makers and the objective information, in this section we will propose a new method of obtaining criteria weights by combining the subjective weights and objective weights, which can reduce the randomness [32]. The AHP method can measure the interrelationships of different criteria, and it performs well in dealing with the problem of non-transitivity in decision making. Therefore, to determine the subjective weights, we will use the AHP method [33]. Entropy is a useful tool to solve the problems of obtaining criteria weights [34]. To determine the objective weights, an entropy-based method will be used in this paper.
For the subjective criteria weights, a decision-maker groups need to express their opinions for the relative importance of criteria using a judgement matrix , where indicates the relative importance for criterion in contrast to . Based on the AHP method, we can obtain the subjective weights .
For the objective weights, recall that the elements of the expected-value vector are the interval grey numbers. Therefore, to use the entropy method, we firstly transform the interval grey numbers to crisp numbers using the core based on Definition 3.
Because there are different three types of criteria, a standardization process for the interval grey numbers should be established. Based the idea of the grey target decision-making method [35], we propose a new method of standardization process.
The core of expected-value vector of decision maker () can be computed as , where .
There are usually differences in the significance and magnitude of criteria values depending on the type of the criteria. Therefore, we need to standardize the criteria to make them comparable to each other. The standardized core of can be computed as follows.
Here, is the expected value for criterion , and indicates the maximum tolerance value.
Considering the core of expected-value vectors of all decision makers, the entropy for criterion can be calculated as
For each criterion, the proportion of entropy in the overall data indicates the degree of disorganization. The entropy value quantifies the contribution of each criterion to the decision. The smaller the entropy value, the greater the weight. The objective criterion weight for can be computed as
The objective criteria weights vector is .
The synthetical criteria weights based on the subjective and objective criteria weights can be computed as , where (, , ).
In the following part, we will determine the values of and .
Let be the standardized core expected-value matrix for all criteria, and be the matrix of subjective and objective criteria weights.
The key to determine the coefficients is making the criteria weights easily distinguishable and helping to enhance the gap between alternatives. Here, we simplify the model by applying the concept of the deviation matrix. The deviation matrix is
Then, compute the maximum eigenvalue of matrix and its corresponding standardized eigenvector .
- (2)
- Obtaining the decision makers’ weights
The mean of standardized core expected values reflects the overall view on the criteria for all decision makers. To obtain the decision makers’ weights, we compute the average standardized core expected value for criterion as
Then, the average standardized core expected vector is , which can be seen as a collective opinion about the criteria. If a decision maker is close to the collective opinion, then he/she is gregarious and should gain more weights. Based on the idea and Euclidean distance [36], we can compute the decision-maker weight () as follows.
- (3)
- Decision process and ranking alternatives
The previous analysis is based on the expected-value vectors of all decision makers to obtain the criteria weights and decision makers’ weights . For the decision matrix (), because the element is a PLTS, we need to transform it to a crisp number. An effective value is proposed to express the value of PLTS considering score function, deviation degree, and hesitancy degree.
The effective value can be computed as
Based on the criteria weights and decision makers’ weights , we can compute the comprehensive value for alternative () as
For any two alternatives and , if , then .
The main decision process of the grey target decision-making method considering the decision-maker expected values can be concluded as follows.
Step 1. Obtain the expected-value vector and decision matrix ().
Step 2. Determine the subjective criteria weights using AHP as .
Step 3. Compute the objective criteria weights using Equations (6) and (7) as .
Step 4. Determine the parameters , , and obtain synthetical criteria weights .
Step 5. Obtain the decision makers’ weights using Equations (8) and (9).
Step 6. Compute the comprehensive value for alternative () and rank all the alternatives.
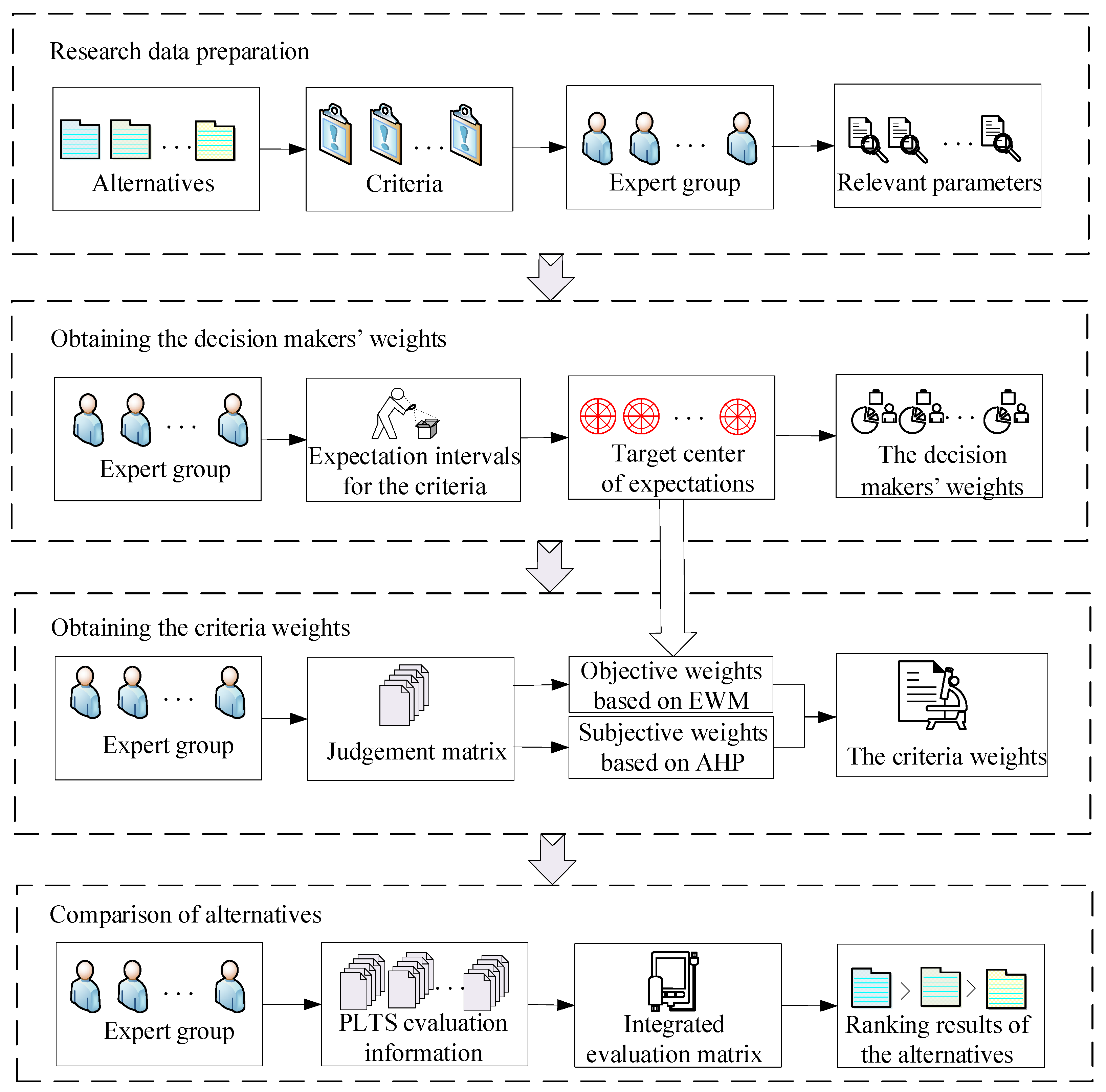
The flowchart of the grey target decision-making method considering the decision-maker expected information is as follows (Figure 1).
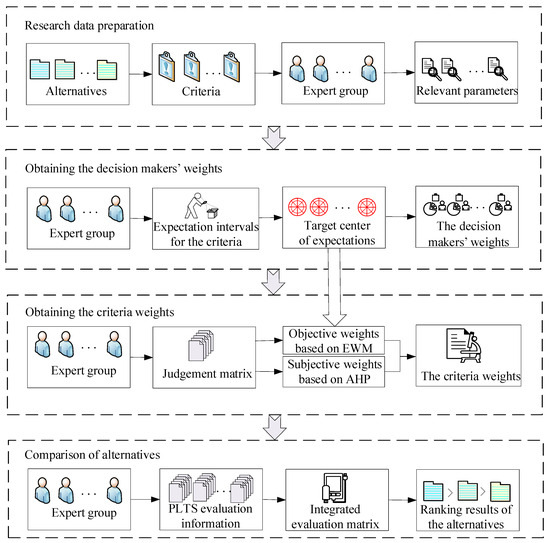
Figure 1.
The flowchart of grey target decision-making method considering the decision-maker expected information.
4. Case Study
4.1. Case Description
The ambulatory cardiac monitoring system is a medical diagnostic device that can be utilized to detect cardiac activity in the elderly, which is widely used in nursing homes. A nursing home needs to maintain an ambulatory cardiac monitoring system. There are four maintenance strategies: , , , . To reduce the cost of risk occurrence and improve the benefit of risk treatment, this nursing home invites five experts , , , , to evaluate the 4 maintenance strategies. The four criteria are security maintenance cost (, cost type, thousand dollar), safety maintenance time (, cost type, hour), risk maintenance efficiency (, benefit type, percent) and the service time of equipment (, fixed type, hour). Five experts provide the expected interval grey number of the criteria based on their knowledge and experience. The expected-value vectors of the decision makers are
The experts evaluate the alternatives according to their expected-value vectors. The decision matrices for the decision makers , , , , are
4.2. Decision Process
The standardized expected-value vectors can be computed as
The judgement matrix and subjective criteria weights are shown as Table 1.

Table 1.
The judgement matrix and subjective criteria weights.
The objective criteria weights are . Then, the synthetical criteria weights .
The decision makers’ weights are .
The comprehensive values for alternatives are
Therefore, the ranking results are .
4.3. Comparison Analysis
To illustrate the effectiveness of our method, we compare our method with other traditional decision-making methods, including the TOPSIS method [37], VIKOR method [38], grey incidence method [39] and modified VIKOR method [40]. The ranking results of these methods can be seen in Table 2.

Table 2.
Ranking results of traditional methods and our proposed method.
As can be seen from Table 2, the best alternatives of all methods are same, but the ranking results are different. The reason for the difference lies in the fact that the criteria weights are different in the methods. The criteria weights reflect the preferences of decision makers for the criteria. Traditional methods use the objective criteria weights, ignoring the experiences of decision makers. Specifically, utilizing the methodology of reference [40] to calculate the case, the comprehensive-values difference between the optimal and the second alternative is only 0.036. This indicates that smaller parameter changes have the potential to change the ranking of the results. Our proposed method takes into account not only the decision matrices of decision makers but also their subjective judgments, which will hold high robustness. Furthermore, our method is based on the idea of grey target decision making, which will make the decision results reasonable. Finally, in our method, three types of criteria are considered, which conforms to the actual situation of decision making.
The basis for the proposed model is the grey target decision-making method. In order to obtain the criteria weights, experts (decision makers) should give their expected evaluations for the criteria. Our proposed method uses the information of expected evaluations to establish a method to determine the criteria weights. In many cases, the experts usually use some uncertain values such as interval grey numbers to express their expected evaluations rather than crisp numbers. The advantages of our method can be concluded as follows:
- (1)
- Keeping the robustness of the results for obtaining criteria weights
Our method uses the grey target decision-making idea to obtain the criteria weights based on experts’ expected evaluations. In traditional decision-making methods using decision matrices, the results of the criteria are determined only by the information of the matrices. If we add a new alternative, the results of criteria weights may change. Our method uses the experts’ expected evaluations, and this will ensure the robustness of results, which is a key factor in obtaining a reasonable decision result.
- (2)
- Reflecting the preferences of experts and making the results of obtaining criteria weights reasonable
The traditional methods of obtaining criteria weights are based on the decision matrices, which will result in the criteria weights having no relation to the preferences of experts. This will lead to the drawback that different decision makers will make a same decision result. Our method can reflect the preferences of experts based on their expected evaluations and make the results of obtaining criteria weights reasonable.
5. Conclusions
In this study, a new grey target decision-making method is presented considering the decision makers’ expected information. Two types of information are considered: (1) decision makers’ expected values, which are expressed in interval grey numbers; (2) evaluation information for alternatives with respect to each criterion, which is a form of probabilistic linguistic term set. To improve the robustness of determining the criteria weights, we design a novel mechanism combining AHP method and entropy method. Based on the grey target idea and decision makers’ expected information, we propose a method to compute the decision makers’ weights. The effective value, considering score function, deviation degree, and hesitancy degree, is used to rank the alternatives. Finally, a case study and some comparisons with four traditional methods are presented to illustrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
Although this paper proposes a new and effective grey target decision-making method, some issues are not considered in this paper, which will be the direction of further research.
(1) Machine learning is a useful tool to solve many decision problems and can sort alternatives. The machine learning method can be used to identify the factors that may affect the change in weights in the grey target decision model.
(2) A consensus reaching process (CRP) is very important for MCGDM. Decision makers will develop trust relationships and modify their evaluations while interacting with others. Thus, the issue of how to develop a CRP in the grey target decision model should be given great importance in future studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.L.; methodology, P.L.; writing—original draft preparation, C.Z.; supervision, P.L.; funding acquisition, P.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Social Science Foundation of China (No. 22AGL032).
Data Availability Statement
All data presented in this article. Further inquiries can contact the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kandakoglu, M.; Walther, G.; Ben Amor, S. The use of multi-criteria decision-making methods in project portfolio selection: A literature review and future research directions. Ann. Oper. Res. 2024, 332, 807–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wei, C. Consensus reaching in multi-criteria social network group decision making: A stochastic multicriteria acceptability analysis-based method. Inf. Fusion 2023, 97, 101825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, P.; Wei, C. Social network group decision-making method based on stochastic multi-criteria acceptability analysis for probabilistic linguistic term sets. Inf. Sci. 2024, 681, 121269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Pedrycz, W. An incremental preference elicitation-based approach to learning potentially non-monotonic preferences in multi-criteria sorting. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2024, 323, 553–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailiang, Z.; Khokhar, M.; Islam, T.; Sharma, A. A model for green-resilient supplier selection: Fuzzy best–worst multi-criteria decision-making method and its applications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 54035–54058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Zhu, Q.; Sarkis, J. Circular economy and circularity supplier selection: A fuzzy group decision approach. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 62, 2307–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Gupta, N.; Matharu, M.; Khan, M.F. Sustainable E-service quality in tourism: Drivers evaluation using AHP-TOPSIS technique. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xu, Z.; Liu, J.; Wei, C. Social network group decision-making for probabilistic linguistic information based on GRA. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 175, 108861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi-Ul-Shan, P.; Bashiri, M.; Kamal, M.M.; Mangla, S.K.; Tjahjono, B. An analysis of fuzzy group decision-making to adopt emerging technologies for fashion supply chain risk management. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2024, 71, 8469–8487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfani, A.; Tavakolan, M. Risk evaluation model of wind energy investment projects using modified fuzzy group decision-making and monte carlo simulation. Arthaniti J. Econ. Theory Pract. 2023, 22, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xu, Z.; Wei, C.; Bai, Q.; Liu, J. A novel PROMETHEE method based on GRA-DEMATEL for PLTSs and its application in selecting renewable energies. Inf. Sci. 2022, 589, 142–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning-III. Inf. Sci. 1975, 9, 43–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.M.; Martinez, L.; Herrera, F. Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2011, 20, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.M.; Martínez, L.; Herrera, F. A group decision making model dealing with comparative linguistic expressions based on hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. Inf. Sci. 2013, 241, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Q.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z. Probabilistic linguistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision making. Inf. Sci. 2016, 369, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.X.; Yang, Y.X.; He, Z.F. Evaluation of emergency logistics suppliers based on the improved TODIM method based on probabilistic linguistic term sets. Oper. Res. Manag. Sci. 2022, 31, 196–203. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liang, X.D.; Li, X.Y.; Luo, P. Collaborative emergency decision-making for public health events: An integrated BWM-TODIM approach with multi-granularity extended probabilistic linguistic term sets. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 144, 110531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.S.; Wei, M.; Che, L.B.; Liu, J.D.; Wang, E.W. Research on the non-personalized recommendation algorithm based on probabilistic linguistic term sets. J. Syst. Sci. Math. Sci. 2023, 43, 2990–3010. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.L. Grey Control System; Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press: Wuhan, China, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.F. The Grey System Theory and Its Application; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, Y.G.; Liu, S.F.; Liu, B. Study on the multi-attribute decision model of grey target based on interval number. Eng. Sci. 2005, 7, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.X.; Dang, Y.G.; Yang, H. Improvements on decision method of grey target. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2009, 31, 2634–2636. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Zhang, Q.J. Evaluation of rock burst level based on combination weighting-cobweb grey target model. Min. Res. Dev. 2024, 44, 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Huang, Z.H.; Forrest, J.Y.L. A multiobjective super conflict grey target negotiation consensus approach. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2024, 54, 3934–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.X.; Liu, S.F.; Jiang, S.Q. Study on the expansion of bidirectional projection grey target decision-making model based on general grey number. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2019, 39, 776–782. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Liu, S.F. Grey target decision model for two-stage equipment maintenance strategy selection. Control Decis. 2023, 38, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Miao, J.; Li, Q. A vetoed multi-objective grey target decision model with application in supplier choice. J. Grey Syst. 2022, 34, 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.F.; Fang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Forrest, J. General grey numbers and their operations. Grey Syst. Theory Appl. 2012, 2, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.F.; Fang, Z.G.; Xie, N.M. Algorithm rules of interval grey numbers based on the “Kernel” and the degree of greyness of grey numbers. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2010, 32, 313–316. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, X.L.; Pan, Y.H. Importance degree determination approach for product service system modules based on user experience. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2020, 26, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D.L.; Wang, Z.; Ren, L.W.; Zhang, J.S. Evaluation of application maturity of intelligent construction based on combinatorial empowerment-cloud model. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2024, 24, 8239–8247. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Xia, J.H. An optimal weights combination method considering both subjective and objective weight information. Math. Pract. Theory 2007, 37, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. How to make a decision: The analytic hierarchy process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1990, 48, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, A.P.; Ma, X.J.; Cheng, Z.N.; Zhang, J.W.; Hou, Y.X. Rated load state performance assessment and analysis of ultra-supercritical coal-fired power plant. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2024, 46, 4579–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.D.; Hu, M.L.; Yang, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.W. Grey target group decision model based on expected intervals of experts. J. Grey Syst. 2020, 32, 77–89. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada, E. Every nonsingular spherical Euclidean distance matrix is a resistance distance matrix. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 2023, 656, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Dai, J. A novel TOPSIS method with decision-theoretic rough fuzzy sets. Inf. Sci. 2022, 608, 1221–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.W.; Chen, Z.Y.; Xu, Z.S.; Gou, X.J.; Herrera, F. Score function based on concentration degree for probabilistic linguistic term sets: An application to TOPSIS and VIKOR. Inf. Sci. 2021, 551, 270–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xie, Y.M.; Ding, S. Grey incidence quantile evaluation method and multidimensional relative poverty measurement. Stat. Decis. 2023, 39, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Lu, L.; Ye, Y.P.; Wan, L. PL-VIKOR group decision-making based on cumulative prospect theory and knowledge rating. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2023, 45, 1762–1771. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).